Integrative Profiling for BBB Permeability Using Capillary Electrochromatography, Experimental Physicochemical Parameters, and Ensemble Machine Learning
Abstract
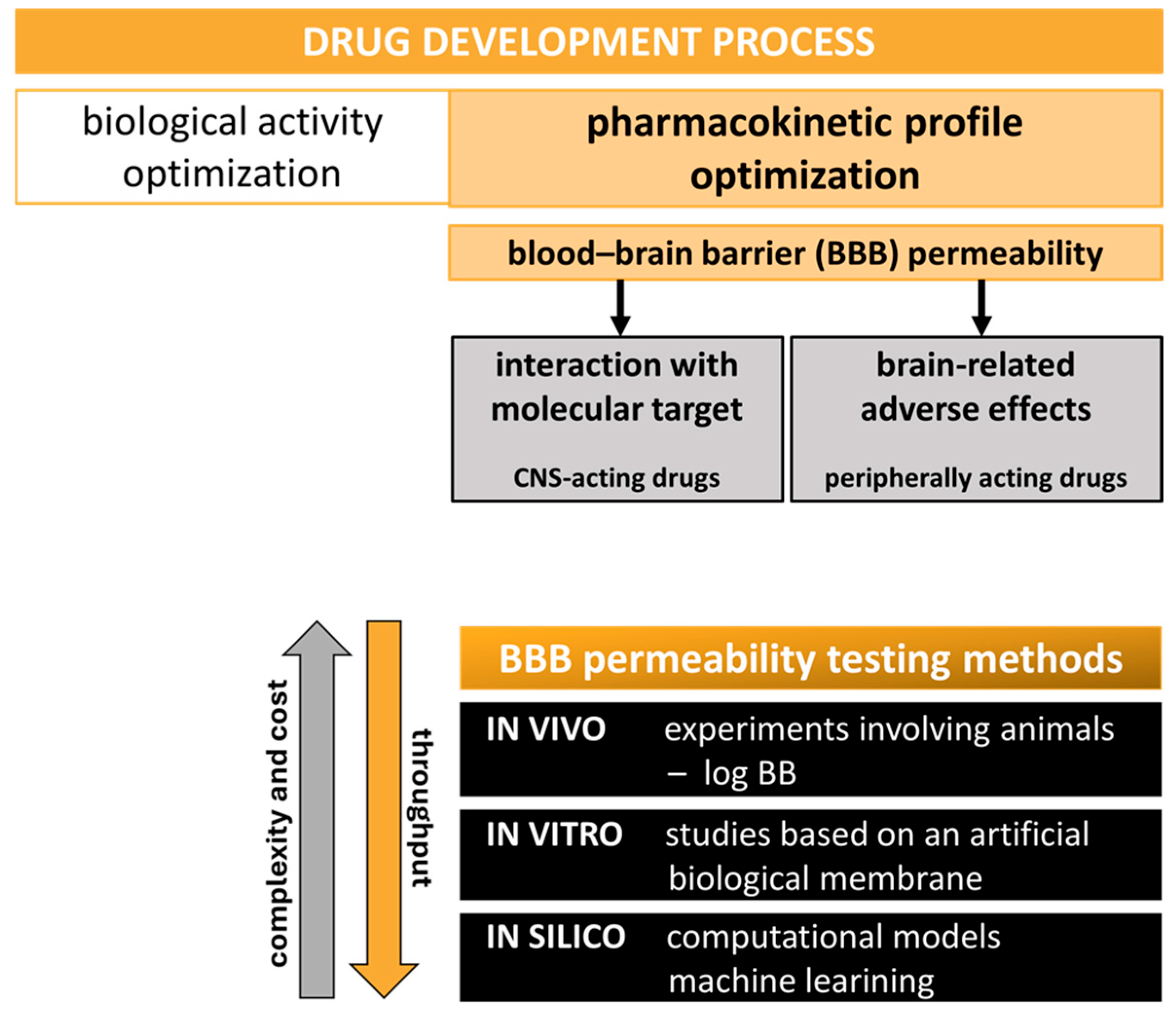
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
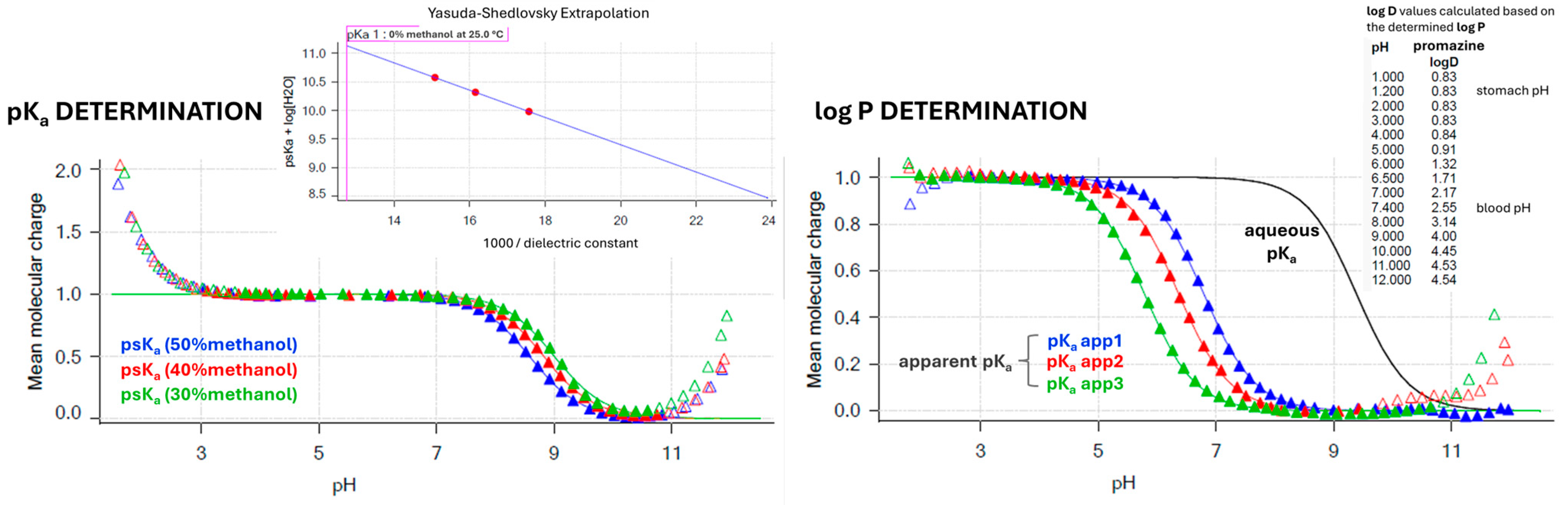
2.1. CEC-Derived Permeability (k′) and Automated Sirius T3 Physicochemical Profiling (pKa, Log P, and Log D7.4)
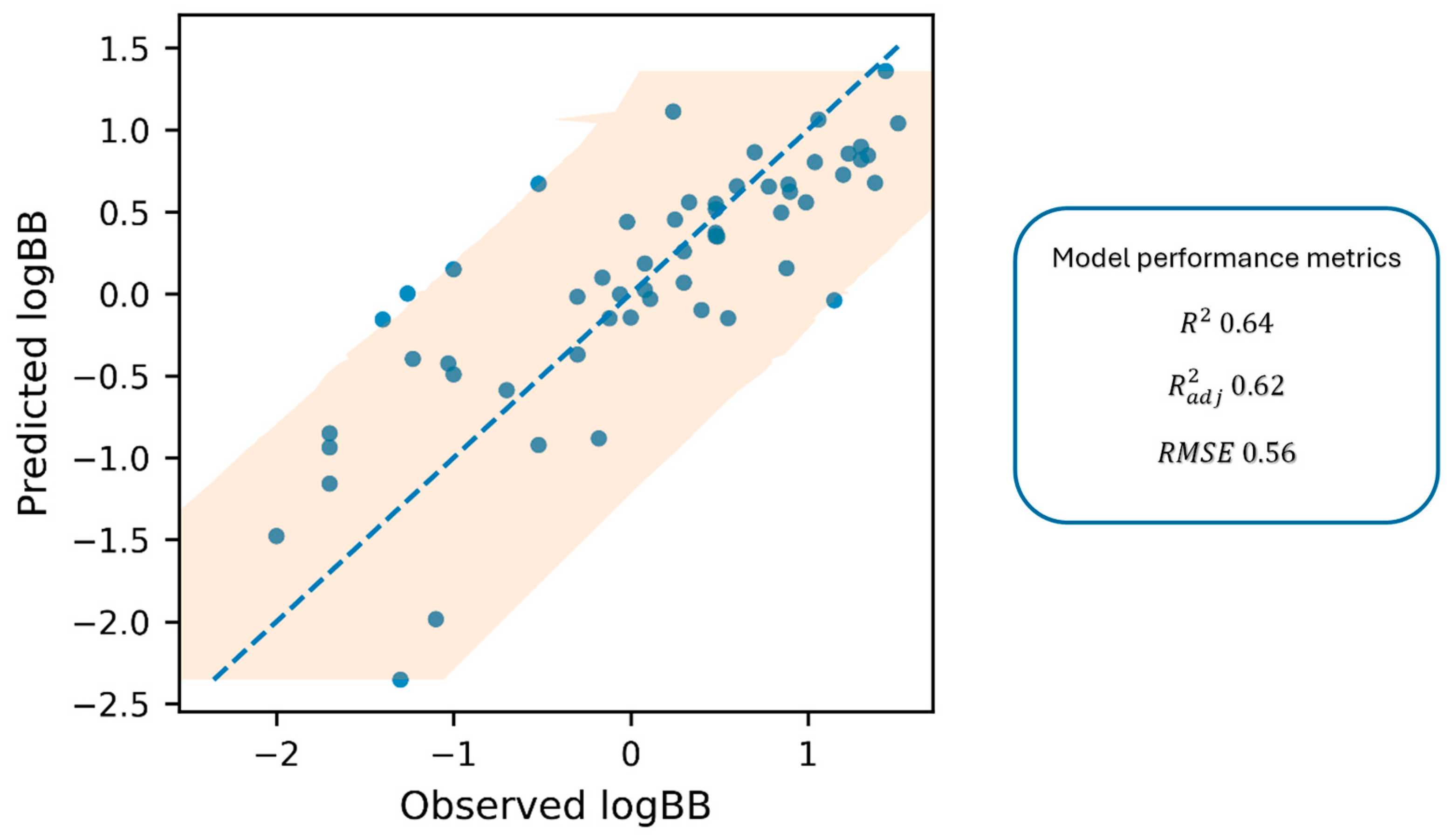
2.2. Quantitative Log BB Estimation—Correlation of In Vitro k′, pKa, and Log D7.4 with In Vivo Data
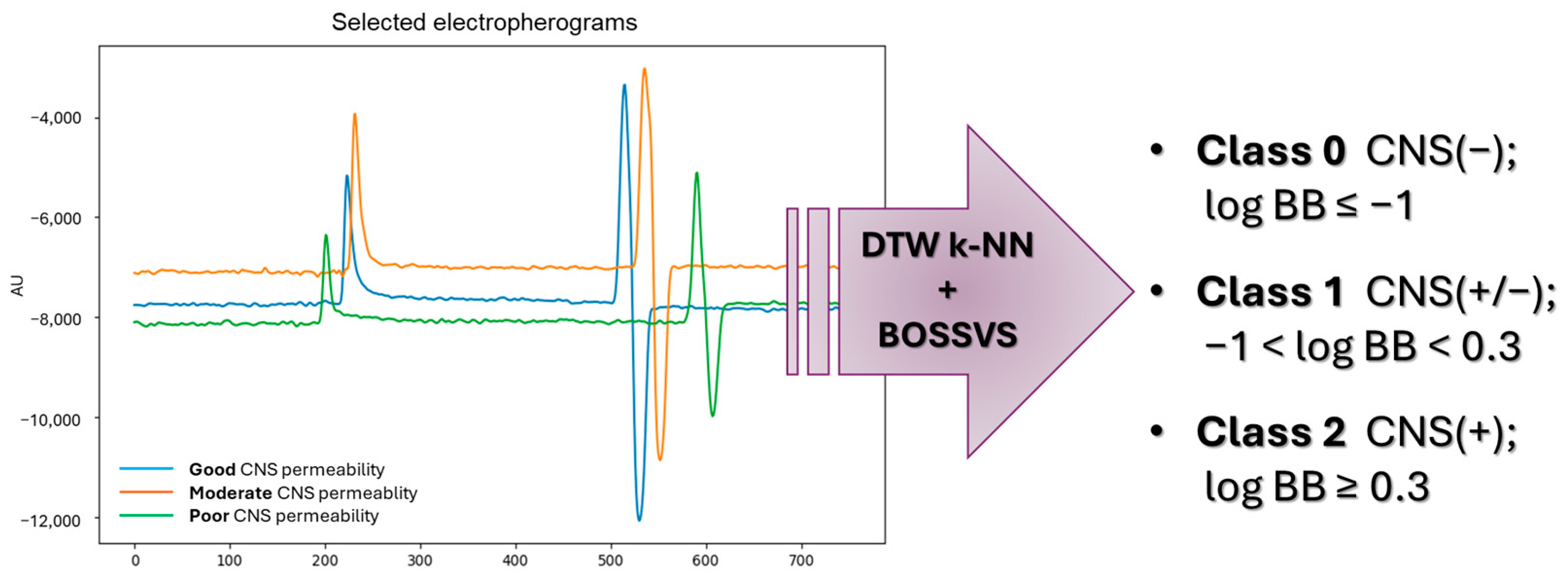
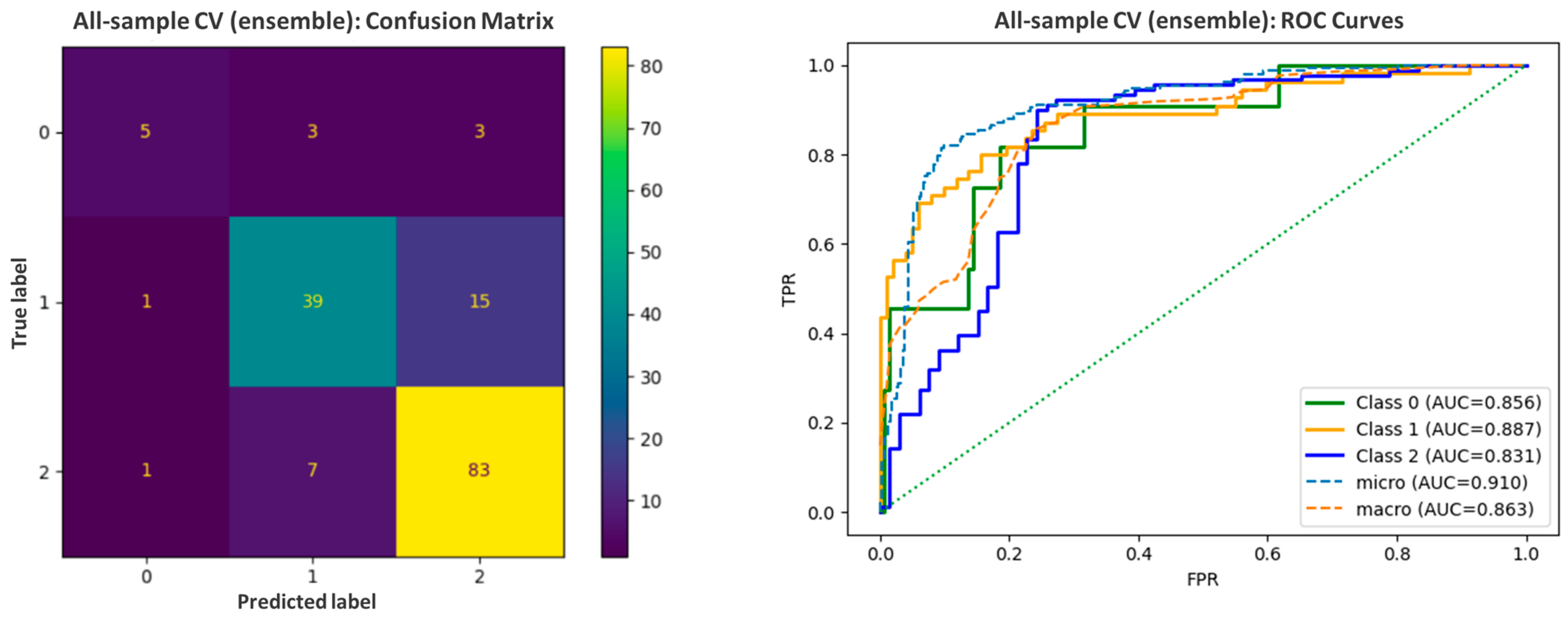
2.3. Qualitative Log BB Estimation—Machine Learning-Based Model
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemicals
3.2. Materials
3.3. Instruments
3.4. Methods
3.4.1. CEC—Determination of Permeability k′ Parameter
3.4.2. Automated Sirius T3 Titrations—Determination of Physicochemical Properties (pKa, Log P, and Log D7.4)
3.4.3. In Silico Ensemble Learning Model
- Class 0—poor CNS permeability (log BB ≤ −1);
- Class 1—moderate CNS permeability (−1 < log BB < 0.3);
- Class 2—good CNS permeability (log BB ≥ 0.3).
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADME | Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, and Excretion |
| AUC | Area Under the Curve |
| BBB | Blood–Brain Barrier |
| BOSSVS | Bag-of-SFA-Symbols in Vector Space |
| CA | California |
| Caco-2 | Human Colorectal Adenocarcinoma Cell Line |
| CE | Capillary Electrophoresis |
| CEC | Capillary Electrochromatography |
| CNS | Central Nervous System |
| CV | Cross-Validation |
| DAD | Diode Array Detector |
| DMSO | Dimethyl Sulfoxide |
| DTW | Dynamic Time Warping |
| EOF | Electroosmotic Flow |
| GPU | Graphics Processing Unit |
| HEPES | 4-(2-hydroxyethyl)-1-piperazine ethane sulfonic acid |
| HPLC | High Performance Liquid Chromatography |
| ISA | Ionic Strength Adjusted |
| k-NN | k-Nearest Neighbors |
| LC-MS | Liquid Chromatography–Mass Spectrometry |
| LEKC | Liposome Electrokinetic Chromatography |
| LUVs | Large Unilamellar Vesicles |
| MDCK-MDR1 | Madin–Darby Canine Kidney Cells Expressing MDR1 |
| MEKC | Micellar Electrokinetic Chromatography |
| ML | Machine Learning |
| NaN | Not a Number |
| OLS | Ordinary Least Squares |
| OOF | Out-Of-Fold |
| PAMPA-BBB | Parallel Artificial Membrane Permeability Assay for the Blood–Brain Barrier |
| POPC | 1-palmitoyl-2-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphocholine |
| PS | Phosphatidylserine |
| ROC | Receiver Operating Characteristic |
| Ro5 | Rule of Five |
| RoCNS | Rule for Central Nervous System Drugs |
| RSD | Relative Standard Deviation |
| SFA | Symbolic Fourier Approximation |
| SVL | Supported Vesicular Layer |
| UV | Ultraviolet |
References
