Liraglutide Attenuates FFA-Induced Retinal Pigment Epithelium Dysfunction via AMPK Activation and Lipid Homeostasis Regulation in ARPE-19 Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
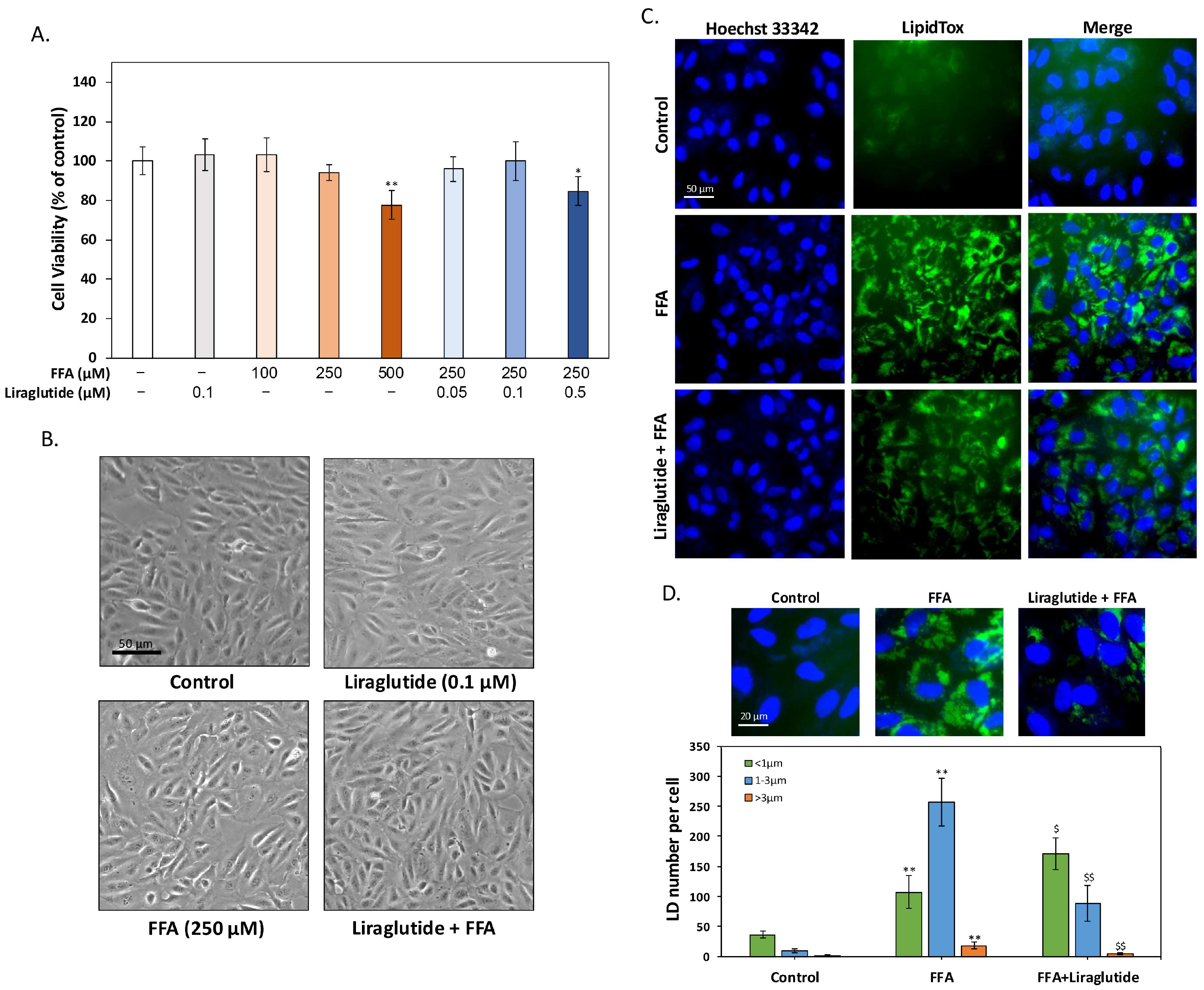
2.1. Liraglutide Reduces FFA-Induced LD Accumulation in ARPE-19 Cells
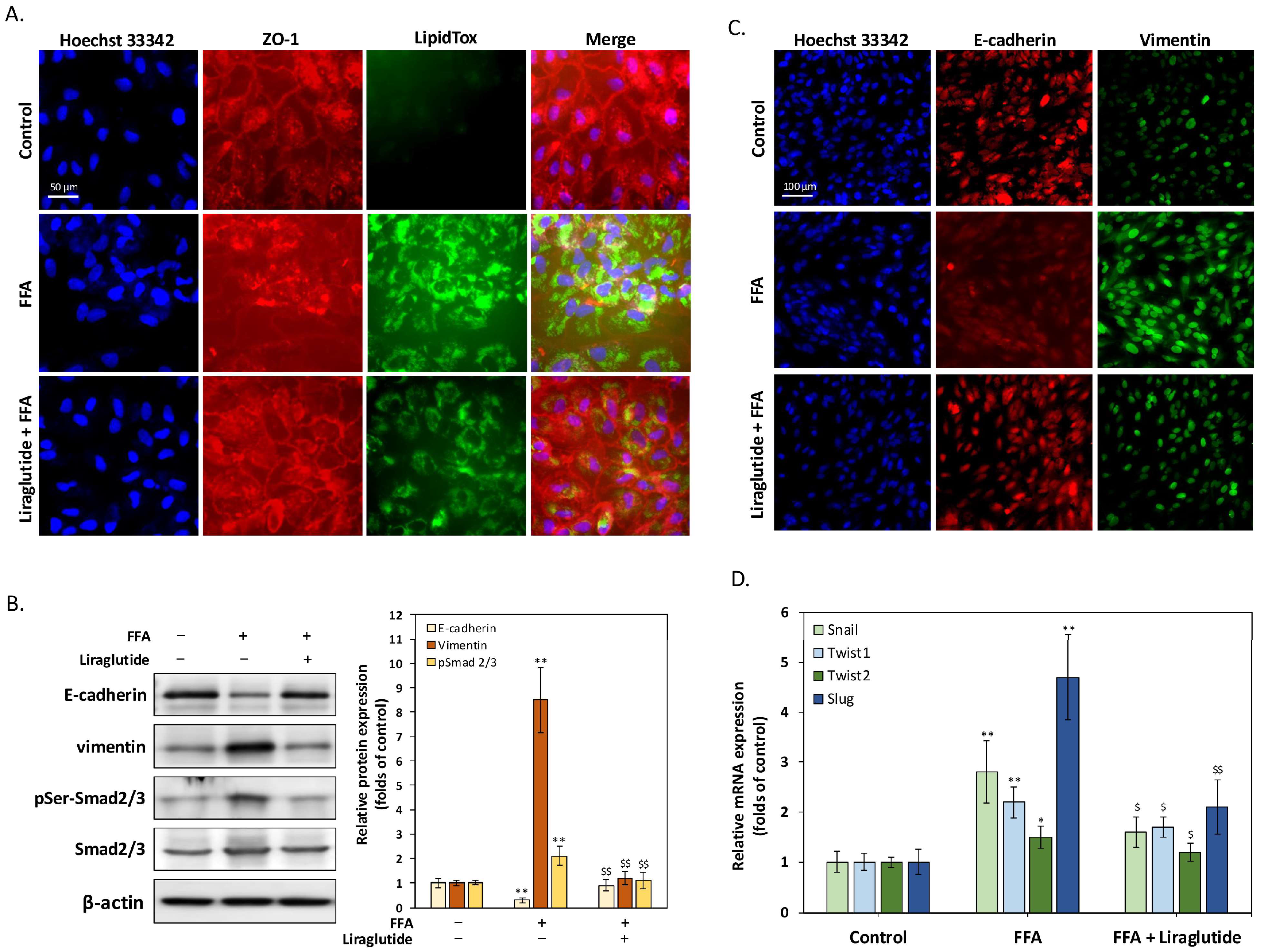
2.2. Liraglutide Suppresses FFA-Induced EMT and Restores Tight Junction Integrity in ARPE-19 Cells
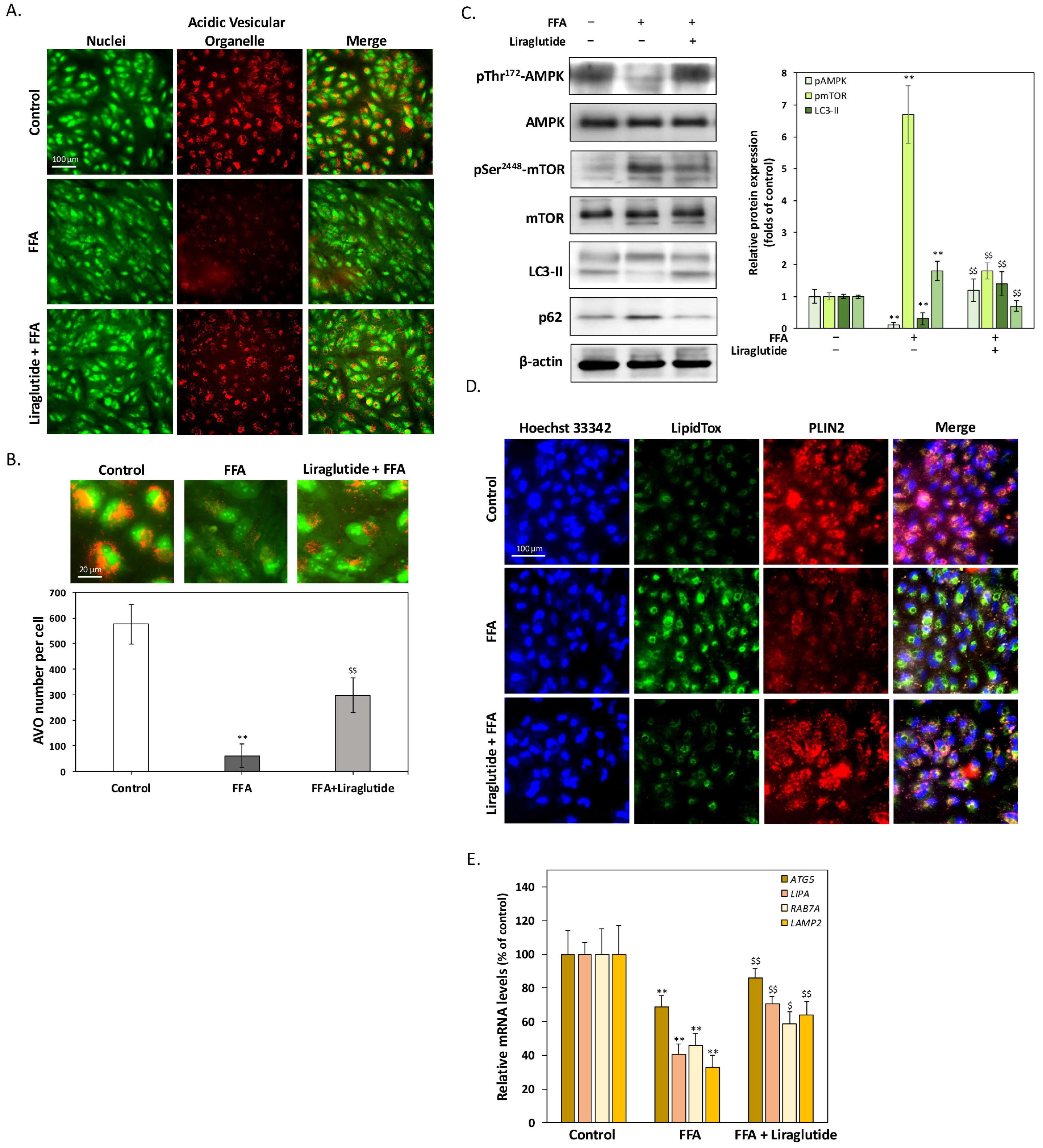
2.3. Liraglutide Enhances Lipophagy to Promote LD Degradation in ARPE-19 Cells
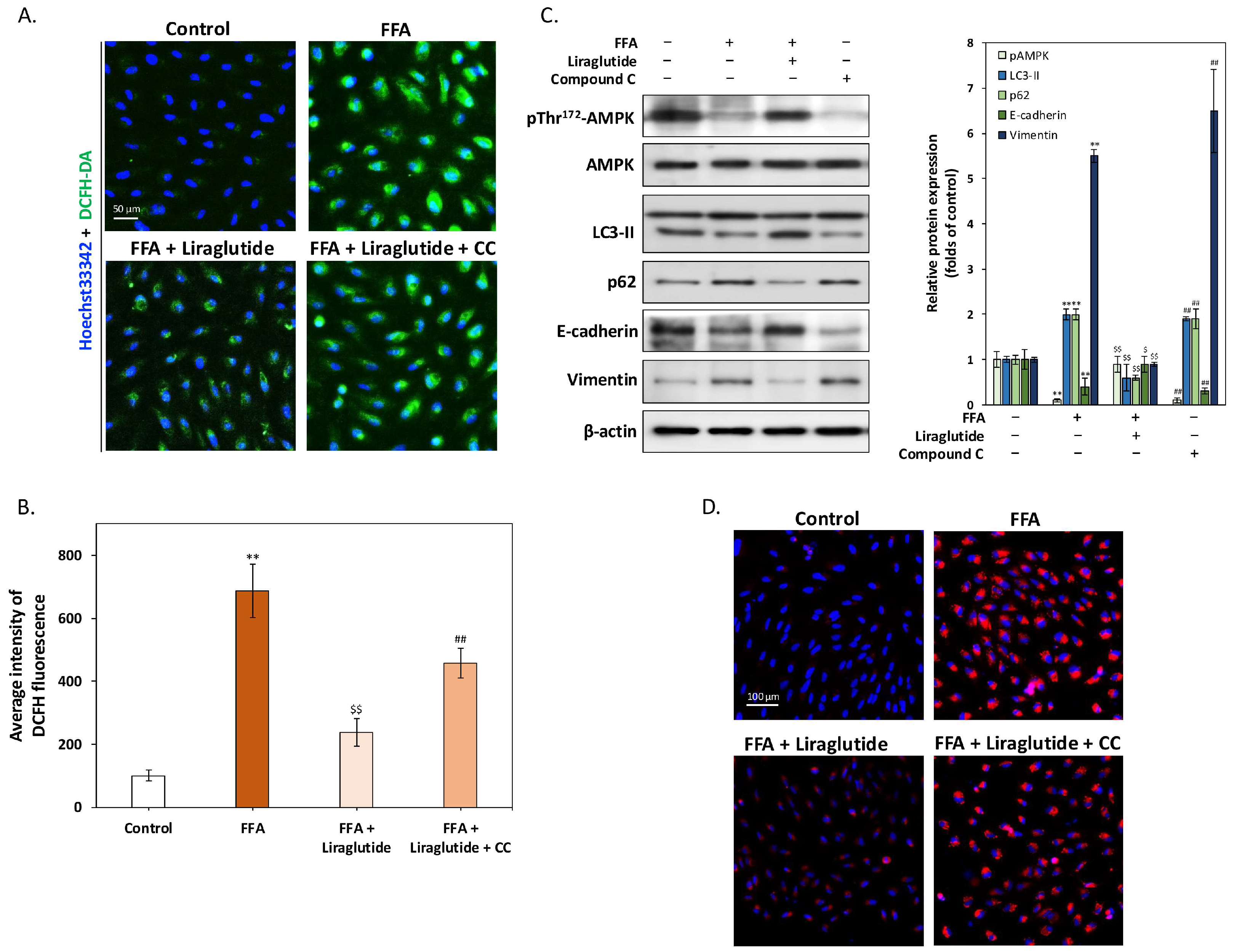
2.4. AMPK Activation Is Essential for Liraglutide-Mediated Reduction of ROS and Lipid Accumulation in ARPE-19 Cells
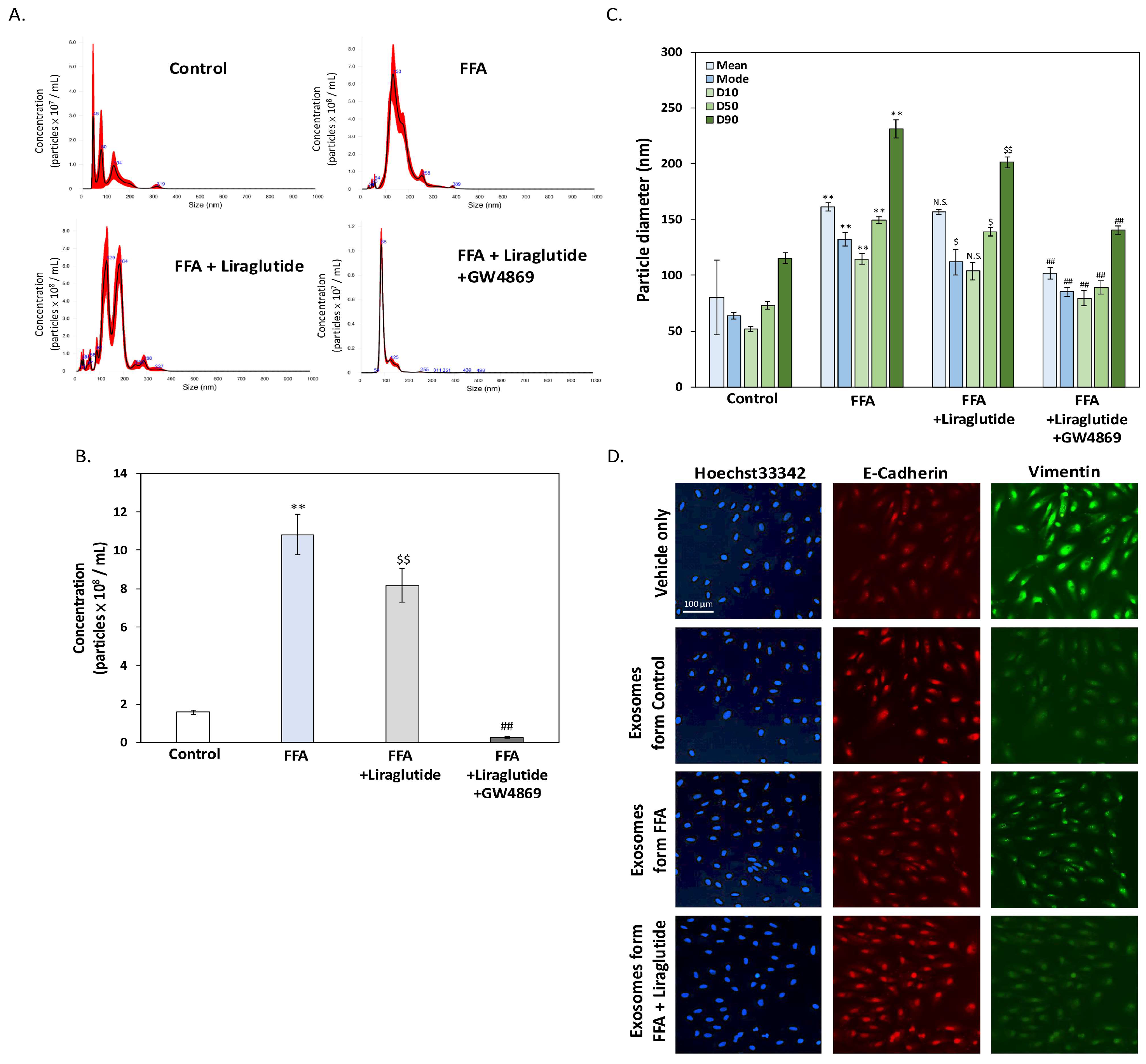
2.5. Liraglutide Modulates Exosome Release and Size Distribution in ARPE-19 Cells Under FFA Stress
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Cell Culture and Viability Assay
4.3. LipidTox Staining and Quantification Using High-Content Analysis (HCA)
4.4. Immunocytochemistry Staining
4.5. Western Blot Analysis
4.6. mRNA Expression Analysis Using qPCR
4.7. Acidic Vesicular Organelles Detection via Acridine Orange Staining
4.8. Quantification of Intracellular ROS Levels
4.9. Assessment of Lipid Accumulation Using Nile Red Staining
4.10. Extracellular Vesicle (EV) Isolation and Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis
4.11. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kim, J.; Lee, Y.J.; Won, J.Y. Molecular Mechanisms of Retinal Pigment Epithelium Dysfunction in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 12298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, C.; Zhou, L.; Sun, H.; Yang, M.M. Age-Related Macular Degeneration: A Disease of Cellular Senescence and Dysregulated Immune