Neighborhood-Regularized Matrix Factorization for lncRNA–Disease Association Identification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Evaluation Metric
2.2. Performance Comparison with Previous Approaches
2.3. Ablation Analysis
2.4. Case Studies
3. Discussion
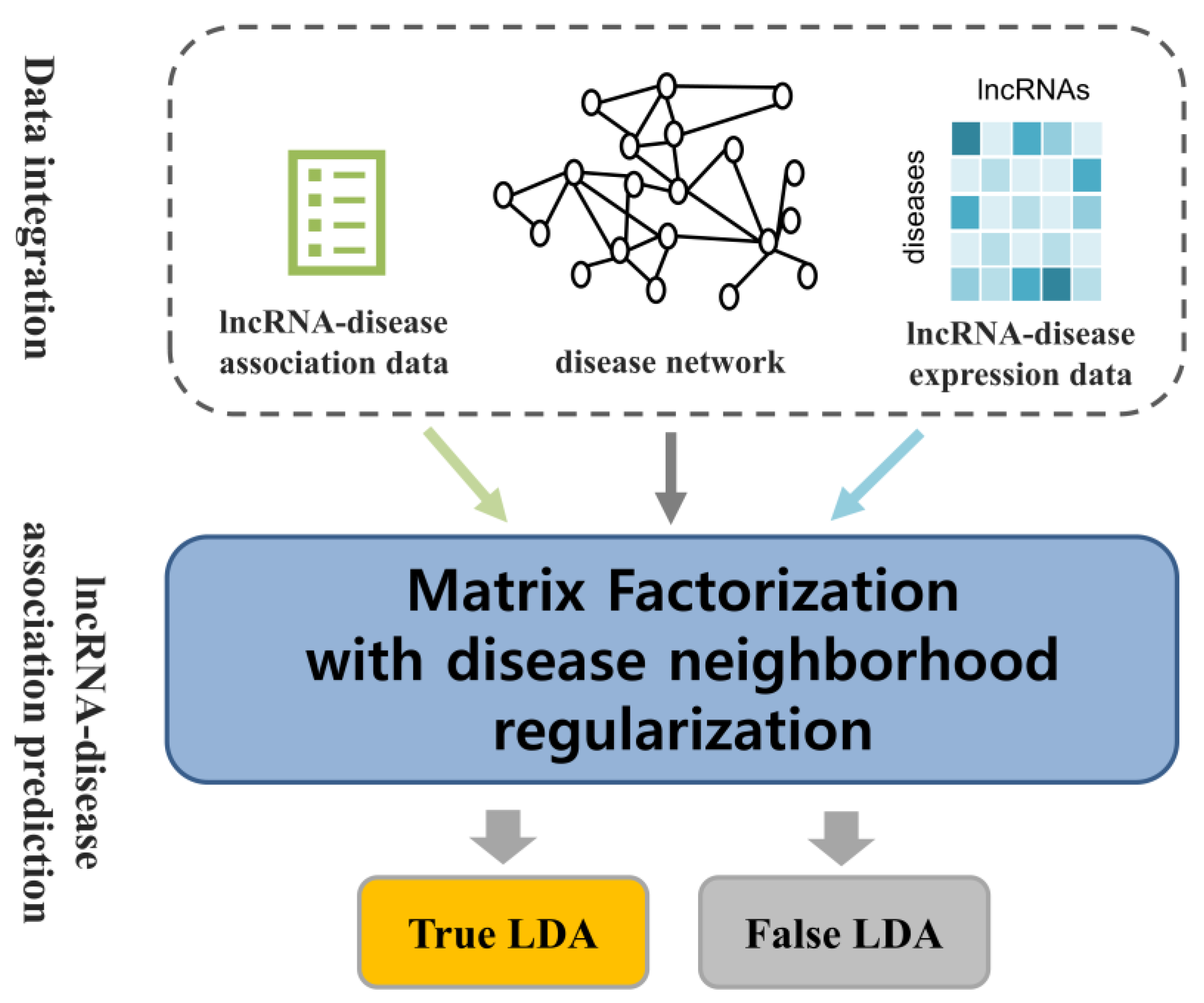
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human lncRNA–Disease Association Data
4.2. lncRNA Expression Data
4.3. Disease Semantic Similarity
4.4. Gaussian Interaction Profile Kernel
4.5. Comprehensive Disease Similarity in Disease Network
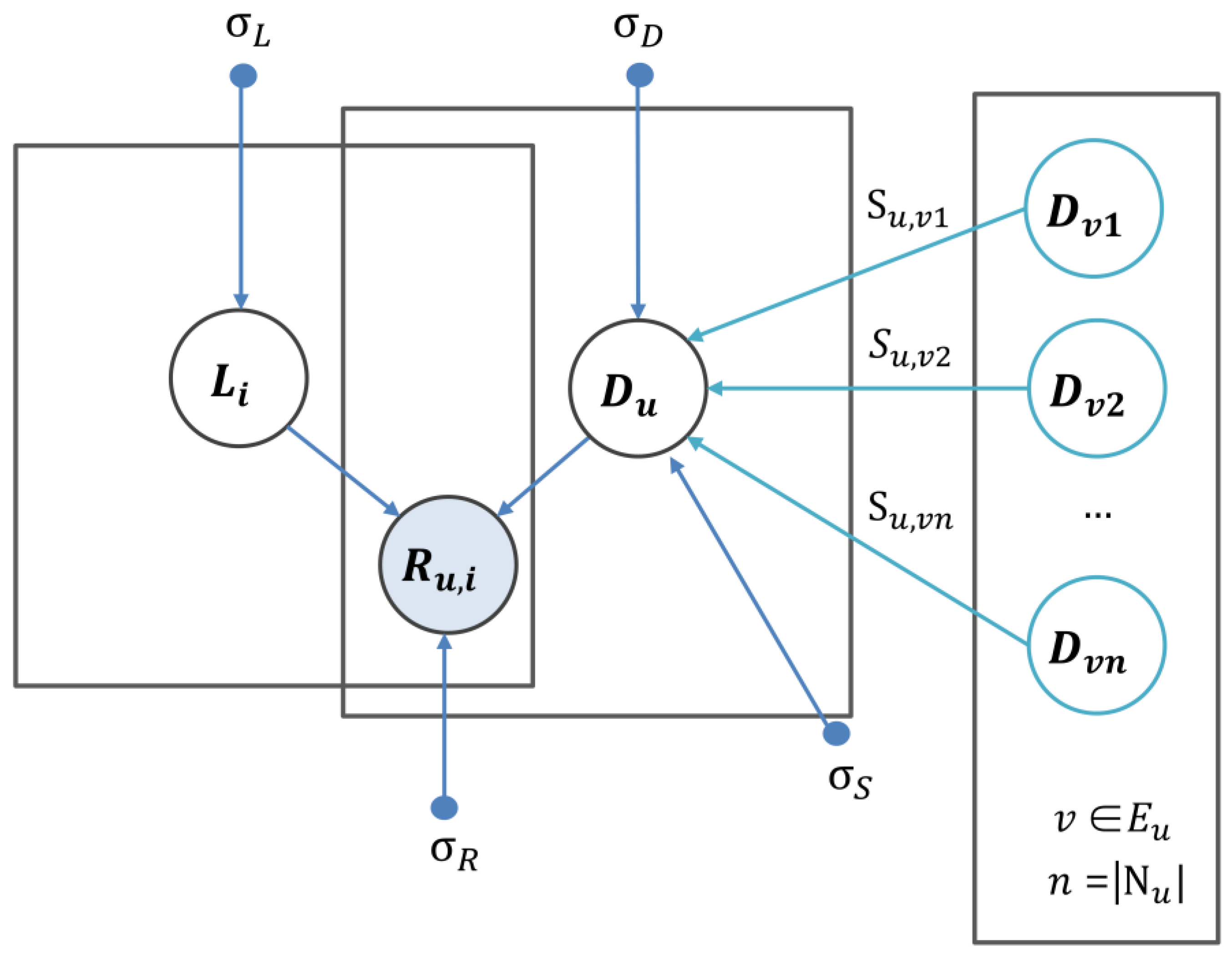
4.6. Similarity Constrained Matrix Factorization
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Crick, F.; Barnett, L.; Brenner, S.; Watts-Tobin, R.J. General Nature of the Genetic Code for Proteins. Nature 1961, 192, 1227–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yanofsky, C. Establishing the Triplet Nature of the Genetic Code. Cell 2007, 128, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anastasiadou, E.; Jacob, L.S.; Slack, F.J. Non-Coding RNA Networks in Cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2018, 18, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ponjavic, J.; Ponting, C.P.; Lunter, G. Functionality or Transcriptional Noise? Evidence for Selection within Long Noncoding RNAs. Genome Res. 2007, 17, 556–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Lan, W.; Wang, J. Mining Featured Patterns of MiRNA Interaction Based on Sequence and Structure Similarity. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 2013, 10, 415–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.C.; Chang, H.Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Long Noncoding RNAs. Mol. Cell 2011, 43, 904–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wapinski, O.; Chang, H.Y. Long Noncoding RNAs and Human Disease. Trends Cell Biol. 2011, 21, 354–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derrien, T.; Johnson, R.; Bussotti, G.; Tanzer, A.; Djebali, S.; Tilgner, H.; Guernec, G.; Martin, D.; Merkel, A.; Knowles, D.G.; et al. The GENCODE v7 Catalog of Human Long Noncoding RNAs: Analysis of Their Gene Structure, Evolution, and Expression. Genome Res. 2012, 22, 