Evaluating the Bidirectional Causal Effects of Alzheimer’s Disease Across Multiple Conditions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Retrieval Strategy
2.2. Criteria for Inclusion and Exclusion of Literature
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
- (1)
- Published articles exploring the causal relationship between AD and multiple diseases using MR methods, including unidirectional or bidirectional MR studies;
- (2)
- Studies using instrumental variable methods (IVW) to report the association between AD and multiple diseases in the form of odds ratios (ORs) and 95% confidence intervals (95% CIs).
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
- (1)
- Articles without sufficient estimated information, those that were irrelevant to the topic, or those on diseases not standardized in ICD-11 were excluded;
- (2)
- Case reports, narrative reviews, letters, opinions, foreign-language translations, reviews, incomplete manuscripts, non-original MR studies, and conference abstracts were excluded;
- (3)
- Articles without extractable indicators were excluded;
- (4)
- Articles with disputed results were excluded;
- (5)
- When there were multiple publications based on the same GWAS (same participants), only publications with the largest sample size or the latest published study (if the sample size was the same) were included, without sample size limitations.
2.3. Literature Screening and Data Extraction
2.4. Literature Quality Evaluation
2.5. Statistical Analysis
2.6. Research Plan Description
3. Results
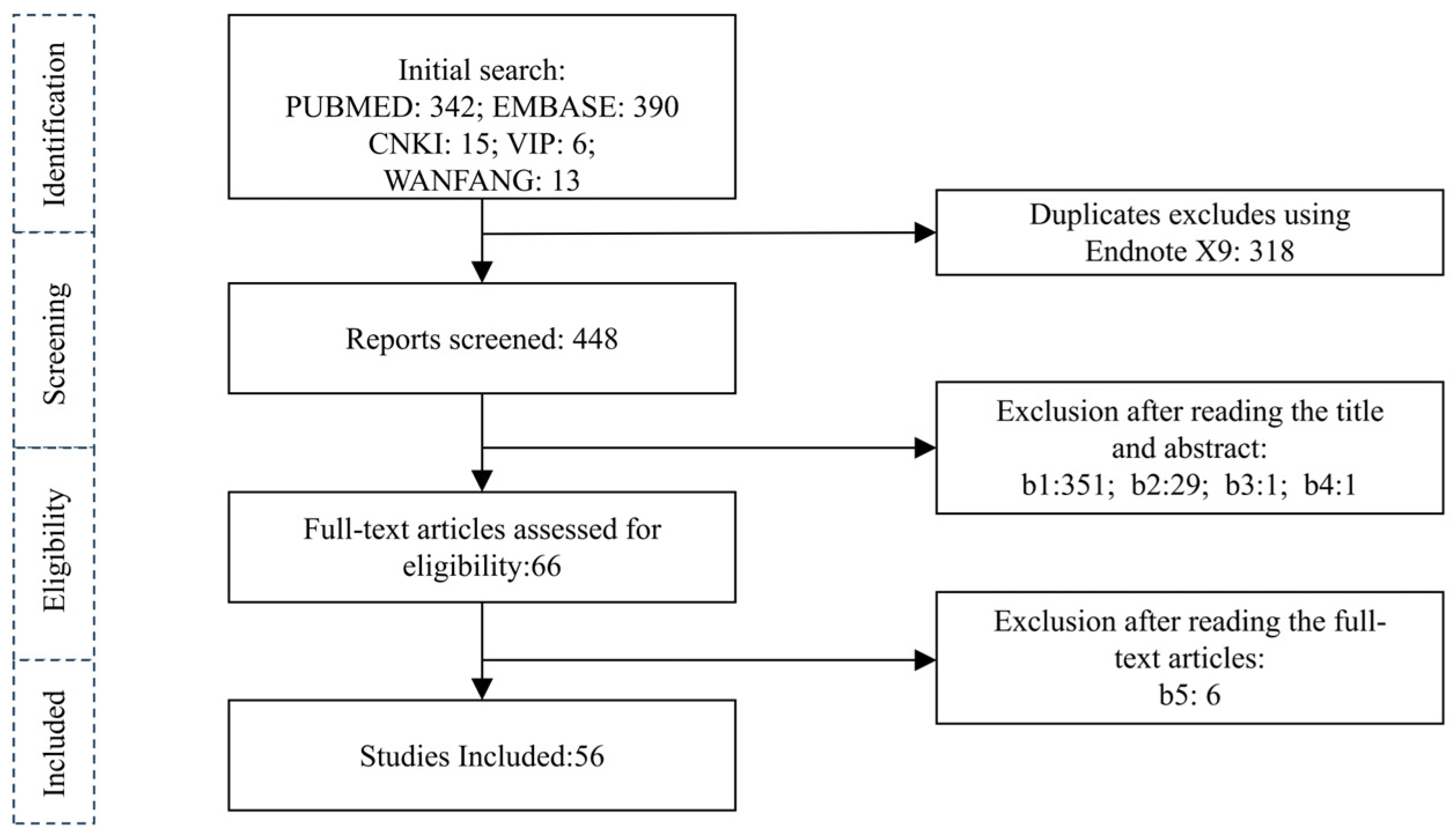
3.1. Literature Search Results
3.2. Basic Characteristics of Included Literature
3.3. Results of Literature Quality Evaluation
3.4. The Bidirectional Causal Relationship Between AD and Multiple Diseases
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| MR | Mendelian randomization |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| PubMed | Public from Medline |
| CNKI | China National Knowledge Infrastructure |
| VIP Database | Chinese Science and Technology Periodical Database |
Appendix A
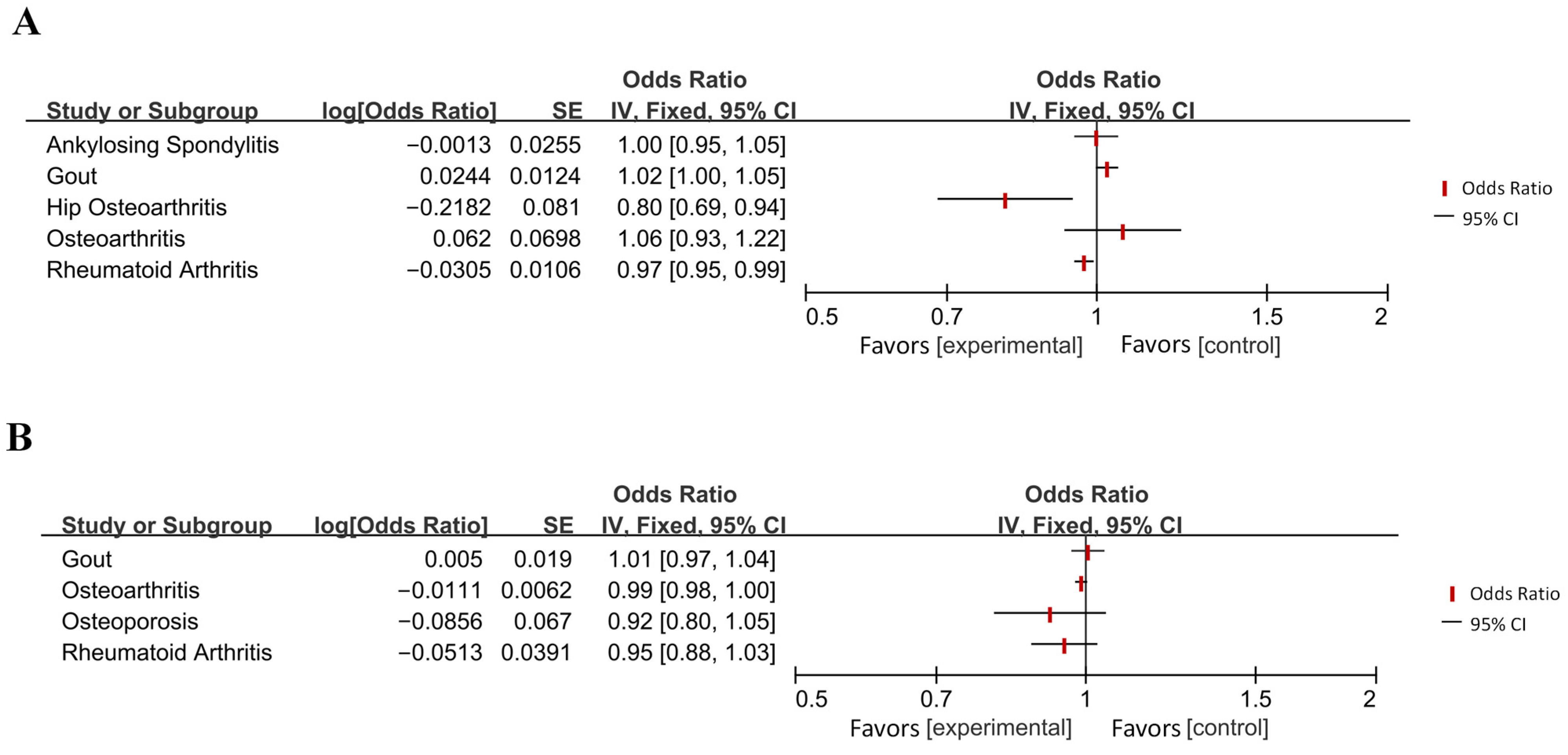

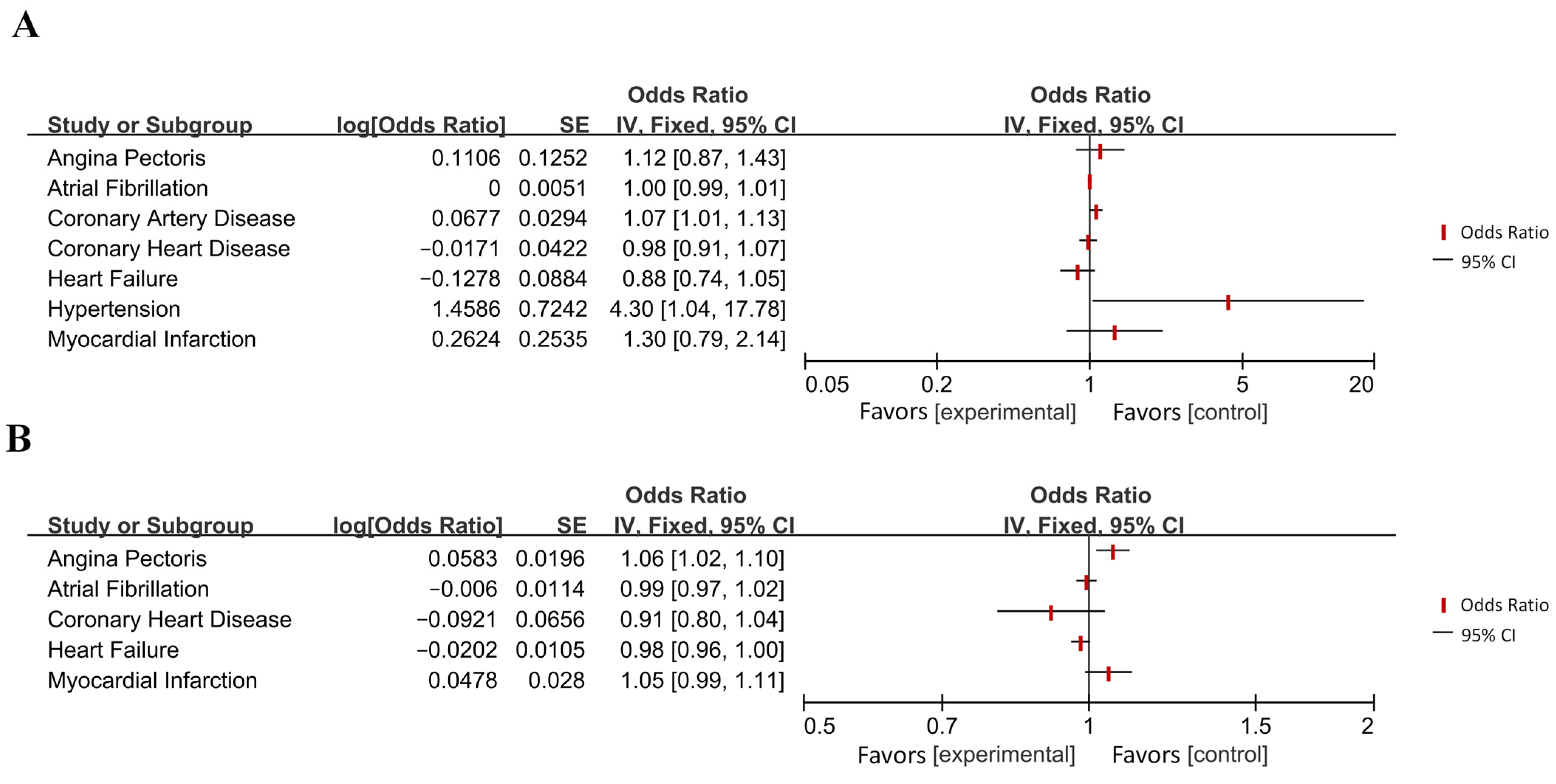
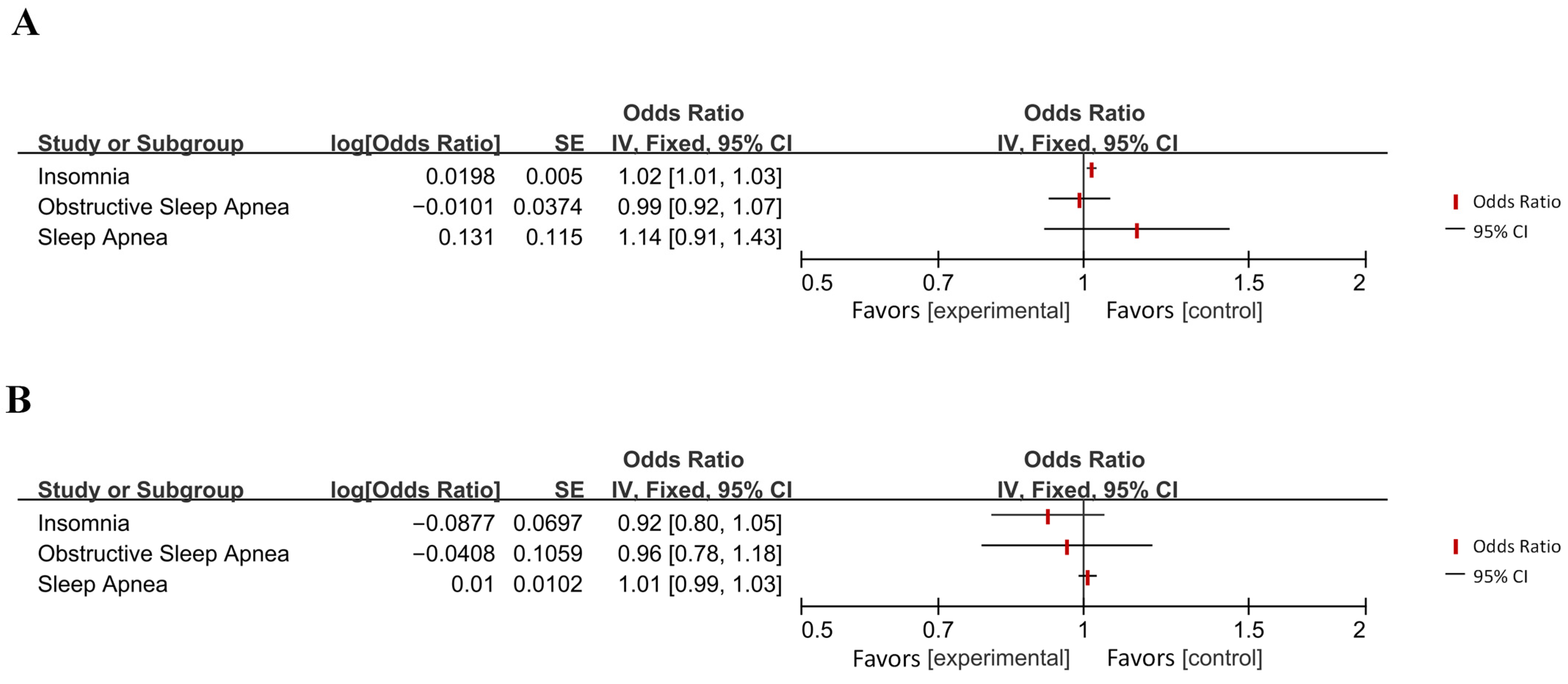
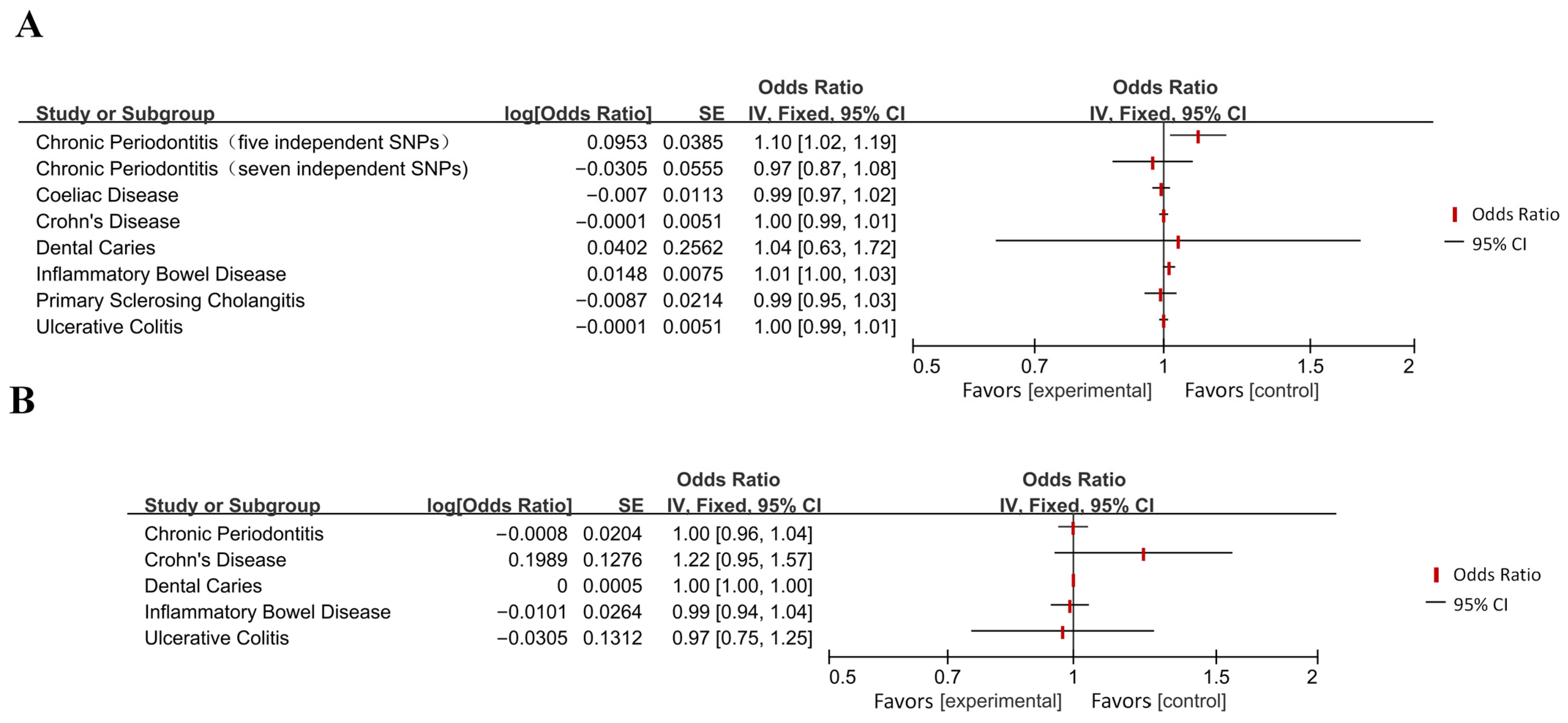





Appendix B
| Database | Search Strategy * |
|---|---|
| PubMed | (((Mendelian Randomization [Title/Abstract]) OR (Mendelian Randomization Analysis [Title/Abstract])) OR (Mendelian Randomization Study [Title/Abstract])) OR (Mendelian Randomization Methods [Title/Abstract]) AND ((((((((((((((((((((Alzheimer’s disease [Title/Abstract]) OR (Alzheimer Dementia [Title/Abstract])) OR (Alzheimer Dementias [Title/Abstract])) OR (Dementia, Alzheimer [Title/Abstract])) OR (Alzheimer’s Disease [Title/Abstract])) OR (Dementia, Senile [Title/Abstract])) OR (Dementia, Alzheimer Type [Title/Abstract])) OR (Alzheimer Type Dementia (ATD [Title/Abstract]))) OR (Dementia, Alzheimer-Type (ATD [Title/Abstract]))) OR (Alzheimer Type Senile Dementia [Title/Abstract])) OR (Dementia, Primary Senile Degenerative [Title/Abstract])) OR (Sclerosis, Alzheimer [Title/Abstract])) OR (Alzheimer Syndrome [Title/Abstract])) OR (Alzheimer’s Diseases [Title/Abstract])) OR (Alzheimer Diseases [Title/Abstract])) OR (Alzheimers Diseases [Title/Abstract])) OR (Senile Dementia, Alzheimer Type [Title/Abstract])) OR (Senile Dementia, Acute Confusional [Title/Abstract])) OR (Dementia, Presenile [Title/Abstract])) OR (Alzheimer Disease, Late Onset [Title/Abstract])) |
| Embase | (Mendelian Randomization or Mendelian Randomization Analysis or Mendelian Randomization Study or Mendelian Randomization Methods).ab. and (alzheimer’s disease or Alzheimer Dementia or Alzheimer Dementias or Dementia, Alzheimer or Alzheimer Syndrome or Alzheimer-Type Dementia or Alzheimer Type Dementia or Dementia, Alzheimer-Type or Alzheimer’s Diseases or Alzheimer Diseases or Alzheimers Diseases or Dementia, Senile or Senile Dementia or Dementia, Alzheimer Type or Alzheimer Type Dementia or Senile Dementia, Alzheimer Type or Alzheimer Type Senile Dementia or Primary Senile Degenerative Dementia or Dementia, Primary Senile Degenerative or Sclerosis, Alzheimer or Senile Dementia, Acute Confusional).ab. |
| CNKI | TKA = (‘阿尔茨海默病’ + ‘阿尔兹海默’ + ‘阿尔茨海默’ + ‘阿尔兹海默病’) AND TKA = (‘孟德尔随机化’ + ‘孟德尔随机化方法’ + ‘孟德尔随机化法’ + ‘孟德尔随机化研究’ + ‘孟德尔随机化试验’ + ‘孟德尔随机化分析’ + ‘孟德尔随机分析’ + ‘孟德尔随机方法’) |
| Wanfang Data | 摘要:(阿尔兹海默症 or 阿尔兹海默 or 阿尔茨海默病) and 摘要:(孟德尔随机化 or 孟德尔随机化方法 or 孟德尔随机化法 or 孟德尔随机化研究 or 孟德尔随机化试验 or 孟德尔随机化分析 or 孟德尔随机分析 or 孟德尔随机方法) |
| VIP Database | U = (阿尔兹海默症 OR 阿尔兹海默 OR 阿尔茨海默病) AND (孟德尔随机化 OR 孟德尔随机化方法 OR 孟德尔随机化法 OR 孟德尔随机化研究 OR 孟德尔随机化试验 OR 孟德尔随机化分析 OR 孟德尔随机分析 OR 孟德尔随机方法) |
| Study (First Author and Year of Publication) | Exposure | Outcome | Method | OR | 95%CI | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bae et al. (2019) [12] | RA | AD | IVW | 0.96 | 0.93–0.99 | 0.021 |
| Cai et al. (2021) [13] | Osteoarthritis | AD | IVW | 1.064 | 0.928–1.219 | 0.374 |
| AD | Osteoarthritis | IVW | 0.979 | 0.972–0.987 | 1.190 × 10−7 | |
| Lee et al. (2019) [14] | Gout | AD | IVW | / | / | 0.445 |
| Harerimana et al. (2022) [15] | Depression | AD | Forward Generalized Summary data-based Mendelian Randomization (GSMR) | / | / | 0.001 |
| AD | Depression | Reverse Generalized Summary data-based Mendelian Randomization (GSMR) | / | / | 0.954 | |
| Pagoni et al. (2022) [16] | Autism spectrum disorder | AD | IVW | 0.99 | 0.97–1.01 | 0.7 |
| AD | Autism spectrum disorder | IVW | 1.19 | 0.94–1.51 | 0.14 | |
| Hyperactivity | AD | IVW | 1 | 0.98–1.02 | 0.39 | |
| AD | Hyperactivity | IVW | 1.12 | 0.86–1.44 | 0.37 | |
| Wei et al. (2022) [17] | Anxiety disorders | AD | IVW | 0.904 | 0.722–1.131 | 0.377 |
| Bidirectional affective disorder | AD | IVW | 1.033 | 0.925–1.153 | 0.564 | |
| Schizophrenia | AD | IVW | 1.039 | 0.986–1.095 | 0.156 | |
| Zheng et al. (2023) [18] | Delirium | AD | IVW | 0.98 | 0.91–1.05 | 0.544 |
| AD | Delirium | IVW | 1.32 | 1.13–1.54 | 0.000391 | |
| Zhang et al. (2023) [19] | Coronary heart disease | AD | IVW | 0.983 | 0.905–1.068 | 0.691 |
| AD | Coronary heart disease | IVW | 0.912 | 0.802–1.037 | 0.159 | |
| Myocardial infarction | AD | IVW | 1.3 | 0.791–2.137 | 0.3 | |
| AD | Myocardial infarction | IVW | 1.049 | 0.993–1.108 | 0.088 | |
| Atrial fibrillation | AD | IVW | 0.994 | 0.951–1.039 | 0.78 | |
| AD | Atrial fibrillation | IVW | 0.994 | 0.972–1.017 | 0.612 | |
