Nano-Spray-Drying of Cyclodextrin/Ibuprofen Complexes with Aerosolization-Enhancing Additives for Pulmonary Drug Delivery
Abstract
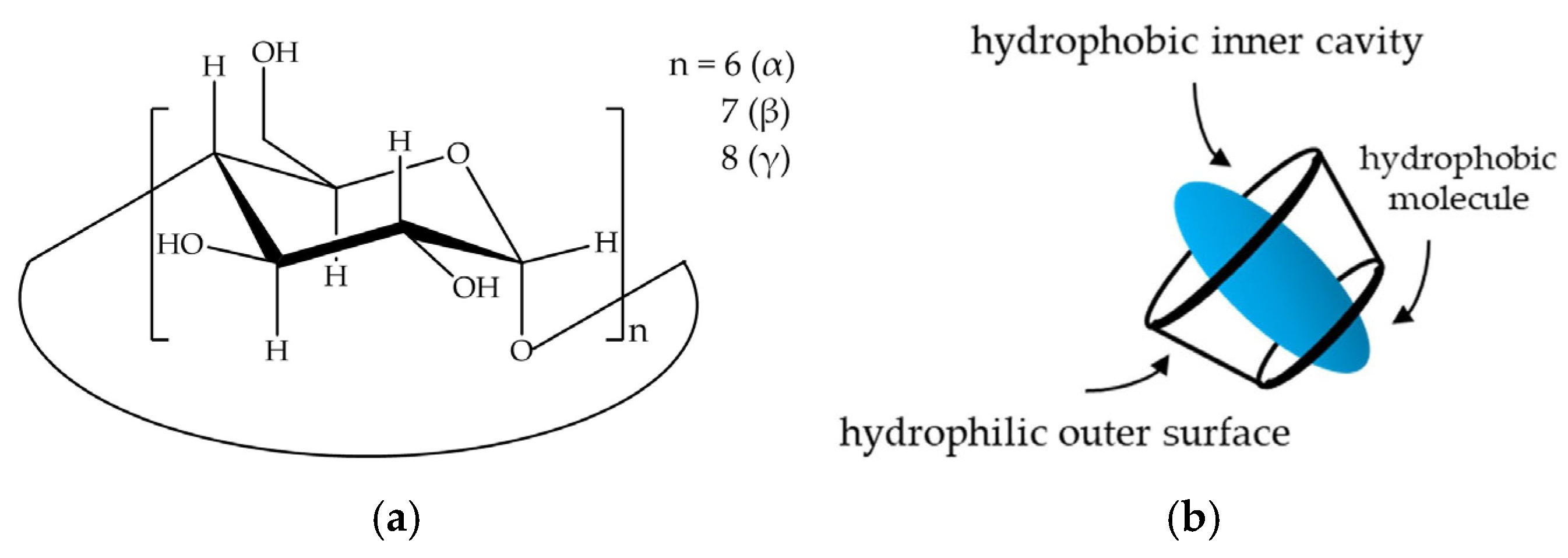
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
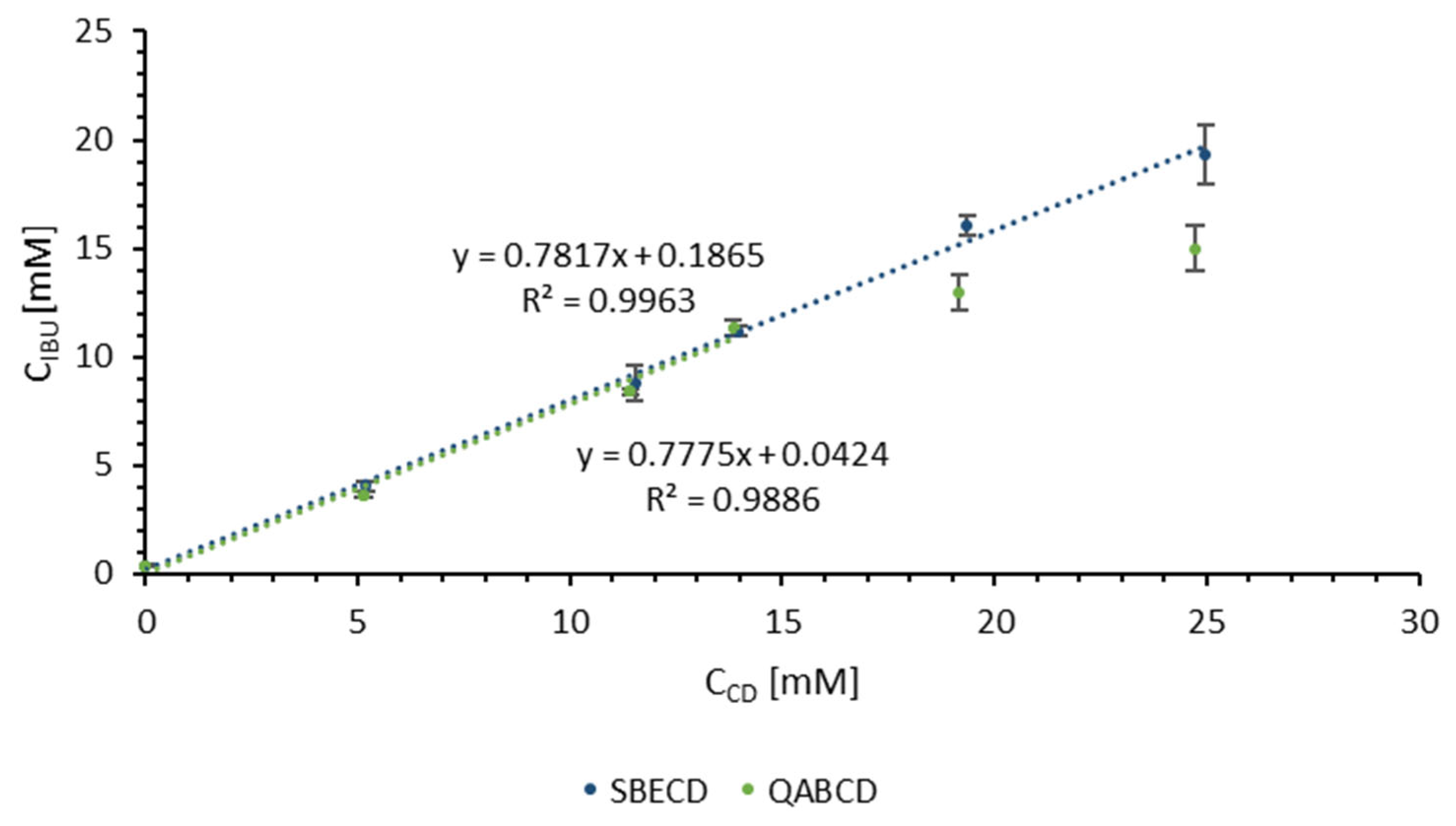
2.1. Determination of CD Concentration and CD/IBU Molar Ratio
2.2. Determination of Particle Size
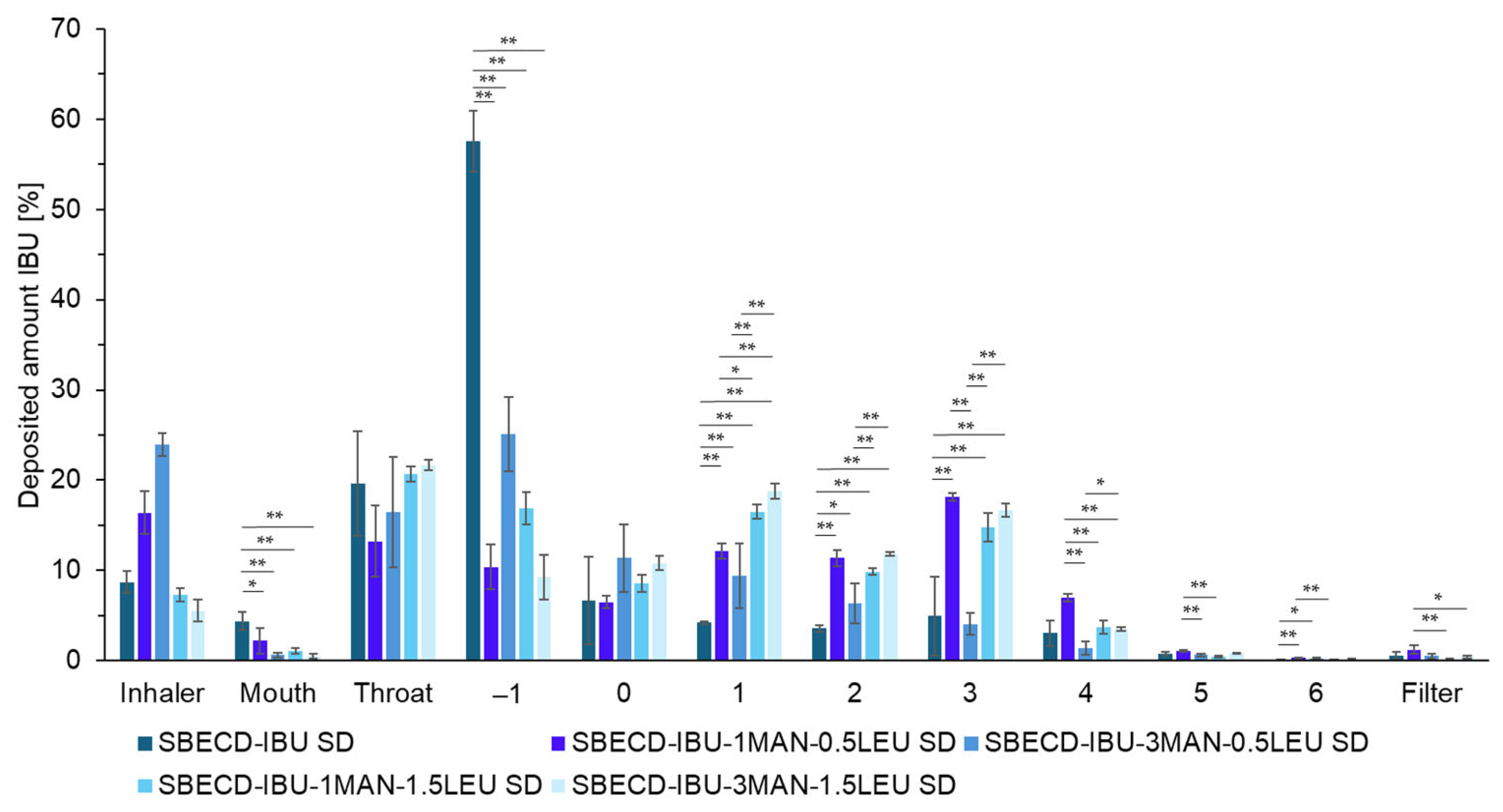
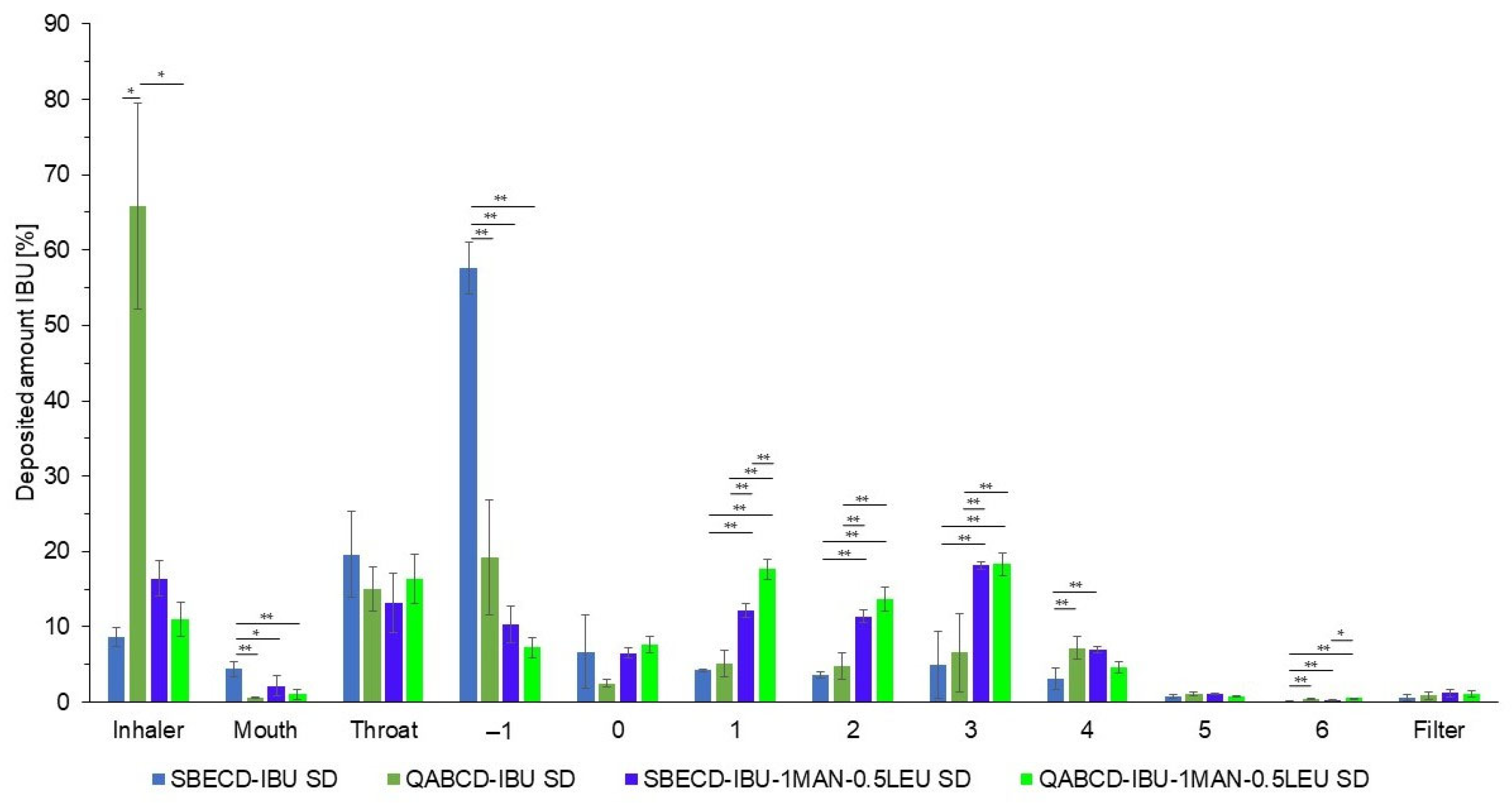
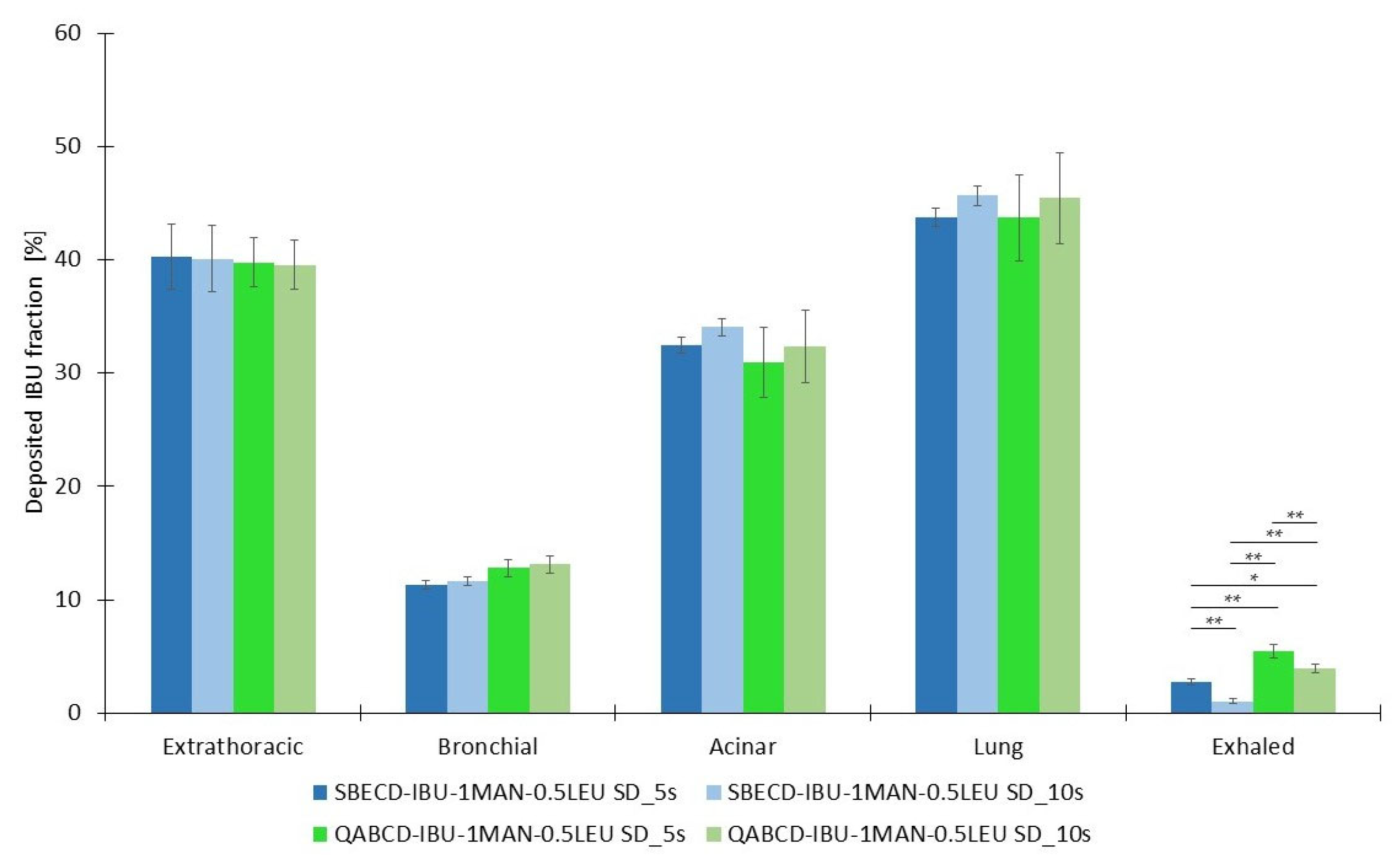
2.3. Investigation of Aerodynamic Properties of Formulations
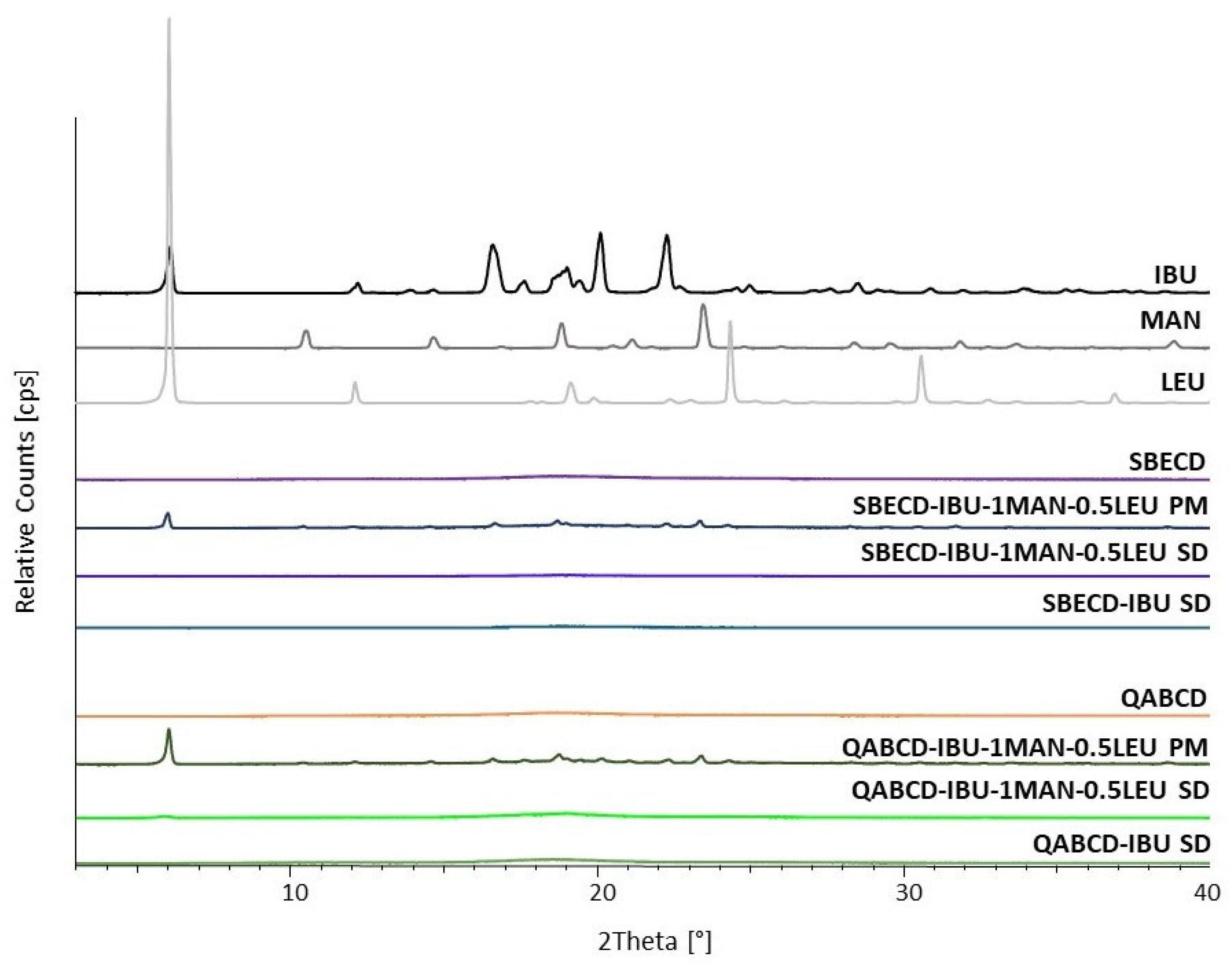
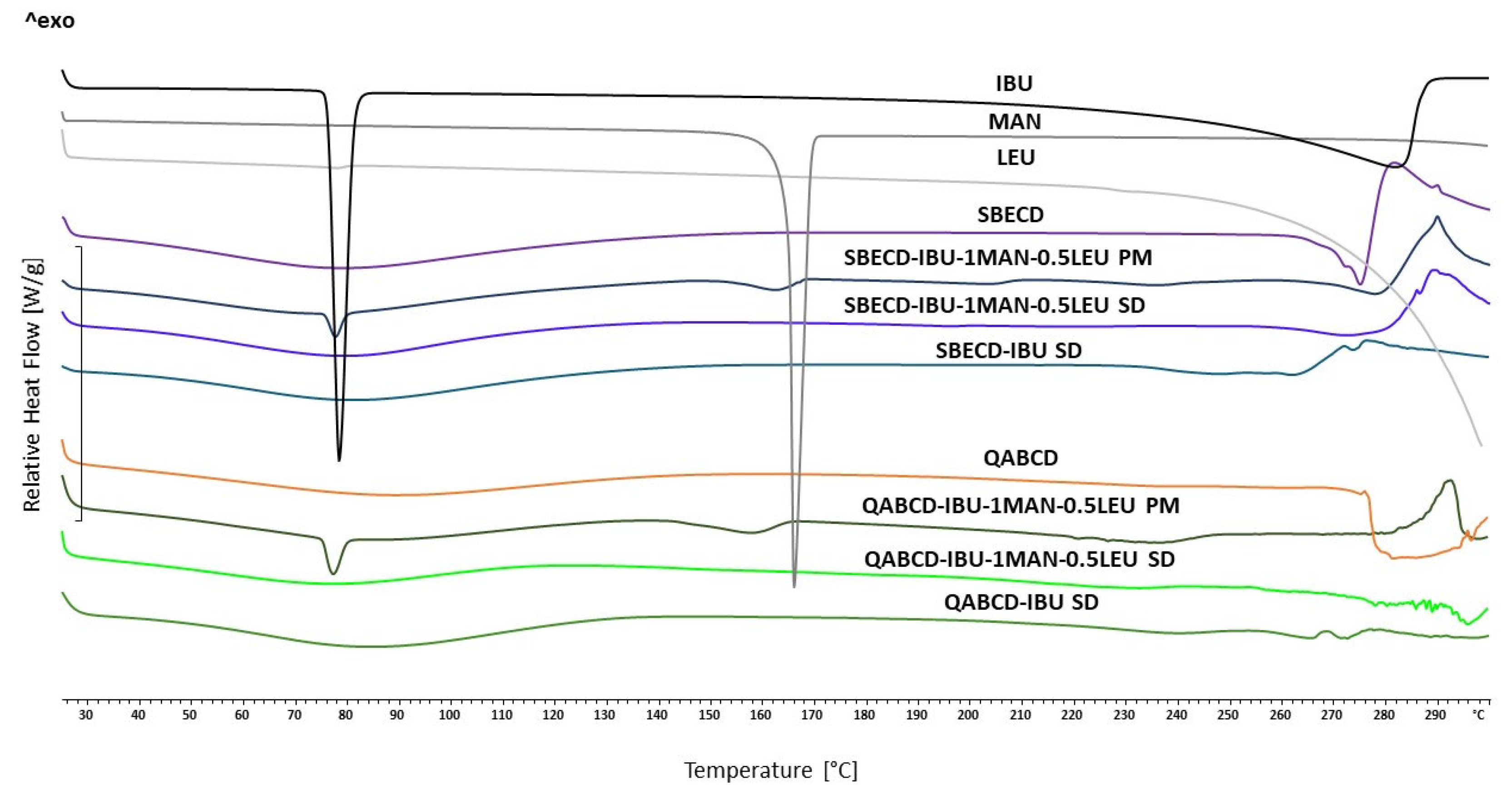
2.4. Characterization of the Optimized Formulations
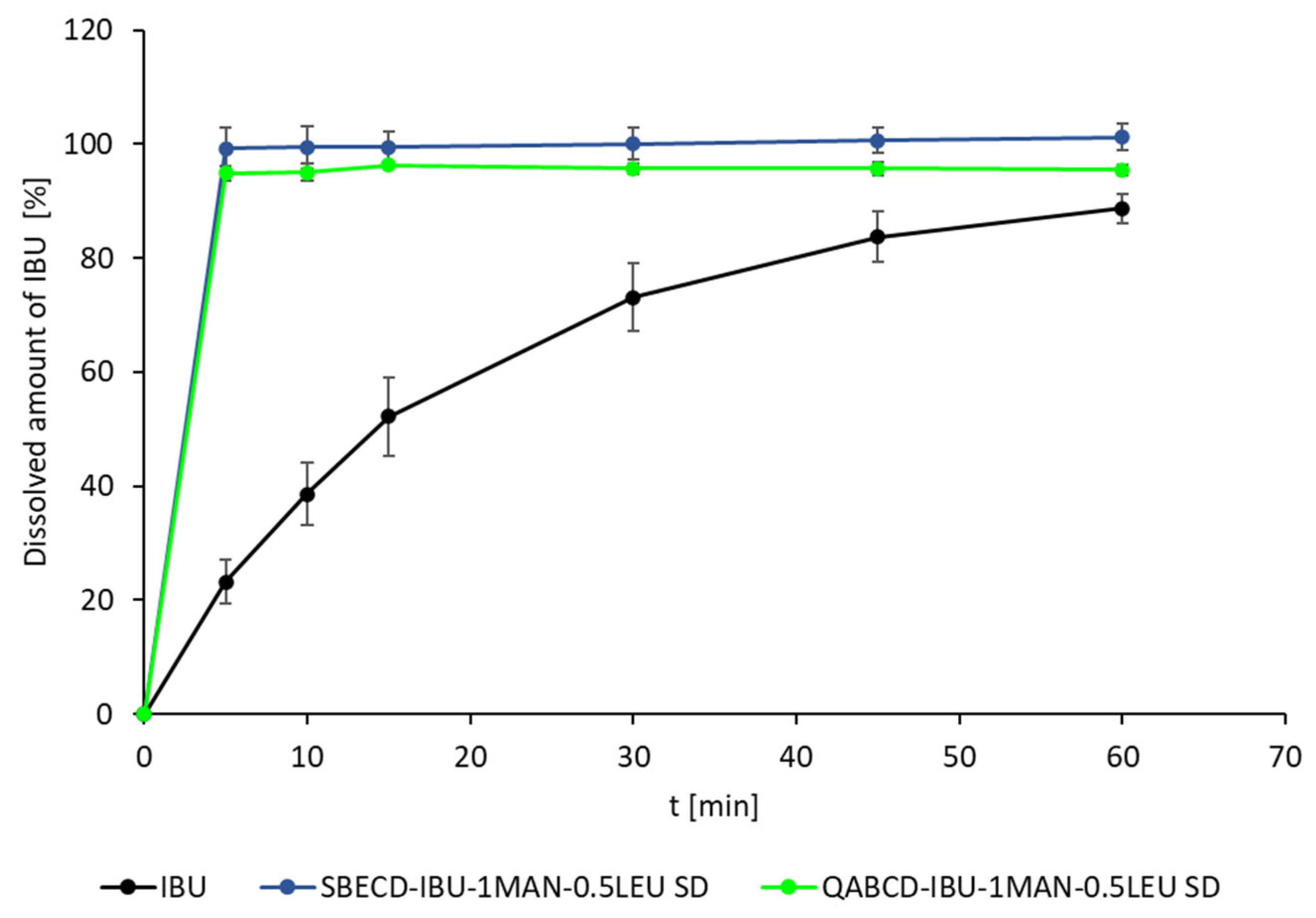
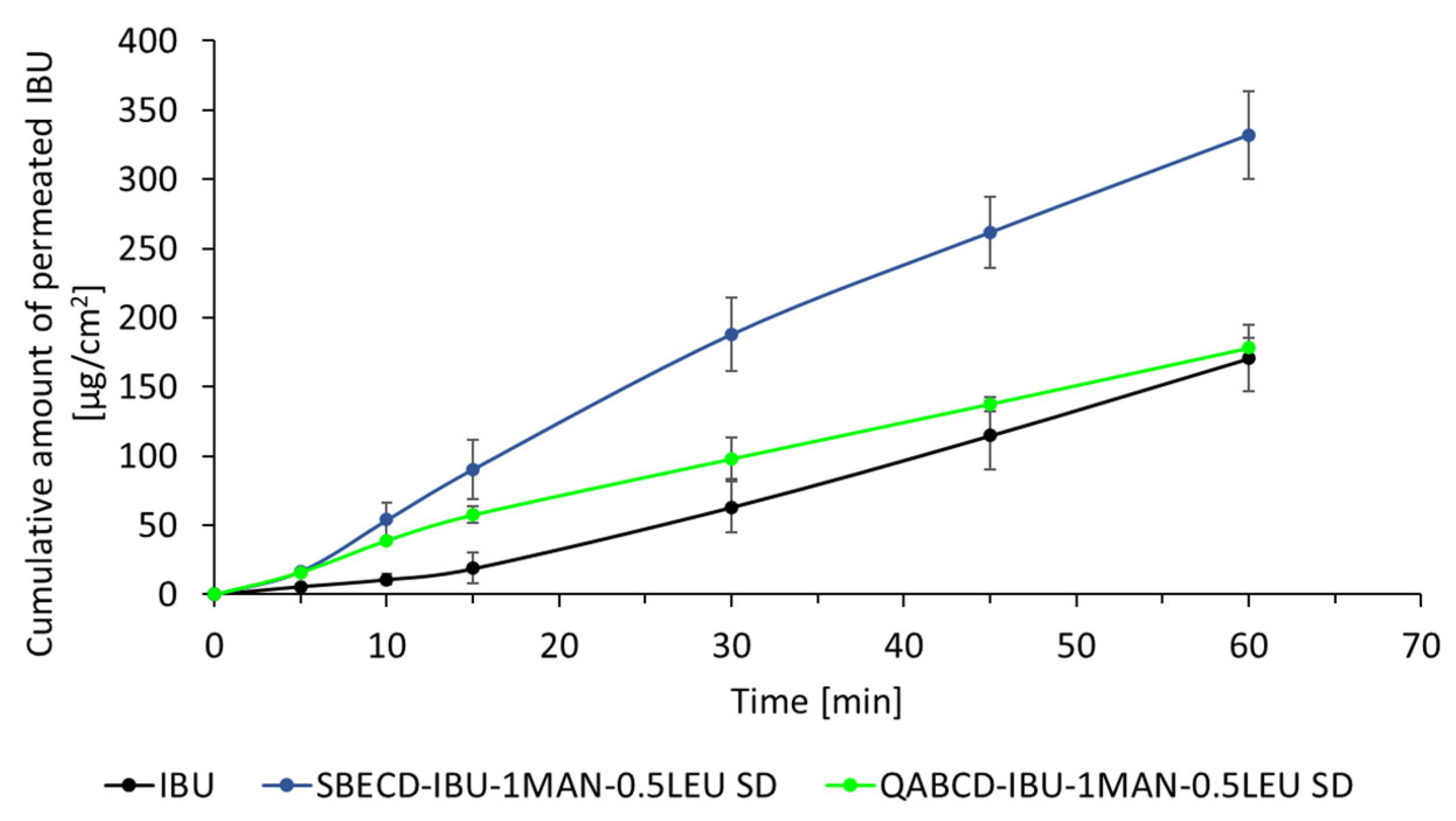
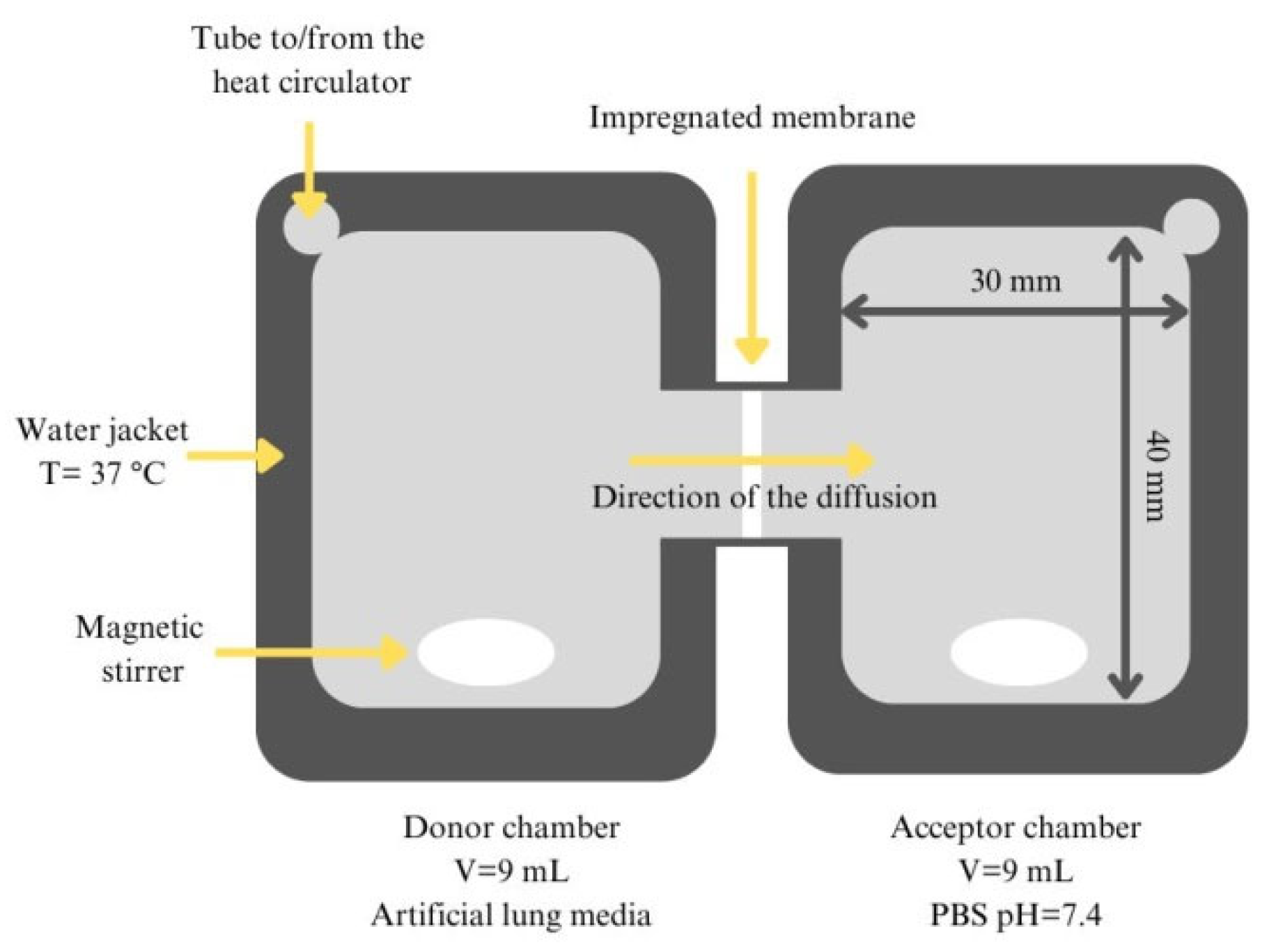
2.5. In Vitro Dissolution and Diffusion Investigations
3. Materials and Methods
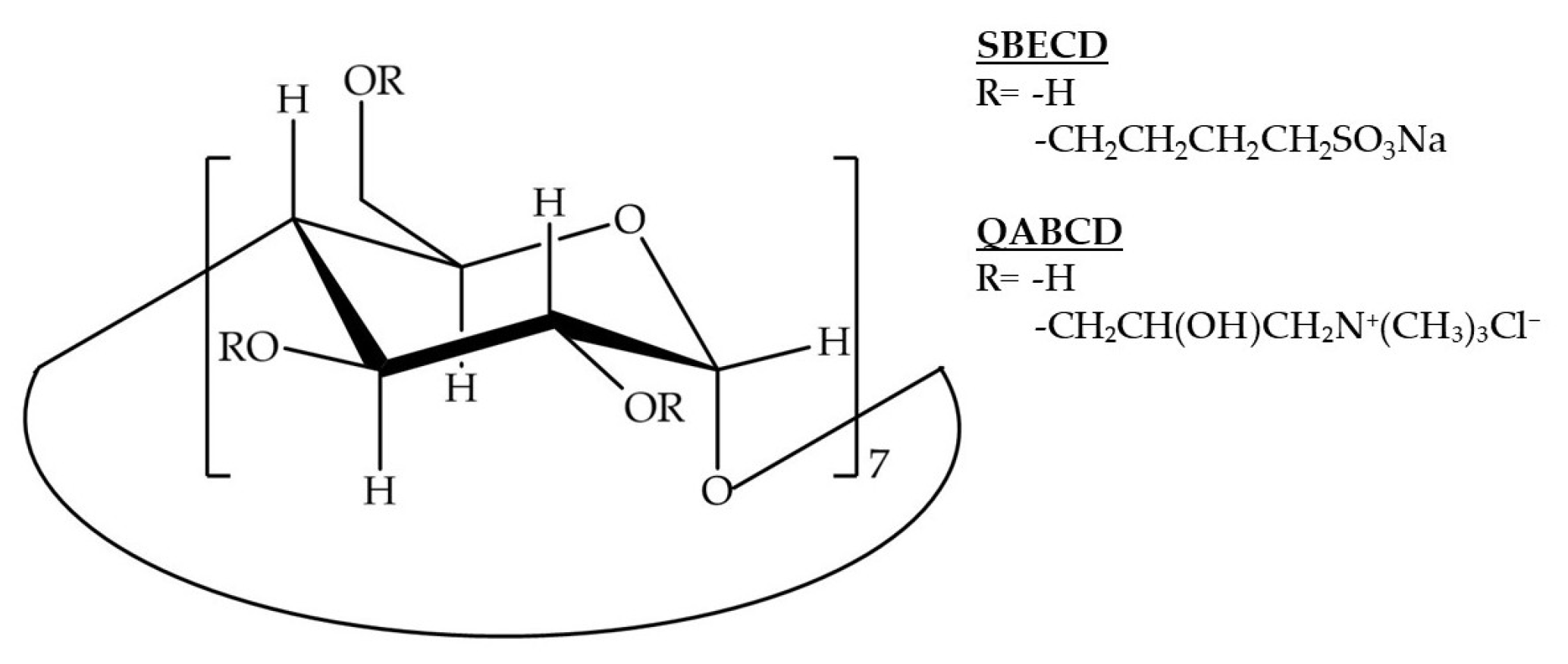
3.1. Materials
3.2. Methods
3.2.1. Preparation of the Samples
Phase Solubility Study
Preparation of the Nano-Spray-Dried Particles
3.2.2. Investigation of the Nano-Spray-Dried Particles
Investigation of the Particle Size of the Nano-Spray-Dried Formulations by Laser Diffraction
In Vitro Aerodynamic Investigation
Determination of Concentration with High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC)
In Silico Characterization
Morphological Examination of the Samples with Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM)
Examination of the Crystallinity of the Formulations by X-Ray Powder Diffraction (XRPD)
Examination of Thermal Properties with Differential Scanning Calorimetry (DSC)
Investigation of Chemical Interactions with Fourier-Transformed Infrared Spectroscopy (FT-IR)
In Vitro Dissolution Measurement
In Vitro Permeability Measurement
Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kurkov, S.V.; Loftsson, T. Cyclodextrins. Int. J. Pharm. 2013, 453, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, S.; Li, X.; Yang, G.; Feng, W.; Zong, L.; Zhao, L.; Ye, F.; Fu, Y. Antibacterial Perillaldehyde/Hydroxypropyl-γ-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex Electrospun Polymer-Free Nanofiber: Improved Water Solubility, Thermostability, and Antioxidant Activity. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 176, 114300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chang, S.-L.; Chang, T.-R.; You, Y.; Wang, X.-D.; Wang, L.-W.; Yuan, X.-F.; Tan, M.-H.; Wang, P.-D.; Xu, P.-W.; et al. Inclusion Complexes of Cannabidiol with β-Cyclodextrin and Its Derivative: Physicochemical Properties, Water Solubility, and Antioxidant Activity. J. Mol. Liq. 2021, 334, 116070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xiao, P.; Lin, L.; Guo, F.; Wang, Q.; Piao, Y.; Diao, G. Study of a Water-Soluble Supramolecular Complex of Curcumin and β-Cyclodextrin Polymer with Electrochemical Property and Potential Anti-Cancer Activity. Chin. Chem. Lett. 2022, 33, 4043–4047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbas, Z.S.; Sulaiman, G.M.; Jabir, M.S.; Mohammed, S.A.A.; Khan, R.A.; Mohammed, H.A.; Al-Subaiyel, A. Galangin/β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex as a Drug-Delivery System for Improved Solubility and Biocompatibility in Breast Cancer Treatment. Molecules 2022, 27, 4521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corazza, F.G.; Ernesto, J.V.; Nambu, F.A.N.; De