Bioinformatics Analysis of the Glutamate-Gated Chloride Channel Family in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Identification of BxGluCls
2.2. Physicochemical Analysis of BxGluCls
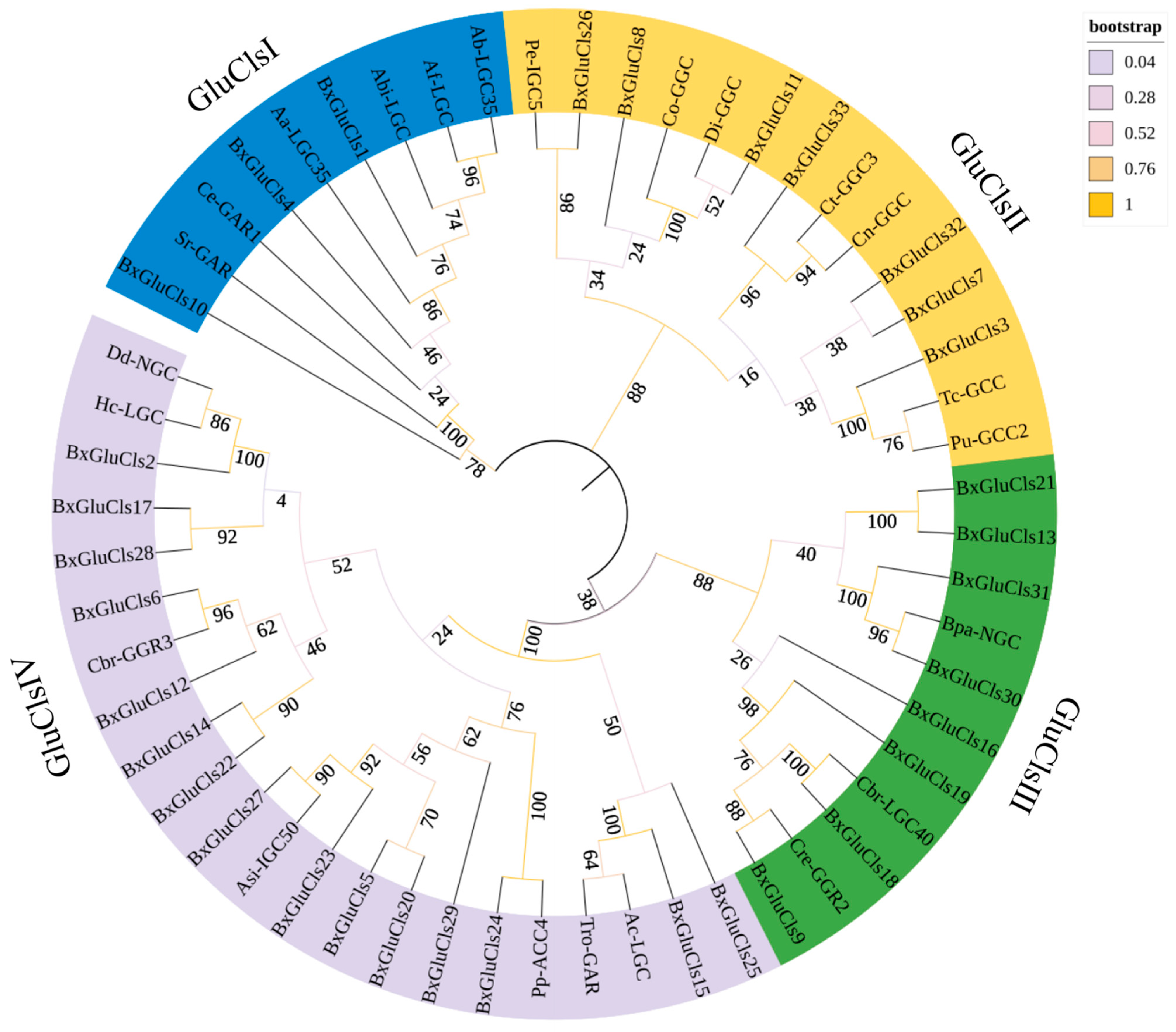
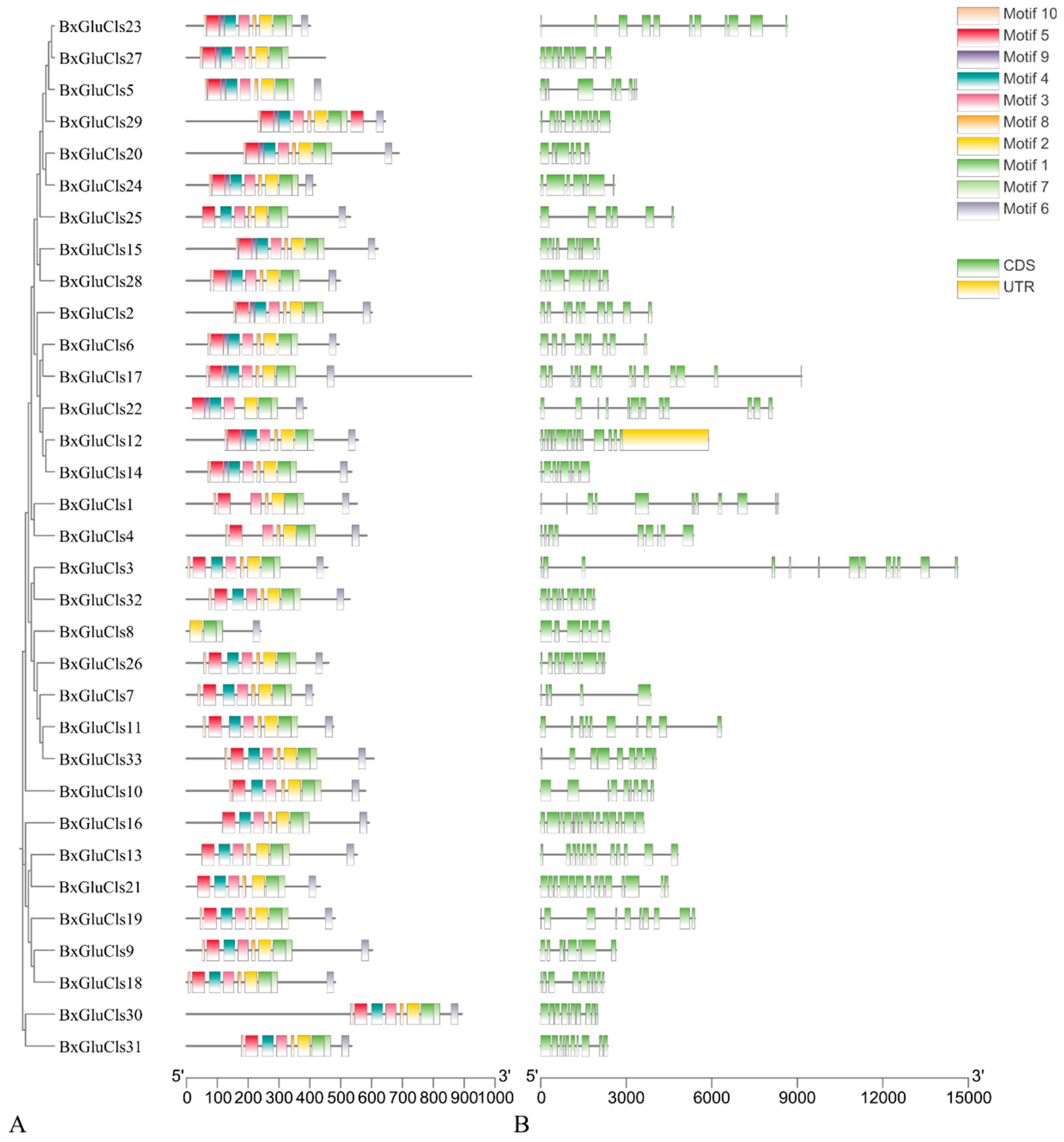
2.3. Phylogenetic and Conserved Motif Analysis of BxGluCls
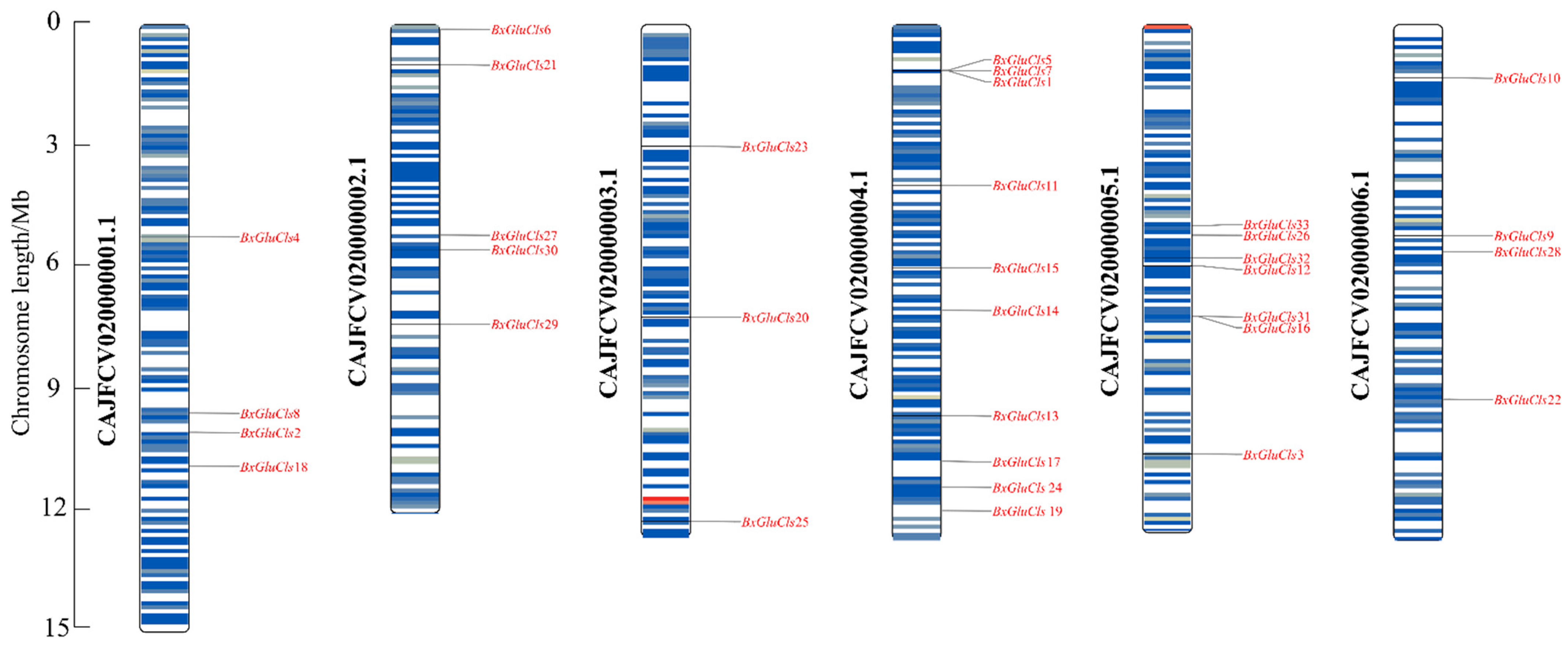
2.4. Chromosomal Distribution of BxGluCls
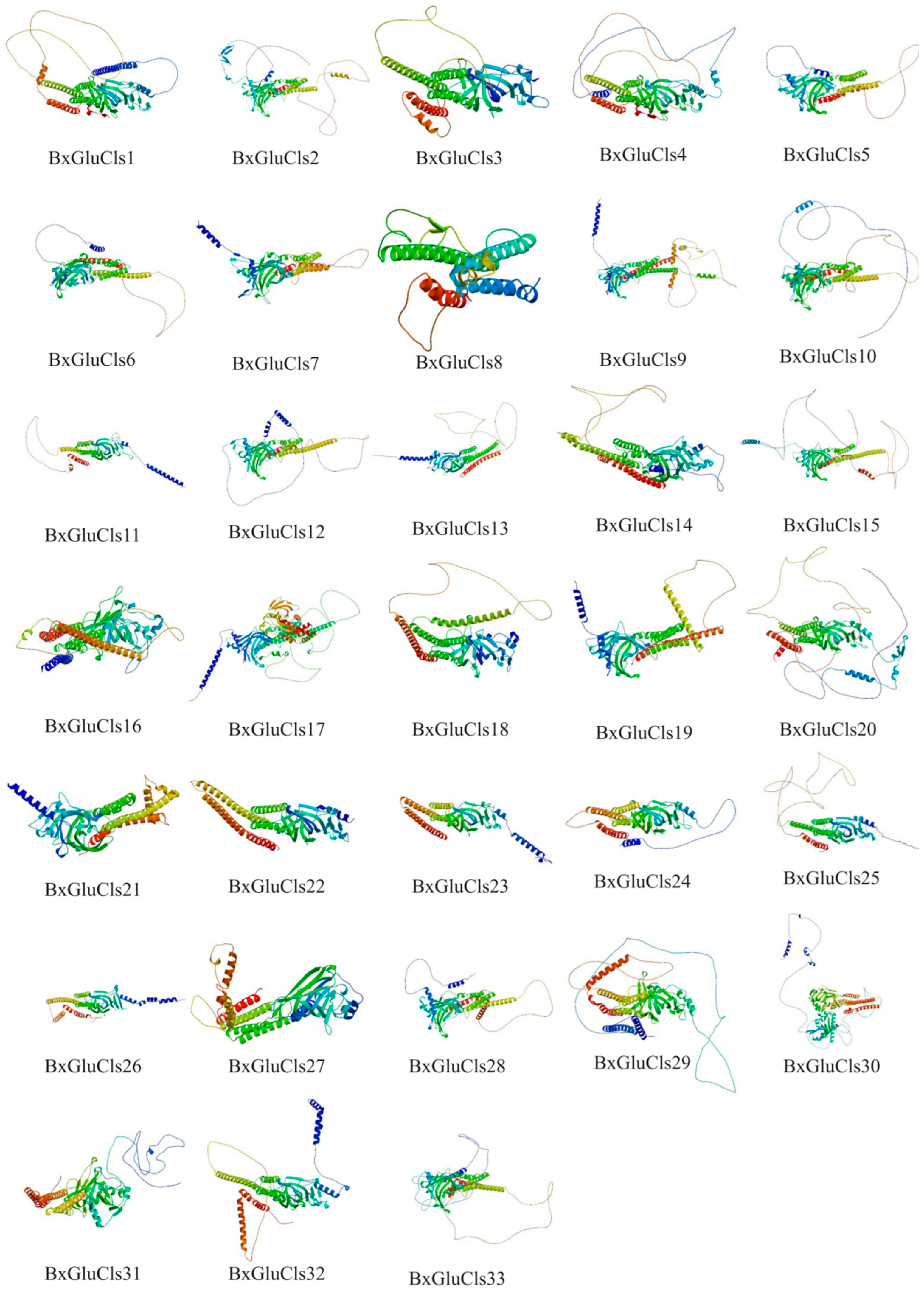
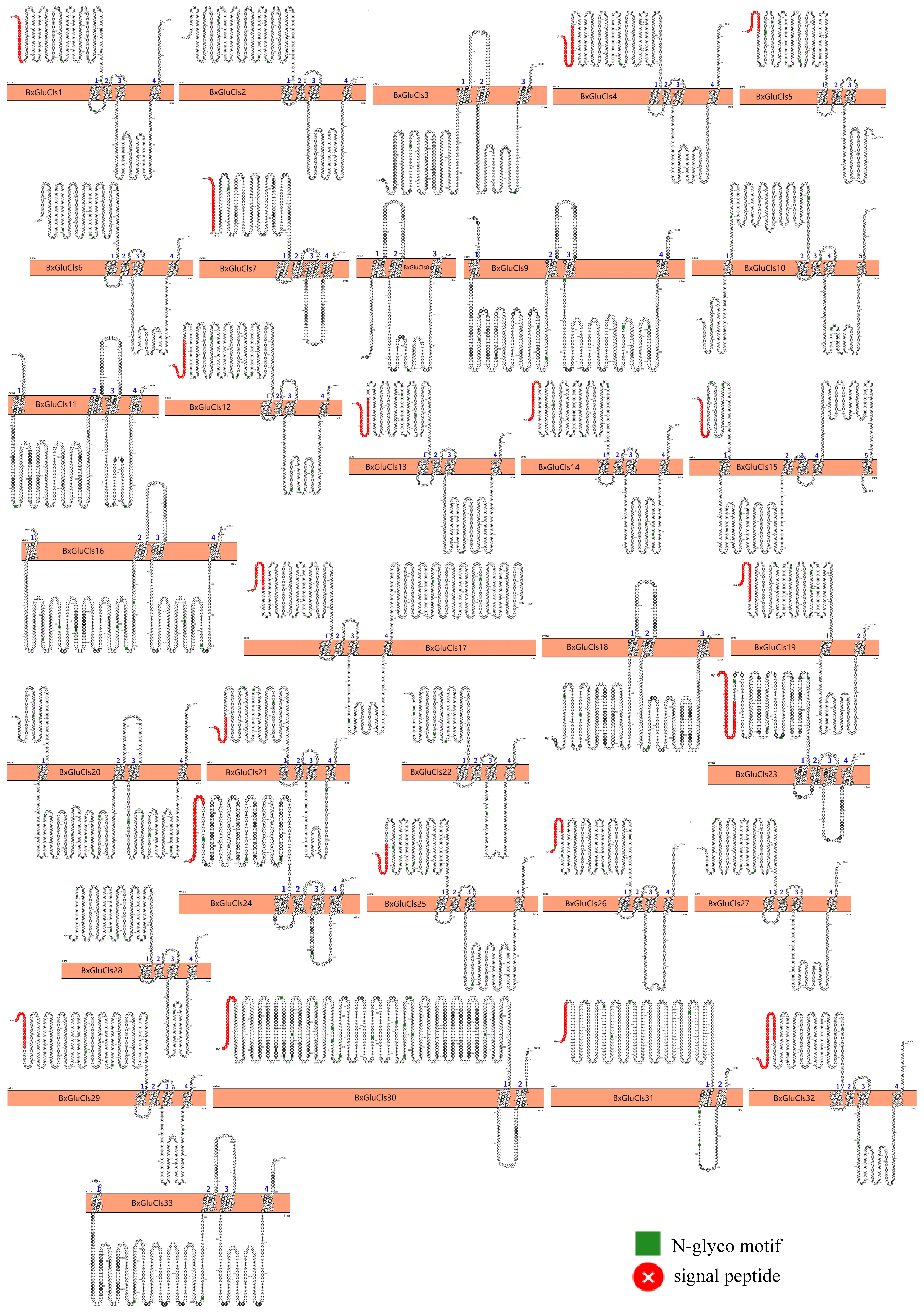
2.5. Protein Structure Analysis of BxGluCls
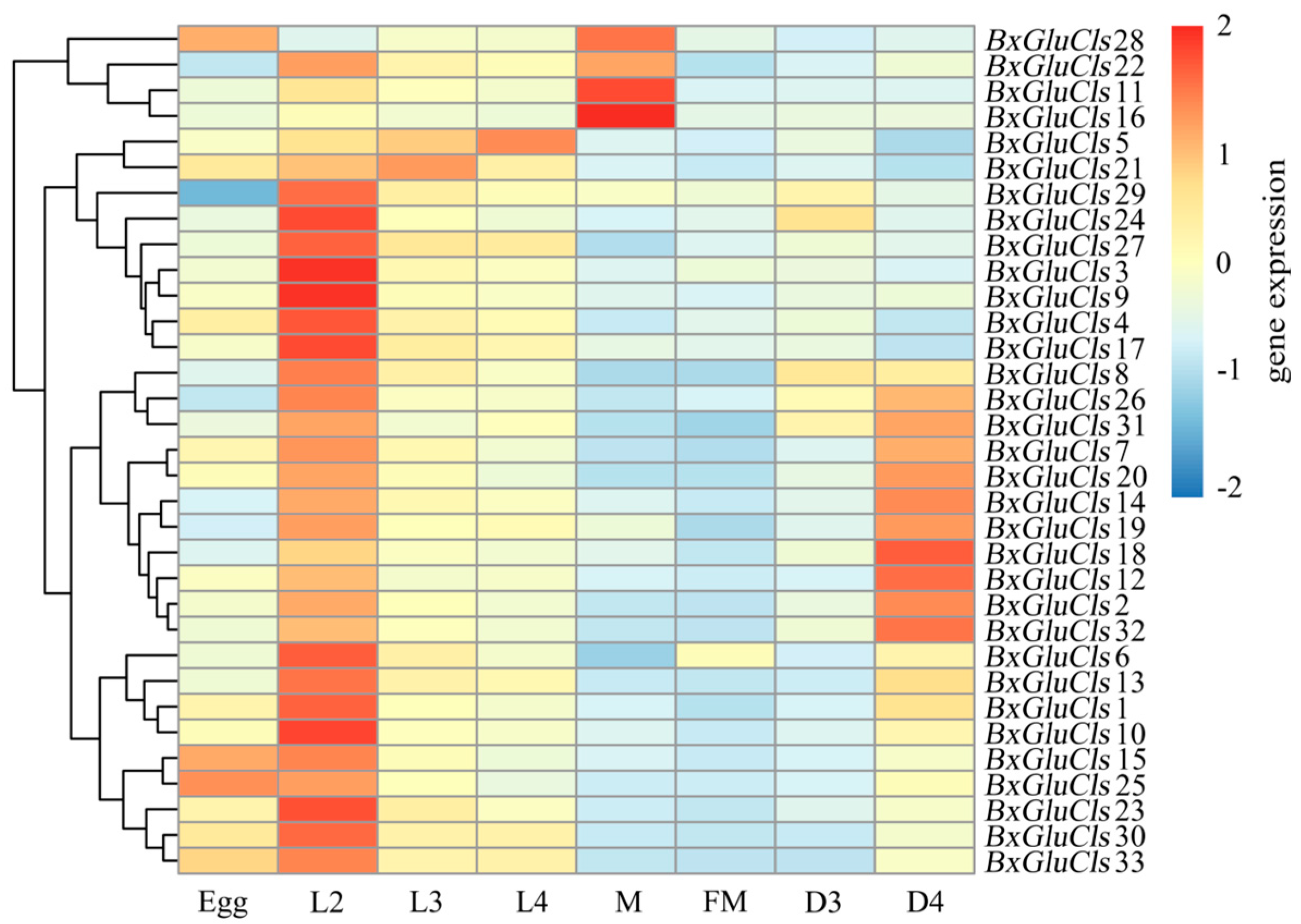
2.6. Expression Profiles of BxGluCls in Different Stages
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Identification of BxGluCls Family Members and Analysis of Their Physicochemical Properties
4.2. Phylogenetic Analysis of the BxGluCls Family and Analysis of Conserved Motifs
4.3. Chromosomal Distribution and Protein Structure Analysis of the BxGluCls Family
4.4. Expression Profiles of BxGluCls Family in Different Developmental Stages
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nickle, W.R.; Golden, A.M.; Mamiya, Y.; Wergin, W.P. On the Taxonomy and morphology of the pine wood nematode, Bursaphelenchus xylophilus (Steiner &Buhrer 1934) Nickle 1970. J. Nematol. 1970, 13, 385–392. [Google Scholar]
- Nickle, W.R. A taxonomic review of the genera of the Aphelenchoidae (Fuchs, 1937) Thorne, 1949 (Nematoda: Tylenchida). J. Nematol. 1970, 2, 374–392. [Google Scholar]
- Li, S.; Sun, H.; Zhou, Y.; Li, X.; Yu, Z.; Dong, Z. Occurrence of major forest pests in China in 2021 and prediction of occurrence trend in 2022. For. Pest Dis. 2022, 41, 44–47. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Y.; Danbolt, N.C. Glutamate as a neurotransmitter in the healthy brain. J. Neural Transm. 2014, 121, 799–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cleland, T.A. Inhibitory glutamate receptor channels. Mol. Neurobiol. 1996, 13, 97–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, A.J. Glutamate-gated chloride channels. J. Biol. Chem. 2012, 287, 40233–40238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhang, L.; Si, Y.; Wen, X.; Wang, L.; Song, L. Unveiling the functional diversity of ionotropic glutamate receptors in the Pacific Oyster (Crassostrea gigas) by systematic studies. Front. Physiol. 2023, 14, 1280553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, A.K.; Sattelle, D.B. The cys-loop ligand-gated ion channel gene superfamily of the red flour beetle, Tribolium castaneum. BMC Genom. 2007, 8, 327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yates, D.M.; Wolstenholme, A.J. An ivermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel subunit from Dirofilaria immitis. Int. J. Parasitol. 