| Ischemic stroke | AD | IVW | 1.077 | 0.890–1.304 | 0.447 | |
| AD | Ischemic stroke | IVW | 1.009 | 0.983–1.036 | 0.502 | |
| Angina pectoris | AD | IVW | 1.117 | 0.874–1.428 | 0.375 | |
| AD | Angina pectoris | IVW | 1.06 | 1.020–1.101 | 0.003 | |
| Cardioembolic stroke | AD | IVW | 0.898 | 0.819–0.986 | 0.024 | |
| AD | Cardioembolic stroke | IVW | 0.953 | 0.900–1.010 | 0.104 | |
| Cardioembolic stroke | AD | IVW | 1.027 | 0.879–1.200 | 0.736 | |
| AD | Cardioembolic stroke | IVW | 1.056 | 0.979–1.139 | 0.155 | |
| Arega et al. (2022) [20] | Heart failure | AD | IVW | 0.752 | 0.621, 0.912 | 0.004 |
| Grace et al. (2018) [21] | Coronary artery disease | LOAD | IVW | 1.07 | 1.01,1.15 | 0.027 |
| Tang et al. (2023) [22] | Hypertension | AD | IVW | 4.3 | 1.04–17.6 | 0.04 |
| Chen et al. (2022) [23] | Insomnia | AD | IVW | 1.02 | 6.7 × 10−6 | |
| Li et al. (2022) [24] | Obstructive sleep disorder | AD | IVW | 0.99 | 0.92–1.08 | 0.26 |
| Cavaillès et al. (2023) [25] | Sleep apnea | AD | Fixed-effects IVW | 1.14 | 0.91–1.43 | / |
| AD | Sleep apnea | Fixed-effects IVW | 1.01 | 0.99–1.02 | / | |
| Enduru et al. (2024) [26] | Celiac disease | AD | IVW | / | / | / |
| Crohn’s disease | AD | IVW | / | / | / | |
| Primary sclerosing cholangitis | AD | IVW | / | / | / | |
| Ulcerative colitis | AD | IVW | / | / | / | |
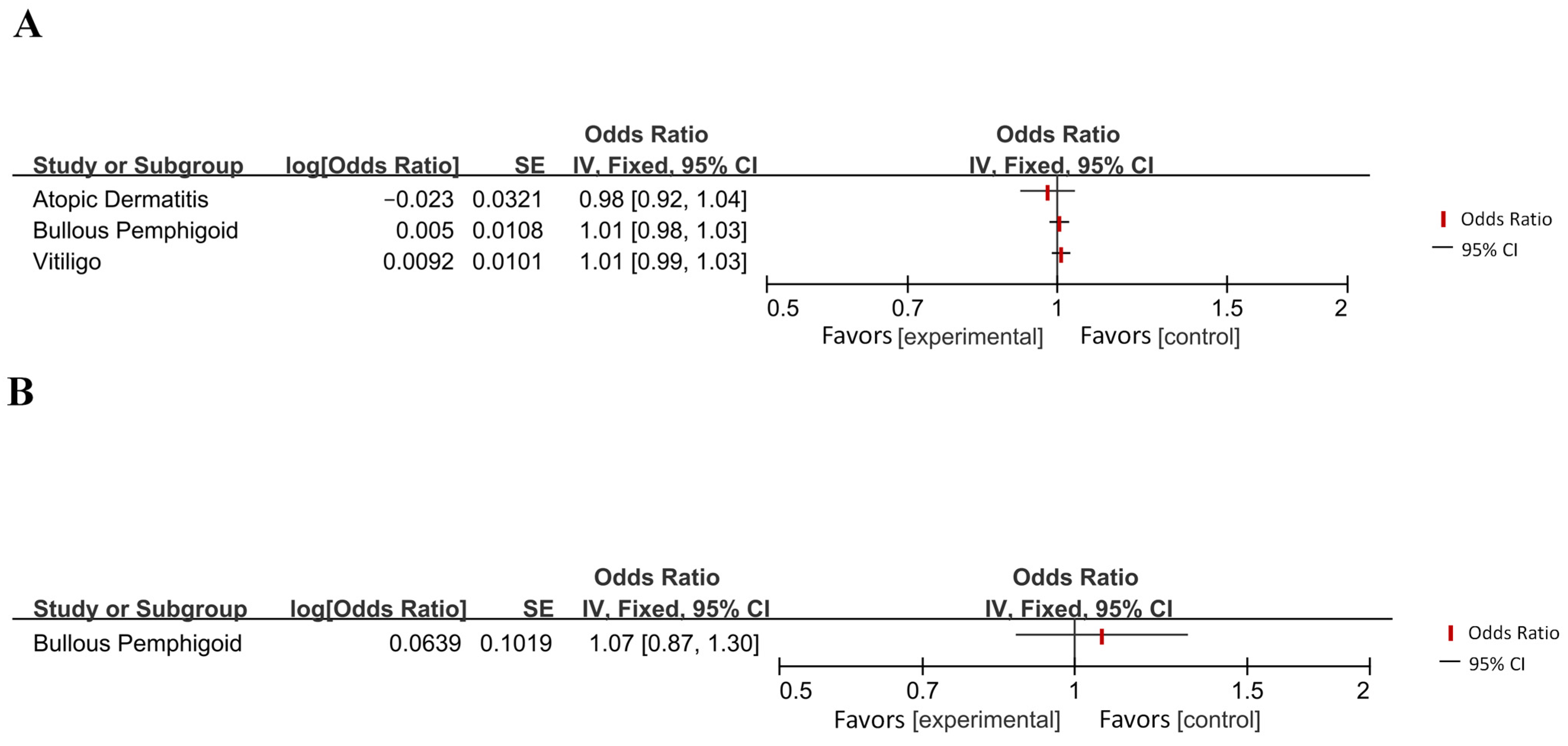
| Specific dermatitis | AD | IVW | / | / | / | |
| Vitiligo | AD | IVW | / | / | / | |
| Hypothyroidism | AD | IVW | / | / | / | |
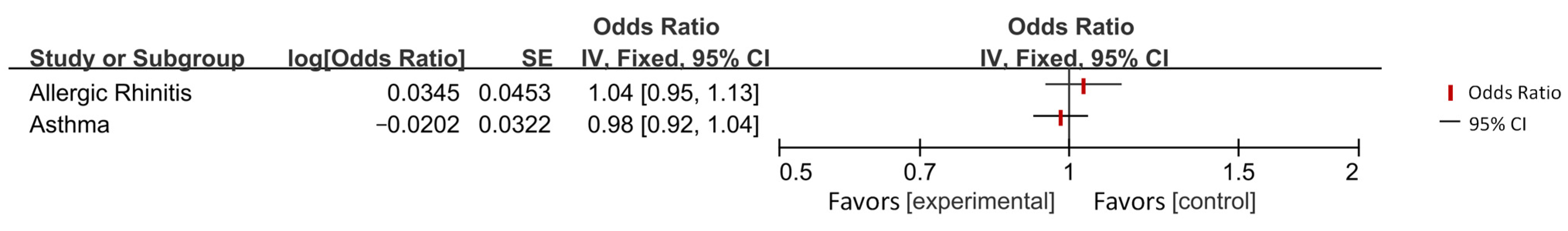
| Asthma | AD | IVW | / | / | / | |
| Allergic rhinitis | AD | IVW | / | / | / | |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | AD | IVW | / | / | / | |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | AD | IVW | / | / | / | |
| Liao et al. (2023) [27] | Dental caries | AD | IVW | 1.041 | 0.630–0.722 | 0.874 |
| AD | Dental caries | IVW | 1 | 0.999–1.001 | 0.717 | |
| Zeng et al. (2023) [28] | Inflammatory bowel disease | AD | IVW | 1.01 | 0.99–1.02 | 0.41 |
| AD | Inflammatory bowel disease | IVW | 0.99 | 0.94–1.05 | >0.05 | |
| Zeng et al. (2023) [29] | Inflammatory bowel disease | AD | IVW | 1.015 | 0.993–1.038 | 0.179 |
| AD | Inflammatory bowel disease | IVW | 0.979 | 0.899–1.066 | 0.628 | |
| Sun et al. (2020) [30] | Chronic periodontitis | AD | IVW | 1.1; 0.97 | 1.02–1.19; 0.87–1.08 | 0.02; 0.59 |
| AD | Chronic periodontitis | IVW | 1 | 0.96–1.04 | 0.85 | |
| Shen et al. (2023) [31] | Bullous pemphigoid | AD | IVW | 1.005 | 0.984–1.027 | 0.629 |
| AD | Bullous pemphigoid | IVW | 1.066 | 0.873–1.358 | 0.603 | |
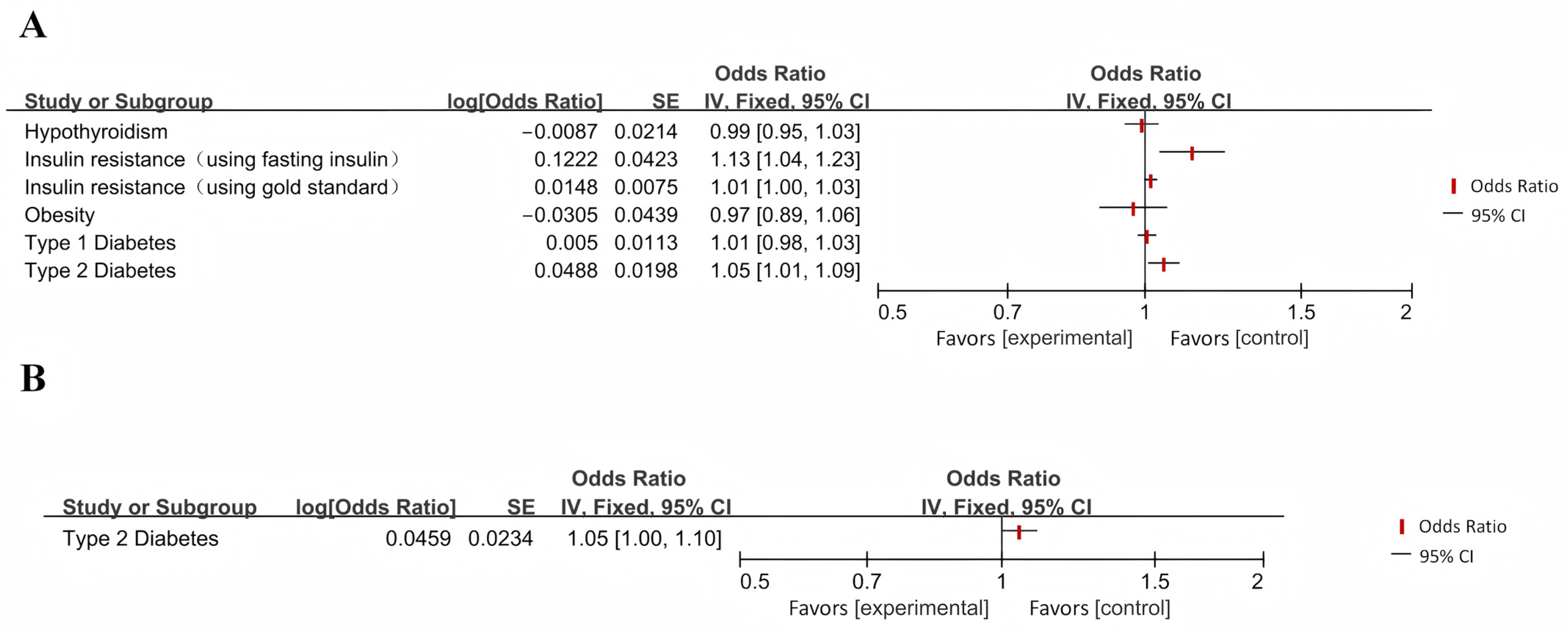
| Zhou et al. (2022) [32] | Insulin resistance | AD | IVW | 1.13 | 1.04–1.23 | 0.004 |
| Xue et al. (2023) [33] | Type I diabetes | AD | IVW | 1.005 | 0.983–1.026 | 0.641 |
| Multiple sclerosis | AD | IVW | 0.984 | 0.950–1.019 | 0.381 | |
| Migraine | AD | IVW | 20.264 | 0.124–3287.978 | 0.246 | |
| Zhuang et al. (2021) [34] | Obesity | AD | IVW | 0.97 | 0.89–1.06 | 0.49 |
| Han et al. (2018) [35] | Parkinson’s disease | AD | IVW | 0.918 | 0.782–1.076 | 0.291 |
| Xu et al. (2023) [36] | AD | Epilepsy | IVW | 1.152 | / | 0.017 |
| Epilepsy | AD | IVW | / | / | / | |
| Wang et al. (2020) [37] | Stroke | AD | IVW | / | / | / |
| Wu et al. (2021) [38] | Glioma | AD | IVW | 1.13 | 1.06–1.21 | 4.8 × 10−4 |
| Seddighi et al. (2019) [39] | Breast cancer | AD | IVW | 0.91 | 0.84–0.99 | 0.019 |
| Lung cancer | AD | IVW | 0.98 | 0.96–0.995 | 0.012 | |
| Leukemia | AD | IVW | 0.94 | 0.89–0.99 | 0.028 | |
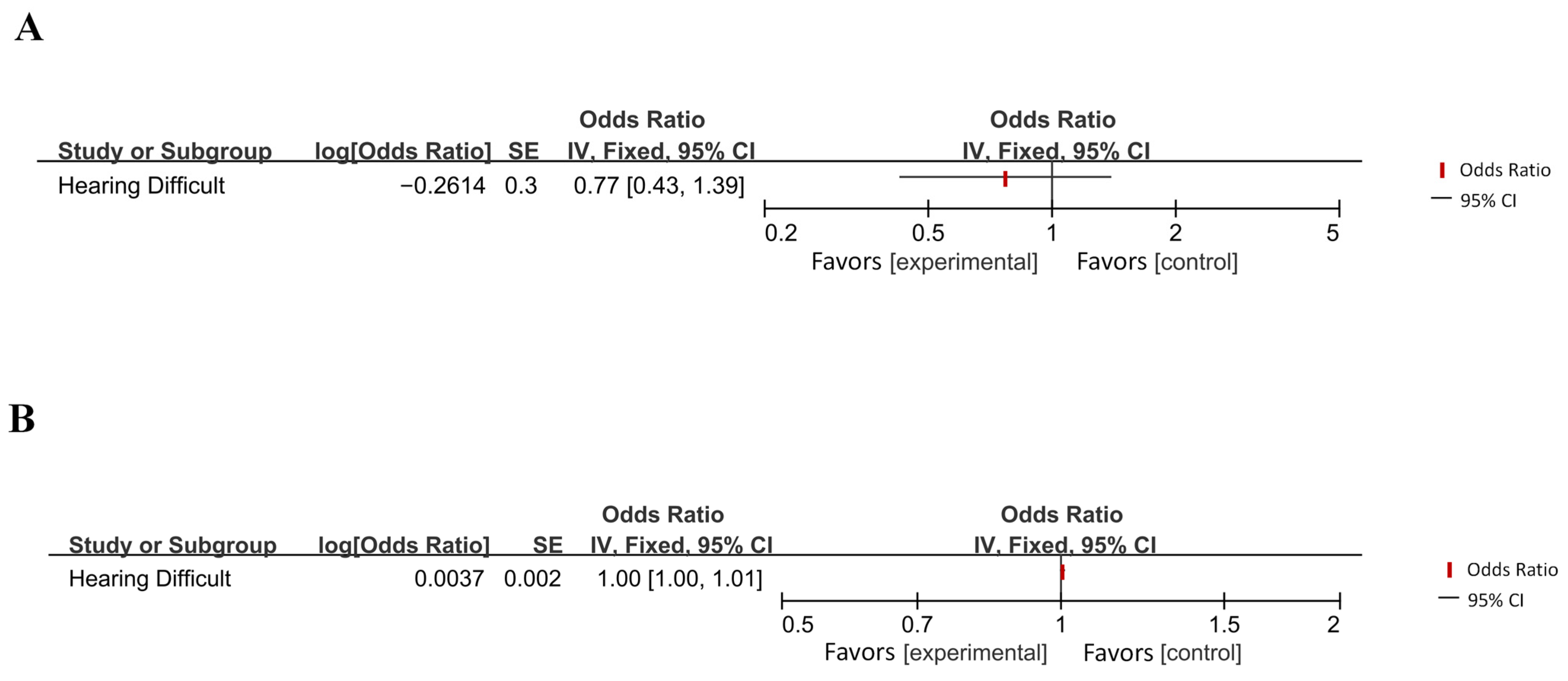
| Abidin et al. (2021) [40] | Hearing difficulties | Late-onset AD | IVW | 0.770 | 0.390 | |
| Late-onset AD | Hearing difficulties | IVW | 1.004 | 0.061 | ||
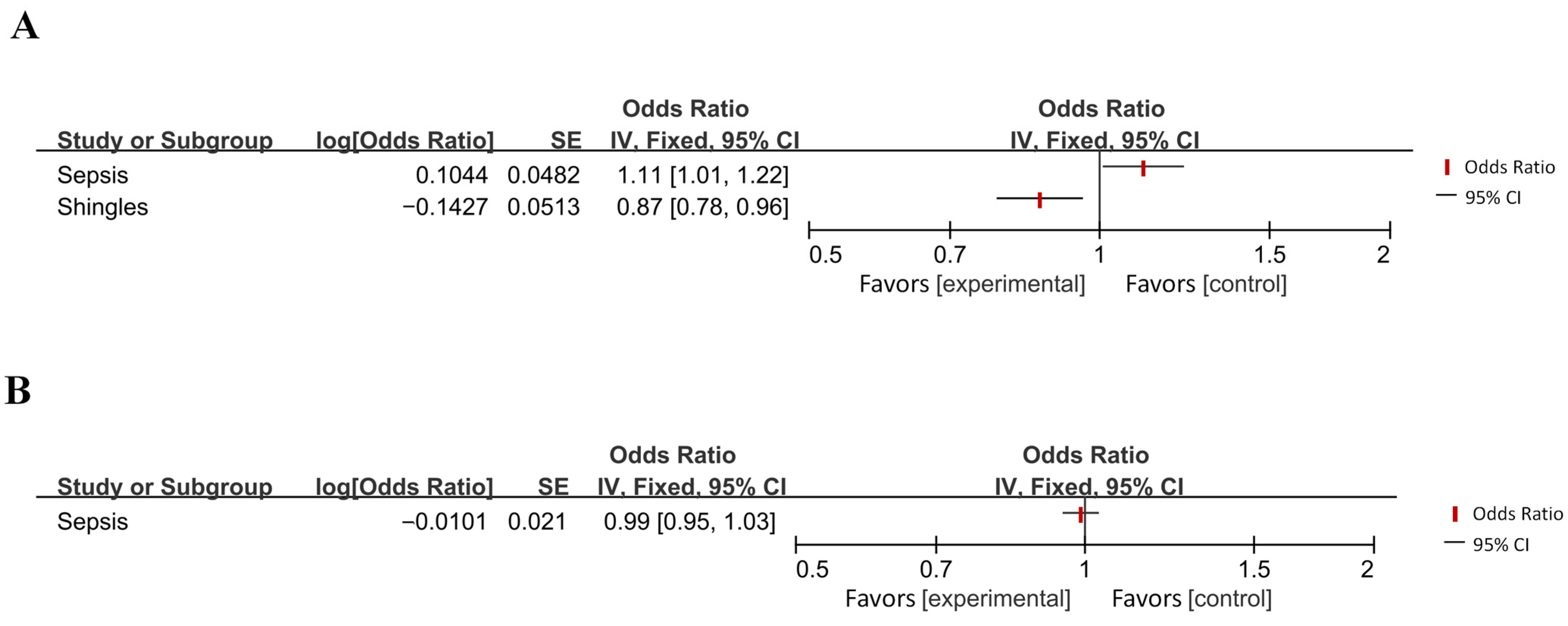
| Huang et al. (2021) [41] | Zoster | AD | IVW | 0.867 | 0.784–0.958 | 0.005 |
| Jiang et al. (2022) [42] | Age-related macular degeneration | AD | IVW | 0.999 | 0.955–1.044 | 0.948 |
| AD | Age-related macular degeneration | IVW | 0.973 | 0.938–1.008 | 0.133 | |
| Man et al. (2023) [43] | Cataracts | AD | IVW | 1.04 | 0.98–1.10 | 0.199 |
| AD | Cataracts | IVW | 0.96 | 0.93–0.99 | / | |
| Liu et al. (2023) [44] | Chronic kidney disease | AD | IVW | 1.03 | 0.95–1.12 | 0.41 |
| Sheng et al. (2022) [45] | Gestational diabetes | AD | IVW | / | / | 0.82 |
| Grover et al. (2022) [46] | Insomnia | AD | IVW | 1.135 | 0.826–1.560 | 0.4017 |
| AD | Insomnia | IVW | 0.916 | 0.799–1.051 | 0.2011 | |
| Tang (2022) [47] | Asthma | AD | IVW | 1.129 | 0.842–1.515 | 0.679 |
| Fu et al. (2022) [48] | Gout | AD | IVW | / | / | / |
| Ou et al. (2022) [49] | Gout | AD | IVW | 1.05 | 1.00–1.11 | 0.057 |
| AD | Gout | IVW | 0.25 | 0.67–1.29 | 0.653 | |
| Li et al. (2022) [50] | Crohn’s disease | AD | IVW | 1 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.26 |
| AD | Crohn’s disease | IVW | 1.2 | 0.80–1.82 | 0.38 | |
| Ulcerative colitis | AD | IVW | 1 | 0.99–1.00 | 0.57 | |
| AD | Ulcerative colitis | IVW | 1.14 | 0.81–1.60 | 0.44 | |
| Pan et al. (2020) [51] | Atrial fibrillation | AD | IVW | 1.002 | 0.996–1.009 | 0.47 |
| Daghlas et al. (2020) [52] | Migraine | AD | IVW of the variant–outcome association with intercept constrained to zero | 1.01 | 1.00–1.02 | 0.07 |
| Zhou et al. (2023) [53] | Ankylosing spondylitis | AD | IVW | 0.976 | 0.955–0.997 | 0.029 |
| Cai et al. (2018) [54] | AD | Rheumatoid arthritis | IVWweighted medianMR Egger | 0.950.96, 0.98 | 0.88–1.03; 0.85–1.07; 0.78–1.22 | 0.451; 0.217; 0.827 |
| Cui et al. (2022) [55] | AD | Inflammatory bowel disease | IVW | / | 0.736–1.331 | 0.945 |
| AD | Ulcerative colitis | IVW | / | 0.544–1.155 | 0.227 | |
| AD | Crohn’s disease | IVW | / | 0.890–1.720 | 0.205 | |
| Dong et al. (2023) [56] | IVW | 0.976 | 0.955–0.997 | 0.029 | ||
| Duan et al. (2021) [57] | Heart failure | AD | IVW | 0.848 | 0.702–1.025 | 0.088 |
| AD | Heart failure | IVW | 0.985 | 0.945–1.026 | 0.471 | |
| Li et al. (2022) [58] | AD | Apoplexy | IVW | 1.02 | 0.99–1.05 | 0.286 |
| AD | Ischemic stroke | IVW | 1 | 0.97–1.04 | 0.966 | |
| AD | Cerebral hemorrhage | IVW | 0.91 | 0.56–1.50 | 0.722 | |
| Tang et al. (2023) [59] | AD | Osteoporosis | IVW | 0.918 | 0.805–1.047 | 0.201 |
| Liu et al. (2022) [60] | AD | Obstructive sleep apnea | IVW | 0.96 | 0.78–1.12 | 0.475 |
| Zhang et al. (2020) [61] | Type II diabetes | AD | IVW | 1.011 | 0.959–1.066 | 0.6921 |
| AD | Type II diabetes | IVW | 1.047 | 1.000–1.096 | 0.049 | |
