Amine-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica for Efficient CO2 Capture: Stability, Performance, and Industrial Feasibility
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics and Classification of Porous Silica Nanoparticles
2.1. Structural Characteristics of Porous Materials and CO2 Adsorption
2.1.1. Differences Between Macroporocity, Mesoporosity, and Microporosity
2.1.2. Influence of Meso/Micro-Pore Size on the Diffusion and Adsorption Rates of CO2 Molecules
2.1.3. Pore Volume and the Feasibility of Amine Functionalization
2.1.4. Specific Surface Area, Pore Volume, and the Feasibility of Amine Functionalization
2.2. Types and Applications of Silica Nanoparticles
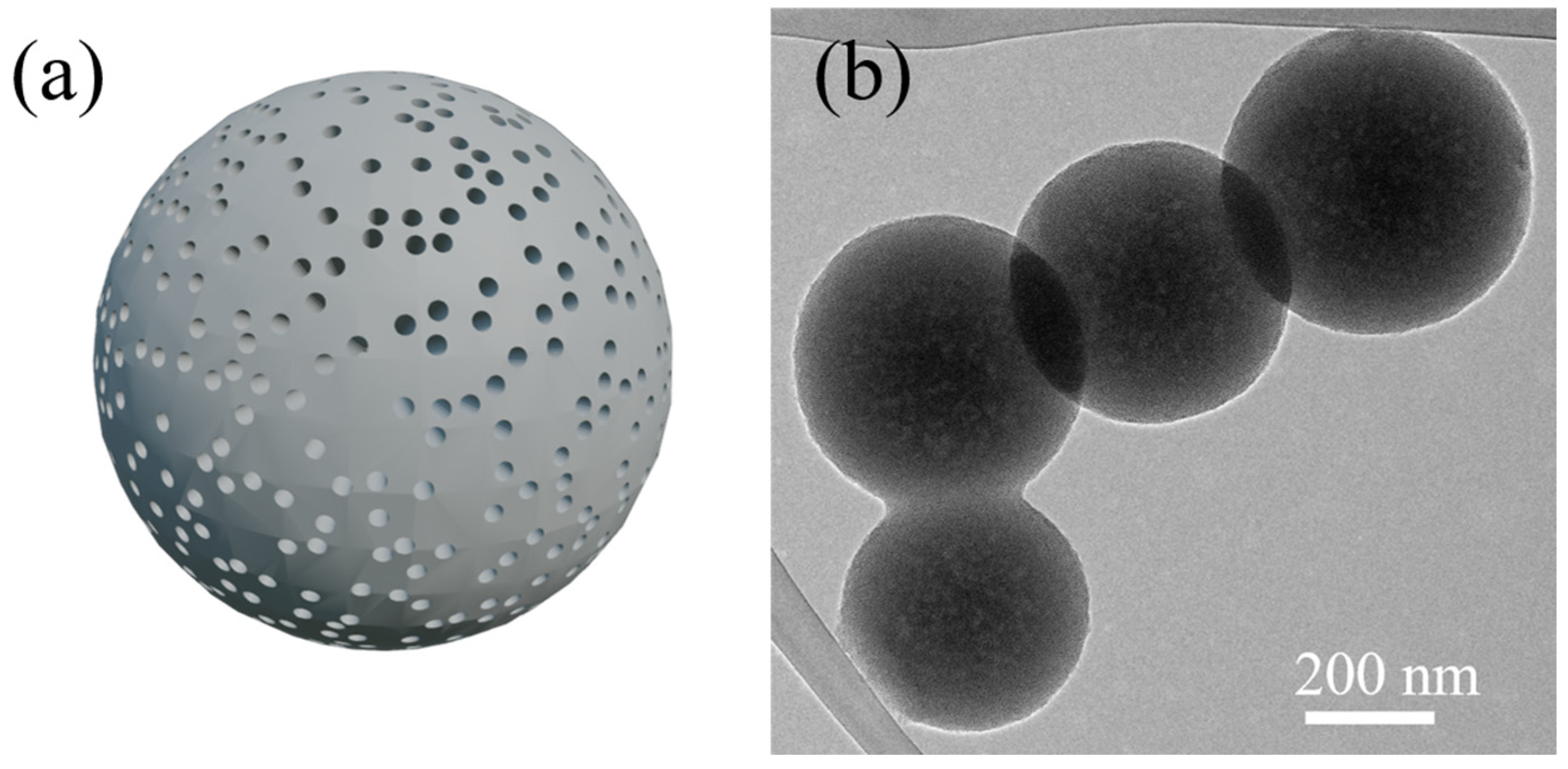
2.2.1. Porous Spherical Silica Nanoparticles
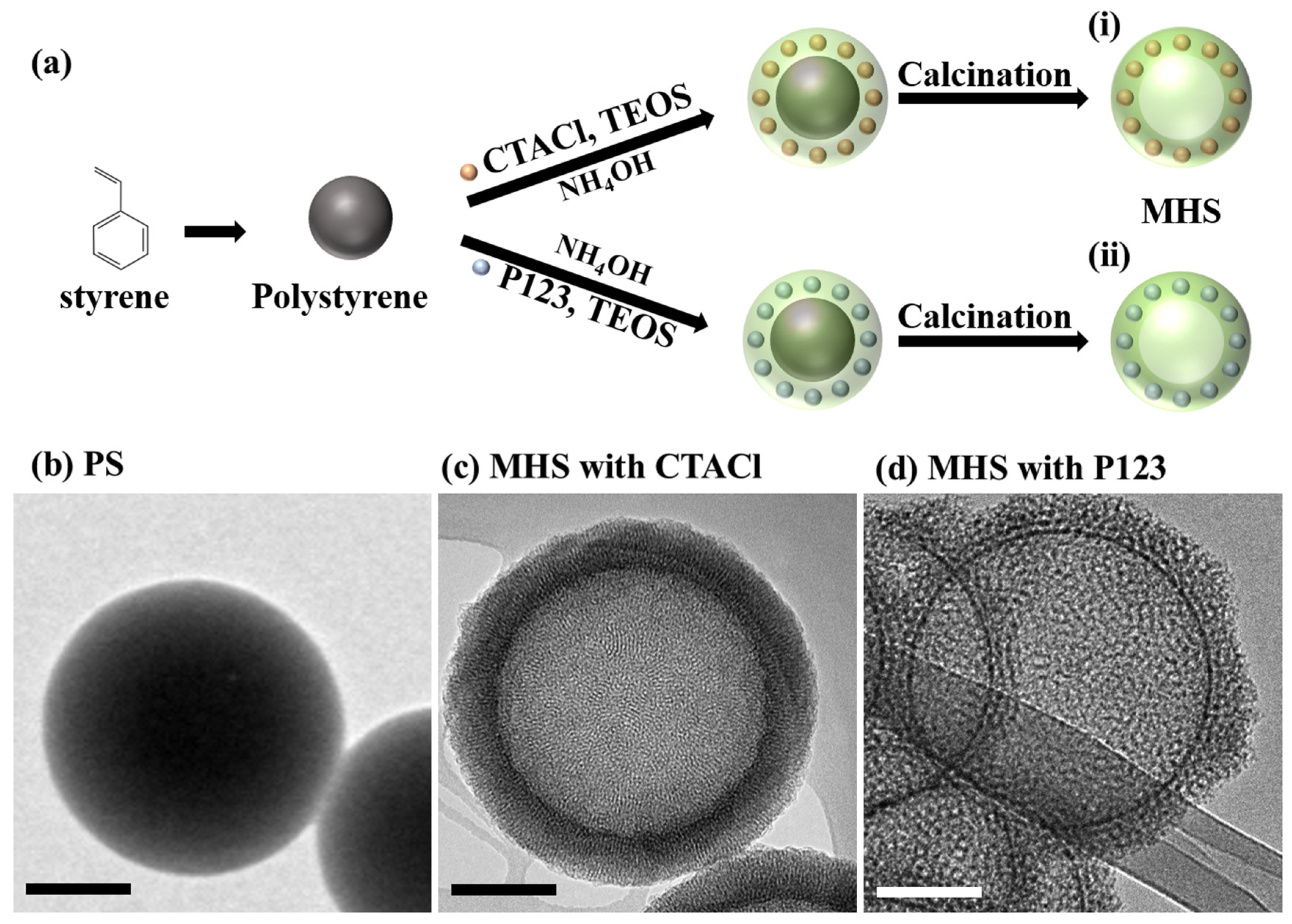
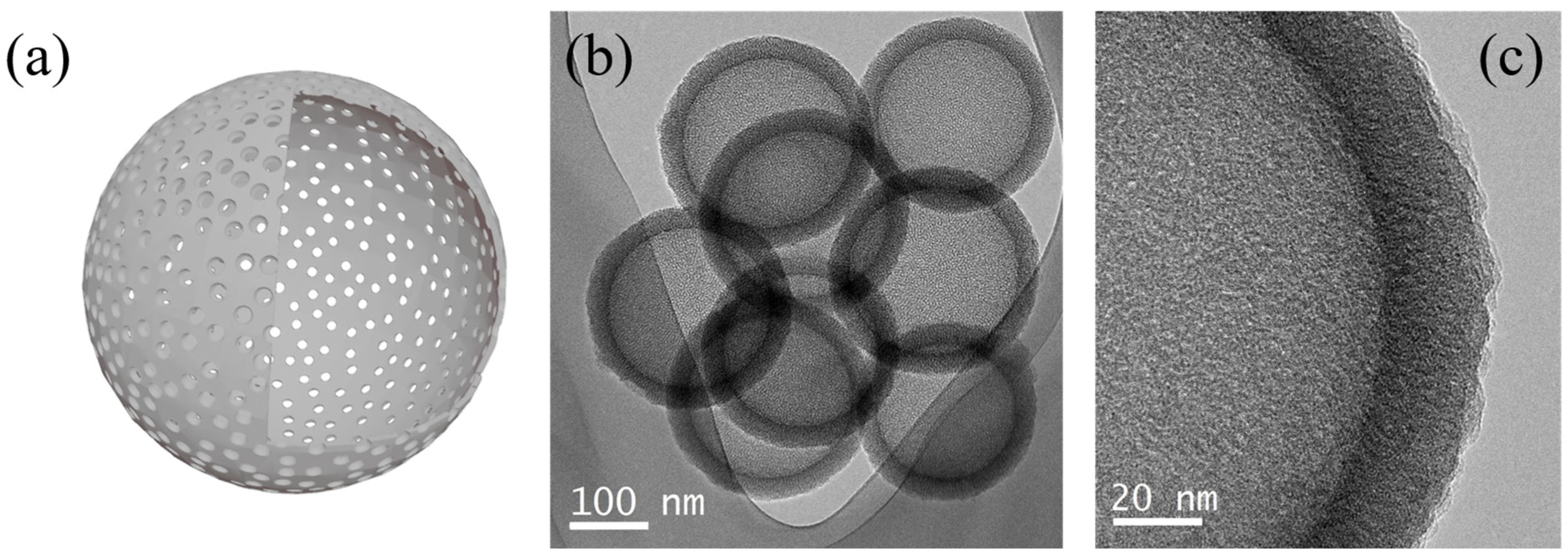
2.2.2. Hollow Silica Nanoparticles
2.2.3. Hierarchical Porous Silica
2.3. Synthesis Techniques of Porous Silica Nanoparticles
2.3.1. Hard Template-Based Silica Nanoparticles
- Template Preparation:
- 2.
- Silica Precursor Coating:
- 3.
- Template Removal:
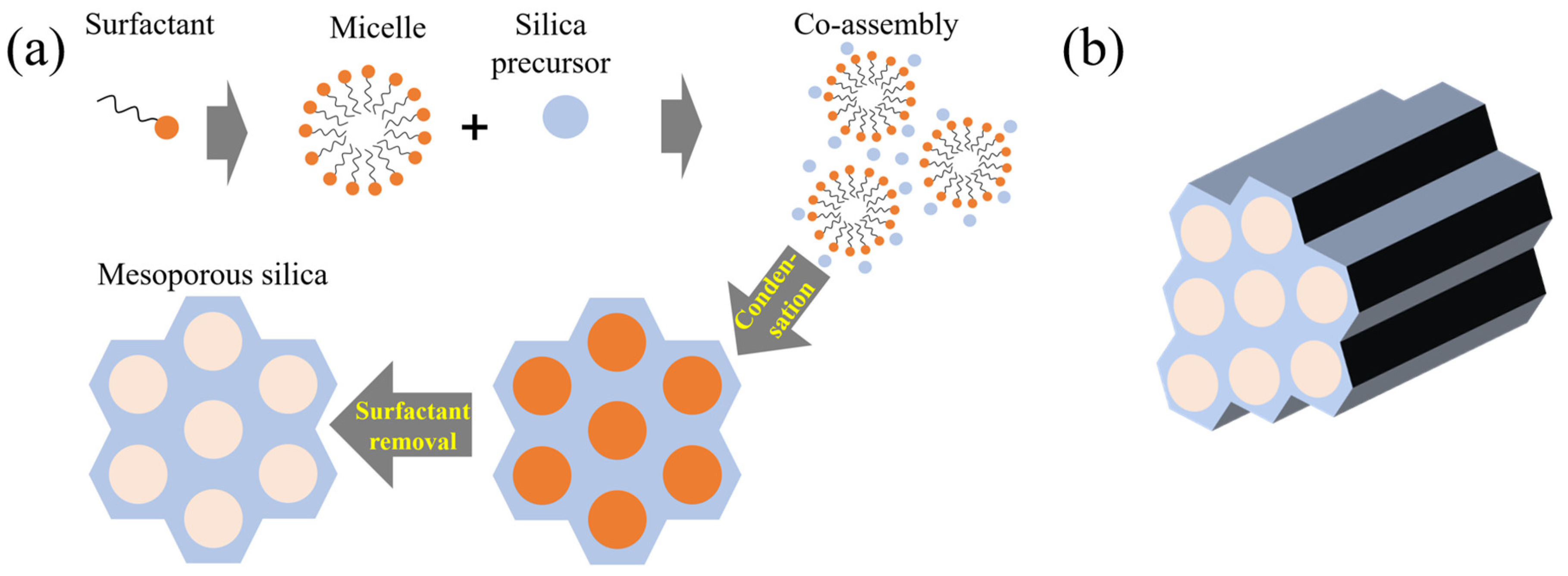
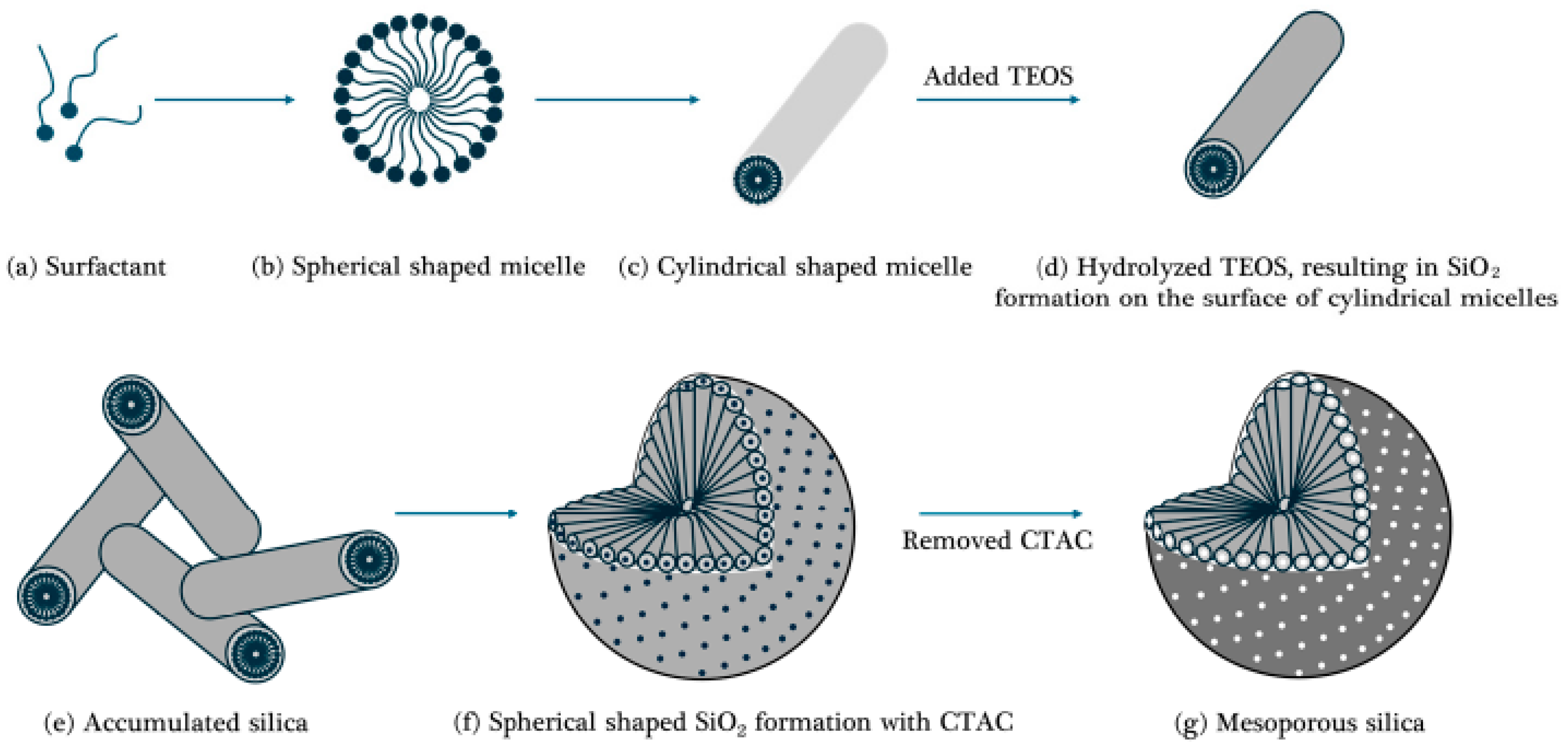
2.3.2. Soft-Template-Based Silica
- Preparation of Surfactant and Cosolvent as illustrated in Figure 5a–c:
- 2.
- Addition of Silica Precursors as depicted in Figure 5d–f:
- 3.
- Removal of Surfactants as shown in Figure 5g:
2.3.3. Template-Free Silica
- Mixing of Precursors and Catalysts:
- 2.
- Spontaneous Pore Formation:
2.3.4. Only-Room-Temperature Synthesized Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles
- Selection of Template and Mixing with precursors:
- 2.
- Template Removal:
- 3.
- Drying:
- CO2 Adsorption:
- 2.
- Formaldehyde Removal:
3. CO2 Adsorption Mechanisms
3.1. Introduction of Amine Functional Groups
3.1.1. Physical (Wet) Impregnation Approach
3.1.2. Chemical Functionalization Method
3.1.3. One-Pot Synthesis
3.2. CO2 Adsorption on Amine-Functionalized MSNs via Physical Impregnation or Chemical Grafting Methods
Chemical Adsorption
- Chemical Adsorption of CO2 by MSNs with Physically Impregnated Amine Groups
- 2.
- Chemical Adsorption of CO2 by MSNs with Chemically Grafted Amine Groups
4. Challenges and Future Directions
4.1. Enhancement of Adsorption Capacity and Selectivity
4.2. Ensuring Durability and Stability
4.3. Environmental Friendliness and Cost Reduction (Low-Cost Raw Materials, Waste Heat Utilization, and Energy-Efficient Regeneration Processes)
4.4. Future Research Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mehmood, A.; Ghafar, H.; Yaqoob, S.; Gohar, U.F.; Ahmad, B. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles: A Review. J. Dev. Drugs 2017, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, L.; Guo, Q. Development of hybrid amine-functionalized MCM-41 sorbents for CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. J. 2015, 260, 573–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Song, C.; Andrésen, J.M.; Miller, B.G.; Scaroni, A.W. Preparation and characterization of novel CO2 “molecular basket’’ adsorbents based on polymer-modified mesoporous molecular sieve MCM-41. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2003, 62, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, S.; Ramli, A.; Yusup, S.; Farooq, M. Adsorption behavior of tetraethylenepentamine-functionalized Si-MCM-41 for CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2017, 122, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widenmeyer, M.; Anwander, R. Pore Size Control of Highly Ordered Mesoporous Silica MCM-48. Chem. Mater. 2002, 14, 1827–1831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anbia, M.; Kargosha, K.; Khoshbooei, S. Heavy metal ions removal from aqueous media by modified magnetic mesoporous silica MCM-48. Chem. Eng. Res. Des. 2015, 93, 779–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stuckert, A.N.; Yang, R.T. CO2 Capture from the Atmosphere and Simultaneous Concentration Using Zeolites and Amine-Grafted SBA-15. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 10257–10264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.L.; Pedernera, M.; Adrover, M.E. Enhanced CO2 capture by functionalization of SBA-15 with APTES and L-lysine. Chem. Eng. J. 2024, 498, 155431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lin, K.S.K.; Chan, J.C.C.; Cheng, S. Direct Synthesis and Catalytic Applications of Ordered Large Pore Aminopropyl-Functionalized SBA-15 Mesoporous Materials. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 1763–1769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, Y.; Yang, G.; Yan, Z. Amine-Modified SBA-15: Effect of Pore Structure on the Performance for CO2 Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2011, 50, 3220–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gargiulo, N.; Peluso, A.; Aprea, P.; Pepe, F.; Caputo, D. CO2 Adsorption on Polyethylenimine-Functionalized SBA-15 Mesoporous Silica: Isotherms and Modeling. J. Chem. Eng. Data 2014, 59, 896–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thommes, M.; Kaneko, K.; Neimark, A.V.; Olivier, J.P.; Rodriguez-Reinoso, F.; Rouquerol, J.; Sing, K.S.W. Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl. Chem. 2015, 87, 1051–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, D.; Feng, J.; Huo, Q.; Melosh, N.; Fedrickson, G.H.; Chmelka, B.F.; Stucky, G.D. Triblock Copolymer Syntheses of Mesoporous Silica with Periodic 50 to 300 Angstrom Pores. Science 1998, 279, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiang, S.; He, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wu, H.; Zhou, W.; Krishna, R.; Chen, B. Microporous metal-organic framework with potential for carbon dioxide capture at ambient conditions. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heras, K.L.; Garcia-Orue, I.; Aguirre, J.J.; La Caba, K.d.; Guerrero, P.; Igartua, M.; Santos-Vizcaino, E.; Hernandez, R.M. Soy protein/β-chitin sponge-like scaffolds laden with human mesenchymal stromal cells from hair follicle or adipose tissue promote diabetic chronic wound healing. Biomater. Adv. 2023, 155, 213682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shang, L.; Wang, S.; Mao, Y. Recent advances in plant-derived polysaccharide scaffolds in tissue engineering: A review. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 277, 133830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azmand, H.R.; Enemuo, A.N.; Seo, S.-W. Active liquid flow control through a polypyrrole-coated macroporous silicon membrane toward chemical stimulation applications. Sens. Actuators A 2021, 318, 112512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia, L.; Rosas, W.; Aguilar-Sanchez, A.; Mathew, A.P.; Palmqvist, A.E.C. Bio-based Micro-/Meso-/Macroporous Hybrid Foams with Ultrahigh Zeolite Loadings for Selective Capture of Carbon Dioxide. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces Adv. 2019, 11, 40424–40431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, B.; Prinsen, P.; Wang, H.; Bai, Z.; Wang, H.; Luque, R.; Xuan, J. Macroporous materials: Microfluidic fabrication, functionalization and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2017, 46, 855–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.Y.; Jang, S.G. Characteristics of CO2 Capture by Tetraethylenepentamine Modified Mesoporous Silica Morphology. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2019, 19, 6291–9296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.Y.; Jang, S.G. Preparation and Characterization of Amine-Functionalized Mesoporous Hollow Silica for CO2 Capture. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2020, 20, 7070–7074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.-T.; Bae, J.Y. Synthesis and Characteristics of Double-Shell Mesoporous Hollow Silica Nanomaterials to Improve CO2 Adsorption Performance. Micromachines 2021, 12, 1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Lee, J.-T.; Bae, J.-Y. Facile Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica at Room Temperature for CO2 Adsorption. Micromachines 2022, 13, 926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, M.; Lee, J.-T.; Kim, M.-K.; Byun, M.; Bae, J.-Y. Facile Mesoporous Hollow Silica Synthesis for Formaldehyde Adsorption. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.M.; Kang, M.; Kim, J.-S.; Bae, J.-Y. Amine-Impregnated Dendritic Mesoporous Silica for the Adsorption of Formaldehyde. Micromachines 2024, 15, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, H.-S.; Kang, M.; Lee, J.-T.; Bae, J.-Y. Synthesis of Mesoporous Silica Sol with Low Refractive Properties for Increasing Transmittance. Micromachines 2024, 15, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.-T.; Kang, M.; Bae, J.-Y. The Facile Synthesis and Application of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with a Vinyl Functional Group for Plastic Recycling. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 2295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaramulu, K.; Devi, B. Hybrid Two-Dimensional Porous Materials. Chem. Mater. 2023, 35, 9473–9492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corma, A. From Microporous to Mesoporous Molecular Sieve Materials and Their Use in Catalysis. Chem. Rev. 1997, 97, 2373–2419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Y.; Jo, C.; Jeong, I.; Lee, J. Functional mesoporous materials for energy applications: Solar cells, fuel cells, and batteries. Nanoscale 2013, 5, 4584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, Q. Adsorption Mechanisms of CO2 on Macroporous Ion-Exchange Resin Organic Amine Composite Materials by the Density Functional Theory. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 17541–17550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kresge, C.T.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Roth, W.J.; Vartuli, J.C.; Beck, J.S. Ordered mesoporous molecular sieves synthesized by a liquid-crystal template mechanism. Nature 1992, 359, 710–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroniec, M.; Solovyov, L.A. Improvement of the Kruk-Jaroniec-Sayari Method for Pore Size Analysis of Ordered Silicas with Cylindrical Mesopores. Langmuir 2006, 22, 6757–6760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faisal, M.; Pamungkas, A.Z.; Krisnandi, Y.K. Study of Amine Functionalized Mesoporous Carbon as CO2 Storage Materials. Processes 2021, 9, 456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dwiningtyas, G.S.; Abdullah, I.; Doi, R.; Krisnandi, Y.K. Bimetallic NiSn supported on mesoporous carbon as an efficient catalyst for selective methanol synthesis from CO2. CRC, 2024; in press. [Google Scholar]