1775–1789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapranov, P.; Cheng, J.; Dike, S.; Nix, D.A.; Duttagupta, R.; Willingham, A.T.; Stadler, P.F.; Hertel, J.; Hackermüller, J.; Hofacker, I.L.; et al. RNA Maps Reveal New RNA Classes and a Possible Function for Pervasive Transcription. Science 2007, 316, 1484–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, T.R.; Dinger, M.E.; Mattick, J.S. Long-Coding RNAs: Insights into Functions. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2009, 10, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman, M.; Russell, P.; Ingolia, N.T.; Weissman, J.S.; Lander, E.S. Ribosome Profiling Provides Evidence that Large Noncoding RNAs Do Not Encode Proteins. Cell 2013, 154, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lander, E.S.; Linton, L.M.; Birren, B.; Nusbaum, C.; Zody, M.C.; Baldwin, J.; Devon, K.; Dewar, K.; Doyle, M.; FitzHugh, W.; et al. Initial Sequencing and Analysis of the Human Genome. Nature 2001, 409, 860–921. [Google Scholar]
- Guttman, M.; Amit, I.; Garber, M.; French, C.; Lin, M.F.; Feldser, D.; Huarte, M.; Zuk, O.; Carey, B.W.; Cassady, J.P.; et al. Chromatin Signature Reveals Over a Thousand Highly Conserved Large Non-Coding RNAs in Mammals. Nature 2009, 458, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman, M.; Rinn, J.L. Modular Regulatory Principles of Large Non-Coding RNAs. Nature 2012, 482, 339–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinn, J.L.; Kertesz, M.; Wang, J.K.; Squazzo, S.L.; Xu, X.; Brugmann, S.A.; Goodnough, L.H.; Helms, J.A.; Farnham, P.J.; Segal, E.; et al. Functional Demarcation of Active and Silent Chromatin Domains in Human HOX Loci by Noncoding RNAs. Cell 2007, 129, 1311–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, K.C.; Yang, Y.W.; Liu, B.; Sanyal, A.; Corces-Zimmerman, R.; Chen, Y.; Lajoie, B.R.; Protacio, A.; Flynn, R.A.; Gupta, R.A.; et al. A Long Noncoding RNA Maintains Active Chromatin to Coordinate Homeotic Gene Expression. Nature 2011, 472, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, M.; Meijer, D.; Setyono-Han, B.; Dorssers, L.C.; van Agthoven, T. Characterization of BCAR4, a Novel Oncogene Causing Endocrine Resistance in Human Breast Cancer Cells. J. Cell Physiol. 2011, 226, 1741–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godinho, M.F.E.