The Behavioral and Neuroinflammatory Impact of Ketamine in a Murine Model of Depression and Liver Damage
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
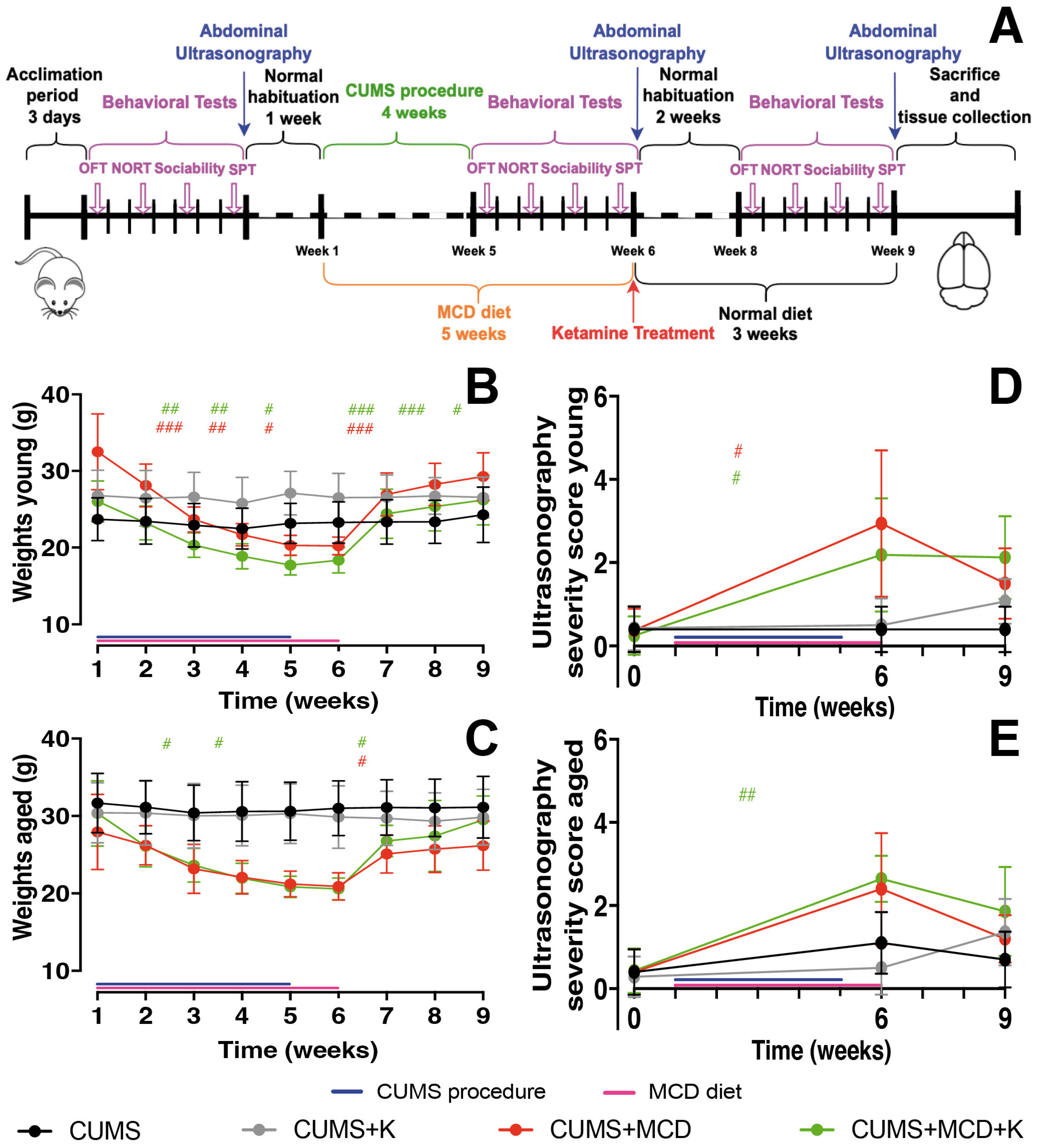
2.1. Acute Administration of Ketamine Does Not Affect the Severity of Liver Injury
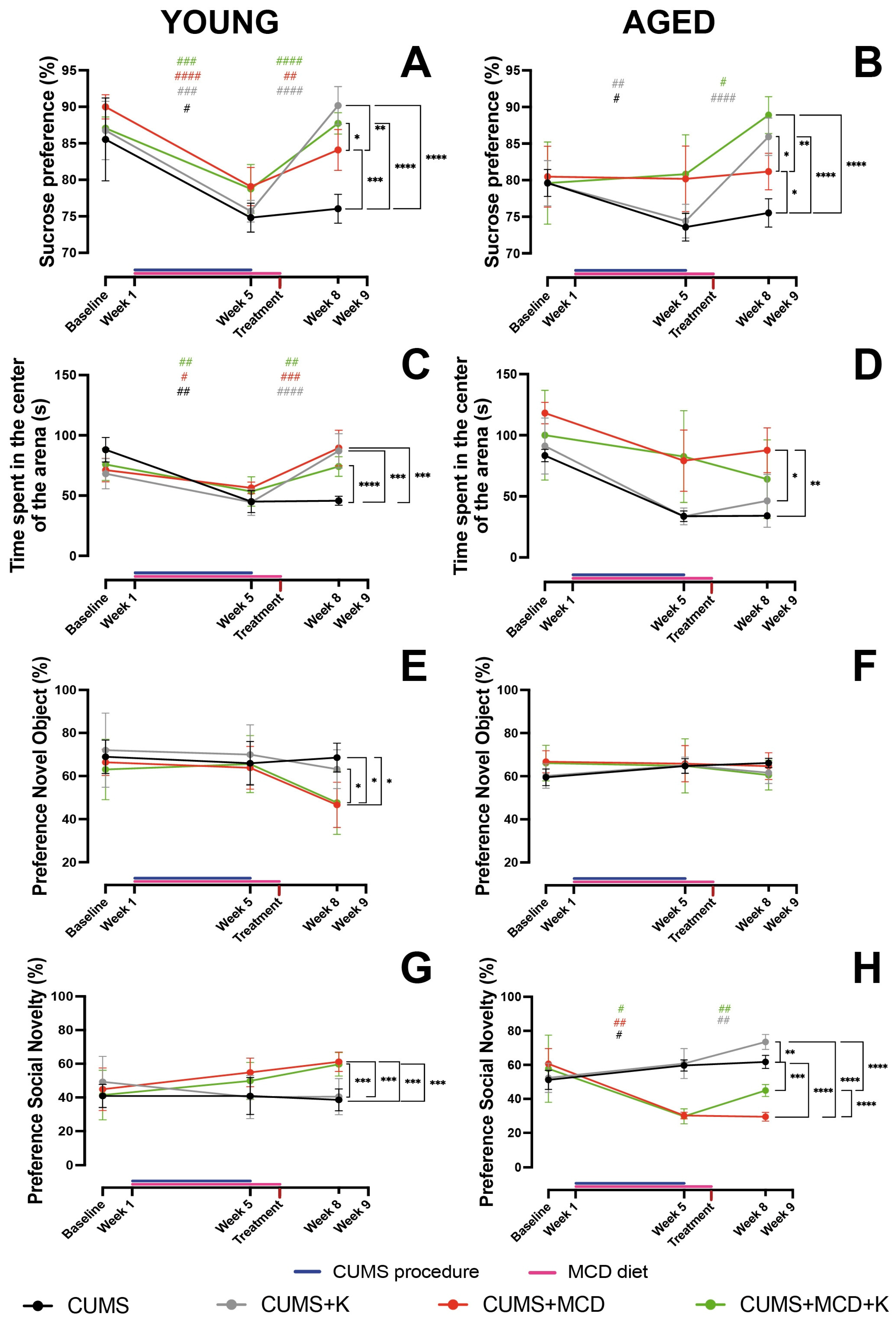
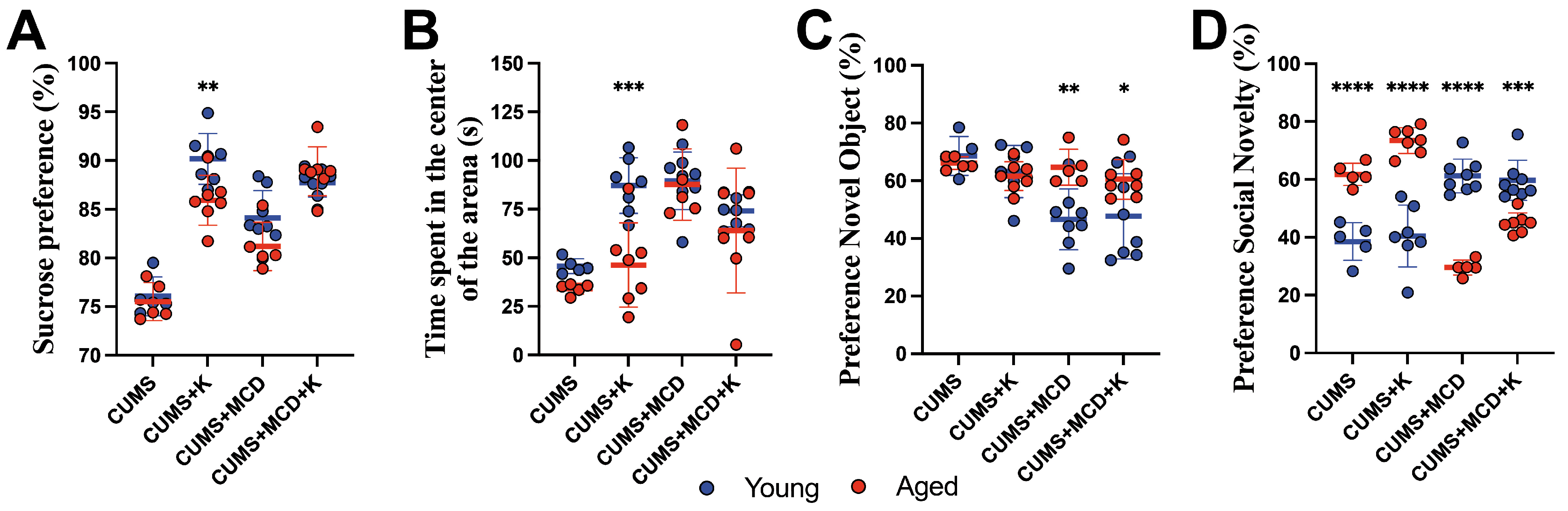
2.2. Ketamine Alleviates Anhedonia and Anxiety-like Behavior, Regardless of Liver Damage
2.3. Ketamine Does Not Enhance Memory in All Animals with Liver Damage, but It Improves Sociability in Aged Ones
2.4. Ketamine Is More Effective in Young Compared to Aged Animals
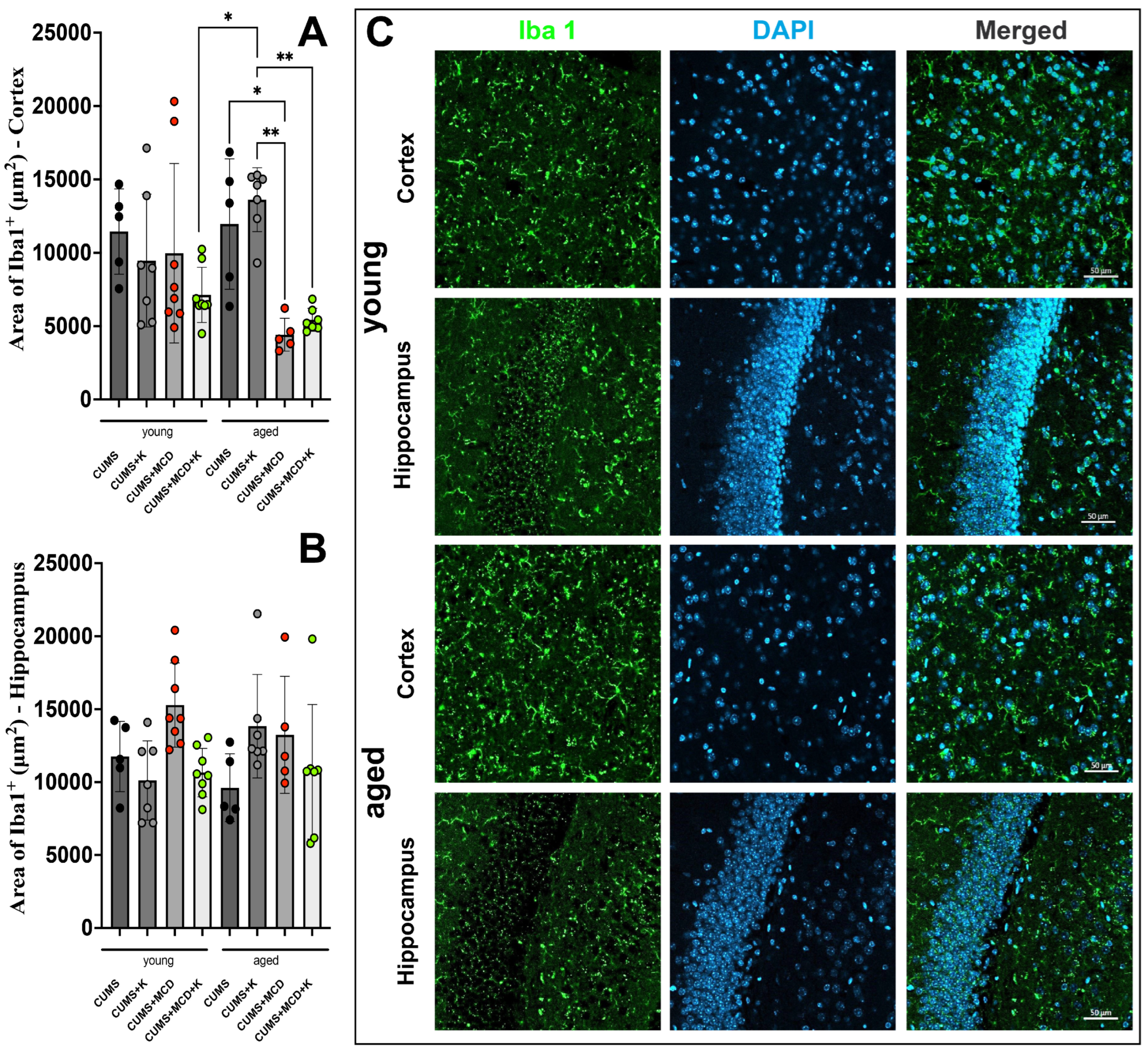
2.5. Acute Ketamine Treatment Can Prevent Astrogliosis and Neuronal Loss
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Experimental Animals
4.2. Induction of Depressive-like Behavior and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease/Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis
4.3. Clinical Evaluation and Behavior Testing
4.4. Abdominal Ultrasonography
4.5. Histopathology and Immunohistochemistry
4.6. Image Analysis
4.7. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CUMS | Chronic unpredictable mild stress |
| GFAP | Glial fibrillary acidic protein |
| Iba 1 | Ionized calcium binding adaptor molecule 1 |
| K | Ketamine |
| KILI | Ketamine-induced liver injury |
| MCD | Methionine–choline deficient |
| NAFLD | Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease |
| NeuN | Neuronal nuclei |
| NORT | Novel object recognition test |
| OFT | Open field test |
| PBS | Phosphate-buffered saline |
| PFA | Paraformaldehyde |
| SD | Standard deviation |
| SPT | Sucrose preference test |
| SSRI’s | Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors |
References
- Liu, Q.; He, H.; Yang, J.; Feng, X.; Zhao, F.; Lyu, J. Changes in the global burden of depression from 1990 to 2017: Findings from the Global Burden of Disease study. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2020, 126, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno-Agostino, D.; Wu, Y.-T.; Daskalopoulou, C.; Hasan, M.T.; Huisman, M.; Prina, M. Global trends in the prevalence and incidence of depression:a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2021, 281, 235–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malhi, G.S.; Mann, J.J. Depression. Lancet 2018, 392, 2299–2312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rubio-Guerra, A.F.; Rodriguez-Lopez, L.; Vargas-Ayala, G.; Huerta-Ramirez, S.; Serna, D.C.; Lozano-Nuevo, J.J. Depression increases the risk for uncontrolled hypertension. Exp. Clin. Cardiol. 2013, 18, 10–12. [Google Scholar]
- Bădescu, S.V.; Tătaru, C.; Kobylinska, L.; Georgescu, E.L.; Zahiu, D.M.; Zăgrean, A.M.; Zăgrean, L. The association between Diabetes mellitus and Depression. J. Med. Life 2016, 9, 120–125. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, H.; Wang, Y.; Xue, Y.; Huang, D.; Kong, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, M. The effect of Xinkeshu tablets on depression and anxiety symptoms in patients with coronary artery disease: Results from a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moussavi, S.; Chatterji, S.; Verdes, E.; Tandon, A.; Patel, V.; Ustun, B. Depression, chronic diseases, and decrements in health: Results from the World Health Surveys. Lancet 2007, 370, 851–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Lim, L.K.E.; Ng, C.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Lim, W.H.; Ho, C.S.H.; Tan, E.X.X.; Sanyal, A.J.; Muthiah, M.D. Is Fatty Liver Associated With Depression? A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review on the Prevalence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes of Depression and Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 691696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Shi, J. Association between nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and depression: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Affect. Disord. 