Carvalho, L.R.; Leite-Silva, V.R.; Varca, G.H.C.; Calixto, L.A.; Vieira, D.P.; Andréo-Filho, N.; Lopes, P.S. Papain-Cyclodextrin Complexes as an Intestinal Permeation Enhancer: Permeability and in Vitro Safety Evaluation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2020, 55, 101413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paprikar, A.; Soni, A.; Kaushal, N.; Lin, S. Sublingual Insulin Administration: Application of Hydroxypropyl Beta-Cyclodextrin and Poloxamer188 as Permeation Enhancers. Pharm. Dev. Technol. 2021, 26, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, P.; Németh, A.; Zeiringer, S.; Roblegg, E.; Budai-Szűcs, M.; Balla-Bartos, C.; Ambrus, R. Formulation and Investigation of Differently Charged β-Cyclodextrin-Based Meloxicam Potassium Containing Nasal Powders. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 202, 106879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adamkiewicz, L.; Szeleszczuk, Ł. Review of Applications of Cyclodextrins as Taste-Masking Excipients for Pharmaceutical Purposes. Molecules 2023, 28, 6964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J.; Díaz-Montaña, E.J.; Asuero, A.G. Cyclodextrins: Past and Present. In Cyclodextrin—A Versatile Ingredient; Arora, P., Dhingra, N., Eds.; InTech: Vienna, Austria, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78923-068-0. [Google Scholar]
- Yadav, M.; Thakore, S.; Jadeja, R. A Review on Remediation Technologies Using Functionalized Cyclodextrin. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whistler, R.L.; BeMiller, J.N. Starch: Chemistry and technology. In Food Science and Technology, International Series, 3rd ed.; Chapter 22-Cyclodextrins: Properties and Applications; Academic Press: London, UK, 2009; ISBN 978-0-12-746275-2. [Google Scholar]
- Bhardwaj, V.K.; Purohit, R. A Comparative Study on Inclusion Complex Formation between Formononetin and β-Cyclodextrin Derivatives through Multiscale Classical and Umbrella Sampling Simulations. Carbohydr. Polym. 2023, 310, 120729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rincón-López, J.; Almanza-Arjona, Y.C.; Riascos, A.P.; Rojas-Aguirre, Y. Technological Evolution of Cyclodextrins in the Pharmaceutical Field. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2021, 61, 102156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puskás, I.; Szente, L.; Szőcs, L.; Fenyvesi, É. Recent List of Cyclodextrin-Containing Drug Products. Period. Polytech. Chem. Eng. 2023, 67, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarabia-Vallejo, Á.; Caja, M.D.M.; Olives, A.I.; Martín, M.A.; Menéndez, J.C. Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes for Improved Drug Bioavailability and Activity: Synthetic and Analytical Aspects. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Party, P.; Klement, M.L.; Szabó-Révész, P.; Ambrus, R. Preparation and Characterization of Ibuprofen Containing Nano-Embedded-Microparticles for Pulmonary Delivery. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motzwickler-Németh, A.; Party, P.; Simon, P.; Sorrenti, M.; Ambrus, R.; Csóka, I. Preparation of Ibuprofen-Loaded Inhalable γCD-MOFs by Freeze-Drying Using the QbD Approach. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurišić Dukovski, B.; Juretić, M.; Bračko, D.; Randjelović, D.; Savić, S.; Crespo Moral, M.; Diebold, Y.; Filipović-Grčić, J.; Pepić, I.; Lovrić, J. Functional Ibuprofen-Loaded Cationic Nanoemulsion: Development and Optimization for Dry Eye Disease Treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 576, 118979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, H.; Ong, H.X.; Bradbury, P.; Kourmatzis, A.; Traini, D.; Young, P.; Li, M.; Cheng, S. Real-Time Quantitative Monitoring of in Vitro Nasal Drug Delivery by a Nasal Epithelial Mucosa-on-a-Chip Model. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2021, 18, 803–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachofen, H.; Schurch, S. Alveolar Surface Forces and Lung Architecture. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2001, 129, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sibbald, W.J.; Warshawski, F.J.; Short, A.K.; Harris, J.; Lefcoe, M.S.; Holliday, R.L. Clinical Studies of Measuring Extravascular Lung Water by the Thermal Dye Technique in Critically III Patients. Chest 1983, 83, 725–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, T.C.; Peters, J.I.; Williams Iii, R.O. Influence of Particle Size on Regional Lung Deposition—What Evidence Is There? Int. J. Pharm. 2011, 406, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Momin, M.A.M.; Tucker, I.G.; Das, S.C. High Dose Dry Powder Inhalers to Overcome the Challenges of Tuberculosis Treatment. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 550, 398–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lands, L.C.; Milner, R.; Cantin, A.M.; Manson, D.; Corey, M. High-Dose Ibuprofen in Cystic Fibrosis: Canadian Safety and Effectiveness Trial. J. Pediatr. 2007, 151, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konstan, M.W. Ibuprofen Therapy for Cystic Fibrosis Lung Disease: Revisited. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2008, 14, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.N.; Marshall-Batty, K.R.; Smolen, J.A.; Tagaev, J.A.; Chen, Q.; Rodesney, C.A.; Le, H.H.; Gordon, V.D.; Greenberg, D.E.; Cannon, C.L. Antimicrobial Activity of Ibuprofen against Cystic Fibrosis-Associated Gram-Negative Pathogens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2018, 62, e01574-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parihar, A.; Prajapati, B.G.; Paliwal, H.; Shukla, M.; Khunt, D.; Devrao Bahadure, S.; Dyawanapelly, S.; Junnuthula, V. Advanced Pulmonary Drug Delivery Formulations for the Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis. Drug Discov. Today 2023, 28, 103729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baxter, L.; Cobo, M.M.; Bhatt, A.; Slater, R.; Sanni, O.; Shinde, N. The Association between Ibuprofen Administration in Children and the Risk of Developing or Exacerbating Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Pulm. Med. 2024, 24, 412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, R.B.; Joshi, S.V. Ibuprofen Isobutanolammonium Salt: Synthesis, Thermal Analysis, PXRD, FTIR and Solubility Investigations. J. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 2020, 139, 1971–1976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.K.; Kahali, N.; Bose, A.; Khanam, J. Physicochemical Characterization and in Vitro Dissolution Performance of Ibuprofen-Captisol® (Sulfobutylether Sodium Salt of β-CD) Inclusion Complexes. J. Mol. Liq. 2018, 261, 239–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Celebioglu, A.; Uyar, T. Fast Dissolving Oral Drug Delivery System Based on Electrospun Nanofibrous Webs of Cyclodextrin/Ibuprofen Inclusion Complex Nanofibers. Mol. Pharm. 