Exosomal microRNA from Plasma in Patients with Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma of Korea
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Diagnosis of PEX Glaucoma
2.3. Patient Selection and Acquisition of Plasma Samples
2.4. Isolation of Exosomes from Plasma Samples
2.5. Western Blot
2.6. Library Preparation and RNA Sequencing
2.7. Data Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographics and Baseline Characteristics of Subjects
3.2. Isolation of Exosomes from Plasma Samples of PEX Patients and Control Subjects
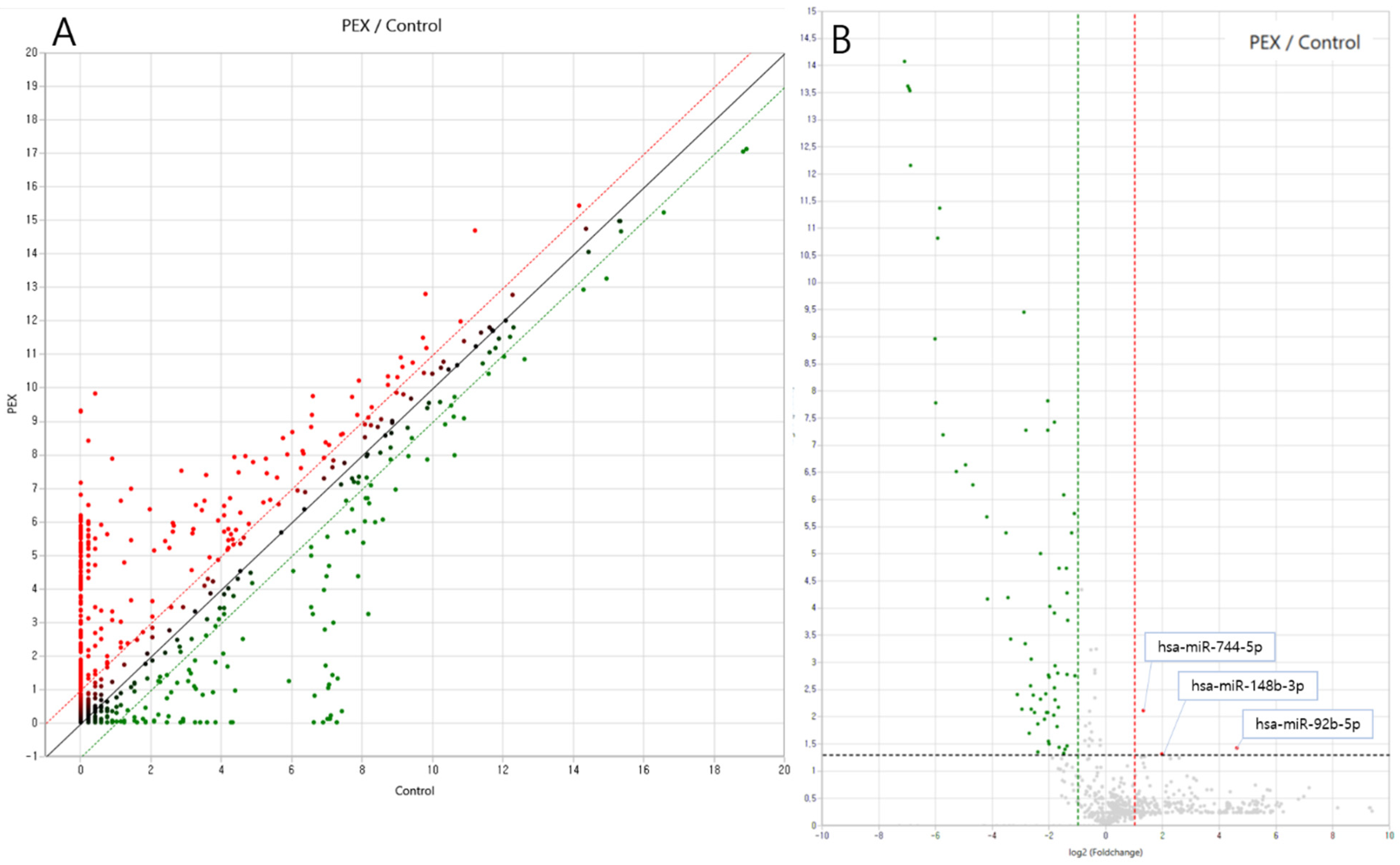
3.3. Differential Exosomal miRNA Expression in Plasma Samples from Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma Patients
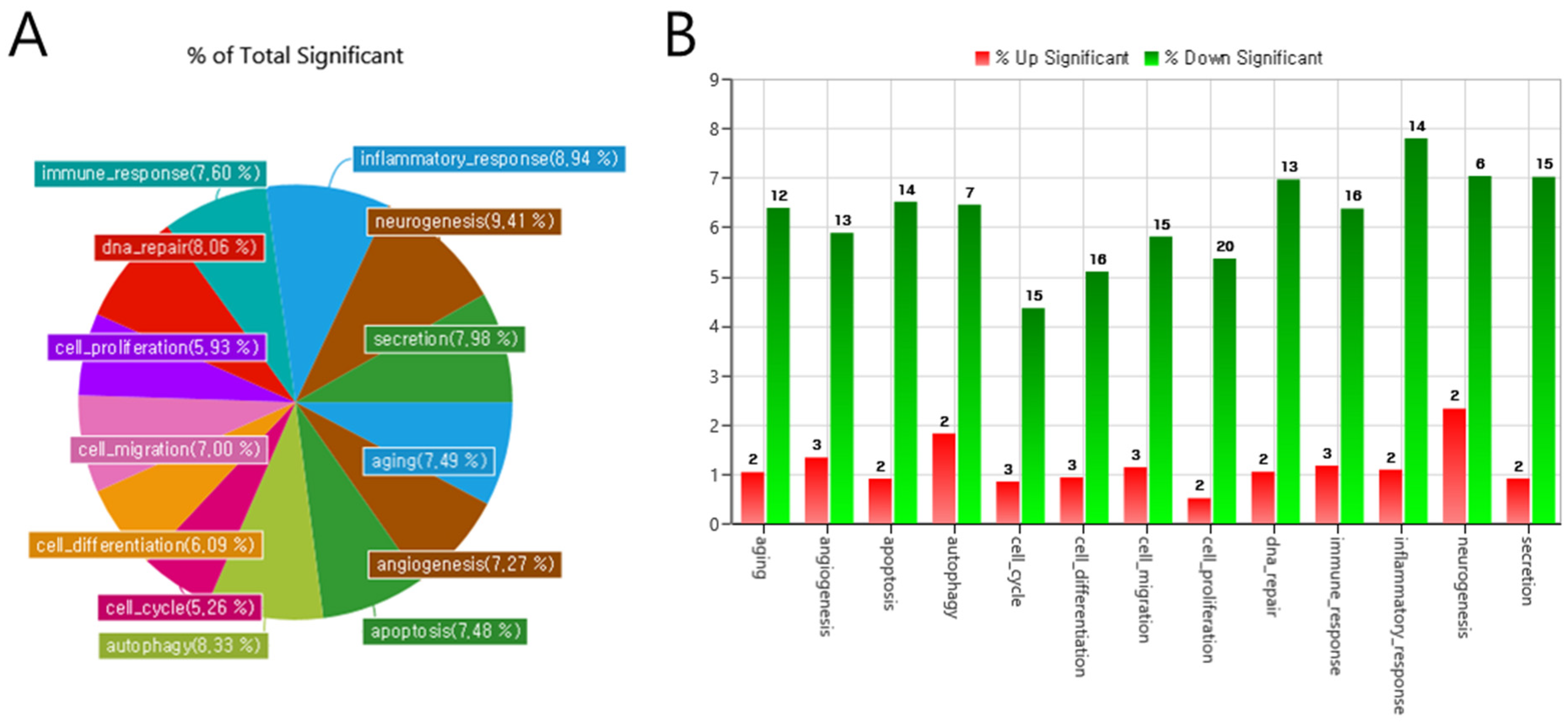
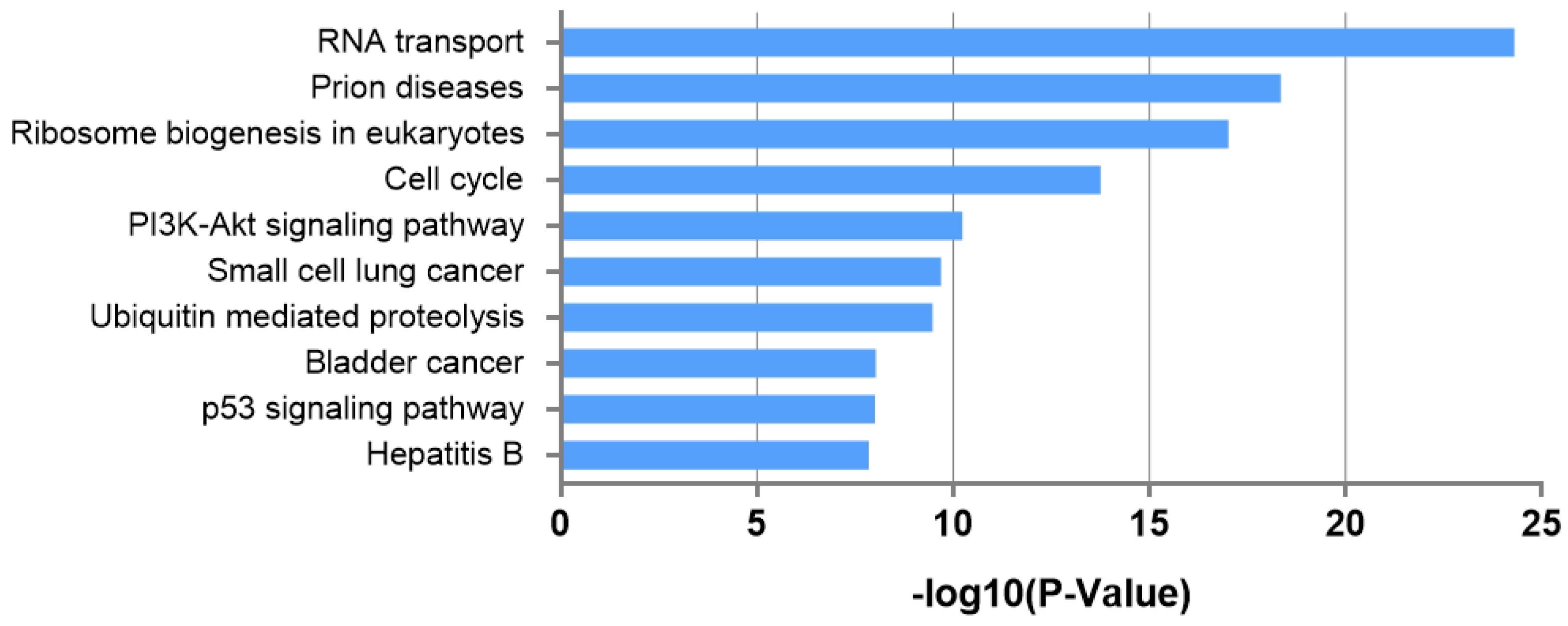
3.4. Biological Interpretation of Differentially Expressed miRNAs
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, N.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Jiang, B. Prevalence of primary open angle glaucoma in the last 20 years: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Sci. Rep. 2011, 11, 13762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tham, Y.C.; Li, X.; Wong, T.Y.; Quigley, H.A.; Aung, T.; Cheng, C.Y. Global prevalence of glaucoma and projections of glaucoma burden through 2040: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ophthalmology 2024, 121, 2081–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinreb, R.N.; Khaw, P.T. Primary open-angle glaucoma. Lancet 2004, 363, 1711–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritch, R. Exfoliation syndrome-the most common identifiable cause of open-angle glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 1994, 3, 176–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Founti, P.; Haidich, A.B.; Chatzikyriakidou, A.; Salonikiou, A.; Anastasopoulos, E.; Pappas, T.; Lambropoulos, A.; Viswanathan, A.C.; Topouzis, F. Ethnicity-Based Differences in the Association of LOXL1 Polymorphisms with Pseudoexfoliation/Pseudoexfoliative Glaucoma: A Meta-Analysis. Ann. Hum. Genet. 2015, 79, 431–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatzikyriakidou, A.; Founti, P.; Melidou, A.; Minti, F.; Bouras, E.; Anastasopoulos, E.; Pappas, T.; Haidich, A.B.; Lambropoulos, A.; Topouzis, F. MicroRNA-related polymorphisms in pseudoexfoliation syndrome, pseudoexfoliative glaucoma, and primary open-angle glaucoma. Ophthalmic Genet. 2018, 39, 603–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, D.Y.; Won, H.H.; Cho, H.K.; Kee, C. Evaluation of lysyl oxidase-like 1 gene polymorphisms in pseudoexfoliation syndrome in a Korean population. Mol. Vis. 2013, 19, 448–453. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, M.C.; Azorsa, D.O. The genomic and proteomic content of cancer cell-derived exosomes. Front. Oncol. 2012, 2, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, D.D.; Lai, J.Y. Synthesis, bioactive properties, and biomedical applications of intrinsically therapeutic nanoparticles for disease treatment. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 435, 134970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, A.; Bajracharya, S.D.; Yuen, P.S.; Zhou, H.; Star, R.A.; Illei, G.G.; Alevizos, I. Exosomes from human saliva as a source of microRNA biomarkers. Oral Dis. 2010, 16, 34–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlassov, A.V.; Magdaleno, S.; Setterquist, R.; Conrad, R. Exosomes: Current knowledge of their composition, biological functions, and diagnostic and therapeutic potentials. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1820, 940–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghaffari Sharaf, M.; Damji, K.F.; Unsworth, L.D. Recent advances in risk factors associated with ocular exfoliation syndrome. Acta Ophthalmol. 2020, 98, 113–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, A.; Simons, M. Exosomes: Vesicular carriers for intercellular communication in neurodegenerative disorders. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 352, 33–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Bailey, J.C.; Helwa, I.; Dismuke, W.M.; Cai, J.; Drewry, M.; Brilliant, M.H.; Budenz, D.L.; Christen, W.G.; Chasman, D.I.; et al. A Common Variant in MIR182 Is Associated With Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma in the NEIGHBORHOOD Consortium. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2016, 57, 4528–4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klingeborn, M.; Michael Dismuke, W.; Bowes Rickman, C.; Stamer, W.D. Roles of exosomes in the normal and diseased eye. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2017, 59, 158–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Merwe, Y.; Steketee, M.B. Extracellular Vesicles: Biomarkers, Therapeutics, and Vehicles in the Visual System. Curr. Ophthalmol. Rep. 2017, 5, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, H.K.; Seong, H.; Kee, C.; Song, D.H.; Kim, S.J.; Seo, S.W.; Kang, S.S. MicroRNA profiles in aqueous humor between pseudoexfoliation glaucoma and normal tension glaucoma patients in a Korean population. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 6217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seong, H.; Cho, H.K.; Kee, C.; Song, D.H.; Cho, M.C.; Kang, S.S. Profiles of microRNA in aqueous humor of normal tension glaucoma patients using RNA sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2011, 11, 19024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- An, H.J.; Cho, H.K.; Song, D.H.; Kee, C. Quantitative analysis of exosomes in the aqueous humor of Korean patients with pseudoexfoliation glaucoma. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 12875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, M.G.; Ko, H.C.; Kim, S.J. Effects of p-coumaric acid on microRNA expression profiles in SNU-16 human gastric cancer cells. Genes Genom. 2020, 42, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinlan, A.R.; Hall, I.M. BEDTools: A flexible suite of utilities for comparing genomic features. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 841–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. Royal. Stat. Soc. Series. B-Stat. Methodol. 1995, 29, 1165–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Baixauli, F.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Sánchez-Madrid, F.; Mittelbrunn, M. Sorting out: Regulation of exosome loading Semin. Cancer Biol. 2014, 28, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villarroya-Beltri, C.; Gutiérrez-Vázquez, C.; Sánchez-Cabo, F.; Pérez-Hernández, D.; Vázquez, J.; Martin-Cofreces, N.; Martinez-Herrera, D.J.; Pascual-Montano, A.; Mittelbrunn, M.; Sánchez-Madrid, F. Sumoylated hnRNOA2B1 controls the sorting of miRNAs into exosomes through binding to specific motifs. Nat. Commun. 2013, 4, 2980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dismuke, W.M.; Challa, P.; Navarro, I.; Stamer, W.D.; Liu, Y. Human aqueous humor exosomes. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 132, 73–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, C.; Fan, F.; Liu, X.; Yang, J.; Zhou, X.; Mei, H.; Lin, X.; Luo, Y. Exosomal miRNA Analysis of Aqueous Humour of Diabetes and Cataract Patients. Curr. Eye Res. 2021, 46, 324–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.F.; Hua, K.; Woung, L.C.; Lin, C.H.; Chen, C.T.; Hsu, C.H.; Liou, S.W.; Tsai, C.Y. Expression Profiling of Exosomal miRNAs Derived from the Aqueous Humor of Myopia Patients. Tohoku. J. Exp. Med. 2019, 249, 213–221. [Google Scholar]
- Hindle, A.G.; Thoonen, R.; Jasien, J.V.; Grange, R.M.H.; Amin, K.; Wise, J.; Ozaki, M.; Ritch, R.; Malhotra, R.; Buys, E.S. Identification of Candidate miRNA Biomarkers for Glaucoma. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2019, 60, 134–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keller, S.; Ridinger, J.; Rupp, A.K.; Janssen, J.W.; Altevogt, P. Body fluid derived exosomes as a novel template for clinical diagnostics. J. Transl. Med. 2011, 9, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dikic, I. Proteasomal and Autophagic Degradation Systems. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017, 86, 193–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Juan-Marcos, L.; Escudero-Domínguez, F.A.; Hernández-Galilea, E.; Cruz-González, F.; Follana-Neira, I.; González-Sarmiento, R. Investigation of Association between Autophagy-Related Gene Polymorphisms and Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome and Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma in a Spanish Population. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2018, 33, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Want, A.; Gillespie, S.R.; Wang, Z.; Gordon, R.; Iomini, C.; Ritch, R.; Wolosin, J.M.; Bernstein, A.M. Autophagy and Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Tenon Fibroblasts from Exfoliation Glaucoma Patients. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.; Drescher, K.M.; Chen, X.M. Exosomal miRNAs: Biological Properties and Therapeutic Potential. Front. Genet. 2012, 3, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Volinia, S.; Calin, G.A.; Liu, C.G.; Ambs, S.; Cimmino, A.; Petrocca, F.; Visone, R.; Iorio, M.; Roldo, C.; Ferracin, M.; et al. A microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer gene targets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 2257–2261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lui, W.O.; Pourmand, N.; Patterson, B.K.; Fire, A. Patterns of known and novel small RNAs in human cervical cancer. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 6031–6043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miñones-Moyano, E.; Porta, S.; Escaramís, G.; Rabionet, R.; Iraola, S.; Kagerbauer, B.; Espinosa-Parrilla, Y.; Ferrer, I.; Estivill, X.; Martí, E. MicroRNA profiling of Parkinson’s disease brains identifies early downregulation of miR-34b/c which modulate mitochondrial function. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 3067–3078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, R.; Zuccato, C.; Belyaev, N.D.; Guest, D.J.; Cattaneo, E.; Buckley, N.J. A microRNA-based gene dysregulation pathway in Huntington’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2008, 29, 438–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buckley, N.J.; Johnson, R.; Zuccato, C.; Bithell, A.; Cattaneo, E. The role of REST in transcriptional and epigenetic dysregulation in Huntington’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2010, 39, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ostenfeld, M.S.; Jeppesen, D.K.; Laurberg, J.R.; Boysen, A.T.; Bramsen, J.B.; Primdal-Bengtson, B.; Hendrix, A.; Lamy, P.