2004, 34, 1075–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheeseman, C.L.; Delany, N.S.; Woods, D.J.; Wolstenholme, A.J. High-affinity Ivermectin Binding to Recombinant Subunits of the Haemonchus contortus Glutamate-gated Chloride Channel. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2001, 114, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolstenholme, A.J.; Rogers, A.T. Glutamate-gated chloride channels and the mode of action of the avermectin/milbemycin an-thelmintics. Parasitology 2005, 131, S85–S95. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tandon, R.; LePage, K.T.; Kaplan, R.M. Cloning and characterization of genes encoding α and β subunits of glutamate-gated chloride channel protein in Cylicocyclus nassatus. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 150, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cully, D.F.; Vassilatis, D.K.; Liu, K.K.; Paress, P.S.; Van der Ploeg, L.H.; Schaeffer, J.M.; Arena, J.P. Cloning of an avermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel from Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 1994, 371, 707–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cully, D.F.; Wilkinson, H.; Vassilatis, D.K.; Etter, A.; Arena, J.P. Molecular biology and electrophysiology of glutamate-gated chloride channels of invertebrates. Parasitology 1996, 113, S191–S200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kane, N.S.; Hirschberg, B.; Qian, S.; Hunt, D.; Thomas, B.; Brochu, R.; Ludmerer, S.W.; Zheng, Y.; Smith, M.; Arena, J.P.; et al. Drug-resistance Drosophila indicate glutamate-gated chloride channels are targets for antiparasitics nodulisporic acid and ivermectin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2000, 97, 13949–13954. [Google Scholar]
- Vassilatis, D.K.; Arena, J.P.; Plasterk, R.H.; Wilkinson, H.A.; Schaeffer, J.M.; Cully, D.F.; Van der Ploeg, L.H. Genetic and biochemical evidence for a novel avermectin-sensitive chloride channel in Caenorhabditis elegans isolation and characterization. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272, 33167–33174. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, L.; Tang, B.; Dong, W.; Liang, P.; Gao, X. Cloning and sequence analysis of cDNA of GluCl receptor alpha gene from the Diamondback moth, Plutella xylostella. Plant Prot. 2010, 36, 49–54. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Y.; Jian, W.; Ding, X.; Ye, J. Genetic Diversity and Population Structure of Bursaphelenchus xylophilus in Guangdong, Guangxi, and Jiangsu Provinces in China. Forests 2024, 15, 934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blomme, T.; Vandepoele, K.; De Bodt, S.; Simillion, C.; Maere, S.; Van de Peer, Y. The gain and loss of genes during 600 million years of vertebrate evolution. Genome Biol. 2006, 