Protective Effects of (-)-Butaclamol Against Gentamicin-Induced Ototoxicity: In Vivo and In Vitro Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
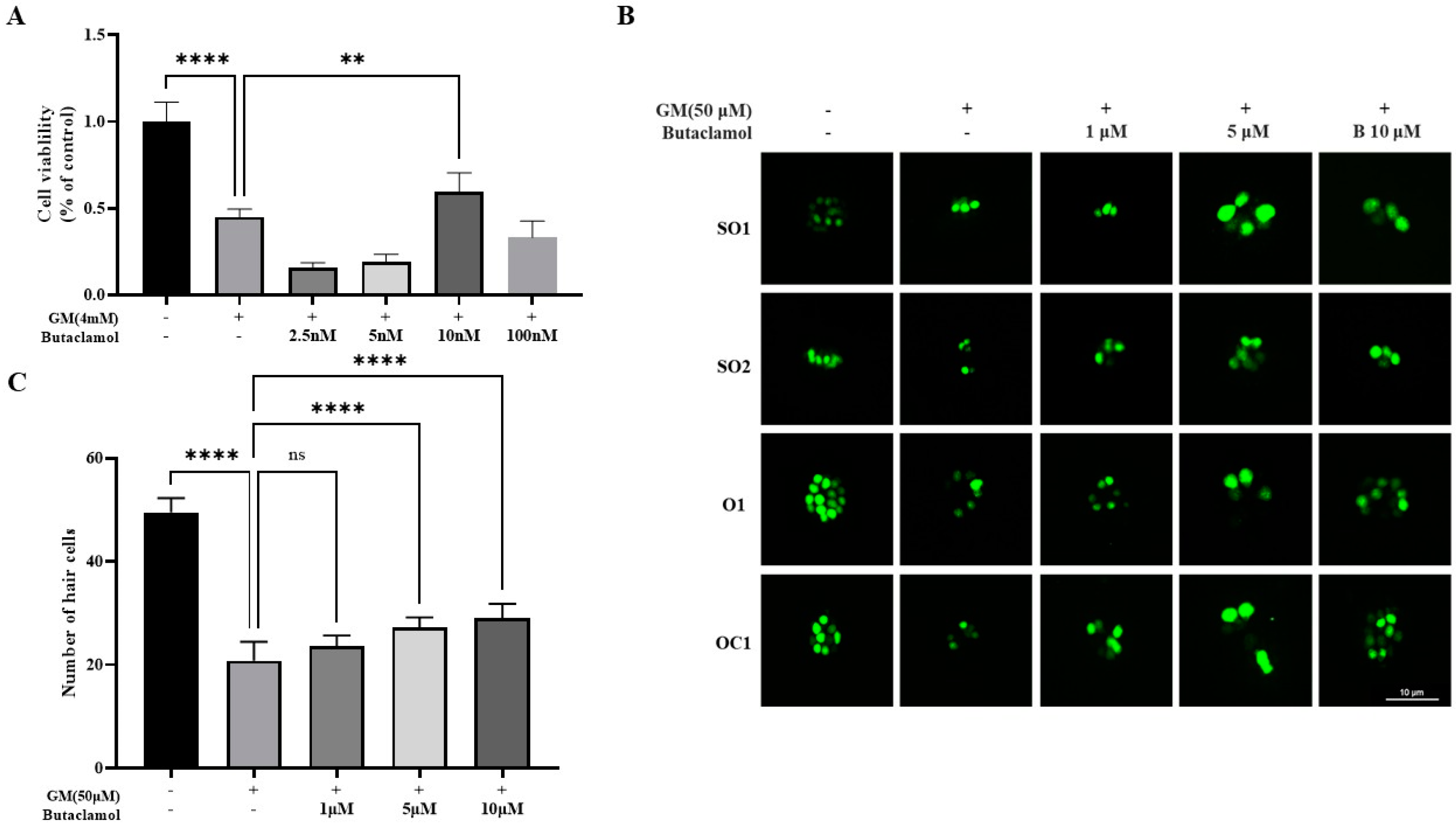
2.1. (-)-Butaclamol Protects Against Gentamicin-Induced Ototoxicity in Both In Vitro and In Vivo Models
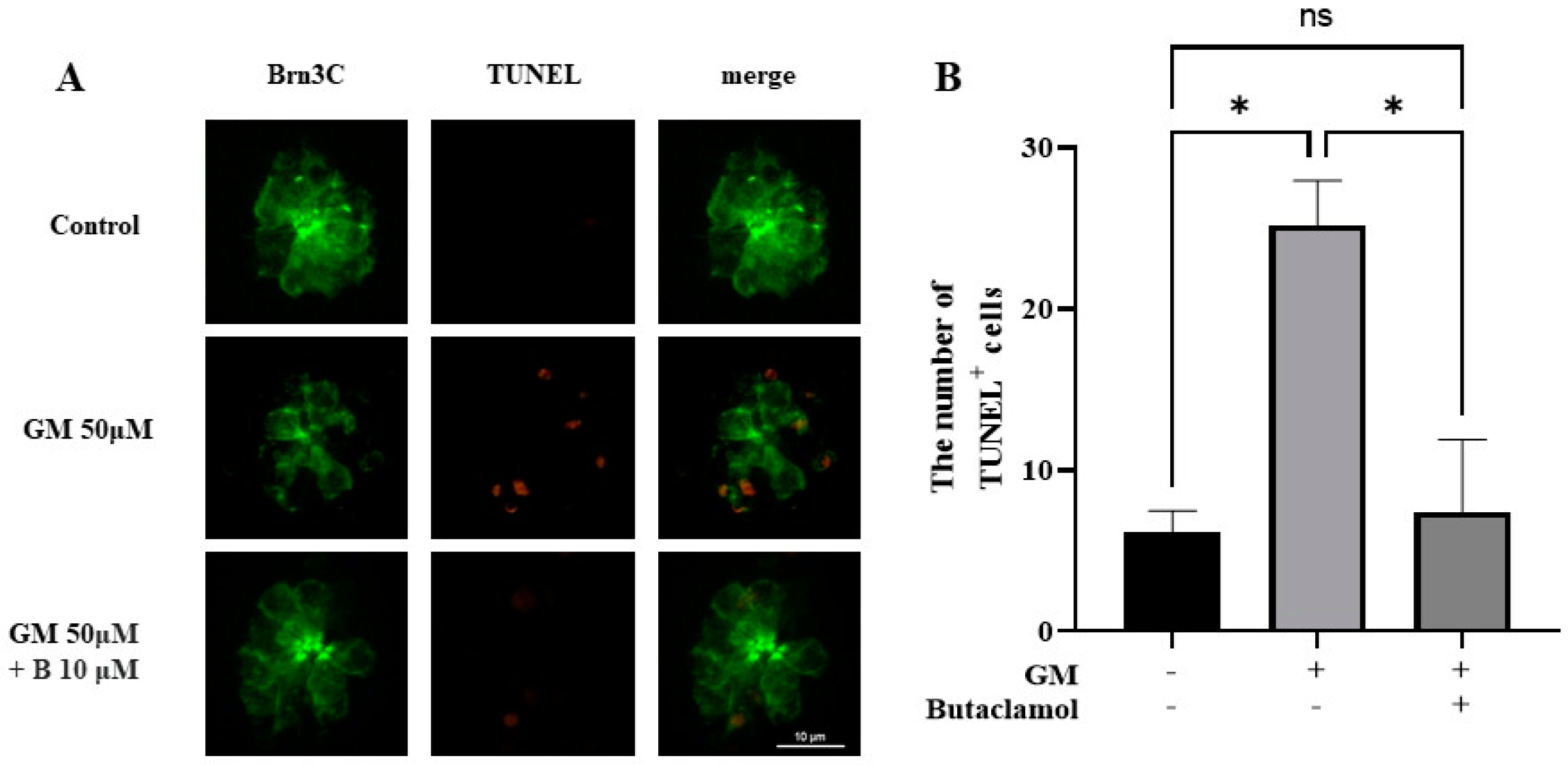
2.2. (-)-Butaclamol Reduces Gentamicin-Induced HC Apoptosis
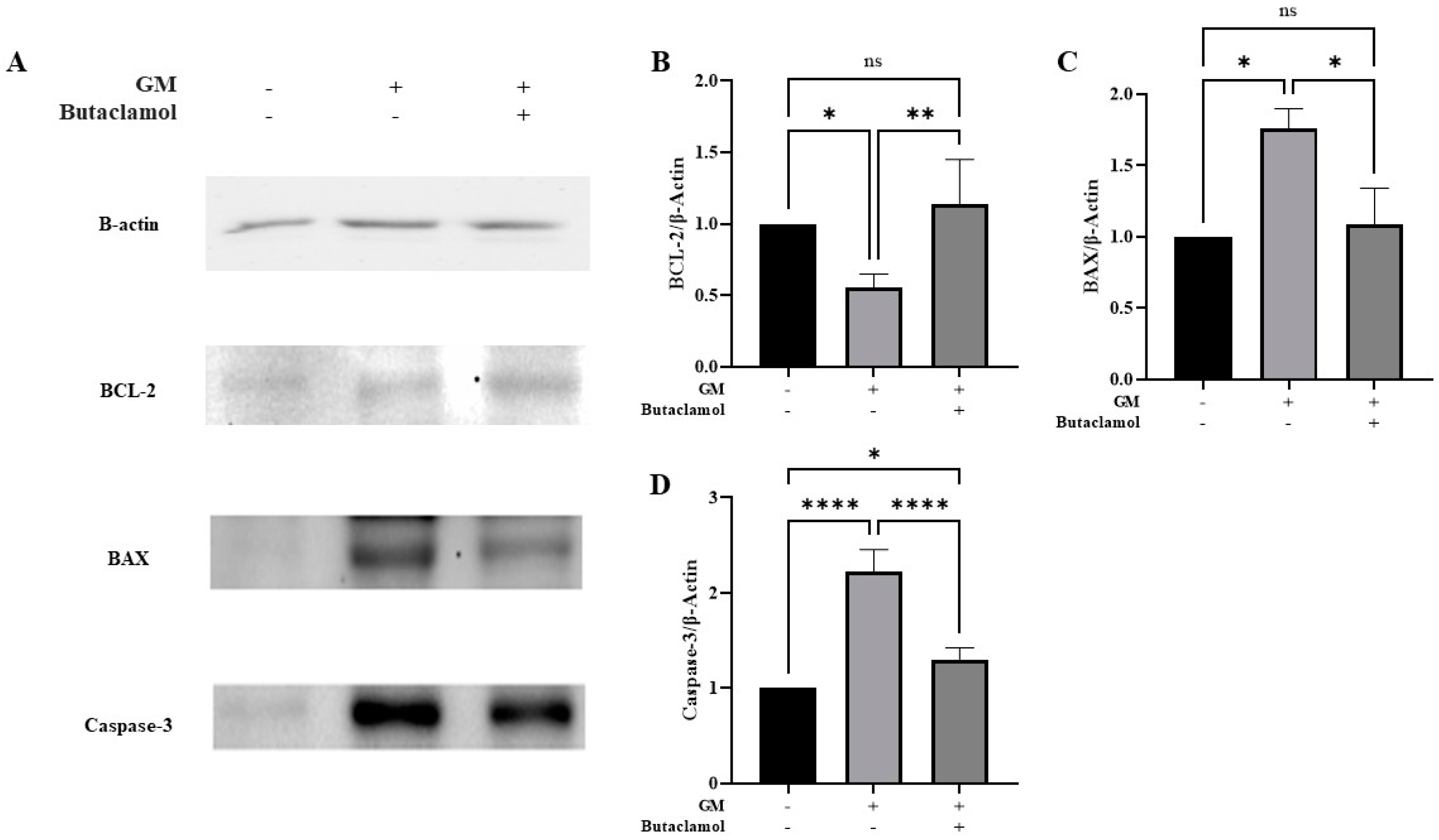
2.3. (-)-Butaclamol Attenuates Gentamicin-Induced Ototoxicity by Inhibiting Intrinsic Apoptotic Signaling
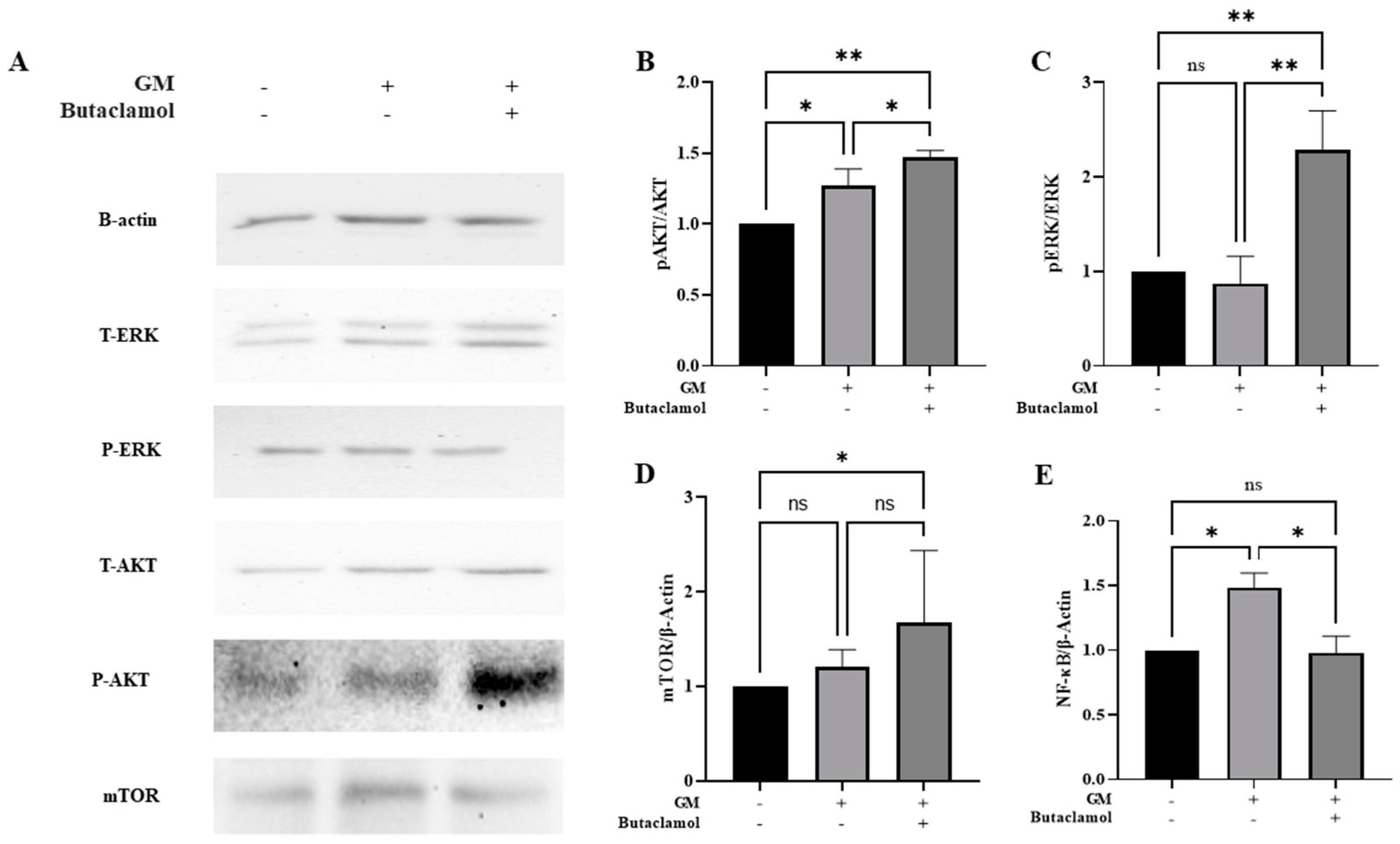
2.4. (-)-Butaclamol Enhances Cell Survival Through ERK and AKT/mTOR Pathway Activation in Gentamicin-Induced Ototoxicity
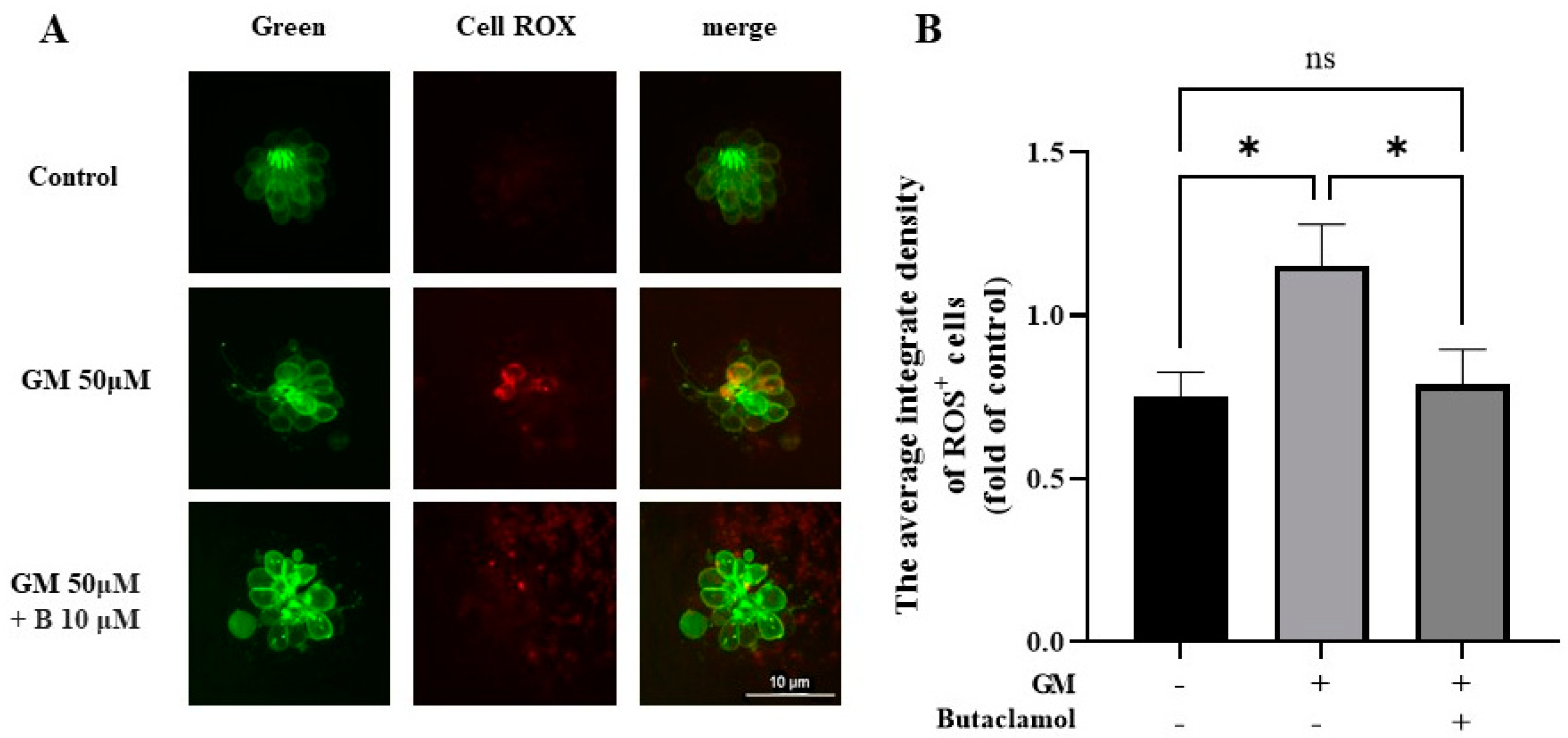
2.5. (-)-Butaclamol Exhibits a Significant Inhibitory Effect on ROS Production
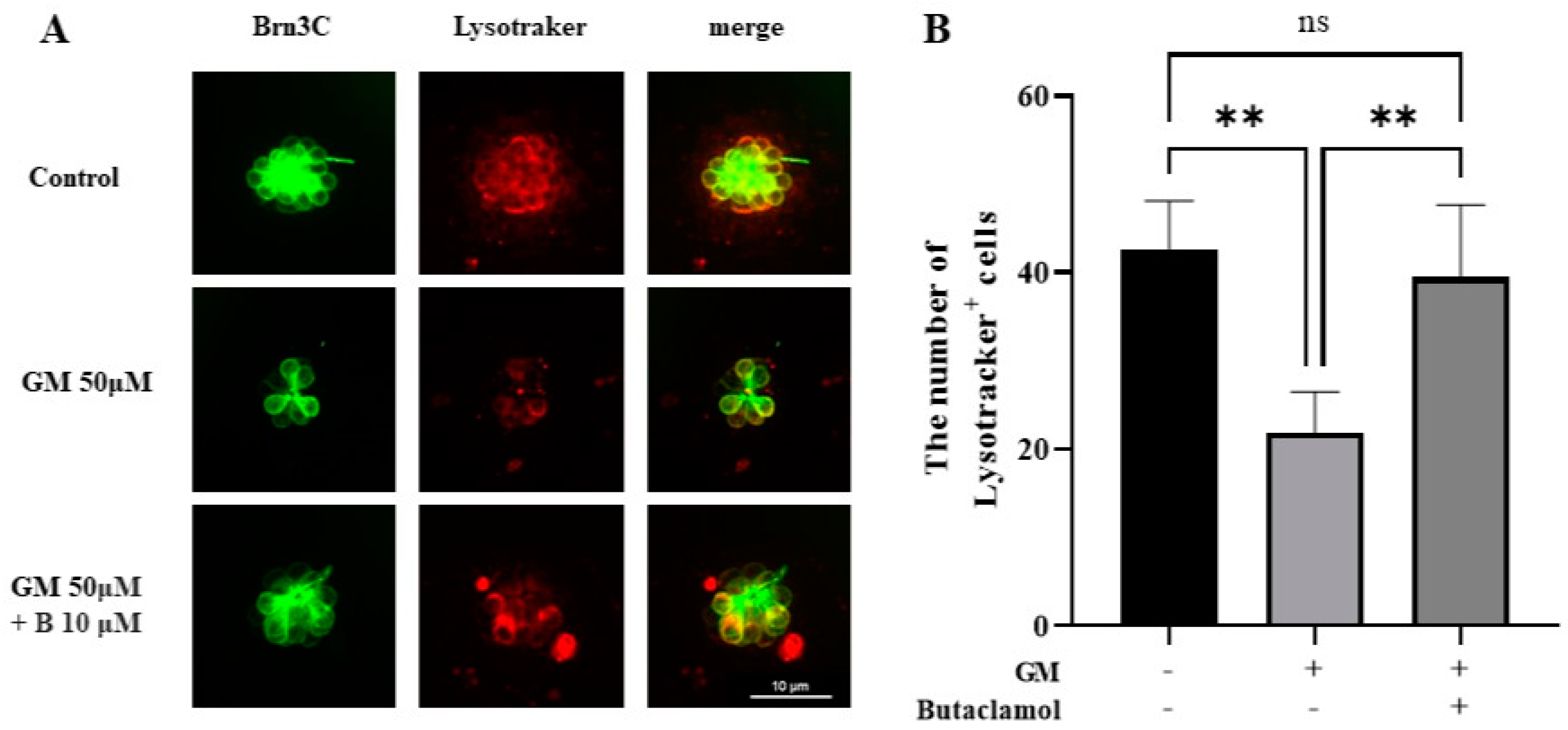
2.6. Autophagy Mediated by (-)-Butaclamol Protects HCs from Gentamicin-Induced Damage
2.7. (-)-Butaclamol Preserves Mitochondrial Membrane Potential in Gentamicin-Treated Zebrafish Hair Cells
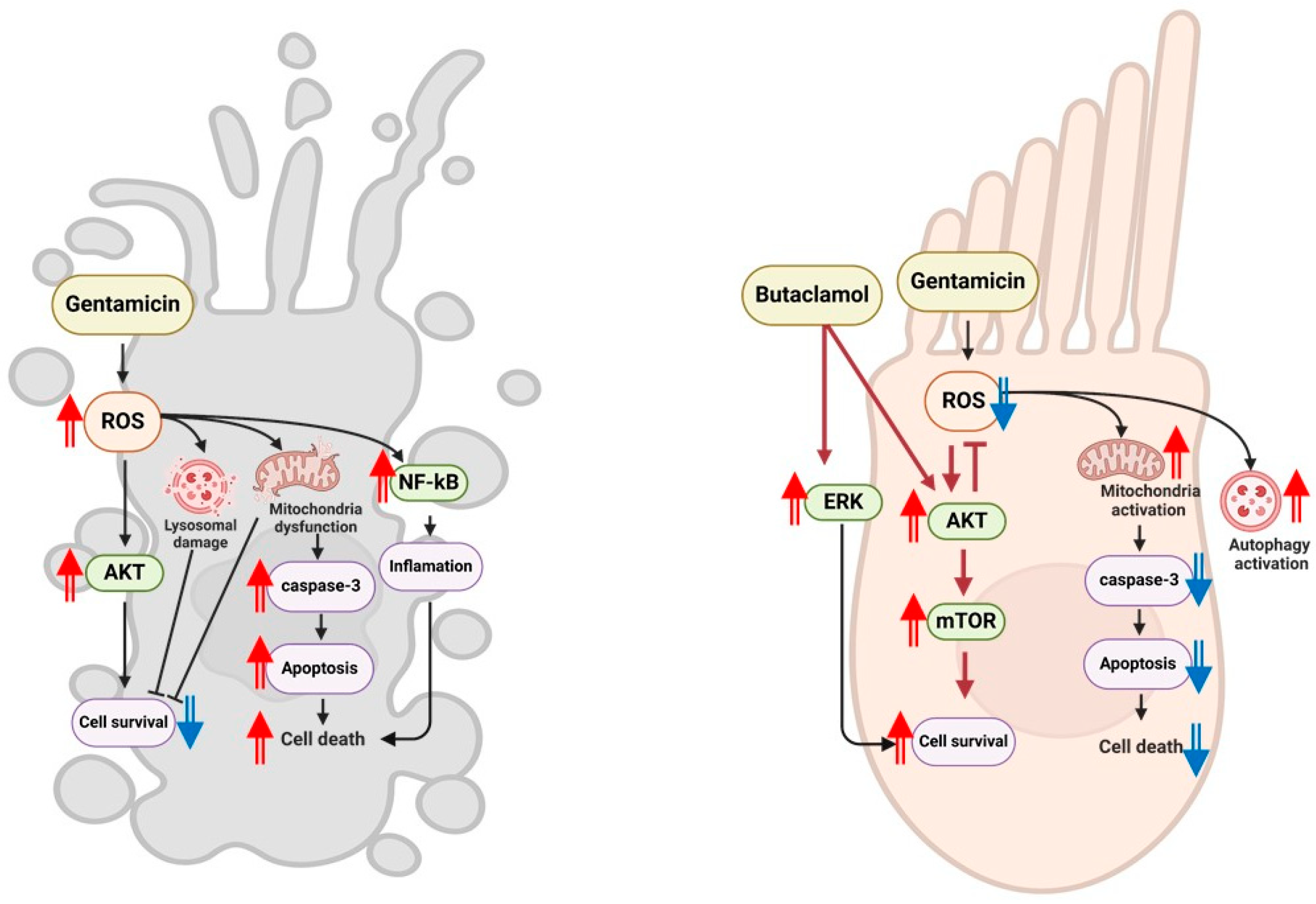
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. In Vitro Drug Screening
4.2. In Vitro Assay
4.3. Zebrafish Housing
4.4. Counting Hair Cells in Neuromasts
4.5. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyltransferase (TdT)-Mediated dUTP-Biotin Nick End Labeling (TUNEL) Assay
4.6. Quantifying ROS Levels in Hair Cells
4.7. Quantifying Mitochondrial Transmembrane Potential (ΔΨm) Loss in Hair Cells
4.8. Qualitative Analysis of Autophagy Activation
4.9. Western Blotting