| Dybjer et al. (2023) [62] | Type II diabetes | AD | IVW | 1.116 | / | 4.37 × 10−1 |
| Litkowski et al. (2023) [63] | Type II diabetes | AD | Two-stage least squares (2SLS) MR | Non-Hispanic White participants: 1.06; non-Hispanic Black participants: 1.12 | Non-Hispanic White participants: 1.02–1.09; non-Hispanic Black participants: 1.02–1.23 | Non-Hispanic White participants: 6.84 × 10−4; non-Hispanic Black participants: 1.60 × 10−2 |
| Luo et al. (2023) [64] | Type II diabetes | AD | IVW | 1.01 | 0.98–1.04 | 0.56 |
| Meng et al. (2022) [6] | Type II diabetes | AD | IVW | 1.34 | 1.05–1.70 | 0.02 |
| Pan et al. (2020) [65] | Type II diabetes | AD | IVW | 1.02 | 0.97–1.07 | 0.52 |
| Gao et al. (2023) [66] | Atrial fibrillation | AD | IVW | 0.977 | 0.943–1.012 | 0.193 |
| Kuo et al. (2022) [67] | Heart failure | AD | IVW | 1.034 | 0.997–1.073 | 0.07 |
| Wang et al. (2023) [68] | Hip osteoarthritis | AD | IVW | 0.804 | 0.686–0.942 | 0.007 |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | AD | IVW | 1.026 | 1.003–1.049 | 0.027 | |
| AD | Rheumatoid arthritis | IVW | 0.565 | 0.323–0.987 | 0.045 | |
| Yuan et al. (2024) [69] | Colorectal cancer | AD | IVW | 0.846 | 0.762–0.929 | / |
| AD | Colorectal cancer | IVW | 1.014 | 1.001–1.027 | / | |
| Zeng et al. (2024) [70] | Sepsis | AD | IVW | 1.11 | 1.01–1.21 | 0.025 |
| AD | Sepsis | IVW | 0.99 | 0.95–1.03 | 0.522 |
References
- Evans, D.A.; Funkenstein, H.H.; Albert, M.S.; Scherr, P.A.; Cook, N.R.; Chown, M.J.; Hebert, L.E.; Hennekens, C.H.; Taylor, J.O. Prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease in a community population of older persons. Higher than previously reported. JAMA 1989, 262, 2551–2556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Se Thoe, E.; Fauzi, A.; Tang, Y.Q.; Chamyuang, S.; Chia, A.Y.Y. A review on advances of treatment modalities for Alzheimer’s disease. Life Sci. 2021, 276, 119129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tahami Monfared, A.A.; Byrnes, M.J.; White, L.A.; Zhang, Q. Alzheimer’s Disease: Epidemiology and Clinical Progression. Neurol. Ther. 2022, 11, 553–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandi, A.; Counts, N.; Chen, S.; Seligman, B.; Tortorice, D.; Vigo, D.; Bloom, D.E. Global and regional projections of the economic burden of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias from 2019 to 2050: A value of statistical life approach. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 51, 101580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Hua, S.; Liao, H.; Wang, M.; Xiong, Y.; Cao, F. An updated meta-analysis of cohort studies: Diabetes and risk of Alzheimer’s disease. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 124, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Wang, Z.; Ji, H.-F.; Shen, L. Causal association evaluation of diabetes with Alzheimer’s disease and genetic analysis of antidiabetic drugs against Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Biosci. 2022, 12, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, L.; Du, Y.; Chu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, F.; Lyu, D.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhu, M.; Jiao, H.; et al. Prevalence, risk factors, and management of dementia and mild cognitive impairment in adults aged 60 years or older in China: A cross-sectional study. Lancet Public Health 2020, 5, e661–e671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roe, C.M.; Fitzpatrick, A.L.; Xiong, C.; Sieh, W.; Kuller, L.; Miller, J.P.; Williams, M.M.; Kopan, R.; Behrens, M.I.; Morris, J.C. Cancer linked to Alzheimer disease but not vascular dementia. Neurology 2010, 74, 106–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, M.; Thanigaimani, S.; Singh, T.P.; Morris, D.; Golledge, J. Systematic review and Meta-Analysis of Mendelian randomisation analyses of Abdominal aortic aneurysms. Int. J. Cardiol. Heart Vasc. 2021, 35, 100836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Singh, S.; Baars, D.P.; Desai, R.; Singh, D.; Pinto-Sietsma, S.-J. Association Between Lipoprotein (a) and Risk of Atrial Fibrillation: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies. Curr. Probl. Cardiol. 2024, 49, 102024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Q.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Xiong, Y.; Tao, C.; Ma, L.; You, C. Genetic Insights into the Risk of Metabolic Syndrome and Its Components on Dementia: A Mendelian Randomization. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2023, 96, 725–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, S.-C.; Lee, Y.H. Causal association between rheumatoid arthritis and a decreased risk of Alzheimer’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Z. Fur Rheumatol. 2019, 78, 359–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, Y.; Zhang, G.; Liang, J.; Jing, Z.; Zhang, R.; Lv, L.; Dang, X. Causal Relationships Between Osteoarthritis and Senile Central Nerve System Dysfunction: A Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 793023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Y.H. Gout and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 1046–1051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harerimana, N.V.; Liu, Y.; Gerasimov, E.S.; Duong, D.; Beach, T.G.; Reiman, E.M.; Schneider, J.A.; Boyle, P.; Lori, A.; Bennett, D.A.; et al. Genetic Evidence Supporting a Causal Role of Depression in Alzheimer’s Disease. Biol. Psychiatry 2022, 92, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagoni, P.; Dardani, C.; Leppert, B.; Korologou-Linden, R.; Smith, G.D.; Howe, L.D.; Anderson, E.L.; Stergiakouli, E. Exploring the causal effects of genetic liability to ADHD and Autism on Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, T.; Guo, Z.; Wang, Z.; Li, C.; Zhu, W.; Zheng, Y.; Yin, Y.; Mi, Y.; Xia, X.; Tang, Y.; et al. Five Major Psychiatric Disorders and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2022, 87, 675–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, J.; Du, X.; Yang, L.; Fu, H. Causal relationships between delirium and Alzheimer’s disease: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2023, 28, 271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Xian, D.; Feng, J.; Ning, L.; Jiang, T.; Xu, W.; Liu, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Peng, M. Causal relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization analysis. Aging 2023, 15, 9022–9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arega, Y.; Shao, Y. Heart failure and late-onset Alzheimer’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 1015674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grace, C.; Clarke, R.; Goel, A.; Farrall, M.; Watkins, H.; Hopewell, J.C. Lack of genetic support for shared aetiology of Coronary Artery Disease and Late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.; Ma, Y.; Lei, X.; Ding, Y.; Yang, S.; He, D. Hypertension linked to Alzheimer’s disease via stroke: Mendelian randomization. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, T.; Jia, J. Sleep and Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease: Shared Genetic Risk Factors, Drug Targets, Molecular Mechanisms, and Causal Effects. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 794202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, L.; Ding, X.; Cui, X.; Qi, L.; Chen, Y. Obstructive sleep apnea and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson disease: A Mendelian randomization study OSA, Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson disease. Sleep Med. 2022, 97, 55–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cavaillès, C.; Andrews, S.J.; Leng, Y.; Chatterjee, A.; Daghlas, I.; Yaffe, K. Causal Associations of Sleep Apnea with Alzheimer’s Disease and Cardiovascular Disease: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Analysis. medRxiv 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enduru, N.; Fernandes, B.S.; Bahrami, S.; Dai, Y.; Andreassen, O.A.; Zhao, Z. Genetic overlap between Alzheimer’s disease and immune-mediated diseases: An atlas of shared genetic determinants and biological convergence. Mol. Psychiatry 2024, 29, 2447–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, Q.; Li, S.-Z.; Tian, F.-F.; Huang, K.; Bi, F.-F. No genetic causal association between dental caries and Alzheimer’s disease: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization analysis. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Wang, J.; Jiang, R.; Yang, J.; Zheng, C.; Wu, H.; Zhuo, Z.; Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Chen, H.; et al. Investigating Causality and Shared Genetic Architecture between Neurodegenerative Disorders and Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Aging Dis. 2023, 14, 1349–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, R.; Wang, J.; Zheng, C.; Jiang, R.; Tong, S.; Wu, H.; Zhuo, Z.; Yang, Q.; Leung, F.W.; Chen, H.; et al. Lack of Causal Associations of Inflammatory Bowel Disease with Parkinson’s Disease and Other Neurodegenerative Disorders. Mov. Disord. Off. J. Mov. Disord. Soc. 2023, 38, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.-Q.; Richmond, R.C.; Chen, Y.; Mai, X.-M. Mixed evidence for the relationship between periodontitis and Alzheimer’s disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, S.; Chu, M.; Miao, H.; Li, L.; Fang, H.; Li, X.; Zhu, Z.; Bai, Y.; Chen, J.; Qiao, H.; et al. Assessment of relationships between bullous pemphigoid and neurological diseases: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e14869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, M.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Pan, Y.; Wang, Y. Causal effect of insulin resistance on small vessel stroke and Alzheimer’s disease: A Mendelian randomization analysis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2022, 29, 698–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, H.; Zeng, L.; Liu, S. Unraveling the link: Exploring the causal relationship between diabetes, multiple sclerosis, migraine, and Alzheimer’s disease through Mendelian randomization. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1233601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhuang, Q.-S.; Meng, L.; Wang, Z.; Shen, L.; Ji, H.-F. Associations Between Obesity and Alzheimer’s Disease: Multiple Bioinformatic Analyses. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2021, 80, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Tian, R.; Ren, P.; Zhou, W.; Wang, P.; Luo, M.; Jin, S.; Jiang, Q. Parkinson’s disease and Alzheimer’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. BMC Med. Genet. 2018, 19 (Suppl. S1), 215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Q. The bidirectional relationship between Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and epilepsy: A Mendelian randomization study. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Ni, Q.-B.; Wang, K.; Han, Z.; Sun, B.-L. Stroke and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Genet. 2020, 11, 581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, L.; Wang, J.; Lin, L.; Li, Y.; Lu, Q.; Deng, H.-W. Systematic identification of risk factors and drug repurposing options for Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Dement. Transl. Res. Clin. Interv. 2012, 7, e12148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddighi, S.; Houck, A.L.; Rowe, J.B.; Pharoah, P.D.P. Evidence of a Causal Association Between Cancer and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abidin, F.N.Z.; Wells, H.R.R.; Altmann, A.; Dawson, S.J. Hearing difficulty is linked to Alzheimer’s disease by common genetic vulnerability, not shared genetic architecture. NPJ Aging Mech. Dis. 2021, 7, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.-Y.; Yang, Y.-X.; Kuo, K.; Li, H.-Q.; Shen, X.-N.; Chen, S.-D.; Cui, M.; Tan, L.; Dong, Q.; Yu, J.-T. Herpesvirus infections and Alzheimer’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.; Li, J.-C.; Tang, B.-S.; Guo, J.-F.; Shen, L. Lack of bidirectional association between age-related macular degeneration and Alzheimer’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2022, 18, 2725–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Man, S.; Chen, B.; Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Liu, Y.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, M. The Associations Between Cataracts and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2023, 92, 1451–1458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Ou, Y.-N.; Ma, Y.-H.; Huang, L.-Y.; Zhang, W.; Tan, L. Renal function and neurodegenerative diseases. a two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Neurol. Res. 2023, 45, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, J.; Liu, J.; Chan, K.H.K. Evaluating the Causal Effects of Gestational Diabetes Mellitus, Heart Disease, and High Body Mass Index on Maternal Alzheimer’s Disease and Dementia: Multivariable Mendelian Randomization. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 833734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grover, S.; Sharma, M.; International Age-related Macular Degeneration Genomics Consortium (IAMDGC). Sleep, Pain, and Neurodegeneration: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 765321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, Z.; Chen, X. Study on the Correlation Between Atopic Dermatitis, Eczema, Asthma, and Aging Phenotype. Ph.D. Thesis, Central South University, Changsha, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Fu, M.; UCLA Precision Health Data Discovery Repository Working Group, UCLA Precision Health ATLAS Working Group; Chang, T.S. Phenome-Wide Association Study of Polygenic Risk Score for Alzheimer’s Disease in Electronic Health Records. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 800375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, Y.-N.; Zhao, B.; Fu, Y.; Sheng, Z.-H.; Gao, P.-Y.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.-T. The Association of Serum Uric Acid Level, Gout, and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2022, 89, 1063–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wen, Z. Effects of ulcerative colitis and Crohn’s disease on neurodegenerative diseases: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 846005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Wang, Y. Investigation of Causal Effect of Atrial Fibrillation on Alzheimer Disease: A Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2020, 9, e014889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daghlas, I.; Rist, P.M.; Chasman, D.I. Effect of genetic liability to migraine on cognition and brain volume: A Mendelian randomization study. Cephalalgia Int. J. Headache 2020, 40, 998–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Cui, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, X.; Tian, Y. Ankylosing spondylitis may increase the risk of mental disorders: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. J. Chongqing Med. Univ. 2023, 48, 1462–1469. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, Q.; Xin, Z.; Zuo, L.; Li, F.; Liu, B. Alzheimer’s Disease and Rheumatoid Arthritis: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, G.; Li, S.; Ye, H.; Yang, Y.; Huang, Q.; Chu, Y.; Shi, Z.; Zhang, X. Are neurodegenerative diseases associated with an increased risk of inflammatory bowel disease? A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 956005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Xu, M.; Sun, X.; Wang, X. Mendelian randomization and transcriptomic analysis reveal an inverse causal relationship between Alzheimer’s disease and cancer. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, C.; Shi, J.; Yuan, G.; Shou, X.; Chen, T.; Zhu, X.; Yang, Y.; Hu, Y. Causal Association Between Heart Failure and Alzheimer’s Disease: A Two-Sample Bidirectional Mendelian Randomization Study. Front. Genet. 2021, 12, 772343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Wang, Y.; Hou, X.; Cao, L.; Zhou, X.; Yuan, W.; Shen, Y.; Tian, T. Genetic predisposition to neurodegenerative diseases and risk of stroke: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 995045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, F.; Wang, S.; Zhao, H.; Xia, D.; Dong, X. Mendelian randomization analysis does not reveal a causal influence of mental diseases on osteoporosis. Front. Endocrinol. 2023, 14, 1125427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Miao, Y.; Zhao, M.; Zhang, Q. A two-sample Mendelian randomization study on the relationship between mental disorders and obstructive sleep apnea. Chin. J. Geriatr. 2022, 41, 1146–1149. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, F.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W.-D.; Sun, C.-Q.; Deng, H.-W. Detecting potential causal relationship between multiple risk factors and Alzheimer’s disease using multivariable Mendelian randomization. Aging 2020, 12, 21747–21757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dybjer, E.; Kumar, A.; Nägga, K.; Engström, G.; Mattsson-Carlgren, N.; Nilsson, P.M.; Melander, O.; Hansson, O. Polygenic risk of type 2 diabetes is associated with incident vascular dementia: A prospective cohort study. Brain Commun. 2023, 5, fcad054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litkowski, E.M.; Logue, M.W.; Zhang, R.; Charest, B.R.; Lange, E.M.; Hokanson, J.E.; Lynch, J.A.; Vujkovic, M.; Phillips, L.S.; Raghavan, S.; et al. Mendelian randomization study of diabetes and dementia in the Million Veteran Program. Alzheimer’s Dement. J. Alzheimer’s Assoc. 2023, 19, 4367–4376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, J.; Thomassen, J.Q.; Bellenguez, C.; Grenier-Boley, B.; de Rojas, I.; Castillo, A.; Parveen, K.; Küçükali, F.; Nicolas, A.; Frikke-Schmidt, R.; et al. Genetic Associations Between Modifiable Risk Factors and Alzheimer Disease. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2313734. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pan, Y.; Chen, W.; Yan, H.; Wang, M.; Xiang, X. Glycemic traits and Alzheimer’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Aging 2020, 12, 22688–22699. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, X.; Zhang, X.; Yang, M.; Luo, W.; Wang, Y.; Xiu, J. Causal relationship between atrial fibrillation and cognitive impairment: A Mendelian randomization study. J. Shanghai Jiao Tong Univ. (Med. Sci.) 2023, 43, 1359–1365. [Google Scholar]
