ACC-1 as a Possible Biochemical Indicator of Lipoapoptosis in In Vivo and In Vitro Models of MAFLD
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
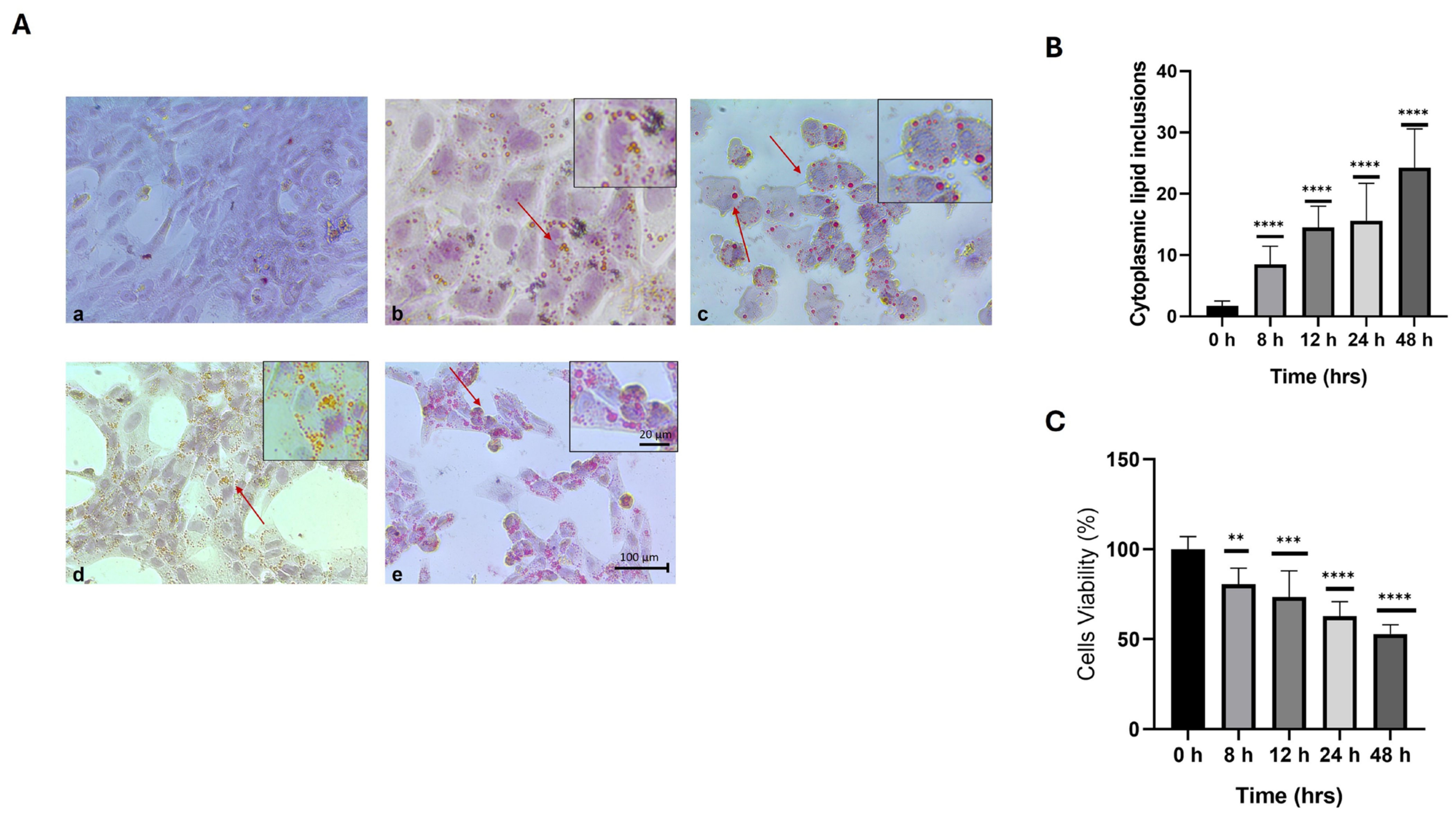
2.1. Effect on the Viability of HepG2 Liver Cells During Their Interaction with the High-Calorie Medium
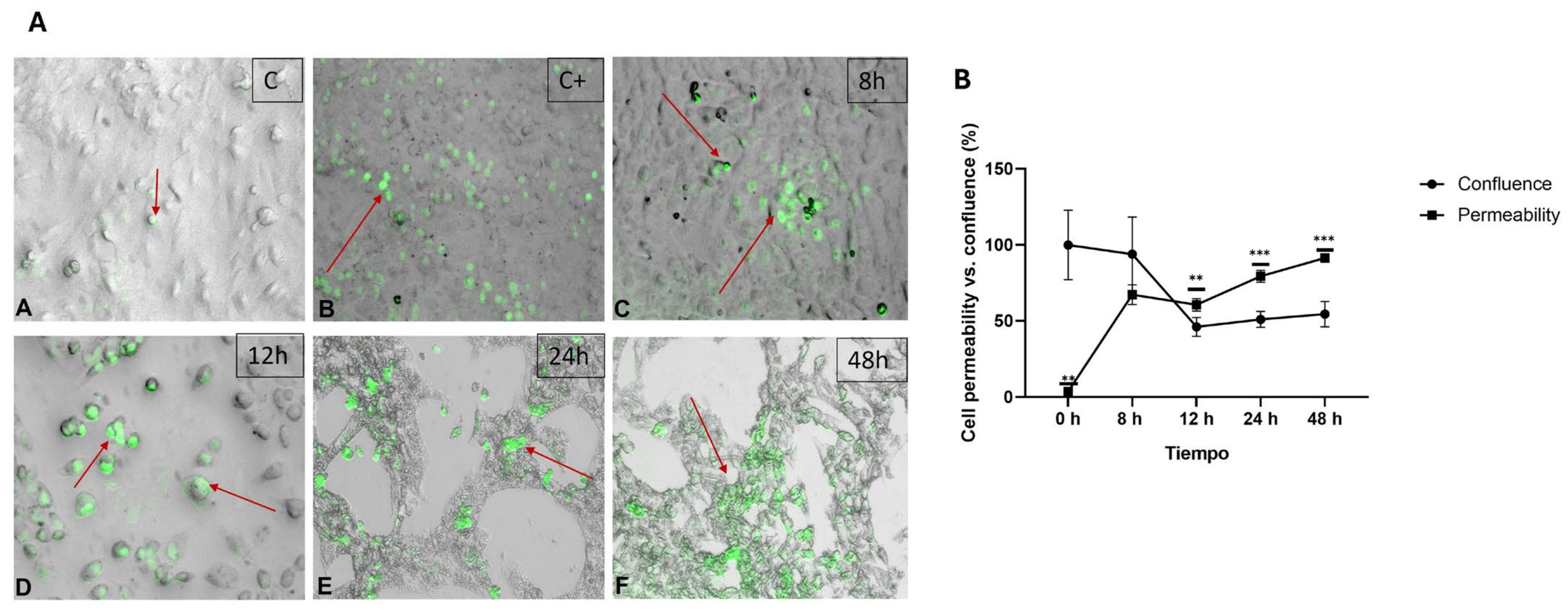
2.2. Effect of the Hypercaloric Medium on Monolayer Integrity and Membrane Permeability in HepG2 Cells
2.3. Lipoapoptotic Effect of the Hypercaloric Medium on HepG2 Cells
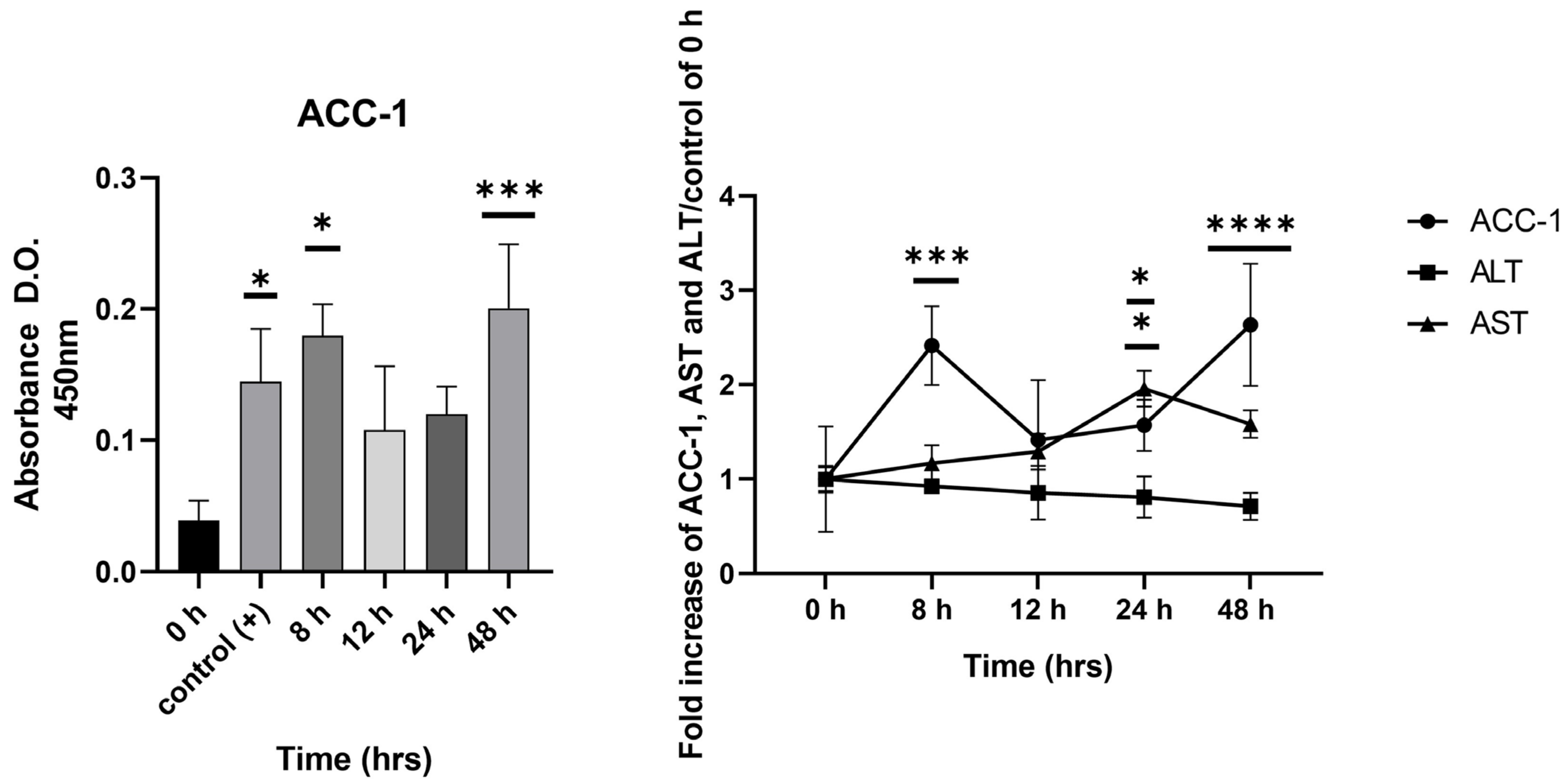
2.4. Detection of ACC-1 in Early Stages of Cellular Damage Compared to Hepatic Enzymes AST and ALT
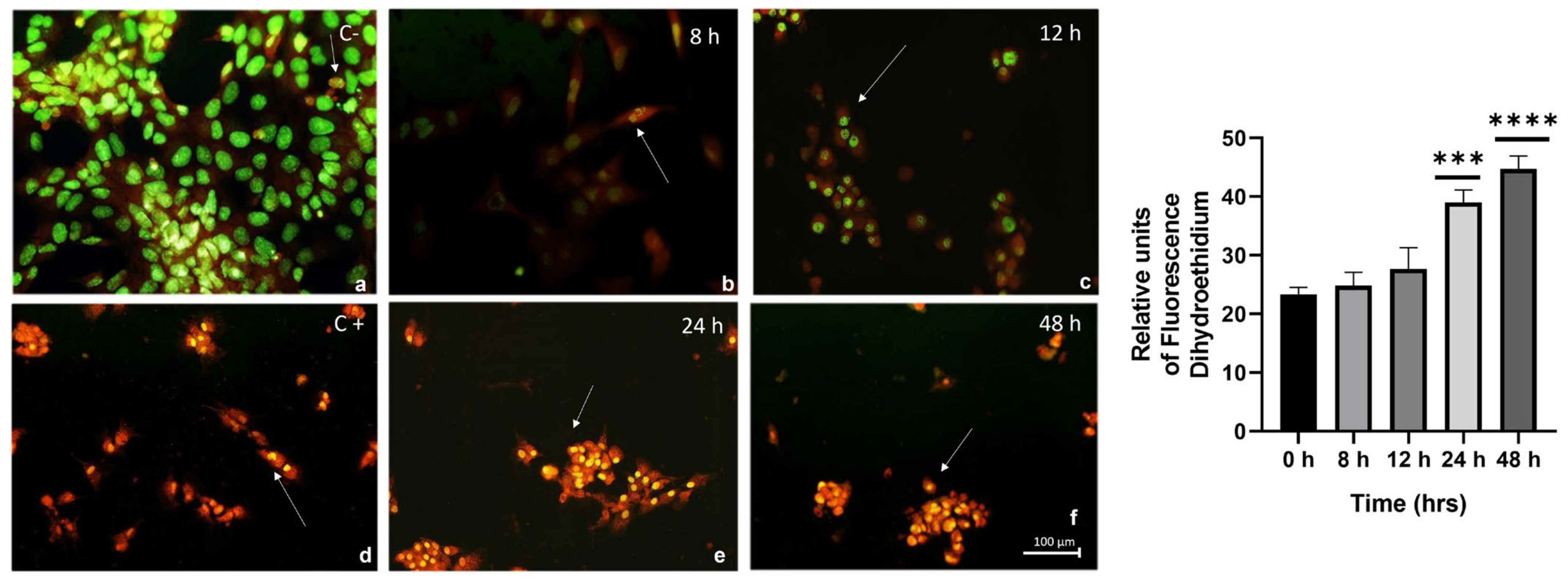
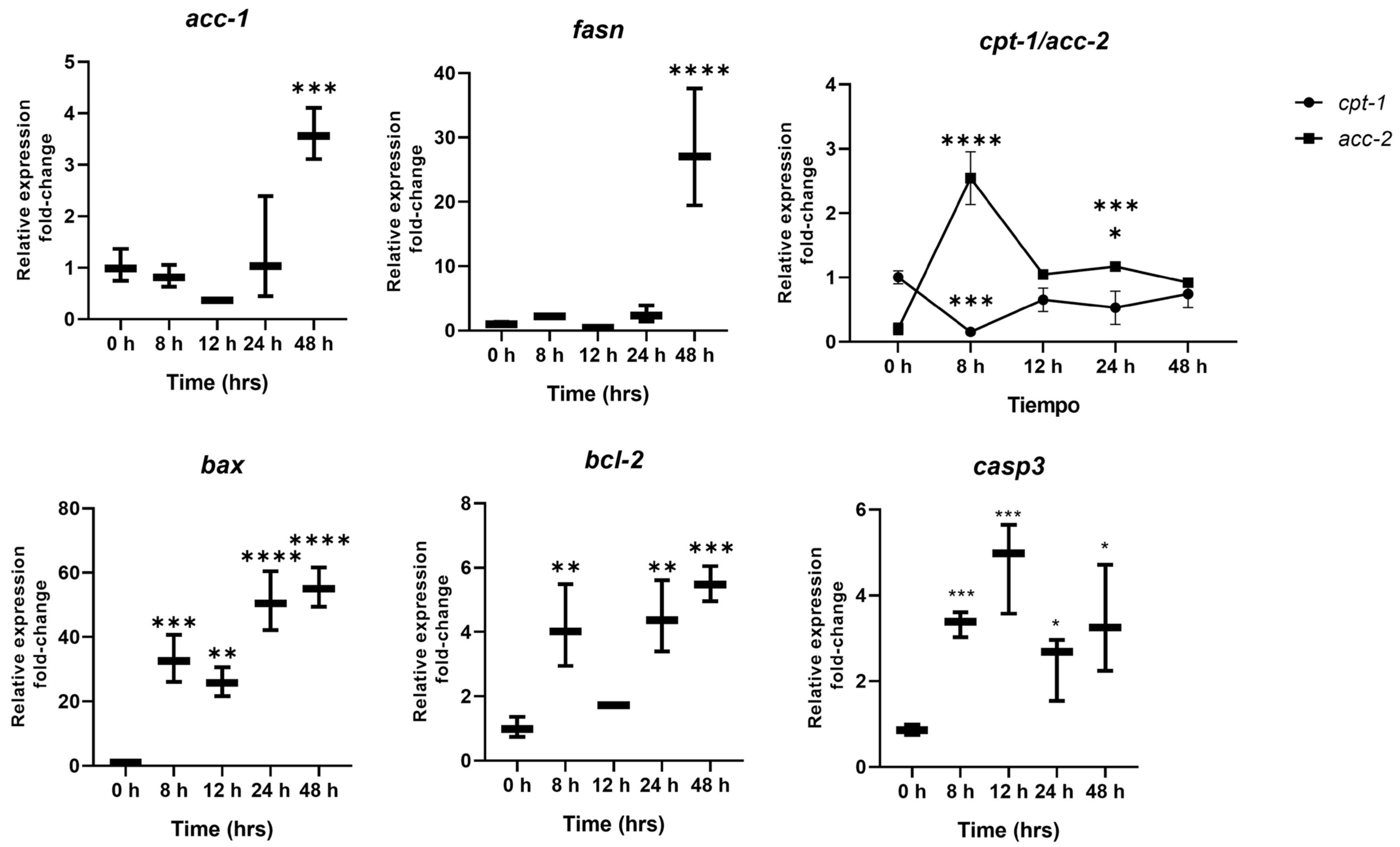
2.5. Expression of Cellular Stress Markers and Lipogenic Enzymes over the Course of Interaction with the Hypercaloric Medium
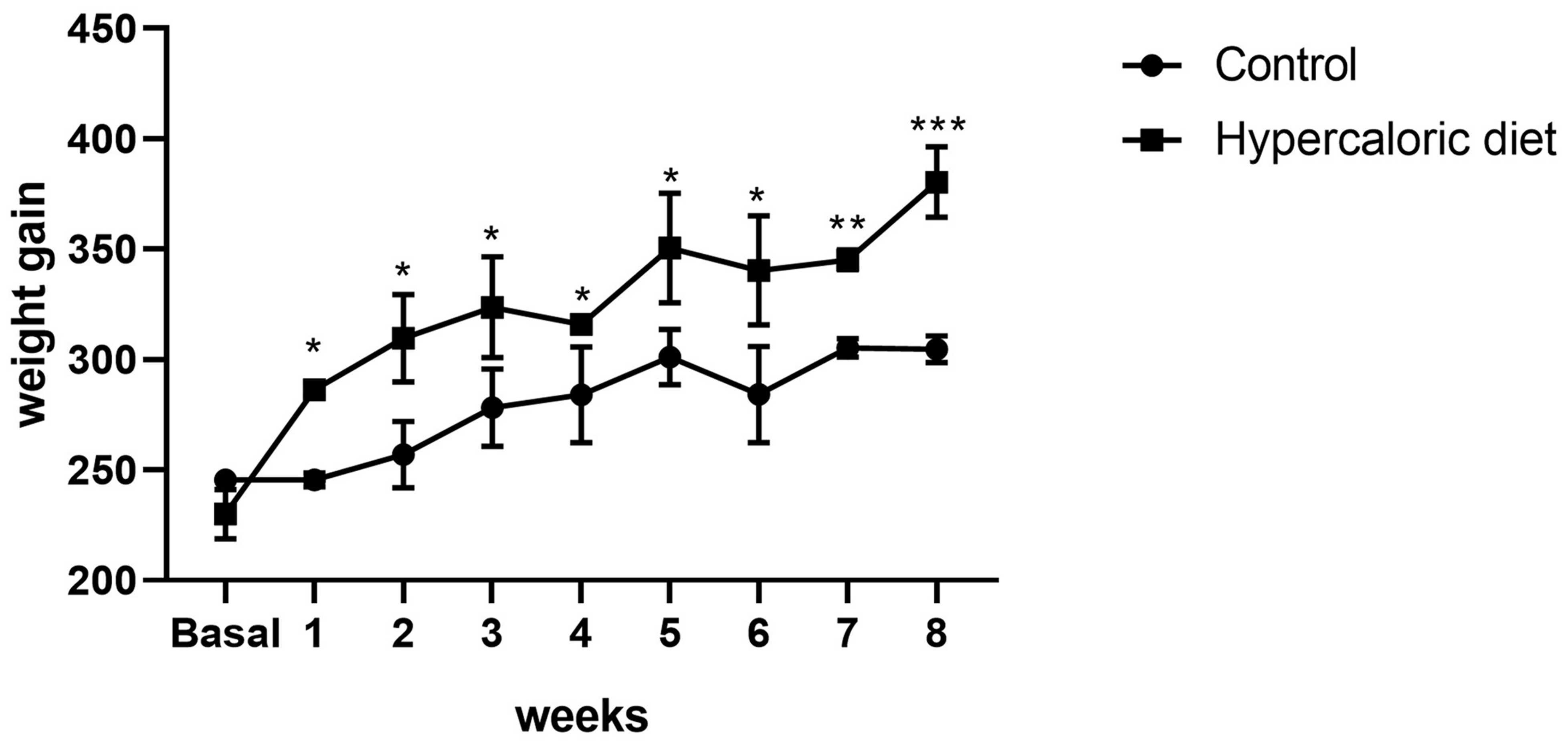
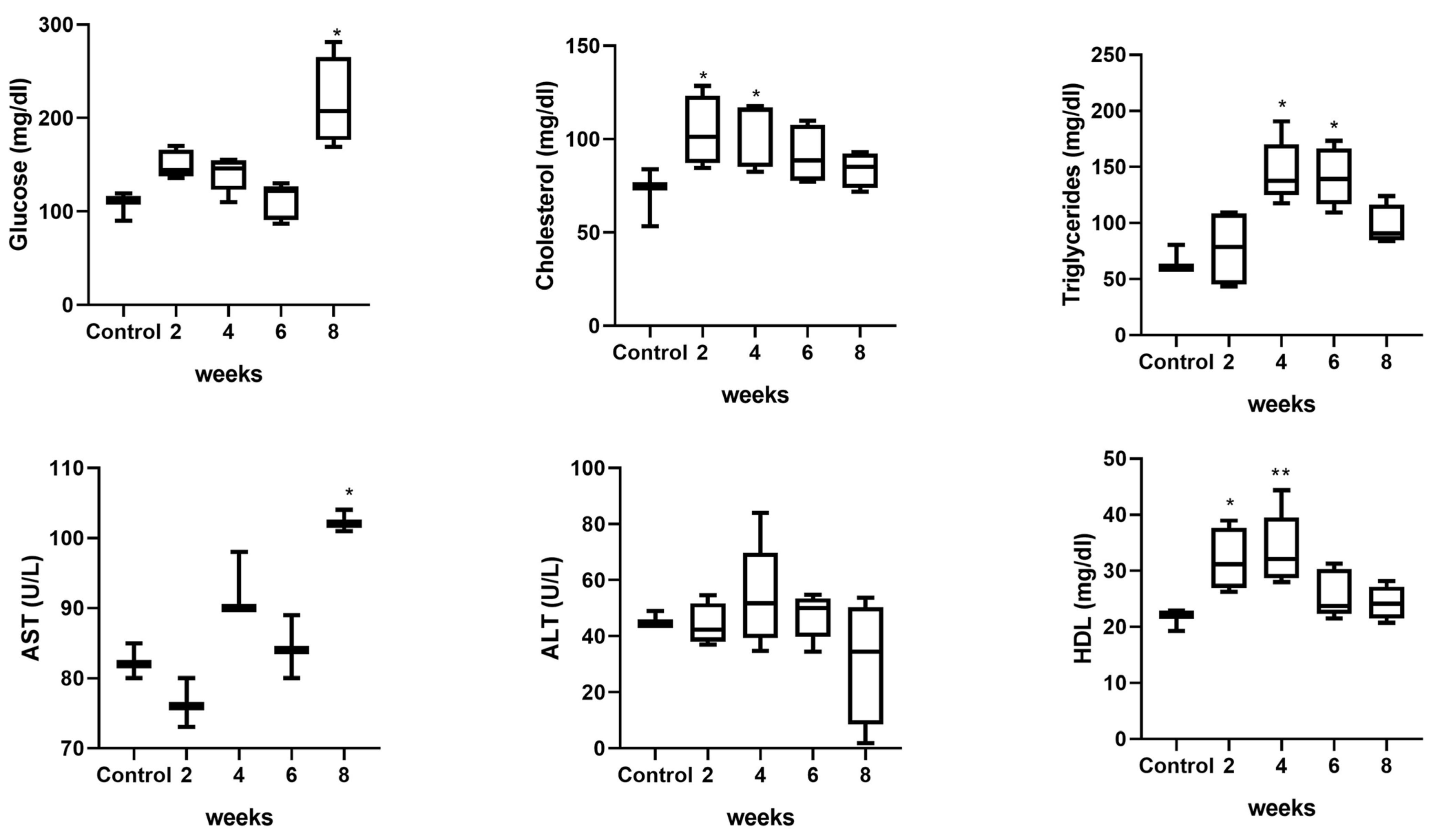
2.6. The Hypercaloric Diet Resulted in an Increase in Weight and Alteration of Metabolic Biochemical Parameters and Liver Damage Markers
2.7. Histopathological Changes Induced by the Hypercaloric Diet and Early Identification of the ACC-1 Enzyme in the Serum of Experimental Animals
3. Discussion
4. Strengths, Limitations, and Perspectives
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Cell Culture
5.2. Induction of Lipotoxicity in HepG2 Cells and MTT Cell Viability Assay
5.3. Oil Red O Staining
5.4. SYTOX Green Staining
5.5. Acridine Orange (AO) Staining
5.6. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress Using Dihydroethidium (DHE)
5.7. Animals
5.8. Histopathology
5.9. Biochemical Markers: Liver Function Tests
5.10. ELISA Determination of the ACC-1 Enzyme
5.11. Quantitative Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction (qRT-PCR)