Homeostasis. Clin. Interv. Aging 2024, 19, 939–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurya, M.; Bora, K.; Blomfield, A.K.; Pavlovich, M.C.; Huang, S.; Liu, C.H.; Chen, J. Oxidative stress in retinal pigment epithelium degeneration: From pathogenesis to therapeutic targets in dry age-related macular degeneration. Neural Regen. Res. 2023, 18, 2173–2181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.H.C.; Ma, J.Y.W.; Jobling, A.I.; Brandli, A.; Greferath, U.; Fletcher, E.L.; Vessey, K.A. Exploring the pathogenesis of age-related macular degeneration: A review of the interplay between retinal pigment epithelium dysfunction and the innate immune system. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1009599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somasundaran, S.; Constable, I.J.; Mellough, C.B.; Carvalho, L.S. Retinal pigment epithelium and age-related macular degeneration: A review of major disease mechanisms. Clin. Experiment. Ophthalmol. 2020, 48, 1043–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nita, M.; Grzybowski, A. Antioxidative Role of Heterophagy, Autophagy, and Mitophagy in the Retina and Their Association with the Age-Related Macular Degeneration (AMD) Etiopathogenesis. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Yang, J.; Xiao, B.; Wang, Y.; Lei, Y.; Lai, D.; Qiu, Q. Aberrant Lipid Metabolism and Complement Activation in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2024, 65, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yako, T.; Otsu, W.; Nakamura, S.; Shimazawa, M.; Hara, H. Lipid Droplet Accumulation Promotes RPE Dysfunction. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, D.T.; Pandey, K.; Engel, A.; Horton, N.; Haydinger, C.D.; Robbings, B.M.; Lim, R.R.; Sadilek, M.; Zhang, Q.; Gulette, G.A.; et al. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase inhibition increases retinal pigment epithelial cell fatty acid flux and restricts apolipoprotein efflux. J. Biol. Chem. 2024, 300, 107772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Lei, C.; Gong, K.; Bai, S.; Sun, L. Palmitic acid promotes human retinal pigment epithelial cells migration by upregulating miR-222 expression and inhibiting NUMB. Aging 2023, 15, 9341–9357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gelat, B.; Malaviya, P.; Rathaur, P.; Trivedi, K.; Chaudhary, P.; Patel, B.; Johar, K.; Gelat, R. Regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in retinal pigment epithelium and its associated cellular signaling cascades: An updated review. Beni-Suef Univ. J. Basic Appl. Sci. 2023, 12, 94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, R.; Cuervo, A.M. Lipophagy: Connecting autophagy and lipid metabolism. Int. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 2012, 282041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Intartaglia, D.; Giamundo, G.; Conte, I. Autophagy in the retinal pigment epithelium: A new vision and future challenges. FEBS J. 2022, 289, 7199–7212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y.; Lee, L.; Zhang, L.; Zhou, Q. Association between fatty acid intake and age-related macular degeneration: A meta-analysis. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1403987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puddu, A.; Sanguineti, R.; Montecucco, F.; Viviani, G.L. Retinal pigment epithelial cells express a functional receptor for glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1). Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 975032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Liu, K.