Ethanolic Extract of Rosa rugosa Roots and Its Bioactive Compound, Oleamide, Prevented Amyloid β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Improved Behavioral Tests in Mice
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
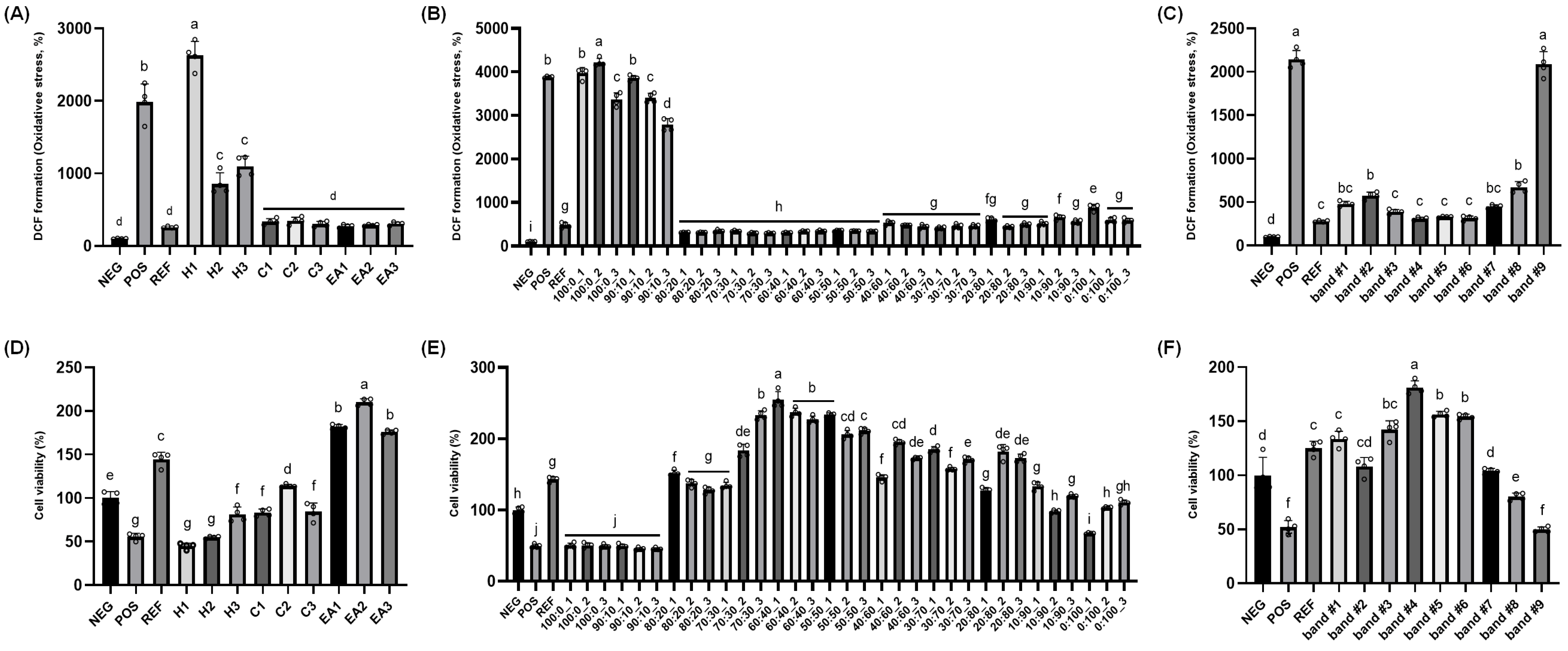
2.1. Screening for Protective Effect of Plant Extracts Against Oxidative Stress In Vitro
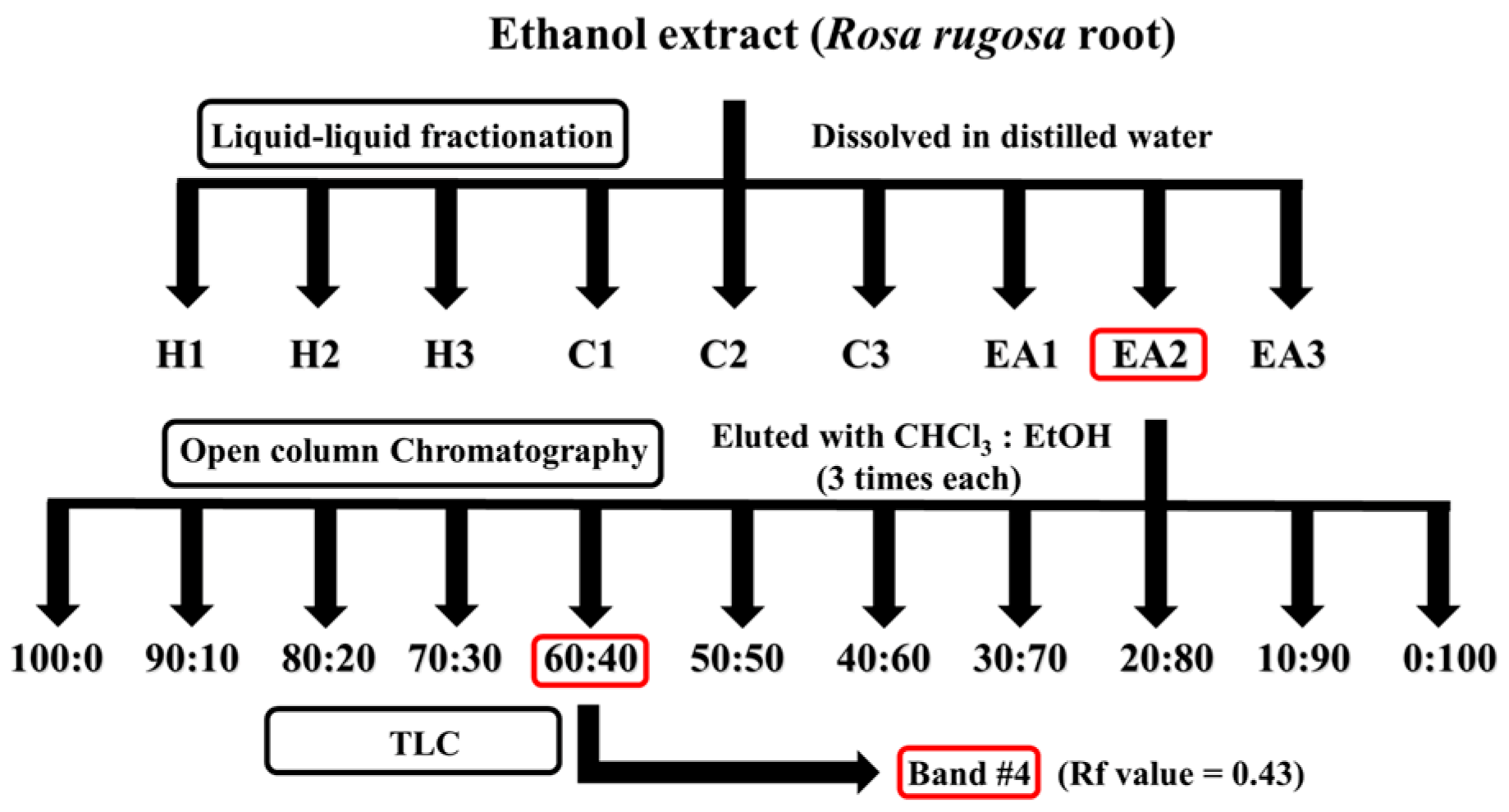
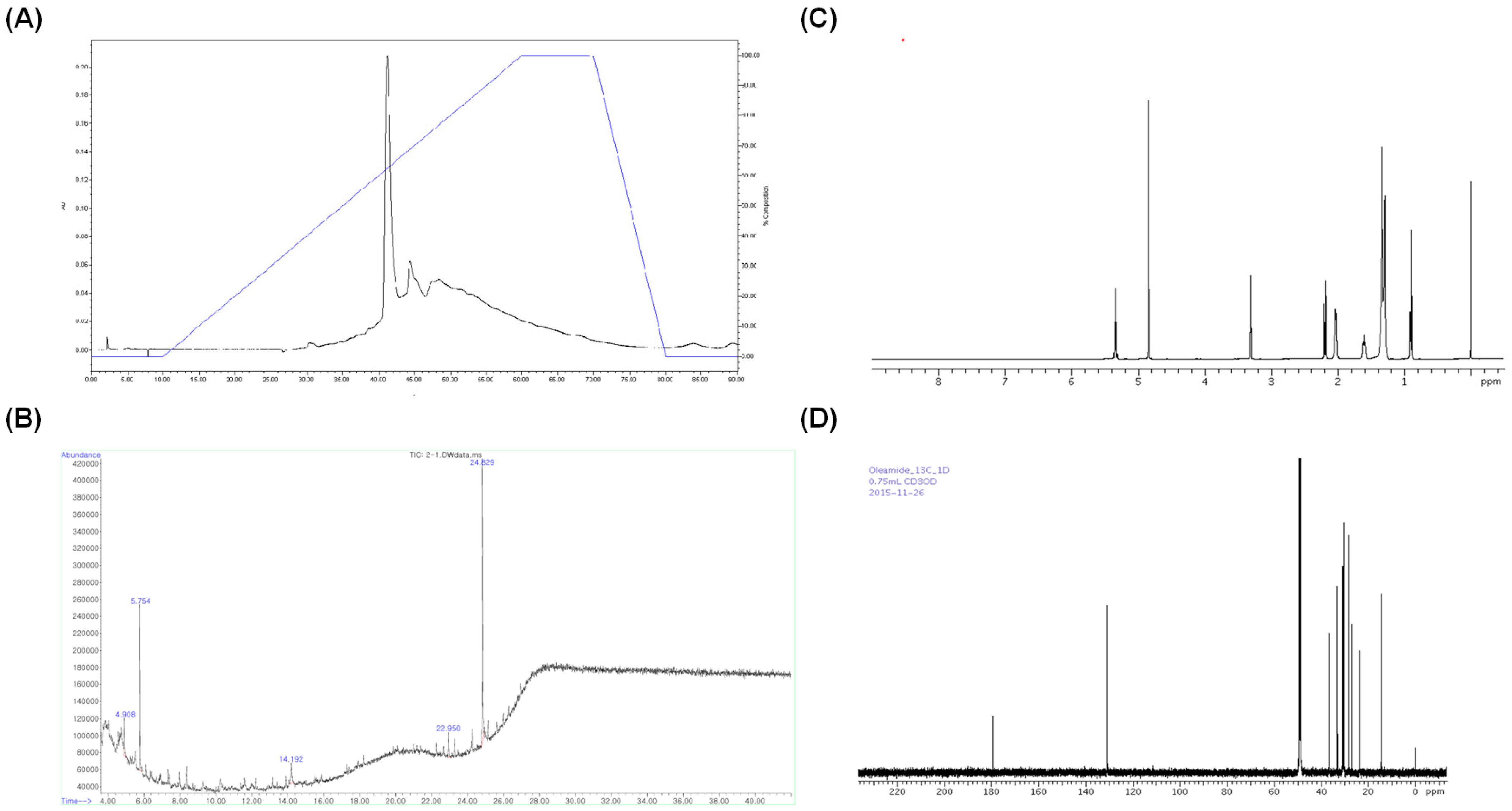
2.2. Identification of Chemical Structure of Active Constituent in the RR Root Extract
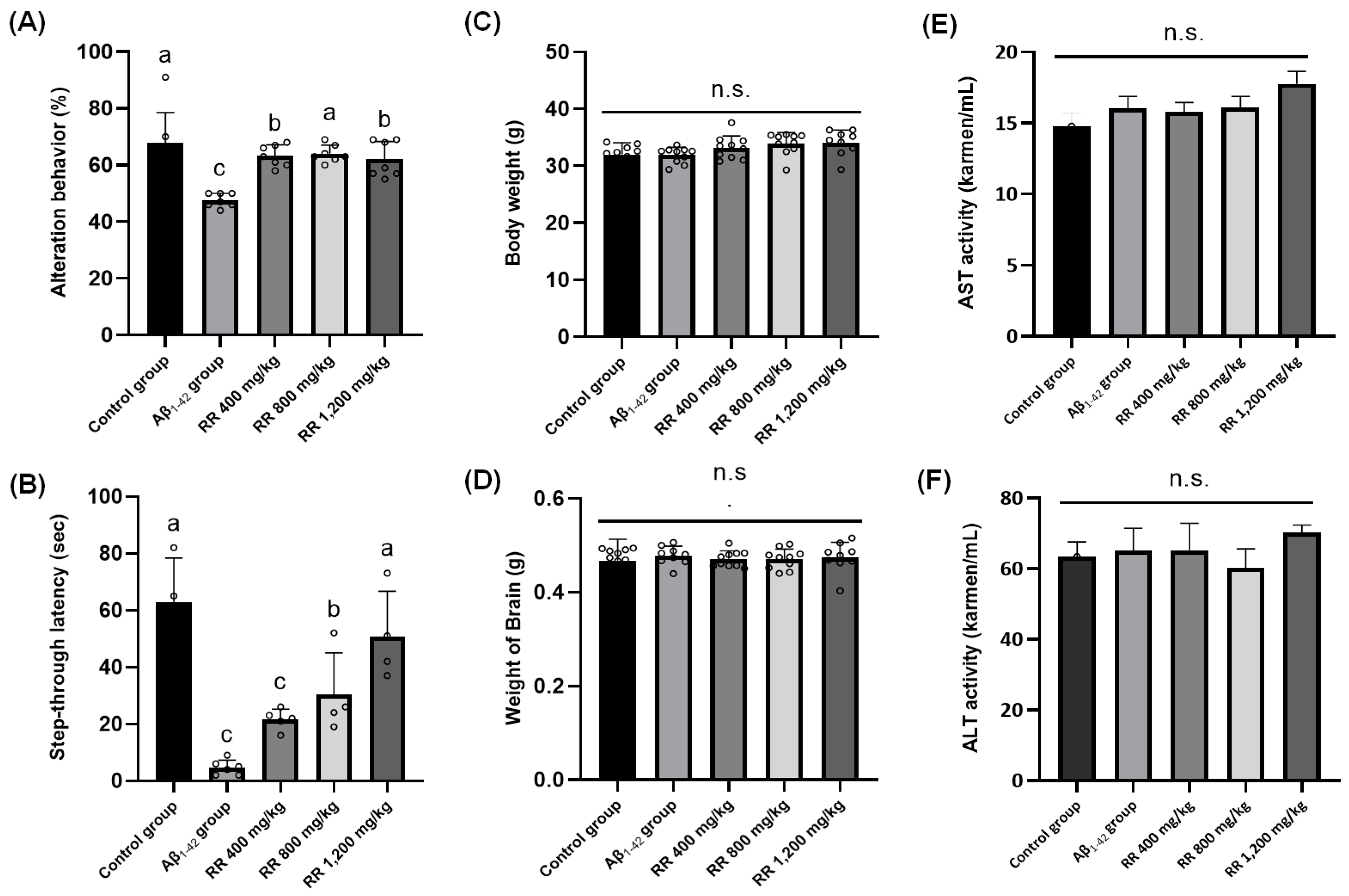
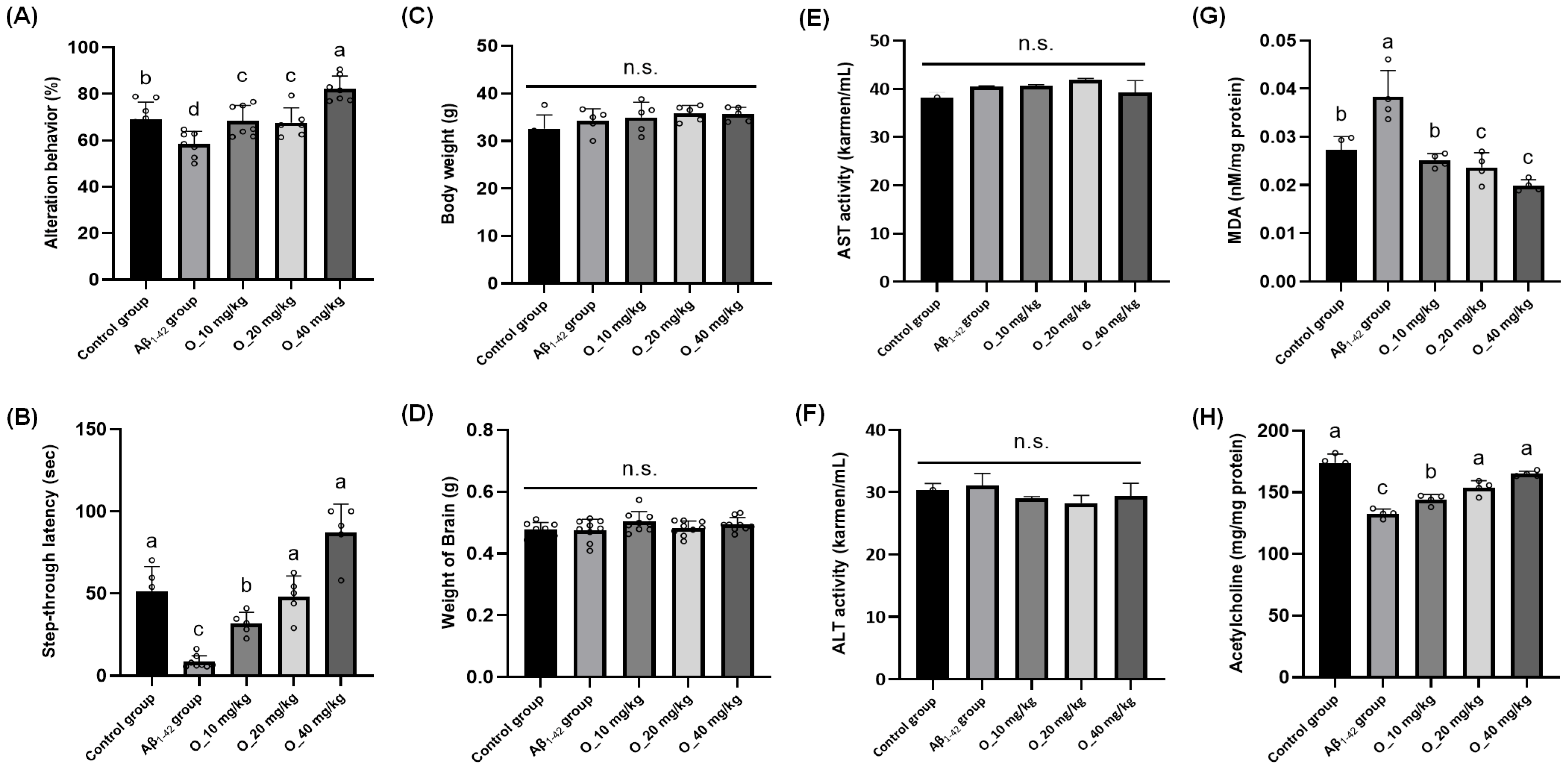
2.3. RR Root Extract and Oleamide Improved Aβ1-42-Induced Behavioral Abnormalities and Brain Biomarkers
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Materials
3.2. Cell Culture Conditions
3.3. Measurement of Intracellular Oxidative Stress in PC12 Cells
3.4. Measurement of Cytotoxicity Using MTT Reduction Assay
3.5. Preparation of Plant Extracts for Screening
3.6. Isolation and Purification of Active Constituent from RR Root Extract: Liquid–Liquid Fractionation, Open-Column Chromatography, and Preparatory Thin Layer Chromatography (TLC)
3.7. High-Pressure Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
3.8. Elucidation of Active Component Structure: Gas Chromatography (GC)–Mass Spectrometry (MS) and 1H and 13C-Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Analyses
3.9. In Vivo Experiment I and II: Mouse Intervention Studies Using RR Roots Extract and Oleamide Therein
3.10. Y-Maze Test: Assessment of Immediate Working Memory
