Hormone Regulation Effect of Blue Light on Soybean Stem Internode Growth Based on the Grey Correlation Analysis Model
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Design
4.1.1. Experiment I: Shading and Blue Light Supplementation
4.1.2. Experiment II: Controlled Environment Chamber Study
4.1.3. Experiment III: Exogenous Hormone Treatments
4.2. Determination Indicators and Methods
4.2.1. Determination of Internode Length and Plant Height
4.2.2. Observation of Anatomical Structure
4.2.3. Hormone Concentration Quantification
4.2.4. Detection of Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analysis
4.2.5. Proteomic Analysis
4.2.6. Correlation Analysis
4.2.7. Grey Correlation Analysis Model
4.3. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| GAs | Gibberellins |
| JA | Jasmonic acid |
| SA | Salicylic acid |
| BR | Brassinolide |
| SLs | Strigolactone |
| IAA | Indol-3-acetic acid |
| R | Red light |
| FR | Far-red light |
| ABA | Abscisic acid |
| CK | Cytokinin |
| LED | Light-emitting diode |
| PBS | Phosphate buffer saline |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
| HY5 | ELONGATED HYPOCOTYL 5 |
| NPR1 | Nonexpressor of pathogenesis-related genes 1 |
| ACAA1 | Acetyl-CoA acyltransferase 1 |
| LOX | Lipoxygenase |
| HPL | Hydroperoxide lyase |
| GID1 | GA-INSENSITIVE DWARF 1 |
| AOC | Allene oxide cyclase |
| AOS | Allene oxide synthase |
| ALDH | Aldehyde dehydrogenase |
| PIFs | Phytochrome-interacting factors |
References
- Xu, Y.; Wang, C.; Zhang, R.; Ma, C.M.; Dong, S.K.; Gong, Z.P. The relationship between internode elongation of soybean stems and spectral distribution of light in the canopy under different plant densities. Plant Prod. Sci. 2020, 24, 326–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Kang, C.Q.; Kaiser, E.; Kuang, Y.; Yang, Q.C.; Li, T. Red/blue light ratios induce morphology and physiology alterations differently in cucumber and tomato. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 281, 109995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Shan, F.X.; Wang, C.; Yang, C.; Dong, S.K.; Xu, Y.; Gong, Z.P.; Ma, C.M. Internode elongation pattern, internode diameter and hormone changes in soybean (Glycine max) under different shading conditions. Crop Pasture Sci. 2020, 71, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, F.; Zou, Y.J.; Hu, Q.X.; Zhang, H.Y.; Ye, D. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals molecular processes involved in pileus morphogenesis in Pleurotus eryngii under different light conditions. Genomics 2020, 112, 1707–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qiu, H.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Y.; Shan, F.X.; Li, H.Y.; Yan, C.; Ma, C.M. Red light regulates metabolic pathways of soybean hypocotyl elongation and thickening. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2022, 199, 104890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Cui, C.; Shan, F.X.; Zhang, R.; Lyu, X.C.; Lyu, L.; Chang, H.W.; Yan, C.; Ma, C.M. Blue light regulates cell wall structure and carbohydrate metabolism of soybean hypocotyl. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Xu, Z.G.; Tang, C.M. Effect of light-emitting diodes on growth and morphogenesis of upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) plantlets in vitro. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2010, 103, 155–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piszczek, P.; Głowacka, B. Effect of the colour of light on cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) seedlings. J. Fruit Ornam. Plant Res. 2008, 68, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dougher, T.A.O.; Bugbee, B. Long-term blue light effects on the histology of lettuce and soybean leaves and stems. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 2004, 129, 467–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, R.; Kubota, C. Physiological responses of cucumber seedlings under different blue and red photon flux ratios using LEDs. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 121, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosgrove, D.J.; Green, P.B. Mechanism of rapid suppression of cell expansion in cucumber hypocotyls after blue-light irradiation. Planta 1988, 176, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wit, M.; Galvao, V.C.; Fankhauser, C. Light-mediated hormonal regulation of plant growth and development. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2016, 67, 513–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, C.W.; Li, L. Hormonal regulation in shade avoidance. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Wit, M.; Lorrain, S.; Fankhauser, C. Auxin-mediated plant architectural changes in response to shade and high temperature. Physiol. Plamtarum 2014, 151, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nozue, K.; Tat, A.V.; Devisetty, U.K.; Robinson, M.; Mumbach, M.R.; Ichihashi, Y.; Lekkala, S.; Maloof, J.N. Shade avoidance components and pathways in adult plants revealed by phenotypic profiling. PLoS Genet. 2015, 11, e1004953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurepin, L.V.; Farrow, S.; Walton, L.J.; Pharis, R.P.; Neil Emery, R.J.; Chinnappa, C.C. Phenotypic plasticity of sun and shade ecotypes of Stellaria longipes in response to light quality signaling, gibberellins and auxin. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2015, 94, 174–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, X.G.; Cheng, Q.C.; Qin, C.; Li, Y.H.; Xu, X.Y.; Ji, R.H.; Mu, R.L.; Li, H.Y.; Zhao, T.; Liu, J.; et al. GmCRY1s modulate gibberellin metabolism to regulate soybean shade avoidance in response to reduced blue light. Mol. Plant 2021, 14, 298–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukuda, N.; Ajima, C.; Yukawa, T.; Olsen, J.E. Antagonistic action of blue and red light on shoot elongation in petunia depends on gibberellin, but the effects on flowering are not generally linked to gibberellin. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2016, 121, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcioni, R.; Moriwaki, T.; Perez-Llorca, M.; Munne-Bosch, S.; Gibin, M.S.; Sato, F.; Pelozo, A.; Pattaro, M.C.; Giacomelli, M.E.; Ruggeberg, M.; et al. Cell wall structure and composition is affected by light quality in tomato seedlings. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 2020, 203, 111745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.K.; Shui, Z.W.; Xu, L.; Yang, H.Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, X.Q.; Shang, J.; Asghar, M.A.; Wu, X.L.; Yu, L.; et al. Gibberellins modulate shade-induced soybean hypocotyl elongation downstream of the mutual promotion of auxin and brassinosteroids. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2020, 150, 209–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khai, H.D.; Hiep, P.P.M.; Tung, H.T.; Phong, H.T.; Mai, N.T.N.; Luan, V.Q.; Cuong, D.M.; Vinh, B.V.T. Selenium nanoparticles promote adventitious rooting without callus formation at the base of passion fruit cuttings via hormonal homeostasis changes. Sci. Hortic. 2024, 323, 112485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.M.; Zhang, L.H.; Ma, L.J.; Li, Y.Y. Elevated carbon dioxide and/or ozone concentrations induce hormonal changes in Pinus tabulaeformis. J. Chem. Ecol. 2011, 37, 779–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettini, P.; Baraldi, R.; Rapparini, F.; Melani, L.; Mauro, M.L.; Bindi, D.; Buiatti, M. The insertion of the Agrobacterium rhizogenes rolC gene in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.) affects plant architecture and endogenous auxin and abscisic acid levels. Sci. Hortic. 2020, 123, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Fan, Y.F.; Wu, X.L.; Cheng, Y.J.; Liu, Q.L.; Feng, L.Y.; Chen, J.X.; Wang, Z.L.; Wang, X.C.; Yong, T.W.; et al. Auxin-to-gibberellin ratio as a signal for light intensity and quality in regulating soybean growth and matter partitioning. Front. Plant Sci. 2018, 9, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, M.X.; Xu, Z.G. Proteomic, physiological, and anatomical analyses reveal the effects of red, blue, and white light on the growth of potato plantlets under in vitro culture. Russ. J. Plant Physiol. 2022, 69, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, X.; Zhao, K.Y.; He, X.R.; Zheng, H.J.; Wang, R.; Liu, C.; Zhou, L.J.; Fahad, S.; Deng, G. Differential protein response to different light quality conditions of industrial hemp cultivation based on DIA technology. Ind. Crops Prod. 2023, 197, 116650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patil, A.N.; Walke, G.A.; Gawkhare, M. Grey relation analysis methodology and its application. Res. Rev. Int. J. Multidiscip. 2019, 4, 409–411. [Google Scholar]