- Duan, L.; Wang, C.; Zhang, W.; Ma, B.; Deng, Y.; Li, W.; Zhao, D. Interfacial Assembly and Applications of Functional Mesoporous Materials. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 14349–14429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Fan, X.; Han, X.; Lv, K.; Zhao, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhao, D. Ultrasmall Inorganic Mesoporous Nanoparticles: Preparation, Functionalization, and Application. Adv. Mater. 2024, 36, 2312374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerritore, M.; Olivieri, F.; Avolio, R.; Castaldo, R.; Cocca, M.; Errico, M.E.; Lavorgna, M.; Silvestri, B.; Ambrogi, V.; Gentile, G. Hierarchical micro-to-macroporous silica nanoparticles obtained by their grafting with hyper-crosslinked resin. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2022, 335, 111864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, F.; Scherillo, F.; Castaldo, R.; Cocca, M.; Squillace, A.; Gentile, G.; Lavorgna, M. Effectiveness of Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles Functionalized with Benzoyl Chloride in pH-Responsive Anticorrosion Polymer Coatings. ACS Appl. Polym. Mater. 2023, 5, 5917–5925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovach, N.C.; Russell-Parks, G.A.; Trewyn, B.G. Strategies for post-synthetic functionalization of mesoporous carbon nanomaterial surfaces. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2022, 329, 111453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sayari, A.; Belmabkhouta, Y.; Serna-Guerrero, R. Flue gas treatment via CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2011, 171, 760–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Wang, Y.; Estevez, L.; Duan, X.; Anako, N.; Park, A.H.A.; Li, W.; Jones, C.W.; Giannelis, E.P. High efficiency nanocomposite sorbents for CO2 capture based on amine-functionalized mesoporous capsules. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, R.; Ambrogi, V.; Avolio, R.; Cocca, M.; Gentile, G.; Errico, M.E.; Avella, M. Functional hyper-crosslinked resins with tailored adsorption properties for environmental applications. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 362, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaldo, R.; Avolio, R.; Cocca, M.; Errico, M.E.; Avella, M.; Gentile, G. Amino-functionalized hyper-crosslinked resins for enhanced adsorption of carbon dioxide and polar dyes. Chem. Eng. J. 2021, 418, 129463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, Y.; Lin, Y.; Hagio, T.; Hu, Y.H. Surface-microporous graphene for CO2 adsorption. Catal. Today 2020, 356, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, D.; Lei, C.; Wang, E.-M.; Li, W.-C.; Lu, A.-H. A Method for Creating Microporous Carbon Materials with Excellent CO2-Adsorption Capacity and Selectivity. ChemSusChem 2014, 7, 291–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heydari-Gorji, A.; Yang, Y.; Sayari, A. Effect of the Pore Length on CO2 Adsorption over Amine-Modified Mesoporous Silicas. Energy Fuels 2011, 25, 4206–4210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Wang, X.; Song, C. “Molecular Basket” Sorbents for Separation of CO2 and H2S from Various Gas Streams. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 5777–5783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leal, O.; Bolivar, C.; Ovalles, C.; Garcia, J.J.; Espidel, Y. Reversible adsorption of carbon dioxide on amine surface-bonded silica gel. Inorg. Chim. Acta 1995, 240, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunauer, S.; Emmett, P.H.; Teller, E. Adsorption of Gases in Multimolecular Layers. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1938, 60, 300–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, S.; Drese, J.H.; Jones, C.W. Adsorbent Materials for Carbon Dioxide Capture from Large Anthropogenic Point Sources. ChemSusChem 2009, 2, 796–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sing, K.S.W.; Everett, D.H.; Haul, R.A.W.; Moscou, L.; Pierotti, R.A.; Rouquerol, J.; Siemieniewska, T. Reporting Physisorption Data For Gas/Solid Systems with Special Reference to the Determination of Surface Area and Porosity. Pure Appl. Chem. 1985, 57, 603–619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruckmann, F.d.S.; Nunes, F.B.; Salles, T.d.R.; Franco, C.; Cadoná, F.C.; Bohn Rhoden, C.R. Biological Applications of Silica-Based Nanoparticles. Magnetochemistry 2022, 8, 131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowing, I.I.; Vivero-Escoto, J.L.; Wu, C.-W.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2008, 60, 1278–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Guan, Y.; Liu, H.; Hao, N.; Liu, T.; Meng, X.; Fu, C.; Li, Y.; Qu, Q.