Bioinformatics Analysis Reveals the Evolutionary Characteristics of the Phoebe bournei ARF Gene Family and Its Expression Patterns in Stress Adaptation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
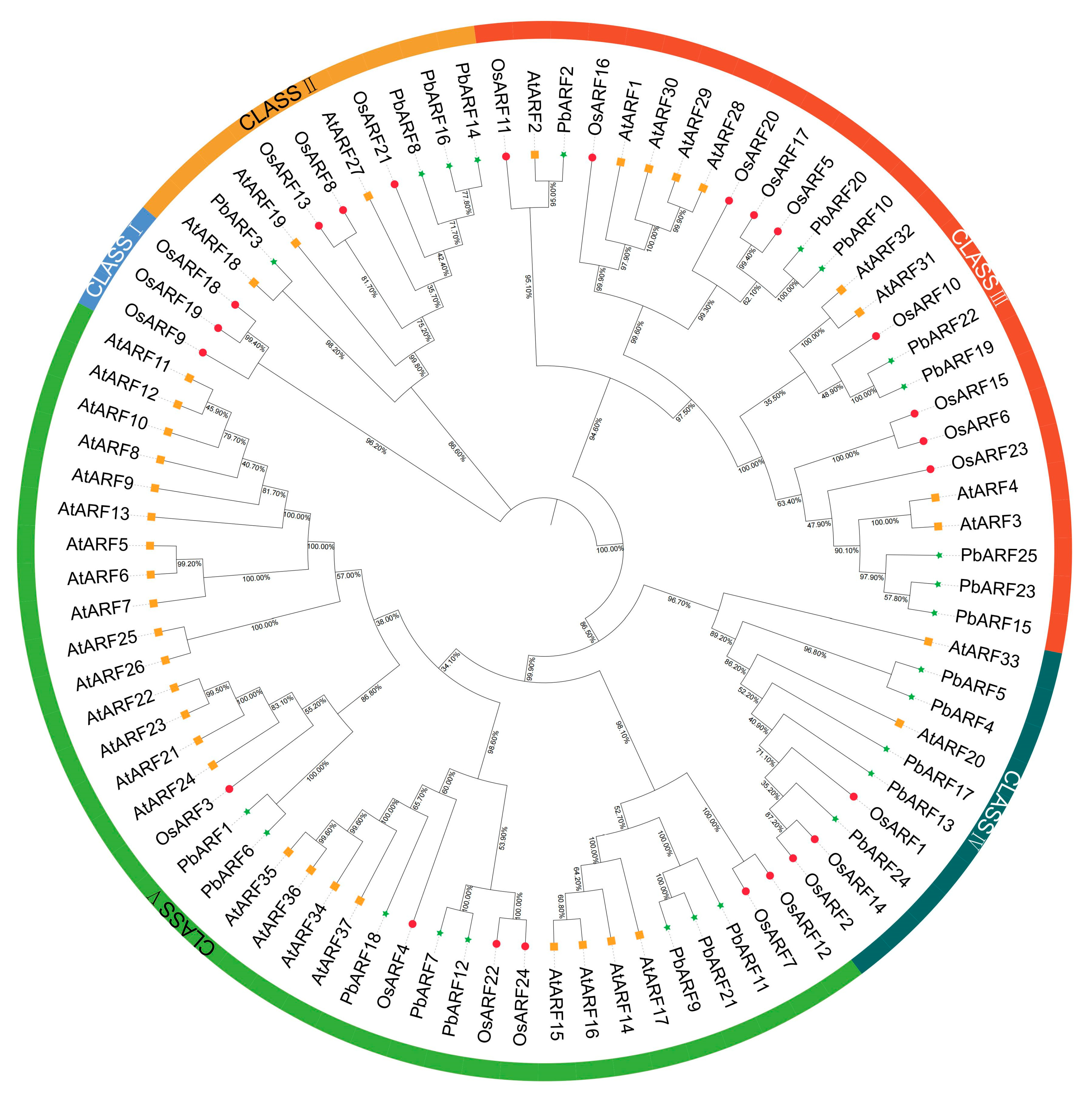
2.1. Identification and Phylogenetic Analysis of ARF Gene Family in Phoebe bournei
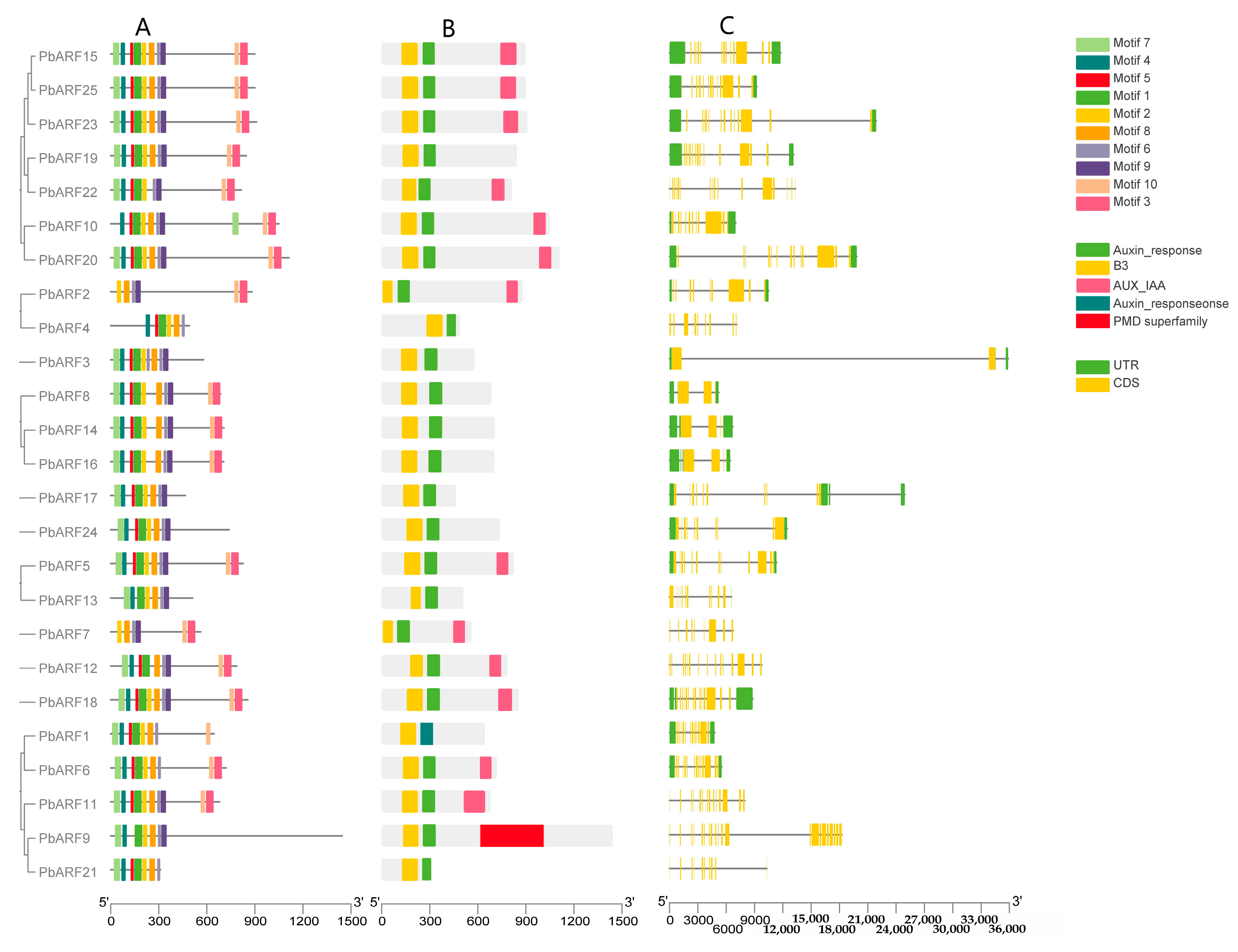
2.2. Protein Motif and Gene Structure Analysis of PbARF Genes
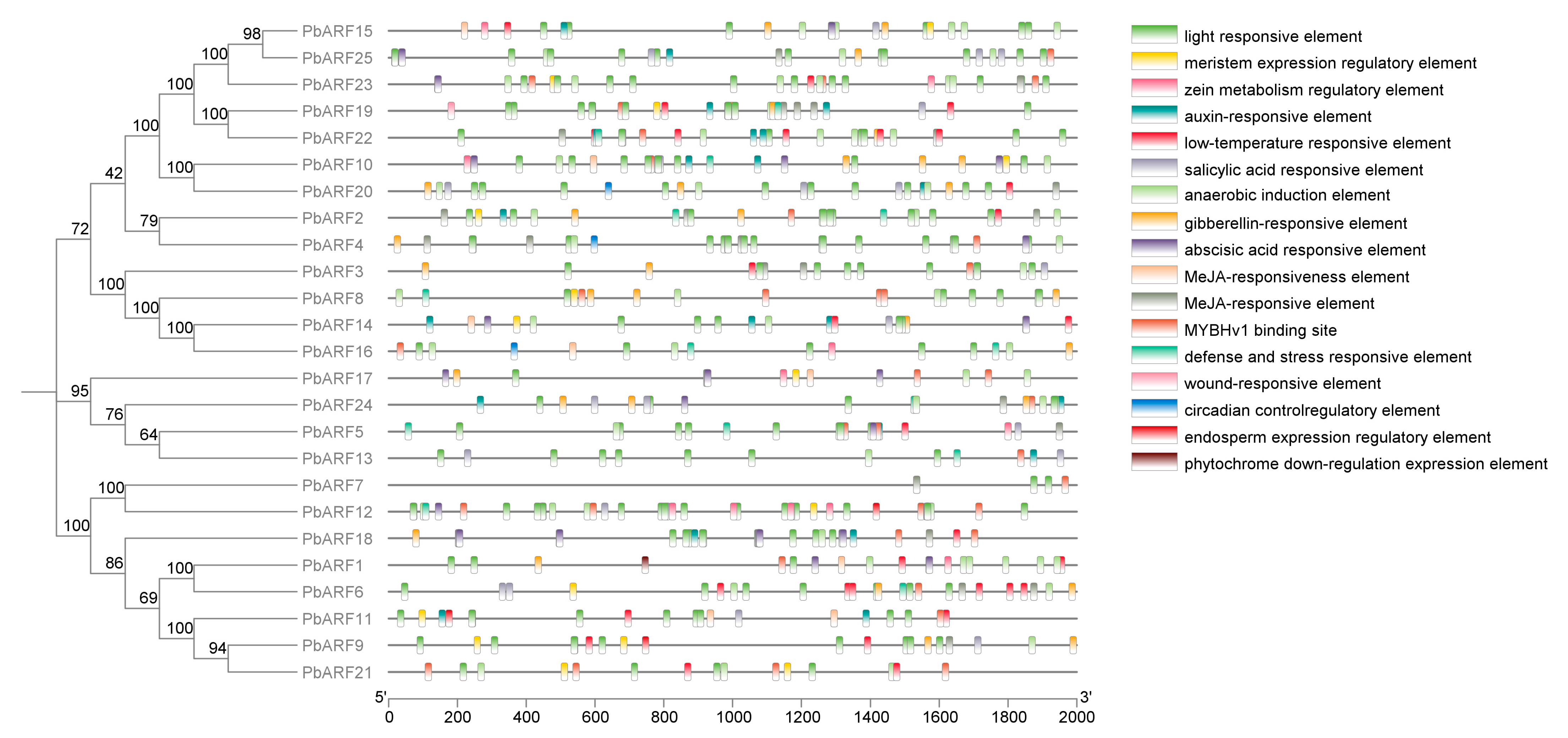
2.3. Cis-Acting Element Analysis of PbARF Gene Family
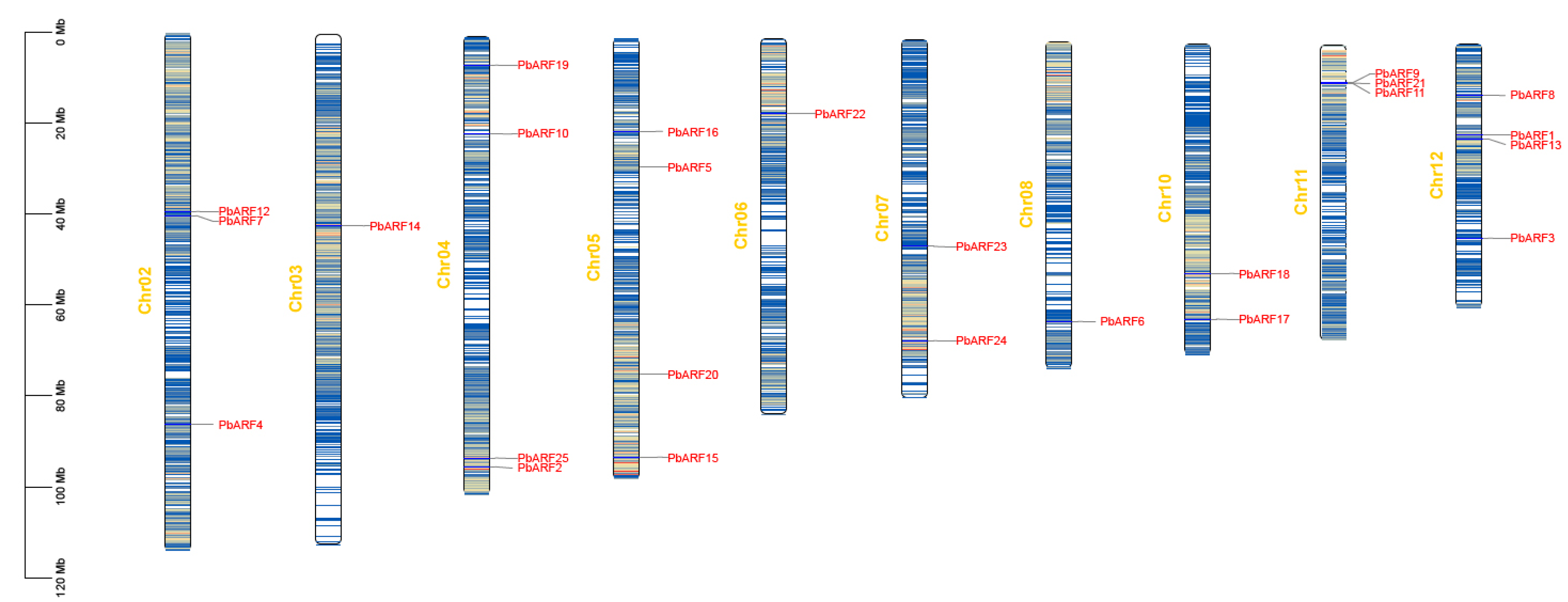
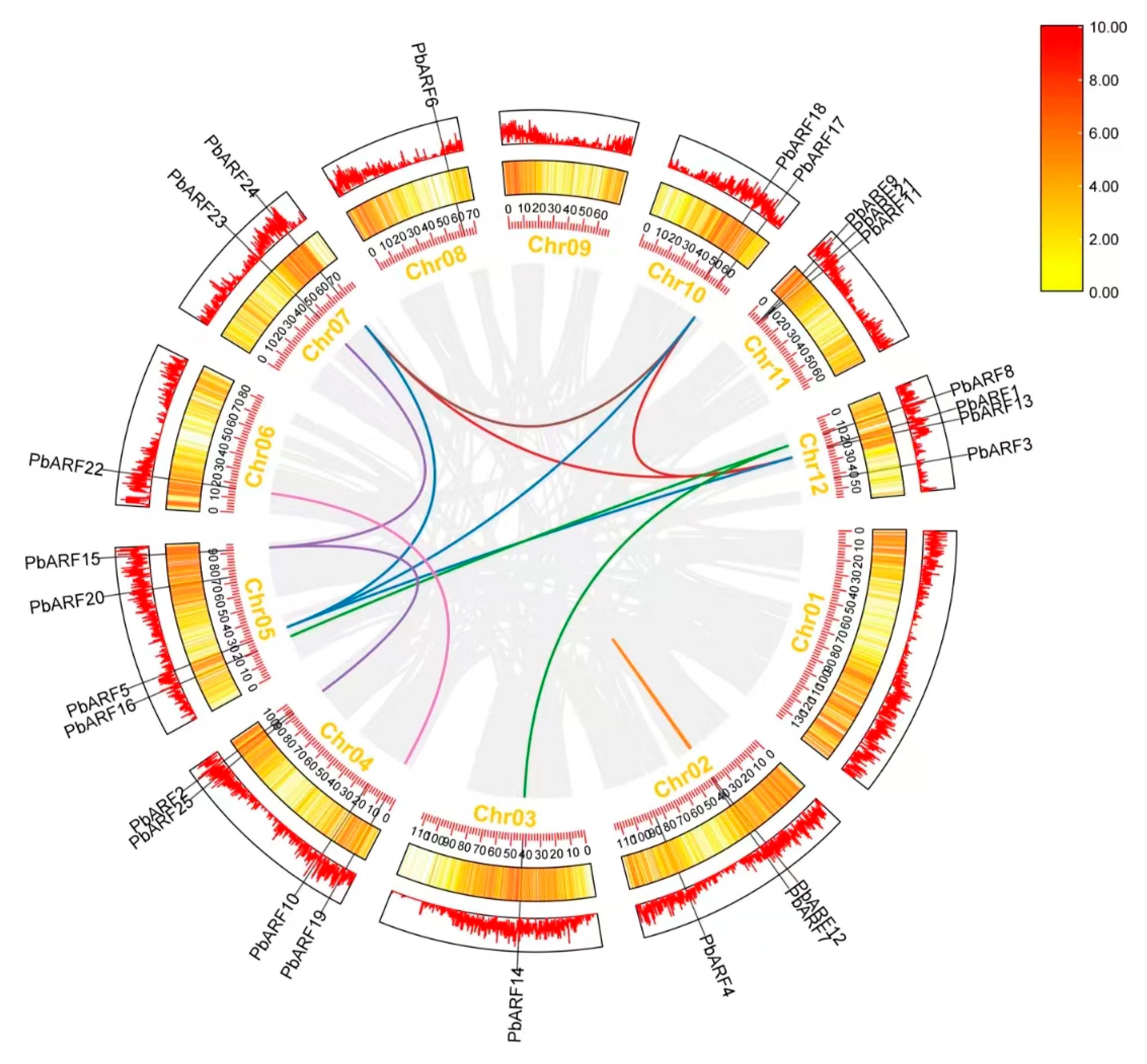
2.4. Synteny Analysis of PbARF Gene Family
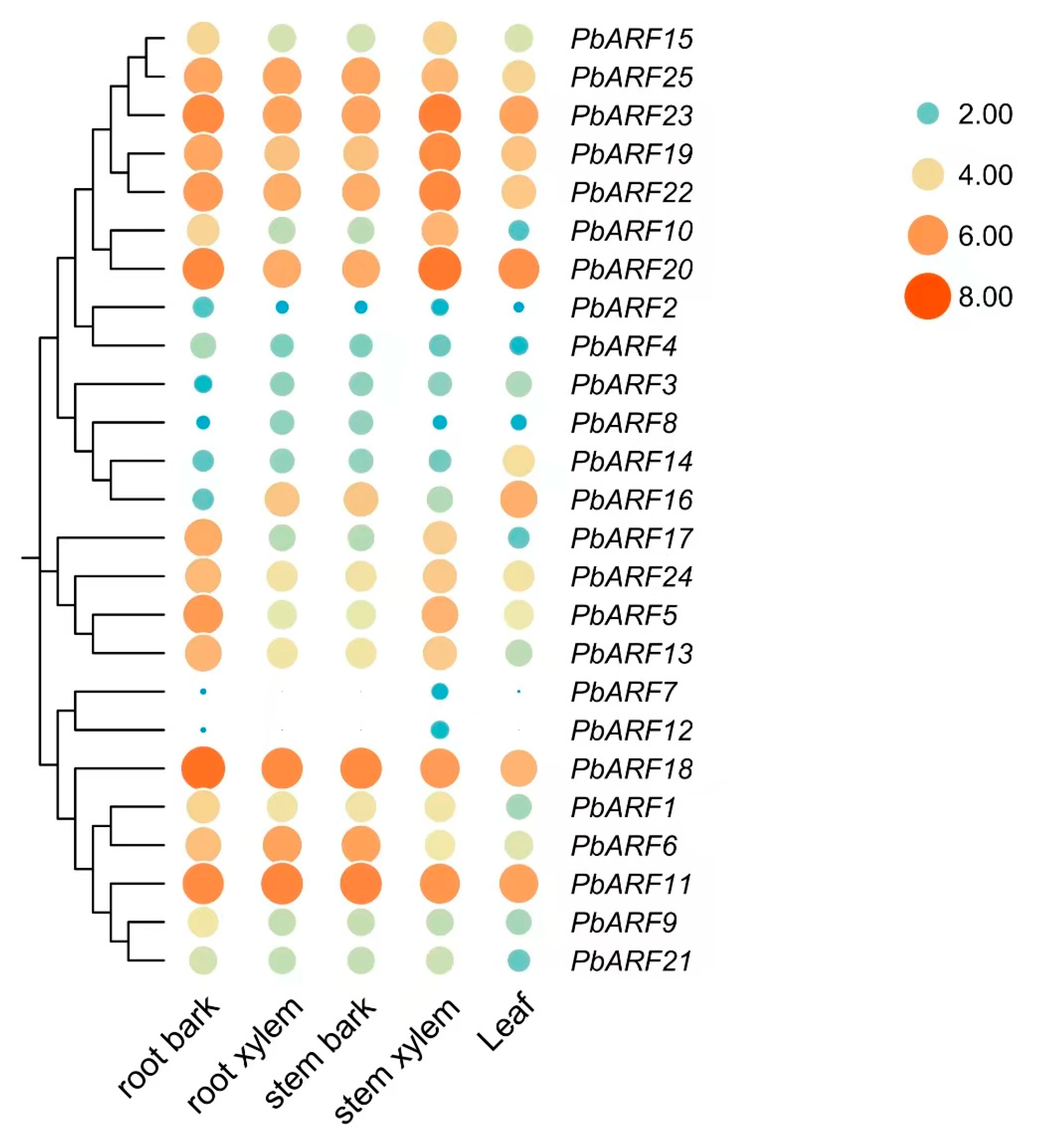
2.5. Expression Analysis of PbARF Gene in Different Tissues of Phoebe bournei
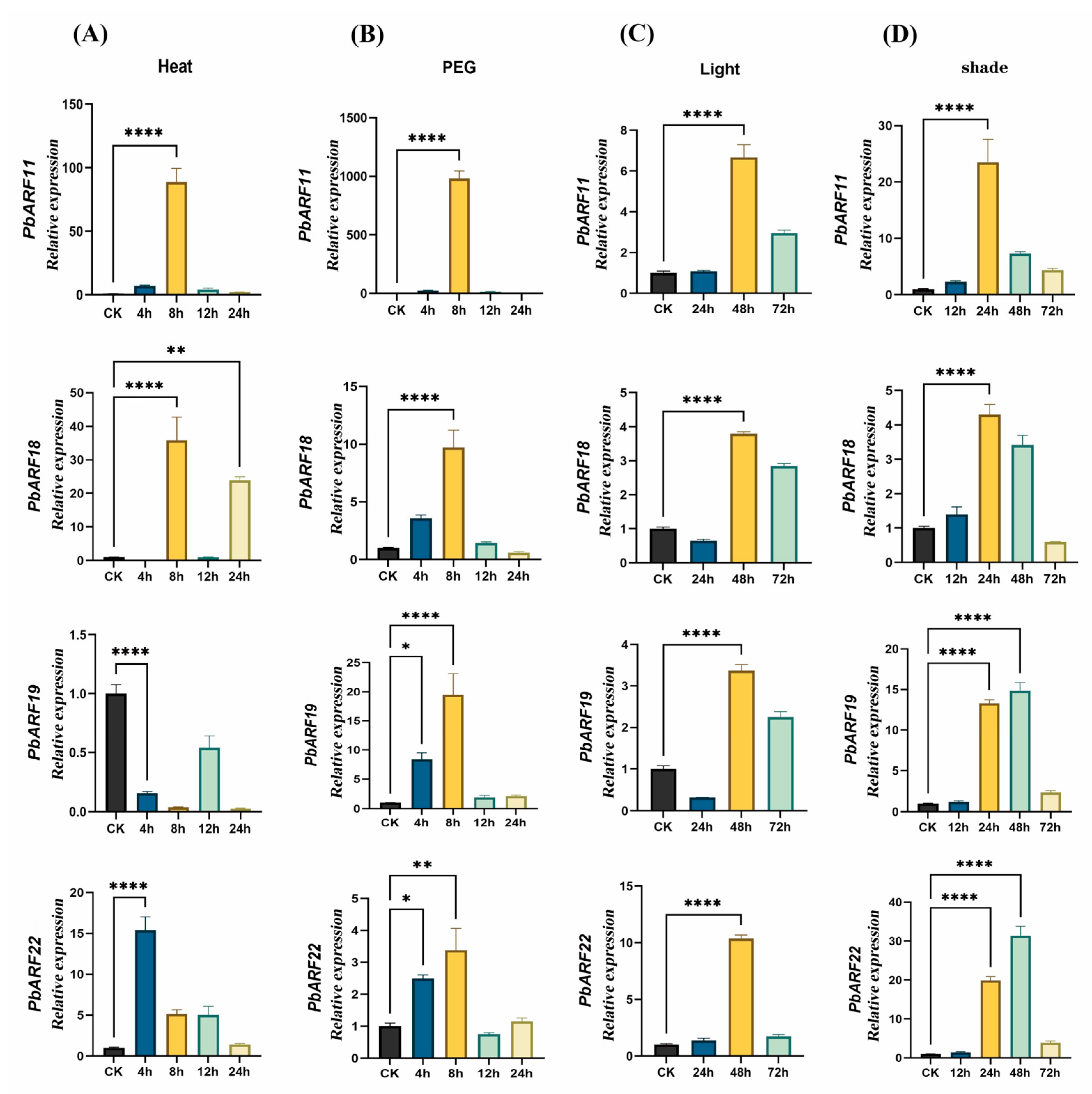
2.6. Expression Analysis of the PbARF Gene Under Different Treatments
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Genome Data and Plant Material Source
4.2. Identification and Analysis of Physical and Chemical Properties
4.3. Chromosomal Distribution and Gene Duplication of PbARF1 Genes
4.4. Collinearity Analysis of PbARF1 Genes
4.5. Phylogenetic Analysis
4.6. Analysis of Conserved Motifs and Gene Structures
4.7. Multiple Sequence Alignment and Promoter Cis-Element Analysis of PbARF1 Genes
4.8. Different Plant Tissues and Abiotic Stress Treatments
4.9. qRT-PCR Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Daviere, J.M.; Wild, M.; Regnault, T.; Baumberger, N.; Eisler, H.; Genschik, P.; Achard, P. Class I TCP-DELLA interactions in inflorescence shoot apex determine plant height. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, 1923–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chai, C.; Valliyodan, B.; Maupin, C.; Annen, B.; Nguyen, H.T. Genome-wide analysis and expression profiling of the PIN auxin transporter gene family in soybean (Glycine max). BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dudhate, A.; Shinde, H.; Yu, P.; Tsugama, D.; Gupta, S.K.; Liu, S.; Takano, T. Comprehensive analysis of NAC transcription factor family uncovers drought and salinity stress response in pearl millet (Pennisetum glaucum). BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, K.; Xia, Y.; Zhan, D.; Xu, T.; Lu, T.; Yang, J.; Kang, X. Genome-Wide Identification of the Eucalyptus urophylla GATA Gene Family and