Host Proteins in Echinococcus multilocularis Metacestodes
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
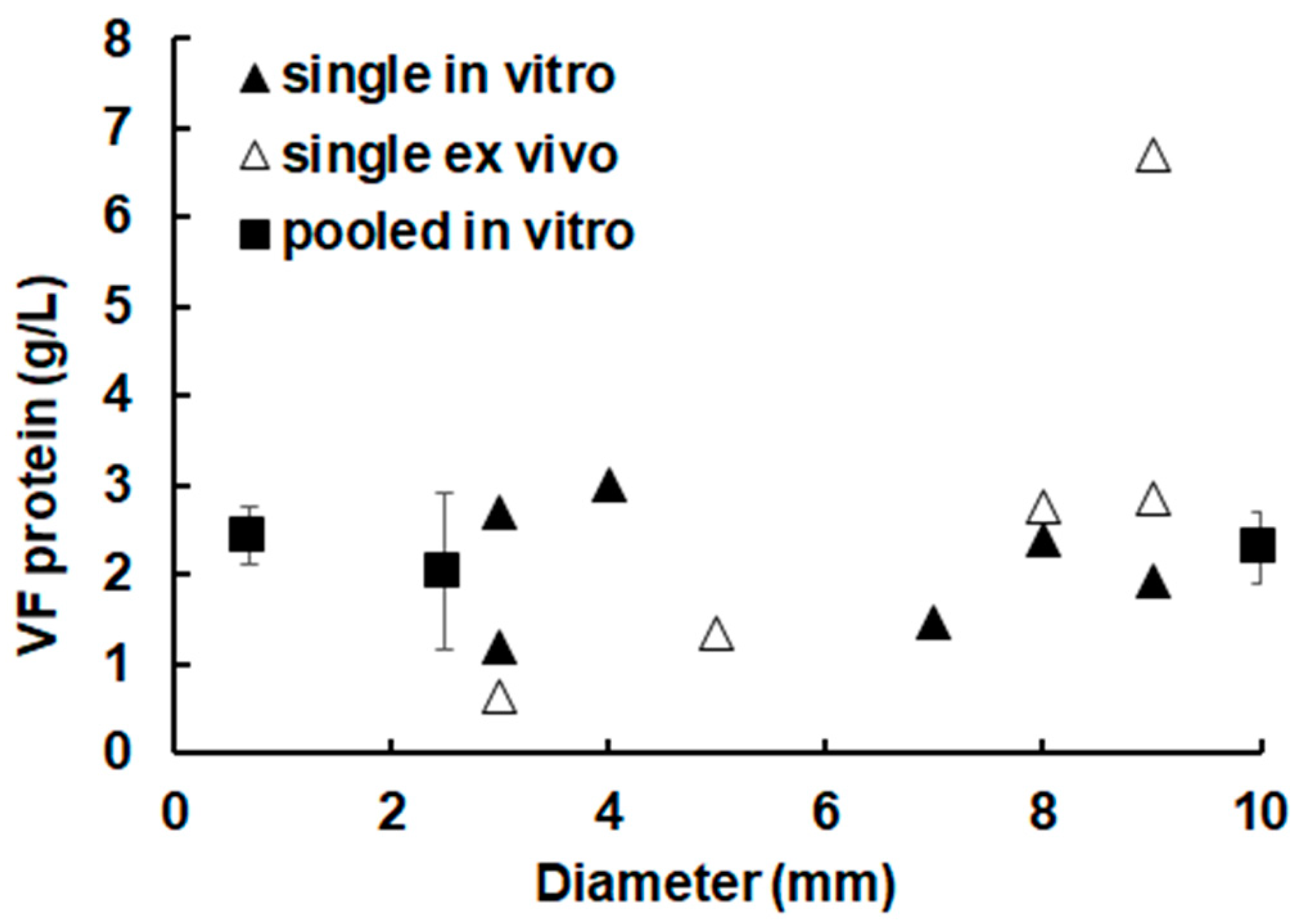
2.1. The Overall Protein Concentration in Metacestode Vesicles Remains Constant
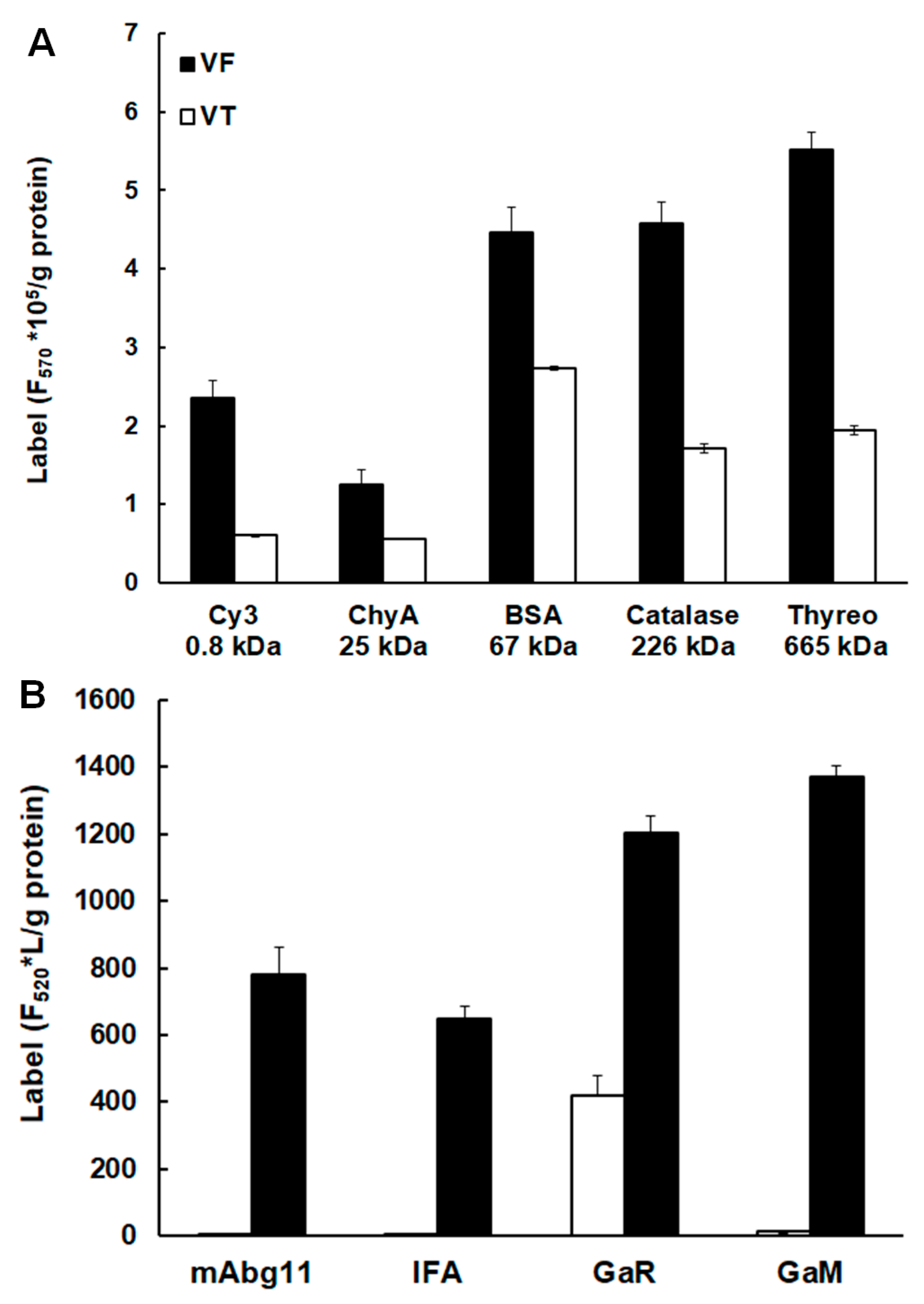
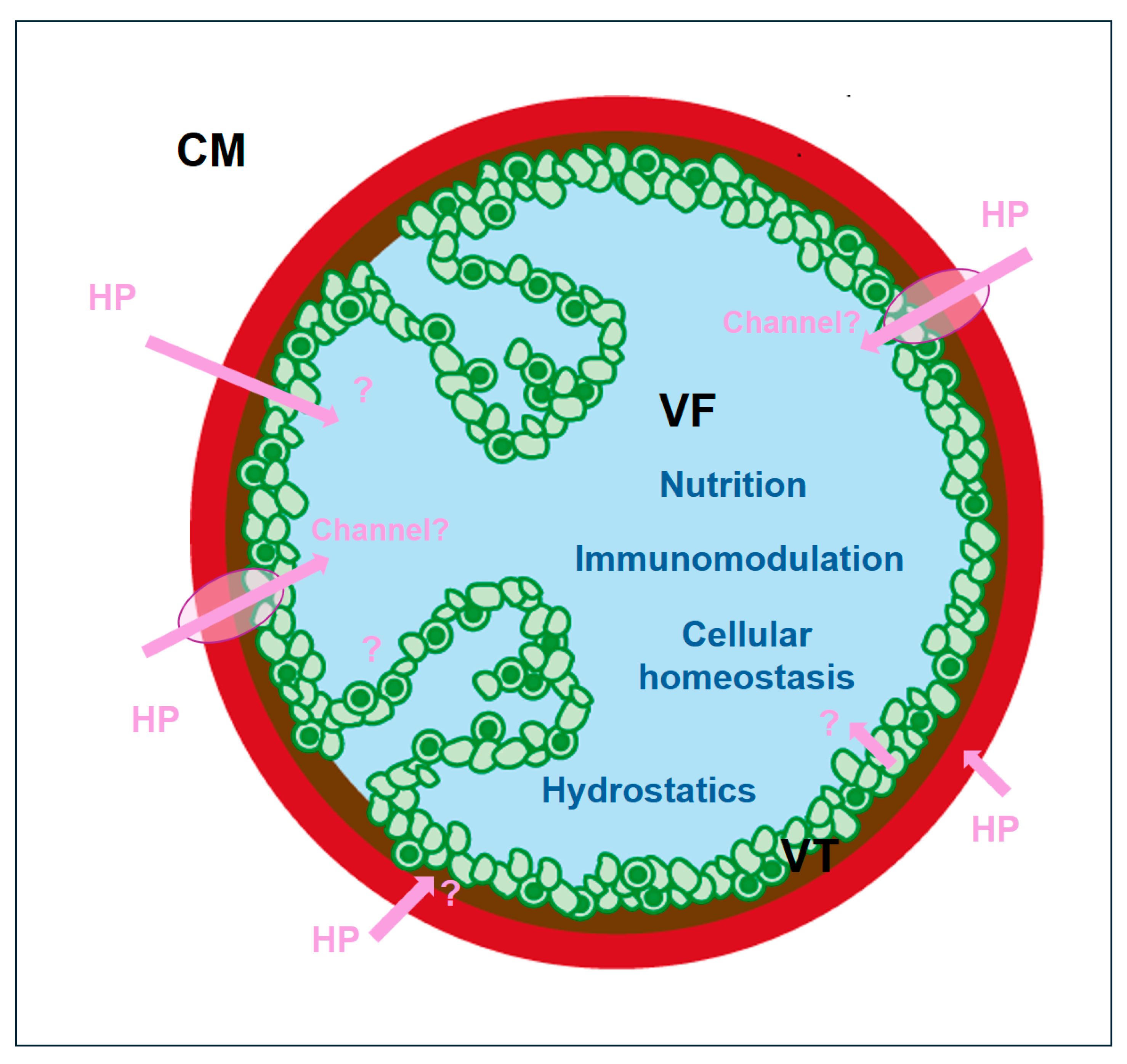
2.2. Uptake of Host Proteins by Metacestode Vesicles
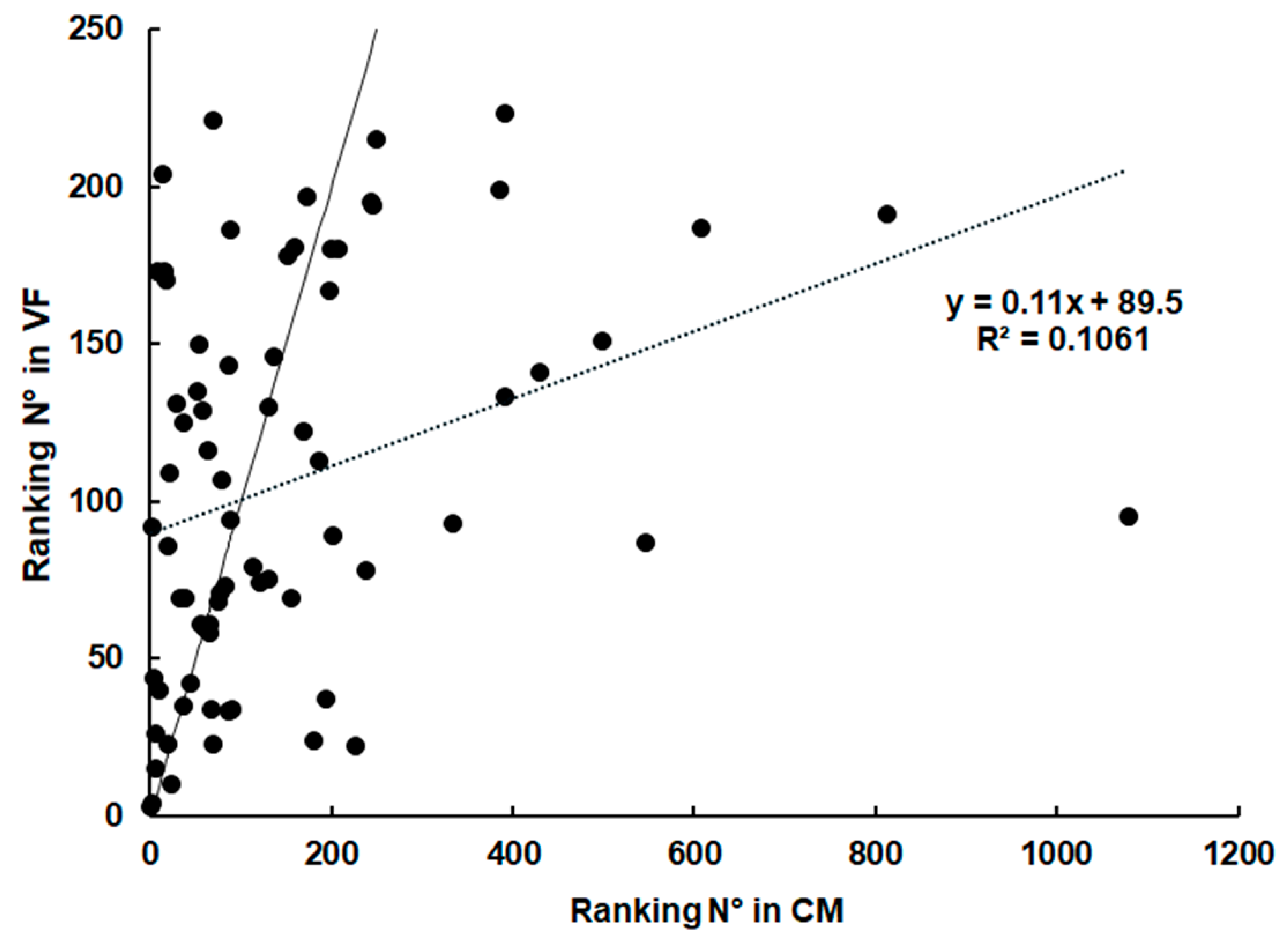
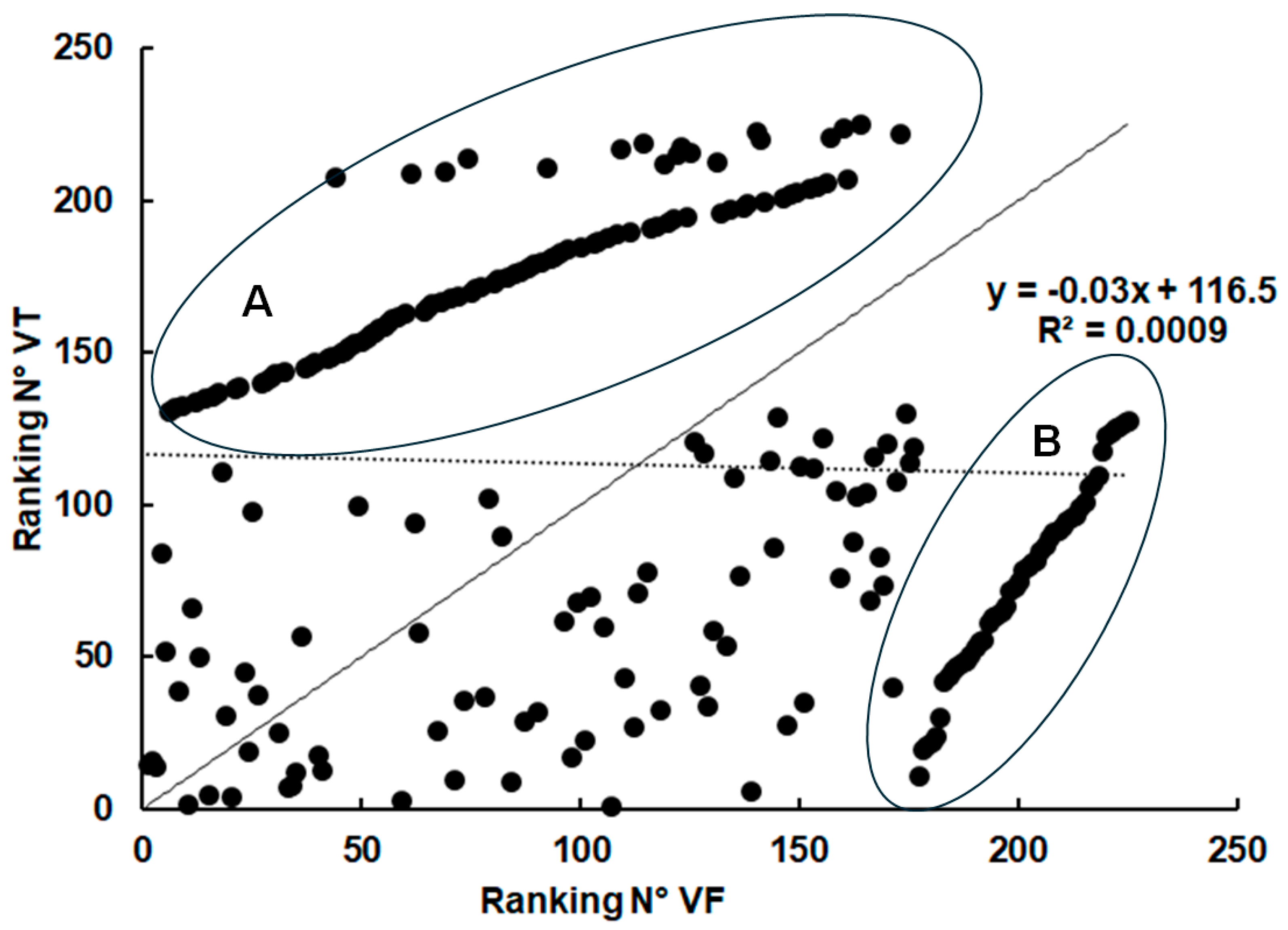
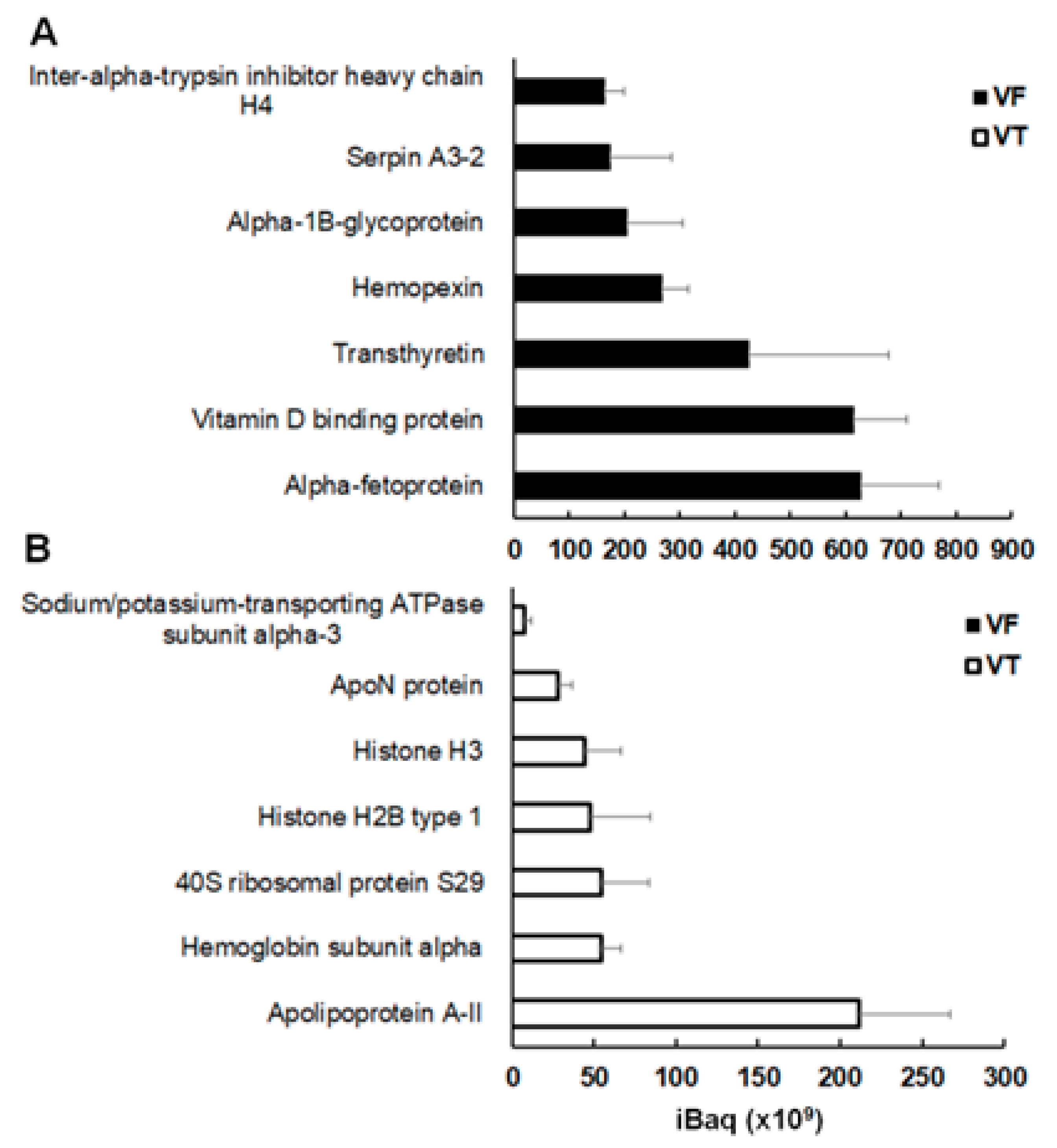
2.3. Spectrum of Host Proteins Differs Between Compartments
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Chemicals
4.2. In Vitro Culture of E. multilocularis Metacestodes
4.3. Parasite Maintenance and Ex Vivo Sample Preparation
4.4. Fluorescence Labeling of Marker Protein
4.5. Proteomics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bouwknegt, M.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Graham, H.; Robertson, L.J.; van der Giessen, J.W.; The Euro-FBP Workshop Participants. Prioritisation of food-borne parasites in Europe, 2016. Eurosurveillance 2018, 23, 17-00161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torgerson, P.R.; Devleesschauwer, B.; Praet, N.; Speybroeck, N.; Willingham, A.L.; Kasuga, F.; Rokni, M.B.; Zhou, X.N.; Fevre, E.M.; Sripa, B.; et al. World Health Organization Estimates of the Global and Regional Disease Burden of 11 Foodborne Parasitic Diseases, 2010: A Data Synthesis. PLoS Med 2015, 12, e1001920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casulli, A.; Abela-Ridder, B.; Petrone, D.; Fabiani, M.; Bobic, B.; Carmena, D.; Soba, B.; Zerem, E.; Gargate, M.J.; Kuzmanovska, G.; et al. Unveiling the incidences and trends of the neglected zoonosis cystic echinococcosis in Europe: A systematic review from the MEmE project. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2023, 23, e95–e107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottstein, B.; Stojkovic, M.; Vuitton, D.A.; Millon, L.; Marcinkute, A.; Deplazes, P. Threat of alveolar echinococcosis to public health--a challenge for Europe. Trends Parasitol. 2015, 31, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trotz-Williams, L.A.; Mercer, N.J.; Walters, J.M.; Wallace, D.; Gottstein, B.; Osterman-Lind, E.; Boggild, A.K.; Peregrine, A.S. Public health follow-up of suspected exposure to Echinococcus multilocularis in Southwestern Ontario. Zoonoses Public Health 2017, 64, 460–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Budke, C.M.; Deplazes, P.; Torgerson, P.R. Global socioeconomic impact of cystic echinococcosis. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2006, 12, 296–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romig, T.; Deplazes, P.; Jenkins, D.; Giraudoux, P.; Massolo, A.; Craig, P.S.; Wassermann, M.; Takahashi, K.; de la Rue, M. Ecology and life cycle patterns of Echinococcus species. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 95, 213–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, M.; Geissbuhler, U.; Howard, J.; Gottstein, B.; Spreng, D.; Frey, C.F. Clinical presentation, diagnosis, therapy and outcome of alveolar echinococcosis in dogs. Vet. Rec. 2015, 177, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kern, P.; Menezes da Silva, A.; Akhan, O.; Mullhaupt, B.; Vizcaychipi, K.A.; Budke, C.; Vuitton, D.A. The echinococcoses: Diagnosis, clinical management and burden of disease. Adv. Parasitol. 2017, 96, 259–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grüner, B.; Kern, P.; Mayer, B.; Grater, T.; Hillenbrand, A.; Barth, T.E.F.; Muche, R.; Henne-Bruns, D.; Kratzer, W.; Kern, P. Comprehensive diagnosis and treatment of alveolar echinococcosis: A single-center, long-term observational study of 312 patients in Germany. GMS Infect. Dis. 2017, 5, Doc01. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salm, L.A.; Lachenmayer, A.; Perrodin, S.F.; Candinas, D.; Beldi, G. Surgical treatment strategies for hepatic alveolar echinococcosis. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brunetti, E.; Kern, P.; Vuitton, D.A.; Writing Panel for the WHO-IWGE. Expert consensus for the diagnosis and treatment of cystic and alveolar echinococcosis in humans. Acta Trop. 2010, 114, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diaz, A.; Casaravilla, C.; Irigoin, F.; Lin, G.; Previato, J.O.; Ferreira, F. Understanding the laminated layer of larval Echinococcus I: Structure. Trends Parasitol. 2011, 27, 204–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koziol, U.; Rauschendorfer, T.; Zanon Rodriguez, L.; Krohne, G.; Brehm, K. The unique stem cell system of the immortal larva of the human parasite Echinococcus multilocularis. Evodevo 2014, 5, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brehm, K.; Koziol, U. On the importance of targeting parasite stem cells in anti-echinococcosis drug development. Parasite 2014, 21, 72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hustead, S.T.; Williams, J.F. Permeability studies on taenid metacestodes: I. Uptake of proteins by larval stages of Taenia taeniaeformis, T. crassiceps, and Echinococcus granulosus. J. Parasitol. 1977, 63, 314–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, S.Z.; Bahr, G.M.; Hira, P.R. Analysis of host components in hydatid cyst fluid and immunoblot diagnosis of human Echinococcus granulosus infection. Ann. Trop. Med. Parasitol. 