Quantification of Urine and Plasma Levels of Extracellular Vesicles in a Cohort of Kidney Transplant Recipients and Chronic Kidney Disease Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
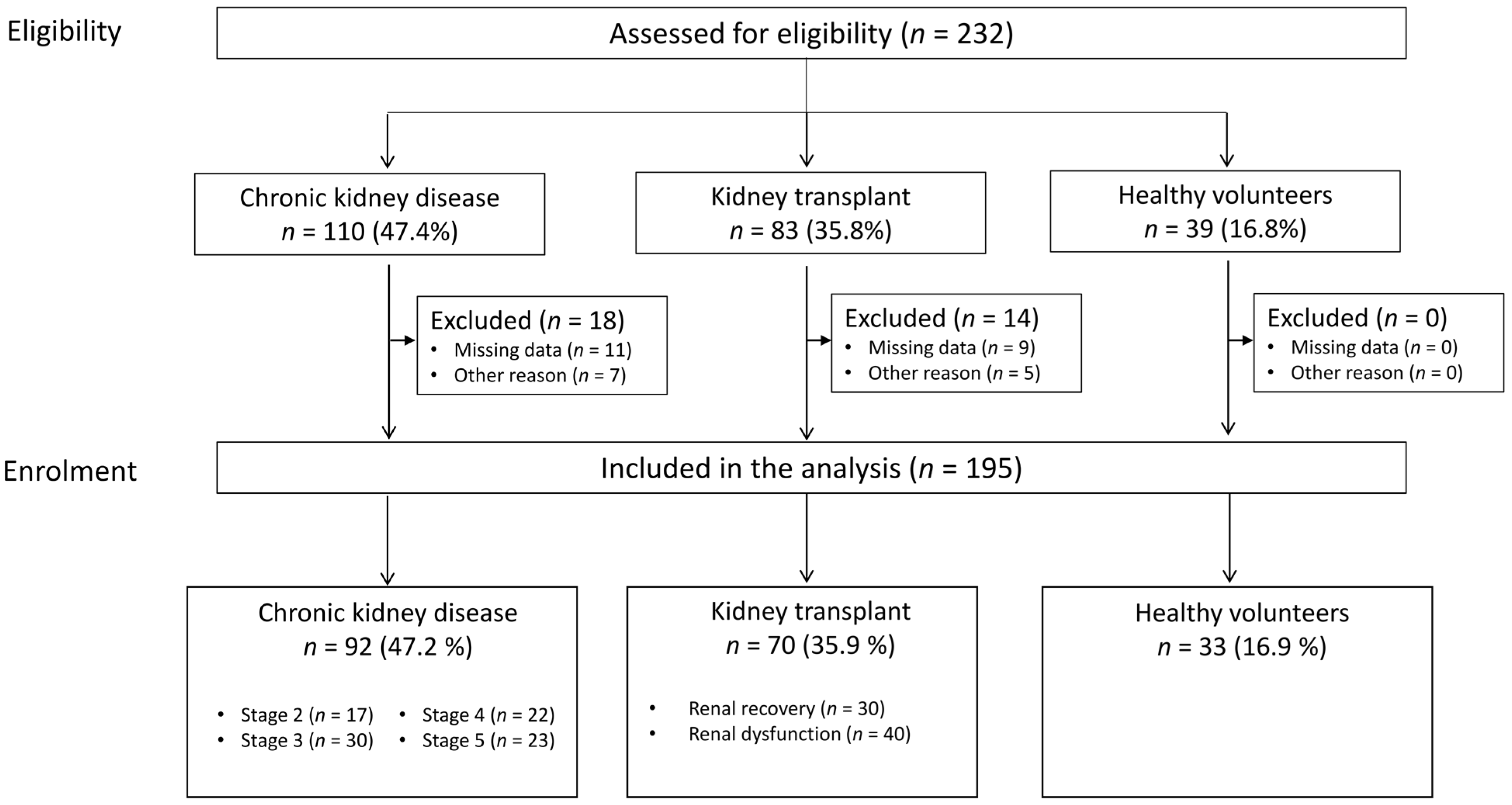
2.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
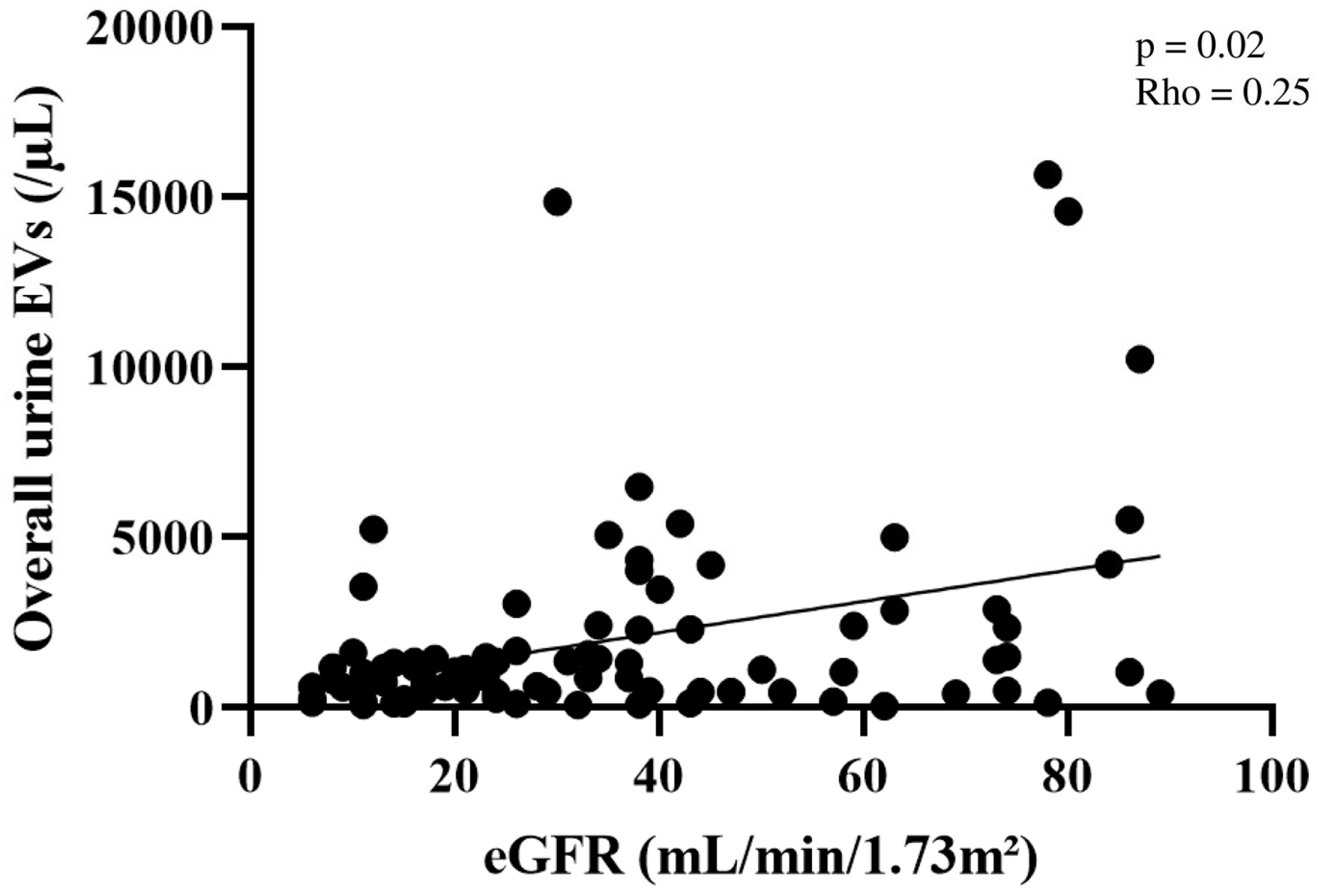
2.2. Quantification of Plasma and Urine EV Concentrations
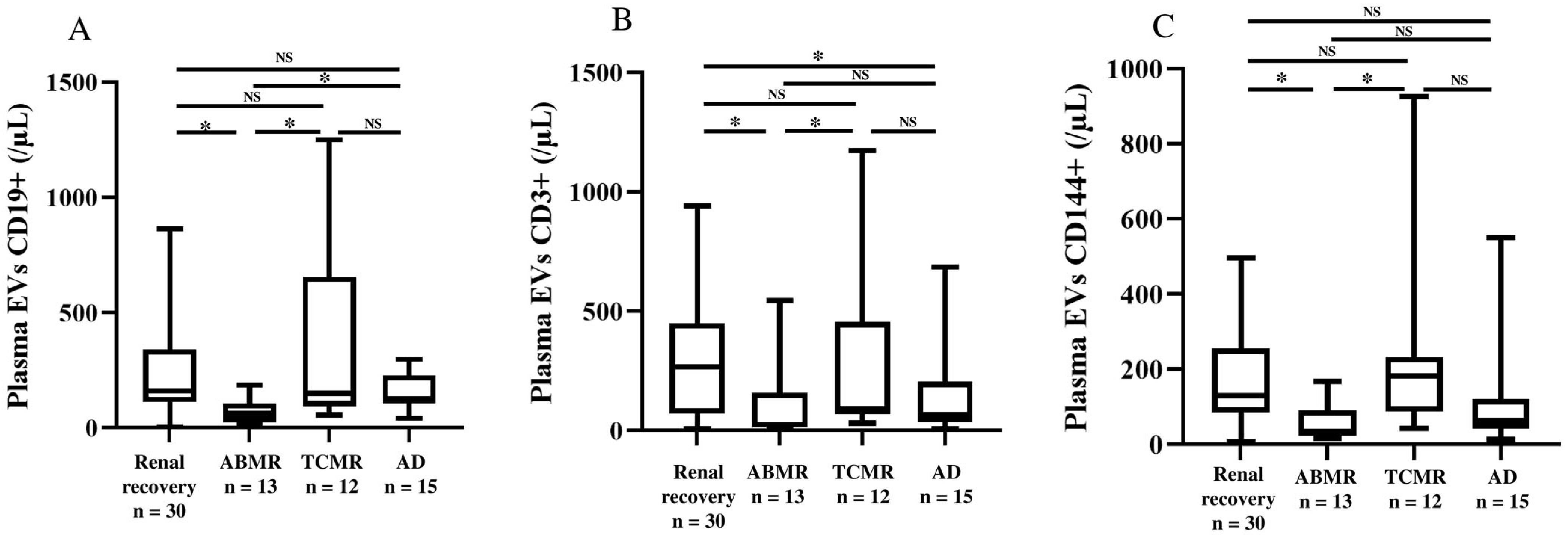
2.3. Characterization of Surface Antigens on Plasma and Urine EVs
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Patient Recruitment
4.2. Sampling Strategy
4.3. EV Characterization
- -
- the glomerulus (podocalyxin+), proximal tubules (aquaporin-1+), endothelium (CD144+), and platelets (CD41+) to localize the pathologic process;
- -
- the immune system B-cells (CD19+), T-cells (CD3+), and natural killer cells (CD16+ and CD56+) to highlight the immune mechanism of the kidney injury;
- -
- the renal progenitors (CD133+) to assess the renal recovery.
4.4. Statistics
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zaborowski, M.P.; Balaj, L.; Breakefield, X.O.; Lai, C.P. Extracellular Vesicles: Composition, Biological Relevance, and Methods of Study. Bioscience 2015, 65, 783–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yáñez-Mó, M.; Siljander, P.R.; Andreu, Z.; Zavec, A.B.; Borràs, F.E.; Buzas, E.I.; Buzas, K.; Casal, E.; Cappello, F.; Carvalho, J.; et al. Biological properties of extracellular vesicles and their physiological functions. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zou, X.; Lei, Q.; Luo, X.; Yin, J.; Chen, S.; Hao, C.; Shiyu, L.; Ma, D. Advances in biological functions and applications of apoptotic vesicles. Cell Commun. Signal 2023, 21, 260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mulcahy, L.A.; Pink, R.C.; Carter, D.R.F. Routes and mechanisms of extracellular vesicle uptake. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 24641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U. Minimal information for studies of extracellular vesicles (MISEV2023): From basic to advanced approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.A.; Choi, C.; Yoo, T.H. Extracellular vesicles in kidneys and their clinical potential in renal diseases. Kidney Res. Clin. Pract. 