Its Diverse Roles in Chlorophyll Biosynthesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 5251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavy, M.; Estelle, M. Mechanisms of auxin signaling. Development 2016, 143, 3226–3229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Tyagi, A.K.; Sharma, A.K. Genome-wide analysis of auxin response factor (ARF) gene family from tomato and analysis of their role in flower and fruit development. Mol. Genet. Genom. 2011, 285, 245–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Pei, K.; Fu, Y.; Sun, Z.; Li, S.; Liu, H.; Tang, K.; Han, B.; Tao, Y. Genome-wide analysis of the auxin response factors (ARF) gene family in rice (Oryza sativa). Gene 2007, 394, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nanao, M.H.; Vinos-Poyo, T.; Brunoud, G.; Thévenon, E.; Mazzoleni, M.; Mast, D.; Lainé, S.; Wang, S.; Hagen, G.; Li, H.; et al. Structural basis for oligomerization of auxin transcriptional regulators. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 3617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Z.; Zhang, F.; Friml, J.; Ding, Z. Auxin signaling: Research advances over the past 30 years. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2022, 64, 371–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korasick, D.A.; Westfall, C.S.; Lee, S.G.; Nanao, M.H.; Dumas, R.; Hagen, G.; Guilfoyle, T.J.; Jez, J.M.; Strader, L.C. Molecular basis for AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR protein interaction and the control of auxin response repression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2014, 111, 5427–5432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okushima, Y.; Overvoorde, P.J.; Arima, K.; Alonso, J.M.; Chan, A.; Chang, C.; Ecker, J.R.; Hughes, B.; Lui, A.; Nguyen, D.; et al. Functional genomic analysis of the AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR gene family members in Arabidopsis thaliana: Unique and overlapping functions of ARF7 and ARF19. Plant Cell 2005, 17, 444–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, H.B.; Cui, B.M.; Ren, Y.L.; Li, J.H.; Liao, W.B.; Xu, N.F.; Peng, M. Research Progresses on Auxin Response Factors. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2006, 48, 622–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Wang, S.; Bai, Y.