The Role of the p21-Activated Kinase Family in Tumor Immunity
Abstract
1. Introduction
1.1. PAK Family
1.2. PAK Structure
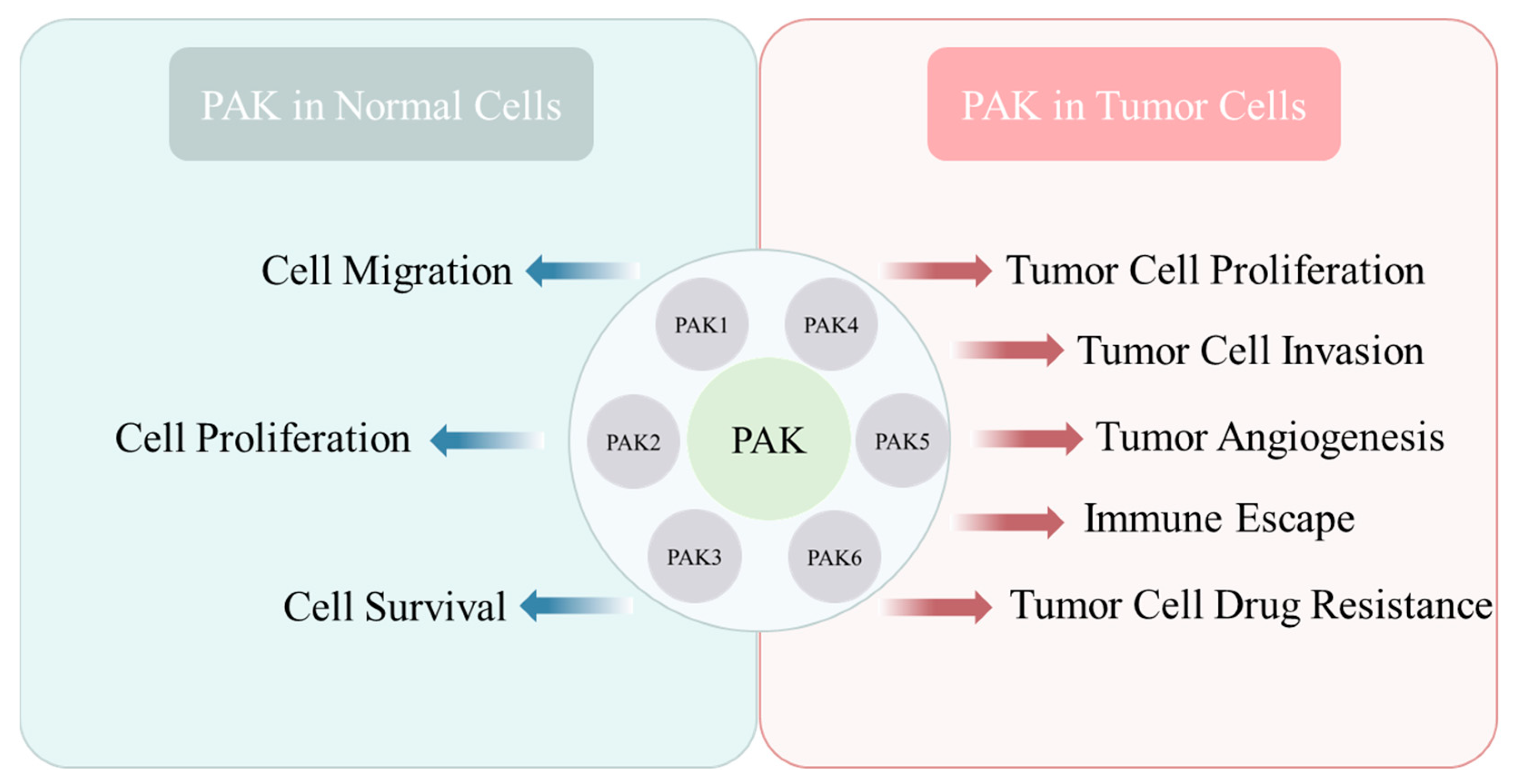
1.3. Functions of PAKs
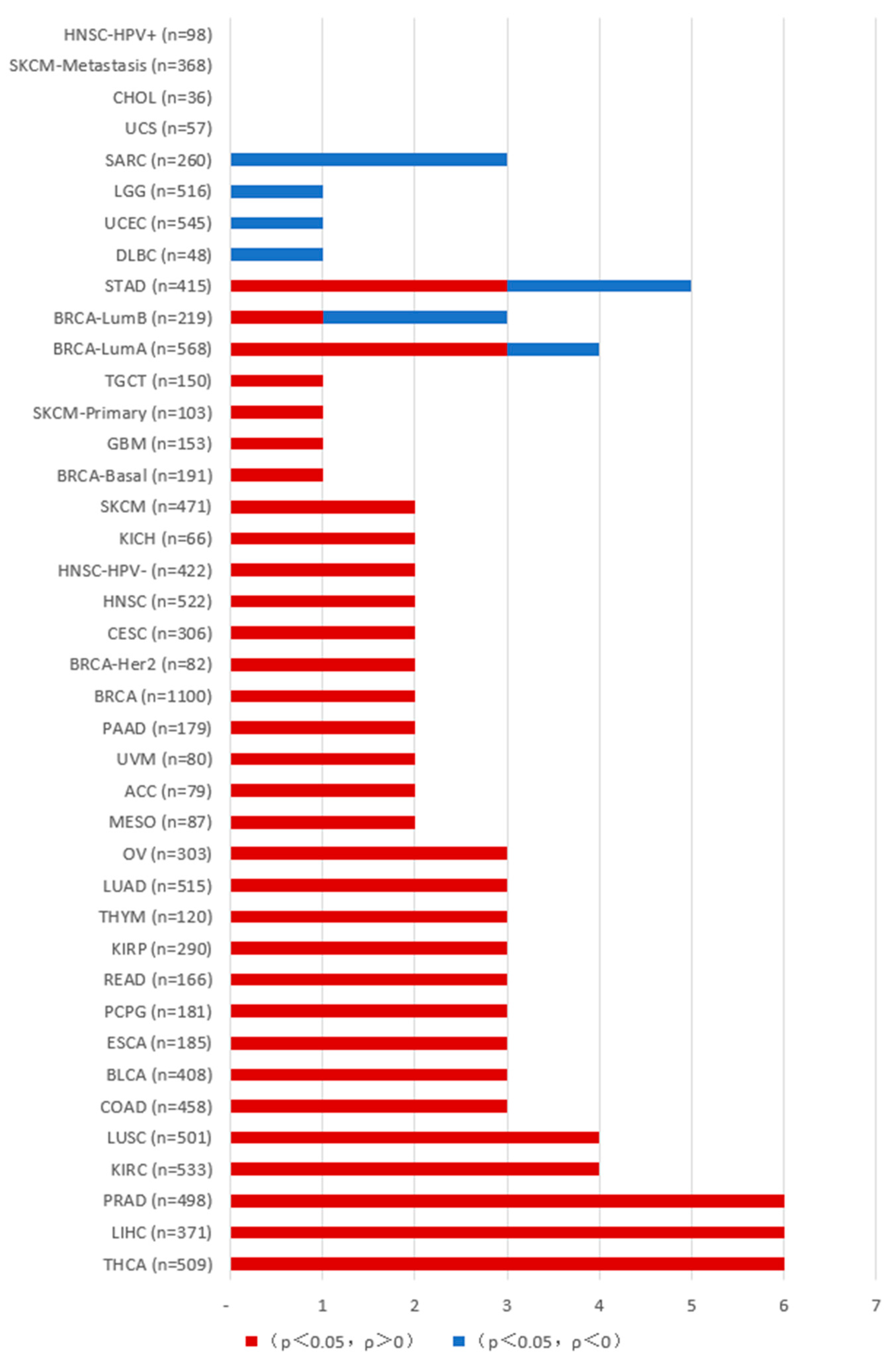
1.4. Role of PAKs in Tumor Development
2. PAKs and Tumor Immunity
2.1. Basic Concepts of Tumor Immunity and Tumor Microenvironment
2.2. PAKs in Tumor Immunity
3. PAK and Small-Molecule Inhibitors
3.1. Group I PAK Inhibitors
| Inhibitors | Discovery Time | Action Site | Biological Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| IPA3 | 2008 | PAK1 regulatory domain | IPA-3 is a selective non-ATP competitive PAK1 inhibitor with IC50 of 2.5 μM, and shows no inhibition to group II PAKs |
| FRAX597 | 2013 | M344 gatekeeper residue and the C-helix in PAK1 | FRAX597 is determined to be a potent, ATP-competitive inhibitor of Group I PAKs (PAK 1-3), with IC50 of 8, 13 and 19 nM for PAK1, 2 and 3. |
| FRAX486 | 2013 | ATP pocket of PAK1 | Inhibition of PAK1/2 phosphorylation, with IC50s of 14, 33 and 39 nM for PAK1, 2 and 3. |
| NVS-PAK1-1 | 2015 | S144 of PAK1 | NVS-PAK1-1 is a potent and selective allosteric PAK1 inhibitor, with an IC50 of 5 nM. |
| FRAX1036 | 2015 | S338 of PAK1 | FRAX1036 is a PAK inhibitor, with Kis of 23.3 nM, 72.4 nM, and 2.4 μM for PAK1, PAK2 and PAK4. |
| G-5555 | 2015 | K299/M344/D398 of PAK1 | G-5555 inhibits the phosphorylation of MEK1(S298), a downstream substrate of PAK1/2, with Kis of 3.7 nM and 11 nM for PAK1 and PAK2. |
| ARC (Artemisinin C) | 2015 | Rac/Cdc42 | ARC may block PAK1 activation induced by Rac/Cdc42. |
| G9791 | 2016 | K299/E315 of PAK1 | A poyridone side chain analogue with Kis values of 0.95 nM and 2.0 nM for PAK1 and PAK2, respectively |
| CAPE (Caffeic Acid Phenethyl Ester) | 2017 | Rac1 | Inactivation of PAK1 by down-regulating the activity of NADPH oxidase. |
| CP734 | 2020 | V342 of PAK1 | CP734 targets the residue V342 of PAK1 and inhibits its ATP activity with an IC50 value of 15.27 μM and without significant inhibitory effect on PAK2, PAK3 or PAK6 [135]. |
| BJG-05-039 | 2022 | S298 of PAK1 | BJG-05-039 inhibits the phosphorylation of MEK S298, thereby reducing the activity of PAK1 [132]. |
3.2. Group II PAK Inhibitors
4. Conclusions and Outlook
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yun, J.; Kim, S.Y.; Yoon, K.S.; Shin, H.; Jeong, H.-S.; Chung, H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Shin, J.; Cha, H.J.; Han, K.M.; et al. P21 (Cdc42/Rac)-activated kinase 1 (pak1) is associated with cardiotoxicity induced by antihistamines. Arch. Pharmacal. Res. 2016, 39, 1644–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, M.; Lu, W.; Meng, W.; Parrini, M.-C.; Eck, M.J.; Mayer, B.J.; Harrison, S.C. Structure of PAK1 in an autoinhibited conformation reveals a multistage activation switch. Cell 2000, 102, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Xu, Y.; Qin, X.; Tao, M.; Gu, X.; Shen, L.; Chen, Y.; Zheng, M.; Qin, S.; Wu, G.; et al. RUNX1, FUS, and ELAVL1-induced circPTPN22 promote gastric cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through miR-6788-5p/PAK1 axis-mediated autophagy. Cell. Mol. Biol. Lett. 2024, 29, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Ren, M.; Li, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Su, J.; Su, B.; Xia, H.; Liu, F.; Jiang, H.; et al. Knockdown of RhoGDI2 represses human gastric cancer cell proliferation, invasion and drug resistance via the Rac1/Pak1/LIMK1 pathway. Cancer Lett. 2020, 492, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Fu, M.; Wang, L.; Liu, J.; Li, Y.; Brakebusch, C.; Mei, Q. p21-activated kinase 1 (PAK1) can promote ERK activation in a kinase-independent manner. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 20093–20099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Baba, C.; Mahadevan, V.; Fahlbusch, F.B.; S, S.M.; Rau, T.T.; Gali-Muhtasib, H.; Schneider-Stock, R. Thymoquinone-induced conformational changes of PAK1 interrupt prosurvival MEK-ERK signaling in colorectal cancer. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, S.; Dai, M.; Liu, Z.; Ma, Y.; Shang, H.; Cao, Y.; Wang, Q. The guanine nucleotide exchange factor Net1 facilitates the specification of dorsal cell fates in zebrafish embryos by promoting maternal β-catenin activation. Cell Res. 2017, 27, 202–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belli, S.; Esposito, D.; Allotta, A.; Servetto, A.; Ciciola, P.; Pesapane, A.; Ascione, C.M.; Napolitano, F.; Di Mauro, C.; Vigliar, E.; et al. Pak1 pathway hyper-activation mediates resistance to endocrine therapy and CDK4/6 inhibitors in ER+ breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2023, 9, 48. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Y.; Wang, X.; Guo, Q.; Zhang, J.; Li, J.; Han, Y.; Miao, Z.; Li, F. PAK1 regulates RUFY3-mediated gastric cancer cell migration and invasion. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dammann, K.; Khare, V.; Gasche, C. Tracing PAKs from GI inflammation to cancer. Gut 2014, 63, 1173–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.; Wen, W.; Rayala, S.K.; Chen, M.; Ma, J.; Zhang, M.; Kumar, R. Serine 88 phosphorylation of the 8-kDa dynein light chain 1 is a molecular switch for its dimerization status and functions. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 4004–4013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, K.H.; Huynh, N.; Patel, O.; Shulkes, A.; Baldwin, G.; He, H. P21-activated kinase 1 promotes colorectal cancer survival by up-regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α. Cancer Lett. 2013, 340, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouquette-Jazdanian, A.K.; Kortum, R.L.; Li, W.; Merrill, R.K.; Nguyen, P.H.; Samelson, L.E.; Sommers, C.L. miR-155 Controls Lymphoproliferation in LAT Mutant Mice by Restraining T-Cell Apoptosis via SHIP-1/mTOR and PAK1/FOXO3/BIM Pathways. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0131823. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Shukla, S.; Farhan, M.; Sinha, S.; Lakra, A.D.; Penta, D.; Kannan, A.; Meeran, S.M. Centchroman prevents metastatic colonization of breast cancer cells and disrupts angiogenesis via inhibition of RAC1/PAK1/β-catenin signaling axis. Life Sci. 2020, 256, 117976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Villasana, V.; Fuentes-Mattei, E.; Ivan, C.; Dalton, H.J.; Rodriguez-Aguayo, C.; Fernandez-de Thomas, R.J.; Aslan, B.; del CMonroig, P.; Velazquez-Torres, G.; Previs, R.A.; et al. Rac1/Pak1/p38/MMP-2 Axis Regulates Angiogenesis in Ovarian Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2015, 21, 2127–2137. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Li, C.-F.; Chan, T.-C.; Fang, F.-M.; Yu, S.-C.; Huang, H.-Y. PAK1 overexpression promotes myxofibrosarcoma angiogenesis through STAT5B-mediated CSF2 transactivation: Clinical and therapeutic relevance of amplification and nuclear entry. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2023, 19, 3920–3936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Zhang, C.; Zheng, Q.; Ma, Z.; Qi, M.; Di, G.; Ling, S.; Xu, H.; Qi, B.; Yao, C.; et al. RhoJ facilitates angiogenesis in glioblastoma via JNK/VEGFR2 mediated activation of PAK and ERK signaling pathways. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2022, 18, 942–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Shin, S.H.; Chen, H.; Liu, T.; Li, Z.; Hu, Y.; Liu, F.; Zhang, C.; Kim, D.J.; Liu, K.; et al. CDK12 and PAK2 as novel therapeutic targets for human gastric cancer. Theranostics 2020, 10, 6201–6215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buikhuisen, J.Y.; Barila, P.M.G.; Cameron, K.; Suijkerbuijk, S.J.E.; Lieftink, C.; di Franco, S.; Garcia, A.K.; Castro, R.U.; Lenos, K.J.; Nijman, L.E.; et al. Subtype-specific kinase dependency regulates growth and metastasis of poor-prognosis mesenchymal colorectal cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2023, 42, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, S.; Wan, X.; Chen, S.; Hu, Y.; Liu, X. p21-activated kinase 2 binds to transcription factor SOX2 and up-regulates DEK to promote the progression of lung squamous cell carcinoma. Mod. Pathol. 2022, 102, 1109–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Kenney, S.R.; Muller, C.Y.; Adams, S.; Rutledge, T.; Romero, E.; Murray-Krezan, C.; Prekeris, R.; Sklar, L.A.; Hudson, L.G.; et al. R-Ketorolac Targets Cdc42 and Rac1 and Alters Ovarian Cancer Cell Behaviors Critical for Invasion and Metastasis. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2015, 14, 2215–2227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Wang, J.; Xu, R.; Huang, X.; Li, Q.; Zhang, C.; Yuan, B. PAK2 promotes proliferation, migration, and invasion of lung squamous cell carcinoma through LIMK1/cofilin signaling pathway. J. Biomed. Res. 2024, 38, 184–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nuche-Berenguer, B.; Ramos-Álvarez, I.; Jensen, R. The p21-activated kinase, PAK2, is important in the activation of numerous pancreatic acinar cell signaling cascades and in the onset of early pancreatitis events. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Basis Dis. 2016, 1862, 1122–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, J.; Wang, Z.; Xu, H.; Liu, C.; Wei, Z.; Zhao, L.; Ren, L. Pak2 inhibition promotes resveratrol-mediated glioblastoma A172 cell apoptosis via modulating the AMPK-YAP signaling pathway. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 6563–6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, C.; Wang, Q.; Mi, J.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, L.; Geng, Z.; Song, X.; Ge, S.; et al. miR-107 regulates the effect of MCM7 on the proliferation and apoptosis of colorectal cancer via the PAK2 pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2021, 190, 114610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Li, Z.; Zhu, S.; Wang, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, D.; Zhang, M.; Zhu, W.; Xu, W.; Xu, C. Molecular mechanisms of pancreatic cancer liver metastasis: The role of PAK2. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1347683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Z.; Zhong, M.; Ye, Z.; Wu, Z.; Xiong, Y.; Ma, J.; Chen, H.; Zhu, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; et al. PAK3 promotes the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by regulating EMT process. J. Cancer 2022, 13, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; Du, R.; Jia, X.; Liu, K.; Qiao, Y.; Wu, Q.; Yao, N.; Yang, L.; Zhou, L.; Liu, X.; et al. CDK15 promotes colorectal cancer progression via phosphorylating PAK4 and regulating β-catenin/MEK-ERK signaling pathway. Cell Death Differ. 2022, 29, 14–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chi, X.-J.; Song, Y.-B.; Zhang, H.; Wei, L.-Q.; Gao, Y.; Miao, X.-J.; Yang, S.-T.; Lin, C.-Y.; Lan, D.; Zhang, X. TBC1D10B promotes tumor progression in colon cancer via PAK4-mediated promotion of the PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway. Apoptosis 2024, 29, 1185–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siu, M.K.Y.; Chan, H.Y.; Kong, D.S.H.; Wong, E.S.Y.; Wong, O.G.W.; Ngan, H.Y.S.; Tam, K.F.; Zhang, H.; Li, Z.; Chan, Q.K.Y.; et al. p21-activated kinase 4 regulates ovarian cancer cell proliferation, migration, and invasion and contributes to poor prognosis in patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 18622–18627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spratley, S.J.; Bastea, L.I.; Döppler, H.; Mizuno, K.; Storz, P. Protein Kinase D Regulates Cofilin Activity through p21-activated Kinase 4. J. Biol. Chem. 2011, 286, 34254–34261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.; Qu, J.-J.; Wang, K.; Li, B.-L.; Zhao, D.; Zhu, Y.-P.; Ye, L.; Lu, W.; Wan, X.-P. Cross-talk between p21-activated kinase 4 and ERα signaling triggers endometrial cancer cell proliferation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 68083–68094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, T.D.F.; Zhuang, T.; Lorent, J.; Turco, E.; Olofsson, H.; Masia-Balague, M.; Zhao, M.; Rabieifar, P.; Robertson, N.; Kuiper, R.; et al. PAK4 suppresses RELB to prevent senescence-like growth arrest in breast cancer. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Feng, J.; Zeng, D.; Ding, Y.; Yu, C.; Yang, B. PAK4 confers cisplatin resistance in gastric cancer cells via PI3K/Akt- and MEK/ERK-dependent pathways. Biosci. Rep. 2014, 34, e00094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Wang, T.; Liang, W.; Zhao, Q.; Yu, Q.; Ma, C.-M.; Zhuo, L.; Guo, D.; Zheng, K.; Zhou, C.; et al. PAK4 Phosphorylates Fumarase and Blocks TGFβ-Induced Cell Growth Arrest in Lung Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1383–1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, X.; Li, Y.; Shao, Y.; Xiao, J.; Zhu, G.; Li, F. PAK4 regulates G6PD activity by p53 degradation involving colon cancer cell growth. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e2820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Liu, F.; Cheng, Z.; Wang, D.; Wang, G.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Y.; Cao, L.; et al. Oncogenic PAK4 regulates Smad2/3 axis involving gastric tumorigenesis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3473–3484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kesanakurti, D.; Maddirela, D.; Banasavadi-Siddegowda, Y.K.; Lai, T.-H.; Qamri, Z.; Jacob, N.K.; Sampath, D.; Mohanam, S.; Kaur, B.; Puduvalli, V.K. A novel interaction of PAK4 with PPARγ to regulate Nox1 and radiation-induced epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in glioma. Oncogene 2017, 36, 5309–5320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.-T.; Lai, W.-L.; Liu, H.-F.; Wong, L.L.-Y.; Ng, I.O.-L.; Ching, Y.P. PAK4 Phosphorylates p53 at Serine 215 to Promote Liver Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2016, 76, 5732–5742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnesutta, N.; Minden, A. Death receptor-induced activation of initiator caspase 8 is antagonized by serine/threonine kinase PAK4. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 7838–7848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnesutta, N.; Qu, J.; Minden, A. The serine/threonine kinase PAK4 prevents caspase activation and protects cells from apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 14414–14419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kesanakurti, D.; Chetty, C.; Maddirela, D.R.; Gujrati, M.; Rao, J.S. Functional cooperativity by direct interaction between PAK4 and MMP-2 in the regulation of anoikis resistance, migration and invasion in glioma. Cell Death Dis. 2012, 3, e445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geng, N.; Li, Y.; Zhang, W.; Wang, F.; Wang, X.; Jin, Z.; Xing, Y.; Li, D.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; et al. A PAK5-DNPEP-USP4 axis dictates breast cancer growth and metastasis. Int. J. Cancer 2020, 146, 1139–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xing, Y.; Li, Y.; Hu, B.; Han, F.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Li, Y.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Jin, F.; et al. PAK5-mediated AIF phosphorylation inhibits its nuclear translocation and promotes breast cancer tumorigenesis. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 1315–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xing, Y.; Wang, X.; Hu, B.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, H.; Han, F.; Geng, N.; Wang, F.; Li, Y.; et al. PAK5 promotes RNA helicase DDX5 sumoylation and miRNA-10b processing in a kinase-dependent manner in breast cancer. Cell Rep. 2021, 37, 110127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Z.-P.; Jiang, B.-G.; Gu, X.-F.; Zhao, B.; Ge, R.-L.; Zhang, F.-B. P21-activated kinase 5 plays essential roles in the proliferation and tumorigenicity of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2014, 35, 82–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, J.; Li, K.; Li, M.; Wu, X.; Zhang, L.; Ding, Q.; Wu, W.; Yang, J.; Mu, J.; Wen, H.; et al. A role for p21-activated kinase 7 in the development of gastric cancer. FEBS J. 2013, 280, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fawdar, S.; Trotter, E.W.; Li, Y.; Stephenson, N.L.; Hanke, F.; Marusiak, A.A.; Edwards, Z.C.; Ientile, S.; Waszkowycz, B.; Miller, C.J.; et al. Targeted genetic dependency screen facilitates identification of actionable mutations in FGFR4, MAP3K9, and PAK5 in lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12426–12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, D.; Pan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, P.; Fang, X. PAK5 Induces EMT and Promotes Cell Migration and Invasion by Activating the PI3K/AKT Pathway in Ovarian Cancer. Anal. Cell. Pathol. 2018, 2018, 8073124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, F.-C.; Pan, Y.-J.; Li, T.-T.; Mou, J.; Pei, D.-S. PAK5 promotes the migration and invasion of cervical cancer cells by phosphorylating SATB1. Cell Death Differ. 2019, 26, 994–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.-X.; Wang, X.-X.; Zhang, S.-N.; Wu, J.-X.; Qian, H.-Y.; Wen, Y.-Y.; Tian, H.; Pei, D.-S.; Zheng, J.-N. Downregulation of PAK5 inhibits glioma cell migration and invasion potentially through the PAK5-Egr1-MMP2 signaling pathway. Brain Tumor Pathol. 2014, 31, 234–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Li, X.; Guo, B.; Ke, Q.; Dong, M.; Li, F. PAK5-mediated E47 phosphorylation promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition and metastasis of colon cancer. Oncogene 2016, 35, 1943–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotteret, S.; Jaffer, Z.M.; Beeser, A.; Chernoff, J. p21-Activated kinase 5 (Pak5) localizes to mitochondria and inhibits apoptosis by phosphorylating BAD. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003, 23, 5526–5539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zheng, J.; Zhang, C.; Li, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Xing, B.; Du, X. p21-activated kinase 6 controls mitosis and hepatocellular carcinoma progression by regulating Eg5. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)-Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 118888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Li, Y.; Gu, H.; Zhu, G.; Li, J.; Cao, L.; Li, F. p21-Activated kinase 6 (PAK6) inhibits prostate cancer growth via phosphorylation of androgen receptor and tumorigenic E3 ligase murine double minute-2 (Mdm2). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 3359–3369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, F.