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Rasmussen, M.H. Cellular disposal of miR23b by RAB27-dependent exosome release is linked to acquisition of metastatic properties. Cancer Res. 2014, 74, 5758–5771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irie, A.; Nakashima, K.I.; Inoue, T.; Kojima, S.; Takihara, Y.; Takahashi, E. Trabeculotomy Using the Kahook Dual Blade for Exfoliation Glaucoma and Primary Open Angle Glaucoma: Comparison of Outcomes According to Incision Range. J. Glaucoma 2024, 33, 270–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Subject Number | Disease Status | Age, y | Sex | Ocular Comorbidity |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | PEX G | 67 | Male | None |
| 2 | PEX G | 58 | Male | None |
| 3 | PEX G | 81 | Female | None |
| 4 | PEX G | 83 | Male | None |
| 5 | PEX G | 81 | Male | None |
| 6 | PEX G | 70 | Male | None |
| 7 | PEX G | 70 | Female | None |
| 8 | Control | 65 | Female | None |
| 9 | Control | 75 | Male | None |
| 10 | Control | 68 | Female | None |
| 11 | Control | 75 | Male | None |
| 12 | Control | 62 | Female | None |
| 13 | Control | 47 | Male | None |
| 14 | Control | 59 | Male | None |
| miRNA | Assay ID | Accession Number | Fold Change | p-Value | Expression Change |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PEX G/Control | PEX G/Control | ||||
| hsa-let-7b-5p | 2 | MIMAT0000063 | 0.284 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-16-5p | 8 | MIMAT0000069 | 0.25 | 0.002 | Down |
| hsa-miR-20a-5p | 14 | MIMAT0000075 | 0.231 | 0.004 | Down |
| hsa-miR-25-5p | 20 | MIMAT0004498 | 0.016 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-93-5p | 32 | MIMAT0000093 | 0.056 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-105-5p | 43 | MIMAT0000102 | 0.252 | 0.032 | Down |
| hsa-miR-197-5p | 48 | MIMAT0022691 | 0.026 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-195-5p | 130 | MIMAT0000461 | 0.017 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-369-5p | 160 | MIMAT0001621 | 0.155 | 0.020 | Down |
| hsa-miR-196b-5p | 195 | MIMAT0001080 | 0.28 | 0.010 | Down |
| hsa-miR-451a | 209 | MI0001729 | 0.395 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-486-5p | 218 | MIMAT0002177 | 0.289 | 0.001 | Down |
| hsa-miR-181d-5p | 235 | MIMAT0002821 | 0.007 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-532-5p | 284 | MIMAT0002888 | 0.088 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-92b-5p | 295 | MIMAT0004792 | 24.678 | 0.038 | Up |
| hsa-miR-1224-5p | 421 | MIMAT0005458 | 0.092 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-744-5p | 465 | MIMAT0004945 | 2.494 | 0.008 | Up |