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Silica NanorattleDoxorubicin-Anchored Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Tumor-Tropic Therapy. ACS Nano 2011, 5, 7462–7470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-Y.; Hu, J.-J.; Xu, Q.; Chen, S.; Jia, H.-Z.; Sun, Y.-X.; Zhuo, R.-X.; Zhang, X.-Z. A redox-responsive drug delivery system based on RGD containing peptide-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles. J. Mater. Chem. B 2015, 3, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Huang, Y.-w.; Zhou, X.-D.; Ma, Y. In vitro toxicity of silica nanoparticles in human lung cancer cells. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2006, 217, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saorin, A.; Martinez-Serra, A.; Paparoni-Bruzual, G.J.; Crozzolin, M.; Lombardi, V.; Back, M.; Riello, P.; Monopoli, M.P.; Rizzolio, F. Understanding the impact of silica nanoparticles in cancer cells through physicochemical and biomolecular characterizations. Mater. Adv. 2024, 5, 5106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serna-Guerreroa, R.; Belmabkhout, Y.; Sayari, A. Modeling CO2 adsorption on amine-functionalized mesoporous silica: 1. A semi-empirical equilibrium model. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 161, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, H.; Zhang, G.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, Y. High CO2 adsorption on amine-functionalized improved macro-/mesoporous multimodal pore silica. Fuel 2022, 315, 123195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Cai, Q.; Yin, C.; Xia, Q.; Cheng, J.; Li, X.; Wang, Y. Facile synthesis of silica nanosheets with hierarchical pore structure and their amine-functionalized composite for enhanced CO2 capture. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2020, 217, 115528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, W.; Bai, H. High-performance CO2 capture on amine-functionalized hierarchically porous silica nanoparticles prepared by a simple template-free method. Adsorption 2016, 22, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henao, W.; Jaramillo, L.Y.; López, D.; Romero-Sáez, M.; Buitrago-Sierra, R. Insights into the CO2 capture over amine-functionalized mesoporous silica adsorbents derived from rice husk ash. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020, 8, 104362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, J.-Y. CO2 Capture by Amine-Functionalized Mesoporous Hollow Silica. J. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 17, 7418–7422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasidharan, M.; Zenibana, H.; Nandi, M.; Bhaumik, A.; Nakashima, K. Synthesis of mesoporous hollow silica nanospheres using polymeric micelles as template and their application as a drug-delivery carrier. Dalton Trans. 2013, 42, 13381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, M.V.; Tran, T.K.T.; Pham, Q.N.; Do, M.H.; Nguyen, T.H.N.; Nguyen, M.T.; Phan, T.T.; To, T.X.H. Controllable Synthesis of Hollow Silica Nanoparticles Using Layered Double Hydroxide Templates and Application for Thermal Insulation Coating. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 31399–31409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, T.; Jelle, B.P.; Sandberg, L.I.C.; Gustavsen, A. Monodisperse Hollow Silica Nanospheres for Nano Insulation Materials: Synthesis, Characterization, and Life Cycle Assessment. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2013, 5, 761–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, R.; Wang, L.; Xu, S.; Lu, Y.; Zhou, S. Silica nanospheres-encapsulated polymer ligands-bound Pd nanoparticles as highly efficient and selective catalysts for semi-hydrogenations of alkynes. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2024, 377, 113213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, G.; Song, Y.; Li, N.; Xu, L.; Tong, C.; Feng, Y.; Chen, T.; Xu, J. Cage-like hierarchically mesoporous hollow silica microspheres templated by mesomorphous polyelectrolyte-surfactant complexes for noble metal nanoparticles immobilization. Coll. Surf. A 2019, 575, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xue, Z.; Feng, S.; Tu, B.; Zhao, D. Facile Mesoporous Hollow Silica Synthesis for Formaldehyde Adsorption. J. Colloid. Interface Sci. 2014, 429, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, N.; Pan, W.; Yu, Z.; Yang, L.; Tang, B. Hollow Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles with Tunable Structures for Controlled Drug Delivery. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2017, 9, 2123–2129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhang, G.; Liu, J.; Li, G.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wu, C.; Wu, W. Amine-functionalized disordered hierarchical porous silica derived from blast furnace slag with high adsorption capability and cyclic stability for CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 478, 147480. [Google Scholar]