- Kuo, K.; Yang, Y.-X.; Zhang, Y.-R.; Chen, S.-D.; Huang, S.-Y.; Wu, B.-S.; Yu, J.-T. Investigating causal relations between heart failure and Alzheimer’s disease: A two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Brain Disord. 2022, 7, 100047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Yang, M.; Tian, Y.; Feng, R.; Xu, K.; Teng, M.; Wang, J.; Wang, Q.; Xu, P. Causal associations between common musculoskeletal disorders and dementia: A Mendelian randomization study. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1253791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Liu, S.; Yang, K.; Xie, F.; Li, Y.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, J.; Cheng, Z. Causal association between colorectal cancer and Alzheimer’s disease: A bidirectional two-sample mendelian randomization study. Front. Genet. 2024, 14, 1180905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Cao, S.; Pang, K.; Tang, J.; Lin, G. Causal Association Between Sepsis and Neurodegenerative Diseases: A Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2024, 97, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au Yeung, S.L.; Gill, D. Standardizing the reporting of Mendelian randomization studies. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Piccinni, A.; Origlia, N.; Veltri, A.; Vizzaccaro, C.; Marazziti, D.; Catena-Dell’osso, M.; Conversano, C.; Moroni, I.; Domenici, L.; Dell’osso, L. Plasma β-amyloid peptides levels: A pilot study in bipolar depressed patients. J. Affect. Disord. 2012, 138, 160–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houck, A.L.; Seddighi, S.; Driver, J.A. At the Crossroads Between Neurodegeneration and Cancer: A Review of Overlapping Biology and Its Implications. Curr. Aging Sci. 2018, 11, 77–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Knowles, J.W.; Xie, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chennamsetty, I.; Assimes, T.L.; Paananen, J.; Hansson, O.; Pankow, J.; Goodarzi, M.O.; Quertermous, T.; et al. Identification and validation of N-acetyltransferase 2 as an insulin sensitivity gene. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 1739–1751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhardwaj, A.; Liyanage, S.I.; Weaver, D.F. Cancer and Alzheimer’s inverse correlation: An immunogenetic analysis. Mol. Neurobiol. 2023, 60, 3086–3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgaletto, C.; Munafò, A.; Di Benedetto, G.; De Francisci, C.; Caraci, F.; Di Mauro, R.; Bucolo, C.; Bernardini, R.; Cantarella, G. The immune system on the TRAIL of Alzheimer’s disease. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.S.; Mellman, I. Oncology meets immunology: The cancer-immunity cycle. Immunity 2013, 39, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Ou, Y.-N.; Hu, H.-Y.; Ma, Y.-H.; Tan, L.; Yu, J.-T. The Association Between Osteoarthritis with Risk of Dementia and Cognitive Impairment: A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. JAD 2022, 89, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, R.A.; Lagou, V.; Welch, R.P.; Wheeler, E.; Montasser, M.E.; Luan, J.; Mägi, R.; Strawbridge, R.J.; Rehnberg, E.; Barroso, I.; et al. Large-scale association analyses identify new loci influencing glycemic traits and provide insight into the underlying biological pathways. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 991–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, L.; Boutwell, B.B.; Messerlian, C.; Adams, C.D. Mendelian randomization reveals apolipoprotein B shortens healthspan and possibly increases risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Namba, Y.; Tsuchiya, H.; Ikeda, K. Apolipoprotein B immunoreactivity in senile plaque and vascular amyloids and neurofibrillary tangles in the brains of patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 1992, 134, 266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Study (First Author and Year of Publication) | Disease | Number of Disease Cases | Sample Size | Population |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bae et al. (2019) [12] | Rheumatoid arthritis | 29,880 | 103,638 | European |
| Cai et al. (2021) [13] | Osteoarthritis | 77,052 | 455,211 | European |
| Lee et al. (2019) [14] | Gout | 968, 4275, 945 | 16,474, 10,547, 2158 | European, Chinese, Japanese |
| Harerimana et al. (2022) [15] | Depression | 246,363 | 807,553 | European |
| Pagoni et al. (2022) [16] | Hyperactivity | 20,183 | 55,374 | European |
| Autism spectrum disorder | 18,381 | 46,350 | European | |
| Wei et al. (2022) [17] | Anxiety disorder | 25,453 | 83,566 | European |
| Bidirectional affective disorder | 20,352 | 51,710 | European | |
| Schizophrenia | 33,640 | 77,096 | European | |
| Zheng et al. (2023) [18] | Delirium | 2612 | 327,918 | European |
| Zhang et al. (2023) [19] | Coronary heart disease | 22,233 | 86,995 | European |
| Myocardial infarction | 11,622 | 199,462 | European | |
| Atrial fibrillation | 65,446 | 588,190 | European | |
| Angina pectoris | 18,168 | 206,520 | European | |
| Ischemic stroke | 34,217 | 440,328 | European | |
| Large atherosclerotic stroke | 4373 | 410,484 | European | |
| Cardioembolic stroke | 7193 | 413,304 | European | |
| Arega et al. (2022) [20] | Heart failure | 47,309 | 977,323 | European |
| Grace et al. (2018) [21] | Coronary artery disease | 60,801 | 184,305 | European |
| Tang et al. (2023) [22] | Hypertension | / | / | European |
| Chen et al. (2022) [23] | Insomnia | 109,402 | 386,533 | European |
| Li et al. (2022) [24] | Obstructive sleep disorder | 16,761 | 217,955 | European |
| Cavaillès et al. (2023) [25] | Sleep apnea | 20,008 | 523,366 | European |
| Enduru et al. (2024) [26] | Celiac disease | 4533 | 15,283 | European |
| Crohn’s disease | 12,194 | 40,266 | European | |
| Primary sclerosing cholangitis | 4796 | 309,154 | European | |
| Ulcerative colitis | 12,366 | 45,975 | European | |
| Specific dermatitis | 10,788 | 40,835 | European | |
| Vitiligo | 4680 | 44,266 | European | |
| Hypothyroidism | 13,043 | 244,890 | European | |
| Asthma | 44,301 | 385,822 | European | |
| Allergic rhinitis | 22,057 | 289,307 | European | |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | 7219 | 23,210 | European | |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 14,361 | 58,284 | European | |
| Liao et al. (2023) [27] | Dental caries | / | / | European |
| Zeng et al. (2023) [28] | Inflammatory bowel disease | 25,042 | About 60,000 | European |
| Zeng et al. (2023) [29] | Inflammatory bowel disease | 3753 | 219,559 | European |
| Sun et al. (2020) [30] | Chronic periodontitis | 4924, 12,289 | 12,225, 34,615 | European |
| Shen et al. (2023) [31] | Bullous pemphigoid | 282 | 218,348 | European |
| Zhou et al. (2022) [32] | Insulin resistance | / | / | European |
| Xue et al. (2023) [33] | Type I diabetes | 9266 | 24,840 | European |
| Multiple sclerosis | 47,429 | 115,803 | European | |
| Migraine | 102,084 | 873,341 | European | |
| Zhuang et al. (2021) [34] | Obesity | 32,858 | 98,697 | European |
| Han et al. (2018) [35] | Parkinson’s disease | 26,035 | 428,235 | European |
| Xu et al. (2023) [36] | Epilepsy | 803 | 30,480 | European |
| Wang et al. (2020) [37] | Stroke | 67,162 | 521,612 | European |
| Wu et al. (2021) [38] | Glioma | / | / | European |
