Physalis peruwiana Fruits and Their Food Products as New Important Components of Functional Foods
Abstract
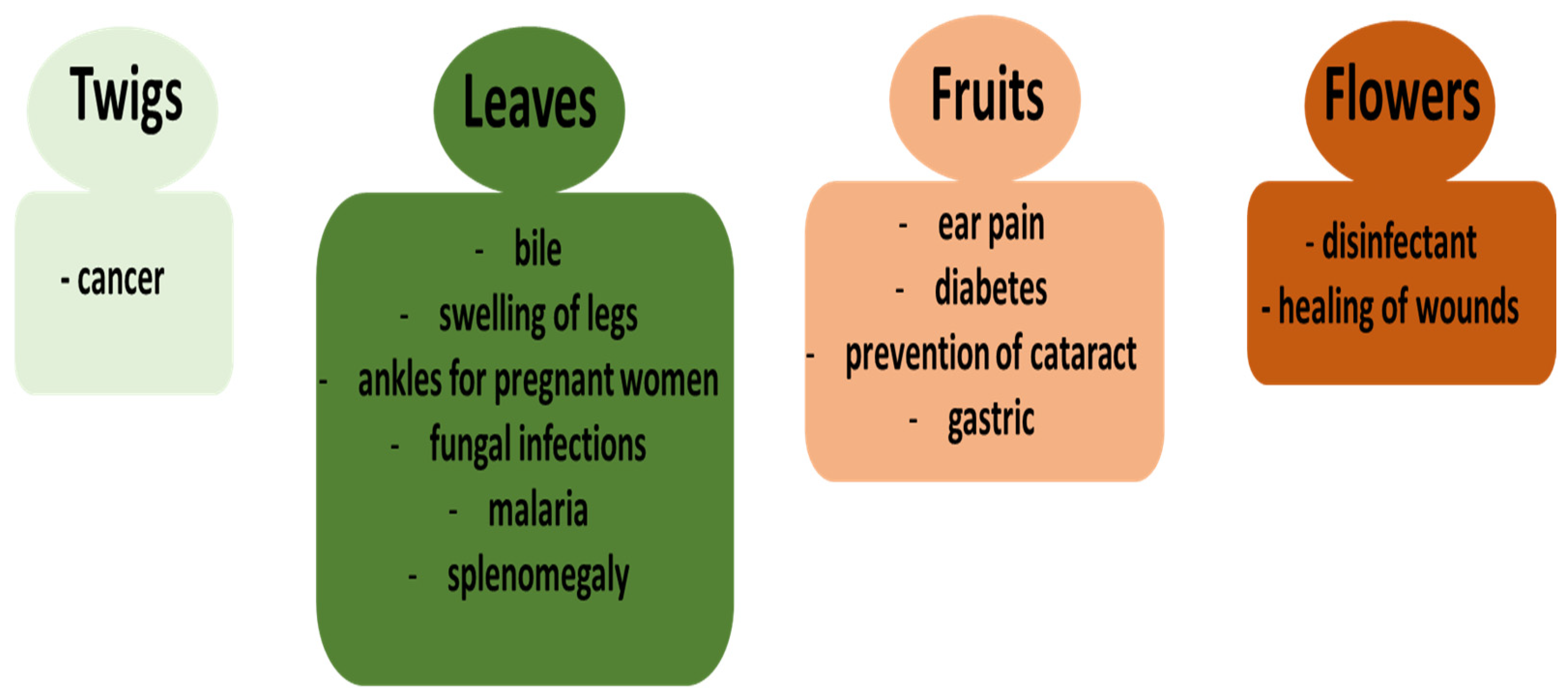
1. Introduction
2. Research Methods
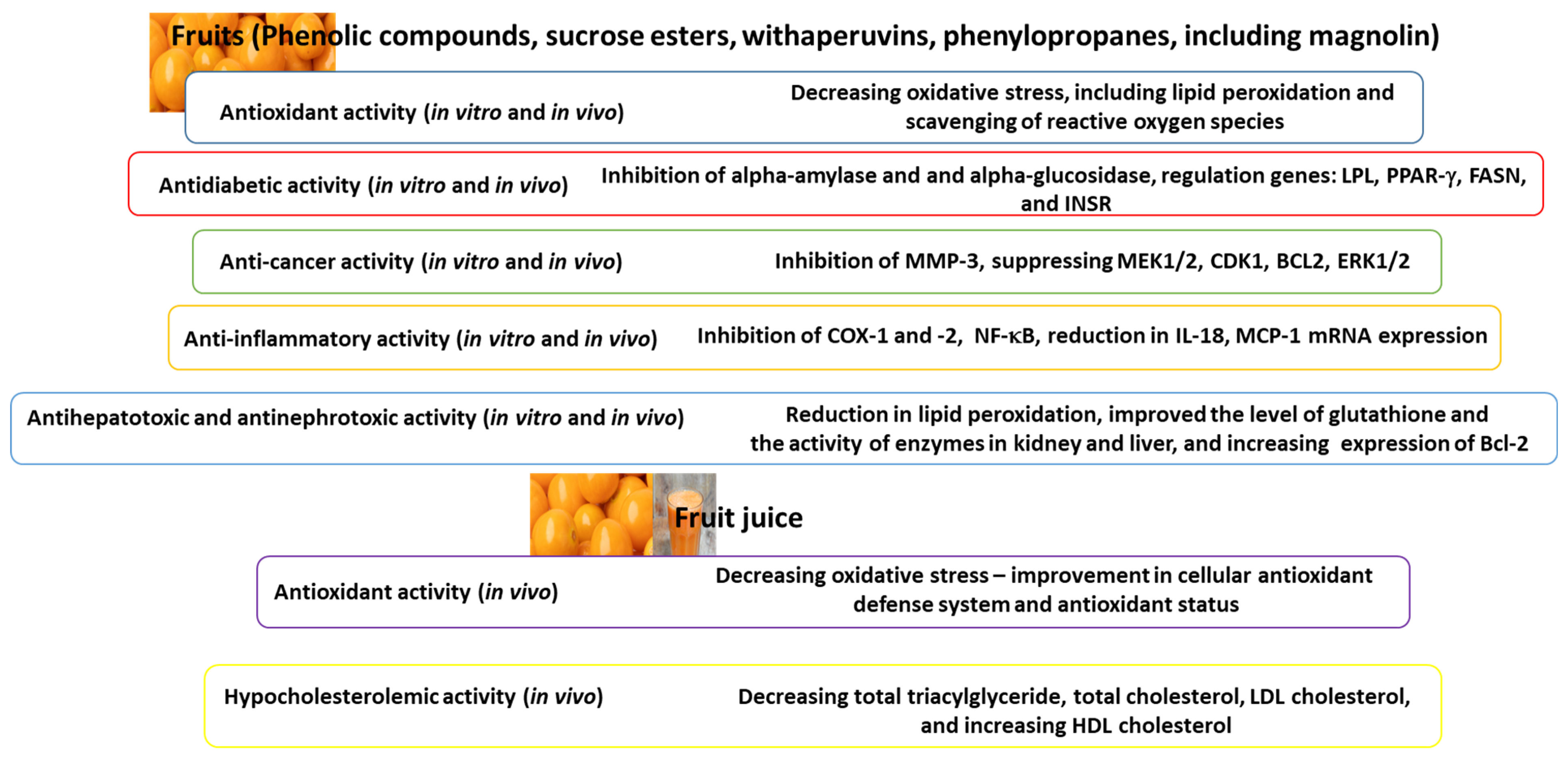
2.1. Bioactive Compounds of Fruits and Their Biological Activity
2.2. Antioxidant Activity (In Vitro and In Vivo)
2.3. Antidiabetic Activity (In Vitro and In Vivo)
2.4. Anti-Cancer Activity (In Vitro and In Vivo)
2.5. Anti-Inflammatory Activity (In Vitro and In Vivo)
2.6. Antihepatotoxic, Antinephrotoxicity, and Other Activities (In Vivo)
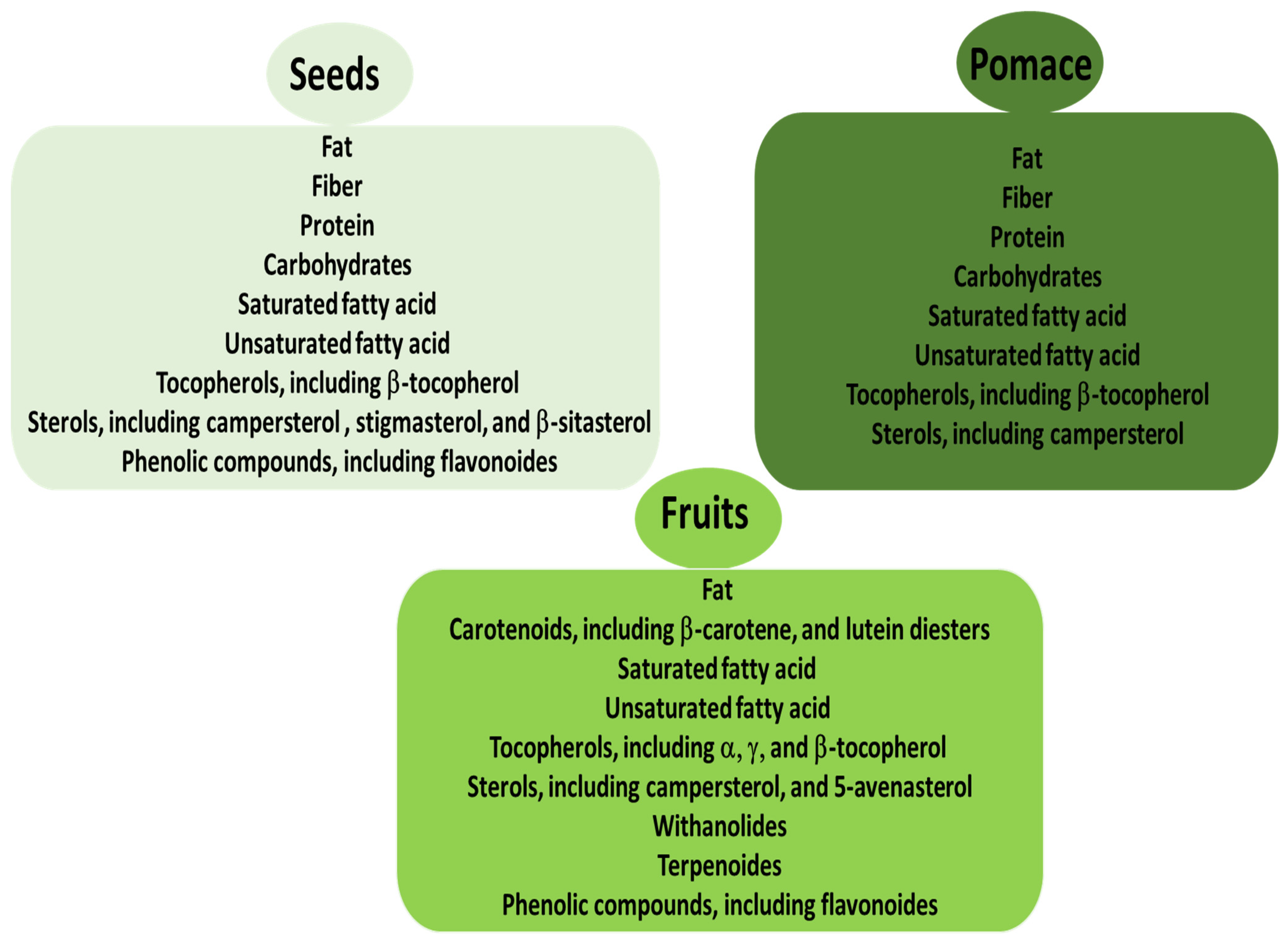
3. Bioactive Compounds of Seeds and Their Biological Activity
4. Bioactive Compounds of Pomace and Its Biological Activity
5. Toxicity and Adverse Effects of P. peruviana Fruits and Their Food Products
6. Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Olivares-Tenorio, M.L.; Dekker, M.; van Boekel, A.J.S.; Verkerk, R. Evaluating the effect of storage conditions on the shelf life of cape gooseberry (Phylasis peruviana L.). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2017, 80, 523–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mokhtar, S.; Swailam, H.; Embaby, H. Physicochemical properties, nutritional value and techno-functional properties of goldenberry (Physalis peruviana) waste powder. Food Chem. 2018, 248, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaillant, F.; Corrales-Agudelo, V.; Moreno-Castellanos, N.; Angel-Martin, A.; Henao-Rojas, J.C.; Munoz-Durango, K.; Poucheret, P. Plasma metabolome profiling by high-performance chemical isotope-labelling LC-MS after acute and medium-term intervention with golden berry fruit (Phylasis peruviana L.), confirming its impact on insulin-associated signaling pathways. Nutrients 2021, 13, 3125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasali, F.M.; Tuyiringire, N.; Peter, E.L.; Ahovegbe, L.Y.; Ali, M.S.; Tusiimire, J.; Ogwang, P.E.; Kadima, J.N.; Agaba, G. Chemical constituents and evidence-based pharmacological properties of Phylasis peruviana L.: An overview. J. Herb. Pharm. 2022, 11, 5–47. [Google Scholar]
- Aminah, N.S.; Tun, K.N.W.; Kristanti, A.N.; Aung, H.T.; Takaya, Y.; Choudhary, M.I. Chemical constituents and their biological activities from Taunggayi (Shan state) medicinal plants. Heliyon 2021, 7, e06173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, M.; He, J.X.; Hu, H.X.; Zhang, K.; Wang, X.N.; Zhao, B.B. Withanolides from the genus Physalis: A review on their phytochemical and pharmacological aspects. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2020, 72, 649–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nocetti, D.; Nunez, H.; Puente, L.; Espinosa, A.; Romero, F. Composition and biological effects of goldenberry byproducts: An overview. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2020, 100, 4335–4346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasali, F.M.; Tusiimire, J.; Kadima, J.N.; Tolo, C.U.; Weisheit, A.; Agaba, A.G. Ethnotherapeutic uses and phytochemical composition of Phylasis peruviana L.: An overview. Sci. World J. 2021, 1, 5212348. [Google Scholar]