7, R43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Tian, C. Gene Family Expansion during the Adaptation of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides to Woody Plants. J. Fungi 2023, 9, 1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, K.; Jiang, C.; Guan, D.; Zhuang, A.; Meng, X.; Wang, J. Characterization of Glutamate-Gated Chloride Channel in Tribolium castaneum. Insects 2023, 14, 580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, W.; Guo, K.; Hu, J.; Shao, H. Molecular characterization and functional analysis of genes mediating emamectin benzoate action to the pinewood nematode (Bursaphelenchus xylophilus). Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2024, 205, 106148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’halloran, D.M. Database of glutamate-gated chloride (GluCl) subunits across 125 nematode species: Patterns of gene accretion and sequence diversification. G3 Genes Genomes Genet. 2022, 12, jkab438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, F.; Guo, K.; Chen, A.; Chen, S.; Lin, H.; Zhou, X. Transcriptomic profiling of effects of emamectin benzoate on the pine wood nematode Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Pest. Manag. Sci. 2020, 76, 747–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dent, J.A.; Smith, M.M.; Vassilatis, D.K.; Avery, L. The genetics of ivermectin resistance in Caenorhabditis elegans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2000, 97, 2674–2679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, A.; Aptel, N.; Portillo, V.; Siney, E.; Sihota, R.; Holden-Dye, L.; Wolstenholme, A. Caenorhabditis elegans ivermectin receptors regulate locomotor behaviour and are functional orthologues of Haemonchus contortus receptors. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2006, 147, 118–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knouse, M.C.; Deutschmann, A.U.; Nenov, M.N.; Wimmer, M.E.; Briand, L.A. Sex differences in pre- and post-synaptic glutamate signaling in the nucleus accumbens core. Biol. Sex Differ. 2023, 14, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louro, M.; Kuzmina, T.A.; Bredtmann, C.M.; Diekmann, I.; de Carvalho, L.M.M.; von Samson-Himmelstjerna, G.; Krücken, J. Genetic variability, cryptic species and phylogenetic relationship of six cyathostomin species based on mitochondrial and nuclear sequences. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 8245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jagannathan, S.; Laughton, D.L.; Critten, C.L.; Skinner, T.M.; Horoszok, L.; Wolstenholme, A.J. Ligand-gated chloride channel subunits encoded by the Haemonchus contortus and Ascaris suum orthologues of the Caenorhabditis elegans gbr-2 (avr-14) gene. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1999, 103, 129–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, A.; Cunha, T.J.; Medeiros, B.A.S.d.; Sato, S.; E Khost, D.; Sackton, T.B.; Giribet, G. Expanding on Our Knowledge of Ecdysozoan Genomes: A Contiguous Assembly of the Meiofaunal Priapulan Tubiluchus corallicola. Genome Biol. Evol. 2023, 15, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenhole, M.; Mermans, C.; De Beer, B.; Xue, W.; Zhao, Y.; Ozoe, Y.; Liu, G.; Dermauw, W.; Van Leeuwen, T. A glutamate-gated chloride channel as the mite-specific target-site of dicofol and other diphenyl carbinol acaricides. Commun. Biol. 2023, 6, 1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, M.G.; The, N.L.; Glastras, S. Maternal obesity and offspring risk of chronic kidney disease. Nephrology 2018, 4, 84–87. [Google Scholar]
- Howe, K.L.; Bolt, B.J.; Shafie, M.; Kersey, P.; Berriman, M. WormBase ParaSite: A comprehensive resource for helminth genomics. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2017, 215, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, S.; Wang, J.; Chitsaz, F.; Derbyshire, M.K.; Geer, R.C.; Gonzales, N.R.; Gwadz, M.; I Hurwitz, D.; Marchler, G.H.; Song, J.S.; et al. CDD/SPARCLE: The conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res. 2020, 48, D265–D268. [Google Scholar]
- Cantelli, G.; Bateman, A.; Brooksbank, C.; I Petrov, A.; Malik-Sheriff, R.S.; Ide-Smith, M.; Hermjakob, H.; Flicek, P.; Apweiler, R.; Birney, E.; et al. The European Bioinformatics Institute (EMBL-EBI) in 2021. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, D11–D19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duvaud, S.; Gabella, C.; Lisacek, F.; Stockinger, H.; Ioannidis, V.; Durinx, C. Expasy, the Swiss Bioinformatics Resource Portal, as designed by its users. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021, 49, W216–W227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, B.; Jin, J.; Guo, A.-Y.; Zhang, H.; Luo, J.; Gao, G. GSDS 2.0: An upgraded gene feature visualization server. Bioinformatics 2015, 31, 1296–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bailey, T.L.; Johnson, J.; Grant, C.E.; Noble, W.S. The MEME suite. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 39–49. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Thomas, H.R.; Frank, M.H.; He, Y.; Xia, R. TBtools: An integrative toolkit developed for interactive analyses of big biological data. Mol. Plant 2020, 13, 1194–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Wu, Y.; Li, J.; Wang, X.; Zeng, Z.; Xu, J.; Liu, Y.; Feng, J.; Chen, H.; He, Y.; et al. TBtools-II: “A one for all, all for one” bioinformatics platform for biological big-data mining. Mol. Plant 2023, 16, 1733–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guirimand, T.; Delmotte, S.; Navratil, V. VirHostNet 