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Look, M.P.; Meijer, D.; Foekens, J.A.; Dorssers, L.C.J.; van Agthoven, T. Relevance of BCAR4 in Tamoxifen Resistance and Tumour Aggressiveness of Human Breast Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2010, 103, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godinho, M.F.E.; Wulfkuhle, J.D.; Look, M.P.; Sieuwerts, A.M.; Sleijfer, S.; Foekens, J.A.; Petricoin, E.F., III; Dorssers, L.C.; van Agthoven, T. BCAR4 Induces Antioestrogen Resistance but Sensitizes Breast Cancer to Lapatinib. Br. J. Cancer 2012, 107, 947–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yan, G.Y. Novel Human LncRNA–Disease Association Inference Based on LncRNA Expression Profiles. Bioinformatics 2013, 29, 2617–2624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X. Predicting LncRNA–Disease Associations and Constructing LncRNA Functional Similarity Network Based on the Information of MiRNA. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; You, Z.H.; Yan, G.Y.; Gong, D.W. IRWRLDA: Improved Random Walk with Restart for LncRNA–Disease Association Prediction. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 57919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Fu, G.; Lu, C.; Ren, Y.; Wang, J. BRWLDA: Bi-Random Walks for Predicting LncRNA–Disease Associations. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 60429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, C.; Liao, B.; Li, X.; Cai, L.; Li, Z.; Li, K.; Yang, J. Global Network Random Walk for Predicting Potential Human LncRNA–Disease Associations. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 12442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Wang, X.; Li, J.; Hao, D.; Wang, Z.; Shi, H.; Sun, J. Prioritizing Candidate Disease-Related Long Non-Coding RNAs by Walking on the Heterogeneous LncRNA and Disease Network. Mol. BioSyst. 2015, 11, 760–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Wang, H.; Ma, C.; Huang, H.; Fang, Z.; Qu, J. LDAGM: Prediction of lncRNA–disease associations by graph convolutional auto-encoder and multilayer perceptron based on multi-view heterogeneous networks. BMC Bioinform. 2024, 25, 332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Qiao, J.; Feng, S. Prediction of lncRNA and disease associations based on residual graph convolutional networks with attention mechanism. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 5185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Park, C. MLMD: Metric Learning for Predicting MiRNA-Disease Associations. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 78847–78858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Kim, H.; Yoon, Y.; Park, S. A Method of Extracting Disease-Related MicroRNAs through the Propagation Algorithm Using the Environmental Factor Based Global MiRNA Network. Biomed. Mater. Eng. 2015, 26 (Suppl. 1), S1763–S1772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Park, C.; Park, C.; Park, S. IMIPMF: Inferring MiRNA-Disease Interactions Using Probabilistic Matrix Factorization. J. Biomed. Inform. 2020, 102, 103358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Park, S. NCMD: Node2vec-Based Neural Collaborative Filtering for Predicting MiRNA-Disease Association. IEEE/ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 2022, 20, 1257–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J.; Park, C.; Park, C.; Park, S. Improved Prediction of MiRNA-Disease Associations Based on Matrix Completion with Network Regularization. Cells 2020, 9, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Li, G. DynHeter-DTA: Dynamic Heterogeneous Graph Representation for Drug-Target Binding Affinity Prediction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, F.; Zhou, J.; Zhang, M.; Yu, D.J. MFP-MFL: Leveraging Graph Attention and Multi-Feature Integration for Superior Multifunctional Bioactive Peptide Prediction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J.; Park, C.; Park, S. PMAMCA: Prediction of MicroRNA-Disease Association Utilizing a Matrix Completion Approach. BMC Syst. Biol. 2019, 13, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J. MDMF: Predicting MiRNA–Disease Association Based on Matrix Factorization with Disease Similarity Constraint. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, C.; Yang, M.; Luo, F.; Wu, F.X.; Li, M.; Pan, Y.; Wang, J. Prediction of LncRNA–Disease Associations Based on Inductive Matrix Completion. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3357–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, G.; Wang, J.; Domeniconi, C.; Yu, G. Matrix Factorization-Based Data Fusion for the Prediction of LncRNA–Disease Associations. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 1529–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xuan, Z.; Li, J.; Yu, J.; Feng, X.; Zhao, B.; Wang, L. A Probabilistic Matrix Factorization Method for Identifying LncRNA–Disease Associations. Genes 2019, 10, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, W.; Wu, X.; Chen, Q.; Peng, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.P. GANLDA: Graph Attention Network for LncRNA–Disease Associations Prediction. Neurocomputing 2022, 469, 384–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, L.; Huang, L.; Su, Q.; Tian, G.; Chen, M.; Han, G. LDA-VGHB: Identifying Potential LncRNA–Disease Associations with Singular Value Decomposition, Variational Graph Auto-Encoder, and Heterogeneous Newton Boosting Machine. Brief. Bioinform. 2024, 25, bbad466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ha, J. LncRNA Expression Profile-Based Matrix Factorization for Identifying LncRNA–Disease Associations. IEEE Access 2024, 12, 70297–70304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cutsem, E.; Sagaert, X.; Topal, B.; Haustermans, K.; Prenen, H. Gastric Cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 2654–2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, N.; Hu, Y.; Juan, L. Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed lncRNAs in gastric cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Chen, T.; Li, G.; Yu, X.; Lu, Y.; Wang, H.; Teng, L. LncRNAs: Emerging Biomarkers in Gastric Cancer. Future Oncol. 2015, 11, 2427–2441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, T.T.; He, J.; Liang, Q.; Ren, L.L.; Yan, T.T.; Yu, T.C.; Tang, J.Y.; Bao, Y.J.; Hu, Y.; Lin, Y.; et al. LncRNA GClnc1 Promotes Gastric Carcinogenesis and May Act as a Modular Scaffold of WDR5 and KAT2A Complexes to Specify the Histone Modification Pattern. Cancer Discov. 2016, 6, 784–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Travis, W.D.; Travis, L.B.; Devesa, S.S. Lung Cancer. Cancer 1995, 75, 191–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Li, C.; Luo, Y.; Li, L.; Liu, J.; Gui, R. Silencing of Long Non-Coding RNA MIAT Sensitizes Lung Cancer Cells to Gefitinib by Epigenetically Regulating miR-34a. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, R.; Wang, R.; Chang, S.; Li, K.; Sun, R.; Wang, M.; Li, Z. Long Non-Coding RNA in Drug Resistance of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: A Mini Review. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Chen, Q.; Liu, X.; Sun, Q.; Zhao, X.; Deng, R.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Xu, M.; Yan, J.; et al. lncRNA H19/miR-675 Axis Represses Prostate Cancer Metastasis by Targeting TGFBI. FEBS J. 2014, 281, 3766–3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawla, P. Epidemiology of Prostate Cancer. World J. Oncol. 2019, 10, 63–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakravarty, D.; Sboner, A.; Nair, S.S.; Giannopoulou, E.; Li, R.; Hennig, S.; Mosquera, J.M.; Pauwels, J.; Park, K.; Kossai, M.; et al. The Oestrogen Receptor Alpha-Regulated lncRNA NEAT1 is a Critical Modulator of Prostate Cancer. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prensner, J.R.; Iyer, M.K.; Balbin, O.A.; Dhanasekaran, S.M.; Cao, Q.; Brenner, J.C.; Laxman, B.; Asangani, I.A.; Grasso, C.S.; Kominsky, H.D.; et al. Transcriptome Sequencing Across a Prostate Cancer Cohort Identifies PCAT-1, an Unannotated LincRNA Implicated in Disease Progression. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 742–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.T.; Fang, L.; Cheng, Y.X.; Sun, Q. LncRNA PVT1 Regulates Prostate Cancer Cell Growth by Inducing the Methylation of miR-146a. Cancer Med. 2016, 5, 3512–3519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, Z.; Yang, Z.; Huang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Cui, Q.; Dong, D. LncRNADisease 2.0: An Updated Database of Long Non-Coding RNA-Associated Diseases. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 1034–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Shang, S.; Guo, S.; Li, X.; Zhou, H.; Liu, H.; Sun, Y.; Wang, J.; Wang, P.; Zhi, H.; et al. Lnc2Cancer 3.0: An Updated Resource for Experimentally Supported LncRNA/CircRNA Cancer Associations and Web Tools Based on RNA-Seq and scRNA-Seq Data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, 1251–1258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Laarhoven, T.; Nabuurs, S.B.; Marchiori, E. Gaussian Interaction