N-(6-Chloro-3-nitropyridin-2-yl)-5-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)isoquinolin-3-amine
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
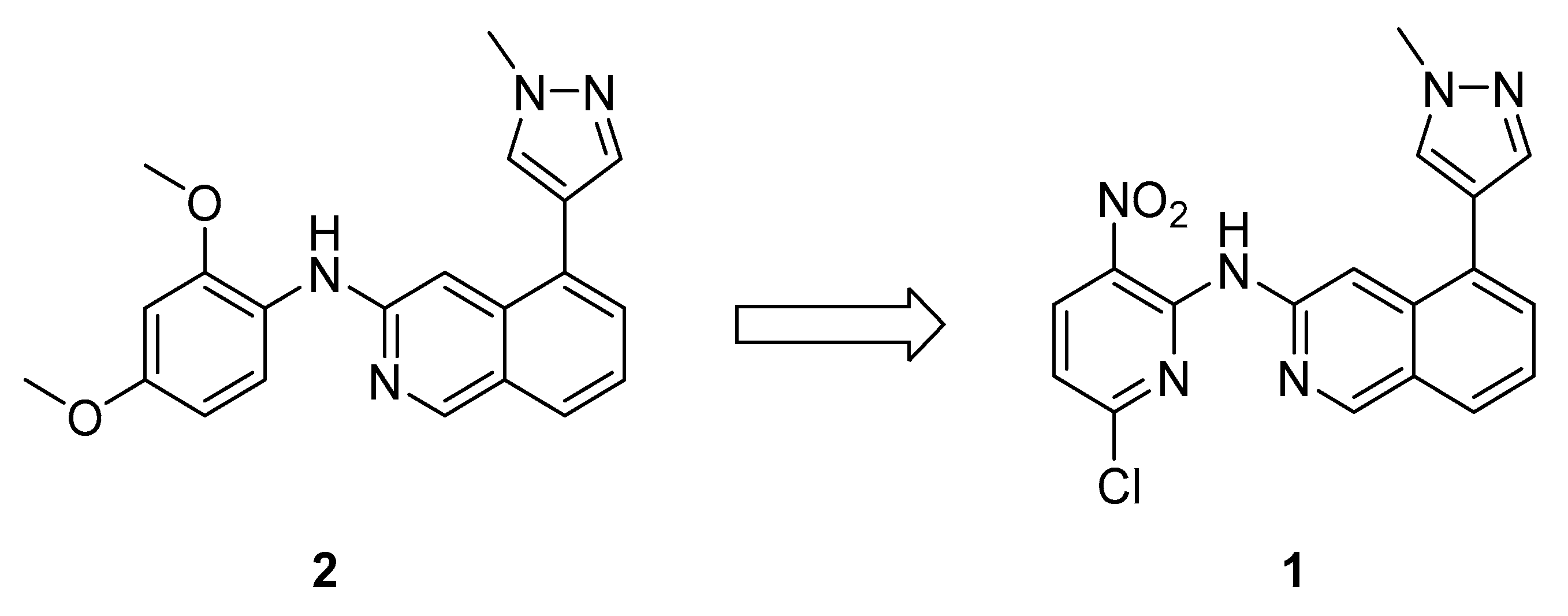
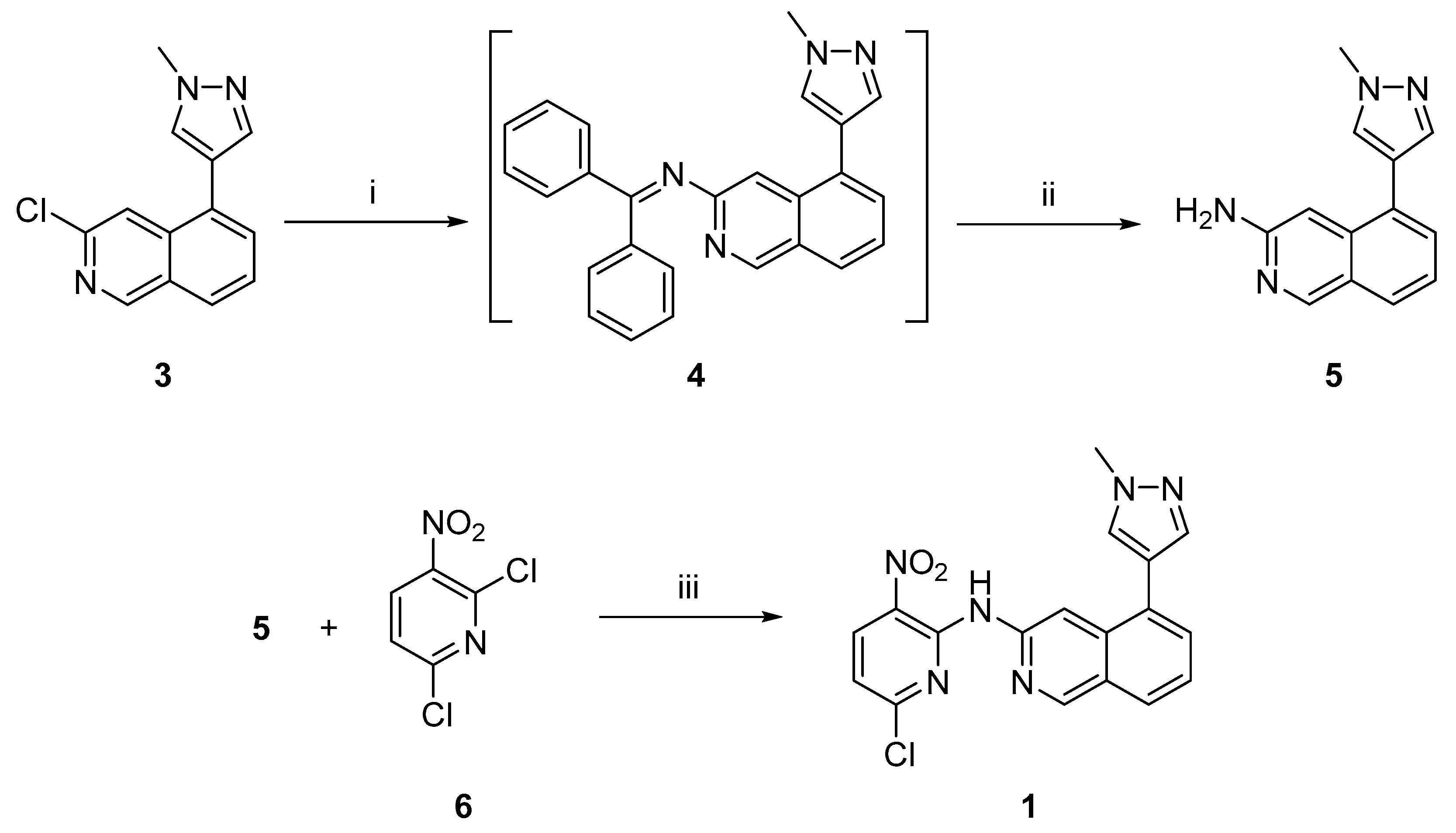
2.1. Chemistry
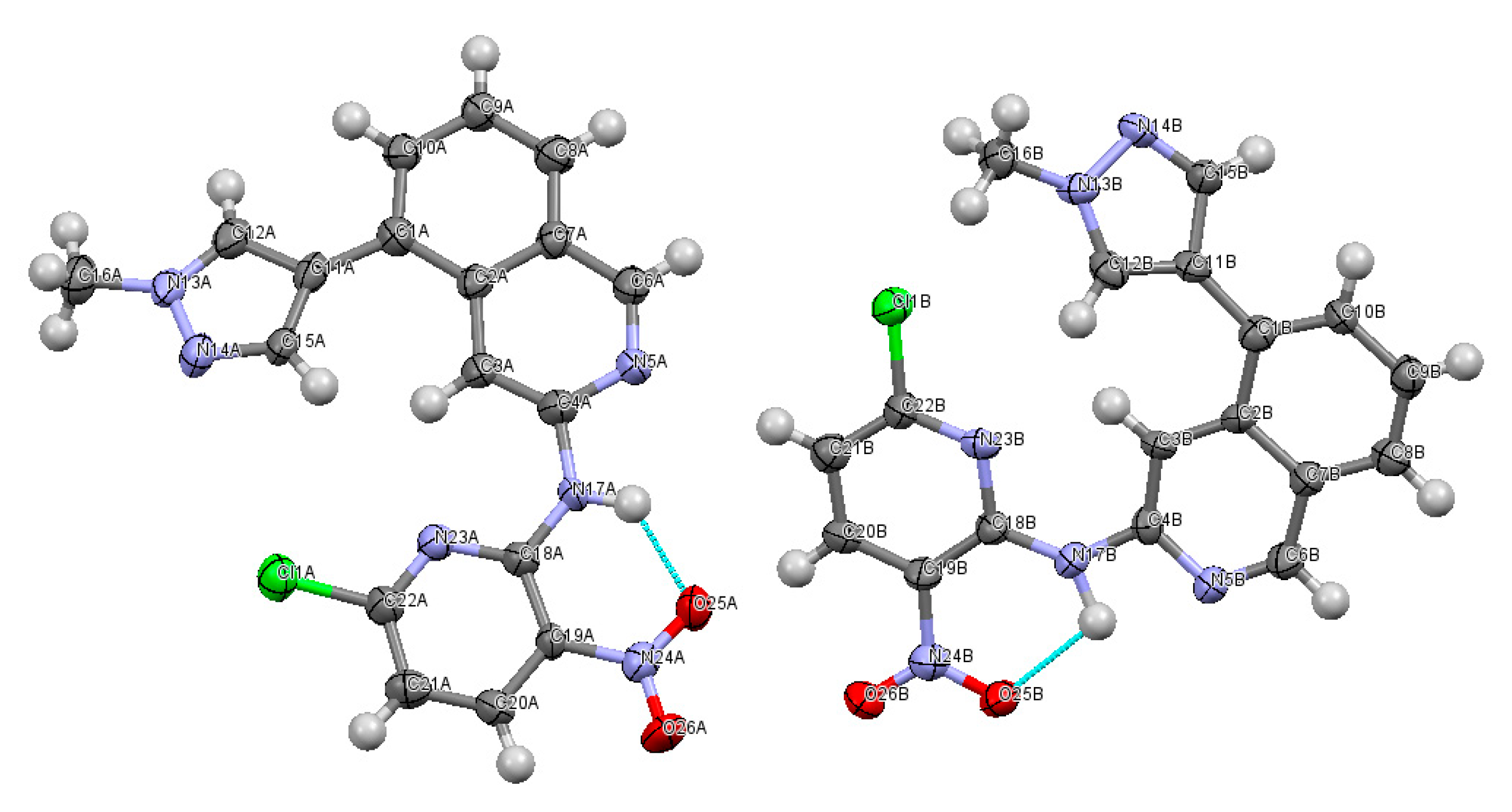
2.2. X-ray Crystallography
2.3. Biological Evaluation
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. General Experimental Section
3.2. Synthetic Procedures
3.2.1. 5-(1-Methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)isoquinolin-3-amine (5)
3.2.2. N-(6-Chloro-3-nitropyridin-2-yl)-5-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)isoquinolin-3-amine (1)
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mills, G.B.; Schmandt, R.; McGill, M.; Amendola, A.; Hill, M.; Jacobs, K.; May, C.; Rodricks, A.M.; Campbell, S.; Hogg, D. Expression of TTK, a novel human protein kinase, is associated with cell proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 16000–16006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maire, V.; Baldeyron, C.; Richardson, M.; Tesson, B.; Vincent-Salomon, A.; Gravier, E.; Marty-Prouvost, B.; De Koning, L.; Rigaill, G.; Dumont, A.; et al. TTK/hMPS1 is an attractive therapeutic target for triple-negative breast cancer. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e63712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulze, V.K.; Klar, U.; Kosemund, D.; Wengner, A.M.; Siemeister, G.; Stöckigt, D.; Neuhaus, R.; Lienau, P.; Bader, B.; Prechtl, S.; et al. Treating cancer by spindle assembly checkpoint abrogation: Discovery of two clinical candidates, BAY 1161909 and BAY 1217389, targeting MPS1 kinase. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 8025–8042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innocenti, P.; Woodward, H.L.; Solanki, S.; Naud, S.; Westwood, I.M.; Cronin, N.; Hayes, A.; Roberts, J.; Henley, A.T.; Baker, R.; et al. Rapid discovery of Pyrido[3,4-d]pyrimidine inhibitors of monopolar spindle kinase 1 (MPS1) using a structure-based hybridization approach. J. Med. Chem. 2016, 59, 3671–3688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaikuad, A.; Koch, P.; Laufer, S.A.; Knapp, S. The cysteinome of protein kinases as a target in drug development. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2018, 57, 4372–4385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehringer, M. Covalent kinase inhibitors: An overview. In Topics in Medicinal Chemistry; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 1–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehringer, M.; Laufer, S.A. Emerging and re-emerging warheads for targeted covalent inhibitors: Applications in medicinal chemistry and chemical biology. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 5673–5724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fairhurst, R.A.; Knoepfel, T.; Leblanc, C.; Buschmann, N.; Gaul, C.; Blank, J.; Galuba, I.; Trappe, J.; Zou, C.; Voshol, J.; et al. Approaches to selective fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 inhibition through targeting the ATP-pocket middle-hinge region. Medchemcomm 2017, 8, 1604–1613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gehringer, M.; Forster, M.; Pfaffenrot, E.; Bauer, S.M.; Laufer, S.A. Novel hinge-binding motifs for janus kinase 3 inhibitors: A comprehensive structure–activity relationship study on tofacitinib bioisosteres. Chem. Med. Chem. 2014, 9, 2516–2527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfe, J.P.; Åhman, J.; Sadighi, J.P.; Singer, R.A.; Buchwald, S.L. An ammonia equivalent for the palladium-catalyzed amination of aryl halides and triflates. Tetrahedron Lett. 1997, 38, 6367–6370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastassiadis, T.; Deacon, S.W.; Devarajan, K.; Ma, H.; Peterson, J.R. Comprehensive assay of kinase catalytic activity reveals features of kinase inhibitor selectivity. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 1039–1045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Kinase | IC50 [nM] 1 |
|---|---|
| MPS1 | >5000 |
| MAPKAPK2 | >25,000 |
| p70S6Kβ | 444 |
| Time [min] | MeOH [%] | 0.01 M KH2PO4-Buffer pH = 2.3 [%] | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | => | 8 | 40 | => | 85 | 60 | => | 15 |
| 8 | => | 13 | 85 | => | 85 | 15 | => | 15 |
