Ephrin Receptors and Ephrin Ligands in Uveal Melanoma: A Big Data Analysis Using Web Resources
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. EPH/EFN Pathogenic Variants (PVs) and Copy Number Alterations (CNAs) in UVM
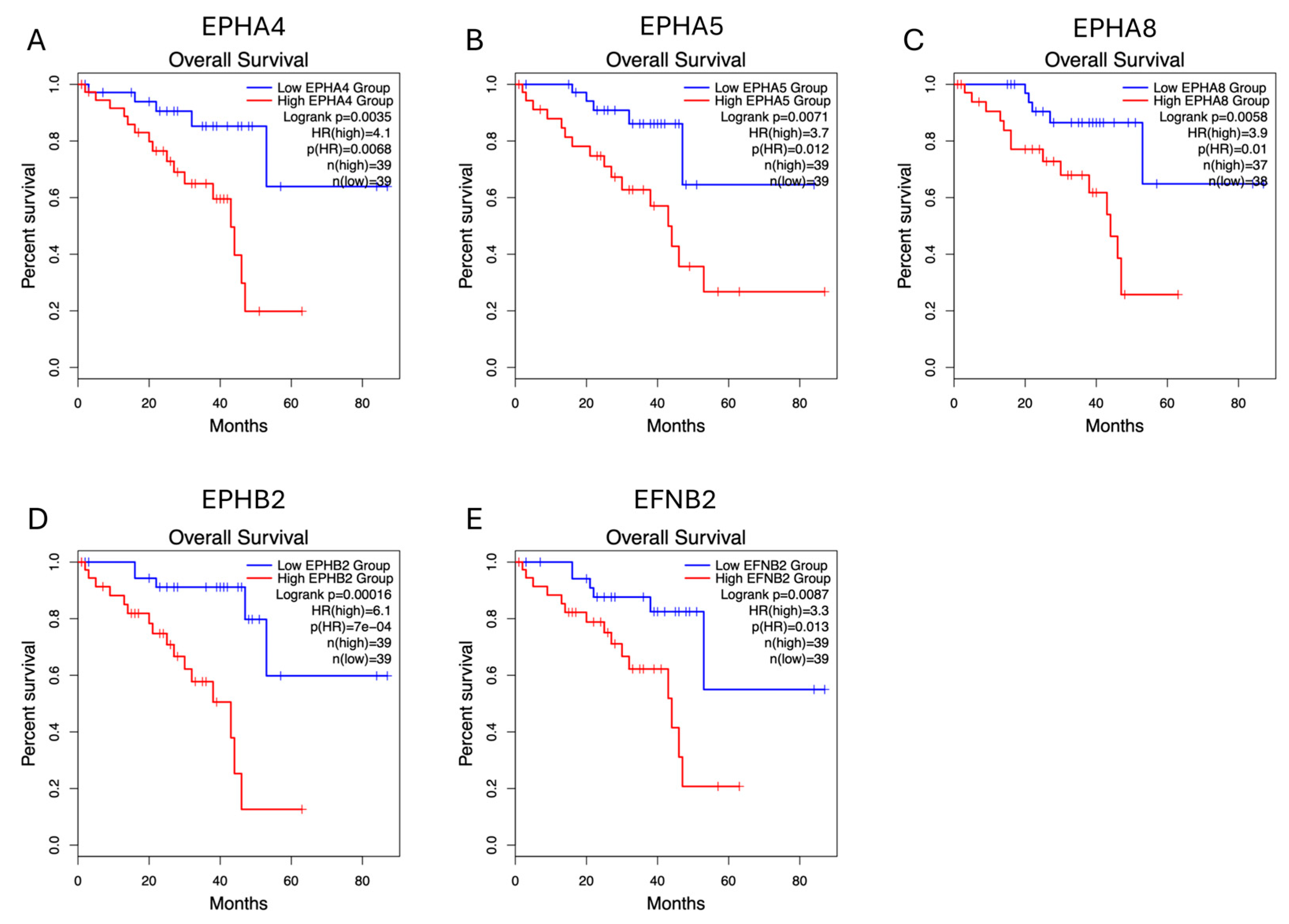
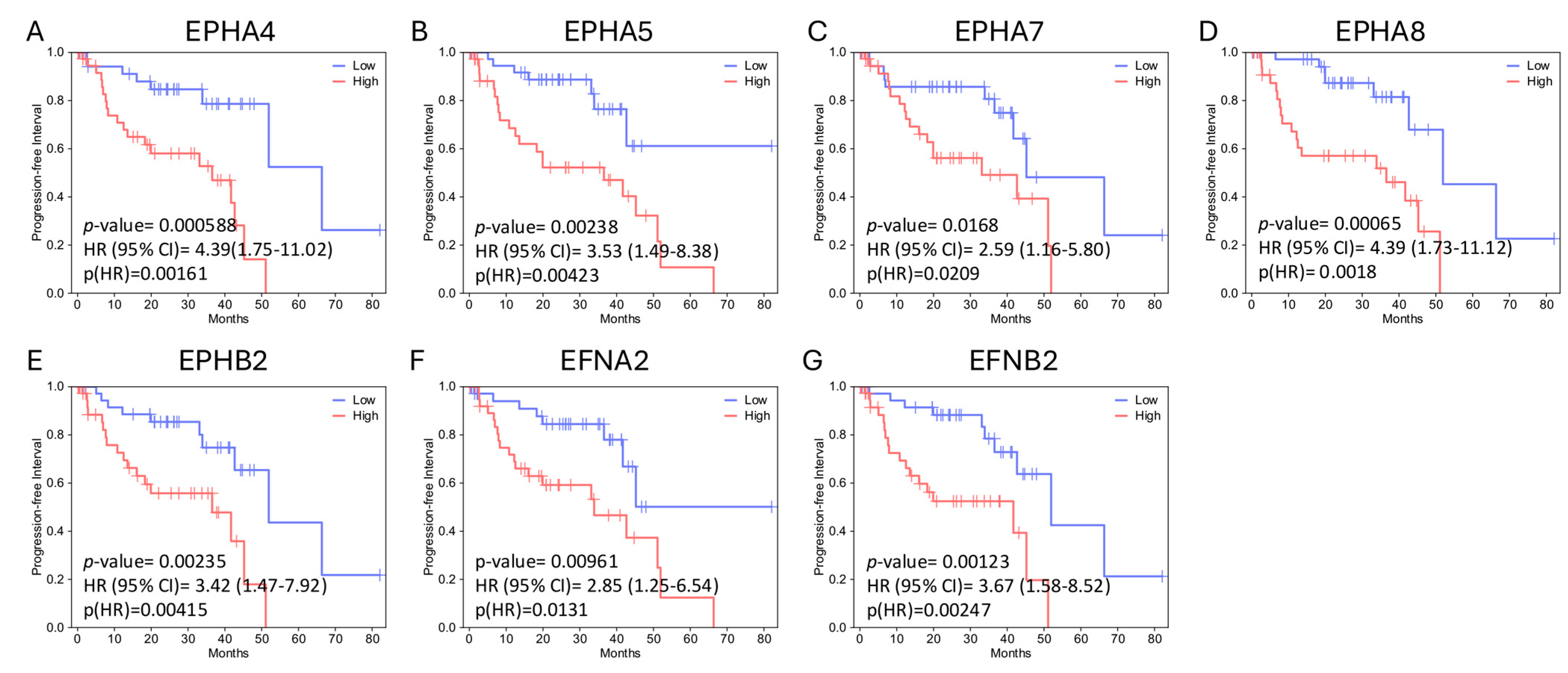
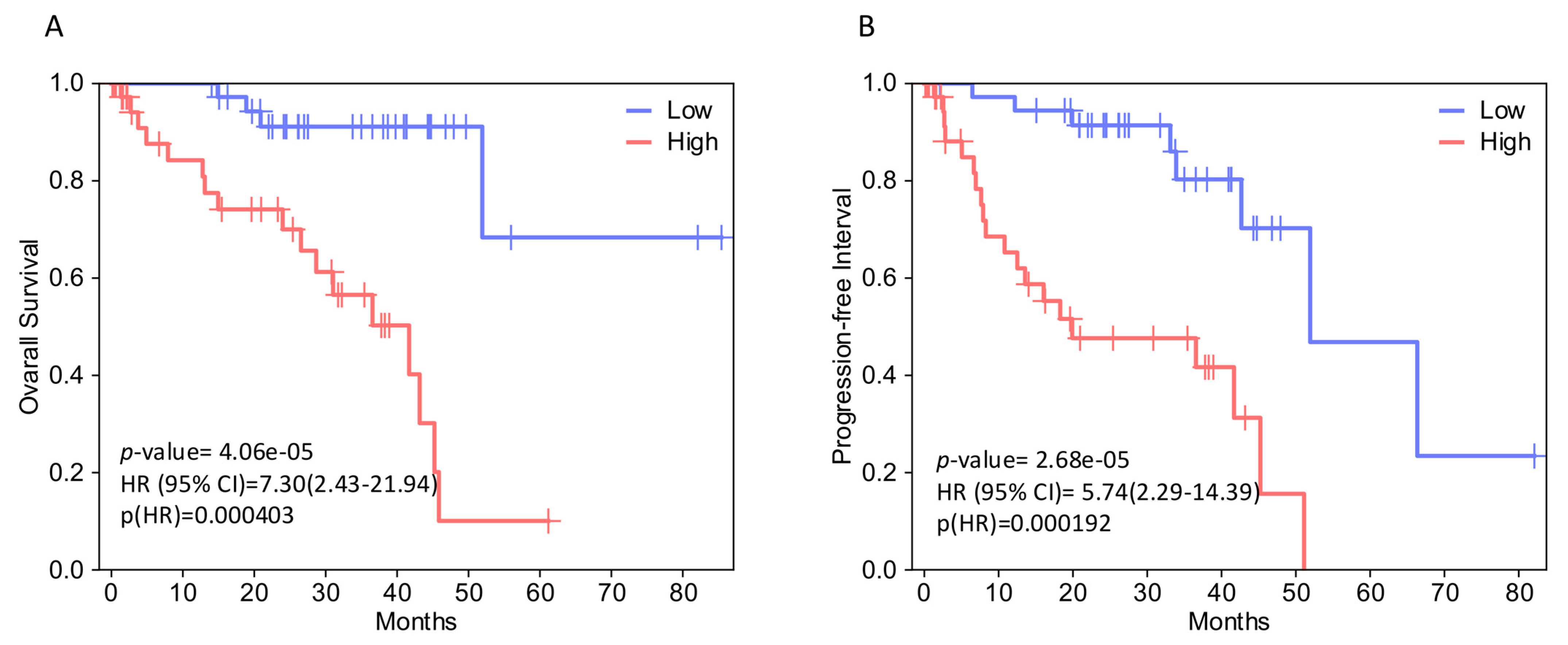
2.2. EPH/EFN Expression Correlates with Overall Survival, Disease-Free Survival, and Progression-Free Interval (OS, DFS, and PFI) in UVM Patients
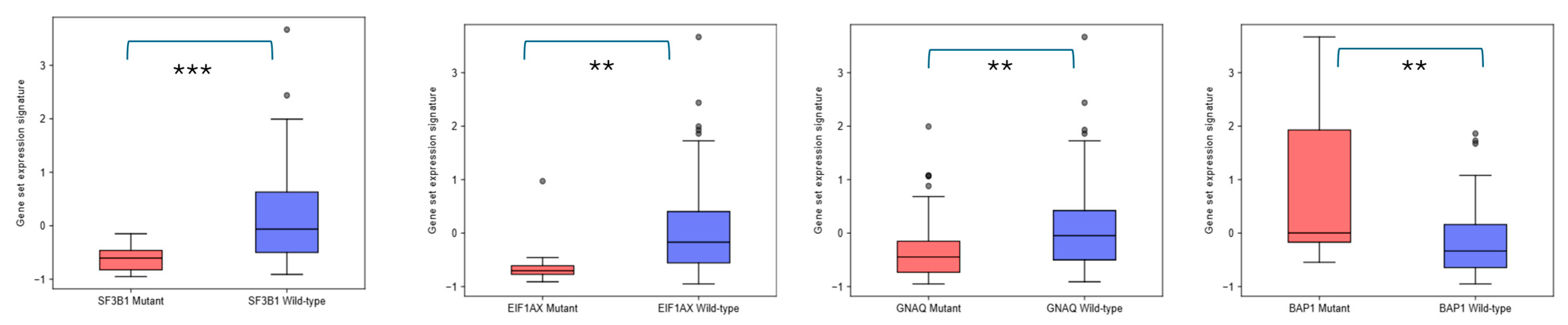
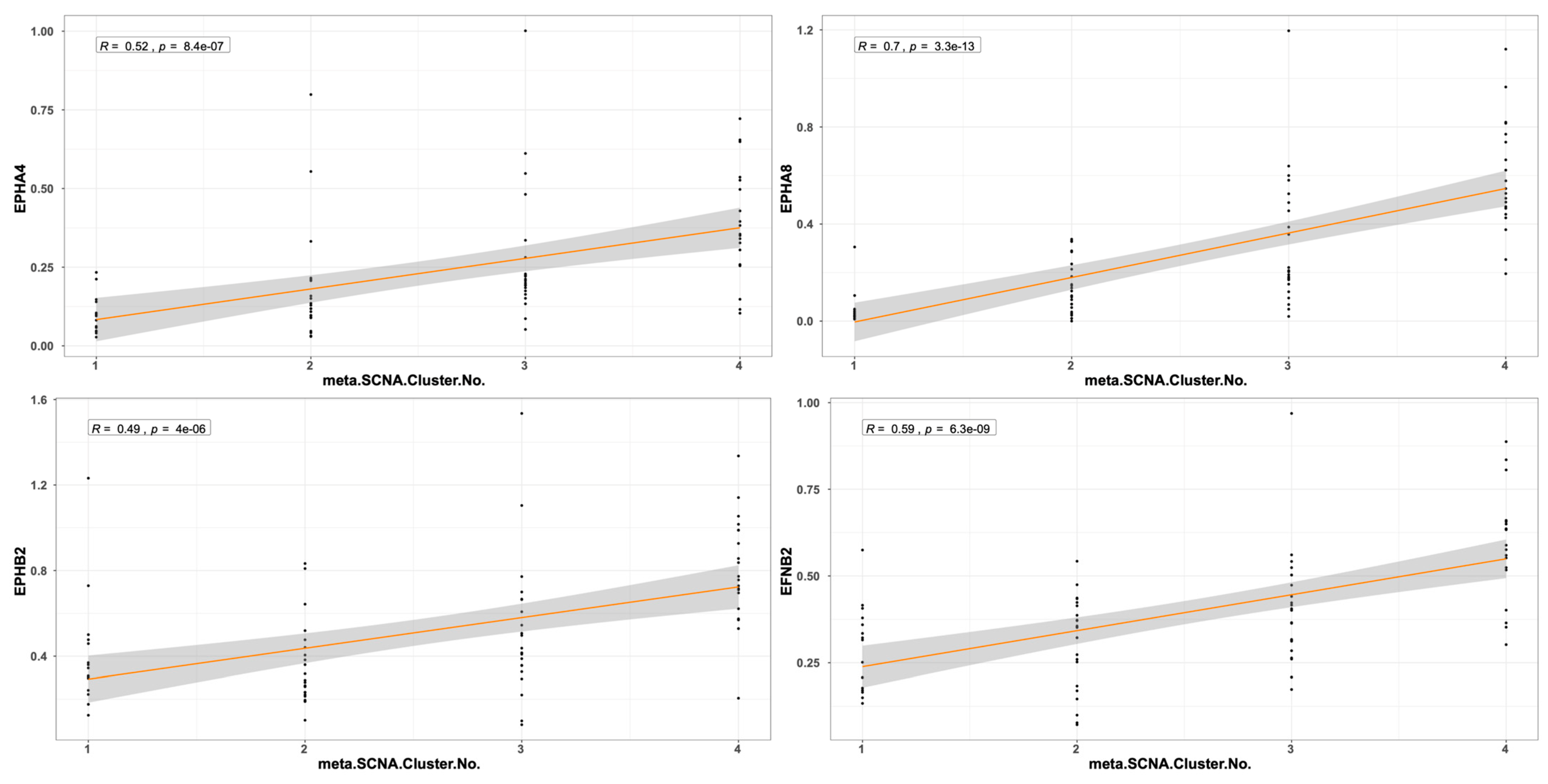
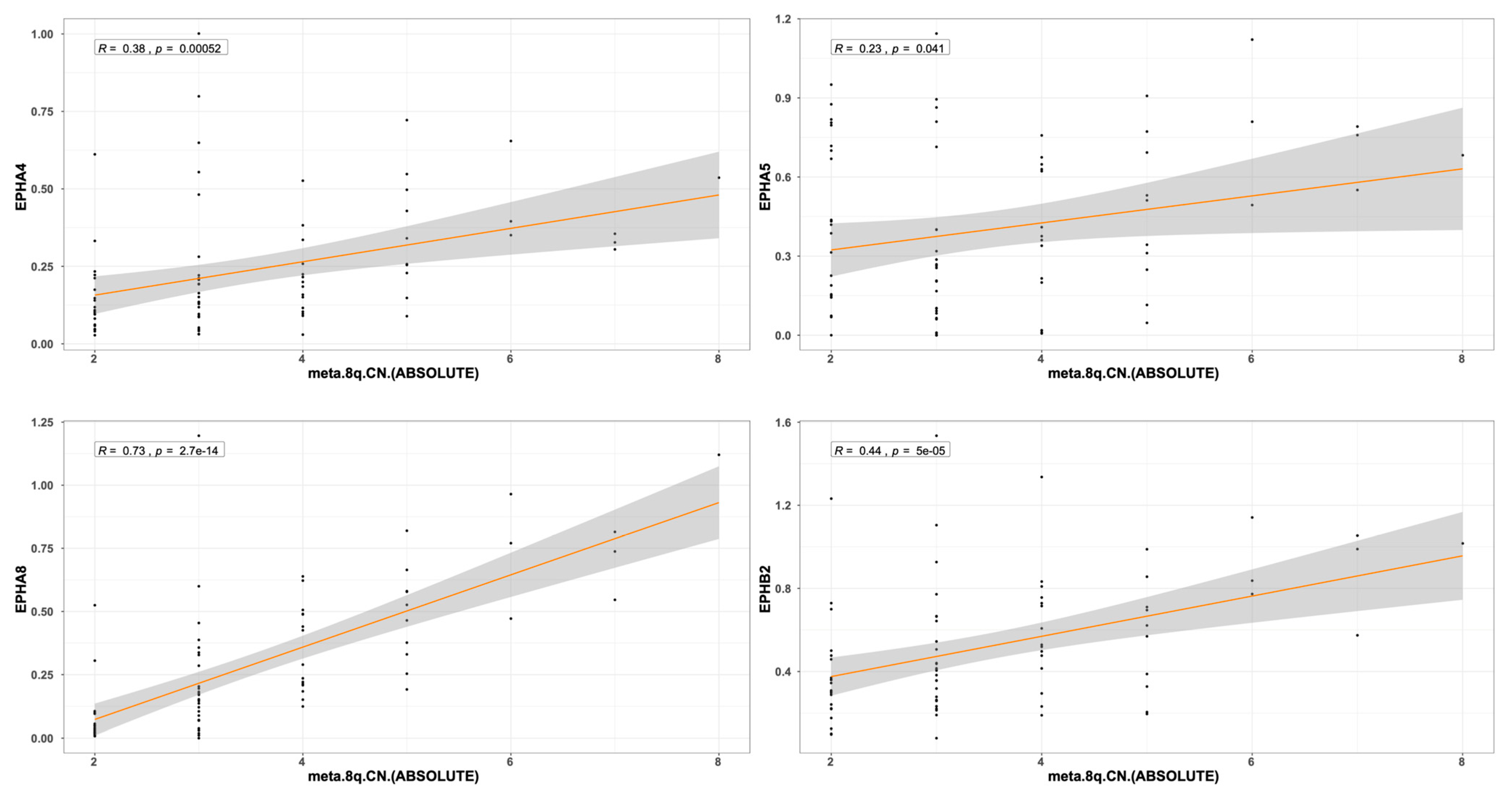
2.3. EPH/EFN Expression in UVM Patients’ Subsets and UVM Molecular Clusters
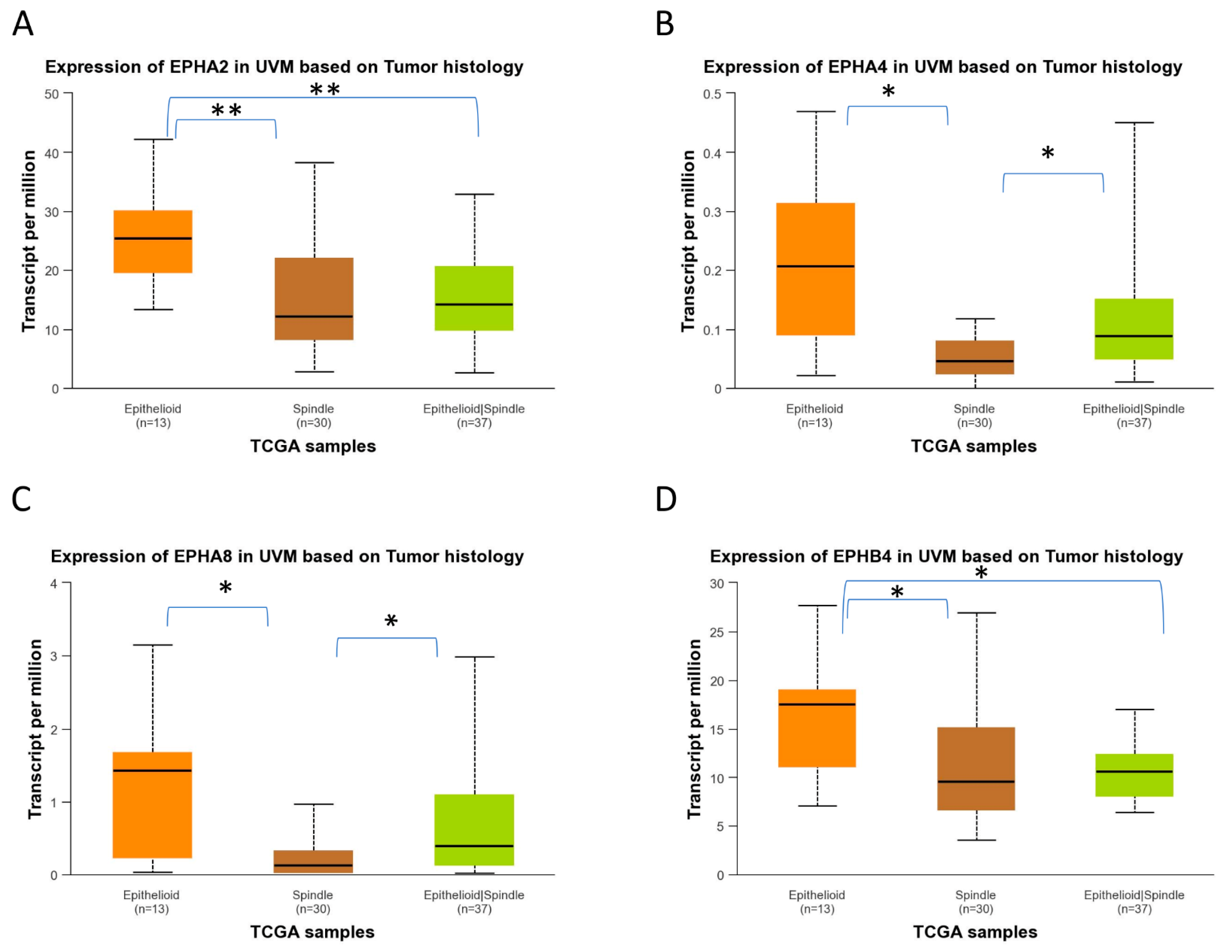
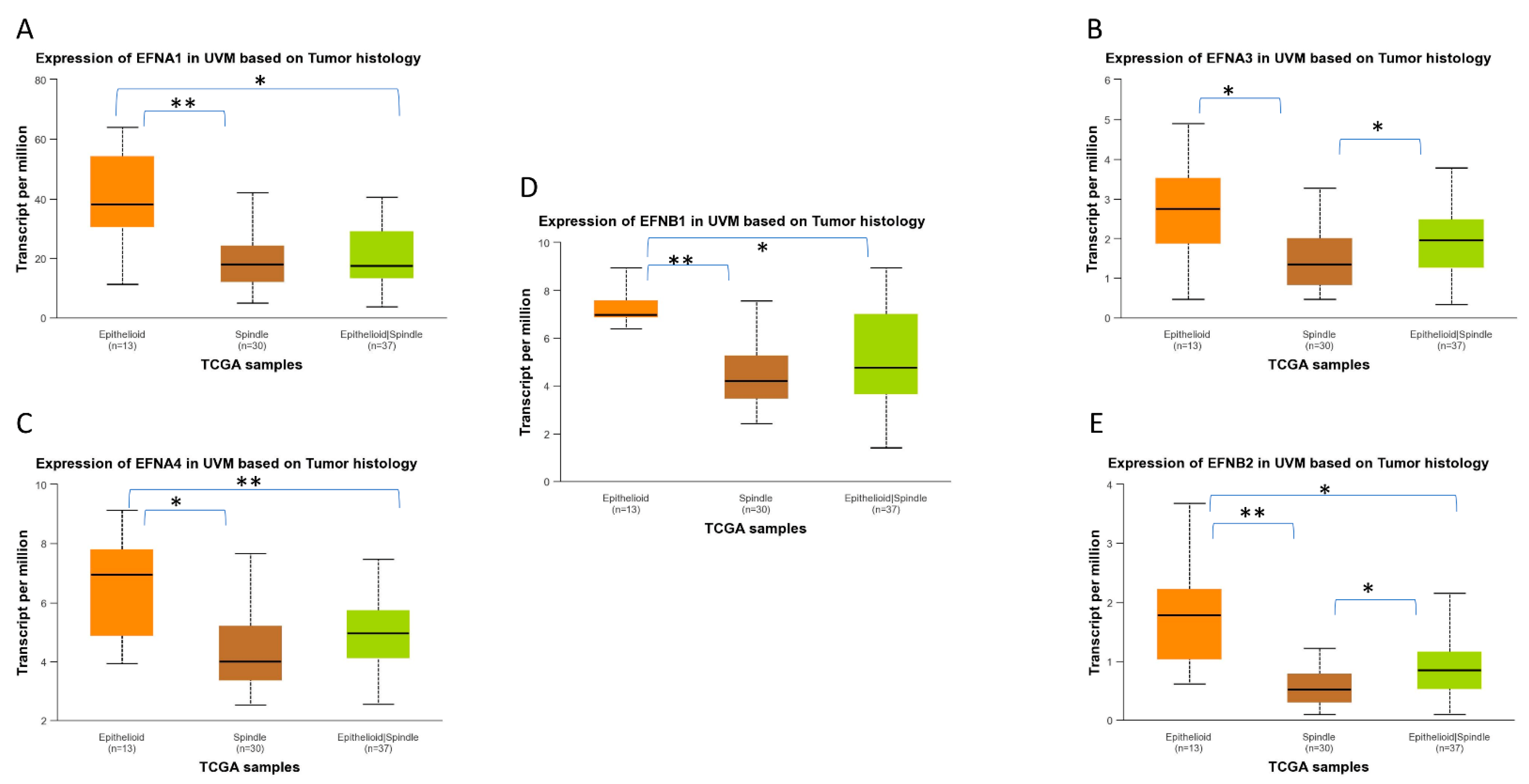
2.4. EPH/EFN Expression in Different Histological Subtypes of UVM
2.5. EPH/EFN Expression Patterns in Different Stages of Uveal Melanoma
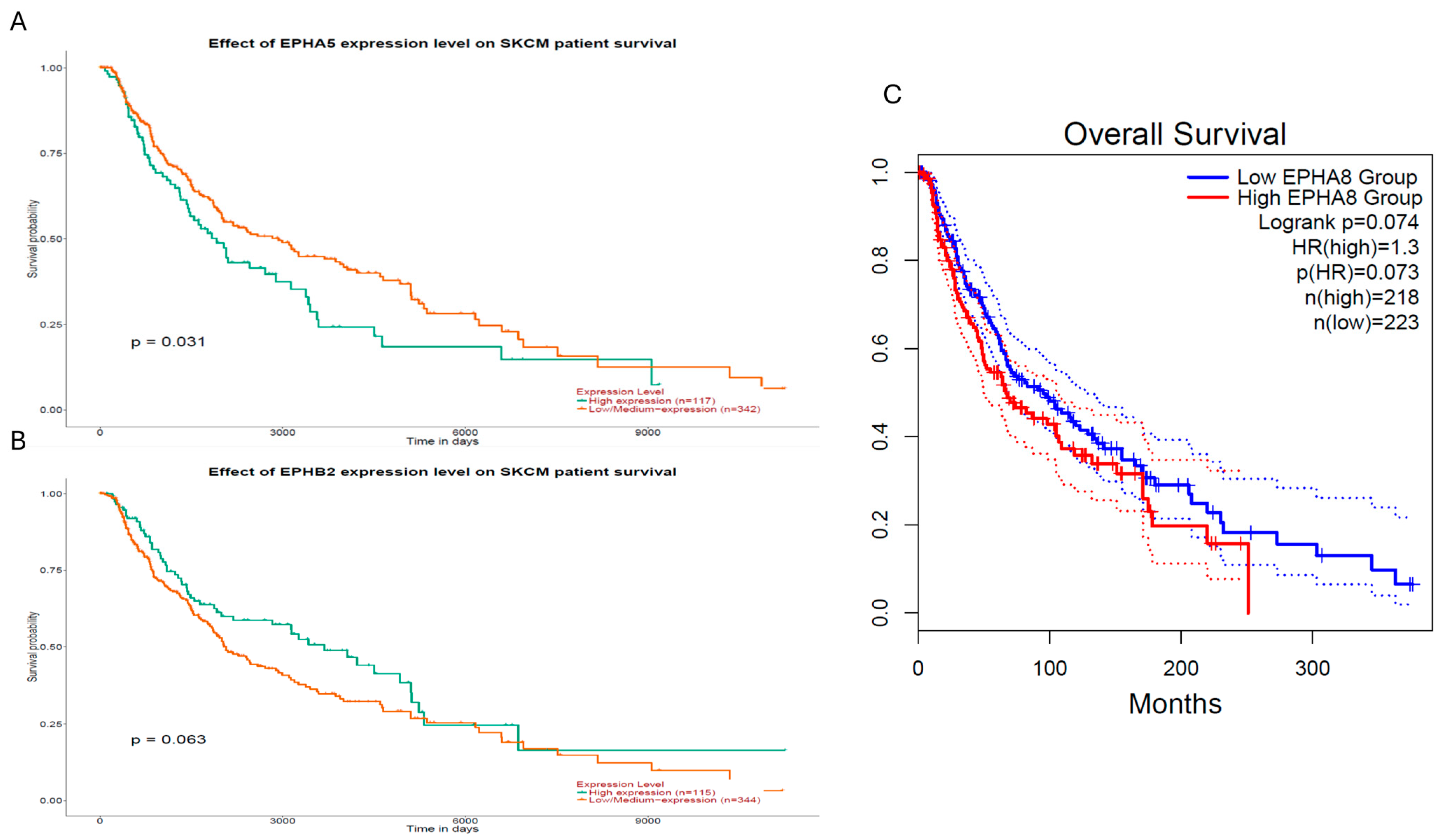
2.6. Evaluation of EPH/EFN Genes’ Correlations with Survival in the TCGA-SKCM (Skin Cutaneous Melanoma) Cohort
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. cBioPortal Analysis
4.2. GEPIA2 and GEPIA3 Analysis
4.3. UALCAN Analysis
4.4. GSCA Analysis
4.5. TCGEx Analysis
4.6. ShinyGeo Analysis [52]
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McLean, I.W.; Saraiva, V.S.; Burnier, M.N. Pathological and prognostic features of uveal melanomas. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 39, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cichorek, M.; Wachulska, M.; Stasiewicz, A. Heterogeneity of neural crest-derived melanocytes. Open Life Sci. 2013, 8, 315–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallenga, C.E.; Franco, E.; Adamo, G.G.; Violanti, S.S.; Tassinari, P.; Tognon, M.; Perri, P. Genetic Basis and Molecular Mechanisms of Uveal Melanoma Metastasis: A Focus on Prognosis. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 828112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, A.; Avitabile, T.; Reibaldi, M.; Bonfiglio, V.; Pignatelli, F.; Fallico, M.; Caltabiano, R.; Broggi, G.; Russo, D.; Varricchio, S.; et al. Iris Melanoma: Management and Prognosis. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelmi, M.C.; Jager, M.J. Uveal melanoma: Current evidence on prognosis, treatment and potential developments. Asia-Pacific J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 13, 100060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banou, L.; Tsani, Z.; Arvanitogiannis, K.; Pavlaki, M.; Dastiridou, A.; Androudi, S. Radiotherapy in Uveal Melanoma: A Review of Ocular Complications. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 6374–6396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rantala, E.S.; Hernberg, M.M.; Piperno-Neumann, S.; Grossniklaus, H.E.; Kivelä, T.T. Metastatic uveal melanoma: The final frontier. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2022, 90, 101041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdzis, M.; Kaczmarek, R.; Gajdzis, P. Novel Prognostic Immunohistochemical Markers in Uveal Melanoma-Literature Review. Cancers 2021, 13, 4031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shields, C.L.; Mellen, P.L.; Morton, S.J. American joint committee on cancer staging of uveal melanoma. Oman J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 6, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onken, M.D.; Worley, L.A.; Ehlers, J.P.; Harbour, J.W. Gene expression profiling in uveal melanoma reveals two molecular classes and predicts metastatic death. Cancer Res. 2004, 64, 7205–7209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onken, M.D.; Worley, L.A.; Char, D.H.; Augsburger, J.J.; Correa, Z.M.; Nudleman, E.; Aaberg, T.M., Jr.; Altaweel, M.M.; Bardenstein, D.S.; Finger, P.T.; et al. Collaborative Ocular Oncology Group Report Number 1: Prospective Validation of a Multi-Gene Prognostic Assay in Uveal Melanoma. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 1596–1603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Decatur, C.L.; Ong, E.; Garg, N.; Anbunathan, H.; Bowcock, A.M.; Field, M.G.; Harbour, J.W. Driver Mutations in Uveal Melanoma: Associations With Gene Expression Profile and Patient Outcomes. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016, 134, 728–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Piaggio, F.; Croce, M.; Reggiani, F.; Monti, P.; Bernardi, C.; Ambrosio, M.; Banelli, B.; Dogrusöz, M.; Jockers, R.; Bordo, D.; et al. In uveal melanoma Gα-protein GNA11 mutations convey a shorter disease-specific survival and are more strongly associated with loss of BAP1 and chromosomal alterations than Gα-protein GNAQ mutations. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 170, 27–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reggiani, F.; Ambrosio, M.; Croce, M.; Tanda, E.T.; Spagnolo, F.; Raposio, E.; Petito, M.; El Rashed, Z.; Forlani, A.; Pfeffer, U.; et al. Interdependence of Molecular Lesions That Drive Uveal Melanoma Metastasis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalonde, E.; Ewens, K.; Richards-Yutz, J.; Ebrahimzedeh, J.; Terai, M.; Gonsalves, C.F.; Sato, T.; Shields, C.L.; Ganguly, A. Improved Uveal Melanoma Copy Number Subtypes Including an Ultra–High-Risk Group. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2022, 2, 100121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronkhorst, I.H.G.; Ly, L.V.; Jordanova, E.S.; Vrolijk, J.; Versluis, M.; Luyten, G.P.M.; Jager, M.J. Detection of M2-Macrophages in Uveal Melanoma and Relation with Survival. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 643–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corrêa, Z.M. Assessing Prognosis in Uveal Melanoma. Cancer Control 2016, 23, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harbour, J.W.; Onken, M.D.; Roberson, E.D.O.; Duan, S.; Cao, L.; Worley, L.A.; Council, M.L.; Matatall, K.A.; Helms, C.; Bowcock, A.M. Frequent Mutation of BAP1 in Metastasizing Uveal Melanomas. Science 2010, 330, 1410–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, A.G.; Shih, J.; Yau, C.; Gibb, E.A.; Oba, J.; Mungall, K.L.; Hess, J.M.; Uzunangelov, V.; Walter, V.; Danilova, L.; et al. Integrative Analysis Identifies Four Molecular and Clinical Subsets in Uveal Melanoma. Cancer Cell 2017, 32, 204–220.e215, Erratum in Cancer Cell 2018, 33, 151.. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazloumi, M.; Vichitvejpaisal, P.; Dalvin, L.A.; Yaghy, A.; Ewens, K.G.; Ganguly, A.; Shields, C.L. Accuracy of The Cancer Genome Atlas Classification vs American Joint Committee on Cancer Classification for Prediction of Metastasis in Patients with Uveal Melanoma. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2020, 138, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eleuteri, A.; Taktak, A.F.; Coupland, S.E.; Heimann, H.; Kalirai, H.; Damato, B. Prognostication of metastatic death in uveal melanoma patients: A Markov multi-state model. Comput. Biol. Med. 2018, 102, 151–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelmi, M.C.; Bas, Z.; Malkani, K.; Ganguly, A.; Shields, C.L.; Jager, M.J. Adding the Cancer Genome Atlas Chromosome Classes to American Joint Committee on Cancer System Offers More Precise Prognostication in Uveal Melanoma. Ophthalmology 2022, 129, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jager, M.J.; Shields, C.L.; Cebulla, C.M.; Abdel-Rahman, M.H.; Grossniklaus, H.E.; Stern, M.H.; Carvajal, R.D.; Belfort, R.N.; Jia, R.; Shields, J.A. Uveal melanoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2020, 6, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, S.A.; Almalki, W.H.; Arora, S.; Kesharwani, P. Recent approaches for the treatment of uveal melanoma: Opportunities and challenges. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2023, 193, 104218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falzone, L.; Bordonaro, R.; Libra, M. SnapShot: Cancer chemotherapy. Cell 2023, 186, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eteghadi, A.; Ebrahimi, M.; Keshel, S.H. New immunotherapy approaches as the most effective treatment for uveal melanoma. Crit. Rev. Oncol. 2024, 194, 104260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, Y.-X.; Luo, J.-T.; Li, Y.; Wei, W.-B.; Li, H.-W. Regional chemotherapy for uveal melanoma liver metastases. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 16, 293–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez-Vidal, C.; Fernandez-Diaz, D.; Fernandez-Marta, B.; Lago-Baameiro, N.; Pardo, M.; Silva, P.; Paniagua, L.; Blanco-Teijeiro, M.J.; Piñeiro, A.; Bande, M. Treatment of Metastatic Uveal Melanoma: Systematic Review. Cancers 2020, 12, 2557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, J.; Manson, D.K.; Marr, B.P.; Carvajal, R.D. Treatment of uveal melanoma: Where are we now? Ther. Adv. Med. Oncol. 