- Yano, A.; Yuki, S.; Shiraishi, A.; Hakozaki, M.; Kanno, Y.; Kimura, K.I.; Uesugi, S. Golden berry leaf extract containing withanolides suppresses TNF-α and IL-17 induced IL-6 expression in HeLa cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2023, 87, 972–980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, P.V.; Trang, V.T.; Lien, L.Q.; Hoan, V.H.; Ngoc, T.M.; Tuan, D.T.; Hien, D.T.T.; Hieu, N.V.; Duc, N.V.; Anh, H.L.T. Withaperuvin O, a new withanolide from Physalis peruviana L. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 1, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Duggal, S.; Singh, H.; Singh, J.; Katekhaye, S. Withanolides: Phytoconstituents with significant pharmacological activities. Int. J. Green. Pharm. 2010, 4, 229–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, L.C.; Sang-ngern, M.; Pezzuto, J.M. Poha berry (Physalis peruviana) with potential anti-inflammatory and cancer prevention activities. Hawaii. J. Med. Public Health 2016, 75, 353–359. [Google Scholar]
- Navarro-Hoyos, M.; Arnaez-Serrano, E.; Quiros-Fallas, M.I.; Vargas-Huertas, F.; Wilhelm-Romero, K.; Vasquez-Castro, F.; Alvarado-Corella, D.; Sanchez-Kopper, A. QTOF-ESI MS characterization and antioxidant activity of Phylasis peruviana L. (cope gooseberry) husks and fruits from Costa Rica. Molecules 2022, 27, 4238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Althubyani, M.A.; Alrefaei, A.F. Protective and therapeutic effects of medicinal plants against food additive-induced toxicity. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2024, 27, 439–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breithaupt, D.E.; Wirt, U.; Bamadi, A. Differentiation between lutein monoester regioisomers and detection of lutein diesters from marigold flowers (Tagetes erecta L.) and several fruits by liquid chromatography—Mass spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2002, 50, 66–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.F.; Jo, J.; Morsel, J.T.; Morsel, M. Oil goldenberry (Phylasis peruviana L.). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2003, 51, 969–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Etzbach, L.; Pfeiffer, A.; Weber, F.; Schieber, A. Characterization of carotenoid profiles in goldenberry (Phylasis peruviana L.) fruits at various ripening stages and in different plant tissues by HPLC-DAD-APCI-MSn. Food Chem. 2018, 245, 508–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Llano, S.M.; Munoz-Jimenez, A.M.; Jimenez-Cartagena, C.; Londono-Londono, J.; Medina, S. Untargeted metabolomics reveals specific withanolides and fatty acyl glycoside as tentative metabolites to differentiate organic and conventional Physalis peruviana fruits. Food Chem. 2017, 244, 120–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotz, A.; Spangenberg, B. New and sensitive TLC method to measure trans-resveratrol in Phylasis peruviana. J. Liq. Chromatogr. Relat. Technol. 2016, 39, 308–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horn, R.C.; Soares, J.C.; Mori, N.C.; Gelatti, G.T.; Manfiro, C.E.; Golle, D.P.; KOefender, J.; Deuschle, R.A.; Oliveira, C. Antioxidant effect of Phylasis peruviana fruit aqueous extract—The antioxidant effect of Phylasis. J. Agric. Sci. 2015, 7, 137–143. [Google Scholar]
- Hassan, H.A.; Ghareb, N.E.; Azhari, G.F. Antioxidant activity and free radical-scavenging of cape gooseberry (Phylasis peruviana L.) in hepatocellular carcinoma rats model. Hepatoma Res. 2017, 3, 27–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dewi, L.; Sulchan, M.; Kisdjamiatun. Potency of cape gooseberry (Phylasis peruviana) juice in improving antioxidant and adiponectin level of high fat diet streptozotocin rat model. Rom. J. Diabetes Nutr. Metab. Dis. 2018, 25, 253–260. [Google Scholar]
- Eken, A.; Unlu-Endirlik, B.; Baldemir, A.; Ilgun, S.; Soykut, B.; Erdem, O. Antioxidant capacity and metal content of Phylasis peruviana L. fruit sold in markets. J. Clin. Anal. Med. 2016, 7, 291–294. [Google Scholar]
- Guine, R.P.F.; Goncalves, F.J.A.; Oliveira, S.F.; Correia, P.M.R. Evaluation of phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity and bioaccessibility in Phylasis peruviana L. Int. J. Fruit Sci. 2020, 20, S470–S490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pino-de la Fuente, F.; Nocetti, D.; Sacristan, C.; Ruiz, P.; Guerrero, J.; Jorquera, G.; Uribe, E.; Bucarey, J.L.; Espinosa, A.; Puente, L. Phylasis peruviana L. pulp prevents liver inflammation and insulin resistance in skeletal muscles of diet0induced obese mice. Nutrients 2020, 12, 700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathyadevi, M.; Suchithra, E.R.; Subramanian, S. Phylasis peruviana Linn. Fruit extract improves insulin sensitivity and ameliorates hyperglycemia in high-fat diet low dose STZ-induced type 2 diabetic rats. J. Pharm. Res. 2014, 8, 625–632. [Google Scholar]