5.12. Statistical Analysis
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, R.T.; Koretz, R.L.; Yee, H.F. Is weight reduction an effective therapy for nonalcoholic fatty liver? A systematic review. Am. J. Med. 2003, 115, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, O.; Kapoor, A.; Puri, P.; Sistrun, S.; Luketic, V.A.; Sargeant, C.C.; Contos, M.J.; Shiffman, M.L.; Stravitz, R.T.; Sterling, R.K.; et al. The impact of fat distribution on the severity of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and metabolic syndrome. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1091–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pettinelli, P.; Obregón, A.M.; Videla, L.A. Molecular mechanisms of steatosis in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Nutr. Hosp. 2011, 26, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuman, M.G.; Cohen, L.B.; Nanau Bsc, R.M. Biomarkers in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Can. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 28, 607–618. [Google Scholar]
- Trefts, E.; Gannon, M.; Wasserman, D.H. The liver. Curr. Biol. 2017, 27, R1147–R1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Huerta-Salgado, C.; Orozco-Aguilar, J.; Aguirre, F.; Tacchi, F.; Simon, F.; Cabello-Verrugio, C. Role of Oxidative Stress in Hepatic and Extrahepatic Dysfunctions during Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD). Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2020, 2020, 1617805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Mauro, S.; Scamporrino, A.; Filippello, A.; Di Pino, A.; Scicali, R.; Malaguarnera, R.; Purrello, F.; Piro, S. Clinical and Molecular Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Staging of NAFLD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 11905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graffigna, M.; Catoira, N.; Soutelo, J.; Azpelicueta, A.; Berg, G.; Perel, C.; Migliano, M.E.; Aranguren, M.; Musso, C.; Farias, J. Diagnóstico de esteatosis hepática por métodos clínicos, bioquímicos y por imágenes. Rev. Argent. Endocrinol. Y Metab. 