| Seddighi et al. (2019) [39] | Breast cancer | / | / | European |
| Lung cancer | / | / | European | |
| Leukemia | / | / | European | |
| Abidin et al. (2021) [40] | Hearing difficulties | 87,056 | 250,389 | European |
| Huang et al. (2021) [41] | Zoster | 16,711 | 134,963 | European |
| Jiang et al. (2022) [42] | Age-related macular degeneration | 16,144 | 33,976 | European |
| Man et al. (2023) [43] | Cataracts | 67,844 | 585,243 | European |
| Liu et al. (2023) [44] | Chronic kidney disease | / | / | European |
| Sheng et al. (2022) [45] | Gestational diabetes | 2062 | / | European |
| Grover et al. (2022) [46] | Insomnia | 109,389 | 386,533 | European |
| Tang (2022) [47] | Asthma | 23,948 | 142,486 | European |
| Fu et al. (2022) [48] | Gout | / | / | European |
| Ou et al. (2022) [49] | Gout | 2115 | 69,374 | European |
| Li et al. (2022) [50] | Crohn’s disease | 5956 | 20,883 | European |
| Ulcerative colitis | 6968 | 27,432 | European | |
| Pan et al. (2020) [51] | Atrial fibrillation | 60,620 | 1,030,836 | European |
| Daghlas et al. (2020) [52] | Migraine | 59,674 | 375,752 | European |
| Zhou et al. (2023) [53] | Ankylosing spondylitis | 9069 | 22,647 | European |
| Cai et al. (2018) [54] | Rheumatoid arthritis | 14,361 | 58,284 | European |
| Cui et al. (2022) [55] | Inflammatory bowel disease | 25,042 | 59,957 | European |
| Ulcerative colitis | 12,366 | 45,975 | European | |
| Crohn’s disease | 12,194 | 40,266 | European | |
| Dong et al. (2023) [56] | Endometrial cancer, etc. | / | / | European |
| Duan et al. (2021) [57] | Heart failure | 47,309 | 977,323 | European |
| Li et al. (2022) [58] | Apoplexy | 40,585 | 446,696 | European |
| Cerebral hemorrhage | 1545 | 3026 | European | |
| Ischemic stroke | 34,217 | 440,328 | European | |
| Tang et al. (2023) [59] | Osteoporosis | 3203 | 212,778 | European |
| Liu et al. (2022) [60] | Obstructive sleep apnea | 20,279 | 259,404 | European |
| Zhang et al. (2020) [61] | Type II diabetes | / | 659,316 | European |
| Dybjer et al. (2023) [62] | Type II diabetes | 74,124 | 898,130 | European |
| Litkowski et al. (2023) [63] | Type II diabetes | 82,980 | 334,672 | European |
| Luo et al. (2023) [64] | Type II diabetes | 39,106 | 440,683 | European |
| Meng et al. (2022) [6] | Type II diabetes | 48,286 | 298,957 | European |
| Pan et al. (2020) [65] | Type II diabetes | / | 212,747 | European |
| Gao et al. (2023) [66] | Atrial fibrillation | / | / | / |
| Kuo et al. (2022) [67] | Heart failure | / | / | / |
| Wang et al. (2023) [68] | Hip osteoarthritis | / | / | / |
| Ankylosing spondylitis | / | / | / | |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | / | / | / | |
| Yuan et al. (2024) [69] | Colorectal cancer | / | / | / |
| Zeng et al. (2024) [70] | Sepsis | / | / | / |
| Study (First Author and Year of Publication) | Items * | Total Score (Out of 14) | % | |||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Title and Abstract | Rationale and Objectives | Study Design | Reporting | Analysis | Assessment of Assumptions | |||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | |||
| Bae et al. (2019) [12] | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | · | 12.5 | 89.3 | |
| Cai et al. (2021) [13] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Lee et al. (2019) [14] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | 12.5 | 89.3 |
| Harerimana et al. (2022) [15] | + | + | + | + | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | · | 12.5 | 89.3 |
| Pagoni et al. (2022) [16] | + | + | + | + | + | · | · | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | 12.5 | 89.3 |
| Wei et al. (2022) [17] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | · | 13 | 92.9 |
| Zheng et al. (2023) [18] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Zhang et al. (2023) [19] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13.5 | 96.4 |
| Arega et al. (2022) [20] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Grace et al. (2018) [21] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | 12.5 | 89.3 |
| Tang et al. (2023) [22] | + | + | + | · | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Chen et al. (2022) [23] | + | − | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | − | 12 | 85.7 |
| Li et al. (2022) [24] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13.5 | 96.4 |
| Cavaillès et al. (2023) [25] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13.5 | 96.4 |
| Enduru et al. (2024) [26] | − | + | + | · | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | · | 11 | 78.6 |
| Liao et al. (2023) [27] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13.5 | 96.4 |
| Zeng et al. (2023) [28] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Zeng et al. (2023) [29] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | · | + | + | + | · | − | 11 | 78.6 |
| Sun et al. (2020) [30] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | · | + | + | · | + | + | 12.5 | 89.3 |
| Shen et al. (2023) [31] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Zhou et al. (2022) [32] | + | + | + | + | + | · | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 12.5 | 89.3 |
| Xue et al. (2023) [33] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Zhuang et al. (2021) [34] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | · | + | + | + | · | − | 11.5 | 82.1 |
| Han et al. (2018) [35] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | 12.5 | 89.3 |
| Xu et al. (2023) [36] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13.5 | 96.4 |
| Wang et al. (2020) [37] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Wu et al. (2021) [38] | + | · | + | − | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | 11.5 | 82.1 |
| Seddighi et al. (2019) [39] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Abidin et al. (2021) [40] | · | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | · | + | − | + | 11.5 | 82.1 |
| Huang et al. (2021) [41] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | · | 13 | 92.9 |
| Jiang et al. (2022) [42] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13.5 | 96.4 |
| Man et al. (2023) [43] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Liu et al. (2023) [44] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Sheng et al. (2022) [45] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13.5 | 96.4 |
| Grover et al. (2022) [46] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | − | 11 | 78.6 |