2.0: Surfing on the web of virus/host molecular interactions data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015, 43, 583–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blom, N.; Gammeltoft, S.; Brunak, S. Sequence and structure-based prediction of eukaryotic protein phosphorylation sites 11 Edited by F. E. Cohen. J. Mol. Biol. 1999, 294, 1351–1362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omasits, U.; Ahrens, C.H.; Müller, S.; Wollscheid, B. Protter: Interactive protein feature visualization and integration with experimental proteomic data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 884–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biasini, M.; Bienert, S.; Waterhouse, A.; Arnold, K.; Studer, G.; Schmidt, T.; Kiefer, F.; Cassarino, T.G.; Bertoni, M.; Bordoli, L.; et al. SWISS-MODEL: Modelling protein tertiary and quaternary structure using evolutionary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, W252–W258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.G. Complex heatmap visualization. iMeta 2022, 1, e43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Protein ID of B. xylophilus | Protein Name | Sequence ID in NCBI | Protein Name in Other Nematodes | Other Nematodes Name | Scores of BlastP 1 | Similarity E-Value 2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BXYJ5.040019200 | BxGluCls1 | KAI6177746.1 | Ligand-Gated ion Channel | Aphelenchoides bicaudatus | 683 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.010220700 | BxGluCls2 | CRZ22203.1 | BMA-AVR-14, isoform b | Brugia malayi | 405 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.050236700 | BxGluCls3 | KAI6190451.1 | Ligand-gated ion channel 50 | Aphelenchoides bicaudatus | 796 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.010094300 | BxGluCls4 | KAI6171507.1 | Glutamate-gated chloride channel subunit beta | Aphelenchoides bicaudatus | 575 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.040019000 | BxGluCls5 | KAI1719268.1 | Neurotransmitter-gated ion-channel ligand binding domain-containing protein | Ditylenchus destructor | 596 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.020004500 | BxGluCls6 | KAI1720087.1 | Neurotransmitter-gated ion-channel ligand binding domain-containing protein | Ditylenchus destructor | 555 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.040019100 | BxGluCls7 | KAI1720087.1 | Neurotransmitter-gated ion-channel ligand binding domain-containing protein | Ditylenchus destructor | 555 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.010211400 | BxGluCls8 | KAI6226376.1 | Glutamate-gated chloride channel | Aphelenchoides fujianensis | 247 | 9 × 10−80 |