2022, 301, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, A.A.; Kallman Price, J.; Stepanova, M.; Poms, L.W.; Fang, Y.; Moon, J.; Nader, F.; Younossi, Z.M. Depression in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and chronic viral hepatitis B and C. Psychosomatics 2011, 52, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labenz, C.; Huber, Y.; Michel, M.; Nagel, M.; Galle, P.R.; Kostev, K.; Schattenberg, J.M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Increases the Risk of Anxiety and Depression. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jung, J.Y.; Park, S.K.; Oh, C.M.; Chung, P.W.; Ryoo, J.H. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Its Association with Depression in Korean General Population. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2019, 34, e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jawad, M.Y.; Meshkat, S.; Tabassum, A.; McKenzie, A.; Di Vincenzo, J.D.; Guo, Z.; Musavi, N.B.; Phan, L.; Ceban, F.; Kwan, A.T.; et al. The bidirectional association of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with depression, bipolar disorder, and schizophrenia. CNS Spectr. 2023, 28, 541–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullish, B.H.; Kabir, M.S.; Thursz, M.R.; Dhar, A. Review article: Depression and the use of antidepressants in patients with chronic liver disease or liver transplantation. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2014, 40, 880–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, C.H.; Xiao, J.; Chew, N.W.S.; Chin, Y.H.; Chan, K.E.; Quek, J.; Lim, W.H.; Tan, D.J.H.; Loke, R.W.K.; Tan, C.; et al. Depression in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with an increased risk of complications and mortality. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 985803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaheen, A.A.; Kaplan, G.G.; Sharkey, K.A.; Lethebe, B.C.; Swain, M.G. Impact of major depression and antidepressant use on alcoholic and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: A population-based study. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 2308–2317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Pu, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, L.; An, C.; Wu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, W.; Qu, S.; Yan, W. Exploring the multifaceted potential of (R)-ketamine beyond antidepressant applications. Front. Pharmacol. 2024, 15, 1337749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potter, D.E.; Choudhury, M. Ketamine: Repurposing and redefining a multifaceted drug. Drug Discov. Today 2014, 19, 1848–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestring, S.; Galuba, V.; Kern, E.; Voita, S.; Berens, F.; Nasiri, D.; Domschke, K.; Normann, C. Ketamine in multiple treatment-resistant depressed inpatients: A naturalistic cohort study. J. Affect. Disord. 2024, 350, 895–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrenek, C.; Duong, B.; Khullar, A.; McRee, C.; Thomas, R.; Swainson, J. Use of ketamine for treatment resistant depression: Updated review of literature and practical applications to a community ketamine program in Edmonton, Alberta, Canada. Front. Psychiatry 2023, 14, 1283733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abbar, M.; Demattei, C.; El-Hage, W.; Llorca, P.M.; Samalin, L.; Demaricourt, P.; Gaillard, R.; Courtet, P.; Vaiva, G.; Gorwood, P.; et al. Ketamine for the acute treatment of severe suicidal ideation: Double blind, randomised placebo controlled trial. BMJ (Clin. Res. Ed.) 2022, 376, e067194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grunebaum, M.F.; Galfalvy, H.C.; Choo, T.H.; Keilp, J.G.; Moitra, V.K.; Parris, M.S.; Marver, J.E.; Burke, A.K.; Milak, M.S.; Sublette, M.E.; et