Effect of Sphingomyelin and Vitamin D3 Intake on the Rabbit Brain
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
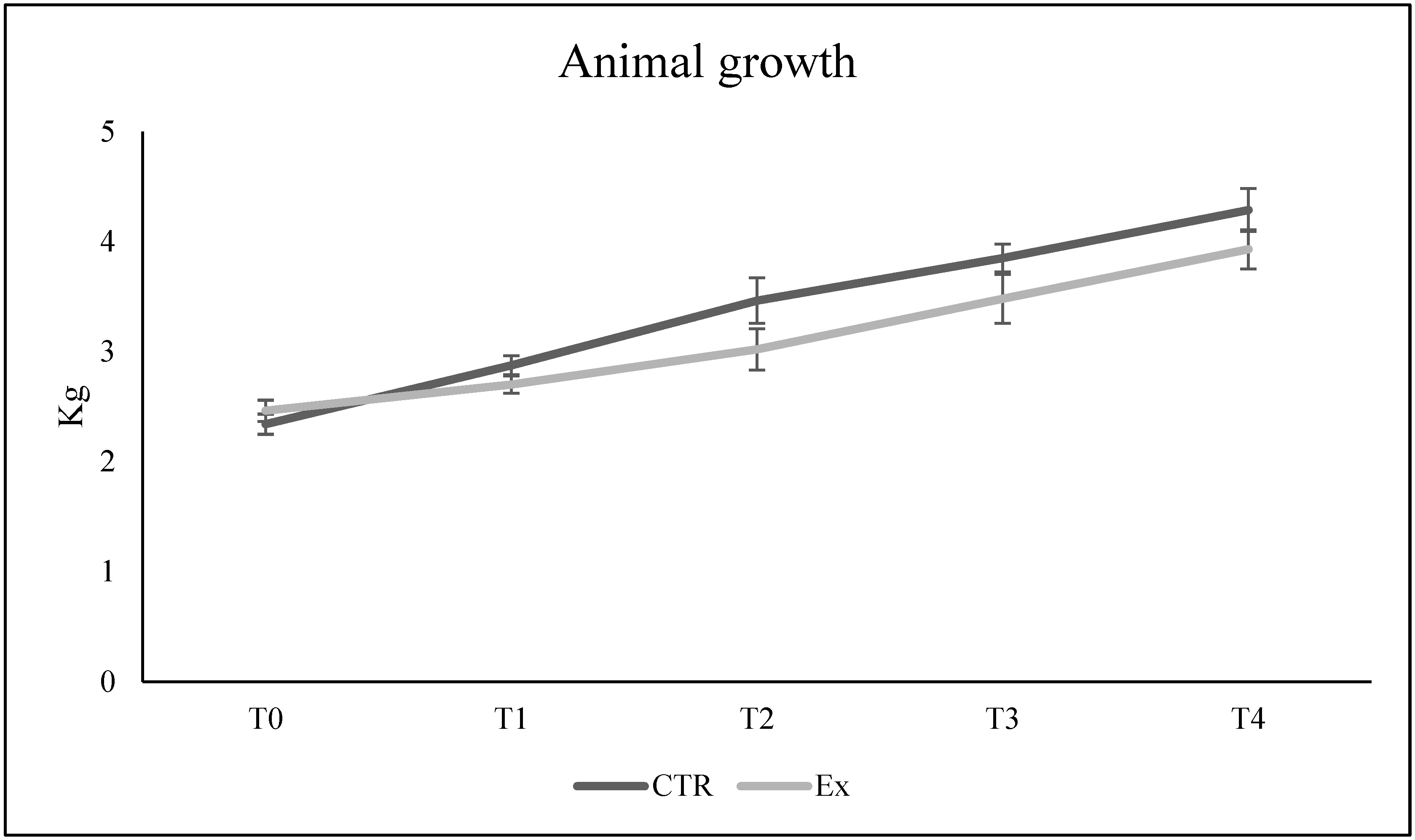
2.1. SM-VD3 Does Not Influence the Growth of Rabbits
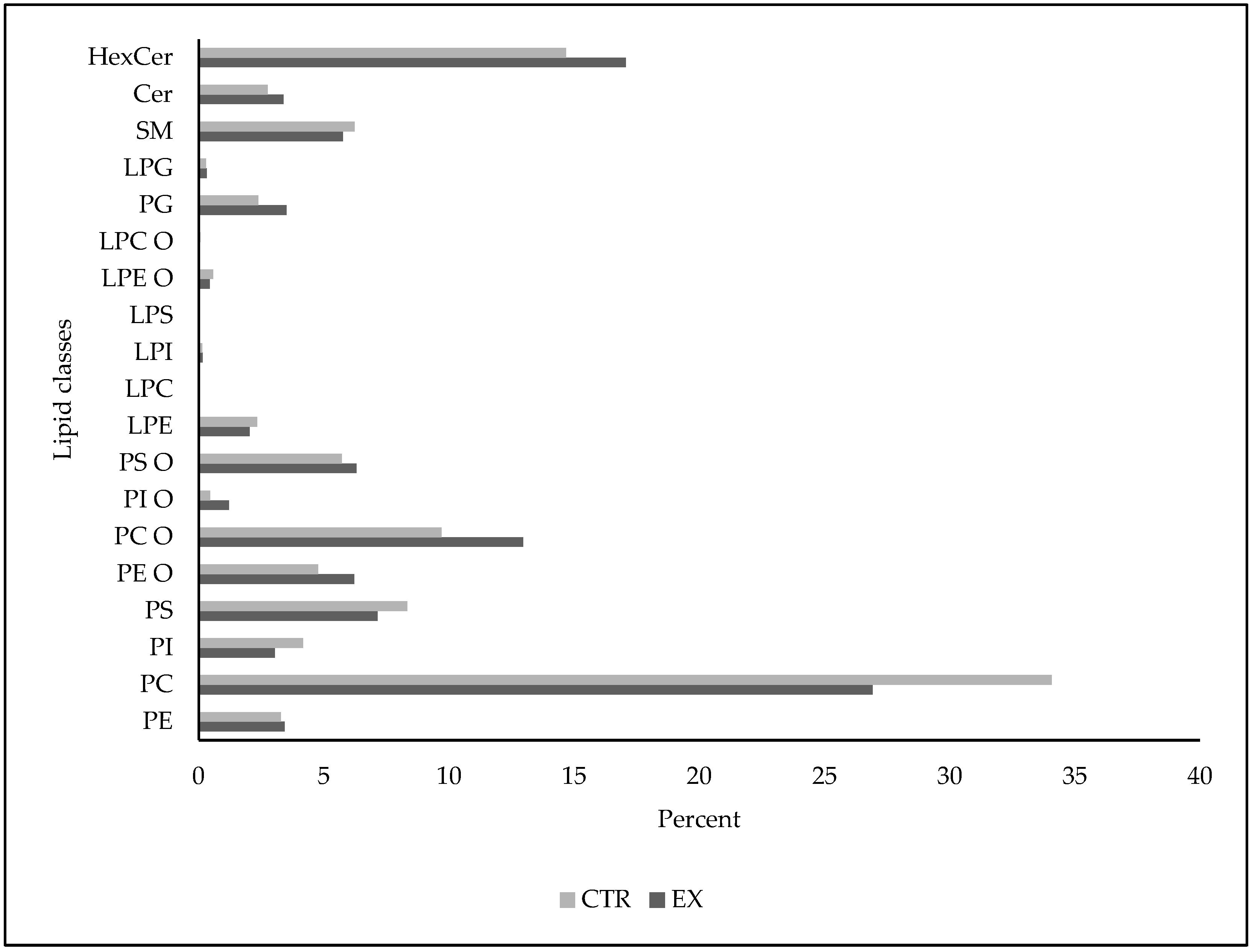
2.2. SM-VD3 Induces Changes in Plasma Phospholipids
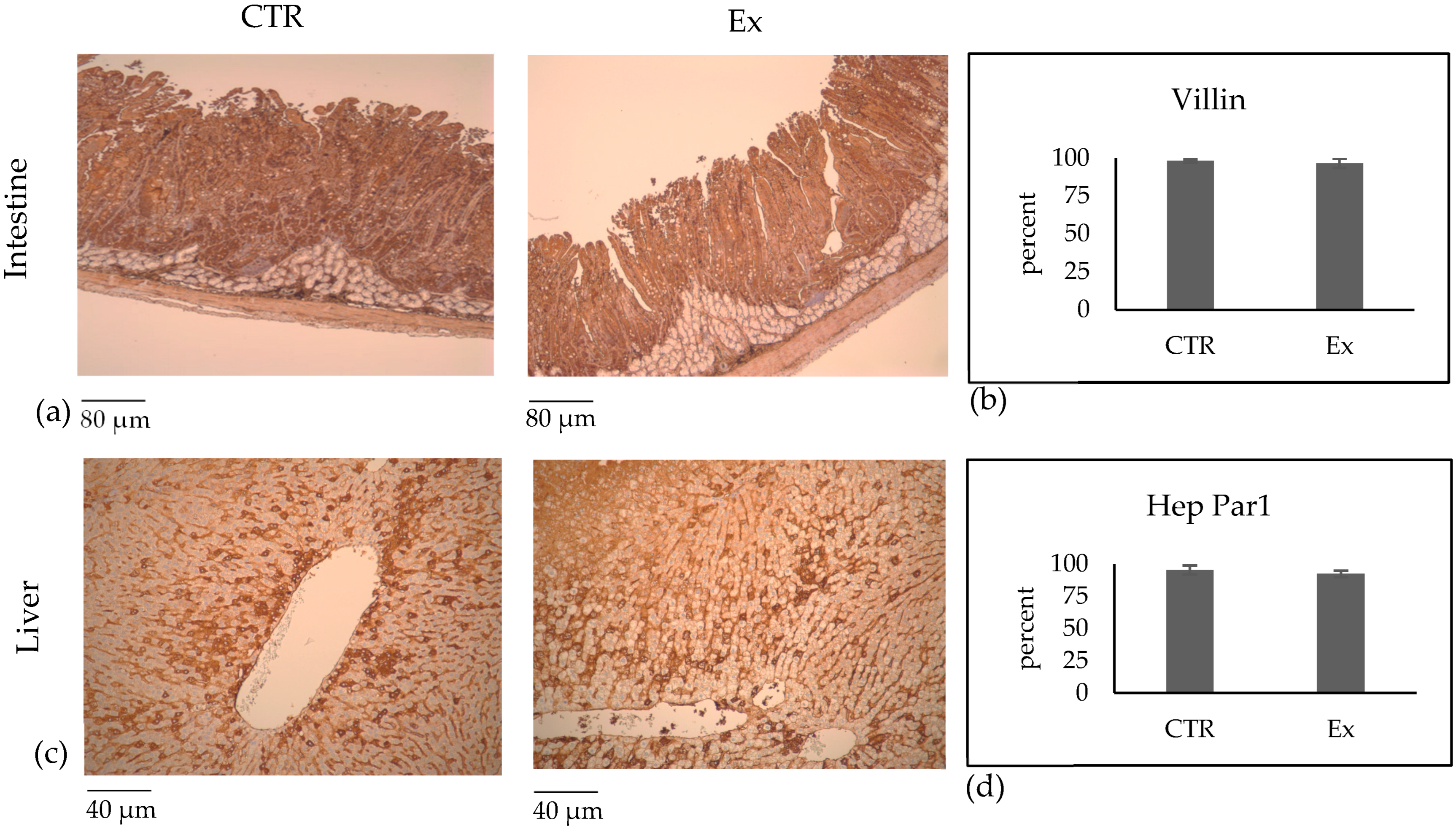
2.3. Effect of SM-VD3 on Intestine
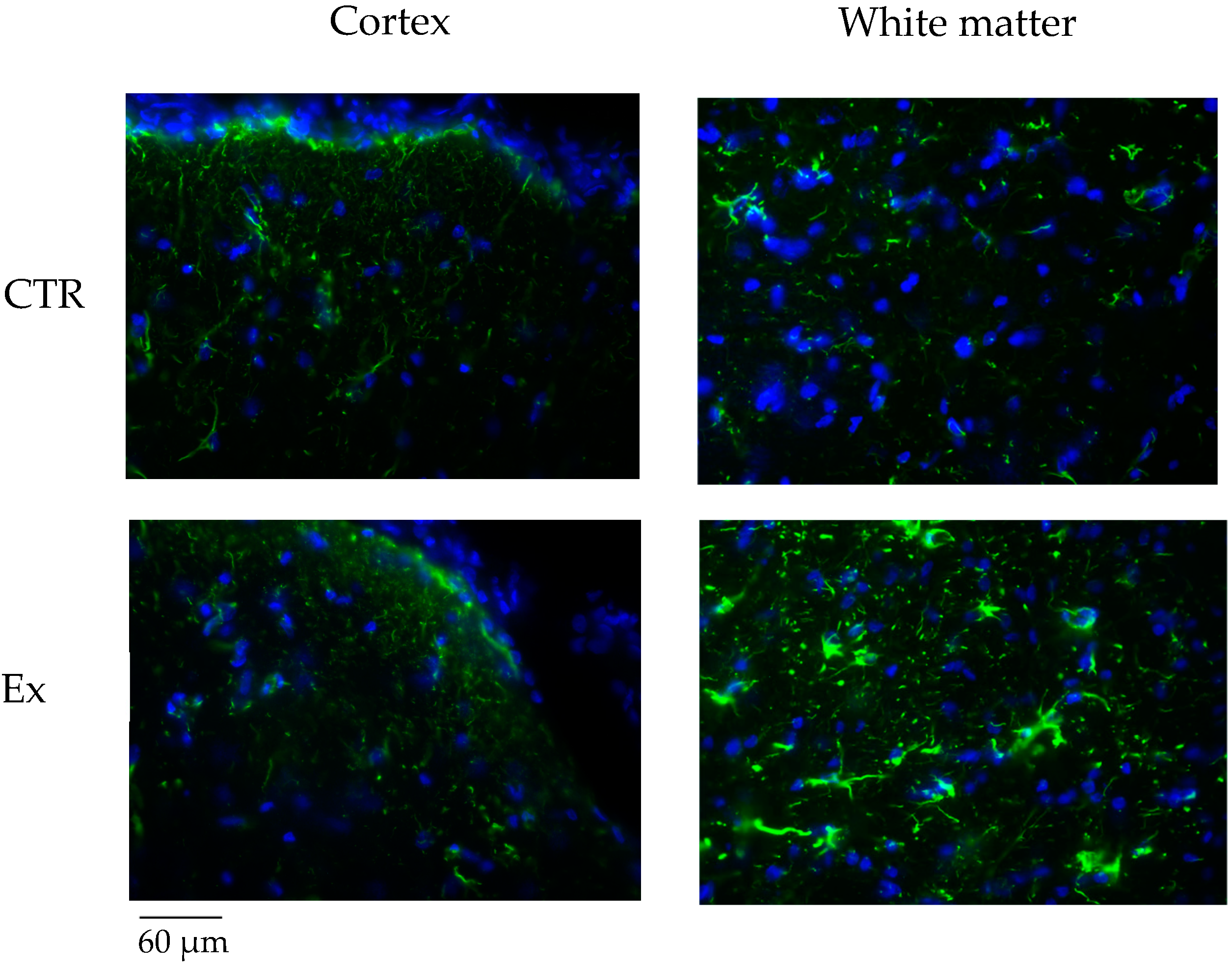
2.4. Effect of SM-VD3 on the Brain
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Animals and Treatment
4.2. Blood Samples
4.3. Tissue Samples and Treatment
4.4. Immunohistochemistry Analysis
4.5. Immunofluorescence
4.6. Lipid Analysis
4.7. LC-MS Analysis
| Time (min) | A (%) | B (%) | C (%) |
| 0.0 | 41 | 33 | 26 |
| 2.5 | 29.75 | 30.5 | 39.75 |
| 4.0 | 20.75 | 28.5 | 50.75 |
| 11.0 | 11.75 | 26.5 | 61.75 |
| 14.0 | 5.45 | 25.1 | 69.45 |
| 20.0 | 5.45 | 25.1 | 69.45 |
| 22.0 | 5.48 | 25.1 | 69.42 |
| 22.1 | 29.75 | 30.5 | 39.75 |
| 25.0 | Stop Run |
4.8. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bienias, K.; Fiedorowicz, A.; Sadowska, A.; Prokopiuk, S.; Car, H. Regulation of sphingomyelin metabolism. Pharmacol. Rep. 2016, 68, 570–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goñi, F.M. Sphingomyelin: What is it good for? Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 633, 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chakraborty, M.; Jiang, X.C. Sphingomyelin and its role in cellular signaling. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 991, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, X.C.; Chiang, Y.P. Sphingomyelin Synthase Family and Phospholipase Cs. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2022, 1372, 1377–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albi, E.; Lazzarini, R.; Magni, M.V. Reverse sphingomyelin-synthase in rat liver chromatin. FEBS Lett. 2003, 549, 152–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deevska, G.; Dotson, P.P.; Mitov, M.; Butterfield, D.A.; Nikolova-Karakashian, M. Onset