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, K.; Wang, B.; Cao, B.; Ma, W.; Zhang, Y.; Cheng, Y.; Hu, J.; Gao, Y. Protective role of pyrroloquinoline quinone against gentamicin induced cochlear hair cell ototoxicity. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2024, 44, 235–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaafar, D.; Baxter, N.; Cranswick, N.; Christodoulou, J.; Gwee, A. Pharmacogenetics of aminoglycoside-related ototoxicity: A systematic review. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2024, 79, 1508–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Chen, L.; Li, Y.; Li, M.; Zhang, X.; Cui, L.; Sun, Y.; Song, X. Cortisol Sensitizes Cochlear Hair Cells to Gentamicin Ototoxicity Via Endogenous Apoptotic Pathway. Otol. Neurotol. 2024, 45, e49–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steyger, P.S. Mechanisms of Ototoxicity and Otoprotection. Otolaryngol. Clin. N. Am. 2021, 54, 1101–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, H.; Zong, T.; Liu, J.; Wang, D.; Gong, K.; Yin, H.; Zhang, W.; Xu, T.; Yang, R. Rutin Attenuates Gentamycin-induced Hair Cell Injury in the Zebrafish Lateral Line via Suppressing STAT1. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 61, 9548–9561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selimoglu, E. Aminoglycoside-induced ototoxicity. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2007, 13, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fogliano, C.; Motta, C.M.; Avallone, B. Salicylate attenuates gentamicin-induced ototoxicity and facilitates the recovery in the basilar papilla of the lizard Podarcis siculus. Neurotoxicology 2022, 93, 301–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kros, C.J.; Steyger, P.S. Aminoglycoside- and Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity: Mechanisms and Otoprotective Strategies. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2019, 9, a033548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Yang, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Jung, H.H.; Im, G.J. Calcium imaging in gentamicin ototoxicity: Increased intracellular calcium relates to oxidative stress and late apoptosis. Int. J. Pediatr. Otorhinolaryngol. 2011, 75, 1616–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Im, G.J.; Chang, J.; Chae, S.W.; Lee, S.H.; Kwon, S.Y.; Chung, A.Y.; Park, H.C.; Jung, H.H. Protective effects of apocynin on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in an auditory cell line and in zebrafish. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2013, 33, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Sun, Y.; Kuang, X.; Hou, S.; Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Liu, H. Mitochondria-targeting nanomedicine: An effective and potent strategy against aminoglycosides-induced ototoxicity. Eur. J. Pharm. Sci. 2019, 126, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rampino, A.; Marakhovskaia, A.; Soares-Silva, T.; Torretta, S.; Veneziani, F.; Beaulieu, J.M. Antipsychotic Drug Responsiveness and Dopamine Receptor Signaling; Old Players and New Prospects. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeman, P. Dopamine D2 receptors as treatment targets in schizophrenia. Clin. Schizophr. Relat. Psychoses 2010, 4, 56–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukardi, H.; Chng, H.T.; Chan, E.C.; Gong, Z.; Lam, S.H. Zebrafish for drug toxicity screening: Bridging the in vitro cell-based models and in vivo mammalian models. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2011, 7, 579–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinec, G.M.; Park, C.; Thein, P.; Kalinec, F. Working with Auditory HEI-OC1 Cells. J. Vis. Exp. 2016, 115, 54425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalinec, G.; Thein, P.; Park, C.; Kalinec, F. HEI-OC1 cells as a model for investigating drug cytotoxicity. Hear. Res. 2016, 335, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustad, E.; Mudrock, E.; Nilles, E.M.; McQuate, A.; Bergado, M.; Gu, A.; Galitan, L.; Gleason, N.; Ou, H.C.; Raible, D.W.; et al. In vivo screening for toxicity-modulating drug interactions identifies antagonism that protects against ototoxicity in zebrafish. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1363545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, K.H.; Park, S.; Han, E.; Yoon, H.S.; Lee, Y.; Hong, S.; Hyun, K.; Baek, S.H.; Baek, H.W.; Chan Rah, Y.; et al. Protective effects of Y-27632 against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity: A zebrafish model Y-27632 and cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2024, 190, 114792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, H.; Simon, J.A.; Rubel, E.W.; Raible, D.W. Screening for chemicals that affect hair cell death and survival in the zebrafish lateral line. Hear. Res. 2012, 288, 58–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Li, L.; Tang, L.; Peijnenburg, W.; Zhang, H.; Xie, D.; Geng, R.; Zheng, T.; Bi, L.; Wei, X.; et al. Ototoxicity of polystyrene nanoplastics in mice, HEI-OC1 cells and zebrafish. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2024, 17, 1345536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmgren, M.; Sheets, L. Using the Zebrafish Lateral Line to Understand the Roles of Mitochondria in Sensorineural Hearing Loss. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 628712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, X.; Yin, N.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Y.; Ji, L.; Zhang, B.; Hu, H. Mangiferin alleviates cisplatin-induced ototoxicity in sensorineural hearing loss. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 178, 117174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, F.; Wei, G.; Gao, Y.; Wang, X.; Gong, J.; Guo, C.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X.; Zhao, J.; Wang, C.; et al. Single-cell RNA-sequencing of zebrafish hair cells reveals novel genes potentially involved in hearing loss. Cell Mol. Life Sci. 2022, 79, 385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Xu, N.; Chen, P.; Liu, Y.; Qi, X.; Liu, S.; Li, C.; Tang, J. Rapamycin Protects Spiral Ganglion Neurons from Gentamicin-Induced Degeneration In Vitro. J. Assoc. Res. Otolaryngol. 2019, 20, 475–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasudevan Sajini, D.; Thaggikuppe Krishnamurthy, P.; Chakkittukandiyil, A.; Mudavath, R.N. Orientin Modulates Nrf2-ARE, PI3K/Akt, JNK-ERK1/2, and TLR4/NF-kB Pathways to Produce Neuroprotective Benefits in Parkinson’s Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2024, 49, 1577–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiau, J.P.; Chuang, Y.T.; Tang, J.Y.; Yang, K.H.; Chang, F.R.; Hou, M.F.; Yen, C.Y.; Chang, H.W. The Impact of Oxidative Stress and AKT Pathway on Cancer Cell Functions and Its Application to Natural Products. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K.; Suzuki, Y.; Fujimoto, C.; Kanzaki, S. Molecular Mechanisms and Biological Functions of Autophagy for Genetics of Hearing Impairment. Genes 2020, 11, 1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, C.; Müller, U.; Zhao, B. Autophagy proteins are essential for aminoglycoside-induced hearing loss. Autophagy 2023, 19, 1599–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Liu, Y.; Muhammad, W.; Liu, D.; Wang, J.; Zhou, H.; Gao, X.; Qian, X. Autophagy-related protein 12 associates with anti-apoptotic B cell lymphoma-2 to promote apoptosis in gentamicin-induced inner ear hair cell loss. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 15, 3819–3825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, H.; Li, H.; Zhou, M.; Sun, G.; Cao, Z.; Man, R.; Wang, H.; Li, J. PINK1 Protects Against Gentamicin-Induced Sensory Hair Cell Damage: Possible Relation to Induction of Autophagy and Inhibition of p53 Signal Pathway. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Sullivan, J.D.B.; Bullen, A.; Mann, Z.F. Mitochondrial form and function in hair cells. Hear. Res. 2023, 428, 108660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, G.; Gao, Y.; Wu, H.; Zhao, T. Gentamicin administration leads to synaptic dysfunction in inner hair cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2024, 391, 86–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youle, R.J.; Strasser, A. The BCL-2 protein family: Opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tait, S.W.; Green, D.R. Mitochondria and cell death: Outer membrane permeabilization and beyond. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 621–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chipuk, J.E.; Bouchier-Hayes, L.; Green, D.R. The BCL-2 family reunion. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Westphal, D.; Dewson, G.; Czabotar, P.E.; Kluck, R.M. Molecular biology of Bax and Bak activation and action. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2011, 1813, 521–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinou, J.C.; Youle, R.J. Mitochondria in apoptosis: Bcl-2 family members and mitochondrial dynamics. Dev. Cell 2011, 21, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Ifuku, M.; Take, S.; Kawamura, J.; Miake, K.; Katafuchi, T. Plasmalogens rescue neuronal cell death through an activation of AKT and ERK survival signaling. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e83508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugiura, R.; Satoh, R.; Takasaki, T. ERK: A Double-Edged Sword in Cancer. ERK-Dependent Apoptosis as a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer. Cells 2021, 10, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, T.; Liu, M.; Ji, B.; Bai, B.; Cheng, B.; Wang, C. Role of the Extracellular Signal-Regulated Kinase 1/2 Signaling Pathway in Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Wang, W.; Chang, X.; Chen, C.; Guo, Z.; Yu, G.; Shao, W.; Wu, S.; Zhang, Q.; Zheng, F.; et al. ROS/mtROS promotes TNTs formation via the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway to protect against mitochondrial damages in glial cells induced by engineered nanomaterials. Part. Fibre Toxicol. 2024, 21, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Hu, X.; Liu, Y.; Dong, S.; Wen, Z.; He, W.; Zhang, S.; Huang, Q.; Shi, M. ROS signaling under metabolic stress: Cross-talk between AMPK and AKT pathway. Mol. Cancer. 