1992, 86, 503–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monteiro, K.M.; de Carvalho, M.O.; Zaha, A.; Ferreira, H.B. Proteomic analysis of the Echinococcus granulosus metacestode during infection of its intermediate host. Proteomics 2010, 10, 1985–1999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziz, A.; Zhang, W.; Li, J.; Loukas, A.; McManus, D.P.; Mulvenna, J. Proteomic characterisation of Echinococcus granulosus hydatid cyst fluid from sheep, cattle and humans. J. Proteom. 2011, 74, 1560–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, S.J.; Xu, L.L.; Zhang, T.; Xu, M.; Yao, J.; Fang, C.Y.; Feng, Z.; Yang, P.Y.; Hu, W.; Liu, F. Proteomic characterization of larval and adult developmental stages in Echinococcus granulosus reveals novel insight into host-parasite interactions. J. Proteomics 2013, 84, 158–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaethner, M.; Preza, M.; Kaempfer, T.; Zumstein, P.; Tamponi, C.; Varcasia, A.; Hemphill, A.; Brehm, K.; Lundstrom-Stadelmann, B. Establishment and application of unbiased in vitro drug screening assays for the identification of compounds against Echinococcus granulosus sensu stricto. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2023, 17, e0011343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemphill, A.; Lundstroem-Stadelmann, B. Echinococcus: The model cestode parasite. Parasitology 2021, 148, 1401–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, K.M.; Lorenzatto, K.R.; de Lima, J.C.; Dos Santos, G.B.; Forster, S.; Paludo, G.P.; Carvalho, P.C.; Brehm, K.; Ferreira, H.B. Comparative proteomics of hydatid fluids from two Echinococcus multilocularis isolates. J. Proteom. 2017, 162, 40–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritler, D.; Rufener, R.; Li, J.V.; Kampfer, U.; Müller, J.; Buhr, C.; Schürch, S.; Lundström-Stadelmann, B. In vitro metabolomic footprint of the Echinococcus multilocularis metacestode. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 19438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Preza, M.; Kaethner, M.; Rufener, R.; Braga, S.; Uldry, A.C.; Heller, M.; Lundstrom-Stadelmann, B. Targeted and non-targeted proteomics to characterize the parasite proteins of Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2023, 13, 1170763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kramer, P.J. Water Relations of Plants; Academic Press: New York, NY, USA, 1983; pp. xi, 489. [Google Scholar]
