DNA Persistent Length in Solutions of Different pH
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
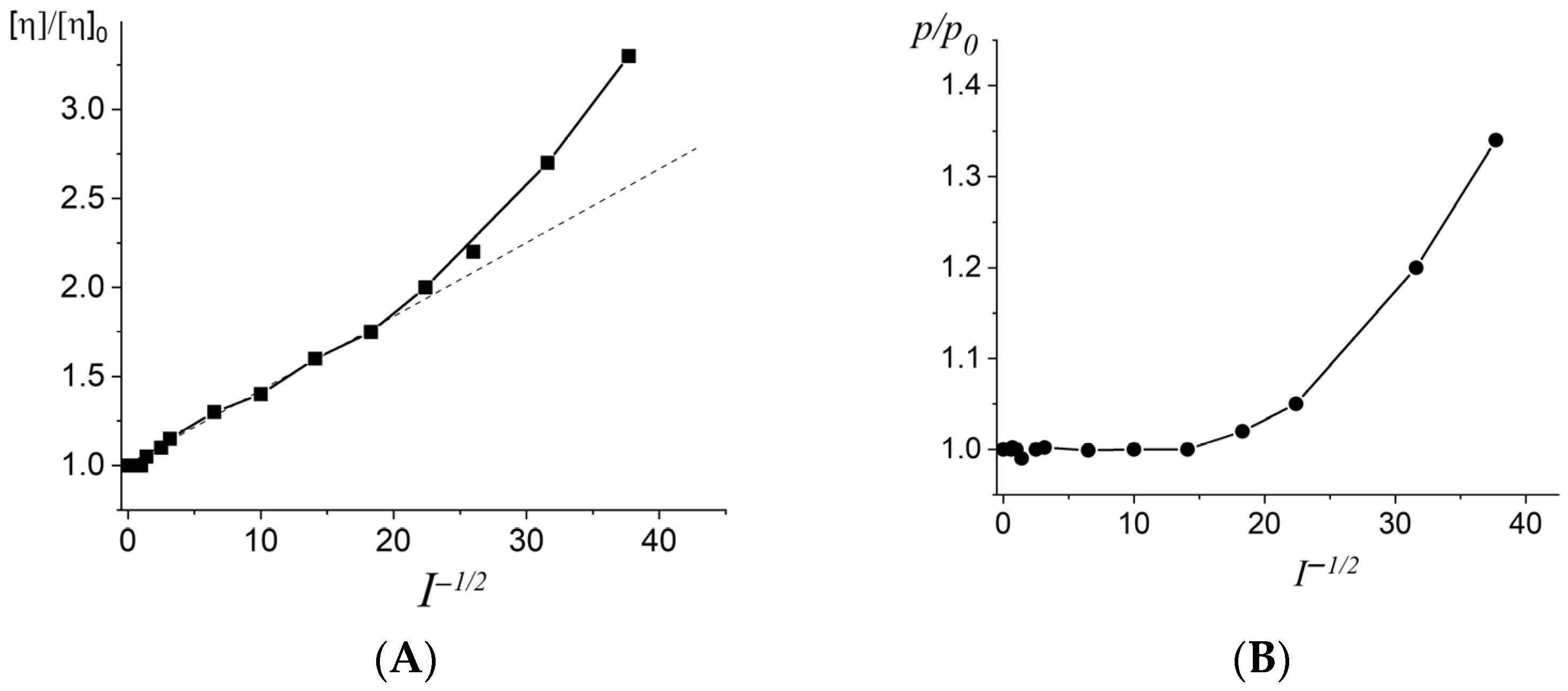
2.1. DNA Rigidity in Solutions with a Neutral pH Value
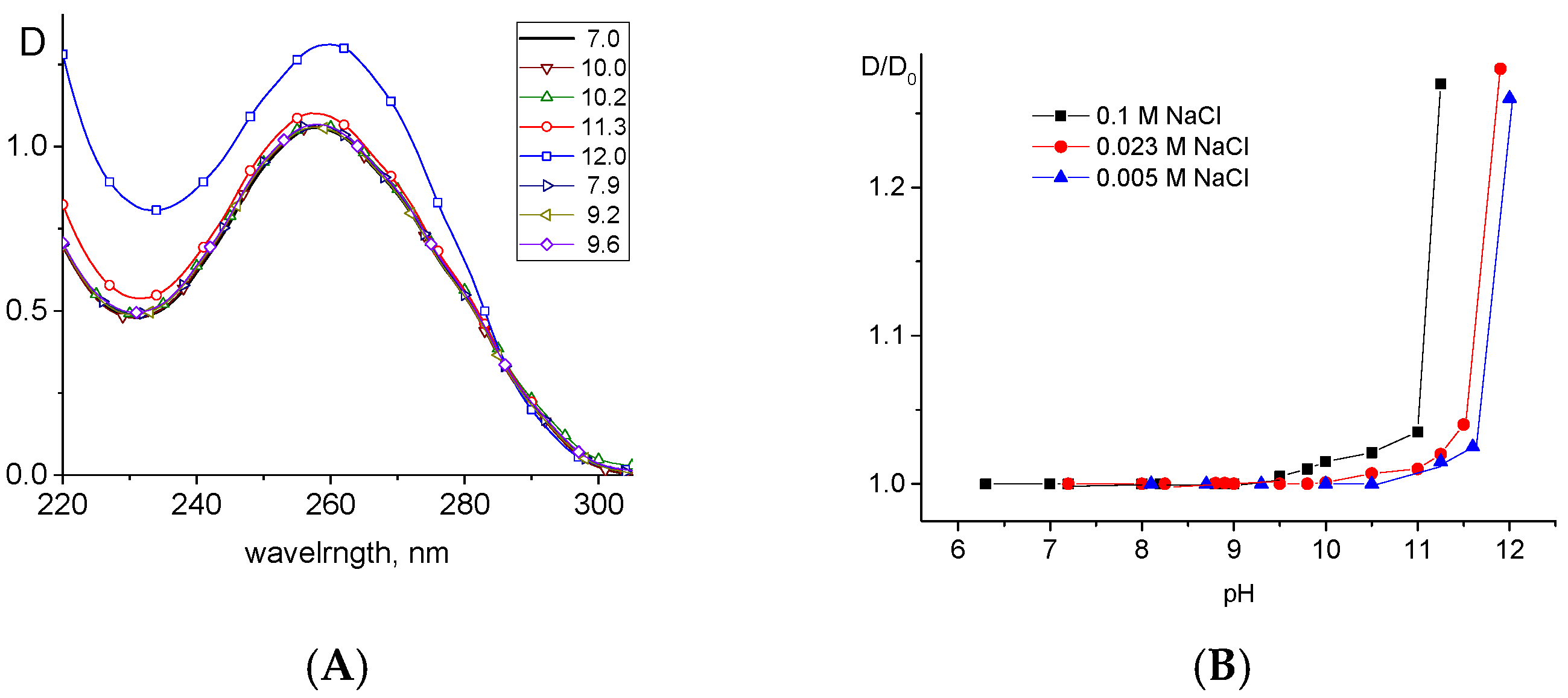
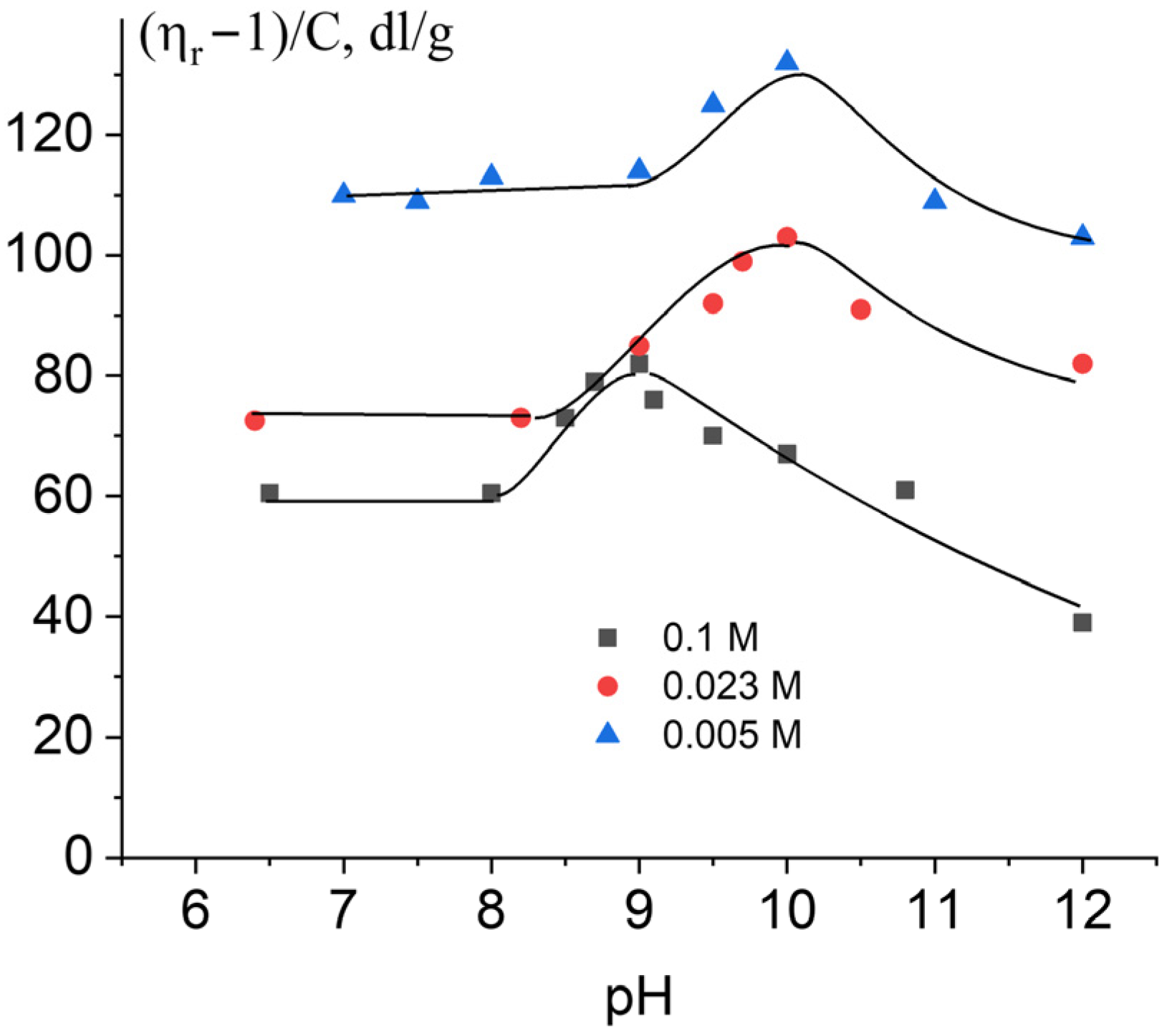
2.2. DNA Deprotonation in Alkaline Solutions
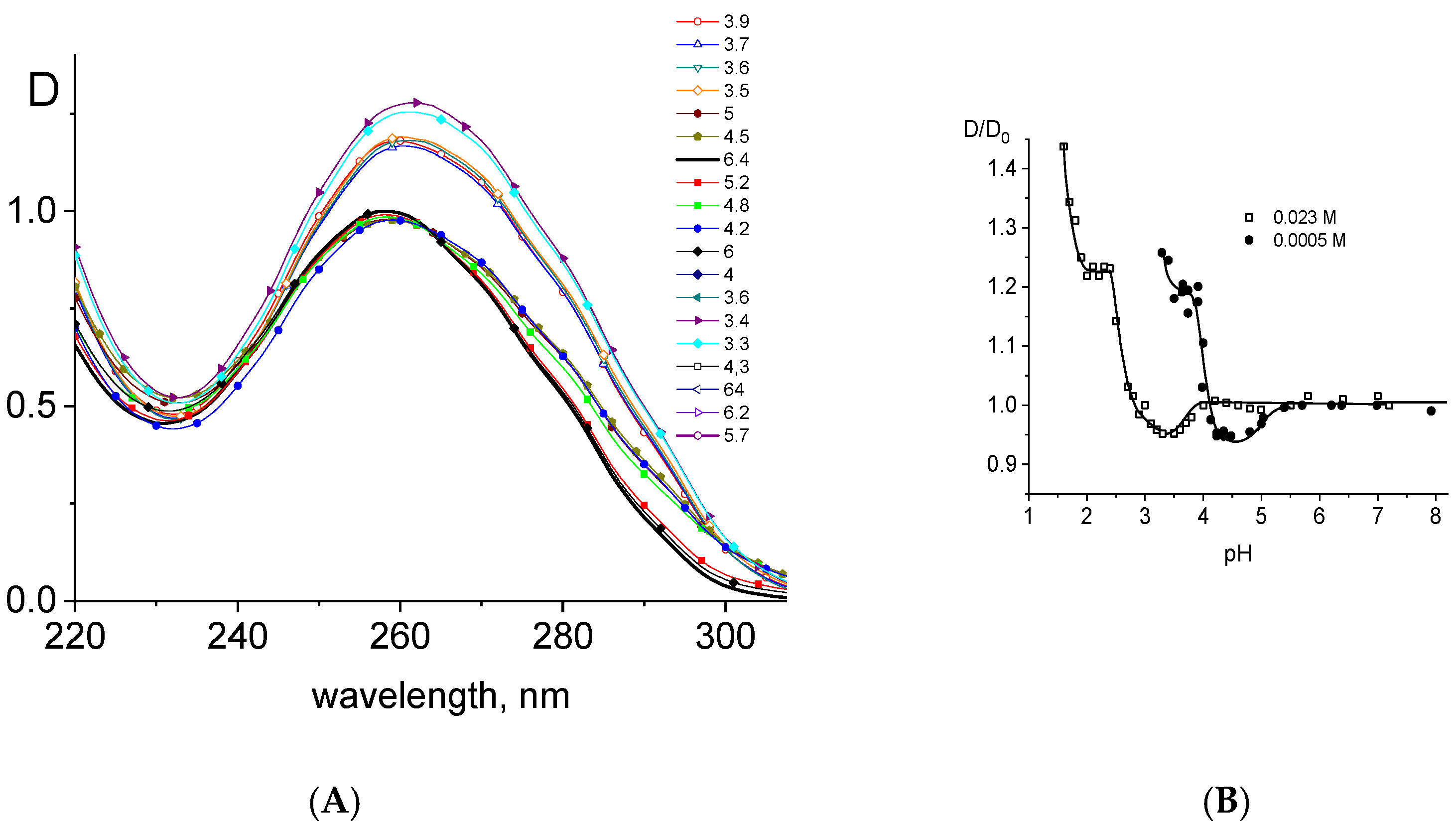
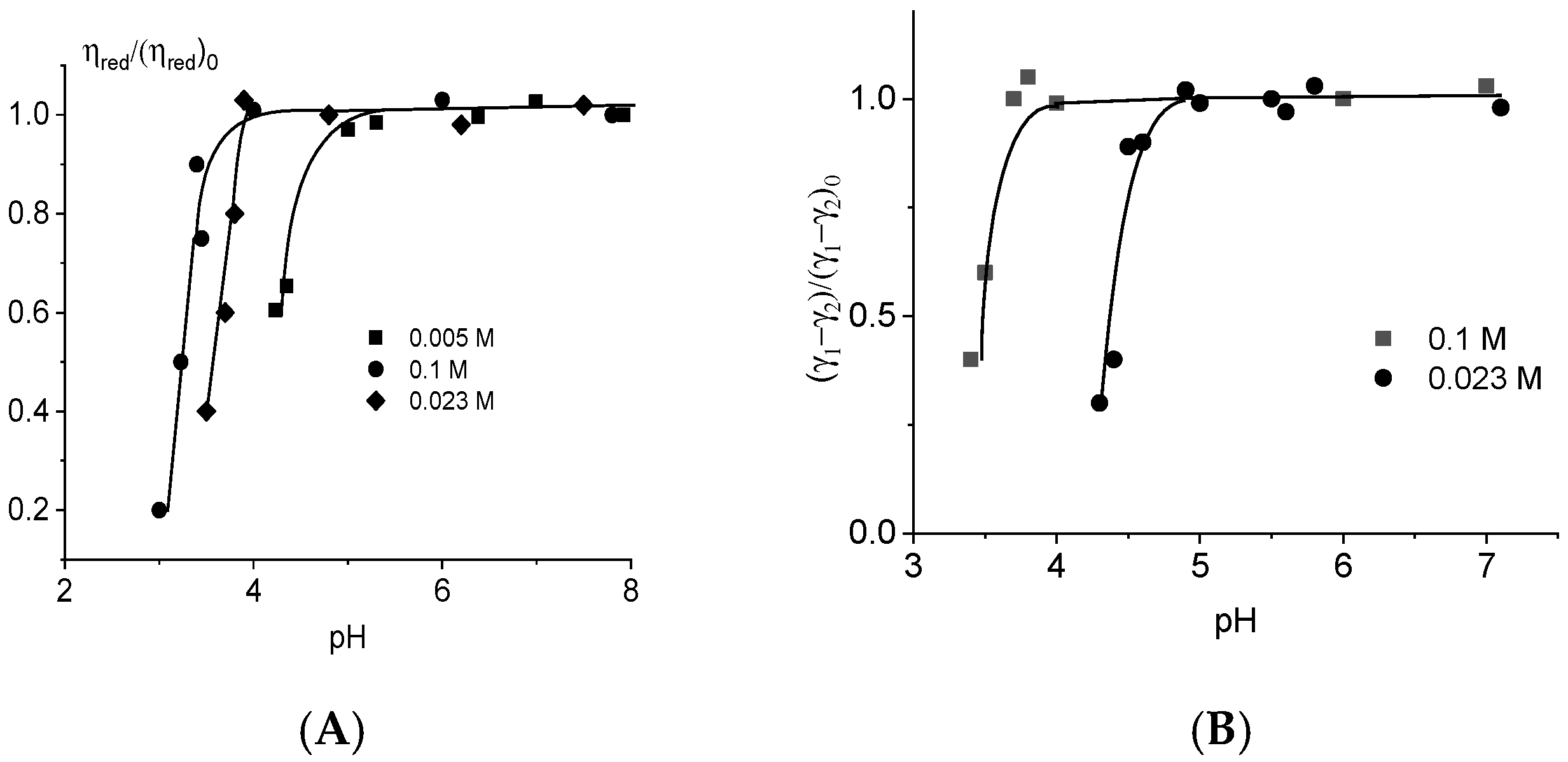
2.3. DNA Protonation in Acid Solutions
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Viscosimetry
3.3. Flow Birefringence
3.4. Spectral Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saenger, W. Principles of Nucleic Acid Structure; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1994. [Google Scholar]
- Fedeles, B.I.; Li, D.; Singh, V. Structural insights into tautomeric dynamics in nucleic acids and in antiviral nucleoside analogs. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 8, 823253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, E.L.; Mlotkowski, A.J.; Hebert, S.P.; Schlegel, H.B.; Chow, C.S. Calculations of pKa values for a series of naturally occurring modified nucleobases. J. Phys. Chem. A 2023, 127, 3526–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gehring, K.; Leroy, J.