2018, 10, 1758834018757175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pandiani, C.; Strub, T.; Nottet, N.; Cheli, Y.; Gambi, G.; Bille, K.; Husser, C.; Dalmasso, M.; Béranger, G.; Lassalle, S.; et al. Single-cell RNA sequencing reveals intratumoral heterogeneity in primary uveal melanomas and identifies HES6 as a driver of the metastatic disease. Cell Death Differ. 2021, 28, 1990–2000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Shi, R.; Xu, L.; Sun, F. Identification of heterogeneity and prognostic key genes associated with uveal melanoma using single-cell RNA-sequencing technology. Melanoma Res. 2021, 32, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, W.; Beasley, A.B.; Ardakani, N.M.; Denisenko, E.; Calapre, L.; Jones, M.; Wood, B.A.; Warburton, L.; Forrest, A.R.R.; Gray, E.S. Intra- and intertumoral heterogeneity of liver metastases in a patient with uveal melanoma revealed by single-cell RNA sequencing. Mol. Case Stud. 2021, 7, a006111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.; Deng, A.; Liang, S.; Liu, S.; Fu, X.; Zhao, X.; Yu, Z. Integration of Bulk RNA Sequencing and Single-Cell RNA Sequencing to Reveal Uveal Melanoma Tumor Heterogeneity and Cells Related to Survival. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 898925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Guo, B.; Xu, L.; Shi, R. Integrated analysis reveals the dysfunction of signaling pathways in uveal melanoma. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gentien, D.; Saberi-Ansari, E.; Servant, N.; Jolly, A.; de la Grange, P.; Némati, F.; Liot, G.; Saule, S.; Teissandier, A.; Bourc’hIs, D.; et al. Multi-omics comparison of malignant and normal uveal melanocytes reveals molecular features of uveal melanoma. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 113132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lisabeth, E.M.; Falivelli, G.; Pasquale, E.B. Eph Receptor Signaling and Ephrins. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2013, 5, a009159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darling, T.K.; Lamb, T.J. Emerging Roles for Eph Receptors and Ephrin Ligands in Immunity. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barquilla, A.; Pasquale, E.B. Eph Receptors and Ephrins: Therapeutic Opportunities. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2015, 55, 465–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasquale, E.B. Eph-Ephrin Bidirectional Signaling in Physiology and Disease. Cell 2008, 133, 38–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergaris, A.; Danas, E.; Goutas, D.; Sykaras, A.G.; Soranidis, A.; Theocharis, S. The Clinical Impact of the EPH/Ephrin System in Cancer: Unwinding the Thread. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 8412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam Nhut Phan, N.N.; Liu, S.; Wang, C.-Y.; Hsu, H.-P.; Lai, M.-D.; Li, C.-Y.; Chen, C.-F.; Chiao, C.-C.; Yen, M.