- Fanali, G.; di Masi, A.; Trezza, V.; Marino, M.; Fasano, M.; Ascenzi, P. Human serum albumin: From bench to bedside. Mol. Aspects Med. 2012, 33, 209–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuller, M.E., 2nd; Brey, W.S., Jr. Nuclear magnetic resonance study of water sorbed on serum albumin. J. Biol. Chem. 1968, 243, 274–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tisi, D.K.; Emard, J.J.; Koski, K.G. Total protein concentration in human amniotic fluid is negatively associated with infant birth weight. J. Nutr. 2004, 134, 1754–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatti, G.; Romero, R.; Gomez-Lopez, N.; Chaiworapongsa, T.; Than, N.G.; Theis, K.R.; Galaz, J.; Gotsch, F.; Pique-Regi, R.; Berry, S.M.; et al. The amniotic fluid proteome changes with term labor and informs biomarker discovery in maternal plasma. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 3136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsnajafabadi, H.; Soheili, Z.S. Amniotic fluid characteristics and its application in stem cell therapy: A review. Int. J. Reprod. Biomed. 2022, 20, 627–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sako, Y.; Yamasaki, H.; Nakaya, K.; Nakao, M.; Ito, A. Cloning and characterization of cathepsin L-like peptidases of Echinococcus multilocularis metacestodes. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2007, 154, 181–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sako, Y.; Nakaya, K.; Ito, A. Echinococcus multilocularis: Identification and functional characterization of cathepsin B-like peptidases from metacestode. Exp. Parasitol. 2011, 127, 693–701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mejri, N.; Gottstein, B. Echinococcus multilocularis metacestode metabolites contain a cysteine protease that digests eotaxin, a CC pro-inflammatory chemokine. Parasitol. Res. 2009, 105, 1253–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marco, M.; Nieto, A. Metalloproteinases in the larvae of Echinococcus granulosus. Int. J. Parasitol. 1991, 21, 743–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Yan, M.; Xu, J.; Liang, Y.; Gu, X.; Xie, Y.; Jing, B.; Lai, W.; Peng, X.; Yang, G. Expression, Tissue Localization and Serodiagnostic Potential of Echinococcus granulosus Leucine Aminopeptidase. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Wei, W.; Zhou, P.; Liu, H.; Yang, B.; Feng, L.; Ge, R.L.; Li, R.; Tang, F. Enzymatic characteristics and preventive effect of leucine aminopeptidase against Echinococcus multilocularis. Acta Trop. 2021, 222, 106066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merckelbach, A.; Ruppel, A. Biochemical properties of an intracellular serpin from Echinococcus multilocularis. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2007, 156, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Sako, Y. The putative serine protease inhibitor (serpin) genes encoded on Echinococcus multilocularis genome and their expressions in metacestodal stage. Vet. Parasitol. 