| BXYJ5.060084300 | BxGluCls9 | KAI6175995.1 | Protein CBR-GGR-2 | Aphelenchoides bicaudatus | 721 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.060015200 | BxGluCls10 | KAI6207390.1 | Unc-49B protein | Aphelenchoides besseyi | 766 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.040069900 | BxGluCls11 | KAI6226375.1 | BMA-AVR-14, isoform b | Aphelenchoides fujianensis | 737 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.050134500 | BxGluCls12 | KAI6192191.1 | Ligand-Gated ion Channel | Aphelenchoides bicaudatus | 647 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.040223500 | BxGluCls13 | KAI6176054.1 | Glycine receptor subunit beta-type 4 | Aphelenchoides bicaudatus | 701 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.040164200 | BxGluCls14 | KAI1717202.1 | Neurotransmitter-gated ion-channel ligand binding domain-containing protein | Ditylenchus destructor | 644 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.040127700 | BxGluCls15 | KAI6236273.1 | Ligand-gated ion channel 50 | Aphelenchoides besseyi | 762 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.050172600 | BxGluCls16 | KAI6199839.1 | Glycine receptor subunit beta-type 4 | Aphelenchoides besseyi | 680 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.040241100 | BxGluCls17 | KAI1719624.1 | Neurotransmitter-gated ion-channel ligand binding domain-containing protein | Ditylenchus destructor | 574 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.010233100 | BxGluCls18 | KAI6173198.1 | Ligand-Gated ion Channel | Aphelenchoides besseyi | 570 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.040257200 | BxGluCls19 | KAI1722739.1 | Neurotransmitter-gated ion-channel ligand binding domain-containing protein | Ditylenchus destructor | 532 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.030152800 | BxGluCls20 | KAH7724515.1 | CRE-LGC-46 protein | Aphelenchoides avenae | 764 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.020020400 | BxGluCls21 | KAI6171345.1 | Glycine receptor subunit beta-type 4 | Aphelenchoides bicaudatus | 440 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.060201900 | BxGluCls22 | KAI6179964.1 | Cation transporter family protein | Aphelenchoides besseyi | 482 | 2 × 10−166 |
| BXYJ5.030045000 | BxGluCls23 | KAI6189254.1 | ACC-1 protein | Aphelenchoides besseyi | 583 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.040248800 | BxGluCls24 | KAI6202533.1 | Acc-4 | Aphelenchoides besseyi | 629 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.030239900 | BxGluCls25 | KAI1716061.1 | Neurotransmitter-gated ion-channel ligand binding domain-containing protein | Ditylenchus destructor | 602 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.050106900 | BxGluCls26 | QBZ81966.1 | Ivermectin-sensitive glutamate-gated