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, S.; Chen, M.; Guilfoyle, T.J.; Wu, P.; Qi, Y. Functional analysis of the structural domain of ARF proteins in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Exp. Bot. 2010, 61, 3971–3981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieffer, M.; Neve, J.; Kepinski, S. Defining auxin response contexts in plant development. Curr. Opin. Plant Biol. 2010, 13, 12–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Jiang, H.Y.; Chen, W.J.; Qian, Y.X.; Ma, Q.; Cheng, B.J.; Zhu, S.W. Genome-wide analysis of the auxin response factor (ARF) gene family in maize (Zea mays). Plant Growth Regul. 2011, 63, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, U.C.; Difazio, S.P.; Brunner, A.M.; Tuskan, G.A. Genome-wide analysis of Aux/IAA and ARF gene families in Populus trichocarpa. BMC Plant Biol. 2007, 7, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paterson, A.H.; Bowers, J.E.; Bruggmann, R.; Dubchak, I.; Grimwood, J.; Gundlach, H.; Haberer, G.; Hellsten, U.; Mitros, T.; Poliakov, A.; et al. The Sorghum bicolor genome and the diversification of grasses. Nature 2009, 457, 551–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, F.; Cheng, L.; Kong, F.; Peng, Z.; Liu, S.; Yu, X.; Lu, G. Identification, isolation and expression analysis of auxin response factor (ARF) genes in Solanum lycopersicum. Plant Cell Rep. 2011, 30, 2059–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, A.; Nishiyama, M.Y.; Fuentes, B.G.; Souza, G.M.; Janies, D.; Gray, J.; Grotewold, E. GRASSIUS: A platform for comparative regulatory genomics across the grasses. Plant Physiol. 2009, 149, 171–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, J.P.; Pekker, I.; Goldshmidt, A.; Blum, E.; Amsellem, Z.; Eshed, Y. Endogenous and synthetic microRNAs stimulate simultaneous, efficient, and localized regulation of multiple targets in diverse species. Plant Cell 2006, 18, 1134–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goetz, M.; Hooper, L.C.; Johnson, S.D.; Rodrigues, J.C.M.; Vivian-Smith, A.; Koltunow, A.M. Expression of aberrant forms of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR8 stimulates parthenocarpy in Arabidopsis and tomato. Plant Physiol. 