-L.; Guéron, M. A tetrameric DNA structure with protonated cytosine-cytosine base pairs. Nature 1993, 363, 561–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, T.; Yu, P.; Zhao, J.; Wang, J. Site specifically probing the unfolding process of human telomere i-motif DNA using vibrationally enhanced alkynyl stretch. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2024, 26, 3857–3868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrano-ChacóN, I.; Mir, B.; Escaja, N.; González, C. Structure of i-motif/duplex junctions at neutral pH. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143, 12919–12923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariottini, D.; Giudice, D.; Ercolani, G.; Stefano, S.; Ricci, F. Dissipative operation of pH-responsive DNA-based nanodevices. Chem. Sci. 2021, 12, 11735–11739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yousefi, A.; Ganjizade, A.; Ashrafizadeh, S.N. DNA translocation through pH-dependent soft nanopores. Eur. Biophys. J. 2021, 50, 905–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kisor, K.P.; Ruiz, D.G.; Jacobson, M.P.; Barber, D.L. A role for pH dynamics regulating transcription factor DNA-binding selectivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2025, 5, gkaf474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Czene, S.; Tibäck, M.; Harms-Ringdahl, M. pH-Dependent DNA breakage in permeabilized human fibroblasts. Biochem. J. 1997, 323, 337–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, L.L.; Li, J.Z.; Li, Y.X.; Gao, J.B.; Dong, J.X.; Gao, Z.F. pH-Responsive DNA Motif: From Rational Design to Analytical Applications. Front. Chem. 2021, 9, 732770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornyshev, A.A.; Leikin, S. Helical structure determines different susceptibilities of dsDNA, dsRNA, and tsDNA to counterion-induced condensation. Biophys. J. 2013, 104, 2031–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Lang, H.P.; Yoshikawa, G.; Gerber, C. Optimization of DNA hybridization efficiency by pH-driven nanomechanical