of Senescence and Steatosis in Hepatocytes as a Consequence of a Shift in the Diacylglycerol/Ceramide Balance at the Plasma Membrane. Cells 2021, 10, 1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albi, E.; Lazzarini, R.; Viola Magni, M. Phosphatidylcholine/sphingomyelin metabolism crosstalk inside the nucleus. Biochem. J. 2008, 410, 381–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, F.S.; Costa, P.T.; Soares, A.M.S.; Fontes, A.L.; Pintado, M.E.; Vidigal, S.S.M.P.; Pimentel, L.L.; Rodríguez-Alcalá, L.M. Novel Lipids to Regulate Obesity and Brain Function: Comparing Available Evidence and Insights from QSAR In Silico Models. Foods 2023, 12, 2576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conte, C.; Cataldi, S.; Arcuri, C.; Mirarchi, A.; Lazzarini, A.; Garcia-Gil, M.; Beccari, T.; Curcio, F.; Albi, E. Vitamin D3 Enriches Ceramide Content in Exosomes Released by Embryonic Hippocampal Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 9287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartoccini, E.; Marini, F.; Damaskopoulou, E.; Lazzarini, R.; Cataldi, S.; Cascianelli, G.; Gil Garcia, M.; Albi, E. Nuclear lipid microdomains regulate nuclear vitamin D3 uptake and influence embryonic hippocampal cell differentiation. Mol. Biol. Cell 2011, 22, 3022–3031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Gil, M.; Pierucci, F.; Vestri, A.; Meacci, E. Crosstalk between sphingolipids and vitamin D3: Potential role in the nervous system. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2017, 174, 605–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yu, S.; Jiao, B.