2007, 145, 351–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, J.L.; Wang, K.; Liu, X.; Chen, S.N.; Chen, J.S. The quantification of tomato microRNAs response to viral infection by stem-loop real-time RT-PCR. Gene 2009, 437, 14–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jong, M.D.; Wolters-Arts, M.; Feron, R.; Mariani, C.; Vriezen, W.H. The Solanum lycopersicum auxin response factor 7 (SlARF7) regulates auxin signaling during tomato fruit set and development. Plant J. 2009, 57, 160–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finet, C.; Berne-Dedieu, A.; Scutt, C.P.; Marletaz, F. Evolution of the ARF gene family in land plants: Old domains, new tricks. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Ma, Y.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, X.; Fan, K.; Hu, X.; Wang, S.; et al. Identification and transcriptome data analysis of ARF family genes in five Orchidaceae species. Plant Mol. Biol. 2023, 112, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Shen, Y.; He, F.; Fu, X.; Yu, H.; Lu, W.; Li, Y.; Li, C.; Fan, D.; Wang, H.C.; et al. Auxin-mediated Aux/IAA-ARF-HB signaling cascade regulates secondary xylem development in Populus. New Phytol. 2019, 222, 752–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahajan, S.; Tuteja, N. Cold, salinity and drought stresses: An overview. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2005, 444, 139–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, J.K. Thriving under Stress: How Plants Balance Growth and the Stress Response. Dev. Cell 2020, 55, 529–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mateusz, L.; Philippe, J. Molecular Advances in Abiotic Stress Signaling in Plants: Focus on Atmospheric Stressors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A. Auxin: A regulator of cold stress response. Physiol. Plant 2013, 147, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waadt, R.; Seller, C.A.; Hsu, P.; Takahashi, Y.H.; Munemasa, S.; Schroeder, J.I. Publisher Correction: Plant hormone regulation of abiotic stress responses. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, J.W. Auxin response factors. Plant Cell Environ. 2016, 39, 1014–1028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panchy, N.; Lehti-Shiu, M.; Shiu, S.H. Evolution of Gene Duplication in Plants. Plant Physiol. 2016, 171, 2294–2316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, K. The interaction and integration of auxin signaling components. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouine, M.; Fu, Y.; Chateigner-Boutin, A.L.; Mila, I.; Frasse, P.; Wang, H.; Audran, C.; Roustan, J.P.; Bouzayen, M. Characterization of the tomato ARF gene family uncovers a multi-levels post-transcriptional regulation including alternative splicing. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e84203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouzroud, S.; Gouiaa, S.; Hu, N.; Bernadac, A.; Mila, I.; Bendaou, N.; Smouni, A.; Bouzayen, M.; Zouine, M. Auxin Response Factors (ARFs) are potential mediators of auxin action in tomato response to biotic and abiotic stress (Solanum lycopersicum). PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0193517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Han, S.; Qi, Y. Advances in structure and function of auxin response factor in plants. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2023, 65, 617–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagen, G.; Guilfoyle, T. Auxin-responsive gene expression: Genes, promoters and regulatory factors. Plant Mol. Biol. 2002, 49, 373–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmasov, T.; Hagen, G.; Guilfoyle, T.J. Activation and repression of transcription by auxin-response factors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 5844–5849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.C.; Purugganan, M.D. The early stages of duplicate gene evolution. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 15682–15687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emanuel, B.S.; Shaikh, T.H. Segmental duplications: An ‘expanding’ role in genomic instability and disease. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2001, 2, 791–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gemayel, R.; Vinces, M.D.; Legendre, M.; Verstrepen, K.J. Variable tandem repeats accelerate evolution of coding and regulatory sequences. Annu. Rev. Genet. 2010, 44, 445–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuskan, G.A.; Difazio, S.; Jansson, S.; Bohlmann, J.; Grigoriev, I.; Hellsten, U.; Putnam, N.; Ralph, S.; Rombauts, S.; Salamov, A.; et al. The genome of black cottonwood, Populus trichocarpa (Torr. & Gray). Science 2006, 313, 1596–1604. [Google Scholar]