3.11. Passive Avoidance Test: Assessment of Aversion Learning Ability
3.12. Evaluation of Acute Toxicity of RR Root Extract and Oleamide In Vivo
3.13. Assessment of Lipid Peroxidation Using the ICR Mice Brain
3.14. Assessment of Acetylcholine (ACh) Levels in the ICR Mice Brain
3.15. Statistical Analysis
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nakabayashi, J.; Yoshimura, M.; Morishima-Kawashima, M.; Funato, H.; Miyakawa, T.; Yamazaki, T.; Ihara, Y. Amyloid (B-protein (Aß) Accumulation in the Putamen and Mammillary Body during Aging and in Alzheimer Disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 1998, 57, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, H.; Hu, M.; Li, Q.; Zhang, L.; Zhu, D.; Li, Q.; Li, S.; Liu, T.; Li, X. Identification of Causal Relationship Between Amyloid-Beta Accumulation and Alzheimer’s Disease Progression via Counterfactual Inference; Optica Imaging Congress (3D, COSI, DH, FLatOptics, IS, pcAOP); Optica Publishing Group: Washington, DC, USA, 2023; p. ITh1C.2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aschenbrenner, D.S. Rn Controversial Approval of New Drug to Treat Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Nurs. 2021, 121, 22–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schelke, M.W.; Hackett, K.; Chen, J.L.; Shih, C.; Shum, J.; Montgomery, M.E.; Chiang, G.C.; Berkowitz, C.; Seifan, A.; Krikorian, R.; et al. Nutritional interventions for Alzheimer’s prevention: A clinical precision medicine approach. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2016, 1367, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.K.; Choi, S.J.; Cho, H.Y.; Hwang, H.-J.; Kim, Y.J.; Lim, S.T.; Kim, C.-J.; Kim, H.K.; Peterson, S.; Shin, D.-H. Protective Effects of Kaempferol (3,4′,5,7-tetrahydroxyflavone) against Amyloid Beta Peptide (Aβ)-Induced Neurotoxicity in ICR Mice. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2010, 74, 397–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Gaamouch, F.; Chen, F.; Ho, L.; Lin, H.Y.; Yuan, C.; Wong, J.; Wang, J. Benefits of dietary polyphenols in Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1019942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nam, M.-H.; Lee, H.-S.; Hong, C.-O.; Koo, Y.-C.; Seomun, Y.; Lee, K.-W. Preventive effects of Rosa rugosa root extract on advanced glycation end product-induced endothelial dysfunction. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 42, 210–216. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, D.H.; Han, J.H.; Hong, M.; Lee, S.Y.; Lee, S.U.; Kwon, T.H. Antioxidant and lipid-reducing effects of Rosa rugosa root extract in 3T3-L1 cell. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 31, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, J.; Wang, C. Medicinal Components and Pharmacological Effects of Rosa rugosa. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2018, 12, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, B.-J. Isolation of main component and antioxidant activities on the stem and root of Rosa rugosa. Korean J. Plant Res. 2008, 21, 402–407. [Google Scholar]