- Abbott, N.J.; Rönnbäck, L.; Hansson, E. Astrocyte–endothelial interactions at the blood–brain barrier. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2006, 7, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbott, N.J.; Patabendige, A.A.K.; Dolman, D.E.M.; Yusof, S.R.; Begley, D.J. Structure and function of the blood–brain barrier. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 37, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mensch, J.; Oyarzabal, J.; Mackie, C.; Augustijns, P. In vivo, in vitro and in silico methods for small molecule transfer across the BBB. J. Pharm. Sci. 2009, 98, 4429–4468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nicolazzo, J.A.; Charman, S.A.; Charman, W.N. Methods to assess drug permeability across the blood-brain barrier. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 281–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaker, B.; Lee, J.; Lee, Y.; Yu, M.S.; Lee, H.M.; Lee, E.; Kang, H.C.; Oh, K.S.; Kim, H.W.; Na, D. A machine learning-based quantitative model (LogBB_Pred) to predict the blood–brain barrier permeability (logBB value) of drug compounds. Bioinformatics 2023, 39, btad577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Yin, L.; Wang, Y.; Fan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, H. ADME properties evaluation in drug discovery: In silico prediction of blood–brain partitioning. Mol. Divers. 2018, 22, 979–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanat, K.; Michalak, K.; Brzezińska, E. Log BB Prediction Models Using TLC and HPLC Retention Values as Protein Affinity Data. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abbott, N.J. Prediction of blood–brain barrier permeation in drug discovery from in vivo, in vitro and in silico models. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2004, 1, 407–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nielsen, P.A.; Andersson, O.; Hansen, S.H.; Simonsen, K.B.; Andersson, G. Models for predicting blood–brain barrier permeation. Drug Discov. Today 2011, 16, 472–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bicker, J.; Alves, G.; Fortuna, A.; Falcão, A. Blood–brain barrier models and their relevance for a successful development of CNS drug delivery systems: A review. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2014, 87, 409–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radan, M.; Djikic, T.; Obradovic, D.; Nikolic, K. Application of in vitro PAMPA technique and in silico computational methods for blood-brain barrier permeability prediction of novel CNS drug candidates. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 168, 106056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagchi, S.; Chhibber, T.; Lahooti, B.; Verma, A.; Borse, V.; Jayant, R.D. In-vitro blood-brain barrier models for drug screening and permeation studies: An overview. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2019, 13, 3591–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kansy, M.; Senner, F.; Gubernator, K. Physicochemical high throughput screening: Parallel artificial membrane permeation assay in the description of passive absorption processes. J. Med. Chem. 1998, 41, 1007–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di, L.; Kerns, E.H.; Fan, K.; McConnell, O.J.; Carter, G.T. High throughput artificial membrane permeability assay for blood-brain barrier. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2003, 38, 223–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, C.H.; Kim, S.J.; Shin, B.S.; Lee, K.C.; Yoo, S.D. Rapid Screening of Blood-Brain Barrier Penetration of Drugs Using the Immobilized Artificial Membrane Phosphatidylcholine Column Chromatography. SLAS Discov. 2006, 11, 13–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciura, K.; Dziomba, S. Application of separation methods for in vitro prediction of blood–brain barrier permeability—The state of the art. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 177, 112891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciura, K.; Ulenberg, S.; Kapica, H.; Kawczak, P.; Belka, M.; Bączek, T. Assessment of blood–brain barrier permeability using micellar electrokinetic chromatography and P_VSA-like descriptors. Microchem. J. 2020, 158, 105236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Liu, H.; He, Z. Rapidly profiling blood-brain barrier penetration with liposome EKC. Electrophoresis 2007, 28, 2391–2395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbato, F.; Grumetto, L.; Carpentiero, C.; Rocco, A.; Fanali, S. Capillary electrochromatography as a new tool to assess drug affinity for membrane phospholipids. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 54, 893–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raevsky, O.A.; Grigorev, V.Y.; Polianczyk, D.E.; Sandakov, G.I.; Solodova, S.L.; Yarkov, A.V.; Bachurin, S.O.; Dearden, J.C. Physicochemical property profile for brain permeability: Comparative study by different approaches. J. Drug Target. 2016, 24, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rankovic, Z. CNS Drug Design: Balancing Physicochemical Properties for Optimal Brain Exposure. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 2584–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talevi, A. In Silico Prediction of CNS Bioavailability. In AAPS Introductions in the Pharmaceutical Sciences; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2024; pp. 93–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.Y.; Liu, H.; Summerfield, S.G.; Luscombe, C.N.; Sahi, J. Integrating in Silico and in Vitro Approaches to Predict Drug Accessibility to the Central Nervous System. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 1540–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, T.B.; Parise-Filho, R. Analysis of the Applicability and Use of Lipinski’s Rule for Central Nervous System Drugs. Lett. Drug Des. Discov. 2016, 13, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manallack, D.T.; Prankerd, R.J.; Yuriev, E.; Oprea, T.I.; Chalmers, D.K. The significance of acid/base properties in drug discovery. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2012, 42, 485–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Jiang, M.; Javeria, H.; Tian, D.; Du, Z. Accurate prediction of Kp,uu,brain based on experimental measurement of Kp,brain and computed physicochemical properties of candidate compounds in CNS drug discovery. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H. A QSAR study of the brain/blood partition coefficients on the basis of pKa values. QSAR Comb. Sci. 2006, 25, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruciani, G.; Milletti, F.; Storchi, L.; Sforna, G.; Goracci, L. In silico pKa prediction and ADME profiling. Chem. Biodivers. 2009, 6, 1812–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Avdeef, A. Physicochemical Profiling (Solubility, Permeability and Charge State). Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2005, 1, 277–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharate, S.S.; Kumar, S.; Vishwakarma, R.A. Determining Partition Coefficient (Log P), Distribution Coefficient (Log D) and Ionization Constant (pKa) in Early Drug Discovery. Comb. Chem. High Throughput Screen. 2016, 19, 461–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardonville, C. Automated techniques in pKa determination: Low, medium and high-throughput screening methods. Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2018, 27, 49–58, Erratum in Drug Discov. Today Technol. 2020, 38, 105–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mtewa, A.G.; Ngwira, K.; Lampiao, F.; Weisheit, A.; Tolo, C.U. Fundamental Methods in Drug Permeability, pKa, LogP and LogDx Determination. J. Drug Res. Dev. 2018, 4, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reijenga, J.; van Hoof, A.; van Loon, A.; Teunissen, B. Development of methods for the determination of pKa values. Anal. Chem. Insights 2013, 8, 53–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Comer, J.; Box, K. High-Throughput Measurement of Drug pKa Values for ADME Screening. JALA J. Assoc. Lab. Autom. 2003, 8, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, K.Y.; Takács-Novák, K. Multi-wavelength spectrophotometric determination of acid dissociation constants: A validation study. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 434, 157–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, D.; Sharma, A.; Siddiqui, M.H.; Kumar, R. Blood Brain Barrier Permeability Prediction Using Machine Learning Techniques: An Update. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2019, 20, 1163–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, L.; Feng, H.; Li, S.; Liu, M.; Zhao, J.; Liu, H. Prediction of the Blood-Brain Barrier (BBB) Permeability of Chemicals Based on Machine-Learning and Ensemble Methods. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 2021, 34, 1456–1467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Yang, H.; Wu, Z.; Wang, T.; Li, W.; Tang, Y.; Liu, G. In Silico Prediction of Blood–Brain Barrier Permeability of Compounds by Machine Learning and Resampling Methods. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 2189–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nabi, A.E.; Pouladvand, P.; Liu, L.; Hua, N.; Ayubcha, C. Machine Learning in Drug Development for Neurological Diseases: A Review of Blood Brain Barrier Permeability Prediction Models. Mol. Inform. 2025, 44, e202400325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alsenan, S.; Al-Turaiki, I.; Hafez, A. A Deep Learning Approach to Predict Blood-Brain Barrier Permeability. PeerJ Comput. Sci. 2021, 7, e515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schäfer, P. Scalable time series classification. Data Min. Knowl. Discov. 2016, 30, 1273–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, L.; Liu, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y. Prediction of blood-brain barrier permeability using machine learning approaches based on various molecular representation. Mol. Inform. 2024, 43, e202300327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen-Vo, T.H.; Do, T.T.T.; Nguyen, B.P. An Effective Ensemble Deep Learning Framework for Blood-brain Barrier Permeability Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2024 IEEE Conference on Artificial Intelligence (CAI), Singapore, 25–27 June 2024; pp. 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godyń, J.; Hebda, M.; Więckowska, A.; Więckowski, K.; Malawska, B.; Bajda, M. Lipophilic properties of anti-Alzheimer’s agents determined by micellar electrokinetic chromatography and reversed-phase thin-layer chromatography. Electrophoresis 2017, 38, 1268–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godyń, J.; Gucwa, D.; Kobrlova, T.; Novak, M.; Soukup, O.; Malawska, B.; Bajda, M. Novel application of capillary electrophoresis with a liposome coated capillary for prediction of blood-brain barrier permeability. Talanta 2020, 217, 121023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, P.; Verma, J. In Silico Prediction of Blood Brain Barrier Permeability: An Artificial Neural Network Model. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2006, 46, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Young, R.C.; Mitchell, R.C.; Brown, T.H.; Ganellin, C.R.; Griffiths, R.; Jones, M.; Rana, K.K.; Saunders, D.; Smith, I.R.; Sore, N.E. Development of a new physicochemical model for brain penetration and its application to the design of centrally acting H2 receptor histamine antagonists. J. Med. Chem. 1988, 31, 656–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose, K.; Hall, L.H.; Kier, L.B. Modeling blood-brain barrier partitioning using the electrotopological state. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2002, 42, 651–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platts, J.A.; Abraham, M.H.; Zhao, Y.H.; Hersey, A.; Ijaz, L.; Butina, D. Correlation and prediction of a large blood-brain distribution data set--an LFER study. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2001, 36, 719–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terabe, S.; Otsuka, K.; Ando, T. Electrokinetic chromatography with micellar solution and open-tubular capillary. Anal. Chem. 1985, 57, 834–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seabold, S.; Perktold, J. Statsmodels: Econometric and Statistical Modeling with Python. In Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference, Austin, TX, USA, 28 June 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volpe, D.A. Drug-permeability and transporter assays in Caco-2 and MDCK cell lines. Future Med. Chem. 2011, 3, 2063–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonenko, Z.; Carnini, A.; Cramb, D. Supported planar bilayer formation by vesicle fusion: The interaction of phospholipid vesicles with surfaces and the effect of gramicidin on bilayer properties using atomic force microscopy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Biomembr. 2000, 1509, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reviakine, I.; Brisson, A. Formation of Supported Phospholipid Bilayers from Unilamellar Vesicles Investigated by Atomic Force Microscopy. Langmuir 2000, 16, 1806–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jass, J.; Tjärnhage, T.; Puu, G. From Liposomes to Supported, Planar Bilayer Structures on Hydrophilic and Hydrophobic Surfaces: An Atomic Force Microscopy Study. Biophys. J. 2000, 79, 3153–3163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiedmer, S.K.; Jussila, M.; Hakala, R.M.S.; Pystynen, K.-H.; Riekkola, M.-L. Piperazine-based buffers for liposome coating of capillaries for electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2005, 26, 1920–1927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, M.R.; Olivero, J.E.; Ok Choi, H.; Liao, C.P.; Kashemirov, B.A.; Katz, J.E.; Gross, M.E.; McKenna, C.E. Synthesis and anti-cancer potential of potent peripheral MAOA inhibitors designed to limit blood:brain penetration. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2023, 92, 117425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhu, H.; Oprea, T.I.; Golbraikh, A.; Tropsha, A. QSAR modeling of the blood–brain barrier permeability for diverse organic compounds. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 1902–1914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saber, R.; Rihana, S. A Classification-Based Blood–Brain Barrier Model: A Comparative Approach. Pharmaceuticals 2025, 18, 773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geler, Z.; Kurbalija, V.; Radovanović, M.; Ivanović, M. Comparison of different weighting schemes for the kNN classifier on time-series data. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2016, 48, 331–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| References | CEC | Sirius T3 pH-Metric Titrations | Log BB 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k′ ± SD 1 | pKa ± SD 2 | Log P ± SD 3 | Log D7.4 4 | ||
