The Beneficial Impact of a Novel Pancreatic Polypeptide Analogue on Islet Cell Lineage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
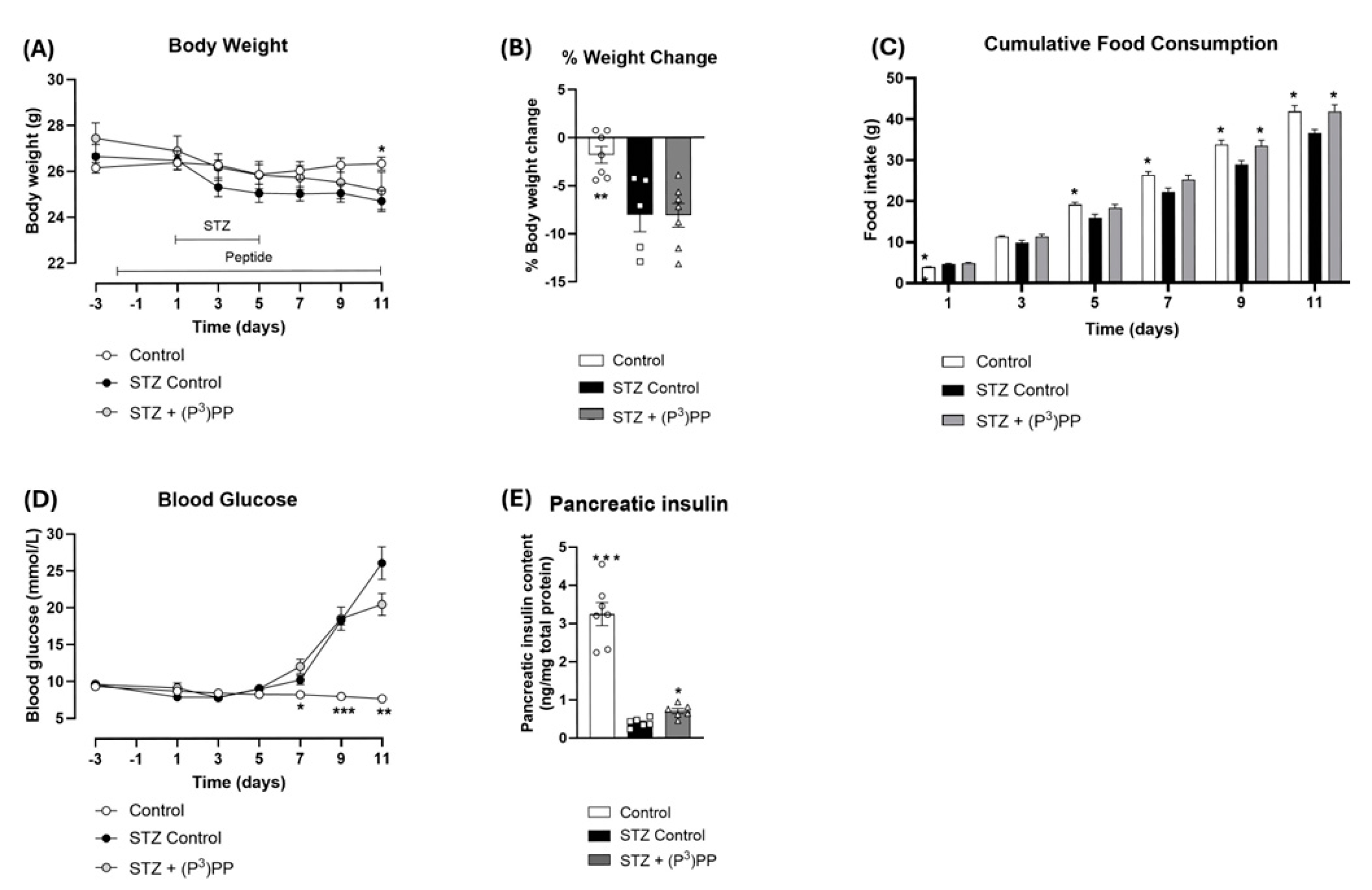
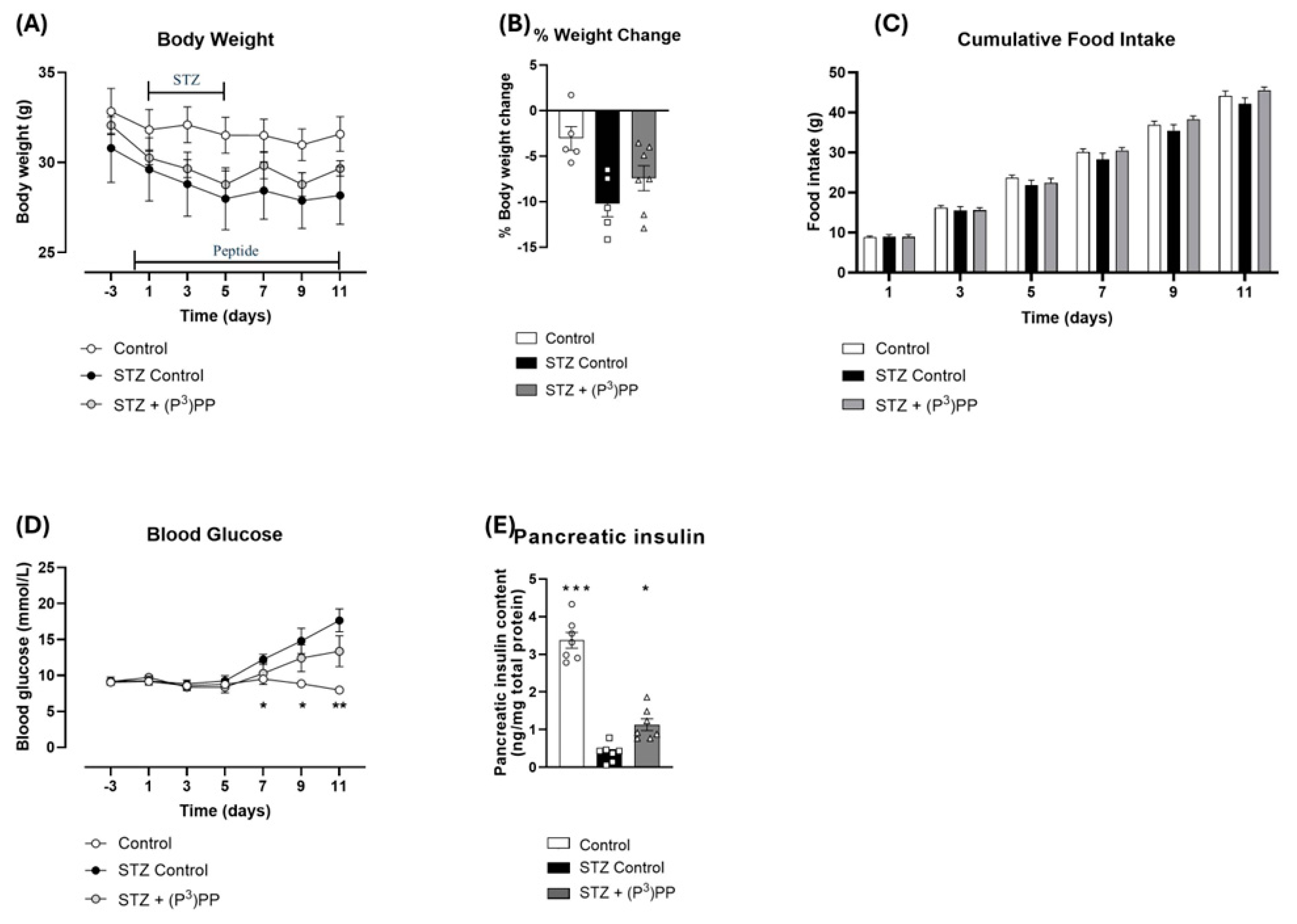
2.1. Effects (P3)PP on Body Weight, Food Intake, Blood Glucose and Pancreatic Insulin Content in STZ-Diabetic Ins1Cre/+;Rosa26-eYFP and GluCreERT2;Rosa26-eYFP Mice
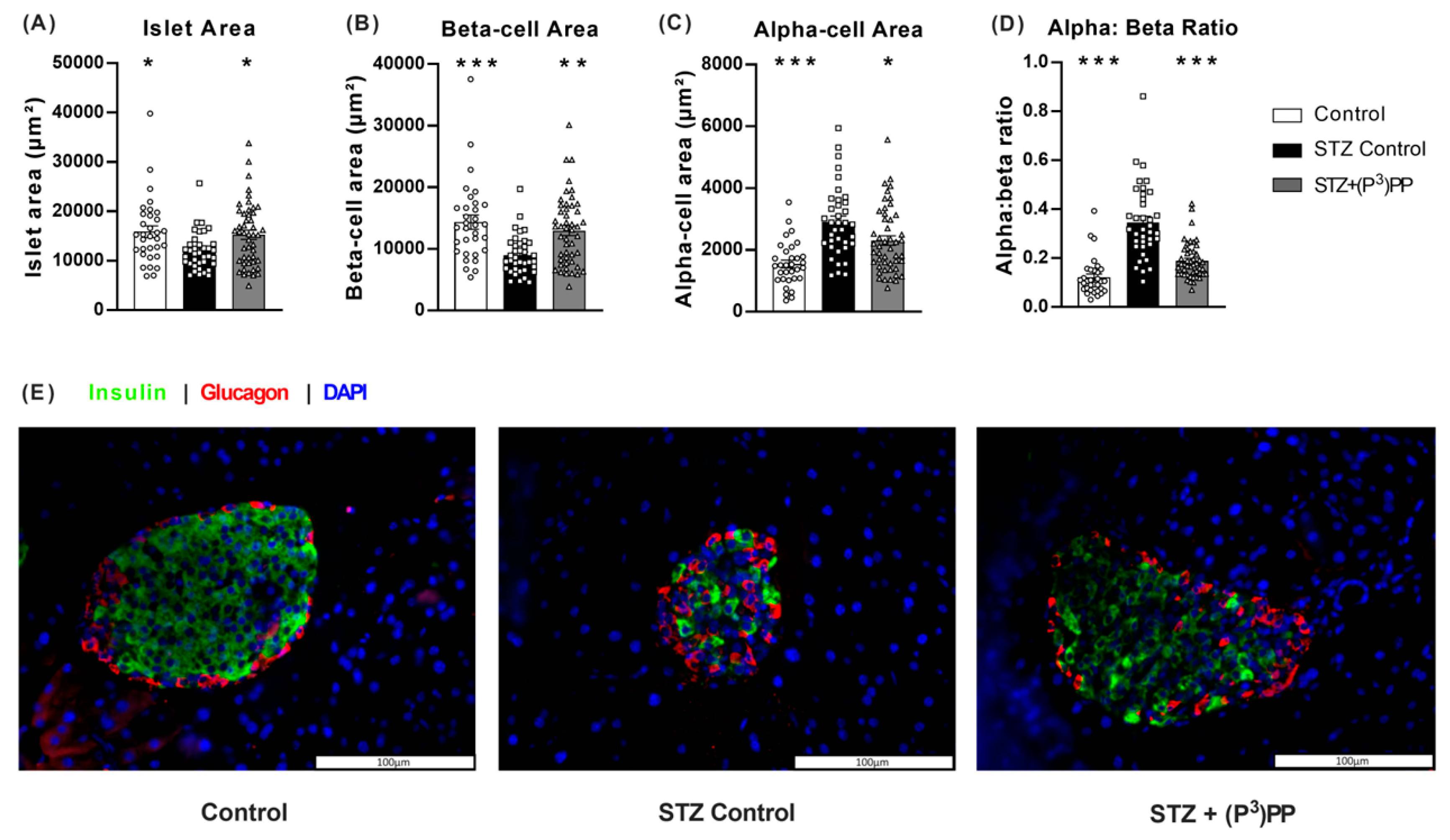
2.2. Effects of (P3)PP on Islet Morphology in STZ-Diabetic Ins1Cre/+;Rosa26-eYFP and GluCreERT2;Rosa26-eYFP Mice
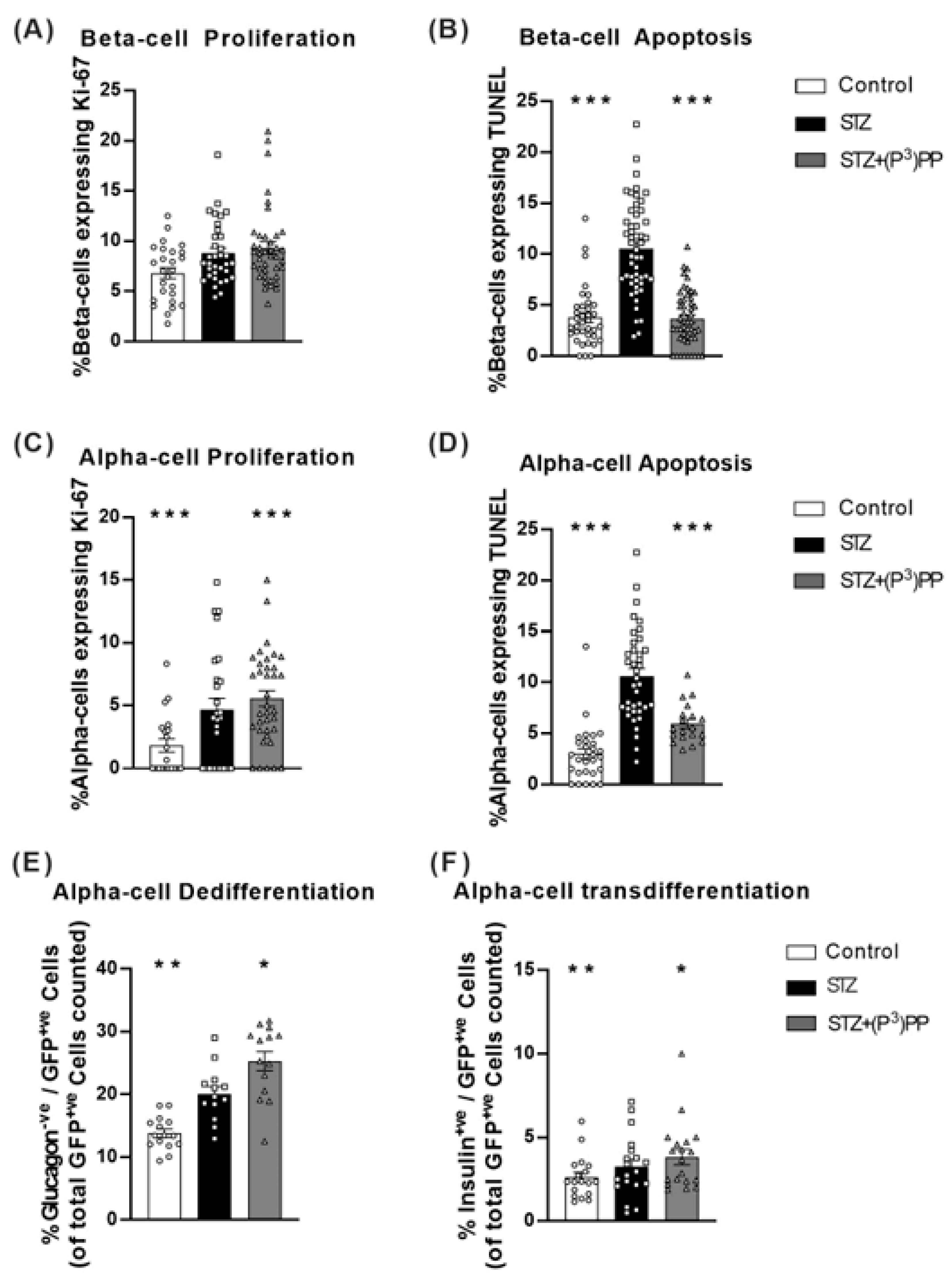
2.3. Effects (P3)PP on Islet Cell Turnover and Plasticity in STZ-Diabetic Ins1Cre/+;Rosa26-eYFP and GluCreERT2;Rosa26-eYFP Mice
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Peptides
4.2. Animals
4.3. Experimental Protocols
4.4. Immunohistochemistry
4.5. Image Analysis
4.6. Biochemical Analysis
4.7. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Aguayo-Mazzucato, C.; Bonner-Weir, S. Pancreatic β Cell Regeneration as a Possible Therapy for Diabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franklin, Z.J.; Tsakmaki, A.; Fonseca Pedro, P.; King, A.J.; Huang, G.C.; Amjad, S.; Persaud, S.J.; Bewick, G.A. Islet neuropeptide Y receptors are functionally conserved and novel targets for the preservation of beta-cell mass. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2018, 20, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Tanday, N.; Lafferty, R.A.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. Novel enzyme-resistant pancreatic polypeptide analogs evoke pancreatic beta-cell rest, enhance islet cell turnover, and inhibit food intake in mice. Biofactors 2024, 50, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanday, N.; Zhu, W.; Tarasov, A.I.