An Autocrine Regulator Loop Involving Tumor Necrosis Factor and Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligand-2 Is Activated by Transforming Growth Factor-β in Rat Basophilic Leukemia-2H3 Mast Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
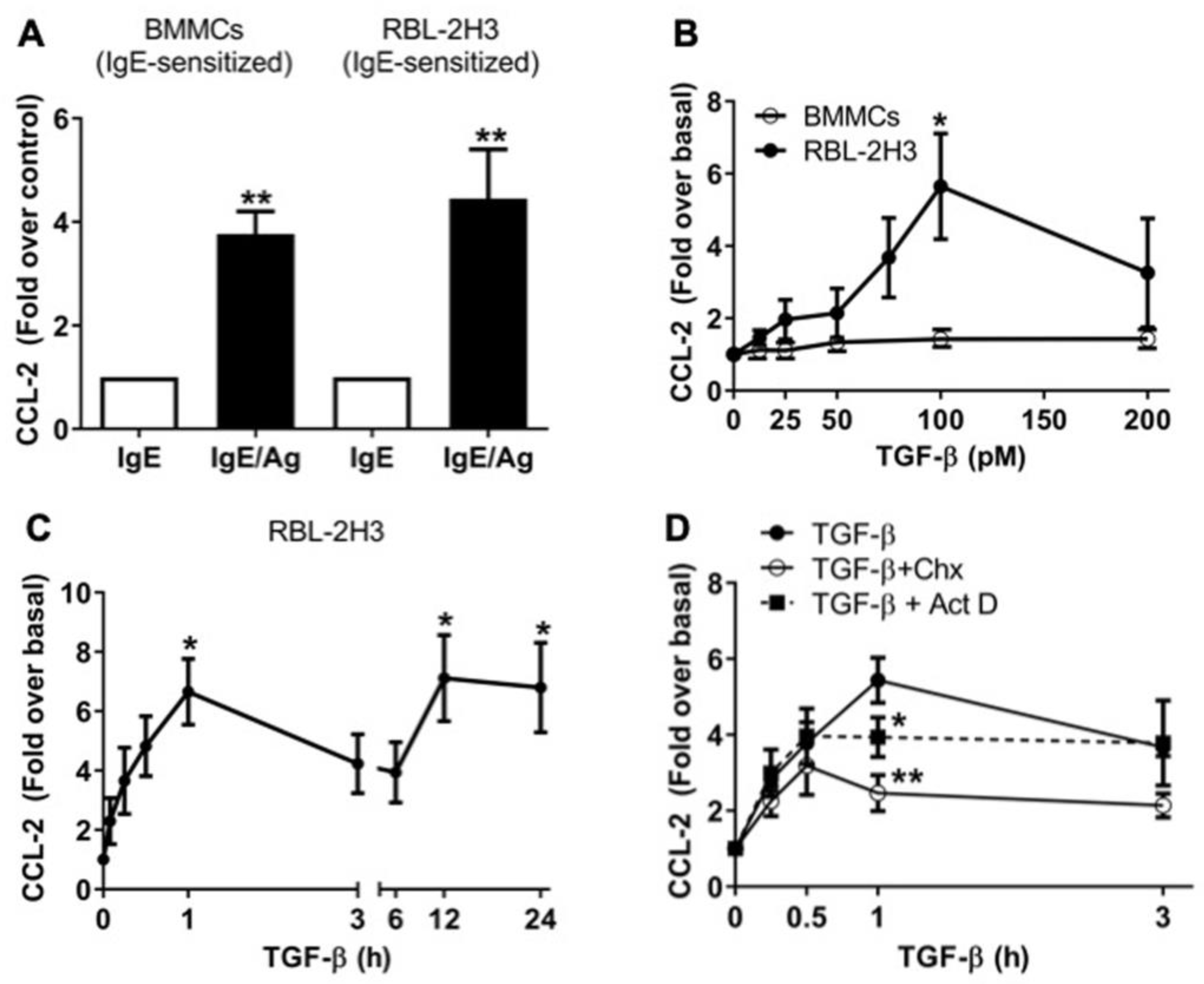
2.1. TGF-β Stimulates the Secretion of Pre-Formed and de Novo-Synthesized CCL-2 Chemokine in RBL-2H3 Mast Cells
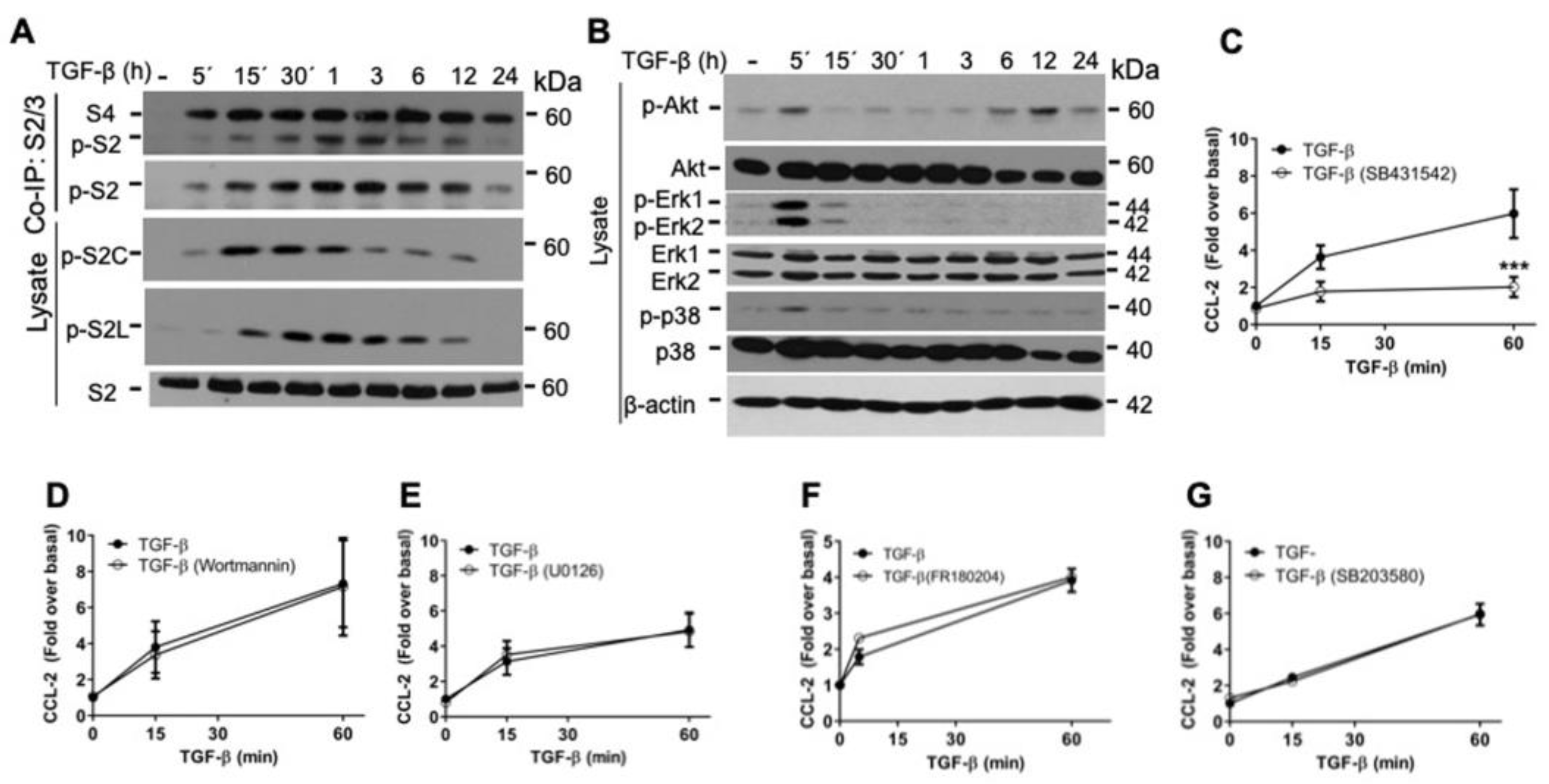
2.2. TGF-β/ALK5 Activates Canonical and Non-Canonical Pathways Implicated in CCL-2 Secretion in RBL-2H3 Cells
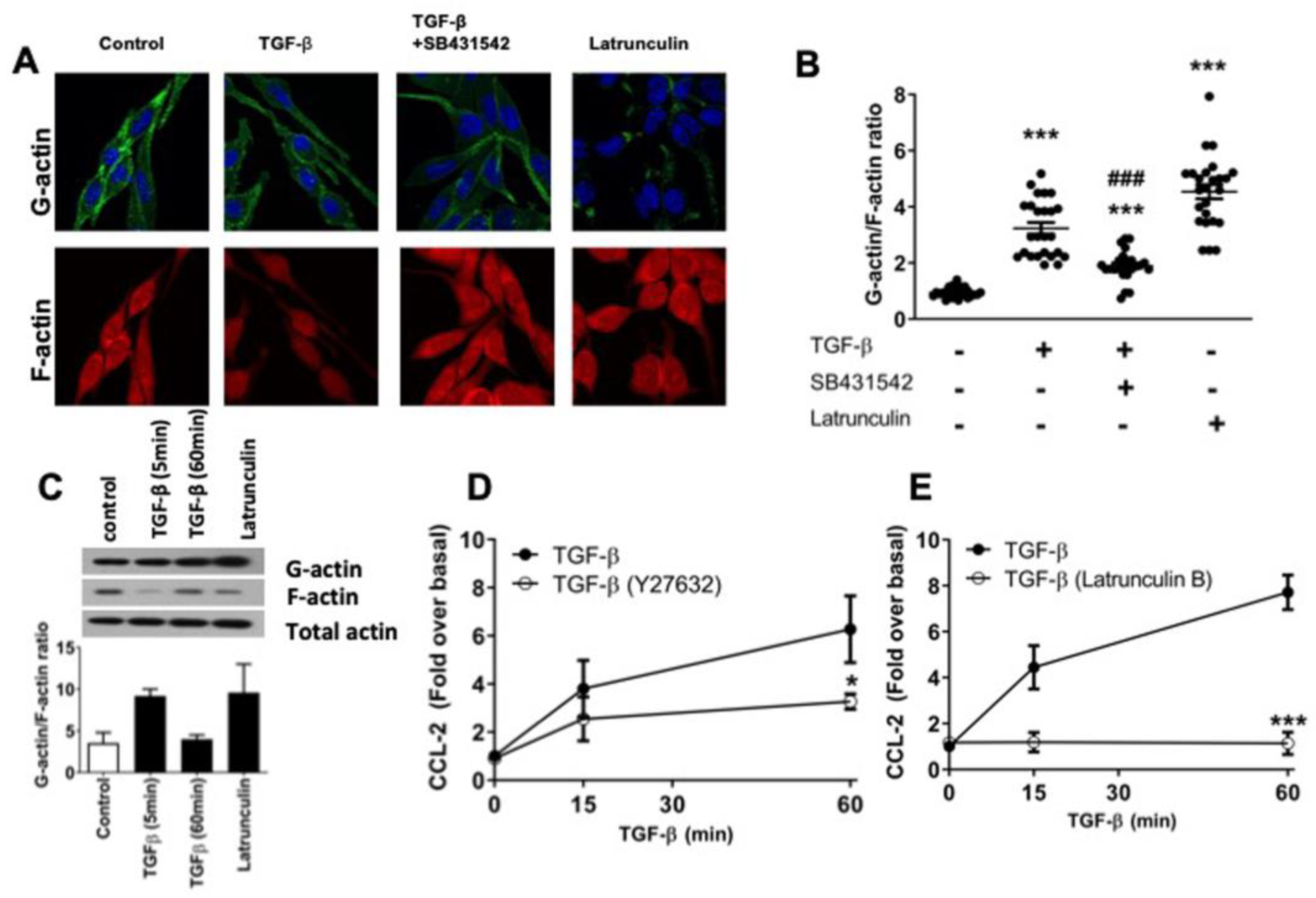
2.3. TGF-β Induces Dynamic Re-Arrangements of the Actin Cytoskeleton Associated with CCL-2 Secretion in RBL-2H3 Cells
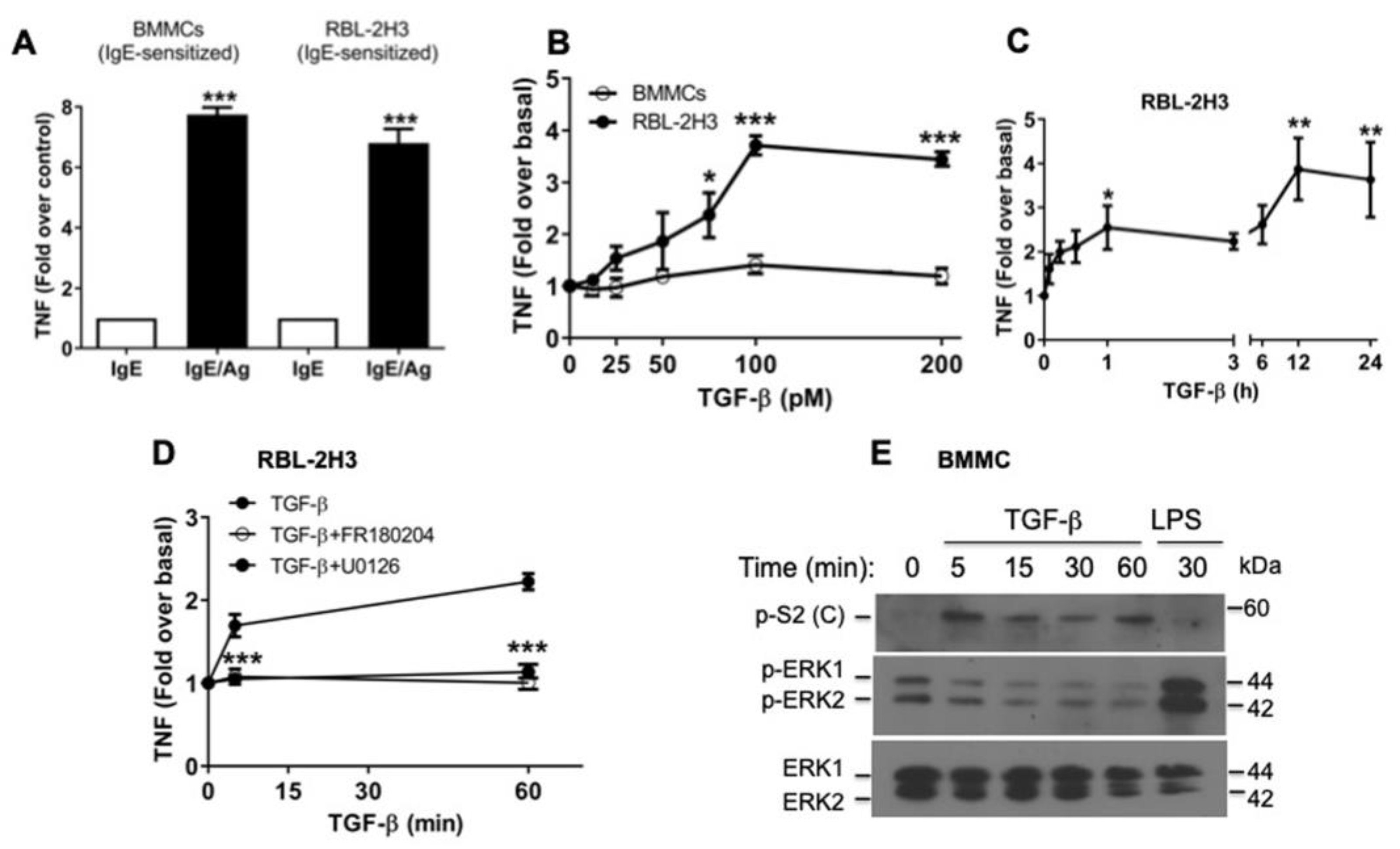
2.4. TGF-β Stimulates the Secretion of Pre-Formed TNF via ERK1/2 Activation in RBL-2H3 Mast Cells
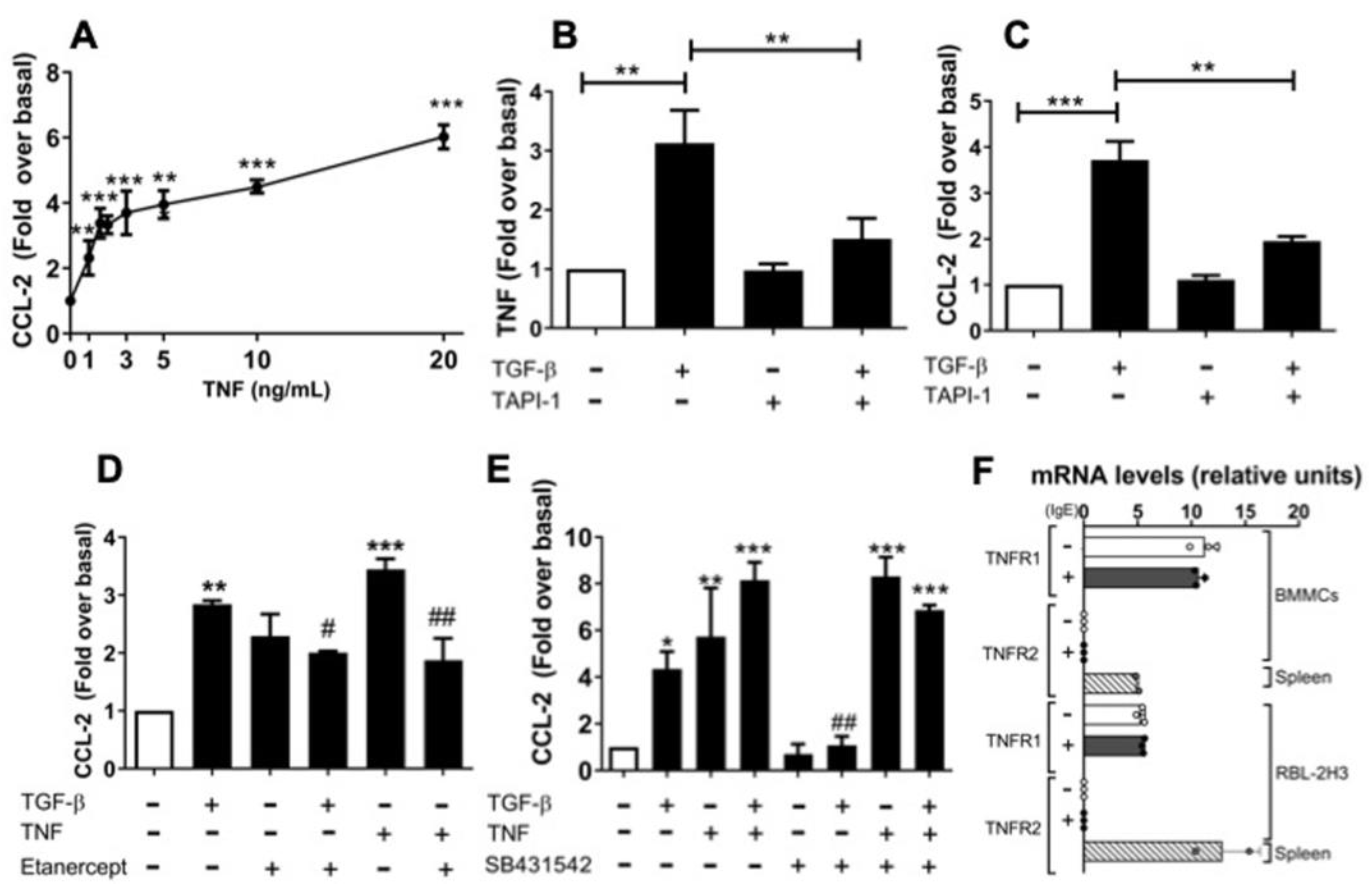
2.5. An Autocrine Regulator Loop Involving TNF Is Activated by TGF-β to Promote Late CCL-2 Secretion in RBL-2H3 Cells
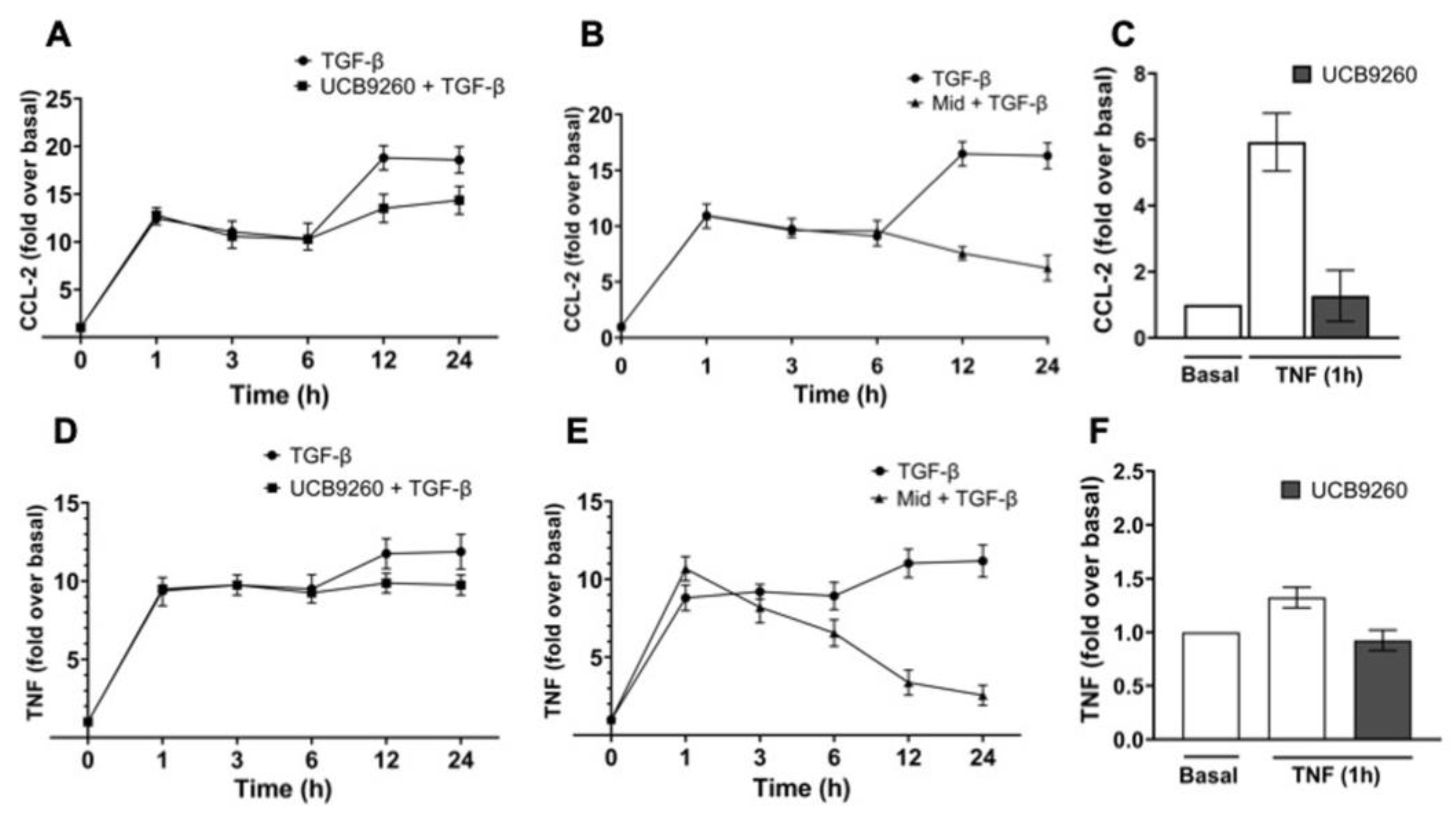
2.6. The Diversity of MCs’ Contexts Contributes to the Differential Secretion of Mediators in Response to TGF-β
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Reagents and Antibodies
4.2. Cell Culture
4.3. ELISA
4.4. Immunofluorescence
4.5. F-Actin/G-Actin Separation
4.6. Western Blot and Immunoprecipitation
4.7. Total RNA and RT-qPCR
4.8. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Massagué, J. TGF-beta signalling in context. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2014, 13, 616–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- David, C.J.; Massagué, J. Contextual determinants of TGFβ action in development, immunity and cancer. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 419–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tecalco-Cruz, A.C.; Ríos-López, D.G.; Vázquez-Victorio, G.; Rosales-Alvarez, R.E.; Macías-Silva, M. Transcriptional Cofactors Ski and SnoN are Major Regulators of TGF-beta/Smad Signaling Pathway in Health and Disease. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2018, 3, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.O.; Wan, Y.Y.; Sanjabi, S.; Robertson, A.-K.L.; Flavell, R.A. Transforming Growth Factor-Β Regulation of Immune Responses. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 24, 99–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batlle, E.; Massagué, J. Transforming Growth Factor-β Signaling in Immunity and Cancer. Immunity 2019, 50, 924–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.; Ten Dijke, P. Immunoregulation by members of the TGFβ superfamily. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016, 16, 723–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.O.; Flavell, R.A. TGF-β, T-cell tolerance and immunotherapy of autoimmune diseases and cancer. Expert. Rev. Clin. Immunol. 