2021, 40, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J.S.; Kim, E.; Bae, Y.U.; Yang, W.M.; Lee, H.; Kim, H.; Noh, H.; Han, D.C.; Ryu, S.; Kwon, S.H. microRNA in Extracellular Vesicles Released by Damaged Podocytes Promote Apoptosis of Renal Tubular Epithelial Cells. Cells 2020, 9, 1409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munkonda, M.N.; Akbari, S.; Landry, C.; Sun, S.; Xiao, F.; Turner, M.; Holterman, C.E.; Nasrallah, R.; Hébert, R.L.; Kennedy, C.R.J.; et al. Podocyte-derived microparticles promote proximal tubule fibrotic signaling via p38 MAPK and CD36. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1432206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borges, F.T.; Reis, L.A.; Schor, N. Extracellular vesicles: Structure, function, and potential clinical uses in renal diseases. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2013, 46, 824–830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshikawa-Hori, S.; Yokota-Ikeda, N.; Sonoda, H.; Sasaki, Y.; Ikeda, M. Reduced urinary release of AQP1- and AQP2-bearing extracellular vesicles in patients with advanced chronic kidney disease. Physiol. Rep. 2021, 9, e15005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Cao, R.; Zhang, X.Y.; Guan, Y. Aquaporins in the kidney: Physiology and pathophysiology. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2020, 318, F193–F203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asvapromtada, S.; Sonoda, H.; Kinouchi, M.; Oshikawa, S.; Takahashi, S.; Hoshino, Y.; Sinlapadeelerdkul, T.; Yokota-Ikeda, N.; Matsuzaki, T.; Ikeda, M. Characterization of urinary exosomal release of aquaporin-1 and -2 after renal ischemia-reperfusion in rats. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 314, F584–F601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, H.; Oshikawa-Hori, S.; Ikeda, M. An Early Decrease in Release of Aquaporin-2 in Urinary Extracellular Vesicles After Cisplatin Treatment in Rats. Cells 2019, 8, 139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Kajiyama, H.; Tsuji, T.; Hu, X.; Leelahavanichkul, A.; Vento, S.; Frank, R.; Kopp, J.B.; Trachtman, H.; Star, R.A.; et al. Urinary exosomal Wilms’ tumor-1 as a potential biomarker for podocyte injury. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2013, 305, F553–F559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimuccio, V.; Ranghino, A.; Praticò Barbato, L.; Fop, F.; Biancone, L.; Camussi, G.; Bussolati, B. Urinary CD133+ extracellular vesicles are decreased in kidney transplanted patients with slow graft function and vascular damage. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e104490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Zhong, X.; Ni, H.F.; Wang, C.; Tang, T.T.; Wang, L.T.; Song, K.Y.; Tang, R.N.; Liu, H.; Liu, B.C.; et al. Urinary small extracellular vesicles derived CCL21 mRNA as biomarker linked with pathogenesis for diabetic nephropathy. J. Transl. Med. 2021, 19, 355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Lv, L.L.; Wu, W.J.; Li, Z.L.; Chen, J.; Ni, H.F.; Zhou, L.T.; Tang, T.T.; Wang, F.M.; Wang, B.; et al. Urinary Exosomes and Exosomal CCL2 mRNA as Biomarkers of Active Histologic Injury in IgA Nephropathy. Am. J. Pathol. 2018, 188, 2542–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almquist, T.; Mobarrez, F.; Jacobson, S.H.; Wallén, H.; Hjemdahl, P. Effects of lipid-lowering treatment on circulating microparticles in patients with diabetes mellitus and chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 944–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Xie, R.; Zhang, Y.; Liang, H.; Hou, L.; Yu, C.; Zhang, J.; Dong, Z.; Tian, Y.; Bi, Y.; et al. Phosphatidylserine on microparticles and associated cells contributes to the hypercoagulable state in diabetic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2018, 33, 2115–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgatzakou, H.T.; Pavlou, E.G.; Papageorgiou, E.G.; Papassideri, I.S.; Kriebardis, A.G.; Antonelou, M.H. The Multi-Faced Extracellular Vesicles in the Plasma of Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qamri, Z.; Pelletier, R.; Foster, J.; Kumar, S.; Momani, H.; Ware, K.; von Visger, J.; Satoskar, A.; Nadasdy, T.; Brodsky, S.V. Early posttransplant changes in circulating endothelial microparticles in patients with kidney transplantation. Transpl. Immunol. 2014, 31, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woud, W.W.; Hesselink, D.A.; Hoogduijn, M.J.; Baan, C.C.; Boer, K. Direct detection of circulating donor-derived extracellular vesicles in kidney transplant recipients. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tower, C.M.; Reyes, M.; Nelson, K.; Leca, N.; Kieran, N.; Muczynski, K.; Jefferson, J.A.; Blosser, C.; Kukla, A.; Maurer, D.; et al. Plasma C4d+ Endothelial Microvesicles Increase in Acute Antibody-Mediated Rejection. Transplantation 2017, 101, 2235–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pisitkun, T.; Shen, R.F.; Knepper, M.A. Identification and proteomic profiling of exosomes in human urine. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13368–13373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Lin, H.Y.; Assaker, J.P.; Jeong, S.; Huang, C.H.; Kurdi, T.; Lee, K.; Fraser, K.; Min, C.; Eskandari, S.; et al. Integrated Kidney Exosome Analysis for the Detection of Kidney Transplant Rejection. ACS Nano 2017, 11, 11041–11046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrello, J.; Monticone, S.; Burrello, A.; Bolis, S.; Cristalli, C.P.; Comai, G.; Corradetti, V.; Grange, C.; Orlando, G.; Bonafè, M.; et al. Identification of a serum and urine extracellular vesicle signature predicting renal outcome after kidney transplant. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38, 764–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona, A.; Guerrero, F.; Buendia, P.; Obrero, T.; Aljama, P.; Carracedo, J. Microvesicles Derived from Indoxyl Sulfate Treated Endothelial Cells Induce Endothelial Progenitor Cells Dysfunction. Front. Physiol. 2017, 8, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez, S.; Suazo, C.; Boltansky, A.; Ursu, M.; Carvajal, D.; Innocenti, G.; Vukusich, A.; Hurtado, M.; Villanueva, S.; Carreño, J.E. Urinary exosomes as a source of kidney dysfunction biomarker in renal transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2013, 45, 3719–3723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sigdel, T.K.; Ng, Y.W.; Lee, S.; Nicora, C.D.; Qian, W.J.; Smith, R.D.; Camp, D.G., 2nd; Sarwal, M.M. Perturbations in the urinary exosome in transplant rejection. Front. Med. 2015, 1, 57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, A.; Ahmed, S.B.; Carrero, J.J.; Foster, B.; Francis, A.; Hall, R.K.; Herrington, W.G.; Hill, G.; Inker, L.A.; Kazancıoğlu, R.; et al. Executive summary of the KDIGO 2024 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Evaluation and Management of Chronic Kidney Disease: Known knowns and known unknowns. Kidney Int. 2024, 105, 684–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacob, V.; Lambour, A.; Swinyard, B.; Zerbib, Y.; Diouf, M.; Soudet, S.; Brochot, E.; Six, I.; Maizel, J.; Slama, M.; et al. Annexin-V positive extracellular vesicles level is increased in severe COVID-19 disease. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1186122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Variables | HVs n = 33 | Patients with CKD n = 92 | KT Recipients n = 70 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical Variables | ||||
| Age, years, median [range] | 29 [26–48] | 66 [54–73] | 55 [49–65] | <0.001 |
| Male sex, n (%) | 19 (57.6) | 44 (47.8) | 44 (62.8) | 0.16 |
| BMI, kg/m2, median [range] | 21.9 [20.7–23.2] | 27.5 [25.0–31.1] | 25.9 [23.5–28.4] | <0.001 |
| Nephropathies, n (%) | ||||
| Vascular | - | 8 (8.7) | 6 (8.6) | 1 |
| Diabetes | - | 21 (22.8) | 3 (4.3) | <0.001 |
| Glomerulonephritis | - | 37 (40.2) | 27 (38.6) | 0.87 |
| Tubulointerstitial nephritis | - | 11 (11.9) | 16 (22.9) | 0.09 |
| Polycystic kidney disease | - | 3 (3.3) | 9 (12.8) | 0.03 |
| Undetermined | - | 7 (7.6) | 6 (8.6) | 1 |
| Other | - | 5 (5.4) | 3 (4.3) | 1 |
| Biochemical Variables—Median [Range] | ||||
| In the plasma | ||||
| Serum creatinine, µmol/L | - | 176 [118–296] | 113 [91–169] | <0.001 |
| eGFR, mL/min/1.73 m2 | - | 30.5 [15.7–45.5] | 60.5 [35.2–73.0] | <0.001 |
| Haemoglobin, g/dL | - | 12.3 [10.9–13.9] | 13.0 [11.7–14.3] | 0.13 |
| White cell count, G/L | - | 7.3 [5.7–9.1] | 7.3 [6.0–8.9] | 0.91 |
| Platelet count, G/L | - | 242 [208–289] | 230 [191–275] | 0.17 |
| In the urine | ||||
| Protein, mg/L | - | 681 [140–1507] | 179 [104–442] | <0.001 |
| Albumin, mg/L | - | 182 [23–859] | 26 [8–139] | <0.001 |
| Creatinine, mmol/L | - | 5.7 [3.8–8.0] | 6.2 [4.5–8.7] | 0.15 |
| Variables | HVs n = 33 | Patients with CKD n = 92 | KT Recipients n = 70 | p |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Urine | ||||
| Overall | 2486 [1330–4746] | 1045 [464–2323] | 1875 [946–3506] | <0.001 |
| Podocalyxin | 1438 [837–2202] | 398 [173–845] | 1154 [321–1998] | <0.001 |
| Aquaporin-1 | 1053 [686–1492] | 362 [171–725] | 757 [288–1441] | <0.001 |
| CD133 | 582 [377–851] | 118 [49–290] | 298 [118–597] | <0.001 |
| CD144 | 843 [315–1008] | 198 [55–433] | 509 [194–1022] | <0.001 |
| CD19 | 455 [175–683] | 151 [55–432] | 358 [190–807] | <0.001 |
| CD3 | 458 [213–783] | 105 [43–283] | 304 [148–680] | <0.001 |
| CD16 | 614 [329–1063] | 195 [75–480] | 450 [174–1107] | <0.001 |