2017, 54, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinou, E.; Pericleous, M.; Stefanova, I.; Kaur, V.; Angelidi, A.M. Diagnostic Modalities of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: From Biochemical Biomarkers to Multi-Omics Non-Invasive Approaches. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, W.; Li, S.; Guo, D.; He, J.; Wang, Y. Acetyl-CoA Carboxylases and Diseases. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 836058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, J.E.C.; Esler, W.P.; Patel, R.; Lanba, A.; Vera, N.B.; Pfefferkorn, J.A.; Vernochet, C. Inhibition of Acetyl-CoA Carboxylase 1 (ACC1) and 2 (ACC2) Reduces Proliferation and De Novo Lipogenesis of EGFRvIII Human Glioblastoma Cells. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Oliveira Santana, K.N.; Lelis, D.F.; Mendes, K.L.; Lula, J.F.; Paraíso, A.F.; Andrade, J.M.O.; Feltenberger, J.D.; Cota, J.; da Costa, D.V.; de Paula, A.M.B.; et al. Metformin Reduces Lipogenesis Markers in Obese Mice Fed a Low-Carbohydrate and High-Fat Diet. Lipids 2016, 51, 1375–1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomba, R.; Kayali, Z.; Noureddin, M.; Ruane, P.; Lawitz, E.J.; Bennett, M.; Wang, L.; Harting, E.; Tarrant, J.M.; McColgan, B.J.; et al. GS-0976 Reduces Hepatic Steatosis and Fibrosis Markers in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1463–1473.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M.; Yashiro, H.; Ogino, H.; Aoyama, K.; Nambu, T.; Nakamura, S.; Nishida, M.; Wang, X.; Erion, D.M.; Kaneko, M. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase 1 and 2 inhibition ameliorates steatosis and hepatic fibrosis in a MC4R knockout murine model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Duan, Y.; Wei, H.; Ning, H.; Bi, C.; Zhao, Y.; Qin, Y.; Li, Y. Acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC) as a therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome and recent developments in ACC1/2 inhibitors. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2019, 28, 917–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, A.C.; de Figueiredo-Mendes, C.; Villela-Nogueira, C.A. Current management of NAFLD/NASH. Liver Int. 2021, 41, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jang, E.; Shin, M.-H.; Kim, K.-S.; Kim, Y.; Na, Y.-C.; Woo, H.-J.; Kim, Y.; Lee, J.-H.; Jang, H.-J. Anti-lipoapoptotic effect of Artemisia capillaris extract on free fatty acids-induced HepG2 cells. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2014, 14, 253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arifin, W.N.; Zahiruddin, W.M. Sample size calculation in animal studies using resource equation approach. Malays. J. Med. Sci. 2017, 24, 101–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Delgado-Venegas, C.S.; Martínez-Hernández, S.L.; Cervantes-García, D.; de Oca-Luna, R.M.; Loera-Arias, M.d.J.; Mata-Martínez, M.G.; Ventura-Juárez, J.; Muñoz-Ortega, M.H. Modulating effects of the probiotic Lactococcus lactis on the hepatic fibrotic process induced by CCl4 in Wistar rats. Exp. Ther. Med. 2021, 21, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Piazzolla, V.A.; Mangia, A. Noninvasive Diagnosis of NAFLD and NASH. Cells 2020, 9, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Poulsen, K.L.; Wu, L.; Liu, S.; Miyata, T.; Song, Q.; Wei, Q.; Zhao, C.; Lin, C.; Yang, J. Targeted therapeutics and novel signaling pathways in non-alcohol-associated fatty liver/steatohepatitis (NAFL/NASH). Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina-Pizaño, M.Y.; Medina-Rosales, M.N.; Martínez-Hernández, S.L.; Aldaba-Muruato, L.R.; Macías-Pérez, J.R.; Sánchez-Alemán, E.; Ventura-Juárez, J.; Muñoz-Ortega, M.H. Protective Effect of Curcumin against Doxazosin- and Carvedilol-Induced Oxidative Stress in HepG2 Cells. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byvaltsev, V.A.; Bardonova, L.A.; Onaka, N.R.; Polkin, R.A.; Ochkal, S.V.; Shepelev, V.V.; Aliyev, M.A.; Potapov, A.A. Acridine Orange: A Review of Novel Applications for Surgical Cancer Imaging and Therapy. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puig, T.; Porta, R.; Colomer, R. Sintasa de ácidos grasos como nueva diana antitumoral. Med. Clin. 2009, 132, 359–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simões, I.C.M.; Fontes, A.; Pinton, P.; Zischka, H.; Wieckowski, M.R. Mitochondria in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2018, 95, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frago, L.M.; Arroba, A.; Chowen, J.A. Fundamentos de la apoptosis celular: Interés en endocrinología. Endocrinología y Nutrición. Endocrinol. Nutr. 2001, 48, 272–280. [Google Scholar]
- Plemel, J.R.; Caprariello, A.V.; Keough, M.B.; Henry, T.J.; Tsutsui, S.; Chu, T.H.; Schenk, G.J.; Klaver, R.; Yong, V.W.; Stys, P.K. Unique spectral signatures of the nucleic acid dye acridine orange can distinguish cell death by apoptosis and necroptosis. J. Cell Biol. 2017, 216, 1163–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panasiuk, A.; Dzieciol, J.; Panasiuk, B.; Prokopowicz, D. Expression of p53, Bax and Bcl-2 proteins in hepatocytes in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 