2006, 2, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Z.; Liu, S.; Xu, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, D.; Liu, J.; Xia, M.; Yi, L.; Shen, Q.; Xu, S.; et al. Adult Connective Tissue-Resident Mast Cells Originate from Late Erythro-Myeloid Progenitors. Immunity 2018, 49, 640–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tauber, M.; Basso, L.; Martin, J.; Bostan, L.; Pinto, M.M.; Thierry, G.R.; Houmadi, R.; Serhan, N.; Loste, A.; Blériot, C.; et al. Landscape of mast cell populations across organs in mice and humans. J. Exp. Med. 2023, 220, e20230570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurer, S.K.; Bronneberg, G.; Penners, C.; Kauffmann, M.; Braunschweig, T.; Liedtke, C.; Huber, M.; Weiskirchen, R. TGFB1 induces mucosal mast cell genes and is negatively regulated by the IL-3/ERK1/2 axis. Cell Commun. Signal 2025, 23, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blank, U.; Madera-Salcedo, I.K.; Danelli, L.; Claver, J.; Tiwari, N.; Sanchez-Miranda, E.; Vázquez-Victorio, G.; Ramírez-Valadez, K.A.; Macías-Silva, M.; González-Espinosa, C. Vesicular trafficking and signaling for cytokine and chemokine secretion in mast cells. Front. Immunol. 2014, 5, 453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solimando, A.G.; Desantis, V.; Ribatti, D. Mast Cells and Interleukins. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 14004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segura-Villalobos, D.; Ramírez-Moreno, I.G.; Martínez-Aguilar, M.; Ibarra-Sánchez, A.; Muñoz-Bello, J.O.; Anaya-Rubio, I.; Padilla, A.; Macías-Silva, M.; Lizano, M.; González-Espinosa, C. Mast Cell–Tumor Interactions: Molecular Mechanisms of Recruitment, Intratumoral Communication and Potential Therapeutic Targets for Tumor Growth. Cells 2022, 11, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frossi, B.; Mion, F.; Sibilano, R.; Danelli, L.; Pucillo, C.E.M. Is it time for a new classification of mast cells? What do we know about mast cell heterogeneity? Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 35–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aitella, E.; Romano, C.; Ginaldi, L.; Cozzolino, D. Mast Cells at the Crossroads of Hypersensitivity Reactions and Neurogenic Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sc. 2025, 26, 927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, T.T.; Frischmeyer-Guerrerio, P.A. The Role of TGFβ and Other Cytokines in Regulating Mast Cell Functions in Allergic Inflammation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukai, K.; Tsai, M.; Saito, H.; Galli, S.J. Mast cells as sources of cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 121–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kelly, A.; Houston, S.A.; Sherwood, E.; Casulli, J.; Travis, M.A. Regulation of Innate and Adaptive Immunity by TGFβ. Adv. Immunol. 