The Potential and Limitations of the MinION/Yenos Platform for miRNA-Enabled Early Cancer Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
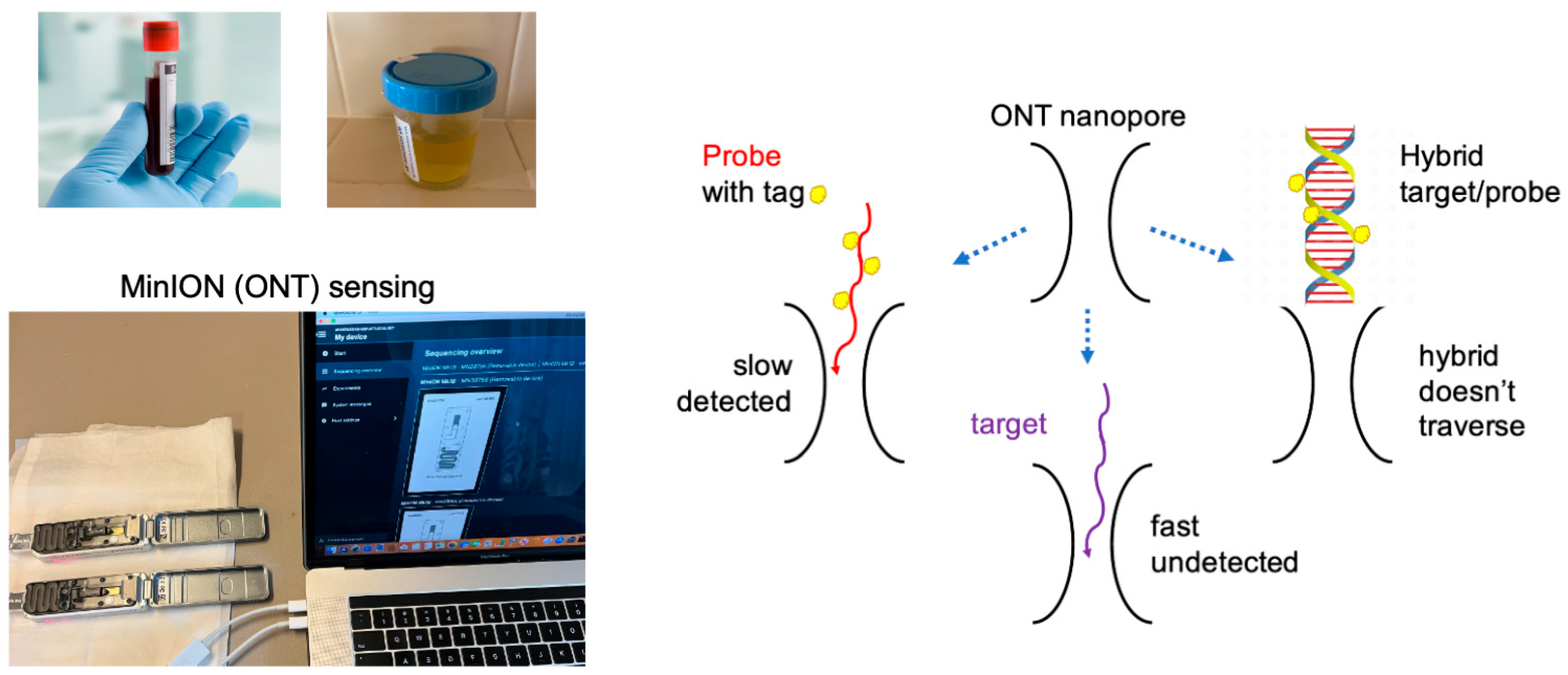
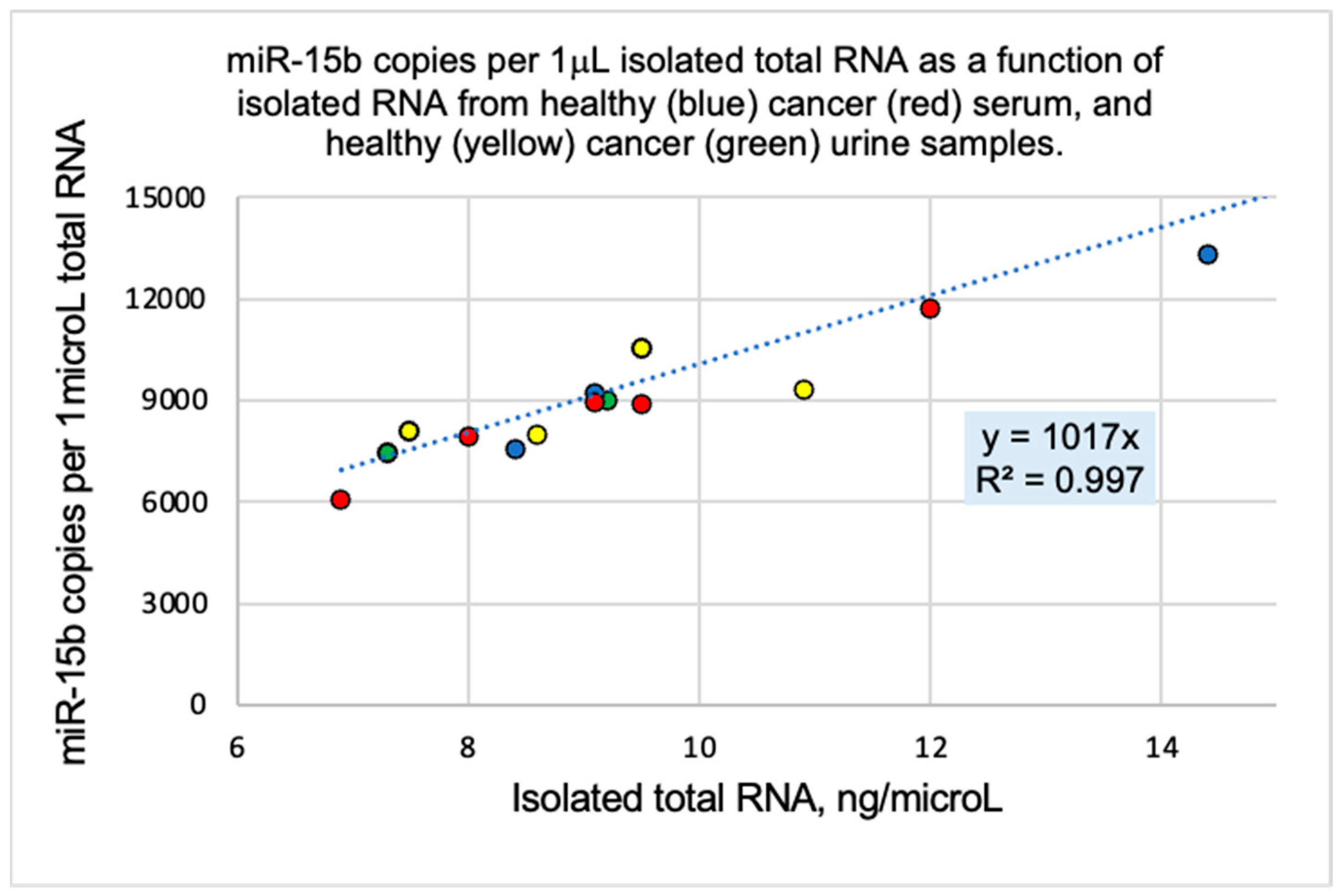
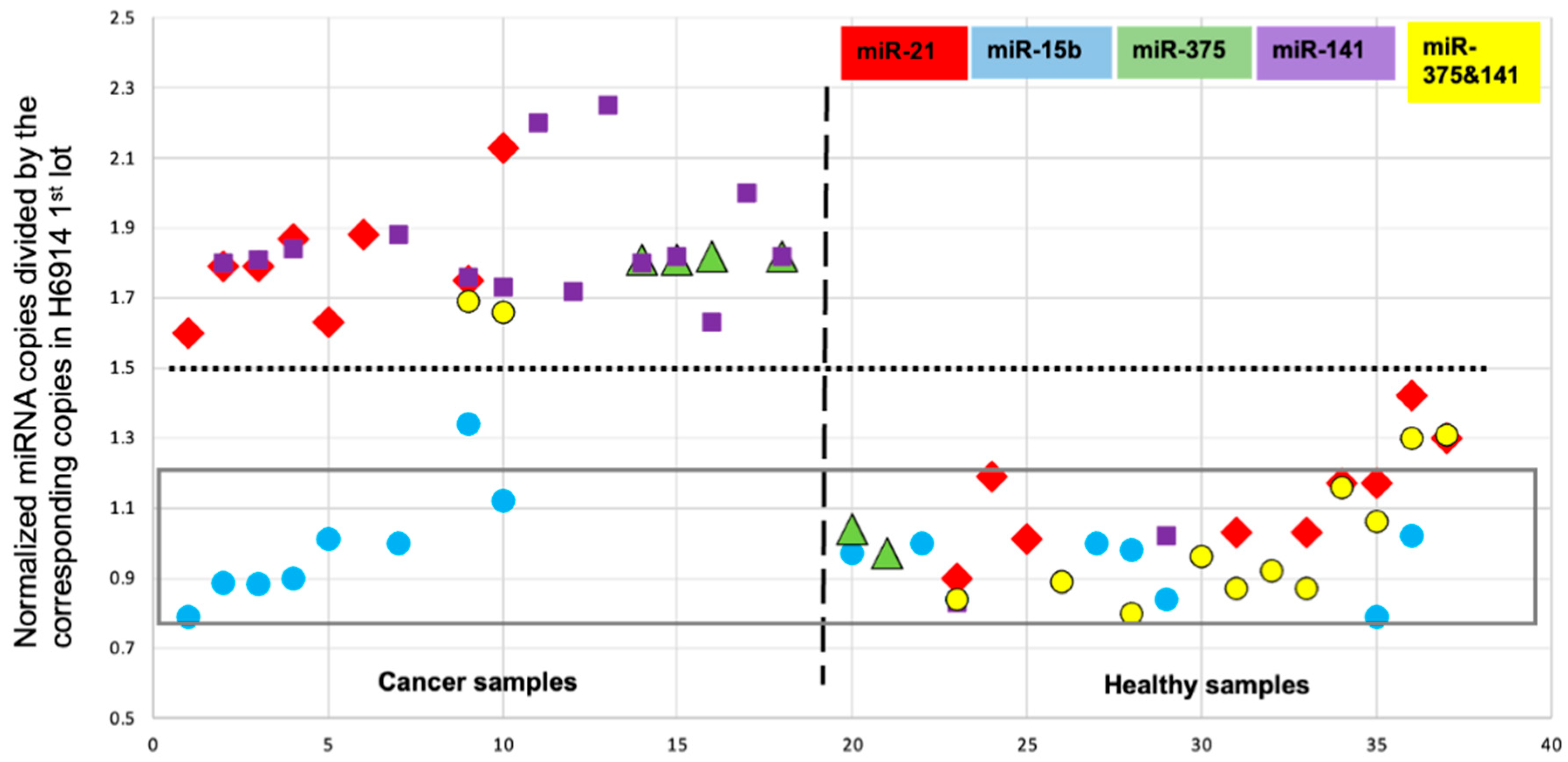
2. Results
3. Discussion
3.1. Comparison of the MinION’s Sequencing vs. Sensing to Detect/Quantify Short SS Nucleic Acids
3.2. The Limitations of the MinION/Yenos Platform for Cancer Screening and Sensing
3.3. The Potential of the MinION/Yenos Platform for Cancer Screening
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Human Samples
4.2. Oligos, Probes, and Other Reagents
| Probe ID | mU is 2’-OMe and dU is 2’-deoxyU; the Partial Sequence Between the A5 and T5 Is Complementary to the Target miRNA. All Five Ts Carry an OsBp tag. | Concentr., fM | No of OsBp, 1 Average |
|---|---|---|---|
| Probe15b | (A)6dUGdUAAACCAdUGAdUGdUGCdUGCdUA(T)5(A)6 | 43.4 | 5.9 |
| Probe21 | (A)5dUCAACAdUCAGdUCdUGAdUAAGCdUA(T)5C(A)6 | 36.6 | 6.2 |
| Probe375 | (A)5dUCACGCGAGCCGAACGAACAAAC(T)5C(A)5 | 41.6 | 5.9 |
| Probe141 | (A)4CCAmUCmUmUmUACCAGACAGmUGmUmUA(T)5(A)5 | 39.0 | 6.3 |
4.3. Sample Preparation
4.4. Single-Molecule Ion Channel Conductance Experiments on the MinION (MinION Mk1B Platform)