- Ning, X.W.; Dong, P.P.; Wu, C.L.; Wang, Y.L.; Zhang, Y. Influence mechanisms of dynamic changes intemperature, precipitation, sunshine duration and active accumulated temperature on soybean resources: A case study of Hulunbuir, China, from 1951 to 2019. Energies 2022, 15, 8347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Li, X.M.; Zhou, Q.; Song, S.; Dong, S.K. Comparison and evaluation of low-temperature tolerance of different soybean cultivars during the early-growth stage. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Jiang, S.M.; Jin, J.L.; Feng, P.; Ning, S.W. Decision-making of irrigation scheme for soybeans in the Huaibei Plain based on grey entropy weight and grey relation–projection pursuit. Entropy 2019, 21, 877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, M.M.; Xia, G.Y.; Cui, T.; Xu, Y.; Gao, X.J.; Su, Y.; Fan, H.F. Effect of moisture, protein, starch, soluble sugar contents and microstructure on mechanical properties of maize kernels. Food Chem. 2022, 379, 132147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qin, S.Y.; Xu, Y.F.; Liu, H.G.; Li, C.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, P. Effect of different boron levels on yield and nutrient content of wheat based on grey relational degree analysis. Acta Physiol. Plant. 2021, 43, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Wang, Y.T.; Yu, J.L.; Zhou, Y.F.; Wu, Q.; Gao, Y.; Xu, W.J.; Huang, R.D. Prioritization of feasible physiological parameters in drought tolerance evaluation in sorghum: A grey relational analysis. Zemdirb. Agric. 2015, 102, 457–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Na, W.; Guan, Y.S.; Yan, S. Drought-resistance index in rice backcross lines after anthesis. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 10, 2659–2664. [Google Scholar]
- Hussain, S.; Iqbal, N.; Pang, T.; Khan, M.N.; Liu, W.G.; Yang, W.Y. Weak stem under shade reveals the lignin reduction behavior. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 60345–60347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.G.; Hussain, S.; Liu, T.; Zou, J.L.; Ren, M.L.; Zhou, T.; Liu, J.; Yang, F.; Yang, W.Y. Shade stress decreases stem strength of soybean through restraining lignin biosynthesis. J. Integr. Agric. 2018, 17, 60345–60347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.X.; Zhang, Y.; Hussain, S.; Wang, S.; Zhang, X.W.; Yang, J.Y.; Xu, M.; Qin, S.S.; Yang, W.Y.; Liu, W.G. Slight shading stress at seedling stage does not reduce lignin biosynthesis or affect lodging resistance of soybean stems. Agronomy 2020, 10, 544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cashmore, A.R. Cryptochromes: Enabling plants and animals to determine circadian time. Cell 2003, 114, 537–543. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, C.T.; Shalitin, D. Cryptochrome structure and signal transduction. Annu. Rev. Plant Biol. 2003, 54, 469–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Hou, P.; Song, M.F.; Zheng, X.; Guo, L.; Xiao, Y.; Yan, L.; Li, W.C.; Yang, J.P. Synergistic and antagonistic action of Phytochrome (Phy) A and PhyB during seedling de-Etiolation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 12199–12212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, Y.T.; Chu, L.; Zhang, Y.M.; Bian, Y.T.; Xiao, J.H.; Xu, D.Q. HY5: A pivotal regulator of light-dependent development in higher plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 800989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alabadi, D.; Gallego-Bartolome, J.; Orlando, L.; Garcia-Carcel, L.; Rubio, V.; Martinez, C.; Frigerio, M.; Iglesias-Pedraz, J.M.; Espinosa, A.; Deng, X.W.; et al. Gibberellins modulate light signaling pathways to prevent Arabidopsis seedling de-etiolation in darkness. Plant J. 2008, 53, 324–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Smith, D.L.; Liu, W.G.; Chen, X.F.; Yang, W.Y. Effects of shade and drought stress on soybean hormones and yield of main-stem and branch. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2011, 10, 14392–14398. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, T.F.; Yuan, J.H.; Hiltbrunner, A. PHYTOCHROME INTERACTING FACTORs in the moss Physcomitrella patens regulate light-controlled gene expression. Physiol. Plant. 2020, 169, 467–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hornitschek, P.; Kohnen, M.V.; Lorrain, S.; Rougemont, J.; Ljung, K.; Lopez-Vidriero, I.; Franco-Zorrilla, J.M.; Solano, R.; Trevisan, M.; Pradervand, S.; et al. Phytochrome interacting factors 4 and 5 control seedling growth in changing light conditions by directly controlling auxin signaling. Plant J. 2012, 71, 699–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Lucas, M.; Davie’re, J.M.; Rodriguez-Falco’n, M.; Pontin, M.; Lglesias-Pedraz, J.M.; Lorrain, S.; Fankhauser, C.; Blazquez, M.A.; Titarenko, E.; Prat, S. A molecular framework for light and gibberellin control of cell elongation. Nature 2008, 451, 480–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kende, H.; Zeevaart, J.A.D. The five “Classical” plant hormones. Plant Cell 1997, 9, 1197–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueguchi-Tanaka, M.; Ashikari, M.; Nakajima, M. Gibberellin insensitive Dwarf1 encodes a soluble receptor for gibberellin. Nature 2005, 437, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Li, H.T.; Li, J.J.; Wang, B.; Dai, C.; Wang, J.; Liu, K. Brassica napus DS-3, encoding a DELLA protein, negatively regulates stem elongation through gibberellin signaling pathway. Theor. Appl. Genet. 