| hsa-miR-1228-5p | 505 | MIMAT0005582 | 0.098 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-1275 | 576 | MI0006415 | 0.192 | 0.014 | Down |
| hsa-miR-1284 | 587 | MI0006431 | 0.008 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-1538 | 605 | MI0007259 | 0.19 | 0.045 | Down |
| hsa-miR-3131 | 657 | MI0014151 | 0.305 | 0.016 | Down |
| hsa-miR-3158-5p | 692 | MIMAT0019211 | 0.236 | 0.008 | Down |
| hsa-miR-3173-5p | 707 | MIMAT0019214 | 0.225 | 0.011 | Down |
| hsa-miR-3605-5p | 828 | MIMAT0017981 | 0.244 | 0.008 | Down |
| hsa-miR-3620-5p | 843 | MIMAT0022967 | 0.243 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-3652 | 852 | MI0016052 | 0.163 | 0.007 | Down |
| hsa-miR-3913-5p | 901 | MIMAT0018187 | 0.161 | 0.001 | Down |
| hsa-miR-3925-5p | 914 | MIMAT0018200 | 0.14 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-4491 | 1038 | MI0016853 | 0.287 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-4492 | 1039 | MI0016854 | 0.38 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-4504 | 1052 | MI0016867 | 0.32 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-4516 | 1065 | MI0016882 | 0.159 | 0.003 | Down |
| hsa-miR-4654 | 1125 | MI0017282 | 0.315 | 0.007 | Down |
| hsa-miR-4732-5p | 1209 | MIMAT0019855 | 0.367 | 0.041 | Down |
| hsa-miR-6509-5p | 1438 | MIMAT0025474 | 0.009 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-6717-5p | 1448 | MIMAT0025846 | 0.388 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-6731-5p | 1463 | MIMAT0027363 | 0.016 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-6734-5p | 1466 | MIMAT0027369 | 0.246 | 0.029 | Down |
| hsa-miR-6760-5p | 1492 | MIMAT0027420 | 0.241 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-6849-5p | 1582 | MIMAT0027598 | 0.019 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-7706 | 1658 | MI0025242 | 0.248 | 0.002 | Down |
| hsa-let-7d-3p | 1728 | MIMAT0004484 | 0.284 | 0.003 | Down |
| hsa-miR-92a-3p | 1753 | MIMAT0000092 | 0.388 | 0.002 | Down |
| hsa-miR-16-2-3p | 1763 | MIMAT0004518 | 0.321 | 0.037 | Down |
| hsa-miR-128-3p | 1813 | MIMAT0000424 | 0.473 | 0.002 | Down |
| hsa-miR-142-3p | 1821 | MIMAT0000434 | 0.016 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-106b-3p | 1850 | MIMAT0004672 | 0.358 | 0.048 | Down |
| hsa-miR-30c-1-3p | 1852 | MIMAT0004674 | 0.116 | 0.004 | Down |
| hsa-miR-148b-3p | 1897 | MIMAT0000759 | 3.962 | 0.048 | Up |
| hsa-miR-486-3p | 1921 | MIMAT0004762 | 0.31 | 0.002 | Down |
| hsa-miR-92b-3p | 1983 | MIMAT0003218 | 0.388 | 0.035 | Down |
| hsa-miR-576-3p | 1989 | MIMAT0004796 | 0.129 | 0.007 | Down |
| hsa-miR-766-3p | 2039 | MIMAT0003888 | 0.174 | 0.008 | Down |
| hsa-miR-708-3p | 2052 | MIMAT0004927 | 0.033 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-1180-3p | 2066 | MIMAT0005825 | 0.171 | 0.004 | Down |