al. Ketamine for Rapid Reduction of Suicidal Thoughts in Major Depression: A Midazolam-Controlled Randomized Clinical Trial. Am. J. Psychiatry 2018, 175, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noppers, I.M.; Niesters, M.; Aarts, L.; Bauer, M.C.R.; Drewes, A.M.; Dahan, A.; Sarton, E.Y. Drug-induced liver injury following a repeated course of ketamine treatment for chronic pain in CRPS type 1 patients: A report of 3 cases. Pain 2011, 152, 2173–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Kohan, L.R.; Goldstein, R.B. Substantial Elevation of Liver Enzymes During Ketamine Infusion: A Case Report. A A Pract. 2020, 14, e01239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartsch, C.J.; Aaflaq, S.; Jacobs, J.T.; Smith, M.; Summa, F.; Skinner, S.; Qasem, E.; Thompson, R.; Li, Z.; Nordman, J.C. A single dose of ketamine enhances early life stress-induced aggression with no effect on fear memory, anxiety-like behavior, or depression-like behavior in mice. Behav. Neurosci. 2023, 137, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, J.; Mugarura, N.E.; Welter, A.L.; Johnson, E.M.; Siegel, J.A. The Effects of Acute and Repeated Administration of Ketamine on Memory, Behavior, and Plasma Corticosterone Levels in Female Mice. Neuroscience 2023, 512, 99–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Soejima, Y.; Fukusato, T. Animal models of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 18, 2300–2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgačević, B.; Mladenović, D.; Ninković, M.; Prokić, V.; Stanković, M.N.; Aleksić, V.; Cerović, I.; Vukićević, R.J.; Vučević, D.; Stanković, M.; et al. Dynamics of oxidative/nitrosative stress in mice with methionine-choline-deficient diet-induced nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 701–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brzezinski, R.; Levin-Kotler, L.; Rabin, N.; Zehava, O.-B.; Zimmer, Y.; Sternfeld, A.; Finchelman, J.; Unis, R.; Lewis, N.; Tepper-Shaihov, O.; et al. Automated thermal imaging for the detection of fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinella, M.E.; Elias, M.S.; Smolak, R.R.; Fu, T.; Borensztajn, J.; Green, R.M. Mechanisms of hepatic steatosis in mice fed a lipogenic methionine choline-deficient diet. J. Lipid Res. 2008, 49, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mușat, M.I.; Cătălin, B.; Hadjiargyrou, M.; Popa-Wagner, A.; Greșiță, A. Advancing Post-Stroke Depression Research: Insights from Murine Models and Behavioral Analyses. Life 2024, 14, 1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pałucha-Poniewiera, A.; Podkowa, K.; Rafało-Ulińska, A.; Brański, P.; Burnat, G. The influence of the duration of chronic unpredictable mild stress on the behavioural responses of C57BL/6J mice. Behav. Pharmacol. 2020, 31, 574–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alqurashi, G.K.; Hindi, E.A.; Zayed, M.A.; Abd El-Aziz, G.S.; Alturkistani, H.A.; Ibrahim, R.F.; Al-Thepyani, M.A.; Bakhlgi, R.; Alzahrani, N.A.; Ashraf, G.M.; et al. The Impact of Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress-Induced Depression on Spatial, Recognition and Reference Memory Tasks in Mice: Behavioral and Histological Study. Behav. Sci. 2022, 12, 166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.-W.; Monteggia, L.M. Increasing doses of ketamine curtail antidepressant responses and suppress associated synaptic signaling pathways. Behav. Brain Res. 2020, 380, 112378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khakpai, F.; Ebrahimi-Ghiri, M.; Alijanpour, S.; Zarrindast, M.-R. Ketamine-induced antidepressant like effects in mice: A possible involvement of cannabinoid system. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 112, 108717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Chen, M.; Jiang, Y.; Xiang, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, Z.; Li, S.; Cui, Y.; Wang, J.; Zhu, Y.; et al. Sustained antidepressant effect of ketamine through NMDAR trapping in the LHb. Nature 2023, 622, 802–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edinoff, A.N.; Akuly, H.A.; Hanna, T.A.; Ochoa, C.O.; Patti, S.J.; Ghaffar, Y.A.; Kaye, A.D.; Viswanath, O.; Urits, I.; Boyer, A.G.; et al. Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors and Adverse Effects: A Narrative Review. Neurol. Int. 2021, 13, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serafini, G.; Howland, R.H.; Rovedi, F.; Girardi, P.; Amore, M. The role of ketamine in treatment-resistant depression: A systematic review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2014, 12, 444–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renemane, L.; Rancans, E. Sertraline induced acute hepatocellular liver injury in patient with major depressive disorder: A case report. Front. Psychiatry 2024, 15, 1456455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Q.; Benson, M.A.; Talbot, T.J.; Devadas, G.; Swanson, H.J.; Olson, J.L.; Kirchner, J.P. Acute Hepatitis Due to Fluoxetine Therapy. Mayo Clin. Proc. 1999, 74, 692–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvajal García-Pando, A.; García del Pozo, J.; Sánchez, A.S.; Velasco, M.A.; Rueda de Castro, A.M.; Lucena, M.I. Hepatotoxicity associated with the new antidepressants. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2002, 63, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duman, R.S. Ketamine and rapid-acting antidepressants: A new era in the battle against depression and suicide. F1000Res 2018, 7, 659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- She, Y.-J.; Pan, J.; Peng, L.-M.; Ma, L.; Guo, X.; Lei, D.-X.; Wang, H.-Z. Ketamine modulates neural stem cell differentiation by regulating TRPC3 expression through the GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. NeuroToxicology 2023, 94, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ommati, M.M.; Mobasheri, A.; Niknahad, H.; Rezaei, M.; Alidaee, S.; Arjmand, A.; Mazloomi, S.; Abdoli, N.; Sadeghian, I.; Sabouri, S.; et al. Low-dose ketamine improves animals’ locomotor activity and decreases brain oxidative stress and inflammation in ammonia-induced neurotoxicity. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 37, e23468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalkan, Y.; Tomak, Y.; Altuner, D.; Tumkaya, L.; Bostan, H.; Yilmaz, A.; Unal, D.; Kara, A.; Turan, A. Hepatic effects of ketamine administration for 2 weeks in rats. Hum. Exp. Toxicol. 2014, 33, 32–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutton, M.; Can, A.T.; Lagopoulos, J.; Hermens, D.F. Oral ketamine may offer a solution to the ketamine conundrum. Psychopharmacology 2023, 240, 2483–2497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinis-Oliveira, R.J. Metabolism and metabolomics of ketamine: A toxicological approach. Forensic Sci. Res. 2017, 2, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephenson, K.; Kennedy, L.; Hargrove, L.; Demieville, J.; Thomson, J.; Alpini, G.; Francis, H. Updates on Dietary Models of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Current Studies and Insights. Gene Expr. 2018, 18, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanos, P.; Brown, K.A.; Georgiou, P.; Yuan, P.; Zarate, C.A., Jr.; Thompson, S.M.; Gould, T.D. NMDA Receptor Activation-Dependent Antidepressant-Relevant Behavioral and Synaptic Actions of Ketamine. J. Neurosci. 2023, 43, 1038–1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.-Y.; Yin, C.-Y.; Zhu, L.-J.; Zhu, X.-H.; Xu, C.; Luo, C.-X.; Chen, H.; Zhu, D.-Y.; Zhou, Q.-G. Sucrose preference test for measurement of stress-induced anhedonia in mice. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 1686–1698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, D.D. Sucrose Preference Test as a Measure of Anhedonic Behavior in a Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Model of Depression: Outstanding Issues. Brain Sci. 2022, 12, 1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraeuter, A.K.; Guest, P.C.; Sarnyai, Z. The Open Field Test for Measuring Locomotor Activity and Anxiety-Like Behavior. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1916, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.A.; Chen, J.D.; Yang, H.Y.; Xia, Y.P.; Huang, Z.Y. Effects of CUMS on excitatory/inhibitory balance of hippocampal and prefrontal cortex pyramidal neurons in anxiety-like mice. Zhongguo Ying Yong Sheng Li Xue Za Zhi 2022, 38, 814–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lueptow, L.M. Novel Object Recognition Test for the Investigation of Learning and Memory in Mice. J. Vis. Exp. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nadler, J.J.; Moy, S.S.; Dold, G.; Trang, D.; Simmons, N.; Perez, A.; Young, N.B.; Barbaro, R.P.; Piven, J.; Magnuson, T.R.; et al. Automated apparatus for quantitation of social approach behaviors in mice. Genes. Brain Behav. 2004, 3, 303–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomeno, W.; Kawashima, K.; Yoneda, M.; Saito, S.; Ogawa, Y.; Honda, Y.; Kessoku, T.; Imajo, K.; Mawatari, H.; Fujita, K.; et al. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease comorbid with major depressive disorder: The pathological features and poor therapeutic efficacy. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 1009–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizki, G.; Arnaboldi, L.; Gabrielli, B.; Yan, J.; Lee, G.S.; Ng, R.K.; Turner, S.M.; Badger, T.M.; Pitas, R.E.; Maher, J.J. Mice fed a lipogenic methionine-choline-deficient diet develop hypermetabolism coincident with hepatic suppression of SCD-1. J. Lipid Res. 2006, 47, 2280–2290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akillioglu, K.; Melik, E.B.; Melik, E.; Boga, A. Effect of ketamine on exploratory behaviour in BALB/C and C57BL/6 mice. Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 2012, 100, 513–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.F.; Tang, Z.H.; Wang, S.Y.; Lei, S.; Zhang, B.; Tian, S.W. Ketamine enhances novel object recognition memory reconsolidation via the BDNF/TrkB pathway in mice. Physiol. Behav. 2021, 242, 113626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morega, S.; Cătălin, B.; Simionescu, C.E.; Sapalidis, K.; Rogoveanu, I. Cerebrolysin Prevents Brain Injury in a Mouse Model of Liver Damage. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popik, P.; Hołuj, M.; Kos, T.; Nowak, G.; Librowski, T.; Sałat, K. Comparison of the Psychopharmacological Effects of Tiletamine and Ketamine in Rodents. Neurotox. Res. 2017, 32, 544–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donahue, R.J.; Muschamp, J.W.; Russo, S.J.; Nestler, E.J.; Carlezon, W.A., Jr. Effects of striatal ΔFosB overexpression and ketamine on social defeat stress-induced anhedonia in mice. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 76, 550–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaseen, A.; Shrivastava, K.; Zuri, Z.; Hatoum, O.A.; Maroun, M. Prefrontal Oxytocin is Involved in Impairments in Prefrontal Plasticity and Social Memory Following Acute Exposure to High Fat Diet in Juvenile Animals. Cereb. Cortex 2019, 29, 1900–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, R.; Kasahara, Y.; Hidema, S.; Fukumitsu, S.; Nakagawa, K.; Nishimori, K. Oxytocin Ameliorates Impaired Behaviors of High Fat Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Front. Endocrinol. 2020, 11, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakajima, S.; Fukasawa, K.; Gotoh, M.; Murakami-Murofushi, K.; Kunugi, H. Saturated fatty acid is a principal cause of anxiety-like behavior in diet-induced obese rats in relation to serum lysophosphatidyl choline level. Int. J. Obes. 2020, 44, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zemdegs, J.; Quesseveur, G.; Jarriault, D.; Pénicaud, L.; Fioramonti, X.; Guiard, B.P. High-fat diet-induced metabolic disorders impairs 5-HT function and anxiety-like behavior in mice. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 173, 2095–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasprowska-Liśkiewicz, D.; Liśkiewicz, A.D.; Nowacka-Chmielewska, M.M.; Nowicka, J.; Małecki, A.; Barski, J.J. The ketogenic diet affects the social behavior of young male rats. Physiol. Behav. 2017, 179, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arqoub, A.M.S.; Flynn, K.G.; Martinez, L.A. Gestational exposure to a ketogenic diet increases sociability in CD-1 mice. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 134, 358–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verpeut, J.L.; DiCicco-Bloom, E.; Bello, N.T. Ketogenic diet exposure during the juvenile period increases social behaviors and forebrain neural activation in adult Engrailed 2 null mice. Physiol. Behav. 2016, 161, 90–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, H.; Ilgin, R.; Koc, B.; Yuksel, O.; Kizildag, S.; Guvendi, G.; Karakilic, A.; Kandis, S.; Hosgorler, F.; Ates, M.; et al. A combination of ketogenic diet and voluntary exercise ameliorates anxiety and depression-like behaviors in Balb/c mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2022, 770, 136443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rawat, R.; Tunc-Ozcan, E.; McGuire, T.L.; Peng, C.-Y.; Kessler, J.A. Ketamine activates adult-born immature granule neurons to rapidly alleviate depression-like behaviors in mice. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotto, B.; Natarajaseenivasan, K.; Langford, D. Astrocyte activation and altered metabolism in normal aging, age-related CNS diseases, and HAND. J. Neurovirol 2019, 25, 722–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellis, R.J.; Fan, Y.; Grelotti, D.; Tang, B.; Letendre, S.; He, J.J. Astrocyte Activation is A Potential Mechanism Underlying Depressed Mood and Apathy in People with HIV. J. Neurol. Psychol. 2022, 9, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lullau, A.P.M.; Haga, E.M.W.; Ronold, E.H.; Dwyer, G.E. Antidepressant mechanisms of ketamine: A review of actions with relevance to treatment-resistance and neuroprogression. Front. Neurosci. 2023, 17, 1223145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sokołowska, P.; Seweryn Karbownik, M.; Jóźwiak-Bębenista, M.; Dobielska, M.; Kowalczyk, E.; Wiktorowska-Owczarek, A. Antidepressant mechanisms of ketamine’s action: NF-κB in the spotlight. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2023, 218, 115918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, S.; Xie, L.; Yu, S.; Zhang, L.; Liu, C.; Zhou, W.; Yu, T. Ketamine Within Clinically Effective Range Inhibits Glutamate Transmission From Astrocytes to Neurons and Disrupts Synchronization of Astrocytic SICs. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2019, 13, 240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aricioğlu, F.; Yalcinkaya, C.; Ozkartal, C.S.; Tuzun, E.; Sirvanci, S.; Kucukali, C.I.; Utkan, T. NLRP1-Mediated Antidepressant Effect of Ketamine in Chronic Unpredictable Mild Stress Model in Rats. Psychiatry Investig. 2020, 17, 283–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tartt, A.N.; Mariani, M.B.; Hen, R.; Mann, J.J.; Boldrini, M. Dysregulation of adult hippocampal neuroplasticity in major depression: Pathogenesis and therapeutic implications. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 2689–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenza, M.; Facchinetti, R.; Torazza, C.; Ciarla, C.; Bronzuoli, M.R.; Balbi, M.; Bonanno, G.; Popoli, M.; Steardo, L.; Milanese, M.; et al. Molecular signatures of astrocytes and microglia maladaptive responses to acute stress are rescued by a single administration of ketamine in a rodent model of PTSD. Transl. Psychiatry 2024, 14, 209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shibakawa, Y.S.; Sasaki, Y.; Goshima, Y.; Echigo, N.; Kamiya, Y.; Kurahashi, K.; Yamada, Y.; Andoh, T. Effects of ketamine and propofol on inflammatory responses of primary glial cell cultures stimulated with lipopolysaccharide. BJA Br. J. Anaesth. 