2017, 16, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; Chai, R. Regulation of autophagy: A promising therapeutic target for the treatment of hearing loss. J. Bio-X Res. 2019, 2, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hong, S.; Han, E.; Park, S.; Hyun, K.; Lee, Y.; Baek, H.w.; Kim, H.-J.; Rah, Y.C.; Choi, J. Protective Effects of (-)-Butaclamol Against Gentamicin-Induced Ototoxicity: In Vivo and In Vitro Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 4201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094201
Hong S, Han E, Park S, Hyun K, Lee Y, Baek Hw, Kim H-J, Rah YC, Choi J. Protective Effects of (-)-Butaclamol Against Gentamicin-Induced Ototoxicity: In Vivo and In Vitro Approaches. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(9):4201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094201
Chicago/Turabian StyleHong, Sumin, Eunjung Han, Saemi Park, Kyungtae Hyun, Yunkyoung Lee, Hyun woo Baek, Hwee-Jin Kim, Yoon Chan Rah, and June Choi. 2025. "Protective Effects of (-)-Butaclamol Against Gentamicin-Induced Ototoxicity: In Vivo and In Vitro Approaches" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 9: 4201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094201
APA StyleHong, S., Han, E., Park, S., Hyun, K., Lee, Y., Baek, H. w., Kim, H.-J., Rah, Y. C., & Choi, J. (2025). Protective Effects of (-)-Butaclamol Against Gentamicin-Induced Ototoxicity: In Vivo and In Vitro Approaches. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(9), 4201. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26094201