- Na, J.-R.; Oh, D.-R.; Han, S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Choi, E.; Bae, D.; Oh, D.H.; Lee, Y.-H.; Kim, S.; Jun, W. Antistress Effects of Rosa rugosa Thunb. on Total Sleep Deprivation–Induced Anxiety-Like Behavior and Cognitive Dysfunction in Rat: Possible Mechanism of Action of 5-HT6 Receptor Antagonist. J. Med. Food 2016, 19, 870–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.C.; Kim, S.C.; Hur, J.M.; Choi, S.H.; Lee, K.Y.; Choi, J.W. Anti-Hepatotoxic Effects of Rosa rugosa Root and Its Compound, Rosamultin, in Rats Intoxicated with Bromobenzene. J. Med. Food 2004, 7, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hestrin, S. The Reaction of Acetylcholine and Other Carboxylic Acid Derivatives with Hydroxylamine, and its Analytical Application. J. Biol. Chem. 1949, 180, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akanmu, M.A.; Adeosun, S.O.; Ilesanmi, O.R. Neuropharmacological effects of oleamide in male and female mice. Behav. Brain Res. 2007, 182, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, W.A.; Kloczewiak, M.A.; Blusztajn, J.K. Amyloid beta-protein reduces acetylcholine synthesis in a cell line derived from cholinergic neurons of the basal forebrain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1996, 93, 8068–8071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, H.-J.; Park, Y.-J.; Suh, Y.-M.; Choi, S.-J.; Kim, M.-J.; Cho, H.-Y.; Chang, Y.-J.; Hong, B.; Kim, H.-K.; Kim, E.; et al. Effects of Oleamide on Choline Acetyltransferase and Cognitive Activities. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2003, 67, 1284–1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ano, Y.; Ozawa, M.; Kutsukake, T.; Sugiyama, S.; Uchida, K.; Yoshida, A.; Nakayama, H. Preventive Effects of a Fermented Dairy Product against Alzheimer’s Disease and Identification of a Novel Oleamide with Enhanced Microglial Phagocytosis and Anti-Inflammatory Activity. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0118512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kita, M.; Ano, Y.; Inoue, A.; Aoki, J. Identification of P2Y receptors involved in oleamide-suppressing inflammatory responses in murine microglia and human dendritic cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahan, K. Stimulation of ADAM10 and decrease in plaques by a sleep-inducing supplement. Alzheimer’s Dement. 2020, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, N.; Xu, H.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Liu, G.; Lei, X.; Sun, H.; Wu, X.; Li, J. Protective mechanism of kaempferol against Aβ25-35-mediated apoptosis of pheochromocytoma (PC-12) cells through the ER/ERK/MAPK signalling pathway. Arch. Med. Sci. 2020, 17, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.K.; Choi, S.J.; Bae, H.; Kim, C.R.; Cho, H.-Y.; Kim, Y.J.; Lim, S.T.; Kim, C.-J.; Kim, H.K.; Peterson, S.; et al. Effects of Methoxsalen from Poncirus trifoliata on Acetylcholinesterase and Trimethyltin-Induced Learning and Memory Impairment. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2011, 75, 1984–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Chang, S.W.; Du, Y.E.; Qi, Y.; Lee, J.S.; Goo, N.; Koo, B.K.; Bae, H.J.; Ryu, J.H.; Jang, D.S. New Depsides and Neuroactive Phenolic Glucosides from the Flower Buds of Rugosa Rose (Rosa rugosa). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 7289–7296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Scientific Name | Protective Effect (%) a | Cell Viability (%) b |
|---|---|---|
| Euryale ferox Salisb. | 77.7 | 90.8 |
| Tussilago farfara L. | 73.7 | 67.1 |
| Chrysosplenium ramosum maxim | 59.8 | 48.4 |
| Allium ascalonicum L. | 60.1 | 50.7 |
| Carya pecan | 78.5 | 78.5 |
| Brassica oleracea var. acephala | 31.6 | 46.0 |
| Ilex paraguayensis | 85.0 | 70.1 |
| Rosa rugosa (roots) | 91.5 | 121.4 |
| Brassica juncea var. integrifolia | 44.2 | 54.9 |
| Perilla frutescens var. japonica (Hassk.) Hara | 35.5 | 46.4 |
| Chrysanthemum coronarium var. spatiosum | 2.5 | 41.6 |
| Prunus salicina | 33.6 | 48.1 |
| Ocimum basilicum | 21.3 | 45.3 |
| Fraxinus rhynchophylla HANCE | 31.3 | 44.7 |
| Pimpinella brachycarpa | 16.5 | 38.0 |
| Spinacia oleracea | 50.8 | 42.7 |
| Phaseolus radiatus | 55.2 | 46.0 |
| Carthamus tinctorius | 31.9 | 45.4 |
| Ulmus pumila L. | 85.3 | 64.1 |
| Adenophora triphylla var. janponica Hara | 38.7 | 45.5 |
| Cuscuta japonica Choisy | 70.0 | 49.4 |
| Brassica napus | 49.0 | 51.9 |
| Acorus gramineus | 31.5 | 46.1 |
| Acorus calamus var. angustatus | 49.8 | 41.3 |
| Cucurbita spp. | 11.3 | 37.8 |