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. (P3)PP, a stable, long-acting pancreatic polypeptide evokes weight lowering and pancreatic beta-cell protective effects in obesity-diabetes. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 4945–4957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanday, N.; Tarasov, A.I.; Moffett, R.C.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. Pancreatic islet cell plasticity: Pathogenic or therapeutically exploitable? Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2024, 26, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, A.E.; Janson, J.; Bonner-Weir, S.; Ritzel, R.; Rizza, R.A.; Butler, P.C. β-Cell Deficit and Increased β-Cell Apoptosis in Humans With Type 2 Diabetes. Diabetes 2003, 52, 102–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talchai, C.; Xuan, S.; Lin, H.V.; Sussel, L.; Accili, D. Pancreatic β cell dedifferentiation as a mechanism of diabetic β cell failure. Cell 2012, 150, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Frances, M.; van Gurp, L.; Abate, M.V.; Cigliola, V.; Furuyama, K.; Bru-Tari, E.; Oropeza, D.; Carreaux, T.; Fujitani, Y.; Thorel, F.; et al. Pancreatic Ppy-expressing γ-cells display mixed phenotypic traits and the adaptive plasticity to engage insulin production | Nature Communications. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fukaishi, T.; Nakagawa, Y.; Fukunaka, A.; Sato, T.; Hara, A.; Nakao, K.; Saito, M.; Kohno, K.; Miyatsuka, T.; Tamaki, M.; et al. Characterisation of Ppy-lineage cells clarifies the functional heterogeneity of pancreatic beta cells in mice. Diabetologia 2021, 64, 2803–2816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, S.; An, Y.; Fan, W.; Teng, F.; Jiang, Z. Comparative transcriptomic analysis reveals the underlying molecular mechanism in high-fat diet-induced islet dysfunction. Biosci. Rep. 2023, 