bending. Langmuir 2012, 28, 6494–6501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.H.; Meng, W.L.; Zhang, C.Y.; Li, X.B.; Wu, J.Z.; Zhang, N.H. The pH-dependent elastic properties of nanoscale DNA films and the resultant bending signals for microcantilever biosensors. Soft Matter 2018, 14, 3028–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunet, A.; Tardin, C.; Salome, L.; Rousseau, P.; Destainville, N.; Manghi, M. Dependence of DNA persistence length on ionic strength of solutions with monovalent and divalent salts: A joint theory-experiment study. Macromolecules 2015, 48, 3641–3652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, R.K.; Yang, J.T. Effect of protonation on the Cotton effects on nucleic acids. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1965, 112, 512–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dove, W.F.; Wallace, T.; Davidson, N. Spectrophotometric study of the protonation of undenatured DNA. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Com. 1959, 1, 312–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luck, G.; Zimmer, C.; Snatzke, G. Circular dichroism of protonated DNA. Biophys. Biochem. Acta 1968, 169, 548–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drew, H.R.; Dickerson, R.E. Structure of a DNA dodecamer. Ill Geometry of hydration. J. Mol. Biol. 1981, 151, 535–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izatt, R.M.; Christensen, J.J.; Rytting, J.H. Sites and thermodynamic quantities associated with proton and metal ion interaction with ribonucleic acid, deoxyribonucleic acid and their constituent basis, nucleosides and nucleotides. Chem. Rev. 1971, 71, 439–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zimmer, C.; Luck, G.; Venner, H.; Fric, J. Study on the conformation of protonated DNA. Biopolymers 1968, 6, 563–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shchagina, L.V.; Rikhter, D.; Frisman, E.V.; Vorob’ev, V.I. Effect of Ionic Strength of Solution on the Thermodynamic Rigidity of the Molecules of Native DNA. Mol. Biol. 1969, 3, 169–174. [Google Scholar]