| acetylsalicylic acid | 0.03441 ± 0.00987 | 3.36 ± 0.00 | 1.31 ± 0.01 | −2.73 | −1.30 |
| amitriptyline | 0.00004 ± 0.00001 | 9.23 ± 0.08 | 4.68 ± 0.02 | 2.84 | 1.30 |
| atenolol | 0.00183 ± 0.00051 | 9.50 ± 0.01 | 0.06 ± 0.01 | −2.04 | −1.00 |
| atropine | 0.00440 ± 0.00309 | 9.84 ± 0.03 | 1.73 ± 0.01 | −0.72 | −0.06 |
| betahistine | 0.03582 ± 0.00587 | 9.84 ± 0.00 | 0.49 ± 0.01 | −1.95 | −0.30 |
| bromperidol | −0.00795 ± 0.00034 | 8.45 ± 0.10 | 3.87 ± 0.05 | 2.81 | 1.38 |
| buspirone | 0.02096 ± 0.00194 | 7.62 ± 0.00 | 2.89 ± 0.02 | 2.47 | 0.48 |
| chlorambucil | 0.00397 ± 0.00087 | 4.72 ± 0.04 | 3.71 ± 0.02 | 1.07 | −1.70 |
| chlorpromazine | 0.34688 ± 0.03015 | 9.07 ± 0.01 | 5.10 ± 0.03 | 3.43 | 1.06 |
| citalopram | 0.00405 ± 0.00229 | 9.43 ± 0.05 | 3.42 ± 0.00 | 1.39 | 0.48 |
| cyclobarbital | 0.00186 ± 0.00088 | 7.71 ± 0.02 | 1.33 ± 0.01 | 1.16 | −0.30 |
| desipramine | −0.01523 ± 0.00343 | 10.25 ± 0.02 | 4.00 ± 0.01 | 1.35 | 1.20 |
| diclofenac | 0.00802 ± 0.00320 | 4.19 ± 0.01 | 4.33 ± 0.01 | 1.26 | −1.70 |
| donepezil | −0.01233 ± 0.00010 | 9.10 ± 0.02 | 3.90 ± 0.02 | 2.19 | 0.89 |
| fluphenazine | 0.11096 ± 0.00192 | 7.79 ± 0.07 | 5.12 ± 0.06 | 4.58 | 1.51 |
| galanthamine | 0.00203 ± 0.00150 | 8.32 ± 0.00 | 1.15 ± 0.00 | 0.18 | 0.00 |
| haloperidol | −0.00906 ± 0.00138 | 8.66 ± 0.08 | 4.37 ± 0.08 | 3.18 | 1.34 |
| hydroxyzine | −0.00058 ± 0.00031 | 7.66 ± 0.04 | 3.73 ± 0.03 | 3.34 | 0.90 |
| ibuprofen | −0.03690 ± 0.00011 | 4.62 ± 0.05 | 3.80 ± 0.00 | 1.07 | −0.18 |
| imipramine | −0.04094 ± 0.00432 | 9.45 ± 0.12 | 4.44 ± 0.01 | 2.39 | 1.30 |
| indomethacin | 0.01869 ± 0.00624 | 4.71 ± 0.01 | 6.31 ± 0.12 | 3.92 | −1.26 |
| ketorolac | 0.02127 ± 0.00131 | 3.64 ± 0.06 | 2.90 ± 0.04 | −0.05 | −2.00 |
| clonidine | 0.00321 ± 0.00046 | 8.12 ± 0.01 | 1.53 ± 0.01 | 0.74 | 0.11 |
| clozapine | 0.00693 ± 0.00245 | 7.58 ± 0.01 | 3.92 ± 0.10 | 3.52 | 0.60 |
| codeine | −0.01188 ± 0.00888 | 8.22 ± 0.05 | 1.14 ± 0.01 | 0.26 | 0.55 |
| levofloxacin | −0.04345 ± 0.00321 | 8.13 6 ± 0.00 | 0.82 ± 0.01 | 0.77 | −0.70 |
| loperamide | 0.01470 ± 0.00102 | 8.69 ± 0.12 | 4.69 ± 0.17 | 3.21 | 0.70 |
| mepyramine | 0.00817 ± 0.00067 | 8.71 ± 0.05 | 2.73 ± 0.02 | 1.48 | 0.49 |
| metoclopramide | −0.00563 ± 0.00136 | 9.32 ± 0.02 | 2.31 ± 0.01 | 0.38 | 0.08 |
| metoprolol | −0.00612 ± 0.00036 | 9.50 ± 0.13 | 1.57 ± 0.01 | −0.53 | 1.15 |
| mianserin | −0.02148 ± 0.00155 | 7.25 ± 0.03 | 3.74 ± 0.01 | 3.50 | 0.99 |
| naproxen | 0.01050 ± 0.00460 | 4.47 ± 0.09 | 3.11 ± 0.00 | 0.27 | −1.70 |
| nicotine | 0.00897 ± 0.00167 | 8.09 ± 0.01 | 1.31 ± 0.01 | 0.54 | 0.40 |
| nortriptyline | −0.01133 ± 0.00210 | 10.05 ± 0.03 | 4.29 ± 0.01 | 1.79 | 1.04 |
| paroxetine | 0.02144 ± 0.00689 | 9.76 ± 0.08 | 3.39 ± 0.04 | 1.19 | 0.48 |
| phenobarbital | −0.01824 ± 0.00855 | 7.43 ± 0.06 | 1.26 ± 0.01 | 0.98 | −0.12 |
| phenylbutazone | 0.00083 ± 0.00015 | 4.58 ± 0.05 | 3.64 ± 0.01 | 0.96 | −0.52 |