43, BSR20230501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Widjaja, J.; Sun, J.; Li, M.; Qiao, Z.; Cao, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Gu, Y.; et al. Bariatric surgery induces pancreatic cell transdifferentiation as indicated by single-cell transcriptomics in Zucker diabetic rats. J. Diabetes 2024, 16, e13521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnobat, D.; Moffett, R.C.; Gault, V.A.; Tanday, N.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. Effects of long-acting GIP, xenin and oxyntomodulin peptide analogues on alpha-cell transdifferentiation in insulin-deficient diabetic GluCreERT2;Rosa26-eYFP mice. Peptides 2020, 125, 170205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bauer, B.M.; Bhattacharya, S.; Bloom-Saldana, E.; Irimia-Dominguez, J.M.; Fueger, P.T. Dose-dependent progression of multiple low-dose streptozotocin-induced diabetes in mice. Physiol. Genom. 2023, 55, 381–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Brien, B.A.; Harmon, B.V.; Cameron, D.P.; Allan, D.J. Beta-cell apoptosis is responsible for the development of IDDM in the multiple low-dose streptozotocin model. J. Pathol. 1996, 178, 176–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Casteels, T.; Frogne, T.; Ingvorsen, C.; Honoré, C.; Courtney, M.; Huber, K.V.M.; Schmitner, N.; Kimmel, R.A.; Romanov, R.A.; et al. Artemisinins Target GABAA Receptor Signaling and Impair α Cell Identity. Cell 2017, 168, 86–100.e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sachs, S.; Bastidas-Ponce, A.; Tritschler, S.; Bakhti, M.; Böttcher, A.; Sánchez-Garrido, M.A.; Tarquis-Medina, M.; Kleinert, M.; Fischer, K.; Jall, S.; et al. Targeted pharmacological therapy restores β-cell function for diabetes remission. Nat. Metab. 2020, 2, 192–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanday, N.