| Cichorium intybus | 53.6 | 38.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, C.K.; Choi, S.J.; Kim, C.R.; Shin, H.R.; Shin, E.-C.; Kim, Y.J.; Cho, T.J.; Shin, D.-H.; Kim, J.K. Ethanolic Extract of Rosa rugosa Roots and Its Bioactive Compound, Oleamide, Prevented Amyloid β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Improved Behavioral Tests in Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094214
Park CK, Choi SJ, Kim CR, Shin HR, Shin E-C, Kim YJ, Cho TJ, Shin D-H, Kim JK. Ethanolic Extract of Rosa rugosa Roots and Its Bioactive Compound, Oleamide, Prevented Amyloid β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Improved Behavioral Tests in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094214
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Chan Kyu, Soo Jung Choi, Cho Rong Kim, Hyo Ri Shin, Eui-Cheol Shin, Young Jun Kim, Tae Jin Cho, Dong-Hoon Shin, and Jae Kyeom Kim. 2025. "Ethanolic Extract of Rosa rugosa Roots and Its Bioactive Compound, Oleamide, Prevented Amyloid β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Improved Behavioral Tests in Mice" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094214
APA StylePark, C. K., Choi, S. J., Kim, C. R., Shin, H. R., Shin, E.-C., Kim, Y. J., Cho, T. J., Shin, D.-H., & Kim, J. K. (2025). Ethanolic Extract of Rosa rugosa Roots and Its Bioactive Compound, Oleamide, Prevented Amyloid β-Induced Oxidative Stress and Improved Behavioral Tests in Mice. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4214. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094214