2017, 134, 137–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.B.; Yang, S.H.; Shen, J.; Deng, K.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Cui, W.; Ye, H. Interaction between regulatory T cells and mast cells via IL-9 and TGF-β production. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, L.A.; Argentieri, R.L.; Farrell, F.X.; Bracht, M.; Sheng, H.; Whitaker, B.; Beck, H.; Tsui, P.; Cochlin, K.; Evanoff, H.L.; et al. Hyper-responsiveness of IPF/UIP fibroblasts: Interplay between TGFβ1, IL-13 and CCL2. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2008, 40, 2174–2182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derakhshan, T.; Hollers, E.; Perniss, A.; Ryan, T.; McGill, A.; Hacker, J.; Bergmark, R.W.; Bhattacharyya, N.; Lee, S.E.; Maxfield, A.Z.; et al. Human intraepithelial mast cell differentiation and effector function are directed by TGF-β signaling. J. Clin. Investig. 2025, 135, e174981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, S.H.; Lukacs, N.W. Stem cell factor and IgE- stimulated murine mast cells produce chemokines (CCL2, CCL17, CCL22) and express chemokine receptors. Inflamm. Res. 2001, 50, 168–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collington, S.J.; Hallgren, J.; Pease, J.E.; Jones, T.G.; Rollins, B.J.; West-wick, J.; Austen, K.F.; Williams, T.J.; Gurish, M.F.; Weller, C.L. The role of the CCL2/CCR2 axis in mouse mast cell migration in vitro and in vivo. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 6114–6123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Lin, J.; Xu, A.; Lou, J.; Qian, C.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Yu, W.; Tao, H. CCL2: An Important Mediator Between Tumor Cells and Host Cells in Tumor Microenvironment. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 722916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Moreno, I.G.; Ibarra-Sánchez, A.; Castillo-Arellano, J.I.; Blank, U.; González-Espinosa, C. Mast Cells Localize in Hypoxic Zones of Tumors and Secrete CCL-2 under Hypoxia through Activation of L-Type Calcium Channels. J. Immunol. 2020, 204, 1056–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harkness, K.A.; Sussman, J.D.; Davies-Jones, G.A.B.; Greenwood, J.; Woodroofe, M.N. Cytokine regulation of MCP-1 expression in brain and retinal microvascular endothelial cells. J. Neuroimmunol. 2003, 142, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chui, R.; Dorovini-Zis, K. Regulation of CCL2 and CCL3 expression in human brain endothelial cells by cytokines and lipopolysaccharide. J. Neuroinflamm. 2010, 7, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, E.Y.; Enciso, J.A.; Refus, A.D. TGF-β1 Inhibits the Release of Histamine and Tumor Necrosis Factor-α from Mast Cells Through an Autocrine Pathway. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 1997, 16, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kashyap, M.; Bailey, D.P.; Gomez, G.; Rivera, J.; Huff, T.F.; Ryan, J.J. TGFB1 inhibits late-stage mast cell maturation. Exp. Hematol. 2005, 33, 1281–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, A.; Chen, Y.; Watanabe, A.; Kitano, S.; Hanasawa, S. TGF-beta induces expression of monocyte chemoattractant JE/monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 via transcriptional factor AP-1 induced by protein kinase in osteoblastic cells. J. Immunol. 1995, 155, 419–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Wang, Q.; Fei, T.; Han, J.J.; Chen, Y. MCP-1 mediates TGF-beta–induced angiogenesis by stimulating vascular smooth muscle cell migration. Blood 2007, 109, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Tsai, S.; Kato, K.; Yamanouchi, D.; Wang, C.; Rafii, S.; Liu, B.; Kent, K.C. Transforming growth factor-β promotes recruitment of bone marrow cells and bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells through stimulation of MCP-1 production in vascular smooth muscle cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 17564–17574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, J.; Diaz Encarnacion, M.M.; Warner, G.M.; Gray, C.E.; Nath, K.A.; Grande, J.P. TGF-beta1 stimulates monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 expression in mesangial cells through a phosphodiesterase isoenzyme 4-dependent process. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 2005, 289, C959–C970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorbacheva, A.M.; Uvarova, A.N.; Ustiugova, A.S.; Bhattacharyya, A.; Korneev, K.V.; Kuprash, D.V.; Mitkin, N.A. EGR1 and RXRA transcription factors link TGF-β pathway and CCL2 expression in triple negative breast cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benitez-Garrido, J.P.; Ibarra-Sanchez, A.; Macías-Silva, M.; Villalobos-Molina, R.; Padilla-Trejo, J.A.; Gonzalez-Espinoza, C. TGFbeta Presence During IgE-dependent Sensitization Primes Mast Cells for Higher VEGF Production After FcRI Activation. Open Allergy J. 2009, 2, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.; Gomez, G.; Yu, S.-H.; Ryan, J.J.; Schwartz, L.B. TGF-beta 1 Attenuates Mediator Release and De Novo Kit Expression by Human Skin Mast Cells through a Smad-Dependent Pathway. J. Immunol. 2008, 181, 7263–7272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndaw, V.S.; Abebayehu, D.; Spence, A.J.; Paez, P.A.; Kolawole, E.M.; Taruselli, M.T.; Caslin, H.L.; Chumanevich, A.P.; Paranjape, A.; Baker, B.; et al. TGF-β1 Suppresses IL-33–Induced Mast Cell Function. J. Immunol. 