| CD56 | 246 [145–470] | 71 [34–147] | 170 [66–328] | <0.001 |
| CD41 | 399 [185–678] | 160 [66–381] | 394 [202–791] | <0.001 |
| Plasma | ||||
| Overall | 1402 [878–1878] | 1171 [549–2082] | 2620 [1062–4272] | <0.001 |
| Podocalyxin | 116 [77–266] | 111 [41–226] | 465 [100–956] | <0.001 |
| Aquaporin-1 | 154 [95–287] | 175 [70–422] | 685 [179–1062] | <0.001 |
| CD133 | undetected | undetected | undetected | - |
| CD144 | 43 [22–67] | 41 [21–85] | 107 [43–200] | <0.001 |
| CD19 | 102 [65–169] | 80 [48–178] | 135 [86–228] | 0.02 |
| CD3 | 52 [36–98] | 48 [22–85] | 130 [39–355] | <0.001 |
| CD16 | 135 [72–207] | 76 [34–217] | 202 [73–489] | 0.008 |
| CD56 | 29 [17–52] | 24 [14–39] | 20 [12–39] | 0.27 |
| CD41 | 1197 [649–1873] | 902 [318–1673] | 1287 [348–2211] | 0.35 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jacob, V.; de Berny, Q.; Brazier, F.; Presne, C.; Lion, J.; Ouled-Haddou, H.; Metzinger-Le Meuth, V.; Choukroun, G.; Metzinger, L.; Guillaume, N. Quantification of Urine and Plasma Levels of Extracellular Vesicles in a Cohort of Kidney Transplant Recipients and Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083635
Jacob V, de Berny Q, Brazier F, Presne C, Lion J, Ouled-Haddou H, Metzinger-Le Meuth V, Choukroun G, Metzinger L, Guillaume N. Quantification of Urine and Plasma Levels of Extracellular Vesicles in a Cohort of Kidney Transplant Recipients and Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083635
Chicago/Turabian StyleJacob, Valentine, Quentin de Berny, François Brazier, Claire Presne, Julien Lion, Hakim Ouled-Haddou, Valérie Metzinger-Le Meuth, Gabriel Choukroun, Laurent Metzinger, and Nicolas Guillaume. 2025. "Quantification of Urine and Plasma Levels of Extracellular Vesicles in a Cohort of Kidney Transplant Recipients and Chronic Kidney Disease Patients" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083635
APA StyleJacob, V., de Berny, Q., Brazier, F., Presne, C., Lion, J., Ouled-Haddou, H., Metzinger-Le Meuth, V., Choukroun, G., Metzinger, L., & Guillaume, N. (2025). Quantification of Urine and Plasma Levels of Extracellular Vesicles in a Cohort of Kidney Transplant Recipients and Chronic Kidney Disease Patients. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3635. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083635