2019, 16, 4387–4398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, T.; Surov, A.; Terekhova, I. Metal–Organic Frameworks Based on β-Cyclodextrin: Design and Selective Entrapment of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs. J. Mater. Sci. 2020, 55, 13193–13205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salústio, P.J.; Feio, G.; Figueirinhas, J.L.; Pinto, J.F.; Cabral Marques, H.M. The Influence of the Preparation Methods on the Inclusion of Model Drugs in a β-Cyclodextrin Cavity. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2009, 71, 377–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereva, S.; Nikolova, V.; Sarafska, T.; Angelova, S.; Spassov, T.; Dudev, T. Inclusion Complexes of Ibuprofen and β-Cyclodextrin: Supramolecular Structure and Stability. J. Mol. Struct. 2020, 1205, 127575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cagno, M.; Stein, P.C.; Skalko-Basnet, N.; Brandl, M.; Bauer-Brandl, A. Solubilization of Ibuprofen with β-Cyclodextrin Derivatives: Energetic and Structural Studies. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 55, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braga, S.S.; Gonçalves, I.S.; Herdtweck, E.; Teixeira-Dias, J.J.C. Solid State Inclusion Compound of S-Ibuprofen in β-Cyclodextrin: Structure and characterisation. New J. Chem. 2003, 27, 597–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gul, M.K.; Farmanull, W.; Jia-bi, Z. Ibuprofen-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complexes: Evaluation of Different Complexation Methods. J. Med. Sci. 2001, 1, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, D.; Karara, H. Characterization, Dissolution and Bioavailability in Rats of Ibuprofen-β-Cyclodextrin Complex System. Int. J. Pharm. 1986, 28, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuelsen, L.; Holm, R.; Lathuile, A.; Schönbeck, C. Correlation between the Stability Constant and pH for β-Cyclodextrin Complexes. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 568, 118523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacovino, R.; Caso, J.; Donato, C.; Malgieri, G.; Palmieri, M.; Russo, L.; Isernia, C. Cyclodextrins as Complexing Agents: Preparation and Applications. Curr. Org. Chem. 2016, 21, 162–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arpagaus, C.; John, P.; Collenberg, A.; Rütti, D. Nanocapsules Formation by Nano Spray Drying. In Nanoencapsulation Technologies for the Food and Nutraceutical Industries; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; pp. 346–401. ISBN 978-0-12-809436-5. [Google Scholar]
- Munir, M.; Kett, V.L.; Dunne, N.J.; McCarthy, H.O. Development of a Spray-Dried Formulation of Peptide-DNA Nanoparticles into a Dry Powder for Pulmonary Delivery Using Factorial Design. Pharm. Res. 2022, 39, 1215–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Party, P.; Kókai, D.; Burián, K.; Nagy, A.; Hopp, B.; Ambrus, R. Development of Extra-Fine Particles Containing Nanosized Meloxicam for Deep Pulmonary Delivery: In Vitro Aerodynamic and Cell Line Measurements. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 176, 106247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adel, I.M.; ElMeligy, M.F.; Abdelrahim, M.E.; Maged, A.; Abdelkhalek, A.A.; Abdelmoteleb, A.M.; Elkasabgy, N.A. Design and Characterization of Spray-Dried Proliposomes for the Pulmonary Delivery of Curcumin. Int. J. Nanomed. 