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, Y.; Ye, W.; Zhang, Y. Exendin-4 alleviates retinal vascular leakage by protecting the blood-retinal barrier and reducing retinal vascular permeability in diabetic Goto-Kakizaki rats. Exp. Eye Res. 2014, 127, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.; Zong, Y.; Ma, Y.; Tian, Y.; Pang, Y.; Zhang, C.; Gao, J. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor: Mechanisms and advances in therapy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Jin, H.J.; Wu, Z.H.; Zhang, B.F.; Wu, J.; Huang, Z.Y.; Huang, Y.P.; Lu, X.W.; Zheng, X.T. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonist exendin 4 ameliorates diabetes-associated vascular calcification by regulating mitophagy through the AMPK signaling pathway. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Tang, L.; Xin, G.; Li, S.; Ma, L.; Xu, Y.; Zhuang, M.; Xiong, Q.; Wei, Z.; Xing, Z.; et al. Oxidative stress mediated by lipid metabolism contributes to high glucose-induced senescence in retinal pigment epithelium. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 130, 48–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Garcia, J.; Usategui-Martin, R.; Sanabria, M.R.; Fernandez-Perez, E.; Telleria, J.J.; Coco-Martin, R.M. Pathophysiology of Age-Related Macular Degeneration: Implications for Treatment. Ophthalmic Res. 2022, 65, 615–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corbet, C.; Bastien, E.; Santiago de Jesus, J.P.; Dierge, E.; Martherus, R.; Vander Linden, C.; Doix, B.; Degavre, C.; Guilbaud, C.; Petit, L.; et al. TGFβ2-induced formation of lipid droplets supports acidosis-driven EMT and the metastatic spreading of cancer cells. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meng, L.H.; Chen, Y.X. Lipid accumulation and protein modifications of Bruch’s membrane in age-related macular degeneration. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 14, 766–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bu, T.; Sun, Z.; Pan, Y.; Deng, X.; Yuan, G. Glucagon-Like Peptide-1: New Regulator in Lipid Metabolism. Diabetes Metab. J. 2024, 48, 354–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Xu, L.; Zhu, L.; Liu, Y.; Yang, S.; Zhao, M. Lipid Droplets, the Central Hub Integrating Cell Metabolism and the Immune System. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 746749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.-C.; Chien, Y.; Yarmishyn, A.A.; Lim, L.-Y.; Tsai, H.-Y.; Kuo, W.-C.; Tsai, P.-H.; Yang, S.-H.; Hong, S.-I.; Chen, S.-J.; et al. Inhibition of oxidative stress-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in retinal pigment epithelial cells of age-related macular degeneration model by suppressing ERK activation. J. Adv. Res. 2024, 60, 141–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, F.; Raciti, G.A.; Nigro, C.; Mannino, G.C.; Procopio, T.; Davalli, A.M.; Beguinot, F.; Sesti, G.; Miele, C.; Folli, F. The GLP-1 receptor agonists exenatide and liraglutide activate Glucose transport by an AMPK-dependent mechanism. J. Transl. Med. 2016, 14, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, T.; Yan, W.; Cui, X.; Liu, N.; Wei, X.; Sun, Y.; Fan, K.; Liu, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, Z.; et al. Liraglutide attenuates type 2 diabetes mellitus-associated non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by activating AMPK/ACC signaling and inhibiting ferroptosis. Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Yang, P.; Liang, Y.; Xia, N.; Li, Y.; Su, H.; Pan, H. Effects of liraglutide on lipolysis and the AC3/PKA/HSL pathway. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2019, 12, 1697–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zhao, T.; Wei, X.; Zhang, D.; Lv, W.; Luo, Z. Dietary Phosphorus Reduced Hepatic Lipid Deposition by Activating Ampk Pathway and Beclin1 Phosphorylation Levels to Activate Lipophagy in Tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 841187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Din, Z.U.; Cui, B.; Wang, C.; Zhang, X.; Mehmood, A.; Peng, F.; Liu, Q. Crosstalk between lipid metabolism and EMT: Emerging mechanisms and cancer therapy. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2024, 480, 103–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kushwah, N.; Bora, K.; Maurya, M.; Pavlovich, M.C.; Chen, J. Oxidative Stress and Antioxidants in Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheth, S.; Patel, A.; Foreman, M.; Mumtaz, M.; Reddy, A.; Sharaf, R.; Sheth, S.; Lucke-wold, B. The protective role of glucagon-like peptide 1 in neuro-ophthalmology. Explor. Drug Sci. 2023, 1, 221–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szekeres, Z.; Nagy, A.; Jahner, K.; Szabados, E. Impact of Selected Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists on Serum Lipids, Adipose Tissue, and Muscle Metabolism—A Narrative Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saw, M.; Wong, V.W.; Ho, I.V.; Liew, G. New anti-hyperglycaemic agents for type 2 diabetes and their effects on diabetic retinopathy. Eye 2019, 33, 1842–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, G.; Wei, Y.; Li, M.; Du, E.; Li, H.; Song, Z.; Tao, Y. RPE-derived exosomes rescue the photoreceptors during retina degeneration: An intraocular approach to deliver exosomes into the subretinal space. Drug Deliv. 