| hsa-miR-1306-3p | 2094 | MIMAT0005950 | 0.039 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-3158-3p | 2131 | MIMAT0015032 | 0.291 | 0.005 | Down |
| hsa-miR-3162-3p | 2133 | MIMAT0019213 | 0.143 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-3177-3p | 2136 | MIMAT0015054 | 0.054 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-3913-3p | 2179 | MIMAT0019225 | 0.205 | 0.005 | Down |
| hsa-miR-4677-3p | 2232 | MIMAT0019761 | 0.008 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-6509-3p | 2383 | MIMAT0025475 | 0.008 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-6729-3p | 2399 | MIMAT0027360 | 0.204 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-6765-3p | 2434 | MIMAT0027431 | 0.467 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-6777-3p | 2446 | MIMAT0027455 | 0.359 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-6880-3p | 2547 | MIMAT0027661 | 0.137 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-6885-3p | 2552 | MIMAT0027671 | 0.437 | 0.000 | Down |
| hsa-miR-7161-3p | 2580 | MIMAT0028233 | 0.256 | 0.000 | Down |
| KEGG Pathway | p-Value (−log10) | Genes Predicted as Target | Related miRNAs |
|---|---|---|---|
| RNA transport | 24.30041521 | 48 | 4 |
| Prion diseases | 18.35492993 | 8 | 4 |
| Ribosome biogenesis in eukaryotes | 17.0221273 | 27 | 2 |
| Cell cycle | 13.76476278 | 33 | 8 |
| PI3K-Akt signaling pathway | 10.23418479 | 62 | 9 |
| Small-cell lung cancer | 9.689671903 | 23 | 8 |
| Ubiquitin-mediated proteolysis | 9.470397836 | 33 | 6 |
| Bladder cancer | 8.029735666 | 14 | 7 |
| p53 signaling pathway | 8.007213183 | 20 | 8 |
| Hepatitis B | 7.848689919 | 33 | 9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
An, H.J.; Song, D.H.; Kee, C.; Cho, H.-k. Exosomal microRNA from Plasma in Patients with Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma of Korea. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094244
An HJ, Song DH, Kee C, Cho H-k. Exosomal microRNA from Plasma in Patients with Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma of Korea. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094244
Chicago/Turabian StyleAn, Hyo Jung, Dae Hyun Song, Changwon Kee, and Hyun-kyung Cho. 2025. "Exosomal microRNA from Plasma in Patients with Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma of Korea" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094244
APA StyleAn, H. J., Song, D. H., Kee, C., & Cho, H.-k. (2025). Exosomal microRNA from Plasma in Patients with Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma of Korea. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094244