- Rey, D.P.; Ospina, L.F.; Aragon, D.M. Inhibitory effects of an extract of fruits of Phylasis peruviana on some intestinal carbohydrates. Rev. Colomb. Cienc. Quim. Farm. 2015, 44, 72–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodriguez Ulloa, S.L.; Rodriguez Ulloa, E.M. Effect of Phylasis peruviana (goldenberry) on postprandial glycemia in young adults. Rev. Med. Vallejiana 2007, 4, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Angel-Martin, A.; Vaillant, F.; Moreno-Castellanos, N. Daily consumption of golden berry (Phylasis peruviana) has been shown to halt the progression of insulin resistance and obesity in obese rats with metabolic syndrome. Nutrients 2024, 16, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez-Buenrostro, N.; Perez-Ramirez, I.F.; Mora, O.; Rios-Lozano, A.; Vazquez-Barrios, M.E.; Reynoso-Camacho, R.; Figueroa-Perez, M.G. Effect of saline stress on the metabolic profile and antidiabetic potential of Phylasis peruviana. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 1, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernal, C.A.; Castellanos, L.; Aragon, D.M.; Martinez-Matamoros, D.; Jimenez, C.; Baena, Y.; Ramos, F.A. Peruvioses A to F, sucrose esters from the exudate of Physalis peruviana fruit as α-amylase inhibitors. Carbohydr. Res. 2018, 461, 4–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, V.P.; Dubey, A.; Al-Shehr, M.; Tripathi, I.P. Exploration of human pancreatic alpha-amylase inhibitors from Phylasis peruviana for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 1031–1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.J.; Ng, L.T.; Chen, C.H.; Lin, D.L.; Wang, S.S.; Lin, C.C. Antihepatoma activity of Physalis angulate and P. peruviana extracts and their effects on apoptosis in human Hep G2 cells. Life Sci. 2004, 74, 2026–2073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Kenawy, A.E.; Elshama, S.S.; Osman, H.H. Effects of Physalis peruviana L. on toxicity and lung cancer induction by nicotine derived nitrosamine ketone in rats. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 2015, 16, 5863–5868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Beltagi, H.S.; Mohamed, H.I.; Safwat, G.; Gamal, M.; Megahed, B.M.H. Chemical composition and biological activity of Physalis peruviana, L. Gesunde Pflanz. 2019, 71, 113–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, S.; Huang, K.; Shi, L.; Zhang, Q. Magnolin inhibits proliferation and invasion of breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by targeting the ERK1/2 signaling pathway. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2020, 68, 421–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M.M.; El-Ghorab, A.H.; Ghanem, K.Z. Volatile compounds, antioxidants, and anticancer activities of cape gooseberry fruit (Phylasis peruviana L.): An in vitro study. J. Arab. Soc. Med. Res. 2015, 10, 56–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mier-Giraldo, H.; Diaz-Barrera, L.E.; Delgado-Murcia, L.G.; Valero-Valdivieso, M.F.; Caez-Ramirez, G. Cytotoxic and