- Vision, T.J.; Brown, D.G.; Tanksley, S.D. The origins of genomic duplications in Arabidopsis. Science 2000, 290, 2114–2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Kaur, N.; Garg, R.; Thakur, J.K.; Tyagi, A.K.; Khurana, J.P. Structure and expression analysis of early auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene family in rice (Oryza sativa). Funct. Integr. Genom. 2006, 6, 47–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Remington, D.L.; Vision, T.J.; Guilfoyle, T.J.; Reed, J.W. Contrasting modes of diversification in the Aux/IAA and ARF gene families. Plant Physiol. 2004, 135, 1738–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilmoth, J.C.; Wang, S.; Tiwari, S.B.; Joshi, A.D.; Hagen, G.; Guilfoyle, T.J.; Alonso, J.M.; Ecker, J.R.; Reed, J.W. NPH4/ARF7 and ARF19 promote leaf expansion and auxin-induced lateral root formation. Plant J. 2005, 43, 118–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harper, R.M.; Stowe-Evans, E.L.; Luesse, D.R.; Muto, H.; Tatematsu, K.; Watahiki, M.K.; Yamamoto, K.; Liscum, E. The NPH4 locus encodes the auxin response factor ARF7, a conditional regulator of differential growth in aerial Arabidopsis tissue. Plant Cell 2000, 12, 757–770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Z.; He, S.; Xu, F.; Wei, X.; Jiang, L.; Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, T.; Xu, P.; Du, S.; et al. Photoexcited CRY1 and phyB interact directly with ARF6 and ARF8 to regulate their DNA-binding activity and auxin-induced hypocotyl elongation in Arabidopsis. New Phytol. 2020, 225, 848–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Targem, M.; Ripper, D.; Bayer, M.; Ragni, L. Auxin and gibberellin signaling cross-talk promotes hypocotyl xylem expansion and cambium homeostasis. J. Exp. Bot. 2021, 72, 3647–3660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Liu, Z.; Yan, J.; Chen, J.; Wang, L.; Yu, W.; Wu, J.; Yan, J. A Torreya grandis ARF transcription factor TgARF15 enhances drought stress tolerance. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2024, 222, 105761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, J.; Han, S.; Chong, S.L.; Meng, G.; Song, M.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Liu, C.; Lou, L.; et al. The chromosome-scale genome of Phoebe bournei reveals contrasting fates of terpene synthase (TPS)-a and TPS-b subfamilies. Plant Commun. 2022, 3, 100410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Liu, D.K.; Wang, Q.Q.; Ke, S.; Li, Y.; Zhang, D.; Zheng, Q.; Zhang, C.; Liu, Z.J.; Lan, S. Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the GRAS gene family in Dendrobium chrysotoxum. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 1058287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J.; Yan, Q.; Li, J.; Feng, L.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, J.; Xia, R.; Zeng, Z.; Liu, Y. The GRAS gene family and its roles in seed development in litchi (Litchi chinensis Sonn). BMC Plant Biol. 2021, 21, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An Integrative Toolkit Developed for Interactive Analyses of Big Biological Data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Debarry, J.D.; Tan, X.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Lee, T.H.; Jin, H.; Marler, B.; Guo, H.; et al. MCScanX: A toolkit for detection and evolutionary analysis of gene synteny and collinearity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012, 40, e49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene Name | Gene ID | AA/aa | MW/kDa | pI | II | AI | GRAVY | Subcelluar Localization | CLASS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OF09010 | PbARF1 | 715 | 80,305.10 | 6.04 | 58.31 | 73.61 | −0.470 | Nucleus | V |
| OF01795 | PbARF2 | 1059 | 117,250.14 | 5.57 | 57.40 | 73.98 | −0.485 | Nucleus | III |
| OF13500 | PbARF3 | 571 | 62,566.62 | 7.56 | 44.58 | 71.84 | −0.337 | Nucleus | II |
| OF12274 | PbARF4 | 490 | 53,867.87 | 9.27 | 56.49 | 81.41 | −0.324 | Nucleus | IV |
| OF00399 | PbARF5 | 826 | 91,562.44 | 6.33 | 43.97 | 73.16 | −0.434 | Nucleus | IV |
| OF14335 | PbARF6 | 720 | 80,909.46 | 6.07 | 57.04 | 73.50 | −0.502 | Nucleus | V |
| OF02341 | PbARF7 | 561 | 62,376.75 | 8.02 | 50.82 | 70.91 | −0.466 | Nucleus | V |
| OF14461 | PbARF8 | 674 | 74,422.02 | 7.01 | 50.77 | 71.31 | −0.413 | Nucleus | II |
| OF14278 | PbARF9 | 1444 | 165,759.74 | 6.70 | 46.97 | 76.20 | −0.467 | Nucleus | V |
| OF15166 | PbARF10 | 1057 | 117,517.64 | 6.22 | 61.66 | 77.31 | −0.477 | Peroxisome | III |
| OF14282 | PbARF11 | 680 | 75,645.98 | 5.99 | 58.56 | 67.81 | −0.553 | Nucleus | V |
| OF21754 | PbARF12 | 787 | 87,876.70 | 6.56 | 52.77 | 72.35 | −0.459 | Nucleus | V |
| OF09049 | PbARF13 | 511 | 56,529.57 | 8.04 | 49.50 | 88.18 | −0.221 | Chloroplast | IV |
| OF05709 | PbARF14 | 707 | 77,550.83 | 7.56 | 46.17 | 74.61 | −0.350 | Nucleus | II |