Profile Kernels for Predicting Drug-Target Interaction. Bioinformatics 2011, 27, 3036–3043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Huang, Y.A.; You, Z.H.; Yan, G.Y.; Wang, X.S. A Novel Approach Based on KATZ Measure to Predict Associations of Human Microbiota with Non-Infectious Diseases. Bioinformatics 2016, 7, 733–739. [Google Scholar]
- Ha, J. Graph Convolutional Network with Neural Collaborative Filtering for Predicting miRNA-Disease Association. Biomedicines 2025, 9, 1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, J. DeepWalk-Based Graph Embeddings for miRNA–Disease Association Prediction Using Deep Neural Network. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

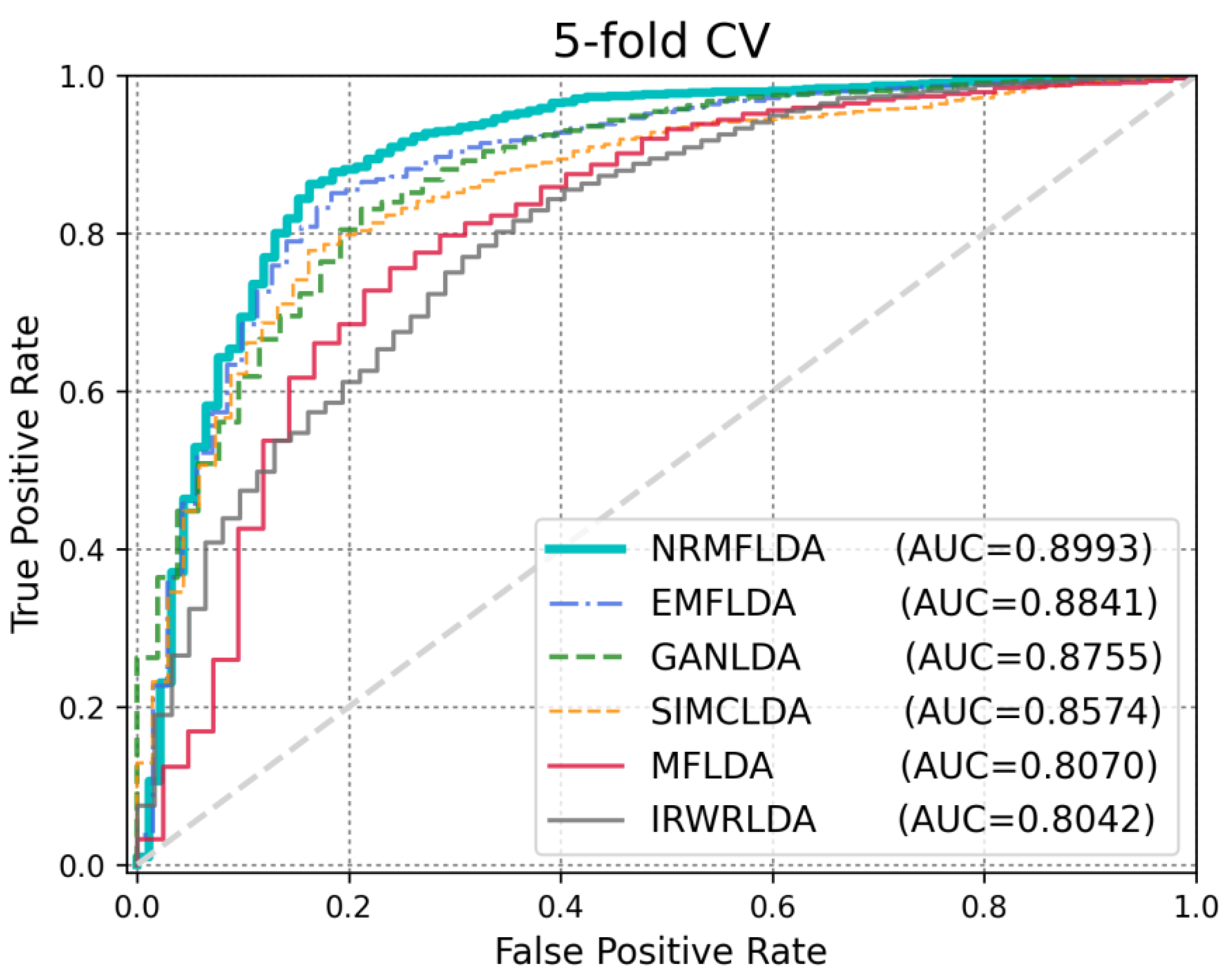
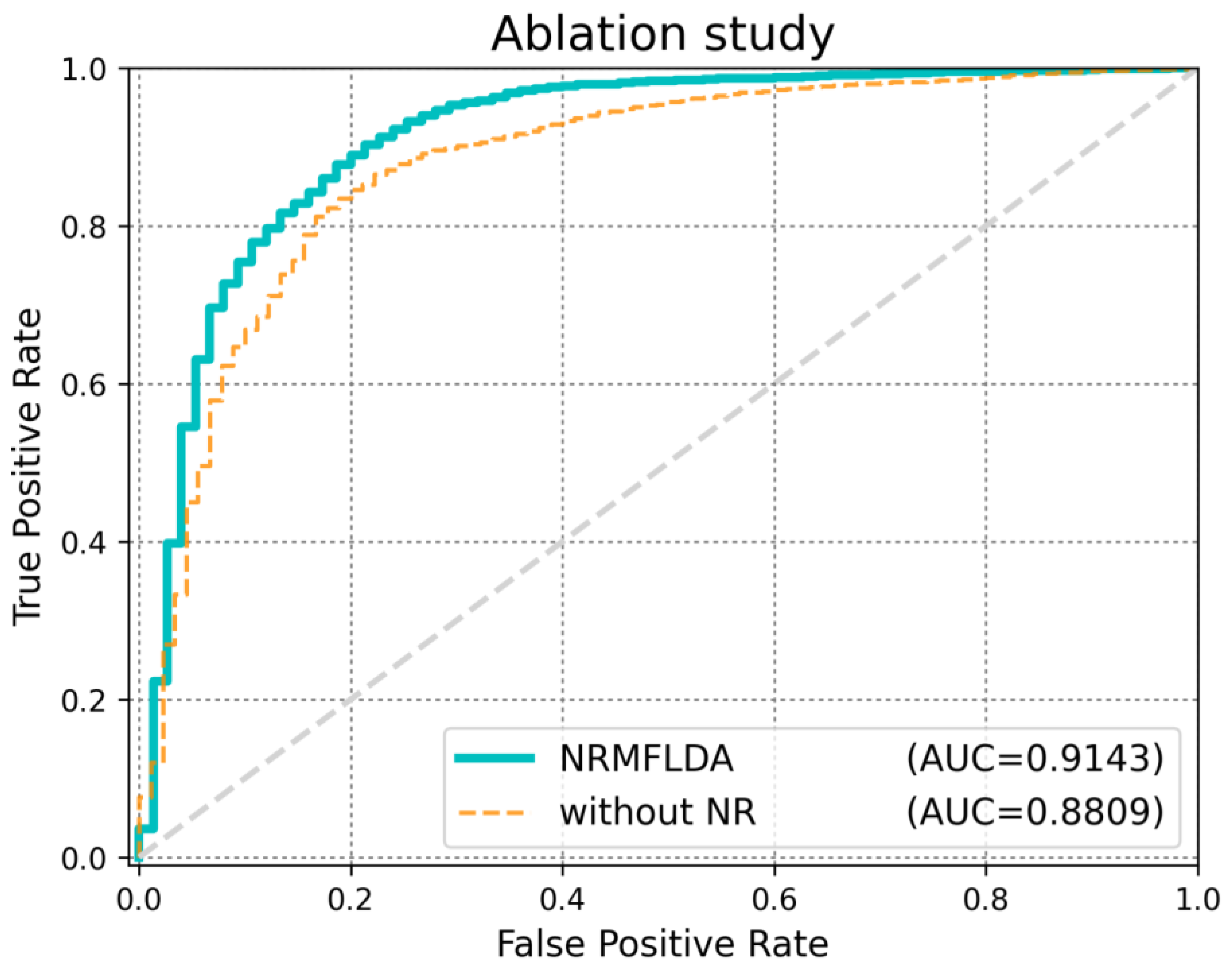
| Method | AUC (LOOCV) | AUC (5-Fold CV) | AUPRC | ACC | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRMFLDA | 0.9143 | 0.8993 | 0.3451 | 0.9013 | 0.7727 |
| EMFLDA | 0.9042 | 0.8841 | 0.2068 | 0.8793 | 0.8912 |
| GANLDA | 0.8813 | 0.8755 | 0.1572 | 0.8735 | 0.8671 |
| SIMCLDA | 0.8664 | 0.8574 | 0.0301 | 0.8481 | 0.8474 |
| MFLDA | 0.8101 | 0.8070 | 0.0138 | 0.8024 | 0.8016 |
| IRWRLDA | 0.7985 | 0.8042 | 0.0043 | 0.7618 | 0.7602 |
| Method | AUC (LOOCV) | AUC (5-Fold CV) | AUPRC | ACC | MCC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRMFLDA | 0.9143 | 0.8993 | 0.3451 | 0.9013 | 0.7727 |
| NRMFLDA without NR | 0.8809 | 0.8041 | 0.1472 | 0.8243 | 0.7361 |
| Rank | LncRNA | Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | RP11-167N4 | lnc2Cancer |
| 2 | MYLK-AS1 | lnc2Cancer |
| 3 | MAFG-AS1 | lnc2Cancer |
| 4 | LINC01071 | lnc2Cancer |
| 5 | AK001058 | lnc2Cancer |
| 6 | LINC00673 | lnc2Cancer |
| 7 | CCAT2 | lnc2Cancer |
| 8 | GIHCG | lnc2Cancer |
| 9 | LINP1 | lnc2Cancer |
| 10 | ZXF2 | lnc2Cancer |
| 11 | RRP1B | lncRNADisease |
| 12 | GCAWKR | lnc2Cancer |
| 13 | EPEL | lnc2Cancer |
| 14 | LINC02407 | lnc2Cancer |
| 15 | LINC00086 | lnc2Cancer |
| Rank | LncRNA | Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | TCF7 | lncRNADisease |
| 2 | SPRY4-IT1 | lncRNADisease |
| 3 | LINC01186 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 4 | LUCAT1 | lncRNADisease |