- Na, K.; Jo, C.; Kim, J.; Cho, K.; Jung, J.; Seo, Y.; Messinger, R.J.; Chmelka, B.F.; Ryoo, R. Directing Zeolite Structures into Hierarchically Nanoporous Architectures. Science 2011, 333, 328–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, W.; Tao, S.; Yu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ma, W. High performance adsorbents based on hierarchically porous silica for purifying multicomponent wastewater. J. Mater. Chem. 2011, 21, 15567–15574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes, K.M.; Onna, D.; Rioual, T.; Huvelle, M.A.L.; Britto, F.; Simian, M.; Sánchez-Domínguez, M.; Soler-Illia, G.J.A.A.; Bilmes, S.A. Copper upcycling by hierarchical porous silica spheres functionalized with branched polyethylenimine: Antimicrobial and catalytic applications. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2021, 327, 111391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Chen, X.; Shen, D.; Wu, F.; Pleixats, R.; Pan, J. Functionalized silica nanoparticles: Classification, synthetic approaches and recent advances in adsorption applications. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 15998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, F.; Pan, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Pleixats, R.; Pan, J. Selective capture of palladium(II) from highly acidic solution by proline-valinol amide functionalized silica nanoparticles. Colloids Surf. A Physicochem. Eng. Asp. 2022, 648, 129374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, B.; Rehman, A.U.; Haq, I.-u.; Al-Dossary, A.A.; Elaissari, A.; Ahmed, N. Exploiting recent trends for the synthesis and surface functionalization of mesoporous silica nanoparticles towards biomedical applications. Int. J. Pharm.-X 2022, 4, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Usgodaarachchi, L.; Thambiliyagodage, C.; Wijesekera, R.; Bakker, M.G. Synthesis of mesoporous silica nanoparticles derived from rice husk and surface-controlled amine functionalization for efficient adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solution. Curr. Res. Green. Sustain. Chem. 2021, 4, 100116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, F.; Castaldo, R.; Cocca, M.; Gentile, G.; Lavorgna, M. Innovative Silver-Based Capping System for Mesoporous Silica Nanocarriers Able to Exploit a Twofold Anticorrosive Mechanism in Composite Polymer Coatings: Tailoring Benzotriazole Release and Capturing Chloride Ions. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2021, 13, 48141–48152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Lang, M.; Li, Y.; Lia, L.; Shi, J. Fabrication of uniform hollow mesoporous silica spheres and ellipsoids of tunable size through a facile hard-templating route. J. Mater. Chem. 2009, 19, 2778–2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanal, A.; Inoue, Y.; Yada, M.; Nakashima, K. Synthesis of Silica Hollow Nanoparticles Templated by Polymeric Micelle with Core-Shell-Corona Structure. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 1534–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Hsu, B.Y.W.; Ren, C.; Li, X.; Wang, J. Silica-based nanocapsules: Synthesis, structure control and biomedical applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2015, 44, 315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.; Lu, Y.; Gates, B.; Xia, Y. Template-Assisted Self-Assembly: A Practical Route to Complex Aggregates of Monodispersed Colloids with Well-Defined Sizes, Shapes, and Structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2001, 123, 8718–8729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, M.; Guillen-Obando, A.; Barbour, A.; Smith, P.; Griffin, A.; Qiang, Z. Direct synthesis of ordered mesoporous materials from thermoplastic elastomers. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, A.-H.; Schüth, F. Nanocasting: AVersatile Strategy for Creating Nanostructured Porous Materials. Adv. Mater. 2006, 18, 1793–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gac, W.; Zawadzki, W.; Słowik, G.; Sienkiewicz, A.; Kierys, A. Nickel catalysts supported on silica microspheres for CO2 methanation. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2018, 272, 79–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, G.; Wang, Y.; Estevez, L.; Switzer, A.K.; Duan, X.; Yang, X.; Giannelis, E.P. Facile and Scalable Synthesis of Monodispersed Spherical Capsules with a Mesoporous Shell. Chem. Mater. 2010, 22, 2693–2695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Deng, W.; Guo, E.; Chung, P.-W.; Chen, S.; Trewyn, B.G.; Brown, R.C.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticle-Stabilized and Manganese-Modified Rhodium Nanoparticles as Catalysts for Highly Selective Synthesis of Ethanol and Acetaldehyde from Syngas. ChemCatChem 2012, 4, 674–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slowing, I.I.; Trewyn, B.G.; Lin, V.S.-Y. Mesoporous Silica Nanoparticles for Intracellular Delivery of Membrane-Impermeable Proteins. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2007, 129, 8845–8849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Li, S.; Shi, R.; Liu, H. Multifunctional mesoporous silica nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, J.S.; Vartuli, J.C.; Roth, W.J.; Leonowicz, M.E.; Kresge, C.T.; Schmitt, K.D.; Chu, C.T.