-Y.; Wong, D.K.-H.; Mak, L.-Y.; Cheung, T.-T.; Zhang, S.-S.; Chau, H.-T.; Hui, R.W.-H.; Seto, W.-K.; Yuen, M.-F. FAT4 loss initiates hepatocarcinogenesis through the switching of canonical to noncanonical WNT signaling pathways. Hepatol. Commun. 2023, 7, e0338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pipili, A.; Babteen, N.A.; Kuwair, L.; Jannet, M.B.; Quist, J.; Ong, K.K.; Pitaluga, R.; Grigoriadis, A.G.; Tutt, A.; Wells, C.M. PAK6 acts downstream of IQGAP3 to promote contractility in triple negative breast cancer cells. Cell. Signal. 2024, 121, 111233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fram, S.; King, H.; Sacks, D.B.; Wells, C.M. A PAK6-IQGAP1 complex promotes disassembly of cell-cell adhesions. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2014, 71, 2759–2773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Wei, Z.; Wang, J.; Liu, P.; Qin, Y.; Zhong, M. MicroRNA-429 inhibits the migration and invasion of colon cancer cells by targeting PAK6/cofilin signaling. Oncol. Rep. 2015, 34, 707–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, Y.; Liu, T.; Hu, B.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Liu, T.; Li, F. Mitochondrial PAK6 inhibits prostate cancer cell apoptosis via the PAK6-SIRT4-ANT2 complex. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2571–2586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, W.; Han, Z.; Sun, Z.; Feng, H.; Zhao, L.; Yuan, Q.; Chen, C.; Yu, S.; Hu, Y.; Yu, J.; et al. PAK6 promotes homologous-recombination to enhance chemoresistance to oxaliplatin through ATR/CHK1 signaling in gastric cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kou, B.; Gao, Y.; Du, C.; Shi, Q.; Xu, S.; Wang, C.Q.; Wang, X.; He, D.; Guo, P. miR-145 inhibits invasion of bladder cancer cells by targeting PAK1. Urol. Oncol.-Semin. Orig. Investig. 2014, 32, 846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Gao, W.; Dou, Q.; Chen, H.; Li, Q.; Nice, E.C.; Huang, C. Ivermectin induces PAK1-mediated cytostatic autophagy in breast cancer. Autophagy 2016, 12, 2498–2499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shrestha, Y.; Schafer, E.J.; Boehm, J.S.; Thomas, S.R.; He, F.; Du, J.; Wang, S.; Barretina, J.; A Weir, B.; Zhao, J.J.; et al. PAK1 is a breast cancer oncogene that coordinately activates MAPK and MET signaling. Oncogene 2012, 31, 3397–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amaral, P.; Carbonell-Sala, S.; De La Vega, F.M.; Faial, T.; Frankish, A.; Gingeras, T.; Guigo, R.; Harrow, J.L.; Hatzigeorgiou, A.G.; Johnson, R.; et al. The status of the human gene catalogue. Nature 2023, 622, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Xu, J.; Gu, J. Prognostic significance of p21-activated kinase 6 expression in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, S575–S583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byun, J.-K.; Lee, S.; Kang, G.W.; Lee, Y.R.; Park, S.Y.; Song, I.-S.; Yun, J.W.; Lee, J.; Choi, Y.-K.; Park, K.-G. Macropinocytosis is an alternative pathway of cysteine acquisition and mitigates sorafenib-induced ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G. FER mediated HGF-independent regulation of HGFR/MET activates RAC1-PAK1 pathway to potentiate metastasis in ovarian cancer. Small GTPases 2020, 11, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Liu, H.; Xu, L.; An, H.; Liu, W.; Liu, Y.; Lin, Z.; Xu, J. p21-activated kinase 1 determines stem-like phenotype and sunitinib resistance via NF-κB/IL-6 activation in renal cell carcinoma. Cell Death Dis. 2015, 6, e1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siu, M.K.; Wong, E.S.; Chan, H.Y.; Kong, D.S.; Woo, N.W.; Tam, K.F.; Ngan, H.Y.; Chan, Q.K.; Chan, D.C.; Chan, K.Y.; et al. Differential expression and phosphorylation of Pak1 and Pak2 in ovarian cancer: Effects on prognosis and cell invasion. Int. J. Cancer 2010, 127, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.; Chen, Y.; Chen, D.; Li, Y.; Wang, T.; Zhu, J.; Hong, Q.; Li, Q. Circular RNA 0001789 sponges miR-140-3p and regulates PAK2 to promote the progression of gastric cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.-Y.; Yang, M.-C.; Ding, L.-Y.; Chen, C.S.; Chu, P.-C. p21-Activated kinase 3 promotes cancer stem cell phenotypes through activating the Akt-GSK3β-β-catenin signaling pathway in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2019, 456, 13–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, T.-Y.; Yang, Y.-C.; Wang, H.-P.; Tien, Y.-W.; Shun, C.-T.; Huang, H.-Y.; Hsiao, M.; Hua, K.-T. Pyruvate kinase M2 promotes pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma invasion and metastasis through phosphorylation and stabilization of PAK2 protein. Oncogene 2018, 37, 1730–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, N.; Ding, B.; Agler, M.; Cockett, M.; McPhee, F. Lethality of PAK3 and SGK2 shRNAs to human papillomavirus positive cervical cancer cells is independent of PAK3 and SGK2 knockdown. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0117357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magne, N.; Rousseau, V.; Duarte, K.; Poëa-Guyon, S.; Gleize, V.; Mutel, A.; Schmitt, C.; Castel, H.; Idbaih, A.; Huillard, E.; et al. PAK3 is a key signature gene of the glioma proneural subtype and affects its proliferation, differentiation and growth. Cell. Oncol. 2021, 44, 1257–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, W.; Azam, Z.; Guo, J.; To, S.S.T. Oncogenic potential of PIK3CD in glioblastoma is exerted through cytoskeletal proteins PAK3 and PLEK2. Lab. Investig. 2022, 102, 1314–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, L.; Gao, Y.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, D.; Li, J.; Liu, C.; Li, F. PAK4 phosphorylating RUNX1 promotes ERα-positive breast cancer-induced osteolytic bone destruction. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 2235–2247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santiago-Gómez, A.; Kedward, T.; Simões, B.M.; Dragoni, I.; NicAmhlaoibh, R.; Trivier, E.; Sabin, V.; Gee, J.M.; Sims, A.H.; Howell, S.J.; et al. PAK4 regulates stemness and progression in endocrine resistant ER-positive metastatic breast cancer. Cancer Lett. 2019, 458, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, H.; Dumesny, C.; Ang, C.