Magnetic and MRI Contrast Properties of HumAfFt-SPIONs: Investigating Superparamagnetic Behavior and Enhanced T2-Weighted Imaging Performance
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
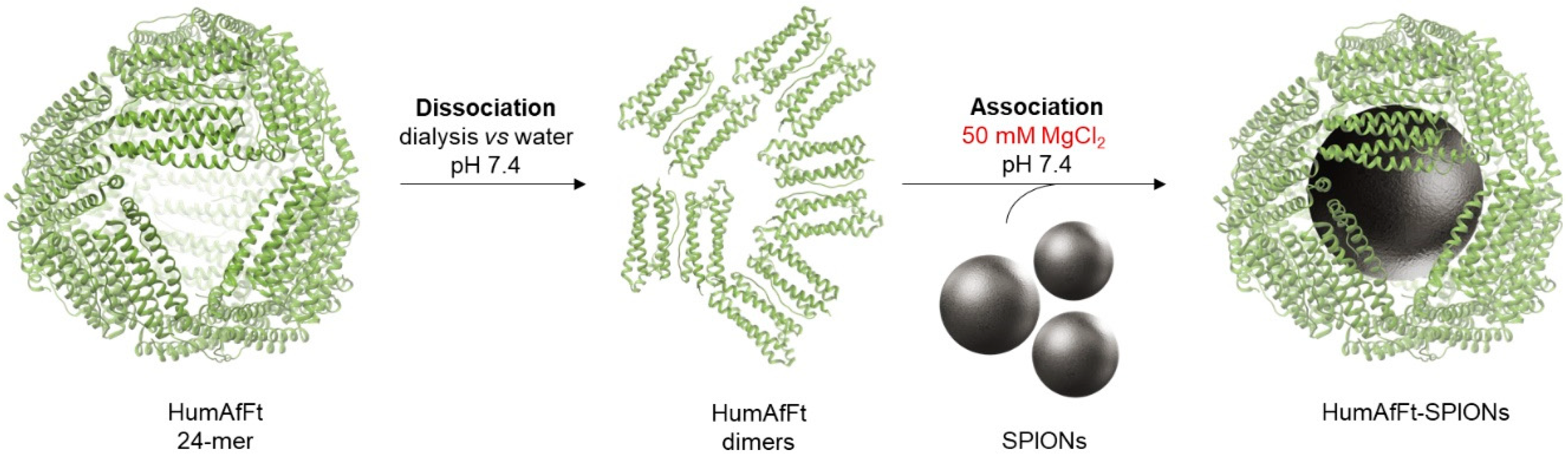
2.1. Preparation of HumaAfFt-SPIONs
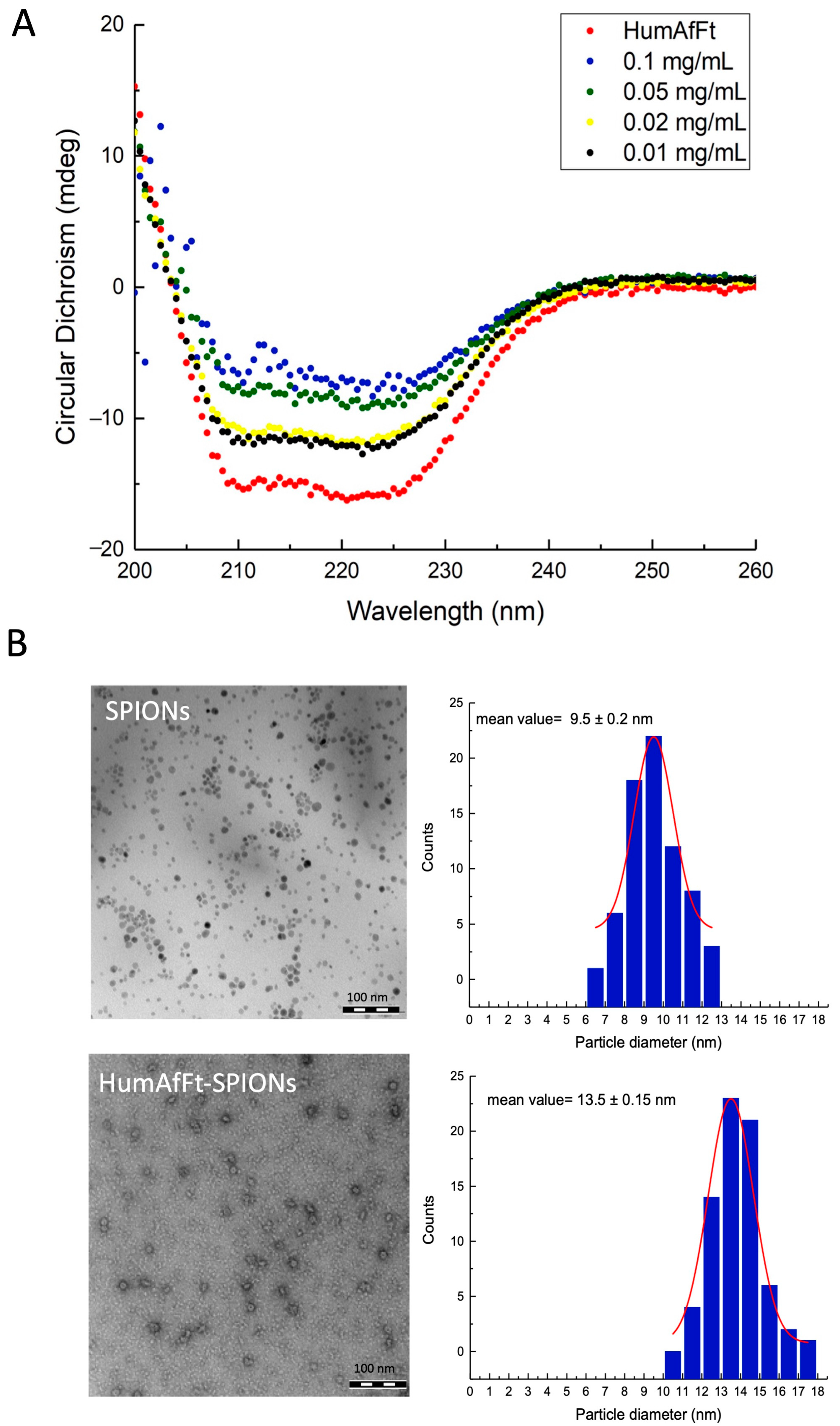
2.2. Characterization of HumAfFt-SPIONs
2.3. Magnetic Properties of HumAfFt-SPIONs
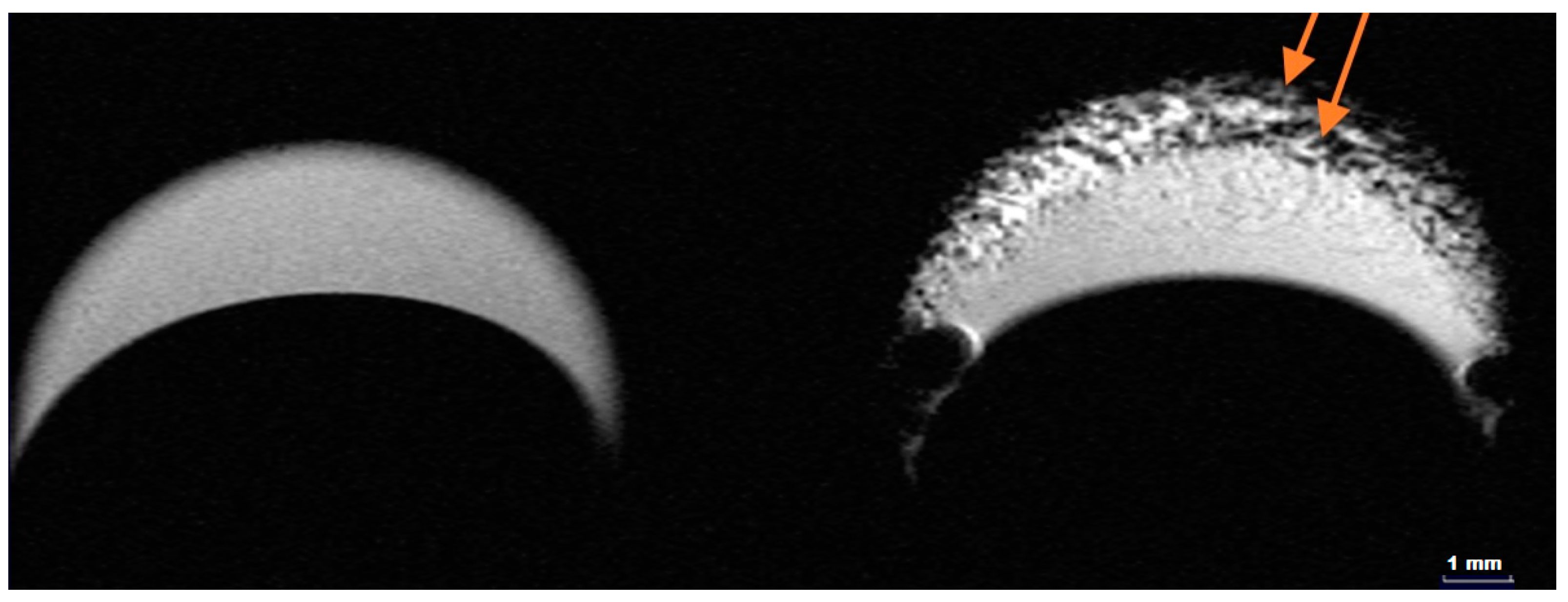
2.4. MRI Contrast Performance of HumAfFt-SPIONs
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Expression and Purification of HumAfFt
3.2. Synthesis of SPIONs Coated with HumAfFt
3.3. Circular Dichroism
3.4. Absorption and Emission Measurements
3.5. Trasmission Electron Microscopy
3.6. Electron Paramagnetic Resonance (EPR)
3.7. Magnetic Characterization
3.8. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) at 7 T
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| SPIONs | Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles |
| MRI | Magnetic resonance imaging |
| HumAfFt | Humanized Archaeoglobus fulgidus ferritin |
| CD | Circular dichroism |
| EPR | Electron paramagnetic resonance |
| ZFC | Zero-field-cooled |
| FC | Field-cooled |
References
- Bioengineering at the nanoscale. Nat. Rev. Bioeng. 2023, 1, 79. [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Saei, A.A.; Behzadi, S.; Panahifar, A.; Mahmoudi, M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for delivery of therapeutic agents: Opportunities and challenges. Expert Opin. Drug Deliv. 2014, 11, 1449–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, L.; Zhou, Z.; Mao, H.; Yang, L. Magnetic nanoparticles for precision oncology: Theranostic magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for image-guided and targeted cancer therapy. Nanomedicine 2017, 12, 73–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hola, K.; Markova, Z.; Zoppellaro, G.; Tucek, J.; Zboril, R. Tailored functionalization of iron oxide nanoparticles for MRI, drug delivery, magnetic separation and immobilization of biosubstances. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1162–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lapusan, R.; Borlan, R.; Focsan, M. Advancing MRI with magnetic nanoparticles: A comprehensive review of translational research and clinical trials. Nanoscale Adv. 2024, 6, 2234–2259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardi, M.; Scialabba, C.; Puleio, R.; Cassata, G.; Cicero, L.; Cavallaro, G.; Giammona, G. Smart copolymer coated SPIONs for colon cancer chemotherapy. Int. J. Pharm. 