-W.; Olson, D.H.; Sheppard, E.W.; McCullen, S.B.; et al. A New Family of Mesoporous Molecular Sieves Prepared with Liquid Crystal Templates. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1992, 114, 10834–10843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolae, S.A.; Szilágyi, P.Á.; Titirici, M.M. Soft templating production of porous carbon adsorbents for CO2 and H2S capture. Carbon 2020, 169, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azhagapillai, P.; Reddy, K.S.K.; Pena, G.D.J.G.; Bojesomo, R.S.; Raj, A.; Anjum, D.H.; Elkadi, M.; Karanikolos, G.N.; Ali, M.I. Synthesis of Mesoporous Carbon Adsorbents Using Biowaste Crude Glycerol as a Carbon Source via a Hard Template Method for Efficient CO2 Capture. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 21664–21676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Bai, X. 3D-mesoporous KIT-6 supported highly dispersed Pd nanocatalyst for dodecahydro-N-ethylcarbazole dehydrogenation. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2022, 335, 111789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Yang, W.; Li, Z.; Lou, Q.; Tian, Y.; Li, J. Nickel Oxide Nanoparticles on KIT-6: An Efficient Catalyst in Methane Combustion. Processes 2023, 11, 1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Wu, H.; Guo, J.; Zhang, L.; Duan, A.; Zhao, Z.; Zhang, F.; Zhou, Y. Synthesis of ZSM-5/KIT-6 with a tunable pore structure and its catalytic application in the hydrodesulfurization of dibenzothiophene and diesel oil. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 28879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, G.; Tüysüz, H.; Duyckaerts, N.; Knossalla, J.; Wang, G.-H.; Schüth, F. Hollow Nano- and Microstructures as Catalysts. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 14056–14119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, L.; Li, L.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yan, L. Template-free synthesis of uniform hollow silica nanoparticles for controllable antireflection coatings. Ceram. Int. 2020, 46, 7453–7458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinker, C.J.; Scherer, G.W. The Physics and Chemistry of Sol-Gel Processing; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1990; pp. 97–234. [Google Scholar]
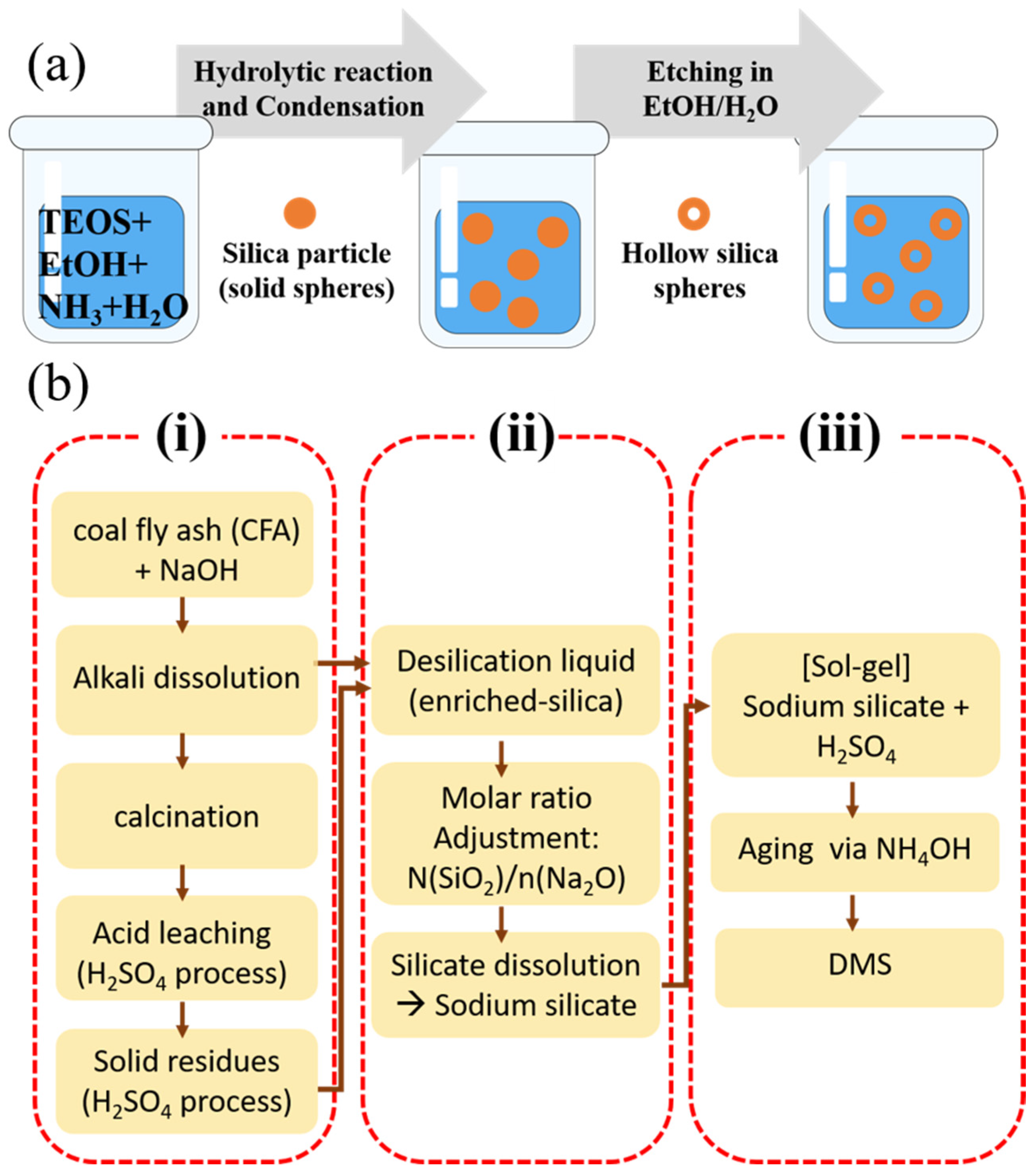
- Liu, D.; Qiao, H.; Qin, S.; Xing, X.; Yan, K. An efficient and template-free synthesis of mesoporous silica from coal fly ash. Asia-Pac. J. Chem. Eng. 2024, 19, e3023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léonard, A.; Vantomme, A.; Bouvy, C.; Moniotte, N.; Mariaulle, P.; Su, B.-L. Highly Ordered Mesoporous and Hierarchically Nanostructured Mesomacroporous Materials for Nanotechnology, Biotechnology, Information Technology and Medical Applications. Nanopages 2006, 1, 1–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saravanan, M.; Sudalai, S.; Dharaneesh, A.B.; Prahaaladhan, V.; Srinivasan, G.; Arumugam, A. An Extensive Review on Mesoporous Silica from Inexpensive Resources: Properties, Synthesis, and Application toward Modern Technologies. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol. 2023, 10, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhao, Z.; Liu, J.; Jiang, G. Effective heavy metal removal from aqueous systems by thiol functionalized magnetic mesoporous silica. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 277–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meky, N.; Salama, E.; Soliman, M.F.; Naeem, S.G.; Ossman, M.; Elsayed, M. Synthesis of Nano-silica Oxide for Heavy Metal Decontamination from Aqueous Solutions. Water Air Soil Poll. 2024, 235, 154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candela-Noguera, V.; Amorós, P.; Aznar, E.; Marcos, M.D.; Martínez-Máñez, R. Systematic study of the implications of calcination and solvent extraction of the surfactant in MCM-41-type mesoporous silica nanoparticles. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2024, 373, 113119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harlick, P.J.E.; Sayari, A. Applications of Pore-Expanded Mesoporous Silica. 5. Triamine Grafted Material with Exceptional CO2 Dynamic and Equilibrium Adsorption Performance. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2007, 46, 446–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-N.; Son, W.-J.; Choi, J.-S.; Ahn, W.-S. CO2 adsorption using amine-functionalized mesoporous silica prepared via anionic surfactant-mediated synthesis. Micropor. Mesopor. Mat. 2008, 115, 497–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hicks, J.C.; Drese, J.H.; Fauth, D.J.; Gray, M.L.; Qi, G.; Jones, C.W. Designing Adsorbents for CO2 Capture from Flue Gas-Hyperbranched Aminosilicas Capable of Capturing CO2 Reversibly. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2008, 130, 2902–2903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Aranguren, P.; Fraile, J.; Vega, L.F.; Domingo, C. Regenerable solid CO2 sorbents prepared by supercritical grafting of aminoalkoxysilane into low-cost mesoporous silica. J. Supercrit. Fluids 2014, 85, 68–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moschetta, E.G.; Sakwa-Novak, M.A.; Greenfield, J.L.; Jones, C.W. Post-Grafting Amination of Alkyl Halide-Functionalized Silica for Applications in Catalysis, Adsorption, and 15N NMR Spectroscopy. Langmuir 2015, 31, 2218–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Aranguren, P.; Builes, S.; Fraile, J.; López-Periago, A.; Vega, L.F.; Domingo, C. Hybrid aminopolymer–silica materials for efficient CO2 adsorption. RSC Adv. 2015, 5, 104943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Pérez, E.S.; Dantas, T.C.M.; Arencibia, A.; Calleja, G.; Guedes, A.P.M.A.; Araujo, A.S.; Sanz, R. Reuse and recycling of amine-functionalized silica materials for CO2 adsorption. Chem. Eng. J. 2017, 308, 1021–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Y.; Landskron, K. CO2-Sorption Properties of Organosilicas with Bridging Amine Functionalities Inside the Framework. J. Phys. Chem. C 2010, 114, 2494–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunathilake, C.; Jaroniec, M. Mesoporous Organosilica with Amidoxime Groups for CO2 Sorption. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2014, 6, 13069–13078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.J.; Gu, F.N.; Wei, F.; Zhou, Y.; Lin, W.G.; Yang, J.; Yang, J.Y.; Wang, Y.; Zou, Z.G.; Zhu, J.H. One-pot synthesis of the amine-modified meso-structured monolith CO2 adsorbent. J. Mater. Chem. 2010, 20, 2840–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klinthong, W.; Huang, C.-H.; Tan, C.-S. One-Pot Synthesis and Pelletizing of Polyethylenimine-Containing Mesoporous Silica Powders for CO2 Capture. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 6481–6491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.; Cheng, W.; Shen, X.; Fan, M.; Russell, A.; Wu, Z.; Yi, X. Mesoporous amine-modified SiO2 aerogel: A potential CO2 sorbent. Energy Environ. Sci. 2011, 4, 2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, Y.; Jiang, G.; Fan, M.; Shen, X.; Cui, S.; Russell, A.G. A new aerogel based CO2 adsorbent developed using a simple sol–gel method along with supercritical drying. Chem. Commun. 2014, 50, 12158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahn, M.W.; Steib, M.; Jentys, A.; Lercher, J.A. Mechanism and Kinetics of CO2 Adsorption on Surface Bonded Amines. J. Phys. Chem. C 2015, 119, 4126–4135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz, R.; Calleja, G.; Arencibia, A.; Sanz-Pérez, E.S. CO2 adsorption on branched polyethyleneimine-impregnated mesoporous silica SBA-15. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2010, 256, 5323–5328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linneen, N.N.; Pfeffer, R.; Lin, Y.S. CO2 adsorption performance for amine grafted particulate silica aerogels. Chem. Eng. J. 2014, 254, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.H.; Celedonio, J.M.; Seo, H.; Park, Y.K.; Ko, Y.S. A study on the effect of the amine structure in CO2 dry sorbents on CO2 capture. Catal. Today 2016, 265, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ko, Y.G.; Lee, H.J.; Oh, H.C.; Choi, U.S. Amines immobilized double-walled silica nanotubes for CO2 capture. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 250–251, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hasan, M.M.F.; First, E.L.; Boukouvala, F.; Floudas, C.A. A multi-scale framework for CO2 capture, utilization, and sequestration: CCUS and CCU. Comput. Chem. Eng. 2015, 81, 2–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maity, A.; Belgamwar, R.; Polshettiwar, V. Facile synthesis to tune size, textural properties and fiber density of dendritic fibrous nanosilica for applications in catalysis and CO2 capture. Nat. Protoc. 2019, 14, 2177–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kole, K.; Das, S.; Samanta, A.; Jana, S. Parametric Study and Detailed Kinetic Understanding of CO2 Adsorption over High-Surface-Area Flowery Silica Nanomaterials. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2020, 59, 21393–21402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anyanwu, J.-T.; Wang, Y.; Yang, R.T. CO2 capture (including direct air capture) and natural gas desulfurization of amine-grafted hierarchical bimodal silica. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 427, 131561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Zhang, S.; Row, K.H.; Ahn, W.-S. Amine–silica composites for CO2 capture: A short review. J. Energy Chem. 2017, 26, 868–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, F.; Castaldo, R.; Cocca, M.; Gentile, G.; Lavorgna, M. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as carriers of active agents for smart anticorrosive organic coatings: A critical review. Nanoscale 2021, 13, 9091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuwahara, Y.; Kang, D.-Y.; Copeland, J.R.; Brunelli, N.A.; Didas, S.A.; Bollini, P.; Sievers, C.; Kamegawa, T.; Yamashita, H.; Jones, C.W. Dramatic Enhancement of CO2 Uptake by Poly(ethyleneimine) Using Zirconosilicate Supports. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 10757–10760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonzio, G.; Mwabonje, O.; Fennell, P.S.; Shah, N. Environmental performance of different sorbents used for direct air capture. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2022, 32, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, B.; Gorji, Z.E.; Singh, R.; Sharma, V.; Repo, T. Silica Gel Supported Solid Amine Sorbents for CO2 Capture. Energy Environ. Mater. 2025, 8, e12832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Z.; Du, Q.; Gao, J.; Bie, R. Waste heat recovery and cascade utilization of CO2 chemical absorption system based on organic amine method in heating season. Appl. Therm. Eng. 2023, 230, 120834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Tian, X.; Shi, Y.; Fan, W.; Liu, Q. Photocatalytic CO2 methanation over the Ni/SiO2 catalysts for performance enhancement. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 2024, 68, 1382–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Sun, C.; Snape, C.E.; Irons, R.; Stebbing, S.; Alderson, T.; Fitzgerald, D.; Liu, H. Process simulations of post-combustion CO2 capture for coal andnatural gas-fired power plants using a polyethyleneimine/silicaadsorbent. Int. J. Greenh. Gas. Control 2017, 58, 276–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaffar, M.M.; Brandoni, C.; Martinez, J.; Snape, C.; Kaldis, S.; Rolfe, A.; Santos, A.; Lysiak, B.; Lappas, A.; Hewitt, N.; et al. Comparative techno-economic analysis of the integration of MEA-based scrubbing and silica PEI adsorbent-based CO2 capture processes into cement plants. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 414, 137666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Property | Microporous Materials | Mesoporous Materials | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pore Size | <2 nm | 2–50 nm | IUPAC standard [12] |
| Adsorption Energy | High (strong CO2 interactions) | Moderate (weaker than micropores) | [14] |
| Diffusion Rate | Slower due to narrow pores | Faster due to larger pores | [13] |
| Adsorption Rate | Slow equilibrium; high selectivity | Fast equilibrium; lower intrinsic selectivity | [29,33] |
| Functionalization Versatility | Limited space for large functional groups | Ample space for grafting and loading amine or polymer layers | [34,35,36,37,38,39,40] |
| Structural Tunability | Limited (framework rigidity) | Highly tunable pore size, shape, and wall thickness | [37] |
| Regeneration Stability | Often stable but can be moisture sensitive | Higher tolerance after hybridization/coating | [37,38] |
| Industrial Scalability | Limited by synthesis complexity | Easier scaling with surfactant-templated routes | [13,36] |
| PEI Content (%) | CO2 Partial Pressure (atm) | CO2 Adsorpt. (mg/g) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore V (cm3/g) | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SBA-15 | PEI Functionalized SBA-15 | SBA-15 | PEI Functionalized SBA-15 | ||||
| 50 | 0.15 | 105 | 803 | 46 | 1.14 | 0.11 | [10] |
| 50 | 1 | 90 | 775 | 49 | 1.1 | 0.09 | [121] |
| 55 | 1 | 173 | 590 | ~0 | 1.14 | ~0 | [47] |
| 0 | 0.15 | 140 | 950 | 80 | 1.31 | 0.2 | [48] |
| 43 | 1 | 70 | 752 | ~0 | 0.7 | ~0 | [11] |
| Support | Amine Type | CO2 Partial Pressure (atm) | CO2 Adsorpt. (mg/g) | BET Surface Area (m2/g) | Total Pore V (cm3/g) | A Method and Types of Amine Functionalized Groups | Ref. | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| W/O PEI | W/PEI | W/O PEI | W/PEI | ||||||
| Amorphous SiO2 | [3-(methylamino)propyl]trimethoxysilane | 0.17 | 57 | 265 | 206 | 1.3 | 1.1 | polymerization < grafting | [123] |
| Particulate silica aerogel | N1-(3-trimethoxysilyl)propyl diethylenetriamine | 1 | 115 | 767 | 417 | 4.2 | 1.1 | mono-amine silane < di-amine silane < tri-amine silane | [122] |
| Double-walled silica nanotube | 3-[2-(2-aminoethylamino) ethylamino] propyl-trimethoxysilane | 1 | 98 | 348 | 60.9 | 1.11 | 0.45 | tertiary amine < secondary amine < primary amine < di-amine < tri-amines | [124] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, J.Y.; Jang, S.G.; Cho, J.; Kang, M. Amine-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica for Efficient CO2 Capture: Stability, Performance, and Industrial Feasibility. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094313
Bae JY, Jang SG, Cho J, Kang M. Amine-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica for Efficient CO2 Capture: Stability, Performance, and Industrial Feasibility. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094313
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Jae Young, Su Guan Jang, Jaehun Cho, and Misun Kang. 2025. "Amine-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica for Efficient CO2 Capture: Stability, Performance, and Industrial Feasibility" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094313
APA StyleBae, J. Y., Jang, S. G., Cho, J., & Kang, M. (2025). Amine-Functionalized Mesoporous Silica for Efficient CO2 Capture: Stability, Performance, and Industrial Feasibility. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4313. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094313