2021, 16, 2667–2687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drumond, N.; Sá Couto, A.; Costa, A.; Cabral-Marques, H. Study of Aerodynamic and Release Properties of Inhaled Particles Containing Cyclodextrins. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2014, 80, 25–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vartiainen, V.; Bimbo, L.M.; Hirvonen, J.; Kauppinen, E.I.; Raula, J. Aerosolization, Drug Permeation and Cellular Interaction of Dry Powder Pulmonary Formulations of Corticosteroids with Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin as a Solubilizer. Pharm. Res. 2017, 34, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Huang, Y.; Cui, Y.; Ma, C.; Wang, G.; Freeman, T.; Lu, X.; Pan, X.; et al. Low Density, Good Flowability Cyclodextrin-Raffinose Binary Carrier for Dry Powder Inhaler: Anti-Hygroscopicity and Aerosolization Performance Enhancement. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2018, 15, 443–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-T.; Chuang, Y.-H.; Lin, H.-C.; Chien, L.-J. Characterization and Aerosolization Performance of HydroxyPropyl-Beta-Cyclodextrin Particles Produced Using Supercritical Assisted Atomization. Polymers 2021, 13, 2260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.-T.; Lin, H.-C.; Tu, Y.-J.; Ng, K.H. Instant Formulation of Inhalable Beclomethasone Dipropionate—Gamma-Cyclodextrin Composite Particles Produced Using Supercritical Assisted Atomization. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, V.; Son, Y.-J.; Dolovich, M.; Xing, Z.; Cranston, E.D.; Thompson, M.R. Screening Amino Acid Additives as Aerosolization Modifiers for Spray Dried Inhalable Viral-Vectored Vaccines. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 76, 103815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Tong, S.; Liao, Q.; Pan, L.; Cheng, M.; Rantanen, J.; Cun, D.; Yang, M. Role of Dispersion Enhancer Selection in the Development of Novel Tratinterol Hydrochloride Dry Powder Inhalation Formulations. Int. J. Pharm. 2023, 635, 122702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munir, M.; Jena, L.; Kett, V.L.; Dunne, N.J.; McCarthy, H.O. Spray Drying: Inhalable Powders for Pulmonary Gene Therapy. Biomater. Adv. 2022, 133, 112601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malamatari, M.; Somavarapu, S.; Kachrimanis, K.; Buckton, G.; Taylor, K.M.G. Preparation of Respirable Nanoparticle Agglomerates of the Low Melting and Ductile Drug Ibuprofen: Impact of Formulation Parameters. Powder Technol. 2017, 308, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molina, C.; Kaialy, W.; Nokhodchi, A. The Crucial Role of Leucine Concentration on Spray Dried Mannitol-Leucine as a Single Carrier to Enhance the Aerosolization Performance of Albuterol Sulfate. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2019, 49, 97–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohtar, N.; Taylor, K.M.G.; Sheikh, K.; Somavarapu, S. Design and Development of Dry Powder Sulfobutylether-β-Cyclodextrin Complex for Pulmonary Delivery of Fisetin. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2017, 113, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matilainen, L.; Toropainen, T.; Vihola, H.; Hirvonen, J.; Järvinen, T.; Jarho, P.; Järvinen, K. In Vitro Toxicity and Permeation of Cyclodextrins in Calu-3 Cells. J. Control. Release 2008, 126, 10–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Martínez, B. Use of Cyclodextrins as Excipients in Pharmaceutical Products: Why Not in Extemporaneous Preparations? Farm. Hosp. 2022, 46, 31–39. [Google Scholar]