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N.; Moffett, R.C. Liraglutide and sitagliptin counter beta- to alpha-cell transdifferentiation in diabetes. J. Endocrinol. 2020, 245, 53–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furman, B.L. Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Models in Mice and Rats. Curr. Protoc. 2021, 1, e78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafferty, R.A.; Tanday, N.; Moffett, R.C.; Reimann, F.; Gribble, F.M.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. Positive Effects of NPY1 Receptor Activation on Islet Structure Are Driven by Pancreatic Alpha- and Beta-Cell Transdifferentiation in Diabetic Mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 633625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, J.R.; Martchenko, A.; Sweeney, M.E.; Maalouf, M.F.; Psichas, A.; Gribble, F.M.; Reimann, F.; Brubaker, P.L. Essential Role of Syntaxin-Binding Protein-1 in the Regulation of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Secretion. Endocrinology 2020, 161, bqaa039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiano, J.P.; Mauvais-Jarvis, F. Importance of oestrogen receptors to preserve functional beta-cell mass in diabetes. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2012, 8, 342–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossini, A.A.; Like, A.A.; Chick, W.L.; Appel, M.C.; Cahill, G.F. Studies of streptozotocin induced insulitis and diabetes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1977, 74, 2485–2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graham, M.L.; Janecek, J.L.; Kittredge, J.A.; Hering, B.J.; Schuurman, H.J. The streptozotocin-induced diabetic nude mouse model: Differences between animals from different sources. Comp. Med. 2011, 61, 356–360. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schüß, C.; Behr, V.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Illuminating the neuropeptide Y4 receptor and its ligand pancreatic polypeptide from a structural, functional, and therapeutic perspective. Neuropeptides 2024, 105, 102416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofmann, S.; Bellmann-Sickert, K.; Beck-Sickinger, A.G. Chemical modification of neuropeptide Y for human Y1 receptor targeting in health and disease. Biol. Chem. 2019, 400, 299–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedrich, M.G.; Sechtem, U.; Schulz-Menger, J.; Holmvang, G.; Alakija, P.; Cooper, L.T.; White, J.A.; Abdel-Aty, H.; Gutberlet, M.; Prasad, S.; et al. International Consensus Group on Cardiovascular Magnetic Resonance in Myocarditis. Cardiovascular magnetic resonance in myocarditis: A JACC White Paper. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 1475–1487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedragosa Badia, X.; Stichel, J.; Beck-Sickinger, A. Neuropeptide Y receptors: How to get subtype selectivity. Front. Endocrinol. 2013, 4, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, W.; Iwasa, H.; Tumurkhuu, M. Role of the Transcription Factor MAFA in the Maintenance of Pancreatic beta-Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón, F.; Karaca, M.; Novials, A.; Maldonado, R.; Maechler, P.; Rubí, B. Pancreatic polypeptide regulates glucagon release through PPYR1 receptors expressed in mouse and human alpha-cells. Biochim. Biophys. Acta—Gen. Subj. 2015, 1850, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Qiu, W.L.; Yu, X.X.; Zhang, Y.; He, M.Y.; Li, L.C.; Yang, L.; Zhang, W.; Franti, M.; Ye, J.; et al. Characterizing pancreatic β-cell heterogeneity in the streptozotocin model by single-cell transcriptomic analysis. Molecualr Metab. 