chloride channel subunit 5 | Parascaris equorum | 523 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.020097700 | BxGluCls27 | AVV64053.1 | Ligand-gated ion channel 50 | Anisakis simplex | 670 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.060095300 | BxGluCls28 | KAI6189662.1 | Cation transporter family protein | Aphelenchoides bicaudatus | 627 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.020169700 | BxGluCls29 | KAI6191605.1 | Cation transporter family protein | Aphelenchoides bicaudatus | 563 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.020110300 | BxGluCls30 | KAI6193159.1 | Glycine receptor subunit alphaZ1 | Aphelenchoides besseyi | 1200 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.050172500 | BxGluCls31 | KAI1705856.1 | Neurotransmitter-gated ion-channel ligand binding domain-containing protein | Ditylenchus destructor | 604 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.050127700 | BxGluCls32 | KAI1727299.1 | Neurotransmitter-gated ion-channel ligand binding domain-containing protein | Ditylenchus destructor | 732 | 0 |
| BXYJ5.050098400 | BxGluCls33 | KAI6190334.1 | Glutamate-gated chloride channel | Aphelenchoides bicaudatus | 709 | 0 |
| Protein Name | Number of Amino Acids | Molecular Weight /kDa | Isoelectric Point | Aliphatic Index 1 | Hydropathicity 2 | Instability Index 3 | Stability |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BxGluCls1 | 553 | 64.59 | 6.68 | 83.74 | −0.188 | 51.19 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls2 | 601 | 68.06 | 8.65 | 82.06 | −0.176 | 50.16 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls3 | 457 | 52.28 | 8.90 | 85.75 | −0.030 | 38.30 | Stable |
| BxGluCls4 | 584 | 66.25 | 6.58 | 90.15 | −0.028 | 41.05 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls5 | 448 | 51.56 | 7.46 | 88.30 | 0.023 | 39.46 | Stable |
| BxGluCls6 | 494 | 56.97 | 8.66 | 89.90 | −0.158 | 44.23 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls7 | 411 | 46.70 | 5.66 | 98.32 | −0.017 | 48.06 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls8 | 241 | 27.29 | 9.76 | 103.53 | 0.101 | 47.60 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls9 | 602 | 70.00 | 8.70 | 83.87 | −0.403 | 41.37 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls10 | 580 | 66.68 | 8.97 | 79.10 | −0.289 | 45.70 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls11 | 476 | 55.44 | 8.98 | 82.48 | −0.224 | 47.19 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls12 | 556 | 63.44 | 6.74 | 87.90 | −0.220 | 46.22 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls13 | 553 | 63.60 | 9.12 | 76.00 | −0.296 | 56.18 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls14 | 535 | 61.09 | 6.43 | 84.06 | −0.226 | 53.42 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls15 | 620 | 71.01 | 8.93 | 84.69 | −0.161 | 41.35 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls16 | 592 | 68.64 | 8.35 | 78.24 | −0.250 | 50.47 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls17 | 923 | 105.70 | 8.79 | 82.99 | −0.272 | 37.64 | Stable |
