Identification of Six Cerebrospinal Fluid Metabolites Causally Associated with Anorexia Nervosa Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
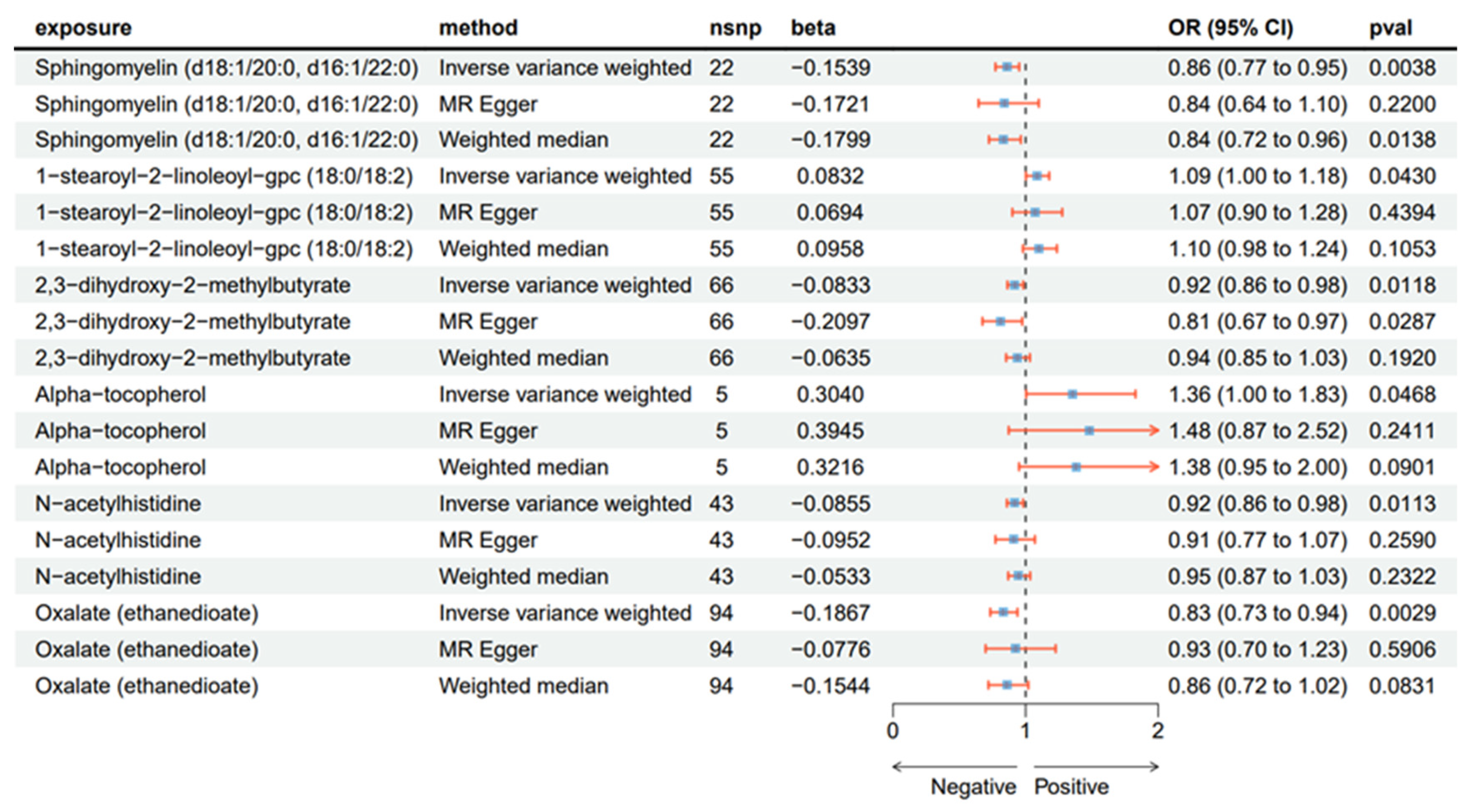
2.1. Causal Effect from CSF to AN
2.2. Sensitivity Analyses
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
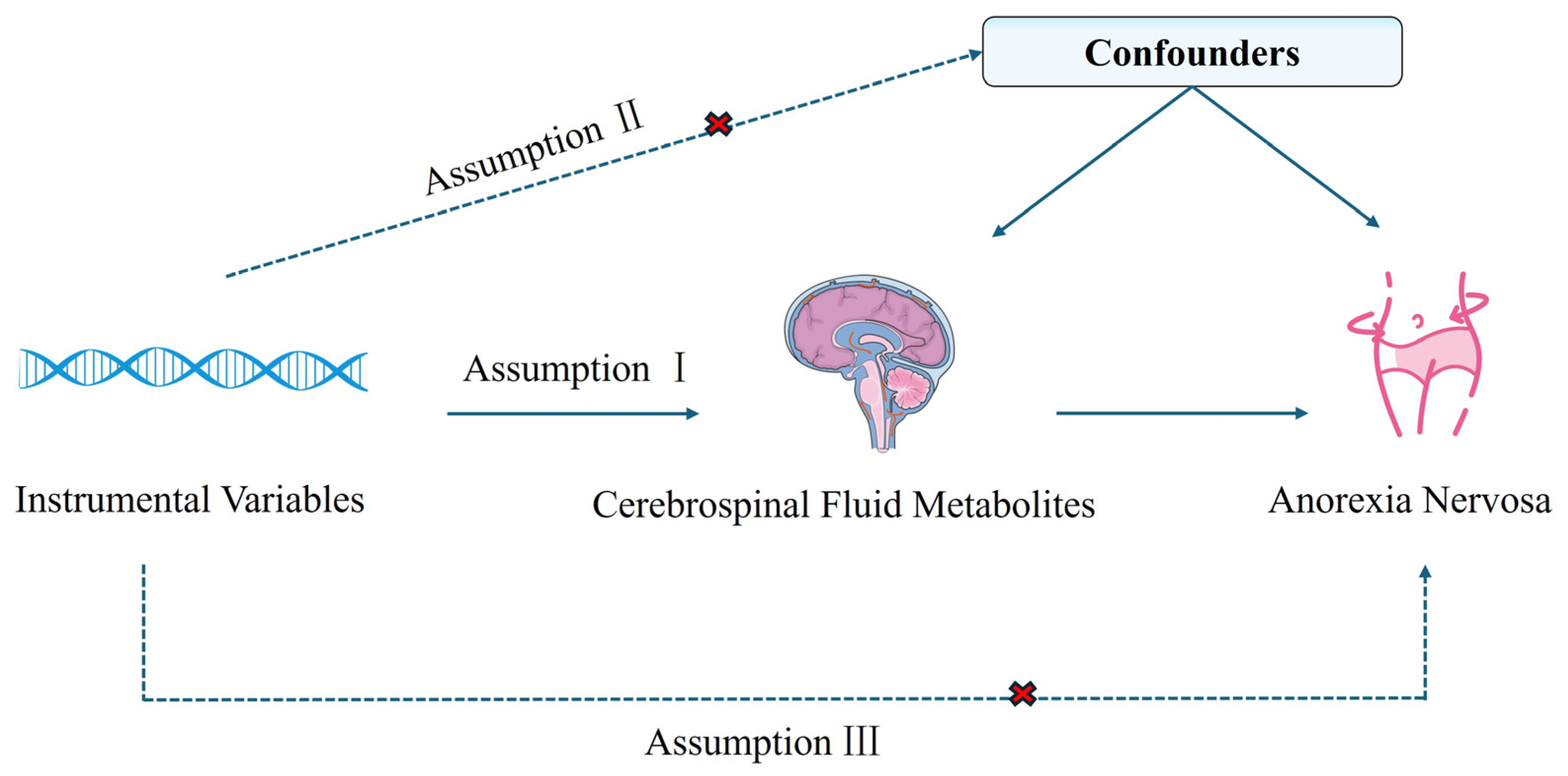
4.1. Study Design
4.2. Data Source
4.3. Instrumental Variable Filtration
4.4. Statistical Analyses
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Dobrescu, S.R.; Dinkler, L.; Gillberg, C.; Råstam, M.; Gillberg, C.; Wentz, E. Anorexia nervosa: 30-year outcome. Br. J. Psychiatry 2020, 216, 97–104. [Google Scholar]
- Strober, M.; Freeman, R.; Lampert, C.; Diamond, J.; Kaye, W. Controlled family study of anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa: Evidence of shared liability and transmission of partial syndromes. Am. J. Psychiatry 2000, 157, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bulik, C.M.; Sullivan, P.F.; Tozzi, F.; Furberg, H.; Lichtenstein, P.; Pedersen, N.L. Prevalence, heritability, and prospective risk factors for anorexia nervosa. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 2006, 63, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudson, J.I.; Hiripi, E.; Pope, H.G., Jr.; Kessler, R.C. The prevalence and correlates of eating disorders in the National Comorbidity Survey Replication. Biol. Psychiatry 2007, 61, 348–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watson, H.J.; Yilmaz, Z.; Thornton, L.M.; Hübel, C.; Coleman, J.R.I.; Gaspar, H.A.; Bryois, J.; Hinney, A.; Leppä, V.M.; Mattheisen, M.; et al. Genome-wide association study identifies eight risk loci and implicates metabo-psychiatric origins for anorexia nervosa. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 1207–1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pomposelli, J.J.; Flores, E.A.; Bistrian, B.R. Role of biochemical mediators in clinical nutrition and surgical metabolism. JPEN J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1988, 12, 212–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Bi, T. Causal effects of gut microbiota, metabolites, immune cells, liposomes, and inflammatory proteins on anorexia nervosa: A mediation joint multi-omics Mendelian randomization analysis. J. Affect. Disord. 2025, 368, 343–358. [Google Scholar]
- Watson, H.J.; Bulik, C.M. Update on the treatment of anorexia nervosa: Review of clinical trials, practice guidelines and emerging interventions. Psychol. Med. 2013, 43, 2477–2500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhausen, H.C.; Jakobsen, H.; Helenius, D.; Munk-Jørgensen, P.; Strober, M. A nation-wide study of the family aggregation and risk factors in anorexia nervosa over three generations. Int. J. Eat. Disord. 2015, 48, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.H.T.; Mo, J.M.Y.; Zhou, M.; Zhao, J.V.; Schooling, C.M.; He, B.; Luo, S.; Au Yeung, S.L. A two-sample Mendelian randomization study explores metabolic profiling of different glycemic traits. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Tang, Y.; Ning, K.; Li, X.; Hu, X. Investigating the causal associations between metabolic biomarkers and the risk of kidney cancer. Commun. Biol. 2024, 7, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.H.; Ivanisevic, J.; Siuzdak, G. Metabolomics: Beyond biomarkers and towards mechanisms. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2016, 17, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, Y.; Hui, L.; Sun, L.; Guo, D.; Shi, M.; Zhang, K.; Yang, P.; Wang, Y.; Liu, F.; Shen, O.; et al. Association Between Human Blood Metabolome and the Risk of Psychiatric Disorders. Schizophr. Bull. 2023, 49, 428–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Freuer, D.; Meisinger, C. Mediation-adjusted multivariable Mendelian randomisation study identified novel metabolites related to mental health. BMJ Ment. Health 2024, 27, e301230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tezenas