2017, 233, 20–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heiss, A.; DuChesne, A.; Denecke, B.; Grotzinger, J.; Yamamoto, K.; Renne, T.; Jahnen-Dechent, W. Structural basis of calcification inhibition by alpha 2-HS glycoprotein/fetuin-A. Formation of colloidal calciprotein particles. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 13333–13341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahnen-Dechent, W.; Schafer, C.; Heiss, A.; Grotzinger, J. Systemic inhibition of spontaneous calcification by the serum protein alpha 2-HS glycoprotein/fetuin. Z. Kardiol. 2001, 90 (Suppl. 3), 47–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Simone, G.; di Masi, A.; Ascenzi, P. Serum Albumin: A Multifaced Enzyme. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 10086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fasano, M.; Curry, S.; Terreno, E.; Galliano, M.; Fanali, G.; Narciso, P.; Notari, S.; Ascenzi, P. The extraordinary ligand binding properties of human serum albumin. IUBMB Life 2005, 57, 787–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duriez, P.; Fruchart, J.C. High-density lipoprotein subclasses and apolipoprotein A-I. Clin. Chim. Acta 1999, 286, 97–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, S.R.; Zhang, Y.; Rye, K.A. The pleiotropic effects of high-density lipoproteins and apolipoprotein A-I. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 37, 101689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bernthaler, P.; Epping, K.; Schmitz, G.; Deplazes, P.; Brehm, K. Molecular characterization of EmABP, an apolipoprotein A-I binding protein secreted by the Echinococcus multilocularis metacestode. Infect. Immun. 2009, 77, 5564–5571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartnikas, T.B. Known and potential roles of transferrin in iron biology. Biometals 2012, 25, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Power, D.M.; Elias, N.P.; Richardson, S.J.; Mendes, J.; Soares, C.M.; Santos, C.R. Evolution of the thyroid hormone-binding protein, transthyretin. Gen. Comp. Endocrinol. 2000, 119, 241–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, R.F. New perspectives on the vitamin D binding protein. Cell Biochem. Funct. 2012, 30, 445–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeksema, M.; van Eijk, M.; Haagsman, H.P.; Hartshorn, K.L. Histones as mediators of host defense, inflammation and thrombosis. Future Microbiol. 