2021, 28, 218–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.F.; Luh, F.; Ho, Y.S.; Yen, Y. Exosomes: A review of biologic function, diagnostic and targeted therapy applications, and clinical trials. J. Biomed. Sci. 2024, 31, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Fan, X.; Rui, H.; Ren, X.; Wen, D.; Zheng, C.; Li, X. Exosomes derived from RPE cells under oxidative stress mediate inflammation and apoptosis of normal RPE cells through Apaf1/caspase-9 axis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2020, 121, 4849–4861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.Y.; Hung, Y.C.; Chou, C.C.; Chen, C.; Cheng, C.M.; Chen, C.; Liou, J.C.; Hsu, M.Y. Isolation of three different sizes of exosomes in an Asian population with different retinal diseases before and after treatment: Preliminary results. Bioengineered 2024, 15, 2297320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, D.; Feng, P.; Guan, X.; Liu, Z.; Li, D.; Xue, C.; Bai, B.; Hölscher, C. Neuroprotective effects of GLP-1 class drugs in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1462240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allan, K.C.; Joo, J.H.; Kim, S.; Shaia, J.; Kaelber, D.C.; Singh, R.; Talcott, K.E.; Rachitskaya, A.V. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Impact on Chronic Ocular Disease Including Age-Related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmology 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos Rego, I.; Silvério, D.; Eufrásio, M.I.; Pinhanços, S.S.; Lopes da Costa, B.; Teixeira, J.; Fernandes, H.; Kong, Y.; Li, Y.; Tsang, S.H.; et al. TRAP1 Is Expressed in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells and Is Required to Maintain their Energetic Status. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Genes | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|
| SNAI1 | CCTCCCTGTCAGATGAGGAC | CCAGGCTGAGGTATTCCTTG |