-S.; Dong, L.; Ma, Y.; Zeng, J.; Nikfarjam, M. A novel PAK4 inhibitor suppresses pancreatic cancer growth and enhances the inhibitory effect of gemcitabine. Transl. Oncol. 2022, 16, 101329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, N.; Marimuthu, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Deshmukh, S.K.; Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, A.P.; McClellan, S.; Carter, J.E.; Singh, S. p-21 activated kinase 4 (PAK4) maintains stem cell-like phenotypes in pancreatic cancer cells through activation of STAT3 signaling. Cancer Lett. 2016, 370, 260–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Chakravarthi, B.V.S.K.; Robinson, A.D.; Anderson, J.C.; Agarwal, S.; Balasubramanya, S.A.H.; Eich, M.-L.; Bajpai, A.K.; Davuluri, S.; Guru, M.S.; et al. Therapeutically actionable PAK4 is amplified, overexpressed, and involved in bladder cancer progression. Oncogene 2020, 39, 4077–4091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, Q.; Su, N.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Miao, Z.; Wang, G.; Cheng, M.; Xu, H.; Cao, L.; Li, F. PAK4 kinase-mediated SCG10 phosphorylation involved in gastric cancer metastasis. Oncogene 2014, 33, 3277–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, S.-X.; Zhang, C.Z.; Luo, R.-Z.; Wang, C.-H.; Liu, L.-L.; Fu, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, H.; Xie, D.; Yun, J.-P. Zic2 promotes tumor growth and metastasis via PAK4 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2017, 402, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dasgupta, A.; Sierra, L.; Tsang, S.V.; Kurenbekova, L.; Patel, T.; Rajapakse, K.; Shuck, R.L.; Rainusso, N.; Landesman, Y.; Unger, T.; et al. Targeting PAK4 Inhibits Ras-Mediated Signaling and Multiple Oncogenic Pathways in High-Risk Rhabdomyosarcoma. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 199–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qasim, S.L.; Sierra, L.; Shuck, R.; Kurenbekova, L.; Patel, T.D.; Rajapakshe, K.; Wulff, J.; Nakahata, K.; Kim, H.R.; Landesman, Y.; et al. p21-activated kinases as viable therapeutic targets for the treatment of high-risk Ewing sarcoma. Oncogene 2021, 40, 1176–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.; Zhao, F.; Li, D.; Qu, J.; Yao, M.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhou, M.; Wang, Y.; Gao, Y.; et al. Synthesis of selective PAK4 inhibitors for lung metastasis of lung cancer and melanoma cells. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2022, 12, 2905–2922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, C.-Y.; You, S.-T.; Kim, J.-H.; Chung, J.H.; Han, S.-B.; Shin, E.-Y.; Kim, E.-G. p21-activated kinase 4 critically regulates melanogenesis via activation of the CREB/MITF and β-catenin/MITF pathways. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1385–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, X.; Cui, X.; Tu, S.; You, L.; Fu, J.; Chen, Z.; Hu, W.; et al. PAK5 facilitates the proliferation, invasion and migration in colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 4777–4790. [Google Scholar]
- Huo, F.-C.; Zhu, Z.-M.; Du, W.-Q.; Pan, Y.-J.; Jiang, X.; Kang, M.-J.; Liu, B.-W.; Mou, J.; Pei, D.-S. HPV E7-drived ALKBH5 promotes cervical cancer progression by modulating m6A modification of PAK5. Pharmacol. Res. 2023, 195, 106863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, Z.; Ji, W.; Yang, Y.; Chen, Z.; Li, Z.; Wang, K.; Lu, T.; Yu, Y.; Xia, W.; Lu, S. PAK5 promotes the cell stemness ability by phosphorylating SOX2 in lung squamous cell carcinomas. Exp. Cell Res. 2020, 395, 112187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.-K.; Zou, J.; Ye, D.-M.; Zeng, Y.; Chen, C.-Y.; Luo, G.-F.; Zeng, X. Human p21-activated kinase 5 (PAK5) expression and potential mechanisms in relevant cancers: Basic and clinical perspectives for molecular cancer therapeutics. Life Sci. 2020, 241, 117113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, K.; Zhou, Y.; Tseng, K.; Hu, H.; Li, K.; Wang, Y.; Gan, Z.; Lin, S.; Sun, Y.; Min, D. PAK5 overexpression is associated with lung metastasis in osteosarcoma. Oncol. Lett. 2018, 15, 2202–2210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hodgson, M.C.; Deryugina, E.I.; Suarez, E.; Lopez, S.M.; Lin, D.; Xue, H.; Gorlov, I.P.; Wang, Y.; Agoulnik, I.U. INPP4B suppresses prostate cancer cell invasion. Cell Commun. Signal 2014, 12, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bejarano, L.; Jordāo, M.J.C.; Joyce, J.A. Therapeutic Targeting of the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 933–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galon, J.; Costes, A.; Sanchez-Cabo, F.; Kirilovsky, A.; Mlecnik, B.; Lagorce-Pagès, C.; Tosolini, M.; Camus, M.; Berger, A.; Wind, P.; et al. Type, density, and location of immune cells within human colorectal tumors predict clinical outcome. Science 2006, 313, 1960–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Angelova, M.; Charoentong, P.; Hackl, H.; Fischer, M.L.; Snajder, R.; Krogsdam, A.M.; Waldner, M.J.; Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Galon, J.; et al. Characterization of the immunophenotypes and antigenomes of colorectal cancers reveals distinct tumor escape mechanisms and novel targets for immunotherapy. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishida, Y.; Agata, Y.; Shibahara, K.; Honjo, T. Induced expression of PD-1, a novel member of the immunoglobulin gene superfamily, upon programmed cell death. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 3887–3895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coca, S.; Perez-Piqueras, J.; Martinez, D.; Colmenarejo, A.; Saez, M.A.; Vallejo, C.; Martos, J.A.; Moreno, M. The prognostic significance of intratumoral natural killer cells in patients with colorectal carcinoma. Cancer 1997, 79, 2320–2328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bindea, G.; Mlecnik, B.; Tosolini, M.; Kirilovsky, A.; Waldner, M.; Obenauf, A.C.; Angell, H.; Fredriksen, T.; Lafontaine, L.; Berger, A.; et al. Spatiotemporal Dynamics of Intratumoral Immune Cells Reveal the Immune Landscape in Human Cancer. Immunity 2013, 39, 782–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robinson, A.; Han, C.Z.; Glass, C.K.; Pollard, J.W. Monocyte Regulation in Homeostasis and Malignancy. Trends Immunol. 