2016, 11, 441–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolaes, G.A.F.; Soehnlein, O. Targeting extranuclear histones to alleviate acute and chronic inflammation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2024, 45, 651–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Bosch, M.H.; Blom, A.B.; Schelbergen, R.F.; Vogl, T.; Roth, J.P.; Sloetjes, A.W.; van den Berg, W.B.; van der Kraan, P.M.; van Lent, P.L. Induction of canonical WNT signaling by the alarmins S100A8/A9 in murine knee joints: Implications for osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2016, 68, 152–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Huang, X.; Chang, X.; Yao, J.; He, Q.; Shen, Z.; Ji, Y.; Wang, K. S100-A9 protein in exosomes derived from follicular fluid promotes inflammation via activation of NF-kappaB pathway in polycystic ovary syndrome. J. Cell Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 114–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prieto, D.; Sotelo, N.; Seija, N.; Sernbo, S.; Abreu, C.; Duran, R.; Gil, M.; Sicco, E.; Irigoin, V.; Oliver, C.; et al. S100-A9 protein in exosomes from chronic lymphocytic leukemia cells promotes NF-kappaB activity during disease progression. Blood 2017, 130, 777–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Playford, M.C.; Kamiya, M. Immune response to Echinococcus multilocularis infection in the mouse model: A review. Jpn. J. Vet. Res. 1992, 40, 113–130. [Google Scholar]
- Zheng, Y. Strategies of Echinococcus species responses to immune attacks: Implications for therapeutic tool development. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2013, 17, 495–501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryser, H.J.; Hancock, R. Histones and basic polyamino acids stimulate the uptake of albumin by tumor cells in culture. Science 1965, 150, 501–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdurmen, W.P.R.; Mazlami, M.; Pluckthun, A. A quantitative comparison of cytosolic delivery via different protein uptake systems. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boubaker, G.; Hemphill, A.; Huber, C.O.; Spiliotis, M.; Babba, H.; Gottstein, B. Prevention and immunotherapy of secondary murine alveolar echinococcosis employing recombinant EmP29 antigen. PLoS Negl. Trop. Dis. 2015, 9, e0003795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Nouir, N.; Gianinazzi, C.; Gorcii, M.; Müller, N.; Nouri, A.; Babba, H.; Gottstein, B. Isolation and molecular characterization of recombinant Echinococcus granulosus P29 protein (recP29) and its assessment for the post-surgical serological follow-up of human cystic echinococcosis in young patients. Trans. R. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 355–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Chang, L.; Yang, J.; Wen, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wu, C.; Zhao, W. Immunogenicity of peptide-based vaccine composed of epitopes from Echinococcus granulosus rEg.P29. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e22819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhou, X.; Yang, Y.; Li, L. Protein translocation through alpha-helical channels and insertases. Structure 2025, 33, 15–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lundström-Stadelmann, B.; Rufener, R.; Ritler, D.; Zurbriggen, R.; Hemphill, A. The importance of being parasiticidal... an update on drug development for the treatment of alveolar echinococcosis. Food Waterborne Parasitol. 2019, 15, e00040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, J.; Boubaker, G.; Müller, N.; Uldry, A.-C.; Braga-Lagache, S.; Heller, M.; Hemphill, A. Investigating antiprotozoal chemotherapies with novel proteomic tools—Chances and limitations: A critical review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tajan, M.; Vousden, K.H. Dietary approaches to cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 2020, 37, 767–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaethner, M.; Zumstein, P.; Müller, J.; Preza, M.; Grossenbacher, P.; Bartetzko, A.; Vetter, L.; Lochner, M.; Schurch, S.; Regnault, C.; et al. Investigation of the threonine metabolism of Echinococcus multilocularis: The threonine dehydrogenase as a potential drug target in alveolar echinococcosis. Int. J. Parasitol. Drugs Drug Resist. 2025, 27, 100581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| FBS (%) | CM Protein (g/L) | Size Class | VF Protein (g/L) |
|---|---|---|---|
| S | 4.4 ± 0.7 | ||
| 5 | 2.6 ± 0.2 | M | 5.2 ± 0.8 |
| L | 5.2 ± 0.8 | ||
| S | 3.1 ± 0.5 | ||
| 10 | 3.8 ± 0.4 | M | 2.9 ± 0.7 |
| L | 5.3 ± 2.2 | ||
| S | 3.8 ± 0.1 | ||
| 20 | 5.5 ± 0.5 | M | 5.1 ± 0.6 |
| L | 4.3 ± 1.1 | ||
| S | 2.1 ± 0.2 | ||
| 50 | 11.5 ± 1.0 | M | 4.4 ± 1.7 |
| L | 3.4 ± 1.0 |
| Samples Analyzed | Unique Peptides | Non Redundant Proteins | Full Dataset |
|---|---|---|---|
| Culture medium (CM) | 12372 | 1170 | Table S1 |
| Vesicle fluid and tissue (VF and VT) | 1932 | 225 | Table S2 |
| Vesicle fluid (VF) ex vivo | 14730 | 1120 | Table S3 |
| Compartment | Protein | Accession | Origin | Rel. abu. (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Culture medium (CM) | ||||
| Serum albumin | P02769 | bovine | 21.4 ± 4.1 | |
| Serotransferrin | P12346 | rat | 2.0 ± 0.4 | |
| Hemiferrin | Q64599 | rat | 1.9 ± 0.9 | |
| Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein | P24090 | rat | 1.8 ± 0.3 | |
| Serum albumin | A0A0G2JSH5 | rat | 1.7 ± 0.3 | |
| Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta | P34058 | rat | 1.6 ± 0.3 | |
| Complement component C2 | Q8CIP8 | rat | 1.5 ± 0.3 | |
| Keratin, type II cytoskeletal | Q6IMF3 | rat | 1.3 ± 0.2 | |
| Vesicle tissue (VT) | ||||
| Histone H4 | G3X807 | bovine | 34.4 ± 6.9 | |
| Actin, alpha cardiac muscle 1 | Q3ZC07 | bovine | 14.0 ± 2.2 | |
| Apolipoprotein A-I | V6F9A2 | bovine | 12.8 ± 1.5 | |
| Peroxiredoxin-4 | Q9Z0V5 | rat | 7.5 ± 0.8 | |
| Heat shock protein HSP 90-beta | A0A0G2K793 | rat | 5.1 ± 0.3 | |
| Hemoglobin fetal subunit beta | P02081 | bovine | 4.0 ± 1.0 | |
| Tubulin beta-4B chain | Q6P9T8 | rat | 2.8 ± 0.1 | |
| Triosephosphate isomerase | Q6SA19 | rat | 2.6 ± 0.3 | |
| Vesicle fluid (VF) | ||||
| Alpha-2-HS-glycoprotein | B0JYN6 | bovine | 40.6 ± 5.7 | |
| Alpha-1-antiproteinase | P34955 | bovine | 17.0 ± 5.5 | |
| Serum albumin | P02769 | bovine | 16.2 ± 9.4 | |
| Serotransferrin | Q29443 | bovine | 5.5 ± 2.8 | |
| Fetuin-B | Q58D62 | bovine | 3.7 ± 0.8 | |
| Alpha-fetoprotein | Q3SZ57 | bovine | 1.7 ± 0.4 | |
| Vitamin D binding protein | I7CT57 | bovine | 1.6 ± 0.3 | |
| Albumin | B0JYQ0 | bovine | 1.3 ± 0.8 | |
| Vesicle fluid (VF) ex vivo | ||||
| Serum albumin | P07724 | mouse | 6.2 ± 1.4 | |
| Hemoglobin subunit beta-1 | P02088 | mouse | 4.6 ± 3.1 | |
| Histone H2B type 1-C/E/G | Q6ZWY9 | mouse | 4.0 ± 2.8 | |
| Hemoglobin subunit alpha | P01942 | mouse | 3.7 ± 2.0 | |
| Immunoglobulin gamma-1 chain C region | P01868 | mouse | 3.6 ± 1.3 | |
| Protein S100-A9 | P31725 | mouse | 3.6 ± 2.4 | |
| Histone H2A type 1-H | C0HKE9 | mouse | 3.3 ± 0.4 | |
| Histone H3.2 | P84228 | mouse | 3.0 ± 1.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Müller, J.; Zumkehr, B.; Heller, M.; Uldry, A.-C.; Braga-Lagache, S.; Lundström-Stadelmann, B. Host Proteins in Echinococcus multilocularis Metacestodes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073266
Müller J, Zumkehr B, Heller M, Uldry A-C, Braga-Lagache S, Lundström-Stadelmann B. Host Proteins in Echinococcus multilocularis Metacestodes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073266
Chicago/Turabian StyleMüller, Joachim, Beatrice Zumkehr, Manfred Heller, Anne-Christine Uldry, Sophie Braga-Lagache, and Britta Lundström-Stadelmann. 2025. "Host Proteins in Echinococcus multilocularis Metacestodes" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073266
APA StyleMüller, J., Zumkehr, B., Heller, M., Uldry, A.-C., Braga-Lagache, S., & Lundström-Stadelmann, B. (2025). Host Proteins in Echinococcus multilocularis Metacestodes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3266. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073266