| Tang et al. (2022) [47] | + | + | + | · | + | · | · | · | · | + | + | + | + | + | 11.5 | 82.1 |
| Fu et al. (2022) [48] | − | + | · | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | 11 | 78.6 |
| Ou et al. (2022) [49] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13.5 | 96.4 |
| Li et al. (2022) [50] | + | + | + | · | + | − | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 12.5 | 89.3 |
| Pan et al. (2020) [51] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | 12.5 | 89.3 |
| Daghlas et al. (2020) [52] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | − | 12 | 85.7 |
| Zhou et al. (2023) [53] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Cai et al. (2018) [54] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | − | · | · | + | 11 | 78.6 |
| Cui et al. (2022) [55] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Dong et al. (2023) [56] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | − | + | 11.5 | 82.1 |
| Duan et al. (2021) [57] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Li et al. (2022) [58] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | 12.5 | 89.3 |
| Tang et al. (2023) [59] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | 12 | 85.7 |
| Liu et al. (2022) [60] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | − | 12 | 85.7 |
| Zhang et al. (2020) [61] | + | + | + | − | + | · | − | + | + | + | + | · | + | − | 10 | 71.4 |
| Dybjer et al. (2023) [62] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | 12.5 | 89.3 |
| Litkowski et al. (2023) [63] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13.5 | 96.4 |
| Luo et al. (2023) [64] | · | − | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | · | 11.5 | 82.1 |
| Meng et al. (2022) [6] | + | + | + | · | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | − | 12 | 85.7 |
| Pan et al. (2020) [65] | + | + | + | + | + | · | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13.5 | 96.4 |
| Gao et al. (2023) [66] | + | + | + | + | + | . | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13.5 | 96.4 |
| Kuo et al. (2022) [67] | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 14 | 100 |
| Wang et al. (2023) [68] | + | + | + | . | + | . | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Yuan et al. (2024) [69] | + | + | + | . | + | . | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Zeng et al. (2024) [70] | + | + | + | . | + | . | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | + | 13 | 92.9 |
| Disease Category | Specific Disease | OR [95% CI] | p-Value 1 | Effect 2 | Directionality 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Diseases of the musculoskeletal system or connective tissue | Gout | 1.02 [1.00, 1.05] | 0.049 (*) | Increased Risk | → AD |
| Hip osteoarthritis | 0.80 [0.69, 0.94] | 0.007 (**) | Reduced Risk | → AD | |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | 0.97 [0.95, 0.99] | 0.004 (**) | Reduced Risk | → AD | |
| Mental, behavioral, or neurodevelopmental disorders | Depression | 1.03 [1.01, 1.05] | 0.001 (**) | Increased Risk | → AD |
| Delirium | 1.32 [1.13, 1.54] | 0.0005 (***) | Increased Risk | AD → | |
| Diseases of the circulatory system | Coronary artery disease | 1.07 [1.01, 1.13] | 0.021 (*) | Increased Risk | → AD |
| Hypertension | 4.30 [1.04, 17.78] | 0.044 (*) | Increased Risk | → AD | |
| Angina | 1.06 [1.02, 1.10] | 0.003 (**) | Increased Risk | AD → | |
| Sleep–wake disorders | Insomnia | 1.02 [1.01, 1.03] | 0.0001 (***) | Increased Risk | → AD |
| Diseases of the digestive system | Chronic periodontitis (5 independent SNPs) | 1.10 [1.02, 1.19] | 0.013 (*) | Increased Risk | → AD |
| Inflammatory bowel disease | 1.01 [1.00, 1.03] | 0.049 (*) | Increased Risk | → AD | |
| Endocrine, nutritional, or metabolic disease | Insulin resistance (using gold standard) | 1.01 [1.00, 1.03] | 0.049 (*) | Increased Risk | → AD |
| Insulin resistance (using fasting insulin) | 1.13 [1.04, 1.23] | 0.004 (**) | Increased Risk | → AD | |
| Type II diabetes | 1.05 [1.01, 1.09]/1.05 [1.00, 1.10] | 0.014 (*)/0.0498 (*) | Increased Risk/Increased Risk | ↔ | |
| Diseases of the nervous system | Cardioembolic stroke | 0.90 [0.82, 0.98] | 0.022 (*) | Reduced Risk | → AD |
| Epilepsy | 1.15 [1.03, 1.29]/1.08 [1.02, 1.15] | 0.017 (*)/0.013 (*) | Increased Risk/Increased Risk | ↔ | |
| Migraine | 1.01 [1.00, 1.02] | 0.046 (*) | Increased Risk | → AD | |
| Certain infectious or parasitic diseases | Sepsis | 1.11 [1.01, 1.22] | 0.03 (*) | Reduced Risk | AD → |
| Shingles | 0.87 [0.78, 0.96] | 0.005 (**) | Reduced Risk | → AD | |
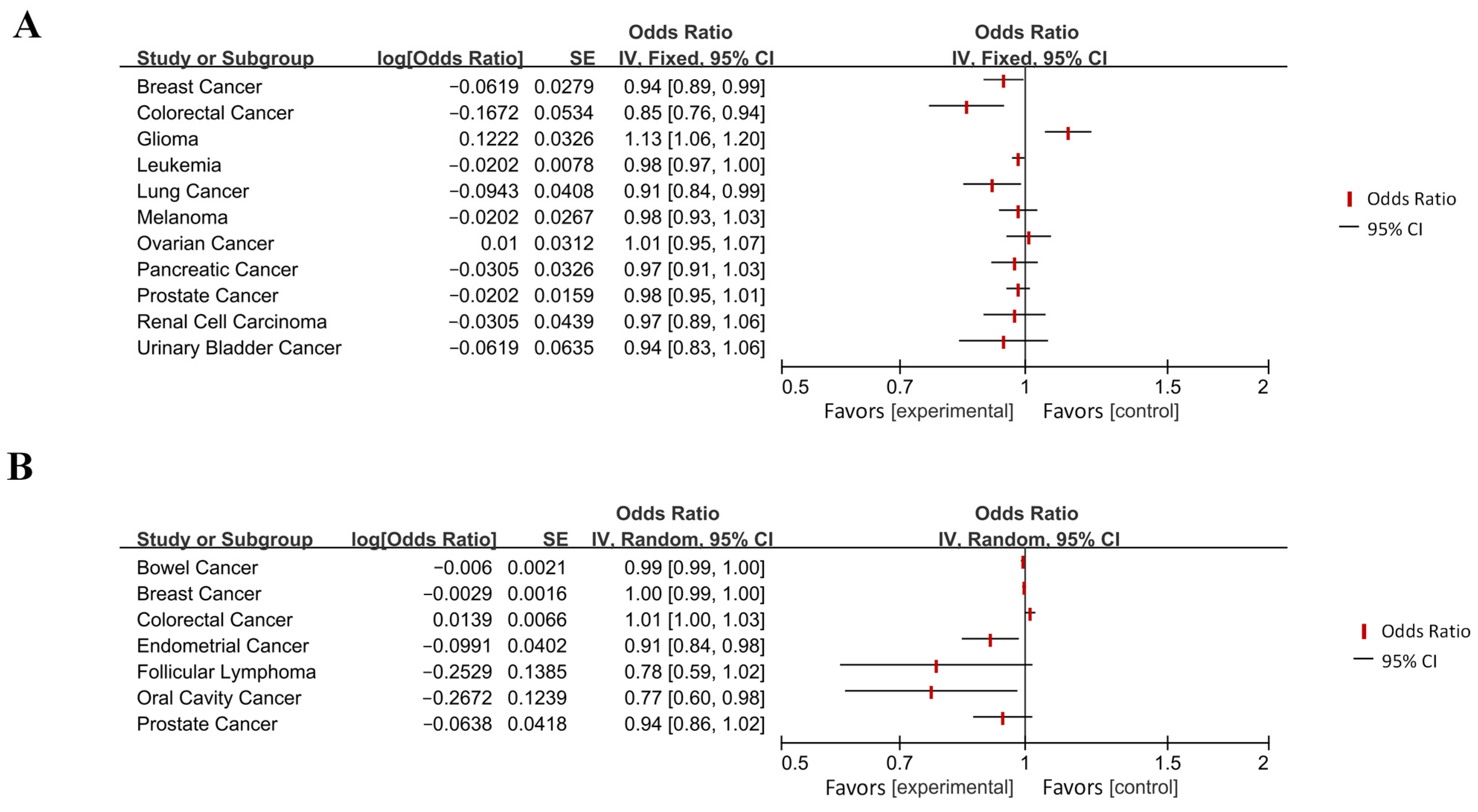
| Neoplasms | Breast cancer | 0.94 [0.89, 0.99] | 0.027 (*) | Reduced Risk | → AD |
| Colorectal cancer | 0.85 [0.76, 0.94]/1.01 [1.001, 1.027] | 0.002 (**)/0.035 (*) | Reduced Risk/Increased Risk | ↔ | |
| Glioma | 1.13 [1.06, 1.20] | 0.0002 (***) | Increased Risk | → AD | |
| Leukemia | 0.98 [0.97, 1.00] | 0.010 (**) | Reduced Risk | → AD | |
| Lung cancer | 0.91 [0.84, 0.99] | 0.021 (*) | Reduced Risk | → AD | |
| Bowel cancer | 0.99 [0.99, 1.00] | 0.004(**) | Reduced Risk | AD → | |
| Endometrial cancer | 0.91 [0.84, 0.98] | 0.014 (*) | Reduced Risk | AD → | |
| Oral cancer | 0.77 [0.60, 0.98] | 0.031 (*) | Reduced Risk | AD → | |
| Diseases of the visual system | Cataracts | 0.96 [0.93, 0.99] | 0.012 (*) | Reduced Risk | AD → |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, H.; Ni, H.; Yang, Q.; Ni, J.; Ji, J.; Yang, S.; Peng, F. Evaluating the Bidirectional Causal Effects of Alzheimer’s Disease Across Multiple Conditions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083589
Zhu H, Ni H, Yang Q, Ni J, Ji J, Yang S, Peng F. Evaluating the Bidirectional Causal Effects of Alzheimer’s Disease Across Multiple Conditions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083589
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Haoning, Huitong Ni, Qiuling Yang, Jiaqi Ni, Jianguang Ji, Shu Yang, and Fu Peng. 2025. "Evaluating the Bidirectional Causal Effects of Alzheimer’s Disease Across Multiple Conditions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083589
APA StyleZhu, H., Ni, H., Yang, Q., Ni, J., Ji, J., Yang, S., & Peng, F. (2025). Evaluating the Bidirectional Causal Effects of Alzheimer’s Disease Across Multiple Conditions: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Mendelian Randomization Studies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3589. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083589