6198–6202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artika, I.M.; Dewi, Y.P.; Nainggolan, I.M.; Siregar, J.E.; Antonjaya, U. Real-Time Polymerase Chain Reaction: Current Techniques, Applications, and Role in COVID-19 Diagnosis. Genes 2022, 13, 2387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Quiroz, L.; Bucio, L.; Souza, V.; Escobar, C.; Farfán, B.; Hernández, E.; Konigsberg, M.; Vargas-Vorackova, F.; Kershenobich, D.; Gutiérrez-Ruiz, M.C. Interleukin 8 response and oxidative stress in HepG2 cells treated with ethanol, acetaldehyde or lipopolysaccharide. Hepatol. Res. 2003, 26, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandy Alhajj, A.; Zubair, M.; Farhana, A. Enzyme Linked Immunosorbent Assay. In StatPearls; StatPearls: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Rameshreddy, P.; Uddandrao, V.V.S.; Brahmanaidu, P.; Vadivukkarasi, S.; Ravindarnaik, R.; Suresh, P.; Swapna, K.; Kalaivani, A.; Parvathi, P.; Tamilmani, P.; et al. Obesity-alleviating potential of asiatic acid and its effects on ACC1, UCP2, and CPT1 mRNA expression in high fat diet-induced obese Sprague–Dawley rats. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 442, 143–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernández-Puga, G.; Laguna-Maldonado, K.D.; Gregg-García, R.; Barrera-Zárate, G.; López-Ortiz, F.D.; Matuz-Mares, D. La AMPK como diana terapéutica del síndrome metabólico [AMPK as a therapeutic target for metabolic syndrome]. Rev. Med. Inst. Mex Seguro. Soc. 2020, 58, 612–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pang, Y.; Xu, X.; Xiang, X.; Li, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Li, J.; Gao, S.; Liu, Q.; Mai, K.; Ai, Q. High Fat Activates O-GlcNAcylation and Affects AMPK/ACC Pathway to Regulate Lipid Metabolism. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martín Domínguez, V.; Casas, R.G.; Mendoza Jiménez-Ridruejo, J.; García Buey, L.; Moreno-Otero, R. Etiopatogenia, diagnóstico y tratamiento de la enfermedad del hígado graso no alcohólica. Rev. Española Enfermedades Dig. 2013, 105, 409–420. [Google Scholar]
- Langouche, L.; Perre, S.V.; Thiessen, S.; Gunst, J.; Hermans, G.; D’Hoore, A.; Kola, B.; Korbonits, M.; Van den Berghe, G. Alterations in Adipose Tissue during Critical Illness An Adaptive and Protective Response? Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2010, 182, 507–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aguillón-Osma, J.; Loango-Chamorro, N.; Landazuri, P. Liver cell models for studying lipid metabolism. Literature review. Rev. Fac. Med. 2019, 67, 109–116. [Google Scholar]
- Noureddin, M.; Harrison, S.A. NASH cirrhosis trials and major adverse liver outcomes: Big data needed. J. Hepatol. 2022, 78, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Gene | Specie | Forward (5′-3′) | Reverse (5′-3′) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 18SrRNA | Human | 5′-AAA CGG CTA CCA CAT CCA AG-3′ | 5′-CCT CCA ATG GAT CCT CGT TA-3′ |
| 18SrRNA | Rat | 5′-CGG CTA CCA CAT CCA AGG A-3′ | 5′-CCA ATT ACA GGG CCT CGA AA-3′ |
| acc-1 | Human | 5′-GGA TGG TGT TCA CTC GGT AAT AGA-3′ | 5′-GGG TGA TAT GTG CTG CTG CAT-3′ |
| acc-1 | Rat | 5′-TAC AAC GCA GGC ATC AGA AG-3′ | 5′-TGT GCT GCA GGA AGA TTG AC-3′ |
| fasn | Human | 5′-CGC TCG GCA TGG CTA TCT-3′ | 5′-CTG GTT GAA GAA CGC ATC CA-3′ |
| fasn | Rat | 5′-TCG AGA CAC ATC GTT TGA GC-3′ | 5′-CCC AGA GGG TGG TTG TTA GA-3′ |
| cpt-1 | Human | 5′-GCA GCG TTC TTT GTG ACG TT-3′ | 5′-AGG AGT GTT CAG CGT TGA GG-3′ |
| acc-2 | Human | 5’-ACATGGCAAGAGAAAAGCGG-3’ | 5’-ACTCTTGGTGATCGGCTTGG-3’ |
| bax | Human | 5′-CGA ACT GGA CAG TAA CAT GGA G-3′ | 5′-CAG TTT GCT GGC AAA GTA GAA A-3′ |