4.5. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Wagle, N.S.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2023, 73, 17–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NIH. National Cancer Institute. Age and Cancer Risk. Available online: https://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/age (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- World Health Organization. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cancer (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Accuracy of Mammograms. Available online: https://www.komen.org/breast-cancer/screening/mammography/accuracy/ (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Seyhan, A.A. Circulating microRNAs as Potential Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer-Advances and Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connal, S.; Cameron, J.M.; Sala, A.; Brennan, P.M.; Palmer, D.S.; Palmer, J.D.; Perlow, H.; Baker, M.J. Liquid biopsies: The future of cancer early detection. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armakolas, A.; Kotsari, M.; Koskinas, J. Liquid Biopsies, Novel Approaches and Future Directions. Cancers 2023, 15, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubinstein, W.S.; Patriotis, C.; Dickherber, A.; Han, P.K.J.; Katki, H.A.; LeeVan, E.; Pinsky, P.F.; Prorok, P.C.; Skarlupka, A.L.; Temkin, S.M.; et al. Cancer screening with multicancer detection tests: A translational science review. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2024, 74, 368–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farooq, M.; Leevan, E.; Ahmed, J.; Ko, B.; Shin, S.; Det Souza, A.l.; Takebe, N. Blood-based multi-cancer detection: A state-of-the-art update. Curr. Probl. Cancer 2024, 48, 101059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minasian, L.M.; Pinsky, P.; Katki, H.A.; Dickherber, T.; Han, P.K.J.; Harris, L.; Patriotis, C.; Srivastava, S.; Weil, C.J.; Prorok, P.C.; et al. Study design considerations for trials to evaluate multicancer early detection assays for clinical utility. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2023, 115, 250–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greene, M.P.; Vassy, J.L. Helping patients understand multi-cancer early detection tests: A scoping review. Per. Med. 2024, 21, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambros, V. MicroRNAs: Tiny regulators with great potential. Cell 2001, 107, 823–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metcalf, G.A.D. MicroRNAs: Circulating biomarkers for the early detection of imperceptible cancers via biosensor and machine-learning advances. Oncogene 2024, 43, 2135–2142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, P.; Parkin, R.K.; Kroh, E.M.; Fritz, B.R.; Wyman, S.K.; Pogosova-Agadjanyan, E.L.; Peterson, A.; Noteboom, J.; O’Briant, K.C.; Allen, A.; et al. Circulating microRNAs as stable blood-based markers for cancer detection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10513–10518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mall, C.; Rocke, D.M.; Durbin-Johnson, B.; Weiss, R.H. Stability of miRNA in Human Urine Supports its Biomarker Potential. Biomark. Med. 2013, 7, 623–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Birgaoanu, M.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: From microRNA sequences to function. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, D155–D162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alles, J.; Fehlmann, T.; Fischer, U.; Backes, C.; Galata, V.; Minet, M.; Hart, M.; Abu-Halima, M.; Grässer, F.A.; Lenhof, H.-P.; et al. An estimate of the total number of true human miRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019, 47, 3353–3364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Search “microRNA Cancer”. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/?term=microRNA+Cancer (accessed on 13 February 2025).