| 5 | PCAT6 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 6 | LCAL1 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 7 | LSINCT3 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 8 | BANCR | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 9 | H19 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 10 | GAS5 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 11 | CASC8 | lncRNADisease |
| 12 | RIOX2 | lncRNADisease |
| 13 | PVT1-5 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 14 | MEG3 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 15 | CCAT2 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| Rank | LncRNA | Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | SPRY4-IT1 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 2 | PCGEM1 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 3 | PCA3 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 4 | SNHG1 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 5 | PCAT2 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 6 | HOTAIR | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 7 | ATB | lncRNADisease |
| 8 | UCA1 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 9 | SNHG5 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 10 | MEG3 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 11 | PRNCR1 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 12 | CBR3-AS1 | lncRNADisease |
| 13 | FALEC | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 14 | DRAIC | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
| 15 | PCAT1 | lnc2Cancer, lncRNADisease |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ha, J.; Kim, K. Neighborhood-Regularized Matrix Factorization for lncRNA–Disease Association Identification. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094283
Ha J, Kim K. Neighborhood-Regularized Matrix Factorization for lncRNA–Disease Association Identification. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094283
Chicago/Turabian StyleHa, Jihwan, and Kwangsu Kim. 2025. "Neighborhood-Regularized Matrix Factorization for lncRNA–Disease Association Identification" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094283
APA StyleHa, J., & Kim, K. (2025). Neighborhood-Regularized Matrix Factorization for lncRNA–Disease Association Identification. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094283