2020, 37, 100982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, B.D.; Holst, J.J. Peptides in the regulation of glucagon secretion. Peptides 2022, 148, 170683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Jiang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Qian, J.; Wang, C.; Yang, T.; Prasadan, K.; Gittes, G.K.; Xiao, X. Insulin-positive ductal cells do not migrate into preexisting islets during pregnancy. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheng, C.; Li, F.; Lin, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, P.; Bu, L.; Sheng, H.; Li, H.; Qu, S. Reversibility of β-Cell-Specific Transcript Factors Expression by Long-Term Caloric Restriction in db/db Mouse. J. Diabetes Res. 2016, 2016, e6035046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Misra, S.; Murthy, K.S.; Zhou, H.; Grider, J.R. Coexpression of Y 1, Y 2, and Y 4 Receptors in Smooth Muscle Coupled to Distinct Signaling Pathways. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2004, 311, 1154–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, M.; Li, H.; Wu, Z.; Yan, J.; Liu, Q.; Ou, C.; Chen, M. A Promising Therapeutic Target for Metabolic Diseases: Neuropeptide Y Receptors in Humans. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 45, 88–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Tanday, N.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. Pancreatic polypeptide revisited: Potential therapeutic effects in obesity-diabetes. Peptides 2023, 160, 170923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, C.; Chen, Y.; Yin, X.; Xu, R.; Yin, C.; Wang, C.; Zhao, Y. Pancreatic endocrine and exocrine signaling and crosstalk in physiological and pathological status. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thorens, B.; Tarussio, D.; Maestro, M.A.; Rovira, M.; Heikkilä, E.; Ferrer, J. Ins1(Cre) knock-in mice for beta cell-specific gene recombination. Diabetologia 2015, 58, 558–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorel, F.; Népote, V.; Avril, I.; Kohno, K.; Desgraz, R.; Chera, S.; Herrera, P.L. Conversion of adult pancreatic alpha-cells to beta-cells after extreme beta-cell loss. Nature 2010, 464, 1149–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanday, N.; Coulter-Parkhill, A.; Moffett, R.C.; Suruli, K.; Dubey, V.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. Sex-based impact of pancreatic islet stressors in GluCreERT2/Rosa26-eYFP mice. J. Endocrinol. 2023, 259, e230174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, W.; Tanday, N.; Flatt, P.R.; Irwin, N. The Beneficial Impact of a Novel Pancreatic Polypeptide Analogue on Islet Cell Lineage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4215. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094215
Zhu W, Tanday N, Flatt PR, Irwin N. The Beneficial Impact of a Novel Pancreatic Polypeptide Analogue on Islet Cell Lineage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4215. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094215
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Wuyun, Neil Tanday, Peter R. Flatt, and Nigel Irwin. 2025. "The Beneficial Impact of a Novel Pancreatic Polypeptide Analogue on Islet Cell Lineage" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4215. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094215
APA StyleZhu, W., Tanday, N., Flatt, P. R., & Irwin, N. (2025). The Beneficial Impact of a Novel Pancreatic Polypeptide Analogue on Islet Cell Lineage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4215. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094215