| OF05094 | PbARF15 | 899 | 99,896.26 | 6.06 | 63.09 | 78.08 | −0.471 | Nucleus | III |
| OF07141 | PbARF16 | 705 | 77,183.54 | 6.56 | 50.96 | 75.80 | −0.301 | Nucleus | II |
| OF20357 | PbARF17 | 662 | 73,604.32 | 6.60 | 51.51 | 72.73 | −0.410 | Peroxisome | IV |
| OF20735 | PbARF18 | 856 | 95,038.56 | 5.82 | 55.64 | 64.68 | −0.620 | Nucleus | V |
| OF22918 | PbARF19 | 828 | 93,545.12 | 6.11 | 60.73 | 71.11 | −0.505 | Nucleus | III |
| OF26137 | PbARF20 | 1113 | 122,852.38 | 6.13 | 60.47 | 74.59 | −0.518 | Nucleus | III |
| OF14279 | PbARF21 | 311 | 35,145.69 | 6.40 | 63.31 | 71.45 | −0.430 | Nucleus | V |
| OF18244 | PbARF22 | 815 | 91,853.67 | 5.88 | 60.23 | 75.24 | −0.437 | Nucleus | III |
| OF15400 | PbARF23 | 910 | 100,774.16 | 6.06 | 71.90 | 76.27 | −0.449 | Nucleus | III |
| OF24604 | PbARF24 | 738 | 81,011.35 | 7.35 | 54.56 | 70.26 | −0.437 | Nucleus | IV |
| OF01686 | PbARF25 | 900 | 99,660.42 | 6.17 | 63.19 | 80.14 | −0.383 | Nucleus | III |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zheng, K.; Feng, Y.; Liu, R.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, D.; Zhong, K.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Cao, S. Bioinformatics Analysis Reveals the Evolutionary Characteristics of the Phoebe bournei ARF Gene Family and Its Expression Patterns in Stress Adaptation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083701
Zheng K, Feng Y, Liu R, Zhang Y, Fan D, Zhong K, Tang X, Zhang Q, Cao S. Bioinformatics Analysis Reveals the Evolutionary Characteristics of the Phoebe bournei ARF Gene Family and Its Expression Patterns in Stress Adaptation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083701
Chicago/Turabian StyleZheng, Kehui, Yizhuo Feng, Ronglin Liu, Yanlin Zhang, Dunjin Fan, Kai Zhong, Xinghao Tang, Qinghua Zhang, and Shijiang Cao. 2025. "Bioinformatics Analysis Reveals the Evolutionary Characteristics of the Phoebe bournei ARF Gene Family and Its Expression Patterns in Stress Adaptation" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083701
APA StyleZheng, K., Feng, Y., Liu, R., Zhang, Y., Fan, D., Zhong, K., Tang, X., Zhang, Q., & Cao, S. (2025). Bioinformatics Analysis Reveals the Evolutionary Characteristics of the Phoebe bournei ARF Gene Family and Its Expression Patterns in Stress Adaptation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083701