| TWIST1 | GCCAGGTACATCGACTTCCTCT | TCCATCCTCCAGACCGAGAAGG |
| TWIST2 | GAGTCCGCAGTCTTACGAGG | GCTCTGCAGCTCCTCGTCT |
| ATG5 | GGAATGGTGTTCGTCCTTCA | CAGGGAAGGAACAGCTTTGA |
| LIPA | GTGGGTCATTCTCAAGGCACCA | CCATAGGGCTAGTACAGAAGGC |
| RAB7A | CCTCGAAAACAGACAAGTGGC | ATTCCGTGCAATCGTCTGGA |
| LAMP2 | TATGTGCAACAAAGAGCAGA | CAGCATGATGGTGCTTGAG |
| GAPDH | GATTCCACCCATGGCAAATTC | CTGGAAGATGGTGATGGGATT |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tsou, S.-H.; Luo, K.-S.; Huang, C.-N.; Kornelius, E.; Cheng, I.-T.; Hung, H.-C.; Hung, Y.-C.; Lin, C.-L.; Hsu, M.-Y. Liraglutide Attenuates FFA-Induced Retinal Pigment Epithelium Dysfunction via AMPK Activation and Lipid Homeostasis Regulation in ARPE-19 Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083704
Tsou S-H, Luo K-S, Huang C-N, Kornelius E, Cheng I-T, Hung H-C, Hung Y-C, Lin C-L, Hsu M-Y. Liraglutide Attenuates FFA-Induced Retinal Pigment Epithelium Dysfunction via AMPK Activation and Lipid Homeostasis Regulation in ARPE-19 Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083704
Chicago/Turabian StyleTsou, Sing-Hua, Kai-Shin Luo, Chien-Ning Huang, Edy Kornelius, I-Ting Cheng, Hui-Chih Hung, Yu-Chien Hung, Chih-Li Lin, and Min-Yen Hsu. 2025. "Liraglutide Attenuates FFA-Induced Retinal Pigment Epithelium Dysfunction via AMPK Activation and Lipid Homeostasis Regulation in ARPE-19 Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083704
APA StyleTsou, S.-H., Luo, K.-S., Huang, C.-N., Kornelius, E., Cheng, I.-T., Hung, H.-C., Hung, Y.-C., Lin, C.-L., & Hsu, M.-Y. (2025). Liraglutide Attenuates FFA-Induced Retinal Pigment Epithelium Dysfunction via AMPK Activation and Lipid Homeostasis Regulation in ARPE-19 Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3704. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083704