| 13 | => | 14 | 85 | => | 40 | 15 | => | 60 |
| 14 | => | 16 | 40 | => | 40 | 60 | => | 60 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wydra, V.; Gerstenecker, S.; Schollmeyer, D.; Andreev, S.; Dimitrov, T.; Massarico Serafim, R.A.; Laufer, S.; Gehringer, M. N-(6-Chloro-3-nitropyridin-2-yl)-5-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)isoquinolin-3-amine. Molbank 2021, 2021, M1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1181
Wydra V, Gerstenecker S, Schollmeyer D, Andreev S, Dimitrov T, Massarico Serafim RA, Laufer S, Gehringer M. N-(6-Chloro-3-nitropyridin-2-yl)-5-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)isoquinolin-3-amine. Molbank. 2021; 2021(1):M1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1181
Chicago/Turabian StyleWydra, Valentin, Stefan Gerstenecker, Dieter Schollmeyer, Stanislav Andreev, Teodor Dimitrov, Ricardo Augusto Massarico Serafim, Stefan Laufer, and Matthias Gehringer. 2021. "N-(6-Chloro-3-nitropyridin-2-yl)-5-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)isoquinolin-3-amine" Molbank 2021, no. 1: M1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1181
APA StyleWydra, V., Gerstenecker, S., Schollmeyer, D., Andreev, S., Dimitrov, T., Massarico Serafim, R. A., Laufer, S., & Gehringer, M. (2021). N-(6-Chloro-3-nitropyridin-2-yl)-5-(1-methyl-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)isoquinolin-3-amine. Molbank, 2021(1), M1181. https://doi.org/10.3390/M1181