- Valihrach, L.; Androvic, P.; Kubista, M. Circulating miRNA analysis for cancer diagnostics and therapy. Mol. Asp. Med. 2020, 72, 100825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacomino, G. miRNAs: The Road from Bench to Bedside. Genes 2023, 14, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hindson, C.M.; Chevillet, J.R.; Briggs, H.A.; Gallichotte, E.N.; Ruf, I.K.; Hindson, B.J.; Vessella, R.L.; Tewari, M. Absolute quantification by droplet digital PCR versus analog real-time PCR. Nat. Methods 2013, 10, 1003–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy, P.M.; Barczak, A.J.; DeHoff, P.; Srinivasan, S.; Etheridge, A.; Galas, D.; Das, S.; Erle, D.J.; Laurent, L.C. Comparison of Reproducibility, Accuracy, Sensitivity, and Specificity of miRNA Quantification Platforms. Cell Rep. 2019, 29, 4212–4222.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loy, C.; Ahmann, L.; De Vlaminck, I.; Gu, W. Liquid Biopsy Based on Cell-Free DNA and RNA. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2024, 26, 169–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddika, T.; Heinemann, I.U. Bringing MicroRNAs to Light: Methods for MicroRNA Quantification and Visualization in Live Cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2021, 8, 619583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Precazzini, F.; Detassis, S.; Imperatori, A.S.; Denti, M.A.; Campomenosi, P. Measurements Methods for the Development of MicroRNA-Based Tests for Cancer Diagnosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Henley, R.Y.; Vazquez-Pagan, A.G.; Johnson, M.; Kanavarioti, A.; Wanunu, M. Osmium-based on pyrimidine contrast tags for enhanced nanopore-based DNA base discrimination. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Y.; Kanavarioti, A. Single pyrimidine discrimination during voltage-driven translocation of osmylated oligodeoxynucleotides via the alpha-hemolysin nanopore. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quint, I.; Simantzik, J.; Kaiser, L.; Laufer, S.; Csuk, R.; Smith, D.; Kohl, M.; Deigner, H.-P. Ready-to-use nanopore platform for label-free small molecule quantification: Ethanolamine as first example. Nanomedicine 2024, 55, 102724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, A.S.W.; Bernasconi, J.G.; Jack, W.; Kanavarioti, A. Ready-to-use nanopore platform for the detection of any DNA/RNA oligo at attomole range using an Osmium tagged complementary probe. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 19790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanavarioti, A.; Kang, A.S.W. See RNA (OsBp) Event Detection Python Package in a Public Repository. Available online: https://github.com/kangaroo96/osbp_detect/blob/master/instructions.md (accessed on 15 April 2025).
- Kanavarioti, A. Femtomolar-level PCR-free quantification of microRNA cancer biomarkers in serum. bioRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanavarioti, A.; Rehman, M.H.; Qureshi, S.; Rafiq, A.; Sultan, M. High Sensitivity and Specificity Platform to Validate MicroRNA Biomarkers in Cancer and Human Diseases. Non-Coding RNA 2024, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porzycki, P.; Ciszkowicz, E.; Semik, M.; Tyrka, M. Combination of three miRNA (miR-141, miR-21, and miR-375) as potential diagnostic tool for prostate cancer recognition. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2018, 50, 1619–1626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenike, A.E.; Halushka, M.K. miR-21: A nonspecific biomarker of all maladies. Review. Biomark. Res. 2021, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Reilly-O’Donnell, B.; Gutierrez, R.; Lucarelli, C.; Ng, F.S.; Gorelik, J.; Ivanov, A.P.; Edel, J.B. Nanopore sequencing of DNA-barcoded probes for highly multiplexed detection of microRNA, proteins, and small biomarkers. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2023, 18, 1483–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Zhou, S.; Wang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Guan, S.; Wang, D.; Wang, L.; Guan, X. Nanopore Single-molecule Analysis of Biomarkers: Providing Possible Clues to Disease Diagnosis. Trends Anal. Chem. 2023, 162, 117060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanavarioti, A. HPLC methods for purity evaluation of man-made single-stranded RNAs. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palecek, E. Probing DNA structure with osmium tetroxide complexes in vitro. Methods Enzymol. 1992, 212, 139–155. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kanavarioti, A.; Greenman, K.L.; Hamalainen, M.; Jain, A.; Johns, A.M.; Melville, C.R.; Kemmish, K.; Andregg, W. Capillary electrophoretic separation-based approach to determine the labeling kinetics of oligodeoxynucleotides. Electrophoresis 2012, 33, 3529–3543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanavarioti, A. False positives and false negatives measure less than 0.001% in labeling ssDNA with osmium tetroxide 2,2’-bipyridine. Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 2016, 7, 1434–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reske, T.; Surkus, A.-E.; Duwensee, H.; Flechsig, G.-U. Kinetics of the labeling reactions of thymine, cytosine and uracil with osmium tetroxide bipyridine. Microchim. Acta 2009, 166, 197–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debnath, T.K.; Okamoto, A. Osmium Tag for Post-transcriptionally Modified RNA. ChemBioChem 2018, 19, 1653–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cancer Serum | ID | miR-15b | miR-21 | miR-375 | miR-141 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| lung | A1 | ν | ν | ν | ν |
| ovarian | A2 | ν | ν | ν | ν |
| “ | A3 | ν | ν | ν | ν |
| “ | A4 | ν | ν | ν | ν |
| “ | A5 | ν | ν | ν | ν |
| CRC 1 | No1 | ν | ν | ν | ν, ν |
| lung | No2 | Ν, ν | X | ν, ν | ν, ν |
| CRC 1 | No3 | ν | ND | ν | ν, ν, ν |
| lung | No4 | ν, ν | ν | ν, ν | ν, ν, ν |
| lung | No6 | ν | ν, ν | X | ν, ν, ν |
| CRC 1 | No7 | ν | ν, ν | ν | ν, ν, ν |
| prostate | D1 | ν | ν | ν | X |
| pancreatic | D2 | ν | ν | X | ν |
| breast | D3 | X | ν | ND | ν |
| “ | D4 | ν | ν | ν | ν |
| prostate | D5 | X | ν | ν | ND |
| “ | D6 | ν | X | ν | ν, ν |
| “ | D7 | ν | ν | ν | ν |
| pancreatic | D8 | ν | ν | ν | ν |
| prostate | D9 | ν | ν | ν | ν |
| breast | D10 | ν | ν | X | ν |
| pancreatic | D11 | ν | ν | X | ν |
| Healthy serum | SQ H6914 | ν, ν, ν | ν, ν, ν | ν, ν | ν, ν |
| H6914 2025 | ν | ν, ν | ν | ND | |
| Healthy urine | Healthy1 | ND | ν, ν | ND | ν, ν |
| Healthy2 | ν, ν | ν, ν | X | ν | |
| Score | 28/30 | 30/32 | 22/27 | 36/37 | |
| % True 2 | 93.3 | 93.8 | 81.5 | 97.3 |
| Sample Volume in μL | 5 μL | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Probe15b copies | Probe15b copies per 1 μL sample | Probe15b copies per 1 μL sample normalized to reference at 16 ng/μL | Probe15b copies per 1 μL sample normalized to the reference at 16 ng/μL and adjusted to target 1.56 HL miR-15b at 17,710 copies per 1 μL RNA from H6914 reference |
| =4 × 43.4 × 600 | =4 × 43.4 × 600/5 | =4 × 43.4 × 600/5 × 16/12.1 | =4 × 43.4 × 600/5 × 16/12.1/17,710 = 1.56 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rafiq, A.; Kanavarioti, A. The Potential and Limitations of the MinION/Yenos Platform for miRNA-Enabled Early Cancer Detection. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083822
Rafiq A, Kanavarioti A. The Potential and Limitations of the MinION/Yenos Platform for miRNA-Enabled Early Cancer Detection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083822
Chicago/Turabian StyleRafiq, Aleena, and Anastassia Kanavarioti. 2025. "The Potential and Limitations of the MinION/Yenos Platform for miRNA-Enabled Early Cancer Detection" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083822
APA StyleRafiq, A., & Kanavarioti, A. (2025). The Potential and Limitations of the MinION/Yenos Platform for miRNA-Enabled Early Cancer Detection. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3822. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083822