-C.; Sun, Z.; et al. Overexpressed gene signature of EPH receptor A/B family in cancer patients-comprehensive analyses from the public high-throughput database. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2020, 13, 1220–1242. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, S.; Dong, C.; Zhang, J.; Fu, S.; Lv, Y.; Wu, J. A comprehensive prognostic and immunological analysis of ephrin family genes in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 943384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gajdzis, M.; Theocharis, S.; Gajdzis, P.; Cassoux, N.; Gardrat, S.; Donizy, P.; Klijanienko, J.; Kaczmarek, R. Ephrin Receptors (Eph): EphA1, EphA5, and EphA7 Expression in Uveal Melanoma—Associations with Clinical Parameters and Patient Survival. Life 2020, 10, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pergaris, A.; Danas, E.; Gajdzis, P.; Levidou, G.; Gajdzis, M.; Cassoux, N.; Gardrat, S.; Donizy, P.; Korkolopoulou, P.; Kavantzas, N.; et al. EPHA2, EPHA4, and EPHA6 Expression in Uveal Melanomas: Searching for the Culprits of Neoplasia. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fallico, M.; Raciti, G.; Longo, A.; Reibaldi, M.; Bonfiglio, V.; Russo, A.; Caltabiano, R.; Gattuso, G.; Falzone, L.; Avitabile, T. Current molecular and clinical insights into uveal melanoma (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2021, 58, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallone, F.; Sacchetti, M.; Lambiase, A.; Moramarco, A. Molecular Insights and Emerging Strategies for Treatment of Metastatic Uveal Melanoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayward, N.K.; Wilmott, J.S.; Waddell, N.; Johansson, P.A.; Field, M.A.; Nones, K.; Patch, A.-M.; Kakavand, H.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Burke, H.; et al. Whole-genome landscapes of major melanoma subtypes. Nature 2017, 545, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Gallo, M.; O’Hara, A.J.; Rudd, M.L.; Urick, M.E.; Hansen, N.F.; O’Neil, N.J.; Price, J.C.; Zhang, S.; England, B.M.; Godwin, A.K.; et al. Exome sequencing of serous endometrial tumors identifies recurrent somatic mutations in chromatin-remodeling and ubiquitin ligase complex genes. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1310–1315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Kang, B.; Li, C.; Chen, T.; Zhang, Z. GEPIA2: An enhanced web server for large-scale expression profiling and interactive analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, W556–W560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.-J.; Pan, L.; Liu, Y.; Rong, Z.; Liu, J.; Liu, F. GEPIA3: Enhanced drug sensitivity and interaction network analysis for cancer research. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 53, W283–W290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kus, M.E.; Sahin, C.; Kilic, E.; Askin, A.; Ozgur, M.M.; Karahanogullari, G.; Aksit, A.; O’cOnnell, R.M.; Ekiz, H.A. TCGEx: A powerful visual interface for exploring and analyzing cancer gene expression data. Embo Rep. 2025, 26, 1863–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumas, J.; Gargano, M.A.; Dancik, G.M. shinyGEO: A web-based application for analyzing gene expression omnibus datasets. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 3679–3681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Essen, T.H.; Van Pelt, S.I.; Bronkhorst, I.H.G.; Versluis, M.; Némati, F.; Laurent, C.; Luyten, G.P.M.; Van Hall, T.; Elsen, P.J.V.D.; Van Der Velden, P.A.; et al. Upregulation of HLA Expression in Primary Uveal Melanoma by Infiltrating Leukocytes. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0164292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, D.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, X.; Hu, Y.; Zhang, R.; Gao, X.; Lin, M.; Guo, T.; Zhang, K. The role of EphA7 in different tumors. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 24, 1274–1289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oki, M.; Yamamoto, H.; Taniguchi, H.; Adachi, Y.; Imai, K.; Shinomura, Y. Overexpression of the receptor tyrosine kinase EphA4 in human gastric cancers. World J. Gastroenterol. 2008, 14, 5650–5656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giaginis, C.; Tsoukalas, N.; Bournakis, E.; Alexandrou, P.; Kavantzas, N.; Patsouris, E.; Theocharis, S. Ephrin (Eph) receptor A1, A4, A5 and A7 expression in human non-small cell lung carcinoma: Associations with clinicopathological parameters, tumor proliferative capacity and patients’ survival. BMC Clin. Pathol. 2014, 14, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Xu, Y.; Jin, Q.; Wang, W.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, X.; Huang, J. EphA8 is a prognostic marker for epithelial ovarian cancer. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 20801–20809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, C.; Cau, W.; Zhang, Y.; Mghanga, F.P.; Lan, X.; Gao, Z.; An, R. Correlation of Clinicopathological Features and Expression of Molecular Markers with Prognosis After 131I Treatment of Differentiated Thyroid Carcinoma. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2012, 37, e40–e46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.-F.; Fokas, E.; Juricko, J.; You, A.; Rose, F.; Pagenstecher, A.; Engenhart-Cabillic, R.; An, H.-X. Increased expression of EphA7 correlates with adverse outcome in primary and recurrent glioblastoma multiforme patients. BMC Cancer 2008, 8, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khansaard, W.; Techasen, A.; Namwat, N.; Yongvanit, P.; Khuntikeo, N.; Puapairoj, A.; Loilome, W. Increased EphB2 expression predicts cholangiocarcinoma metastasis. Tumor Biol. 2014, 35, 10031–10041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, F.; Dai, S.-N.; Xu, D.-L.; Hou, C.-Q.; Liu, T.-T.; Chen, Q.-Y.; Wu, J.-L.; Miao, Y. EFNB2 facilitates cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma via the p53/p21 pathway and EMT. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 125, 109972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oweida, A.; Bhatia, S.; Hirsch, K.; Calame, D.; Griego, A.; Keysar, S.; Pitts, T.; Sharma, J.; Eckhardt, G.; Jimeno, A.; et al. Ephrin-B2 overexpression predicts for poor prognosis and response to therapy in solid tumors. Mol. Carcinog. 2016, 56, 1189–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, S.M.; Fujimoto, J.; Jahan, I.; Sato, E.; Tamaya, T. Coexpression of EphB4 and ephrinB2 in tumour advancement of ovarian cancers. Br. J. Cancer 2008, 98, 845–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, S.; Fujimoto, J.; Jahan, I.; Sato, E.; Tamaya, T. Overexpression of ephrinB2 and EphB4 in tumor advancement of uterine endometrial cancers. Ann. Oncol. 2006, 18, 485–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magic, Z.; Sandström, J.; Perez-Tenorio, G. Ephrin-B2 inhibits cell proliferation and motility in vitro and predicts longer metastasis-free survival in breast cancer. Int. J. Oncol. 2019, 55, 1275–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Castrillón, L.M.; Wurmser, M.; Öhlund, D.; Wilson, S.I. Dysregulation of core neurodevelopmental pathways—A common feature of cancers with perineural invasion. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1181775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, J.; Aksoy, B.A.; Dogrusoz, U.; Dresdner, G.; Gross, B.E.; Sumer, S.O.; Sun, Y.; Jacobsen, A.; Sinha, R.; Larsson, E.; et al. Integrative Analysis of Complex Cancer Genomics and Clinical Profiles Using the cBioPortal. Sci. Signal. 2013, 6, pl1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoadley, K.A.; Yau, C.; Hinoue, T.; Wolf, D.M.; Lazar, A.J.; Drill, E.; Shen, R.; Taylor, A.M.; Cherniack, A.D.; Thorsson, V.; et al. Cell-of-Origin Patterns Dominate the Molecular Classification of 10,000 Tumors from 33 Types of Cancer. Cell 2018, 173, 291–304.e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, P.; Aoude, L.G.; Wadt, K.; Glasson, W.J.; Warrier, S.K.; Hewitt, A.W.; Kiilgaard, J.F.; Heegaard, S.; Isaacs, T.; Franchina, M.; et al. Deep sequencing of uveal melanoma identifies a recurrent mutation in PLCB4. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 4624–4631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakravarty, D.; Gao, J.; Phillips, S.; Kundra, R.; Zhang, H.; Wang, J.; Rudolph, J.E.; Yaeger, R.; Soumerai, T.; Nissan, M.H.; et al. OncoKB: A Precision Oncology Knowledge Base. JCO Precis. Oncol. 2017, 2017, PO.17.00011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tate, J.G.; Bamford, S.; Jubb, H.C.; Sondka, Z.; Beare, D.M.; Bindal, N.; Boutselakis, H.; Cole, C.G.; Creatore, C.; Dawson, E.; et al. COSMIC: The Catalogue of Somatic Mutations in Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D941–D947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Karthikeyan, S.K.; Korla, P.K.; Patel, H.; Shovon, A.R.; Athar, M.; Netto, G.J.; Qin, Z.S.; Kumar, S.; Manne, U.; et al. UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 2022, 25, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-J.; Hu, F.