2017, 181, 866–873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigeri, L.; Apgar, J.R. The Role of Actin Microfilaments in the Down-Regulation of the Degranulation Response in RBL-2H3 Mast Cells. J. Immunol. 1999, 162, 2243–2250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Valadez, K.A.; Vázquez-Victorio, G.; Macías-Silva, M.; González-Espinosa, C. Fyn kinase mediates cortical actin ring depolymerization required for mast cell migration in response to TGF-β in mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2017, 47, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edlund, S.; Landström, M.; Heldin, C.H.; Aspenstrom, P. Transforming growth factor-beta-induced mobilization of actin cytoskeleton requires signaling by small GTPases Cdc42 and RhoA. Mol. Biol. Cell 2002, 13, 902–914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soond, S.M.; Everson, B.; Riches, D.W.; Murphy, G. ERK-mediated phosphorylation of Thr735 in TNF-α-converting enzyme and its potential role in TACE protein trafficking. J. Cell Sci. 2005, 118, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rousseau, S.; Papoutsopoulou, M.; Symons, A.; Cook, D.; Lucocq, J.M.; Prescott, A.R.; Cohen, P. TPL2-mediated activation of ERK1 and ERK2 regulates the processing of pre-TNF-α in LPS-stimulated macrophages. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 149–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, K.; Kikuchi, S.; Shubayev, V.I.; Myers, R.R. Distribution and tumor necrosis factor-alpha isoform binding specificity of locally administered etanercept into injured and uninjured rat sciatic nerve. Neuroscience 2009, 160, 492–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grattendick, K.J.; Nakashima, J.M.; Feng, L.; Giri, S.N.; Margolin, S.B. Effects of three anti-TNF-α drugs: Etanercept, infliximab and pirfenidone on release of TNF-α in medium and TNF-α associated with the cell in vitro. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2008, 8, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falcone, F.H.; Wan, D.; Barwary, N.; Sagi-Eisenberg, R. RBL cells as models for in vitro studies of mast cells and basophils. Immunol. Rev. 2018, 282, 47–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuburich, N.A.; Sabapathy, T.; Demestichas, B.R.; Maddela, J.J.; den Hollandera, P.; Mani, S.A. Proactive and reactive roles of TGF-β in cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023, 95, 120–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akin, C.; Siebenhaar, F.; Wechsler, J.B.; Youngblood, B.A.; Maurer, M. Detecting Changes in Mast Cell Numbers Versus Activation in Human Disease: A Roadblock for Current Biomarkers? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2024, 12, 1727–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olsson, N.; Piek, E.; ten Dijke, P.; Nilsson, G. Human mast cell migration in response to members of the transforming growth factor-beta family. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2000, 67, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez, G.; Ramirez, C.D.; Rivera, J.; Patel, M.; Norozian, F.; Wright, H.; Kashyap, M.V.; Barnstein, B.O.; Fischer-Stenger, K.; Schwartz, L.B.; et al. TGF-β1 Inhibits Mast Cell FcεRI Expression. J. Immunol. 2005, 174, 5987–5993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernando, J.F.; Faber, T.W.; Pullen, N.; Falanga, Y.T.; Kolawole, E.M.; Oskeritzian, C.A.; Barnstein, B.O.; Bandara, G.; Li, G.; Schwartz, L.B.; et al. Genotype-Dependent Effects of TGF-β1 on Mast Cell Function: Targeting the Stat5 Pathway. J. Immunol. 2013, 4505–4513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimura, T. The chemokine MCP-1 (CCL2) in the host interaction with cancer: A foe or ally? Cell Mol. Immunol. 2018, 15, 335–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinberg, M.W.; Shimizu, K.; Lebedeva, M.; Haspel, R.; Takayama, K.; Chen, Z.; Frederick, J.P.; Wang, X.F.; Simon, D.I.; Libby, P.; et al. Essential Role for Smad3 in Regulating MCP-1 Expression and Vascular Inflammation. Circ. Res. 2004, 94, 601–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langert, K.A.; Von Zee, C.L.; Stubbs, E.B. Cdc42 GTPases facilitate TNF-α-mediated secretion of CCL2 from peripheral nerve microvascular endoneurial endothelial cells. J. Peripher. Nerv. Syst. 2013, 18, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, L.; Lu, J.; Xiao, W. Blockage of TNF-α by infliximab reduces CCL2 and CCR2 levels in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J. Investig. Med. 2011, 59, 961–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Tamayo, J.; Ibarra-Sánchez, A.; Padilla-Trejo, A.; Gonzalez-Espinosa, C. IgE-dependent sensitization increases responsiveness to LPS but does not modify development of endotoxin tolerance in mast cells. Inflamm. Res. 2011, 60, 19–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandig, H.; Bulfone-Paus, S. TLR signaling in mast cells: Common and unique features. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 27433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madera-Salcedo, I.K.; Cruz, S.L.; Gonzalez-Espinosa, C. Morphine prevents lipopolysaccharide-induced TNF secretion in mast cells blocking IκB kinase activation and SNAP-23 phosphorylation: Correlation with the formation of a β-arrestin/TRAF6 complex. J. Immunol. 2013, 191, 3400–3409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guzman-Mejia, F.; López-Rubalcava, C.; González-Espinoza, C. Stimulation of nAchRα7 Receptor Inhibits TNF Synthesis and Secretion in Response to LPS Treatment of Mast Cells by Targeting ERK1/2 and TACE Activation. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 39–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamby, M.E.; Gragnolati, A.R.; Hewett, S.J.; Hewett, J.A. TGFβ1 and TNFα potentiate nitric oxide production in astrocyte cultures by recruiting distinct subpopulations of cells to express NOS-2. Neurochem. Int. 2008, 52, 962–971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGee, D.W.; Bamberg, T.; Vitkus, S.J.; McGhee, J.R. A synergistic relationship between TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta, and TGF-beta 1 on IL-6 secretion by the IEC-6 intestinal epithelial cell line. Immunology 1995, 86, 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Franke, K.; Zuberbier, T.; Babina, M. Cytokine stimulation by MRGPRX2 occurs with lower potency than by FceRI aggregation but with similar dependence on the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 module in human skin mast cells. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 142, 414–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katanov, C.; Lerrer, S.; Liubomirski, Y.; Leider-Trejo, L.; Meshel, T.; Bar, J.; Feniger-Barish, R.; Kamer, I.; Soria-Artzi, G.; Kahani, H.; et al. Regulation of the inflammatory profile of stromal cells in human breast cancer: Prominent roles for TNF-a and the NFkB pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2015, 6, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yip, A.J.W.; Lee, Y.Z.; Kow, A.S.F.; Wong, C.S.A.; Lee, M.T.; Tham, C.L.; Tan, J.W. Current utilization trend of immortalized mast cell lines in allergy research: A systematic review. Immunol. Res. 2025, 73, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayo, T.E.; Adhikari, P.; Xu, H. TNFR1 links TNF exocytosis to TNF production in allergen-activated RBL-2H3 cells. Cell Signal 2023, 105, 110607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zunke, F.; Rose-John, S. The shedding protease ADAM17: Physiology and pathophysiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 2059–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Queiroz, T.M.; Lakkappa, N.; Lazartigues, E. ADAM17-Mediated Shedding of Inflammatory Cytokines in Hypertension. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahima, H.T.; Dwyer, D.F. Update on mast cell biology. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2025, 155, 1115–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kannen, V.; Grant, D.M.; Matthews, J. The mast cell-T lymphocyte axis impacts cancer: Friend or foe? Cancer Lett. 2024, 588, 216805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Savage, A.; Risquez, C.; Gomi, K.; Schreiner, R.; Borczuk, A.C.; Worgall, S.; Silver, R.B. The mast cell exosome-fibroblast connection: A novel pro-fibrotic pathway. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1139397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meurer, S.K.; Neß, M.; Weiskirchen, S.; Kim, P.; Tag, C.G.; Kauffmann, M.; Huber, M.; Weiskirchen, R. Isolation of mature (Peritoneum-Derived) mast cells and immature (Bone Marrow- Derived) mast cell precursors from mice. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0158104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, Y.; Chen, J.; Lim, Y.B.; Finch-Edmondson, M.L.; Seshachalam, V.P.; Qin, L.; Jiang, T.; Low, B.C.; Singh, H.; Lim, C.T.; et al. YAP Regulates Actin Dynamics through ARHGAP29 and Promotes Metastasis. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 1495–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wakasuki, T.; Schwab, B.; Thompson, N.C.; Elson, E.L. Effects of cytochalasin D and latrunculin B on mechanical properties of cells. J. Cell Sci. 2001, 114, 1025–1036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Avila-Rodríguez, D.; Ibarra-Sánchez, A.; Sosa-Garrocho, M.; Vázquez-Victorio, G.; Caligaris, C.; Anaya-Rubio, I.; Segura-Villalobos, D.; Blank, U.; González-Espinosa, C.; Macias-Silva, M. An Autocrine Regulator Loop Involving Tumor Necrosis Factor and Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligand-2 Is Activated by Transforming Growth Factor-β in Rat Basophilic Leukemia-2H3 Mast Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094263
Avila-Rodríguez D, Ibarra-Sánchez A, Sosa-Garrocho M, Vázquez-Victorio G, Caligaris C, Anaya-Rubio I, Segura-Villalobos D, Blank U, González-Espinosa C, Macias-Silva M. An Autocrine Regulator Loop Involving Tumor Necrosis Factor and Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligand-2 Is Activated by Transforming Growth Factor-β in Rat Basophilic Leukemia-2H3 Mast Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094263
Chicago/Turabian StyleAvila-Rodríguez, Dulce, Alfredo Ibarra-Sánchez, Marcela Sosa-Garrocho, Genaro Vázquez-Victorio, Cassandre Caligaris, Isabel Anaya-Rubio, Deisy Segura-Villalobos, Ulrich Blank, Claudia González-Espinosa, and Marina Macias-Silva. 2025. "An Autocrine Regulator Loop Involving Tumor Necrosis Factor and Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligand-2 Is Activated by Transforming Growth Factor-β in Rat Basophilic Leukemia-2H3 Mast Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094263
APA StyleAvila-Rodríguez, D., Ibarra-Sánchez, A., Sosa-Garrocho, M., Vázquez-Victorio, G., Caligaris, C., Anaya-Rubio, I., Segura-Villalobos, D., Blank, U., González-Espinosa, C., & Macias-Silva, M. (2025). An Autocrine Regulator Loop Involving Tumor Necrosis Factor and Chemokine (C-C motif) Ligand-2 Is Activated by Transforming Growth Factor-β in Rat Basophilic Leukemia-2H3 Mast Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4263. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094263