| BxGluCls18 | 482 | 55.83 | 6.50 | 81.35 | −0.213 | 41.91 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls19 | 481 | 55.51 | 9.02 | 84.74 | −0.140 | 53.86 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls20 | 688 | 78.86 | 8.55 | 77.02 | −0.320 | 57.41 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls21 | 433 | 50.49 | 5.78 | 88.24 | −0.064 | 50.73 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls22 | 389 | 45.71 | 8.76 | 94.42 | 0.020 | 39.73 | Stable |
| BxGluCls23 | 401 | 47.40 | 8.84 | 95.79 | 0.064 | 40.84 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls24 | 418 | 48.00 | 7.05 | 98.11 | 0.183 | 45.42 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls25 | 531 | 60.66 | 8.70 | 78.17 | −0.195 | 59.36 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls26 | 461 | 53.17 | 9.38 | 95.14 | −0.092 | 37.57 | Stable |
| BxGluCls27 | 467 | 54.15 | 6.34 | 86.57 | −0.049 | 46.27 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls28 | 498 | 58.03 | 6.22 | 82.93 | −0.216 | 54.99 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls29 | 644 | 74.16 | 5.53 | 83.82 | −0.212 | 48.58 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls30 | 893 | 102.02 | 4.79 | 85.69 | −0.370 | 42.28 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls31 | 535 | 61.84 | 6.45 | 96.69 | 0.023 | 47.45 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls32 | 529 | 61.57 | 9.12 | 89.91 | −0.222 | 50.42 | Unstable |
| BxGluCls33 | 590 | 67.24 | 9.08 | 82.58 | −0.331 | 44.58 | Unstable |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, H.; Wang, R.; Pan, J.; Chen, J.; Hao, X. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Glutamate-Gated Chloride Channel Family in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083477
Li H, Wang R, Pan J, Chen J, Hao X. Bioinformatics Analysis of the Glutamate-Gated Chloride Channel Family in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083477
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Haixiang, Rui Wang, Jialiang Pan, Jie Chen, and Xin Hao. 2025. "Bioinformatics Analysis of the Glutamate-Gated Chloride Channel Family in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083477
APA StyleLi, H., Wang, R., Pan, J., Chen, J., & Hao, X. (2025). Bioinformatics Analysis of the Glutamate-Gated Chloride Channel Family in Bursaphelenchus xylophilus. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3477. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083477