2017, 130, 727–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.Y.; Yu, X.H.; Foo, E.; Symons, G.M.; Lopez, J.; Bendehakkalu, K.T.; Xiang, J.; Weller, J.L.; Liu, X.M.; Reid, J.B.; et al. A study of gibberellin homeostasis and cryptochrome-mediated blue light inhibition of hypocotyl elongation. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 106–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saniewski, M.; Okubo, H.; Miyamoto, K.; Ueda, J. Auxin induces growth of stem excised from growing shoot of cooled tulip bulbs. J. Fac. Agric. Kyushu Univ. 2005, 50, 481–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, D.Y.; Kong, S.J.; Chu, X.; Li, X.; Pan, H. De Novo biosynthesis of indole-3-acetic acid in engineered Escherichia coli. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 8186–8190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, T.; Law, D.M.; Davies, P.J. Magnitude and kinetics of stem elongation induced by exogenous indole-3-acetic acid in intact light-crown pea seedlings. Plant Physiol. 1993, 102, 717–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Que, F.; Khadr, A.; Wang, G.L.; Li, T.; Wang, Y.H.; Xu, Z.S.; Xiong, A.S. Exogenous brassinosteroids altered cell length, gibberellin content, and cellulose deposition in promoting carrot petiole elongation. Plant Sci. 2018, 277, 110–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franck-Duchenne, M.; Wang, Y.W.; Tahar, S.B.; Beachy, R.N. In vitro stem elongation of sweet pepper in media containing 24-epi-brassinolide. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 1998, 53, 79–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, W.H.; Sun, X.F.; Zhao, L.L.; Huang, L.J.; Wang, P.C. Exogenous hormone application regulates dwarf mutant plant height in Sophora davidii (Franch). Skeels by changing endogenous hormone levels. Chil. J. Agric. Res. 2023, 83, 195–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.D.; Cui, X.Y.; Wu, C.; Shi, S.X.; Yan, S.P. Salicylic acid inhibits gibberellin signaling through receptor interactions. Mol. Plant 2022, 11, 1759–1771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolomiets, M.V.; Hannapel, D.J.; Chen, H.; Tymeson, M.; Gladon, R.J. Lipoxygenase is involved in the control of potato tuber development. Plant Cell 2001, 13, 613–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noordermeer, M.A.; Dijken, A.J.H.V.; Smeekens, S.C.M.; Veldink, G.A.; Vliegenthart, J.F.G. Characterization of three cloned and expressed 13-hydroperoxide lyase isoenzymes from alfalfa with unusual N-terminal sequences and different enzyme kinetics. Eur. J. Biochem. 2000, 267, 2473–2482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.X.; Fu, S.Y.; Chen, Y.; Jin, W.J.; Zhai, B.; Li, Y.F.; Sun, G.R.; Han, R.L.; Wang, Y.B.; Tian, Y.D.; et al. MicroRNA-15a Regulates the Differentiation of Intramuscular Preadipocytes by Targeting ACAA1, ACOX1 and SCP2 in Chickens. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Su, G.G.; He, S.L.; Shi, L.Y.; He, D.; Shang, W.Q.; Yang, D.J. Effects of root pruning on adventitious root formation, enzyme activities, and hormone levels in Paeonia sufruticosa ‘Fengdanbai’ Seedlings. Hortic. Sci. Technol. 2021, 39, 10–22. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, J.W.; Guo, S.J.; Wang, G.Y. Effects of in vitro subculture on the physiological characteristics of adventitious root formation in microshoots of Castanea mollissima cv. ‘yanshanhong’. J. For. Res. 2010, 21, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quan, J.E.; Ni, R.Y.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.J.; Ma, M.Y.; Bi, H.T. Effects of diferent growth regulators on the rooting of catalpa bignonioides softwood cuttings. Life 2022, 12, 1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
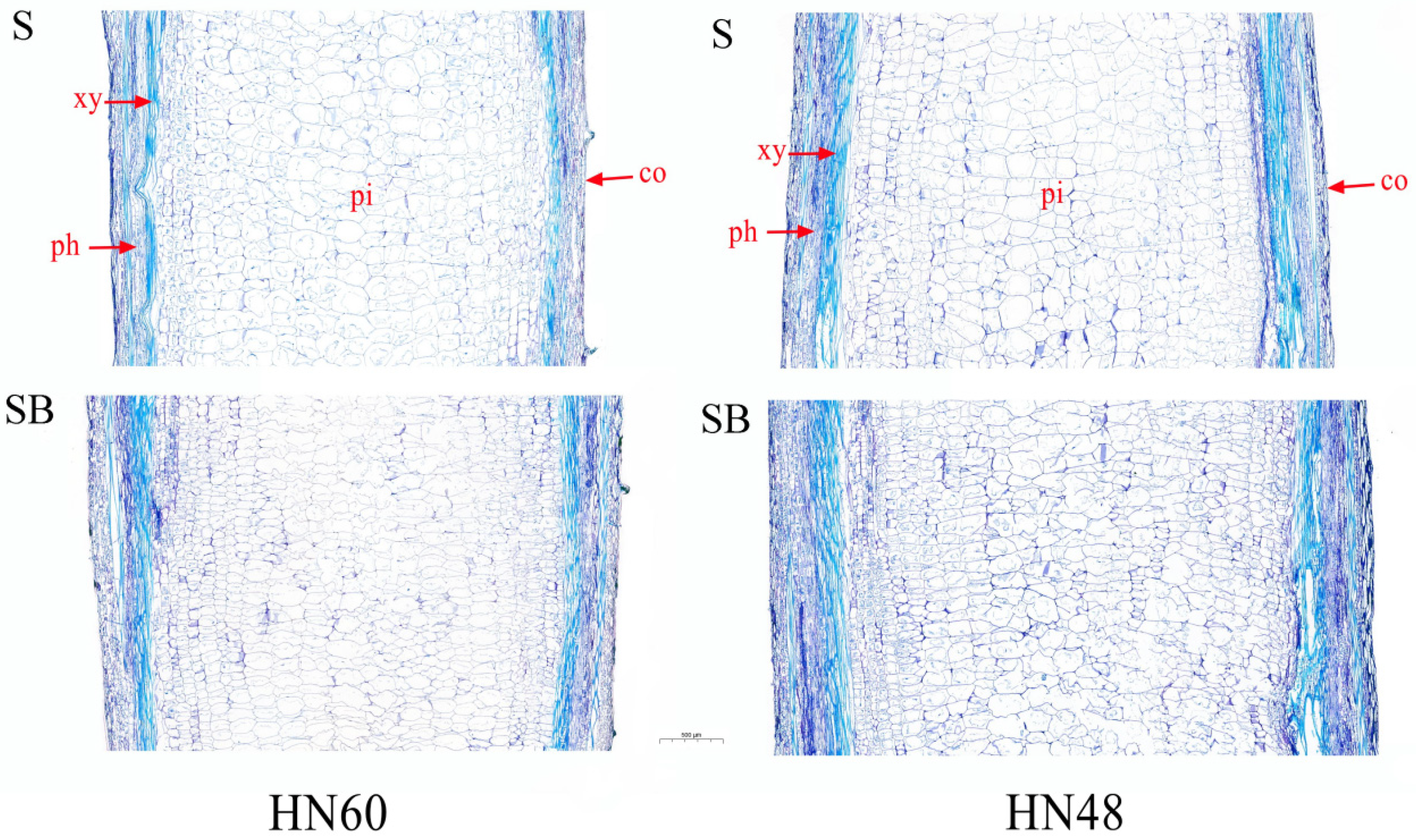

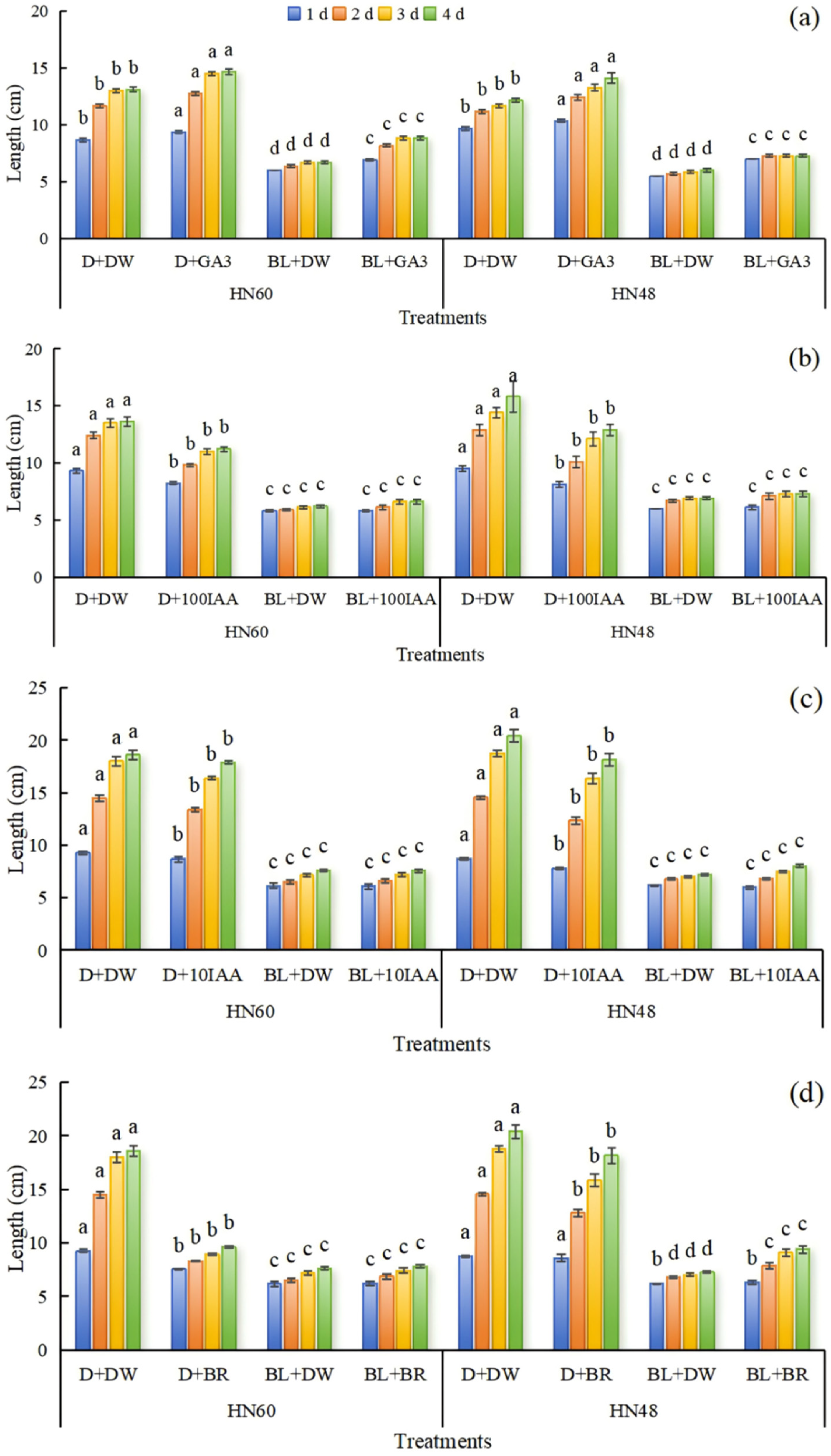
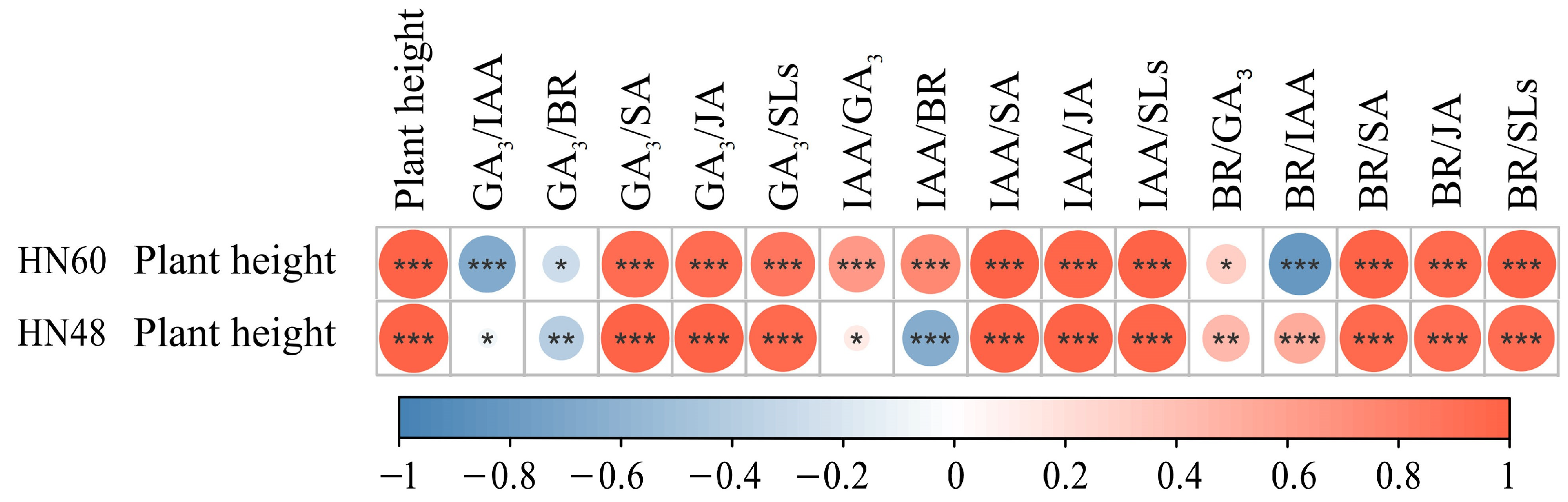

| Treatments | 0 d | 1 d | 3 d | 5 d | 7 d | Plant Height | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HN60 | Darkness | 5.13 ± 0.13 a | 9.00 ± 0.41 a | 14.50 ± 0.65 a | 15.25 ± 0.66 a | 15.25 ± 0.66 a | 36.90 ± 0.29 a |
| BL | 5.13 ± 0.13 a | 5.50 ± 0.00 b | 6.00 ± 0.29 b | 6.00 ± 0.29 b | 6.00 ± 0.29 b | 13.28 ± 0.82 b | |
| HN48 | Darkness | 5.00 ± 0.00 a | 9.75 ± 0.32 a | 16.25 ± 0.66 a | 16.88 ± 0.31 a | 16.88 ± 0.31 a | 38.18 ± 0.22 a |
| BL | 5.00 ± 0.00 a | 5.25 ± 0.14 b | 6.00 ± 0.00 b | 6.13 ± 0.13 b | 6.13 ± 0.13 b | 13.50 ± 0.54 b | |
| Varieties | Treatments | GA3 (ng g−1) | IAA (ng g−1) | BR (ng g−1) | JA (ng g−1) | SA (μg g−1) | SLs (ng g−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HN60 | 3rd internode | S | 54.77 ± 0.41 a | 36.17 ± 0.46 a | 7.25 ± 0.09 a | 3.81 ± 0.06 b | 15.48 ± 0.13 b | 107.41 ± 0.46 b |
| SB | 42.62 ± 0.31 b | 28.75 ± 0.65 b | 6.08 ± 0.03 b | 4.64 ± 0.03 a | 17.93 ± 0.20 a | 136.13 ± 0.59 a | ||
| 4th internode | S | 46.28 ± 0.52 a | 34.34 ± 0.6 a | 6.83 ± 0.06 a | 3.62 ± 0.04 b | 15.49 ± 0.13 b | 109.96 ± 0.16 b | |
| SB | 42.86 ± 0.33 b | 28.31 ± 0.08 b | 6.02 ± 0.01 b | 4.44 ± 0.02 a | 17.93 ± 0.20 a | 133.47 ± 0.22 a | ||
| 5th internode | S | 43.78 ± 0.07 a | 34.30 ± 0.35 a | 7.11 ± 0.04 a | 3.58 ± 0.05 b | 13.65 ± 0.56 b | 110.80 ± 0.28 b | |
| SB | 40.98 ± 0.39 b | 26.41 ± 0.29 b | 5.81 ± 0.07 b | 4.27 ± 0.04 a | 17.18 ± 0.03 a | 126.12 ± 1.69 a | ||
| HN48 | 3rd internode | S | 55.64 ± 0.07 a | 46.08 ± 0.58 a | 6.32 ± 0.12 a | 4.78 ± 0.14 b | 10.69 ± 0.24 b | 103.39 ± 1.44 b |
| SB | 46.99 ± 1.27 b | 43.30 ± 0.03 b | 6.10 ± 0.06 a | 7.15 ± 0.07 a | 15.03 ± 0.14 a | 128.86 ± 0.25 a | ||
| 4th internode | S | 48.91 ± 0.08 a | 45.79 ± 0.48 a | 6.98 ± 0.14 a | 4.71 ± 0.24 b | 9.66 ± 0.09 b | 96.49 ± 0.04 b | |