2021, 42, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mantovani, A.; Marchesi, F.; Jaillon, S.; Garlanda, C.; Allavena, P. Tumor-associated myeloid cells: Diversity and therapeutic targeting. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 566–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.R.; Maute, R.L.; Dulken, B.W.; Hutter, G.; George, B.M.; McCracken, M.N.; Gupta, R.; Tsai, J.M.; Sinha, R.; Corey, D.; et al. PD-1 expression by tumour-associated macrophages inhibits phagocytosis and tumour immunity. Nature 2017, 545, 495–499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dixon, K.O.; Tabaka, M.; Schramm, M.A.; Xiao, S.; Tang, R.; Dionne, D.; Anderson, A.C.; Rozenblatt-Rosen, O.; Regev, A.; Kuchroo, V.K. TIM-3 restrains anti-tumour immunity by regulating inflammasome activation. Nature 2021, 595, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.; Zhang, Z.; Li, S.; Li, B.; Wang, X. Melittin inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion of bladder cancer cells by regulating key genes based on bioinformatics and experimental assays. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 655–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knippler, C.M.; Saji, M.; Rajan, N.; Porter, K.; La Perle, K.M.D.; Ringel, M.D. MAPK- and AKT-activated thyroid cancers are sensitive to group I PAK inhibition. Endocr.-Relat. Cancer 2019, 26, 699–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.-Y.B.; Du, F.; Han, Q.; Wang, E.-H.; Luo, E.-J.; Liu, Y. Knockdown of PAK1 Inhibits the Proliferation and Invasion of Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Cells Through the ERK Pathway. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2020, 28, 602–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Jubb, A.M.; Lyle, K.; Xiao, Q.; Ong, C.C.; Desai, R.; Fu, L.; Gnad, F.; Song, Q.; Haverty, P.M.; et al. PAK1 mediates pancreatic cancer cell migration and resistance to MET inhibition. J. Pathol. 2014, 234, 502–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Zhan, Y.; Huynh, N.; Dumesny, C.; Wang, X.; Asadi, K.; Herrmann, D.; Timpson, P.; Yang, Y.; Walsh, K.; et al. Inhibition of PAK1 suppresses pancreatic cancer by stimulation of anti-tumour immunity through down-regulation of PD-L1. Cancer Lett. 2020, 472, 8–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; He, K.; Li, C.; Ni, Y.; Li, M.; Chen, L.; Hou, M.; Zhou, Z.; Xu, Z.; Ji, M. P21 activated kinase-1 (PAK1) in macrophages is required for promotion of Th17 cell response during helminth infection. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 14325–14338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mainiero, F.; Soriani, A.; Strippoli, R.; Jacobelli, J.; Gismondi, A.; Piccoli, M.; Frati, L.; Santoni, A. RAC1/P38 MAPK signaling pathway controls β1 integrin-induced interleukin-8 production in human natural killer cells. Immunity 2000, 12, 7–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, K.; Luo, M.; Tu, Z.; Lv, S.; Liu, J.; Gong, C.; Ye, M.; Wu, M.; Sheng, Y.; Long, X.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of the prognostic implications and functional exploration of PAK gene family in human cancer. Cancer Cell Int. 2022, 22, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’hagan, K.L.; Choi, J.; Pryshchep, O.; Chernoff, J.; Phee, H. Pak2 Links TCR Signaling Strength to the Development of Regulatory T Cells and Maintains Peripheral Tolerance. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 1564–1577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Hahn, S.; Stokes, J.; Hoffman, E.A.; Schmelz, M.; Proytcheva, M.; Chernoff, J.; Katsanis, E. Pak2 regulates myeloid-derived suppressor cell development in mice. Blood Adv. 2017, 1, 1923–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, E.Y.; Mai, Y.; Shah, U.A.; Wei, Y.; Ishida, E.; Kataoka, K.; Ren, X.; Pradhan, K.; Bartholdy, B.; Wei, X.; et al. PAK Kinase Inhibition Has Therapeutic Activity in Novel Preclinical Models of Adult T-Cell Leukemia/Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019, 25, 3589–3601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sorger, H.; Dey, S.; Vieyra-Garcia, P.A.; Pölöske, D.; Teufelberger, A.R.; de Araujo, E.D.; Sedighi, A.; Graf, R.; Spiegl, B.; Lazzeri, I.; et al. Blocking STAT3/5 through direct or upstream kinase targeting in leukemic cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Embo Mol. Med. 2022, 14, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, W.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, R.; Yang, F.; Zhang, D.; Huang, M.; Zhang, L.; Dorsey, J.F.; Binder, Z.A.; O’rourke, D.M.; et al. Targeting PAK4 to reprogram the vascular microenvironment and improve CAR-T immunotherapy for glioblastoma. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 83–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abril-Rodriguez, G.; Torrejon, D.Y.; Liu, W.; Zaretsky, J.M.; Nowicki, T.S.; Tsoi, J.; Puig-Saus, C.; Baselga-Carretero, I.; Medina, E.; Quist, M.J.; et al. PAK4 inhibition improves PD-1 blockade immunotherapy. Nat. Cancer 2020, 1, 46–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Shao, Y.; Tong, Y.; Shen, T.; Zhang, J.; Li, Y.; Gu, H.; Li, F. Nucleo-cytoplasmic shuttling of PAK4 modulates β-catenin intracellular translocation and signaling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 465–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- König, S.; Nimtz, M.; Scheiter, M.; Ljunggren, H.-G.; Bryceson, Y.T.; Jänsch, L. Kinome analysis of receptor-induced phosphorylation in human natural killer cells. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e29672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Yu, T.; Zhang, N.; Chen, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, S.; Luo, L.; Cui, Z.; Qin, Y.; Liu, F. Nuclear E-Cadherin Acetylation Promotes Colorectal Tumorigenesis via Enhancing β-Catenin Activity. Mol. Cancer Res. 2019, 17, 655–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morse, E.M.; Sun, X.; Olberding, J.R.; Ha, B.H.; Boggon, T.J.; Calderwood, D.A. PAK6 targets to cell-cell adhesions through its N-terminus in a Cdc42-dependent manner to drive epithelial colony escape. J. Cell Sci. 2016, 129, 380–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavillet, M.; Martinod, K.; Renella, R.; Wagner, D.D.; Williams, D.A. A key role for Rac and Pak signaling in neutrophil extracellular traps (NETs) formation defines a new potential therapeutic target. Am. J. Hematol. 2018, 93, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Alvarez, I.; Lee, L.; Jensen, R.T. Group II p21-activated kinase, PAK4, is needed for activation of focal adhesion kinases, MAPK, GSK3, and β-catenin in rat pancreatic acinar cells. Am. J. Physiol.-Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2020, 318, G490–G503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, L.; Li, H.; Lu, K.; Jiang, S.; Li, H. PAK inhibitor FRAX486 decreases the metastatic potential of triple-negative breast cancer cells by blocking autophagy. Br. J. Cancer 2024, 130, 394–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kořánová, T.; Dvořáček, L.; Grebeňová, D.; Röselová, P.; Obr, A.; Kuželová, K. PAK1 and PAK2 in cell metabolism regulation. J. Cell. Biochem. 2022, 123, 375–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radu, M.; Semenova, G.; Kosoff, R.; Chernoff, J. PAK signalling during the development and progression of cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2014, 14, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Viaud, J.; Peterson, J.R. An allosteric kinase inhibitor binds the p21-activated kinase autoregulatory domain covalently. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2009, 8, 2559–2565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spel, L.; Zaffalon, L.; Hou, C.; Nganko, N.; Chapuis, C.; Martinon, F. CDC42 regulates PYRIN inflammasome assembly. Cell Rep. 2022, 41, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, T.; Zhang, P.; Chen, T.; Fan, Z.; Tan, X. P21-activated kinase 1 mediates angiotensin II-induced differentiation of human atrial fibroblasts via the JNK/c-Jun pathway. Mol. Med. Rep. 2021, 23, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karpov, A.S.; Amiri, P.; Bellamacina, C.; Bellance, M.-H.; Breitenstein, W.; Daniel, D.; Denay, R.; Fabbro, D.; Fernandez, C.; Galuba, I.; et al. Optimization of a Dibenzodiazepine Hit to a Potent and Selective Allosteric PAK1 Inhibitor. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2015, 6, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hawley, E.; Gehlhausen, J.; Karchugina, S.; Chow, H.-Y.; Araiza-Olivera, D.; Radu, M.; Smith, A.; Burks, C.; Jiang, L.; Li, X.; et al. PAK1 inhibition reduces tumor size and extends the lifespan of mice in a genetically engineered mouse model of Neurofibromatosis Type 2 (NF2). Hum. Mol. Genet. 2021, 30, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chow, H.-Y.; Karchugina, S.; Groendyke, B.J.; Toenjes, S.; Hatcher, J.; Donovan, K.A.; Fischer, E.S.; Abalakov, G.; Faezov, B.; Dunbrack, R.; et al. Development and Utility of a PAK1-Selective Degrader. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 15627–15641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, C.C.; Gierke, S.; Pitt, C.; Sagolla, M.; Cheng, C.K.; Zhou, W.; Jubb, A.M.; Strickland, L.; Schmidt, M.; Duron, S.G.; et al. Small molecule inhibition of group I p21-activated kinases in breast cancer induces apoptosis and potentiates the activity of microtubule stabilizing agents. Breast Cancer Res. 2015, 17, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, C.; Hu, X.; Wang, S.; Yu, X.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L.; Qi, K.; Li, Z.; Xu, K. Inhibition of PAK1 generates an ameliorative effect on MPLW515L mouse model of myeloproliferative neoplasms by regulating the differentiation and survival of megakaryocytes. Exp. Hematol. 2023, 127, 59–69.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Zhu, L.; Zhao, J.; Yang, Y.; Cai, X.; Hu, C.; Rosell, R.; et al. Identification of a novel PAK1 inhibitor to treat pancreatic cancer. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2020, 10, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.; Oh, E.; McCown, E.M.; Wang, X.; Veluthakal, R.; Thurmond, D.C. A requirement for PAK1 to support mitochondrial function and maintain cellular redox balance via electron transport chain proteins to prevent β-cell apoptosis. Metabolism 2021, 115, 154431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messerli, S.M.; Ahn, M.; Kunimasa, K.; Yanagihara, M.; Tatefuji, T.; Hashimoto, K.; Mautner, V.; Uto, Y.; Hori, H.; Kumazawa, S.; et al. Artepillin C (ARC) in Brazilian green propolis selectively blocks oncogenic PAK1 signaling and suppresses the growth of NF tumors in mice. Phytotherapy Res. 2009, 23, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, B.W.; Guo, C.; Piraino, J.; Westwick, J.K.; Zhang, C.; Lamerdin, J.; Dagostino, E.; Knighton, D.; Loi, C.-M.; Zager, M.; et al. Small-molecule p21-activated kinase inhibitor PF-3758309 is a potent inhibitor of oncogenic signaling and tumor growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 9446–9451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboukameel, A.; Muqbil, I.; Senapedis, W.; Baloglu, E.; Landesman, Y.; Shacham, S.; Kauffman, M.; Philip, P.A.; Mohammad, R.M.; Azmi, A.S. Novel p21-Activated Kinase 4 (PAK4) Allosteric Modulators Overcome Drug Resistance and Stemness in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2017, 16, 76–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Wang, J.; You, L.-H.; Zhou, R.-Z.; Zhao, D.-M.; Cheng, M.-S.; Li, F. GL-1196 Suppresses the Proliferation and Invasion of Gastric Cancer Cells via Targeting PAK4 and Inhibiting PAK4-Mediated Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.-Y.; Zhang, J.; Hao, C.-Z.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Cheng, M.-S.; Zhao, D.-M.; Li, F. LC-0882 targets PAK4 and inhibits PAK4-related signaling pathways to suppress the proliferation and invasion of gastric cancer cells. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 2736–2747. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, J.; Guo, Q.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Peng, H.; Cheng, M.; Zhao, D.; Li, F. LCH-7749944, a novel and potent p21-activated kinase 4 inhibitor, suppresses proliferation and invasion in human gastric cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2012, 317, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wang, T.; Wu, T.; Zhang, K.; Yin, W.; Zhu, M.; Pang, Y.; Hao, C.; He, Z.; Cheng, M.; et al. Synthesis, bioconversion, pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic evaluation of N-isopropyl-oxy-carbonyloxymethyl prodrugs of CZh-226, a potent and selective PAK4 inhibitor. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 186, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, P.-L.; Wang, G.; Su, Y.; Wang, H.-X.; Wang, J.; Li, F.; Cheng, M.-S. Strategy and validation of a structure-based method for the discovery of selective inhibitors of PAK isoforms and the evaluation of their anti-cancer activity. Bioorganic Chem. 2019, 91, 103168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
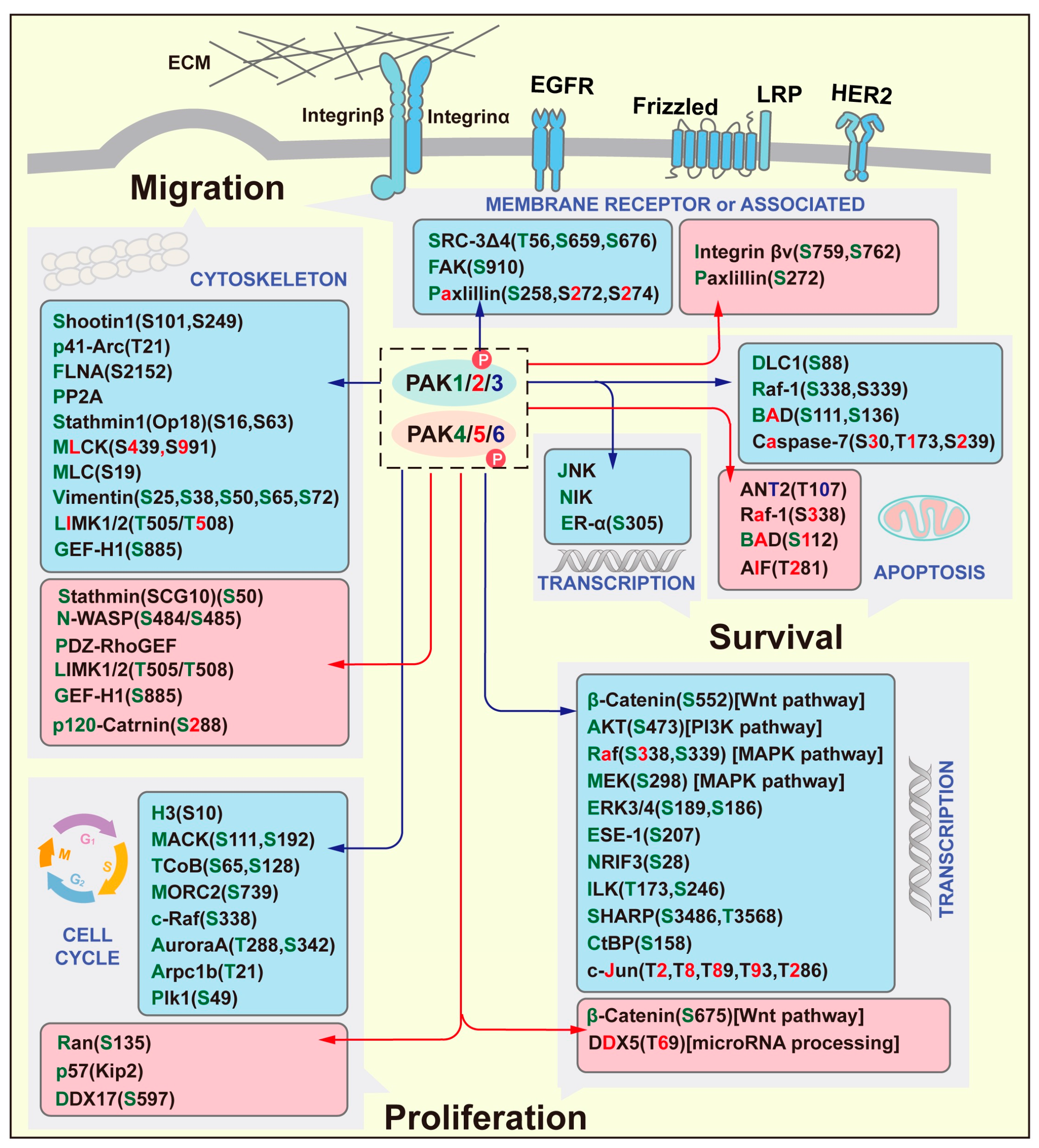
| Group I PAKs | Functionality | Molecular Pathways |
|---|---|---|
| PAK1 | Proliferation | PAK1/PI3K/Akt [3] PAK1/LIMK1 [4] PAK1/RAF/MEK/ERK [5,6] PAK1/Wnt/β-catenin/CyclinD1 [7] |
| Invasion | PAK1/MMP [7] PAK1/MEK1 [8] PAK1/RUFY3 [9] | |
| Survival | PAK1/NF-κB [10] PAK1/Bim [11] PAK1/HIF-1α [12] PAK1/FOXO3 [13] | |
| Angiogenesis | PAK1/β-catenin [14] PAK1/p38/MMP-2 [15] PAK1/STAT5B/CSF2 [16] | |
| PAK2 | Proliferation | PAK2/ERK [17] PAK2/MAPK [18] |
| Invasion | PAK2/RhoA [19] PAK2/SOX2/DEK [20] PAK2/Cdc42, Rac1 [21] PAK2/LIMK1/cofilin [22] PAK2/PYK2 [23] | |
| Survival | PAK2/AMPK/YAP [24] PAK2/MCM7 [25] | |
| Angiogenesis | PAK2/TGF-β [26] | |
| PAK3 | Invasion | EMT [27] |
| Group II PAKs | Functionality | Molecular Pathways |
|---|---|---|
| PAK4 | Proliferation | PAK4/β-catenin/c-Myc [28] PAK4/MEK/ERK [28] PAK4/PI3K/AKT/mTOR [29] PAK4/c-Src/EGFR/CyclinD1 [30] PAK4/LIMK [31] PAK4/ERα [32] PAK4/RELB [33] PAK4/PI3K/Akt [34] PAK4/FH [35] PAK4/Mdm2/p53/G6PD [36] PAK4/Smad2, Smad3/TGF-β [37] |
| Invasion | PAK4/PI3K/AKT/mTOR [30] PAK4/LIMK/Cofilin [32] PAK4/PPARγ/Nox1 [38] PAK4/P53 [36,39] | |
| Survival | PAK4/caspase 8 [40] PAK4/Bad [41] | |
| Angiogenesis | PAK4/ERK/MMP-2 [42] | |
| PAK5 | Proliferation | PAK5/DNPEP/USP4 [43] PAK5/AIF [44] PAK5/DDX5 [45] PAK5/Cyclin D1, β-catenin [46] PAK5/CDK2, CDC25A, Cyclin D1 [47] PAK5/ERK [48] |
| Invasion | PAK5/DNPEP/USP4 [43] PAK5/PI3K/AKT [49] PAK5/STATB1 [50] PAK5/DDX5 [45] PAK5/Egr1/MMP2 [51] PAK5/E47 [52] | |
| Survival | PAK5/AIF [44] PAK5/Bad [53] | |
| PAK6 | Proliferation | PAK6/Eg5 [54] PAK6/Mdm2 [55] PAK6/WNT/β-catenin [56] |
| Invasion | PAK6/IQGAP3/RhoA [57] PAK6/IQGAP1/E-cadherin/β-catenin [58] PAK6/cofilin [59] | |
| Survival | PAK6/SIRT4/ANT2 [60] PAK6/ATR/CHK1 [61] |
| Group I PAKs | Gene Expression Status | Access to Cancers |
| PAK1 | + | Bladder cancer (↑) [62] |
| + | Breast cancer (↑) [63,64] | |
| + | Gastric cancer (↑) [65,66] | |
| + | Liver cancer (↑) [67] | |
| + | Ovarian cancer (↑) [16,68] | |
| + | Renal cell carcinoma (↑) [66,69] | |
| PAK2 | + | Ovarian cancer (↑) [70] |
| + | Gastric cancer (↑) [18,71] | |
| + | Pancreatic cancer (↑) [72,73] | |
| + | Colorectal cancer (↑) [19] | |
| PAK3 | + | Hepatocellular carcinoma (↑) [27] |
| − | Cervical cancer (↓) [74] | |
| − | Glioma(↓) [75,76] | |
| + | Pancreatic cancer (↑) [72] | |
| Group II PAKs | Gene Expression Status | Access to Cancers |
| PAK4 | + | Breast cancer (↑) [33,77,78] |
| + | Pancreatic cancer (↑) [79,80] | |
| + | Ovarian cancer (↑) [30] | |
| + | Gallbladder cancer (↑) [81] | |
| + | Gastric cancer (↑) [37,82] | |
| + | Hepatocellular cancer (↑) [39,83] | |
| + | Sarcomas (↑) [84,85] | |
| + | Endometrial cancer (↑) * | |
| + | Melanoma (↑) [86,87] | |
| PAK5 | + | Breast cancer (↑) [43,44] |
| + | Colorectal cancer (↑) [52,88] | |
| + | Cervical cancer (↑) [50,89] | |
| + | Lung cancer (↑) [90,91] | |
| + | Ovarian cancer (↑) * | |
| + | Osteosarcoma (↑) [92] | |
| PAK6 | + | Prostate cancer (↓) [60,93] |
| + | Colorectal cancer (↑) [59] | |
| + | Renal cancer (↓) [66] | |
| − | Hepatocellular cancer (↑) [54,56] |
| Inhibitors | Discovery Time | Action Site | Biological Activity |
|---|---|---|---|
| PF-3758309 | 2010 | C502/L472 of PAK4 | Inhibition of all PAKs with an IC50 of 39nM to PAK1 and 15nM to PAK4. |
| LCH-7749944 | 2012 | PAK4 ATP binding pocket | Acts as an ATP-competitive inhibitor. LCH-7749944 is a potent PAK4 inhibitor with an IC50 of 14.93 μM. |
| KPT9274 | 2014 | PAK4 kinase domain | An orally bioavailable, dual PAK4/Nicotinamide phosphoribosyl transferase (Nampt) inhibitor, with IC50s of <100 nM and 120 nM. |
| GNE-2861 | 2015 | DFG-out pocket | GNE-2861 inhibits PAK4, PAK5 and PAK6 with IC50s of 7.5, 36, 126 nM. |
| GL-1196 | 2016 | L398\A348\K350\L447\V335\A402\G330\S331 of PAK4 | Inhibition of PAK4. |
| LC-0882 | 2017 | L398/A348/K350/A492/I327/V335 of PAK4 | Inhibition of PAK4. |
| CZH226 | 2017 | E396/L398/M395/V335/D458 of PAK4 | A potent and selective PAK4 inhibitor (PAK4 Ki = 9 nM; PAK1 Ki = 3112 nM). |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lu, T.; Huo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Li, X. The Role of the p21-Activated Kinase Family in Tumor Immunity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3885. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083885
Lu T, Huo Z, Zhang Y, Li X. The Role of the p21-Activated Kinase Family in Tumor Immunity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3885. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083885
Chicago/Turabian StyleLu, Tianqi, Zijun Huo, Yiran Zhang, and Xiaodong Li. 2025. "The Role of the p21-Activated Kinase Family in Tumor Immunity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3885. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083885
APA StyleLu, T., Huo, Z., Zhang, Y., & Li, X. (2025). The Role of the p21-Activated Kinase Family in Tumor Immunity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3885. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083885