immunomodulatory potential of Phylasis peruviana fruit extracts on cervical cancer (HeLa) and fibroblast (L929) cell. J. Evid. Based Complement. Alter. Med. 2017, 22, 777–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serag, H.M.; Hassan, H.A.; Qadir, M.S. Efficiency of cape gooseberry in attenuating some biochemical disorders and oxidative stress associated with hepatocellular carcinoma. Wulfenia 2015, 22, 62–89. [Google Scholar]
- Sayed, A.; El-Hawary, S.S.; Abdelmohsen, U.R.; Gharreb, M.A. Antiproliferative potential of Physalis peruviana—Derived magnolin against pancreatic cancer: A comprehensive in vitro and in silico study. Food Funct. 2022, 13, 11733–11743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.J.; Lee, M.H.; Yoo, S.M.; Choi, K.I.; Song, J.H.; Jang, J.H.; Oh, S.R.; Ryu, H.W.; Lee, H.S.; Surh, Y.J.; et al. Magnolin inhibits cell migration and invasion by targeting the ERKs/RSK2 signaling pathway. BMC Cancer 2015, 15, 576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.H.; Lee, C.J.; An, H.J.; Yoo, S.M.; Kang, H.C.; Lee, J.Y.; Kim, K.D.; Kim, D.J.; Lee, H.S.; Ch, Y.Y. Magnolin targeting of ERK1/2 inhibits cell proliferation and colony growth by induction of cellular senescence in ovarian cancer cells. Mol. Carcinog. 2019, 58, 88–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, N.; Chung, G.; Son, S.R.; Park, J.H.; Lee, Y.H.; Park, K.T.; Cho, I.H.; Jang, D.S.; Kim, S.K. Magnolin inhibits paclitaxel-induced cold allodynia and ERK1/2 activation in mice. Plats 2023, 12, 2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moya, D.; Mirada, K.; Rivera, M.; Arredondo, M. Effects of an extract of Phylasis peruviana Linnaeus on the expression of inflammatory markers in the Caco-2 intestinal epithelium-like cell line. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2024, 27, 156–165. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed, R.S.; Ibrahim, F.M.; El-Akad, R.H.; Al-Mokaddem, A.K.; Ahmed, K.A.; Ashour, W.E.-S.; Attia, H.N. Antiarthritic activity of Phylasis peruviana fruit extract via inhibition of inflammatory mediators: Integrated in vitro, in vivo and in silico study. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 321, 117502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pardo, J.M.; Fontanilla, M.R.; Ospina, L.F.; Espinosa, L. Determining the pharmacological activity of Phylasis peruviana juice on rabbit eyes and fibroblast primary cultures. Invest. Ophtalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 3074–3079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Natania, F.; Iriwati, I.; Ayuningtyas, F.D.; Barlian, A. Potential of plant-derived exosome-like nanoparticles from Phylasis peruviana fruit for human dermal fibroblast regeneration and remodeling. Pharm. Nanotechnol. 