- Musuc, A.M. Cyclodextrins: Advances in Chemistry, Toxicology, and Multifaceted Applications. Molecules 2024, 29, 5319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerri, L.; Migone, C.; Vizzoni, L.; Grassiri, B.; Fabiano, A.; Piras, A.M.; Zambito, Y. Cross-Linked Thiolated Hydroxypropil-β-Cyclodextrin for Pulmonary Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 9394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewster, M.E.; Loftsson, T. Cyclodextrins as Pharmaceutical Solubilizers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2007, 59, 645–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leclercq, L.; Schmitzer, A.R. Multiple Equilibria in the Complexation of Dibenzylimidazolium Bromide Salts by Cyclodextrins: Toward Controlled Self-Assembly. J. Phys. Chem. B 2008, 112, 11064–11070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jankowski, C.K.; Lamouroux, C.; Jiménez-Estrada, M.; Arseneau, S.; Wagner, B.D. Factors Affecting the Formation of 2:1 Host:Guest Inclusion Complexes of 2-[(R-Phenyl)Amine]-1,4-Naphthalenediones (PAN) in β- and γ-Cyclodextrins. Molecules 2016, 21, 1568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Party, P.; Piszman, Z.I.; Farkas, Á.; Ambrus, R. Comprehensive In Vitro and In Silico Aerodynamic Analysis of High-Dose Ibuprofen- and Mannitol-Containing Dry Powder Inhalers for the Treatment of Cystic Fibrosis. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharif, S.; Muneer, S.; Izake, E.L.; Islam, N. Impact of Leucine and Magnesium Stearate on the Physicochemical Properties and Aerosolization Behavior of Wet Milled Inhalable Ibuprofen Microparticles for Developing Dry Powder Inhaler Formulation. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corzo, C.; Fuchsbichler, A.; Savencu, I.; Afonso Urich, J.; Zimmer, A.; Lochmann, D.; Reyer, S.; Salar-Behzadi, S. Lipid-Microparticles for Pulmonary Delivery of Active Pharmaceutical Ingredients: Impact of Lipid Crystallization on Spray-Drying Processability. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 610, 121259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varga, P.; Ambrus, R.; Szabó-Révész, P.; Kókai, D.; Burián, K.; Bella, Z.; Fenyvesi, F.; Bartos, C. Physico-Chemical, In Vitro and Ex Vivo Characterization of Meloxicam Potassium-Cyclodextrin Nanospheres. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simon, A.; Amaro, M.I.; Cabral, L.M.; Healy, A.M.; De Sousa, V.P. Development of a Novel Dry Powder Inhalation Formulation for the Delivery of Rivastigmine Hydrogen Tartrate. Int. J. Pharm. 2016, 501, 124–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Wan, W.; Lu, J.; Quan, G.; Pan, X.; Liu, P. Effects of L-Leucine on the Properties of Spray-Dried Swellable Microparticles with Wrinkled Surfaces for Inhalation Therapy of Pulmonary Fibrosis. Int. J. Pharm. 