2019, 556, 57–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayashi, K.; Nakamura, M.; Sakamoto, W.; Yogo, T.; Miki, H.; Ozaki, S.; Abe, M.; Matsumoto, T.; Ishimura, K. Superparamagnetic nanoparticle clusters for cancer theranostics combining magnetic resonance imaging and hyperthermia treatment. Theranostics 2013, 3, 366–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musielak, M.; Piotrowski, I.; Suchorska, W.M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs) as a multifunctional tool in various cancer therapies. Rep. Pract. Oncol. Radiother. 2019, 24, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Estelrich, J.; Escribano, E.; Queralt, J.; Busquets, M.A. Iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetically-guided and magnetically-responsive drug delivery. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 8070–8101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wierzbinski, K.R.; Szymanski, T.; Rozwadowska, N.; Rybka, J.D.; Zimna, A.; Zalewski, T.; Nowicka-Bauer, K.; Malcher, A.; Nowaczyk, M.; Krupinski, M.; et al. Potential use of superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for in vitro and in vivo bioimaging of human myoblasts. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scialabba, C.; Puleio, R.; Peddis, D.; Varvaro, G.; Calandra, P.; Cassata, G.; Cicero, L.; Licciardi, M.; Giammona, G. Folate targeted coated SPIONs as efficient tool for MRI. Nano Res. 2017, 10, 3212–3227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyad, N.; Ahmad, M.S.; Alkhatib, S.G.; Hjouj, M. Gadolinium contrast agents- challenges and opportunities of a multidisciplinary approach: Literature review. Eur. J. Radiol. Open 2023, 11, 100503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Xu, J.; Cui, H. Functional nanoparticles for magnetic resonance imaging. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2016, 8, 814–841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortajarena, A.L.; Ortega, D.; Ocampo, S.M.; Gonzalez-García, A.; Couleaud, P.; Miranda, R.; Belda-Iniesta, C.; Ayuso-Sacido, A. Engineering Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Clinical Settings. Nanobiomedicine 2014, 1, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pucci, C.; Degl’Innocenti, A.; Gümüş, M.B.; Ciofani, G. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for magnetic hyperthermia: Recent advancements, molecular effects, and future directions in the omics era. Biomater. Sci. 2022, 10, 2103–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.N.; Pham, T.H.G.; Nguyen, D.T.; Phan, Q.T.; Le, T.T.H.; Ha, P.T.; Do, H.M.; Hoang, T.M.N.; Nguyen, X.P. Magnetic inductive heating of organs of mouse models treated by copolymer coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Adv. Nat. Sci. Nanosci. Nanotechnol. 2017, 8, 025013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Gupta, M. Synthesis and surface engineering of iron oxide nanoparticles for biomedical applications. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 3995–4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laurent, S.; Forge, D.; Port, M.; Roch, A.; Robic, C.; Elst, L.V.; Muller, R.N. Magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles: Synthesis, stabilization, vectorization, physicochemical characterizations and biological applications. Chem. Rev. 2008, 108, 2064–2110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallakpour, S.; Madani, M. A review of current coupling agents for modification of metal oxide nanoparticles. Prog. Org. Coat. 2015, 86, 194–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.K.; Naregalkar, R.R.; Vaidya, V.D.; Gupta, M. Recent advances on surface engineering of magnetic iron oxide nanoparticles and their biomedical applications. Nanomedicine 2007, 2, 23–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, D.; Lee, N.; Hyeon, T. Chemical synthesis and assembly of uniformly sized iron oxide nanoparticles for medical applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2015, 48, 1276–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Craparo, E.F.; Pitarresi, G.; Bondi, M.L.; Casaletto, M.P.; Licciardi, M.; Giammona, G. A nanoparticulate drug-delivery system for rivastigmine: Physico-chemical and in vitro biological characterization. Macromol. Biosci. 2008, 8, 247–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, K.; Gao, L.; Yan, X. Human ferritin for tumor detection and therapy. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2013, 5, 287–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebrahimi, K.H.; Bill, E.; Hagedoorn, P.L.; Hagen, W.R. The catalytic center of ferritin regulates iron storage via Fe(II)-Fe(III) displacement. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2012, 8, 941–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arosio, P.; Elia, L.; Poli, M. Ferritin, cellular iron storage and regulation. IUBMB Life 2017, 69, 414–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, A.; Parida, A.; Raut, R.K.; Behera, R.K. Ferritin: A Promising Nanoreactor and Nanocarrier for Bionanotechnology. ACS Bio Med Chem Au 2022, 2, 258–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tesarova, B.; Musilek, K.; Rex, S.; Heger, Z. Taking advantage of cellular uptake of ferritin nanocages for targeted drug delivery. J. Control. Release 2020, 325, 176–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudarev, V.V.; Dolotova, S.M.; Bukhalovich, S.M.; Bazhenov, S.V.; Ryzhykau, Y.L.; Uversky, V.N.; Bondarev, N.A.; Osipov, S.D.; Mikhailov, A.E.; Kuklina, D.D.; et al. Ferritin self-assembly, structure, function, and biotechnological applications. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 224, 319–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rother, M.; Nussbaumer, M.G.; Renggli, K.; Bruns, N. Protein cages and synthetic polymers: A fruitful symbiosis for drug delivery applications, bionanotechnology and materials science. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016, 45, 6213–6249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, X.; Liu, Y.; Zang, J.; Zhang, T.; Zhao, G. Hyperthermostability of prawn ferritin nanocage facilitates its application as a robust nanovehicle for nutraceuticals. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2021, 191, 152–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, W.; Li, H.; Ning, J.; Huang, S.; Jiang, L.; Xu, P.; Huang, M.; Yuan, C. Engineered protein cages with enhanced extracellular drug release for elevated antitumor efficacy. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2024, 267, 131492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habashy, H.O.; Powe, D.G.; Staka, C.M.; Rakha, E.A.; Ball, G.; Green, A.R.; Aleskandarany, M.; Paish, E.C.; MacMillan, R.D.; Nicholson, R.I.; et al. Transferrin receptor (CD71) is a marker of poor prognosis in breast cancer and can predict response to tamoxifen. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2010, 119, 283–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Fang, C.J.; Ryan, J.C.; Niemi, E.C.; Lebrón, J.A.; Björkman, P.J.; Arase, H.; Torti, F.M.; Torti, S.V.; Nakamura, M.C.; et al. Binding and uptake of H-ferritin are mediated by human transferrin receptor-1. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 3505–3510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansen, F.J.; Mittelstädt, A.; Clausen, F.N.; Knoedler, S.; Knoedler, L.; Klöckner, S.; Kuchenreuther, I.; Mazurie, J.; Arnold, L.S.; Anthuber, A.; et al. CD71 expressing circulating neutrophils serve as a novel prognostic biomarker for metastatic spread and reduced outcome in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma patients. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launay, P. 11P Preclinical evaluation of an anti-transferrin receptor antibody drug conjugate targeting triple-negative breast cancer. ESMO Open 2025, 10, 104167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falvo, E.; Damiani, V.; Conti, G.; Boschi, F.; Messana, K.; Giacomini, P.; Milella, M.; De Laurenzi, V.; Morea, V.; Sala, G.; et al. High activity and low toxicity of a novel CD71-targeting nanotherapeutic named The-0504 on preclinical models of several human aggressive tumors. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 40, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tortorella, S.; Karagiannis, T.C. Transferrin receptor-mediated endocytosis: A useful target for cancer therapy. J. Membr. Biol. 2014, 247, 291–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.; Cascio, D.; Sawaya, M.R.; Gingery, M.; Schröder, I. Crystal structures of a tetrahedral open pore ferritin from the hyperthermophilic Archaeon Archaeoglobus fulgidus. Structure 2005, 13, 637–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calisti, L.; Benni, I.; Trabuco, M.C.; Baiocco, P.; Ruzicka, B.; Boffi, A.; Falvo, E.; Malatesta, F.; Bonamore, A. Probing bulky ligand entry in engineered archaeal ferritins. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2017, 1861, 450–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Rho, Y.; Jin, K.S.; Ahn, B.; Jung, S.; Kim, H.; Ree, M. PH-dependent structures of ferritin and apoferritin in solution: Disassembly and reassembly. Biomacromolecules 2011, 12, 1629–1640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Turris, V.; Trabuco, M.C.; Peruzzi, G.; Boffi, A.; Testi, C.; Vallone, B.; Montemiglio, L.C.; Georges, A.D.; Calisti, L.; Benni, I.; et al. Humanized archaeal ferritin as a tool for cell targeted delivery. Nanoscale 2017, 9, 647–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Incocciati, A.; Bertuccini, L.; Boffi, A.; Macone, A.; Bonamore, A. Unlocking the Treasure Box: The Role of HEPES Buffer in Disassembling an Uncommon Ferritin Nanoparticle. Separations 2022, 9, 222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macone, A.; Masciarelli, S.; Palombarini, F.; Quaglio, D.; Boffi, A.; Trabuco, M.C.; Baiocco, P.; Fazi, F.; Bonamore, A. Ferritin nanovehicle for targeted delivery of cytochrome C to cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 11749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palombarini, F.; Masciarelli, S.; Incocciati, A.; Liccardo, F.; Di Fabio, E.; Iazzetti, A.; Fabrizi, G.; Fazi, F.; Macone, A.; Bonamore, A.; et al. Self-assembling ferritin-dendrimer nanoparticles for targeted delivery of nucleic acids to myeloid leukemia cells. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2021, 19, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Affatigato, L.; Licciardi, M.; Bonamore, A.; Martorana, A.; Incocciati, A.; Boffi, A.; Militello, V. Ferritin-Coated SPIONs as New Cancer Cell Targeted Magnetic Nanocarrier. Molecules 2023, 28, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, W.; Liu, X.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, D.; Li, J.; Ji, L.; Hua, Z. Expression, purification, and characterization of recombinant human L-chain ferritin. Protein Expr. Purif. 2016, 119, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miles, A.J.; Janes, R.W.; Wallace, B.A. Tools and methods for circular dichroism spectroscopy of proteins: A tutorial review. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 8400–8413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Song, W.; Wang, J.; Yan, Y.; Chen, J.; Liu, R. Mechanism of Dimercaptosuccinic Acid Coated Superparamagnetic Iron Oxide Nanoparticles with Human Serum Albumin. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2015, 29, 579–586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vetri, V.; D’Amico, M.; Foderà, V.; Leone, M.; Ponzoni, A.; Sberveglieri, G.; Militello, V. Bovine Serum Albumin protofibril-like aggregates formation: Solo but not simple mechanism. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2011, 508, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incocciati, A.; Kubeš, J.; Piacentini, R.; Cappelletti, C.; Botta, S.; Bertuccini, L.; Šimůnek, T.; Boffi, A.; Macone, A.; Bonamore, A. Hydrophobicity-enhanced ferritin nanoparticles for efficient encapsulation and targeted delivery of hydrophobic drugs to tumor cells. Protein Sci. 2023, 32, e4819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, C.; Liu, X.; Hu, H.; Li, H.; Yu, L.; Geng, D.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, J. Dual-targeting and excretable ultrasmall SPIONs for: T 1-weighted positive MR imaging of intracranial glioblastoma cells by targeting the lipoprotein receptor-related protein. J. Mater. Chem. B 2020, 8, 2296–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Köseoǧlu, Y. Effect of surfactant coating on magnetic properties of Fe3O4 nanoparticles: ESR study. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 2006, 300, e327–e330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licciardi, M.; Scialabba, C.; Cavallaro, G.; Sangregorio, C.; Fantechi, E.; Giammona, G. Cell uptake enhancement of folate targeted polymer coated magnetic nanoparticles. J. Biomed. Nanotechnol. 2013, 9, 949–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Yang, J.; Xu, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wang, Z.; Shi, X.; Zhang, G. Facile Synthesis of Folic Acid-Modified Iron Oxide Nanoparticles for Targeted MR Imaging in Pulmonary Tumor Xenografts. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2016, 18, 569–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi, S.; Seyednejad, H.; Laurent, S.; Atyabi, F.; Saei, A.A.; Mahmoudi, M. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles for in vivo molecular and cellular imaging. Contrast Media Mol. Imaging 2015, 10, 329–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palombarini, F.; Ghirga, F.; Boffi, A.; Macone, A.; Bonamore, A. Application of crossflow ultrafiltration for scaling up the purification of a recombinant ferritin. Protein Expr. Purif. 2019, 163, 105451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, J.; Semelka, R.C.; Ramalho, M.; Nunes, R.H.; AlObaidy, M.; Castillo, M. Gadolinium-based contrast agent accumulation and toxicity: An update. Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hasebroock, K.M.; Serkova, N.J. Toxicity of MRI and CT contrast agents. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2009, 5, 403–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macone, A.; Cappelletti, C.; Incocciati, A.; Piacentini, R.; Botta, S.; Boffi, A.; Bonamore, A. Challenges in Exploiting Human H Ferritin Nanoparticles for Drug Delivery: Navigating Physiological Constraints. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2024, 16, e2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, B.T.T.; Colvin, E.K.; Pham, N.T.H.; Kim, B.J.; Fuller, E.S.; Moon, E.A.; Barbey, R.; Yuen, S.; Rickman, B.H.; Bryce, N.S.; et al. Biodistribution and clearance of stable superparamagnetic maghemite iron oxide nanoparticles in mice following intraperitoneal administration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaltbeitzel, J.; Wich, P.R. Protein-based Nanoparticles: From Drug Delivery to Imaging, Nanocatalysis and Protein Therapy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2023, 62, e202216097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikitin, A.A.; Ivanova, A.V.; Semkina, A.S.; Lazareva, P.A.; Abakumov, M.A. Magneto-Mechanical Approach in Biomedicine: Benefits, Challenges, and Future Perspectives. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 11134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akhatova, F.; Konnova, S.; Kryuchkova, M.; Batasheva, S.; Mazurova, K.; Vikulina, A.; Volodkin, D.; Rozhina, E. Comparative Characterization of Iron and Silver Nanoparticles: Extract-Stabilized and Classical Synthesis Methods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 9274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Affatigato, L.; Licciardi, M.; D’Oca, M.C.; Cicero, L.; Bonamore, A.; Incocciati, A.; Macone, A.; Buch, C.D.; Piligkos, S.; Boffi, A.; et al. Magnetic and MRI Contrast Properties of HumAfFt-SPIONs: Investigating Superparamagnetic Behavior and Enhanced T2-Weighted Imaging Performance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083505
Affatigato L, Licciardi M, D’Oca MC, Cicero L, Bonamore A, Incocciati A, Macone A, Buch CD, Piligkos S, Boffi A, et al. Magnetic and MRI Contrast Properties of HumAfFt-SPIONs: Investigating Superparamagnetic Behavior and Enhanced T2-Weighted Imaging Performance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083505
Chicago/Turabian StyleAffatigato, Luisa, Mariano Licciardi, Maria Cristina D’Oca, Luca Cicero, Alessandra Bonamore, Alessio Incocciati, Alberto Macone, Christian Dirk Buch, Stergios Piligkos, Alberto Boffi, and et al. 2025. "Magnetic and MRI Contrast Properties of HumAfFt-SPIONs: Investigating Superparamagnetic Behavior and Enhanced T2-Weighted Imaging Performance" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083505
APA StyleAffatigato, L., Licciardi, M., D’Oca, M. C., Cicero, L., Bonamore, A., Incocciati, A., Macone, A., Buch, C. D., Piligkos, S., Boffi, A., & Militello, V. (2025). Magnetic and MRI Contrast Properties of HumAfFt-SPIONs: Investigating Superparamagnetic Behavior and Enhanced T2-Weighted Imaging Performance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3505. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083505