2025, 13, 358–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanessa, V.; Rachmawati, H.; Barlian, A. Anti-inflammatory potential of goldenberry-derived exosome-like nanoparticles in macrophage polarization. Future Aci. OA 2024, 10, FSO943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aboulthana, W.M.; Omar, N.I.; El-Faky, A.M.; Hassan, A.K.; Hasna, E.A.; Seif, M.; Youssef, A.M. Phyto- and biochemical study on cape gooseberry (Phylasis peruviana L.) extract incorporated with metal nanoparticles against hepatic injury induced in rats. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 1, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sang-ngern, M.; Youn, U.J.; Park, E.J.; Kondratyuk, T.P.; Simmons, C.J.; Wall, M.M.; Ruf, M.; Lorch, S.E.; Leong, E.; Pezzuto, J.M.; et al. Withanolides derived from Physalis peruviana (Poha) with potential anti-inflammatory activity. Bioorg Med. Chem. Lett. 2016, 26, 2755–2759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dkhil, M.A.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Diab, M.M.; Othman, M.S.; Aref, A.M.; Abdel Moneim, A.E. The potential protective role of Phylasis peruviana L. fruit in cadmium-induced hepatotoxicity and nephrotoxicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2014, 74, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taj, D.; Khan, H.; Sultana, V.; Ara, J.; Ehteshamul-Haque, S. Antihepatotoxic effect of golden berry (Phylasis peruviana Linn.) in carbon tetrachloride (CCl4) intoxicated rats. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 27, 491–494. [Google Scholar]
- Arun, M.; Asham, V.V. Preliminary studies on antihepatotoxic effect of Phylasis peruviana Linn. (Solanaceae) against carbon tetrachloride induced acute liver injury in rats. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2007, 111, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Moneim, A.E. Prevention of carbon tetrachloride (CCl4)-induced toxicity in testes of rats treated with Phylasis peruviana L. fruit. Toxicol. Ind. Health 2016, 32, 1064–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramadan, M.F.; Hassan, N.A.; Elsanhoty, R.M.; Sitohy, M.Z. Goldenberry (Phylasis peruviana) juice rich in health-beneficial compounds suppresses high-cholesterol diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in rats. J. Food Biochem. 2013, 37, 708–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ocampo, Y.C.; Castro, J.P.; Pajaro, I.B.; Caro, D.; Talero, E.; Motilva, V.; Franco, L.A. Protective effect of sucrose esters from cape gooseberry (Phylasis peruviana L.) in TNBS-induced colitis. PloS ONE 2024, 19, e0299687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- More, G.P.D.; Rey, D.P.; Valderrama, I.H.; Ospina, L.F.; Aragon, D.M. Rutin and Phylasis peruviana extract: Population pharmacokinetics in New Zealand rabbits. Pharamaceutics 2024, 16, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiran, U.; Prajapati, T. Study of fatty acid composition of fruit seed oils. Int. Acad. Res. Dev. 2017, 2, 36–40. [Google Scholar]