2021, 610, 121223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kislalioglu, M.S.; Khan, M.A.; Blount, C.; Goettsch, R.W.; Bolton, S. Physical Characterization and Dissolution Properties of Lbuprofen: Eudragit Coprecipitates. J. Pharm. Sci. 1991, 80, 799–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudognon, E.; Danède, F.; Descamps, M.; Correia, N.T. Evidence for a New Crystalline Phase of Racemic Ibuprofen. Pharm. Res. 2008, 25, 2853–2858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulse, W.L.; Forbes, R.T.; Bonner, M.C.; Getrost, M. The Characterization and Comparison of Spray-Dried Mannitol Samples. Drug Dev. Ind. Pharm. 2009, 35, 712–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cannavà, C.; Crupi, V.; Guardo, M.; Majolino, D.; Stancanelli, R.; Tommasini, S.; Ventura, C.A.; Venuti, V. Phase Solubility and FTIR-ATR Studies of Idebenone/Sulfobutyl Ether β-Cyclodextrin Inclusion Complex. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2013, 75, 255–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, K.; Türk, M.; Wahl, M.A. Comparative Evaluation of Ibuprofen/β-Cyclodextrin Complexes Obtained by Supercritical Carbon Dioxide and Other Conventional Methods. Pharm. Res. 2007, 24, 585–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pongsamart, K.; Limwikrant, W.; Ruktanonchai, U.R.; Charoenthai, N.; Puttipipatkhachorn, S. Preparation, Characterization and Antimalarial Activity of Dihydroartemisinin / β-Cyclodextrin Spray-Dried Powder. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2022, 73, 103434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadota, K.; Tse, J.Y.; Fujita, S.; Suzuki, N.; Uchiyama, H.; Tozuka, Y.; Tanaka, S. Drug-Facilitated Crystallization of Spray-Dried CD-MOFs with Tunable Morphology, Porosity, And Dissolution Profile. ACS Appl. Bio Mater. 2023, 6, 3451–3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, V.M.; Haslam, J.L.; Stella, V.J. Controlled and Complete Release of a Model Poorly Water-soluble Drug, Prednisolone, from Hydroxypropyl Methylcellulose Matrix Tablets Using (SBE) 7m-β-cyclodextrin as a Solubilizing Agent. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 807–816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Niu, B.; Luo, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Quan, G.; Pan, X.; Wu, C. Cyclodextrin-Based Metal-Organic Frameworks for Pulmonary Delivery of Curcumin with Improved Solubility and Fine Aerodynamic Performance. Int. J. Pharm. 2020, 588, 119777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, R.; Chaudhary, S.; Rana, V. Preparation and Characterization of Clopidogrel Bisulfate-Hydroxypropyl-β-Cyclodextrin Mixed Inclusion Complex for Improved Intestinal Solubility and Anti-Thrombotic Efficacy. J. Pharm. Sci. 2023, 112, 166–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Anton, N.; Arpagaus, C.; Belleteix, F.; Vandamme, T.F. Nanoparticles by Spray Drying Using Innovative New Technology: The Büchi Nano Spray Dryer B-90. J. Control. Release 2010, 147, 304–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, W. Modelling Inhaled Particle Deposition in the Human Lung—A Review. J. Aerosol Sci. 2011, 42, 693–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, Á.; Jókay, Á.; Fűri, P.; Balásházy, I.; Müller, V.; Odler, B.; Horváth, A. Computer Modelling as a Tool in Characterization and Optimization of Aerosol Drug Delivery. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 2015, 15, 2466–2474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farkas, Á.; Jókay, Á.; Balásházy, I.; Füri, P.; Müller, V.; Tomisa, G.; Horváth, A. Numerical Simulation of Emitted Particle Characteristics and Airway Deposition Distribution of Symbicort® Turbuhaler® Dry Powder Fixed Combination Aerosol Drug. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2016, 93, 371–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieszinger, P.; Kiss, T.; Szabó-Révész, P.; Ambrus, R. The Development of an In Vitro Horizontal Diffusion Cell to Monitor Nasal Powder Penetration Inline. Pharmaceutics 2021, 13, 809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| SBECD | QABCD | |
|---|---|---|
| K [M−1] | 9753 | 9521 |
| CE | 3.58 | 3.49 |
| IBU:CD | 1:1.27 | 1:1.29 |
| D(0.1) [μm] | D(0.5) [μm] | D(0.9) [μm] | Span | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBECD-IBU SD | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 2.5 ± 0.1 | 28.6 ± 11.6 | 11.6 ± 11.1 |
| SBECD-IBU-1MAN-0.5LEU SD | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 3.1 ± 1.1 | 32.5 ± 2.1 | 10.8 ± 4.6 |
| SBECD-IBU-3MAN-0.5LEU SD | 1.7 ± 0.1 | 4.2 ± 2.6 | 148 ± 164.6 | 164.6 ± 16.9 |
| SBECD-IBU-1MAN-1.5LEU SD | 1.3 ± 0.1 | 2.9 ± 0.6 | 23.8 ± 22.9 | 2.9 ± 1.4 |
| SBECD-IBU-3MAN-1.5LEU SD | 1.3 ± 0.2 | 3.3 ± 0.7 | 54.4 ± 22.9 | 17.2 ± 11.3 |
| Sample | FPF [%] | MMAD [µm] |
|---|---|---|
| SBECD-IBU SD | 15.11 ± 7.54 | no data |
| SBECD-IBU-1MAN-0.5LEU SD | 50.05 ± 1.05 | 3.83 ± 0.19 |
| SBECD-IBU-3MAN-0.5LEU SD | 19.46 ± 1.02 | 7.98 ± 0.68 |
| SBECD-IBU-1MAN-1.5LEU SD | 35.70 ± 1.39 | 5.14 ± 0.26 |
| SBECD-IBU-3MAN-1.5LEU SD | 40.07 ± 2.02 | 4.65 ± 0.18 |
| Sample | FPF [%] | MMAD [µm] |
|---|---|---|
| SBECD-IBU SD | 15.11 ± 7.54 | no data |
| QABCD-IBU SD | 35.20 ± 9.42 | 5.19 ± 1.98 |
| SBECD-IBU-1MAN-0.5LEU SD | 50.05 ± 1.05 | 3.83 ± 0.19 |
| QABCD-IBU-1MAN-0.5LEU SD | 51.01 ± 4.06 | 4.10 ± 0.16 |
| Sample | Distilled Water [mL] | SBECD [mg] | IBU [mg] | MAN [mg] | LEU [mg] |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBECD-IBU | 10 | 331.88 | 23.80 | – | – |
| SBECD-IBU-1MAN-0.5LEU-SD | 10 | 331.88 | 23.80 | 23.80 | 11.90 |
| SBECD-IBU-3MAN-0.5LEU SD | 10 | 331.88 | 23.80 | 71.41 | 11.90 |
| SBECD-IBU-1MAN-1.5LEU SD | 10 | 331.88 | 23.80 | 23.80 | 35.70 |
| SBECD-IBU-3MAN-1.5LEU SD | 10 | 331.88 | 23.80 | 71.42 | 35.70 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Motzwickler-Németh, A.; Körmendi, E.; Farkas, Á.; Csóka, I.; Ambrus, R. Nano-Spray-Drying of Cyclodextrin/Ibuprofen Complexes with Aerosolization-Enhancing Additives for Pulmonary Drug Delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094320
Motzwickler-Németh A, Körmendi E, Farkas Á, Csóka I, Ambrus R. Nano-Spray-Drying of Cyclodextrin/Ibuprofen Complexes with Aerosolization-Enhancing Additives for Pulmonary Drug Delivery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094320
Chicago/Turabian StyleMotzwickler-Németh, Anett, Endre Körmendi, Árpád Farkas, Ildikó Csóka, and Rita Ambrus. 2025. "Nano-Spray-Drying of Cyclodextrin/Ibuprofen Complexes with Aerosolization-Enhancing Additives for Pulmonary Drug Delivery" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094320
APA StyleMotzwickler-Németh, A., Körmendi, E., Farkas, Á., Csóka, I., & Ambrus, R. (2025). Nano-Spray-Drying of Cyclodextrin/Ibuprofen Complexes with Aerosolization-Enhancing Additives for Pulmonary Drug Delivery. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4320. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094320