-F.; Xie, G.-Y.; Miao, Y.-R.; Li, X.-W.; Zeng, Y.; Guo, A.-Y. GSCA: An integrated platform for gene set cancer analysis at genomic, pharmacogenomic and immunogenomic levels. Briefings Bioinform. 2022, 24, bbac558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.-J.; Hu, F.-F.; Xia, M.-X.; Han, L.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, A.-Y. GSCALite: A web server for gene set cancer analysis. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3771–3772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hänzelmann, S.; Castelo, R.; Guinney, J. GSVA: Gene set variation analysis for microarray and RNA-Seq data. BMC Bioinform. 2013, 14, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
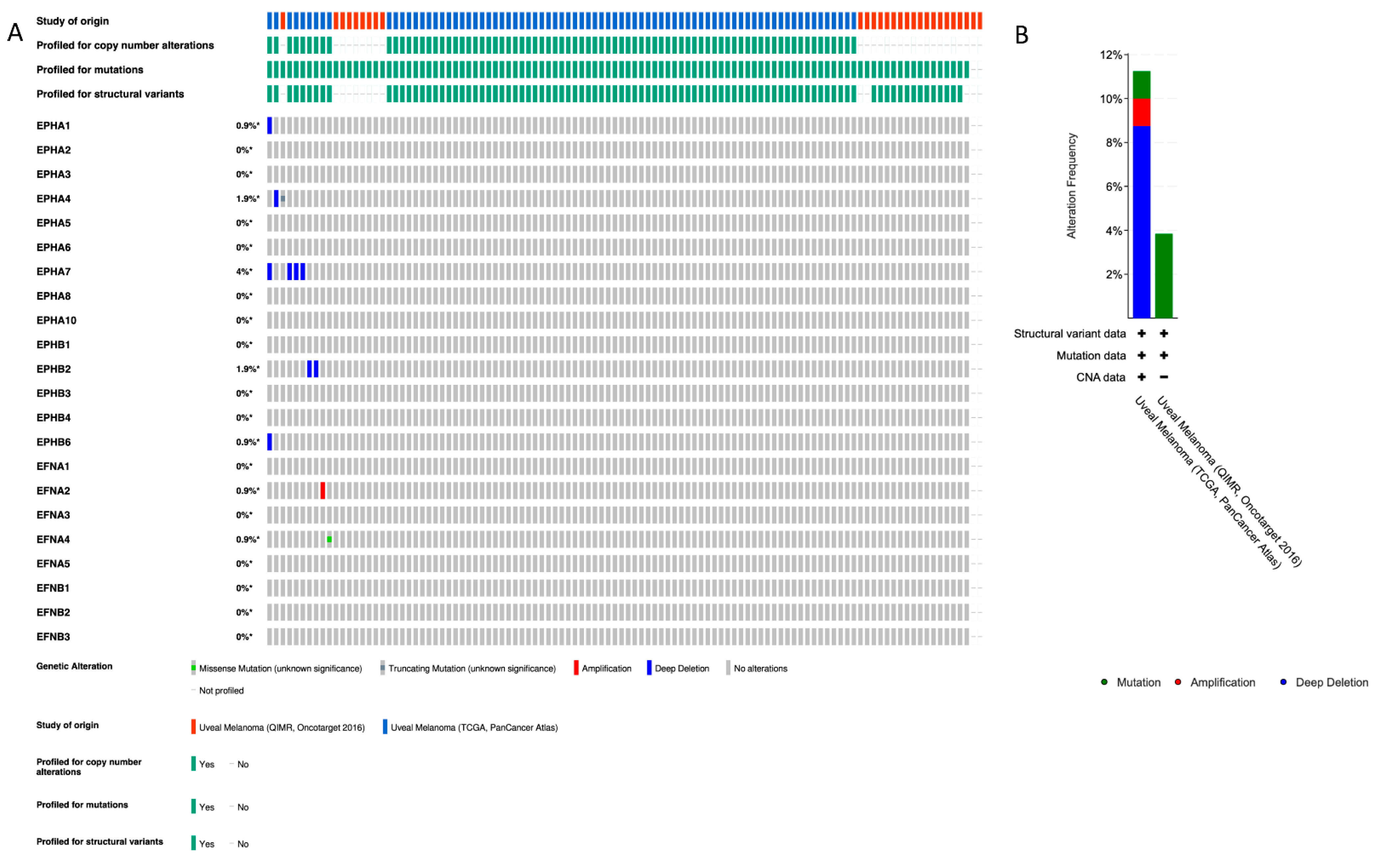
| Gene (Location) | Genomic Alteration (Percentage of Patients) | OS | DFS/PFI | UVM Histology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| EPHA1 (7q34–q35) | Homodeletion (0.9%) | |||
| EPHA2 (1p36.13) | Epithelioid | |||
| EPHA4 (2q36.1) | Homodeletion (0.9%), p.R230* nonsense PV (c.688C>T) (0.9%) | ↓ | ↓ | Epithelioid |
| EPHA5 (4q13.1–q13.2) | ↓ | ↓ | ||
| EPHA7 (6q16.1) | Homodeletion (4%) | ↓ | ||
| EPHA8 (1p36.12) | ↓ | ↓ | Epithelioid | |
| EPHB2 (1p36.13) | Homodeletion (1.9%) | ↓ | ↓ | |
| EPHB4 (7q22.1) | Epithelioid | |||
| EPHB6 (7q34) | Homodeletion (0.9%) | |||
| EFNA1 (1q22) | Epithelioid | |||
| EFNA2 (19p13.3) | Amplification (0.9%) | ↓ | ||
| EFNA3 (1q21.3) | Epithelioid | |||
| EFNA4 (1q21.3) | R196H missense PV (587G>A) (0.9%) | Epithelioid | ||
| EFNB2 (13q33.3) | ↓ | ↓ | Epithelioid |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Mandrakis, G.; Flessa, C.-M.; Keratsa, P.; Zaravinos, A.; Theocharis, S.; Sykaras, A.G. Ephrin Receptors and Ephrin Ligands in Uveal Melanoma: A Big Data Analysis Using Web Resources. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010442
Mandrakis G, Flessa C-M, Keratsa P, Zaravinos A, Theocharis S, Sykaras AG. Ephrin Receptors and Ephrin Ligands in Uveal Melanoma: A Big Data Analysis Using Web Resources. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010442
Chicago/Turabian StyleMandrakis, Georgios, Christina-Maria Flessa, Panoraia Keratsa, Apostolos Zaravinos, Stamatios Theocharis, and Alexandros G. Sykaras. 2026. "Ephrin Receptors and Ephrin Ligands in Uveal Melanoma: A Big Data Analysis Using Web Resources" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010442
APA StyleMandrakis, G., Flessa, C.-M., Keratsa, P., Zaravinos, A., Theocharis, S., & Sykaras, A. G. (2026). Ephrin Receptors and Ephrin Ligands in Uveal Melanoma: A Big Data Analysis Using Web Resources. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 442. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010442