| physostigmine | 0.01268 ± 0.00087 | 8.24 ± 0.04 | 1.69 ± 0.03 | 0.81 | 0.08 |
| pindolol | 0.00127 ± 0.00052 | 9.62 ± 0.07 | 1.91 ± 0.01 | −0.28 | 0.30 |
| promazine | −0.01399 ± 0.00228 | 9.39 ± 0.00 | 4.54 ± 0.00 | 2.55 | 1.23 |
| propranolol | 0.00202 ± 0.00061 | 9.46 ± 0.01 | 3.31 ± 0.01 | 1.29 | 0.85 |
| quinidine | 0.00340 ± 0.00040 | 8.82 ± 0.03 | 3.50 ± 0.00 | 2.08 | 0.33 |
| ranitidine | −0.00256 ± 0.00041 | 8.43 ± 0.01 | 0.34 ± 0.02 | −0.75 | −1.23 |
| risperidone | 0.00698 ± 0.00377 | 8.27 ± 0.04 | 3.09 ± 0.03 | 2.17 | −0.02 |
| ropinirole | −0.01252 ± 0.00126 | 9.70 ± 0.05 | 3.24 ± 0.01 | 0.94 | 0.25 |
| rivastigmine | −0.00018 ± 0.00009 | 8.91 ± 0.01 | 2.18 ± 0.01 | 0.66 | 0.88 |
| salbutamol | −0.01030 ± 0.00502 | 9.60 ± 0.01 | 0.30 ± 0.04 | −1.90 | −1.03 |
| salicylic acid | 0.02255 ± 0.00676 | 2.79 ± 0.01 | 2.31 ± 0.01 | −0.98 | −1.10 |
| thioperamide | 0.01849 ± 0.00363 | 6.90 ± 0.04 | 2.39 ± 0.02 | 2.27 | −0.16 |
| thioridazine | 0.00911 ± 0.00062 | 9.25 ± 0.01 | 5.38 ± 0.03 | 3.54 | 0.24 |
| trazodone | −0.01080 ± 0.00292 | 6.83 ± 0.04 | 2.98 ± 0.00 | 2.88 | 0.30 |
| trifluoperazine | 0.20277 ± 0.00151 | 7.88 ± 0.04 | 6.14 ± 0.01 | 5.53 | 1.44 |
| triprolidine | 0.01006 ± 0.00233 | 9.39 ± 0.06 | 3.87 ± 0.01 | 1.88 | 0.78 |
| venlafaxine | −0.01411 ± 0.00205 | 9.67 ± 0.02 | 2.97 ± 0.00 | 0.70 | 0.48 |
| verapamil | 0.00675 ± 0.00054 | 8.84 ± 0.06 | 3.89 ± 0.01 | 2.44 | −0.52 |
| zidovudine | 0.00428 ± 0.00056 | 9.51 ± 0.00 | 0.09 ± 0.01 | 0.09 | −1.00 |
| zolmitriptan | −0.00882 ± 0.00356 | 9.60 ± 0.05 | 1.19 ± 0.01 | −1.01 | −1.40 |
| Capillary/Coating | 50 µm Uncoated | 50 µm POPC/PS 2 |
|---|---|---|
| µEOF, × 10−8 [m2 × s−1 × V−1] | 5.79 1 | 4.68 1 |
| RSD [%] | 5.27 | 5.18 |
| number of measurements | 170 | 170 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Godyń, J.; Jończyk, J.; Więckowska, A.; Bajda, M. Integrative Profiling for BBB Permeability Using Capillary Electrochromatography, Experimental Physicochemical Parameters, and Ensemble Machine Learning. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010328
Godyń J, Jończyk J, Więckowska A, Bajda M. Integrative Profiling for BBB Permeability Using Capillary Electrochromatography, Experimental Physicochemical Parameters, and Ensemble Machine Learning. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010328
Chicago/Turabian StyleGodyń, Justyna, Jakub Jończyk, Anna Więckowska, and Marek Bajda. 2026. "Integrative Profiling for BBB Permeability Using Capillary Electrochromatography, Experimental Physicochemical Parameters, and Ensemble Machine Learning" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010328
APA StyleGodyń, J., Jończyk, J., Więckowska, A., & Bajda, M. (2026). Integrative Profiling for BBB Permeability Using Capillary Electrochromatography, Experimental Physicochemical Parameters, and Ensemble Machine Learning. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 328. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010328