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, K.; Liu, B.; Zhang, X. Vitamin D3 Attenuates Neuropathic Pain via Suppression of Mitochondria-Associated Ferroptosis by Inhibiting PKCα/NOX4 Signaling Pathway. CNS Neurosci. Ther. 2024, 30, e70067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masbough, F.; Kouchek, M.; Koosha, M.; Salarian, S.; Miri, M.; Raoufi, M.; Taherpour, N.; Amniati, S.; Sistanizad, M. Investigating the Effect of High-Dose Vitamin D3 Administration on Inflammatory Biomarkers in Patients with Moderate to Severe Traumatic Brain Injury: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Iran J. Med. Sci. 2024, 49, 643–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Chen, L.; Chen, J.; Chen, Y. Calcitriol restrains microglial M1 polarization and alleviates dopaminergic degeneration in hemiparkinsonian mice by boosting regulatory T-cell expansion. Brain Behav. 2024, 14, e3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viljetić, B.; Blažetić, S.; Labak, I.; Ivić, V.; Zjalić, M.; Heffer, M.; Balog, M. Lipid Rafts: The Maestros of Normal Brain Development. Biomolecules 2024, 14, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cataldi, S.; Codini, M.; Cascianelli, G.; Tringali, S.; Tringali, A.R.; Lazzarini, A.; Floridi, A.; Bartoccini, E.; Garcia-Gil, M.; Lazzarini, R.; et al. Nuclear lipid microdomain as resting place of dexamethasone to impair cell proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 19832–19846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wang, K.K.W. Glial fibrillary acidic protein: From intermediate filament assembly and gliosis to neurobiomarker. Trends Neurosci. 2015, 38, 364–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meikle, P.J.; Barlow, C.K.; Mellett, N.A.; Mundra, P.A.; Bonham, M.P.; Larsen, A.; Cameron-Smith, D.; Sinclair, A.; Nestel, P.J.; Wong, G. Postprandial Plasma Phospholipids in Men Are Influenced by the Source of Dietary. Fat. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 2012–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Athman, R.; Louvard, D.; Robine, S. The epithelial cell cytoskeleton and intracellular trafficking. III. How is villin involved in the actin cytoskeleton dynamics in intestinal cells? Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2002, 283, G496–G502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sales, C.B.S.; Dias, R.B.; de Faro Valverde, L.; Bomfim, L.M.; Silva, L.A.; de Carvalho, N.C.; Bastos, J.L.A.; Tilli, T.M.; Rocha, G.V.; Soares, M.B.P.; et al. Hedgehog components are overexpressed in a series of liver cancer cases. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 19507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chen, G. The nutritional functions of dietary sphingomyelin and its applications in food. Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 1002574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.D. Alkaline sphingomyelinase: An old enzyme with novel implications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2006, 1761, 281–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reboul, E.; Goncalves, A.; Comera, C.; Bott, R.; Nowicki, M.; Landrier, J.F.; Jourdheuil-Rahmani, D.; Dufour, C.; Collet, X.; Borel, P. Vitamin D intestinal absorption is not a simple passive diffusion: Evidences for involvement of cholesterol transporters. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2011, 55, 691–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lecomte, M.; Bourlieu, C.; Meugnier, E.; Penhoat, A.; Cheillan, D.; Pineau, G.; Loizon, E.; Trauchessec, M.; Claude, M.; Ménard, O.; et al. Milk Polar Lipids Affect In Vitro Digestive Lipolysis and Postprandial Lipid Metabolism in Mice. J. Nutr. 2015, 145, 1770–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Geng, Y.; Yang, K.; Hu, Y.; Xue, M.; Cui, X.; Zhang, L.; Wang, S.; Li, T.; Luo, X.; et al. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 enhances the expression of phosphorus transporters via vitamin D receptor in ligated duodenal loops of Arbor Acres male broilers. Poult. Sci. 2024, 103, 104503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eguchi, K.; Mikami, D.; Sun, H.; Tsumita, T.; Takahashi, K.; Mukai, K.; Yuyama, K.; Igarashi, Y. Blood-brain barrier permeability analysis of plant ceramides. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0241640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, Y.; Zhao, J.; Liu, Q.; Liu, Y.; Liu, Y.; Tian, X.; Qiao, W.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chen, L. Human milk sphingomyelin: Function, metabolism, composition and mimicking. Food Chem. 2024, 447, 138991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deoni, S.C.; Beauchemin, J.; D’Sa, V.; Bonham, K.; Klepac-Ceraj, V. Enhanced Brain Myelination and Cognitive Development in Young Children Associated with Milk Fat Globule Membrane (MFGM) Intake: A Temporal Cohort Study. Res. Sq. 2024, rs.3.rs-4999582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alashmali, S. Nutritional roles and therapeutic potentials of dietary sphingomyelin in brain diseases. J. Clin. Biochem. Nutr. 2024, 74, 185–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albi, E.; Arcuri, C.; Kobayashi, T.; Tomishige, N.; Cas, M.D.; Paroni, R.; Signorelli, P.; Cerquiglini, L.; Troiani, S.; Gizzi, C.; et al. Sphingomyelin in Human Breast Milk might be Essential for the Hippocampus Maturation. Front. Biosci. 2022, 27, 247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bignami, A.; Dahl, D. Astrocyte-specific protein and radial glia in the cerebral cortex of newborn rat. Nature 1974, 252, 55–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rowitch, D.H.; Kriegstein, A.R. Developmental genetics of vertebrate glial-cell specification. Nature 2010, 468, 214–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stevens, B.; Allen, N.J.; Vazquez, L.E.; Howell, G.R.; Christopherson, K.S.; Nouri, N.; Micheva, K.D.; Mehalow, A.K.; Huberman, A.D.; Stafford, B.; et al. The classical complement cascade mediates CNS synapse elimination. Cell 2007, 31, 1164–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Achour, S.; Pascual, O. Glia: The many ways to modulate synaptic plasticity. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 57, 440–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.M.; Lodhi, I.J. Structural and functional roles of ether lipids. Protein Cell. 2018, 9, 96–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorninger, F.; Gundacker, A.; Zeitler, G.; Pollak, D.D.; Berger, J. Ether Lipid Deficiency in Mice Produces a Complex Behavioral Phenotype Mimicking Aspects of Human Psychiatric Disorders. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wanders, R.J.A.; Baes, M.; Ribeiro, D.; Ferdinandusse, S.; Waterham, H.R. The physiological functions of human peroxisomes. Physiol. Rev. 2023, 103, 957–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, C.J. Cellular signalling: The role of the peroxisome. Cell Signal. 1996, 8, 197–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, M.S.; Abe, Y.; Ali, F.; Youssef, M.; Honsho, M.; Fujiki, Y.; Katafuchi, T. Reduction of Ether-Type Glycerophospholipids, Plasmalogens, by NF-kappaB Signal Leading to Microglial Activation. J. Neurosci. 2017, 37, 4074–4092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larsson, S.; Voss, U. Neuroprotective effects of vitamin D on high fat diet- and palmitic acid-induced enteric neuronal loss in mice. BMC Gastroenterol. 2018, 18, 175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inskeep, K.A.; Crase, B.; Dayarathna, T.; Stottmann, R.W. SMPD4-mediated sphingolipid metabolism regulates brain and primary cilia development. Development 2024, 151, dev202645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Degroote, S.; Wolthoorn, J.; van Meer, G. The cell biology of glycosphingolipids. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2004, 15, 375–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moretti, S.; Nucci, N.; Menicali, E.; Morelli, S.; Bini, V.; Colella, R.; Mandarano, M.; Sidoni, A.; Puxeddu, E. The Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Is Expressed in Thyroid Carcinoma and Appears to Mediate Epithelial-Mesenchymal-Transition. Cancers 2020, 12, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arcuri, C.; Giambanco, I.; Bianchi, R.; Donato, R. Annexin V, annexin VI, S100A1 and S100B in developing and adult avian skeletal muscles. Neuroscience 2002, 109, 371–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pellegrino, R.M.; Di Veroli, A.; Valeri, A.; Goracci, L.; Cruciani, G. LC/MS Lipid Profiling from Human Serum: A New Method for Global Lipid Extraction. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 7937–7948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Fiorani, F.; Quattrone, A.; Cataldi, S.; Pellegrino, R.M.; Emiliani, C.; Arcuri, C.; Mirarchi, A.; Curone, G.; Menchetti, L.; Beccari, T.; et al. Effect of Sphingomyelin and Vitamin D3 Intake on the Rabbit Brain. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073269
Fiorani F, Quattrone A, Cataldi S, Pellegrino RM, Emiliani C, Arcuri C, Mirarchi A, Curone G, Menchetti L, Beccari T, et al. Effect of Sphingomyelin and Vitamin D3 Intake on the Rabbit Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073269
Chicago/Turabian StyleFiorani, Federico, Alda Quattrone, Samuela Cataldi, Roberto Maria Pellegrino, Carla Emiliani, Cataldo Arcuri, Alessandra Mirarchi, Giulio Curone, Laura Menchetti, Tommaso Beccari, and et al. 2025. "Effect of Sphingomyelin and Vitamin D3 Intake on the Rabbit Brain" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073269
APA StyleFiorani, F., Quattrone, A., Cataldi, S., Pellegrino, R. M., Emiliani, C., Arcuri, C., Mirarchi, A., Curone, G., Menchetti, L., Beccari, T., Floridi, C., Mandarano, M., Brecchia, G., & Albi, E. (2025). Effect of Sphingomyelin and Vitamin D3 Intake on the Rabbit Brain. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3269. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073269