| SB | 44.05 ± 0.08 b | 38.52 ± 0.24 b | 5.19 ± 0.15 b | 7.09 ± 0.03 a | 14.10 ± 0.14 a | 126.42 ± 0.22 a | ||
| 5th internode | S | 45.84 ± 0.09 a | 44.43 ± 0.33 a | 7.08 ± 0.15 a | 4.37 ± 0.30 b | 9.22 ± 0.46 b | 98.93 ± 0.36 b | |
| SB | 41.07 ± 0.48 b | 37.26 ± 0.33 b | 5.12 ± 0.27 b | 6.76 ± 0.11 a | 13.10 ± 0.23 a | 125.14 ± 2.52 a | ||
| Treatments | GA3 (ng g−1) | IAA (ng g−1) | BR (ng g−1) | JA (ng g−1) | SA (μg g−1) | SLs (ng g−1) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HN60 | Darkness | 48.28 ± 0.54 a | 55.34 ± 0.86 a | 7.50 ± 0.20 a | 4.36 ± 0.02 b | 9.47 ± 0.04 b | 128.11 ± 3.62 b |
| BL | 41.47 ± 0.69 b | 40.71 ± 0.51 b | 6.19 ± 0.03 b | 5.01 ± 0.09 a | 14.80 ± 0.43 a | 220.56 ± 0.78 a | |
| HN48 | Darkness | 54.00 ± 0.84 a | 54.87 ± 1.32 a | 7.26 ± 0.08 a | 4.05 ± 0.02 b | 10.82 ± 0.06 b | 137.70 ± 1.23 b |
| BL | 43.71 ± 1.02 b | 37.01 ± 0.27 b | 5.61 ± 0.23 b | 5.58 ± 0.27 a | 15.26 ± 0.09 a | 215.96 ± 9.48 a | |
| KO(Name) | BL/Dark | t-Test p-Value | Regulation | Hormones Involved |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| K14508(NPR1) | 1.401 | 0.001 | Up | Salicylic acid |
| K14493(GID1) | 0.816 | 0.018 | Down | Gibberellin |
| K07513(ACAA1) | 1.480 | 0.001 | Up | Jasmonic acid |
| K15718(LOX1_5) | 1.471 | 0.025 | Up | |
| K15718(LOX1_5) | 1.308 | 0.046 | Up | |
| K00454(LOX2S) | 1.254 | 0.001 | Up | |
| K10528(HPL) | 1.371 | 0.011 | Up | |
| K10525(AOC) | 0.740 | 0.015 | Down | |
| K01723(AOS) | 0.788 | 0.000 | Down | |
| K01723(AOS) | 0.772 | 0.000 | Down | |
| K00128(ALDH) | 0.726 | 0.006 | Down | Indole-3-acetic acid |
| K00128(ALDH) | 0.719 | 0.024 | Down | |
| K14085(ALDH7A1) | 0.595 | 0.000 | Down | |
| K14085(ALDH7A1) | 0.550 | 0.003 | Down |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, C.; Huang, S.; Yu, B.; Shan, F.; Lyu, X.; Yan, C.; Ma, C.; Jiang, B. Hormone Regulation Effect of Blue Light on Soybean Stem Internode Growth Based on the Grey Correlation Analysis Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094411
Wang C, Huang S, Yu B, Shan F, Lyu X, Yan C, Ma C, Jiang B. Hormone Regulation Effect of Blue Light on Soybean Stem Internode Growth Based on the Grey Correlation Analysis Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094411
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Chang, Shuo Huang, Baiyang Yu, Fuxin Shan, Xiaochen Lyu, Chao Yan, Chunmei Ma, and Baiwen Jiang. 2025. "Hormone Regulation Effect of Blue Light on Soybean Stem Internode Growth Based on the Grey Correlation Analysis Model" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094411
APA StyleWang, C., Huang, S., Yu, B., Shan, F., Lyu, X., Yan, C., Ma, C., & Jiang, B. (2025). Hormone Regulation Effect of Blue Light on Soybean Stem Internode Growth Based on the Grey Correlation Analysis Model. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4411. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094411