| bcl-2 | Human | 5′- GAC TTC GCC GAG ATG TCC AG-3′ | 5′-GAA CTC AAA GAA GGC CAC AAT C-3′ |
| caspase 3 | Human | 5′-TGG AAC CAA AGA TCA TAC ATG G-3′ | 5′-GTT TGC TGC ATC GAC ATC TG-3′ |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Martínez, D.I.; Muñoz Nieto, I.A.; Hernández Marín, D.A.; Ventura Juárez, J.; Martínez Hernández, S.L.; Sánchez Alemán, E.; Guerrero Alba, R.; Muñoz Ortega, M. ACC-1 as a Possible Biochemical Indicator of Lipoapoptosis in In Vivo and In Vitro Models of MAFLD. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083459
Martínez DI, Muñoz Nieto IA, Hernández Marín DA, Ventura Juárez J, Martínez Hernández SL, Sánchez Alemán E, Guerrero Alba R, Muñoz Ortega M. ACC-1 as a Possible Biochemical Indicator of Lipoapoptosis in In Vivo and In Vitro Models of MAFLD. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(8):3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083459
Chicago/Turabian StyleMartínez, David Ibarra, Israel Alejandro Muñoz Nieto, David Alejandro Hernández Marín, Javier Ventura Juárez, Sandra Luz Martínez Hernández, Esperanza Sánchez Alemán, Raquel Guerrero Alba, and Martín Muñoz Ortega. 2025. "ACC-1 as a Possible Biochemical Indicator of Lipoapoptosis in In Vivo and In Vitro Models of MAFLD" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 8: 3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083459
APA StyleMartínez, D. I., Muñoz Nieto, I. A., Hernández Marín, D. A., Ventura Juárez, J., Martínez Hernández, S. L., Sánchez Alemán, E., Guerrero Alba, R., & Muñoz Ortega, M. (2025). ACC-1 as a Possible Biochemical Indicator of Lipoapoptosis in In Vivo and In Vitro Models of MAFLD. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(8), 3459. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26083459