2005, 95, 803–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scragg, J.; Hallsworth, K.; Taylor, G.; Cassidy, S.; Haigh, L.; Boyle, M.; Anstee, Q.; McPherson, S.; Avery, L. Factors associated with engagement and adherence to a low-energy diet to promote 10% weight loss in patients with clinically significant non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2021, 8, e000678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dajani, A.I.; Popovic, B. Essential phospholipids for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease associated with metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. World J. Clin. Cases 2020, 8, 5235–5249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mușat, M.I.; Militaru, F.; Gheorman, V.; Udriștoiu, I.; Mitran, S.I.; Cătălin, B. Moderate Alcohol Consumption Increases the Risk of Clinical Relapse in Male Depressed Patients Treated with Serotonin-Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mușat, M.I.; Militaru, F.; Udriștoiu, I.; Mitran, S.I.; Cătălin, B. Alcohol Consumption Is a Coping Mechanism for Male Patients with Severe Anxiety Disorders Treated with Antidepressants Monotherapy. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mușat, M.I.; Mitran, S.I.; Udriștoiu, I.; Albu, C.V.; Cătălin, B. The impact of stress on the behavior of C57BL/6 mice with liver injury: A comparative study. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2024, 18, 1358964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, S.; Chawla, S.; Kumar, P.; Ahmad, R.; Kumar Verma, P. The chronic unpredictable mild stress (CUMS) Paradigm: Bridging the gap in depression research from bench to bedside. Brain Res. 2024, 1843, 149123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pałucha-Poniewiera, A.; Podkowa, K.; Rafało-Ulińska, A. The group II mGlu receptor antagonist LY341495 induces a rapid antidepressant-like effect and enhances the effect of ketamine in the chronic unpredictable mild stress model of depression in C57BL/6J mice. Prog. Neuropsychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2021, 109, 110239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morega, S.; Gresita, A.; Mitran, S.I.; Musat, M.I.; Boboc, I.K.S.; Gheorman, V.; Udristoiu, I.; Albu, C.V.; Streba, C.T.; Catalin, B.; et al. Cerebrolysin Use in Patients with Liver Damage-A Translational Study. Life 2022, 12, 1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaignier, F.; Legrand-Frossi, C.; Stragier, E.; Mathiot, J.; Merlin, J.-L.; Cohen-Salmon, C.; Lanfumey, L.; Frippiat, J.-P. A Model of Chronic Exposure to Unpredictable Mild Socio-Environmental Stressors Replicates Some Spaceflight-Induced Immunological Changes. Front. Physiol. 2018, 9, 514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Li, A.; Yang, Q.; Li, J.; Zheng, L.; Wang, G.; Sun, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, M.; Song, Z.; et al. Matrine alleviates depressive-like behaviors via modulating microbiota-gut-brain axis in CUMS-induced mice. J. Transl. Med. 2023, 21, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Lei, C.; Tian, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhang, R. Rb1, the Primary Active Ingredient in Panax ginseng C.A. Meyer, Exerts Antidepressant-Like Effects via the BDNF–Trkb–CREB Pathway. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Fu, Q.; Li, Y.; Li, S.; Xue, J.; Ma, S. Emodin opposes chronic unpredictable mild stress induced depressive-like behavior in mice by upregulating the levels of hippocampal glucocorticoid receptor and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. Fitoterapia 2014, 98, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.H.; Lim, Y.; Park, J.B.; Kwak, J.H.; Kim, K.J.; Kim, J.H.; Song, H.; Cho, J.Y.; Hwang, D.Y.; Kim, K.S.; et al. Comparative study of fatty liver induced by methionine and choline-deficiency in C57BL/6N mice originating from three different sources. Lab. Anim. Res. 2017, 33, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, H.H.; Wang, S. Strain differences in the chronic mild stress animal model of depression. Behav. Brain Res. 2010, 213, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, K.; Wei, M.; Zhang, M.; Wang, Z.; Pan, P.; Shaligram, S.S.; Huang, J.; Prado, L.B.D.; Wong, J.; Su, H. Reduction of neuroinflammation alleviated mouse post bone fracture and stroke memory dysfunction. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2021, 41, 2162–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsao, C.H.; Wu, K.Y.; Su, N.C.; Edwards, A.; Huang, G.J. The influence of sex difference on behavior and adult hippocampal neurogenesis in C57BL/6 mice. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 17297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaidanovich-Beilin, O.; Lipina, T.; Vukobradovic, I.; Roder, J.; Woodgett, J. Assessment of Social Interaction Behaviors. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2011, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cătălin, B.; Stopper, L.; Bălşeanu, T.-A.; Scheller, A. The in situ morphology of microglia is highly sensitive to the mode of tissue fixation. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2017, 86, 59–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godeanu, S.; Mușat, M.I.; Scheller, A.; Osiac, E.; Cătălin, B. Minimal differences observed when comparing the morphological profiling of microglia obtained by confocal laser scanning and optical sectioning microscopy. Front. Neuroanat. 2025, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelea, G.; Mușat, M.I.; Mitran, S.I.; Ciorbagiu, M.C.; Cătălin, B. Morphological Differences in Hippocampal Microglia in C57BL/6N Mice with Liver Injury and Depressive-Like Behavior. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2024, 50, 577–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nedelea, G.; Mușat, M.I.; Buican-Chirea, A.C.; Ciorbagiu, M.C.; Cătălin, B. Depressive-Like Behavior and Liver Damage Generate Behavioral and Cortical Microglial Morphological Differences in Mice. Curr. Health Sci. J. 2024, 50, 546–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedelea, G.; Muşat, M.I.; Mitran, S.I.; Ciorbagiu, M.C.; Cătălin, B. Acute liver damage generates age independent microglia morphology changes in mice. Rom. J. Morphol. Embryol. 2024, 65, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mușat, M.I.; Ifrim-Predoi, A.-M.; Mitran, S.I.; Osiac, E.; Cătălin, B. The Behavioral and Neuroinflammatory Impact of Ketamine in a Murine Model of Depression and Liver Damage. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083558
Mușat MI, Ifrim-Predoi A-M, Mitran SI, Osiac E, Cătălin B. The Behavioral and Neuroinflammatory Impact of Ketamine in a Murine Model of Depression and Liver Damage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083558
Chicago/Turabian StyleMușat, Mădălina Iuliana, Ana-Maria Ifrim-Predoi, Smaranda Ioana Mitran, Eugen Osiac, and Bogdan Cătălin. 2025. "The Behavioral and Neuroinflammatory Impact of Ketamine in a Murine Model of Depression and Liver Damage" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083558
APA StyleMușat, M. I., Ifrim-Predoi, A.-M., Mitran, S. I., Osiac, E., & Cătălin, B. (2025). The Behavioral and Neuroinflammatory Impact of Ketamine in a Murine Model of Depression and Liver Damage. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3558. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083558





