Tobacco OPBP1 Enhances Salt Tolerance and Disease Resistance of Transgenic Rice
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Expression of stress-inducible genes in OPBP1 transgenic plants
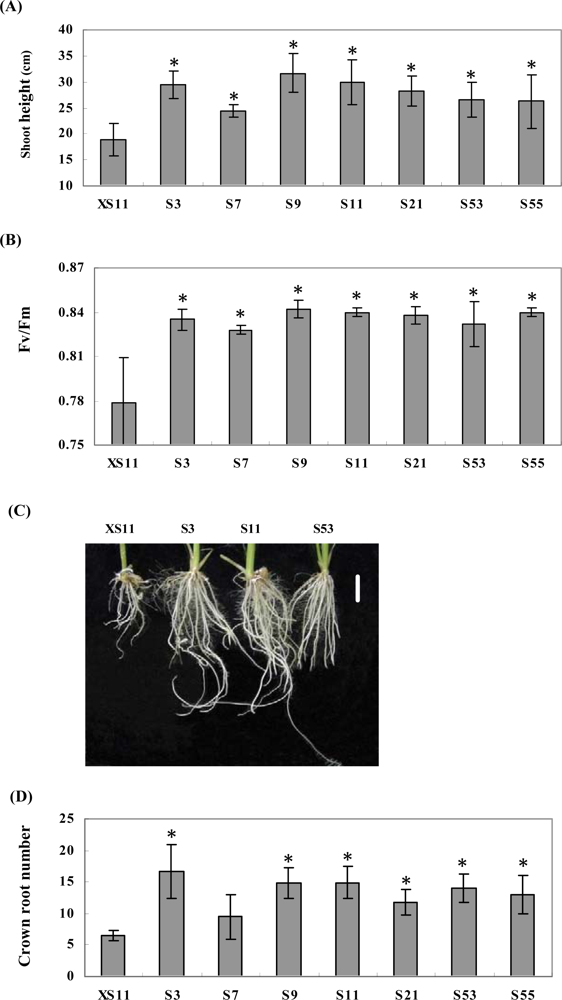
2.2. Expression of OPBP1 enhances salt tolerance in rice
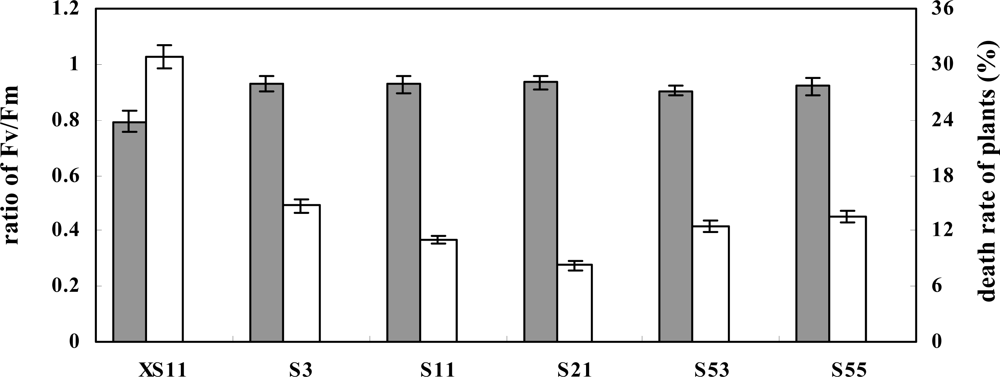
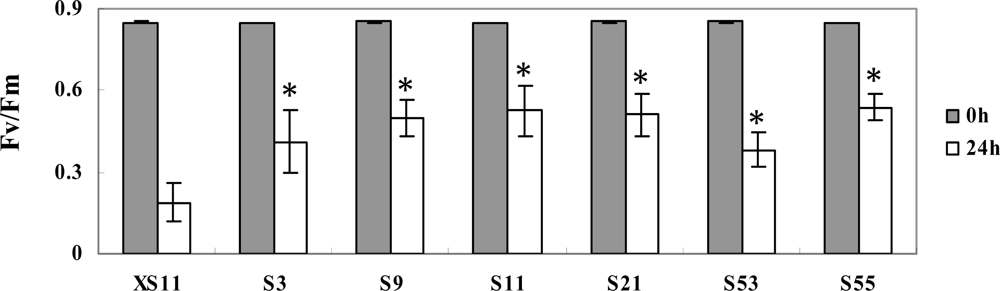
2.3. Overexpression of OPBP1 increases tolerance to oxidative damage and resistance against rice fungal pathogens
3. Discussion
4. Experimental Section
4.1. Construction of plasmids and rice transformation
4.2. RNA isolation and northern blot
4.3. Chemical treatments
4.4. Determination of chlorophyll fluorescence
4.5. Pathogen inoculation
4.6. RT-PCR analysis
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
References
- Ramanjulu, S; Bartels, D. Drought- and desiccation-induced modulation of genes expression in plants. Plan Cell Environ 2002, 25, 141–151. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Wise, M; Tunnaciliffe, A. POPP the question: What do LEA proteins do? Trends Plant Sci 2004, 9, 13–17. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Garg, AK; Kim, JK; Owen, TG; Ranwala, AP; Choi, YD; Kochian, LV; Wu, RJ. Trehalose accumulation in rice plants confers high tolerance levels to different abiotic stresses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 15898–15903. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Ohme-Takagi, M; Shinshi, H. Ethylene-inducible DNA binding proteins that interact with an ethylene-responsive element. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Liu, Q; Kasuga, M; Sakuma, Y; Abe, H; Mirua, S; Yamaquchi-Shinozaki, K; Shinozaki, K. Two transcription factors, DREB1 and DREB2, with an EREBP/AP2 DNA-binding domain separate two cellular signal transduction pathways in drought and low-temperature-responsive gene expression in Arbidopsis. Plant Cell 1998, 10, 1391–1406. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Nakano, T; Suzuki, K; Fujimura, T; Shinshi, H. Genome-Wide analysis of the ERF gene family in arabidopsis and rice. Plant Physiol 2006, 140, 411–432. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Tang, W; Newton, RJ; Lin, J; Charles, TM. Expression of a transcription factor from Capsicum annuum in pine calli counteracts the inhibitory effects of salt stress on adventitious shoot formation. Mol. Genet. Genomics 2006, 276, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Jung, J; Won, SY; Suh, SC; Kim, H; Wing, R; Jeong, Y; Hwang, I; Kim, M. The barley ERF-type transcription factor HvRAF confers enhanced pathogen resistance and salt tolerance in Arabidopsis. Planta 2007, 225, 575–588. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Stockinger, EJ; Gilmour, SJ; Thomashow, MF. Arabidopsis thaliana CBF1 encodes an AP2 domain-containing transcription activator that binds to the C-repeat/DRE, a cis-acting DNA regulatory element that stimulates transcription in response to low temperature and water deficit. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 1035–1040. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Kasuga, Ml; Liu, Q; Miura, S; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K; Shinozaki, K. Improving plant drought, salt, and freezing tolerance by gene transfer of a single stress-inducible transcription factor. Nat. Biotech 1999, 17, 287–291. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Dubouzet, JG; Sakuma, Y; Ito, Y; Kasuga, M; Dubouzet, EG; Miura, S; Seki, M; Shinozaki, K. OsDREB genes in rice, Oryza sativa L., encode transcription activators that function in drought-, high-salt- and cold-responsive gene expression. Plant J 2003, 33, 751–763. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Guo, ZJ; Chen, XJ; Wu, XL; Ling, JQ; Xu, P. Overexpression of the Ap2/EREBP transcription factor OPBP1 enhances disease resistance salt tolerance in tobacco. Plant Mol. Biol 2004, 55, 607–618. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Igarashi, Y; Yoshiba, Y; Sanada, Y; Yamaguchi-Shinozaki, K; Wada, K; Shinozaki, K. Characterization of the gene for ∠ 1-pyrroline-5-carboxylate synthetase and correlation between the expression of the gene and salt tolerance in Oryza sativa L. Plant Mol. Biol 1997, 33, 857–865. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Soranzo, N; Sari-Gorla, M; Mizzi, L; De-Toma, G; Frova, C. Organisation and structural evolution of the rice glutathione S-transferase gene family. Mol. Gen. Genomics 2004, 271, 511–521. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Kong, J; Gong, JM; Zhang, ZG; Zhang, JS; Chen, SY. A new AOX homologous gene OsIM1 from rice (Oryza Sativa L.) with an alternative splicing mechanism under salt stress. Theor. Appl. Genet 2003, 107, 326–331. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Zhu, JK. Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 2001, 6, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hasegawa, PM; Bressan, RA; Zhu, JK; Bohnert, HJ. Plant cellular and molecular response to high salinity. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol 2000, 51, 463–499. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Roxas, VP; Smith, RK, Jr; Allen, ER; Allen, RD. Overexpression of glutathione-S-transferase/glutathione peroxidase enhances the growth of transgenic tobacco seedlings during stress. Nat. Biotechnol 1997, 15, 988–991. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Demmig-Adams, B; Gilmore, AM; Adams, WW, III. Carotenoids 3: in vivo functions of carotenoids in higher plants. FASEB J 1996, 10, 403–412. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Bohnert, HJ; Nelson, DE; Jensen, RG. Adaptations to Environmental Stresses. Plant Cell 1995, 7, 1099–1111. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Hiei, Y; Ohta, S; Komari, T; Kumashiro, T. Efficient transformation of rice (Oryza sativa L.) mediated by Agrobacterium and sequence analysis of the boundaries of the T-DNA. Plant J 1994, 6, 271–282. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Moradi, F; Ismail, AM. Responses of Photosynthesis, Chlorophyll Fluorescence and ROS-Scavenging Systems to Salt Stress During Seedling and Reproductive Stages in Rice. Ann. Bot 2007, 99, 1161–1173. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Sallaud, C; Lorieux, M; Roumen, E; Tharreau, D; Berruyer, R; Svestasrani, P; Garsmeur, O; Ghesquiere, A; Notteghem, JL. Identification of five new blast resistance genes in the highly blast-resistant rice variety IR64 using a QTL mapping strategy. Theor. Appl. Genet 2003, 106, 794–803. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]
- Jia, Y; Correa-Victoria, F; McClung, A; Zhu, L; Liu, G; Wamishe, Y. Rapid Determination of Rice Cultivar Responses to the Sheath Blight Pathogen Rhizoctonia Solani Using a Micro-Chamber Screening Method. Plant Disease 2007, 91, 485–489. [Google Scholar] [Green Version]



© 2008 by the authors; licensee Molecular Diversity Preservation International, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/). This article is an open-access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, X.; Guo, Z. Tobacco OPBP1 Enhances Salt Tolerance and Disease Resistance of Transgenic Rice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2008, 9, 2601-2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms9122601
Chen X, Guo Z. Tobacco OPBP1 Enhances Salt Tolerance and Disease Resistance of Transgenic Rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2008; 9(12):2601-2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms9122601
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Xujun, and Zejian Guo. 2008. "Tobacco OPBP1 Enhances Salt Tolerance and Disease Resistance of Transgenic Rice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 9, no. 12: 2601-2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms9122601
APA StyleChen, X., & Guo, Z. (2008). Tobacco OPBP1 Enhances Salt Tolerance and Disease Resistance of Transgenic Rice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 9(12), 2601-2613. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms9122601