- Hagerman, P. Investigation of the flexibility of DNA using transient electric birefringence. Biopolymers 1981, 20, 1503–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maret, G.; Weil, G. Magnetic birefringence of the electrostatic and intrinsic persistence length of DNA. Biopolymers 1983, 22, 2727–2744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Meisburger, S.P.; Pabit, S.A.; Sutton, J.L.; Webb, W.W.; Pollack, L. Ionic strength-dependent persistence lengths of single-stranded RNA and DNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisman, E.V.; Kas’ianenko, N.A. Hydrodynamic and optical behaviour of DNA molecule in a solutions of large ionic strength. Mol. Biol. 1990, 24, 318–327. [Google Scholar]
- Odijk, T. Polyelectrolytes near the rod limit. J. Polym. Sci. 1977, 15, 477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skolnick, J.; Fixman, M. Electrostatic Persistence Length of a Wormlike Polyelectrolyte. Macromolecules 1977, 10, 944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisman, E.V.; Schagina, L.V.; Vorob’ev, V.I. A glass rotation viscometer. Biorheology 1965, 2, 189–194. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
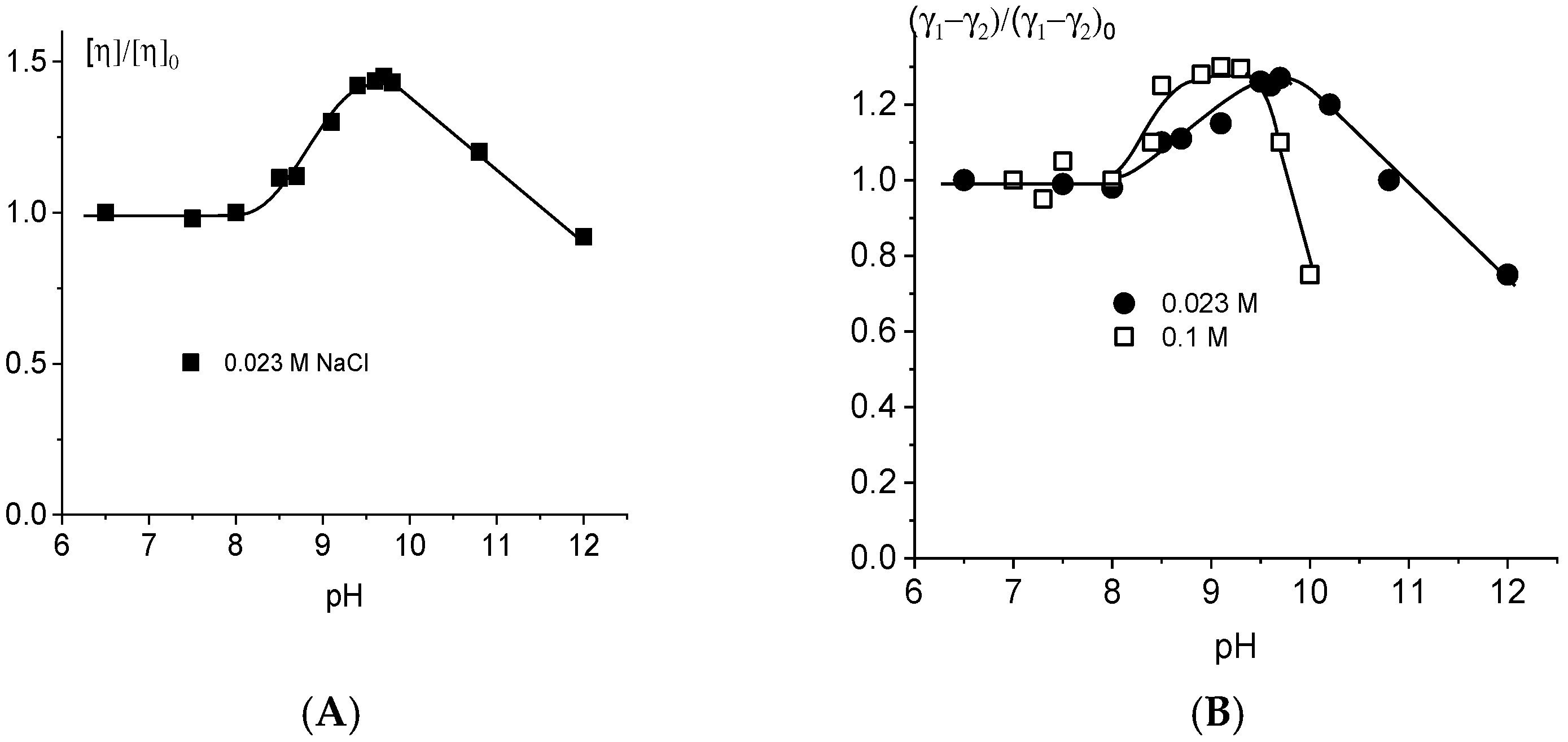
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license.
Share and Cite
Kasyanenko, N.; Khansetsen, B.; Baryshev, A.; Sokolov, P. DNA Persistent Length in Solutions of Different pH. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2026, 27, 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010316
Kasyanenko N, Khansetsen B, Baryshev A, Sokolov P. DNA Persistent Length in Solutions of Different pH. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2026; 27(1):316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010316
Chicago/Turabian StyleKasyanenko, Nina, Bolorkhuu Khansetsen, Andrey Baryshev, and Petr Sokolov. 2026. "DNA Persistent Length in Solutions of Different pH" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 27, no. 1: 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010316
APA StyleKasyanenko, N., Khansetsen, B., Baryshev, A., & Sokolov, P. (2026). DNA Persistent Length in Solutions of Different pH. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 27(1), 316. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms27010316