- Cardona, M.; Toro, R.; Costa, G.; Ospina, L.; Castellanos, L.; Ramos, F.; Aragon, D.M. Influence of extraction process on antioxidant activity and rutin content in Phylasis peruviana calyces extract. J. Appl. Pharm. 2017, 7, 164–168. [Google Scholar]
- Erturk, O.; Ayvaz, M.; Can, Z.; Karaman, U.; Korkmaz, K. Antioxidant, antimicrobial activities and phenolic and chemical contents of Physalis peruviana L. from Trabzon, Turkey. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. 2017, 51, s213–s216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharmila, S.; Kalaichelvi, K.; Rajeswari, M.; Anjanadevi, N. Studies on the folklore medicinal uses of some indigenous the tribes of Thiashola, Manjoor, Nilgiris south division, Western ghats. Int. Plant Anim. Environ. Sci. 2014, 4, 14–22. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajaiah, S.; Prakash, J. Chemical composition and bioactivity of pomace from selected fruits. Int. J. Fruit. Sci. 2016, 16, 423–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, M. Phylasis peruviana pomace suppresses high-cholesterol diet-induced hypercholesterolemia in rats. Grasa Aceites 2012, 63, 411–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perk, B.; Ilgin, S.; Atli, O.; Duymus, H.; Sirmagul, B. Acute and subchronic toxic effects of the fruits of Phylasis peruviana L. Evid. Based Complement. Alernat Med. 2013, 1, 707285. [Google Scholar]
- Acar, A. Ameliorative effects of cape gooseberry (Phylasis peruviana L.) against monosodium glutamate (MSG)-induced toxicity: Genetic and biochemical approach. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 18035–18049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Olas, B. Physalis peruwiana Fruits and Their Food Products as New Important Components of Functional Foods. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083493
Olas B. Physalis peruwiana Fruits and Their Food Products as New Important Components of Functional Foods. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083493
Chicago/Turabian StyleOlas, Beata. 2025. "Physalis peruwiana Fruits and Their Food Products as New Important Components of Functional Foods" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083493
APA StyleOlas, B. (2025). Physalis peruwiana Fruits and Their Food Products as New Important Components of Functional Foods. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3493. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083493