du Montcel, C.; Duriez, P.; Cao, J.; Lebrun, N.; Ramoz, N.; Viltart, O.; Gorwood, P.; Tolle, V. The role of dysregulated ghrelin/LEAP-2 balance in anorexia nervosa. iScience 2023, 26, 107996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, H.; Chen, Y.; Meng, Z.; Chu, Z. The causal relationship between CSF metabolites and GBM: A two-sample mendelian randomization analysis. BMC Cancer 2024, 24, 1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mravinacová, S.; Alanko, V.; Bergström, S.; Bridel, C.; Pijnenburg, Y.; Hagman, G.; Kivipelto, M.; Teunissen, C.; Nilsson, P.; Matton, A.; et al. CSF protein ratios with enhanced potential to reflect Alzheimer’s disease pathology and neurodegeneration. Mol. Neurodegener. 2024, 19, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Artmann, H.; Grau, H.; Adelmann, M.; Schleiffer, R. Reversible and non-reversible enlargement of cerebrospinal fluid spaces in anorexia nervosa. Neuroradiology 1985, 27, 304–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curzio, O.; Calderoni, S.; Maestro, S.; Rossi, G.; De Pasquale, C.F.; Belmonti, V.; Apicella, F.; Muratori, F.; Retico, A. Lower gray matter volumes of frontal lobes and insula in adolescents with anorexia nervosa restricting type: Findings from a Brain Morphometry Study. Eur. Psychiatry 2020, 63, e27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Z.; Xing, N.; Hou, L. Cerebrospinal fluid metabolites as potential biomarkers for epilepsy: Insights from genome-wide association studies. Epilepsia Open 2024, 10, 233–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, R.; Lu, Q.; Kang, H.; Suridjan, I.; Kollmorgen, G.; Wild, N.; Deming, Y.; Van Hulle, C.A.; Anderson, R.M.; Zetterberg, H.; et al. CSF metabolites associated with biomarkers of Alzheimer’s disease pathology. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1214932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jie, J.; Gong, Y.; Hu, H.; Liu, S. The role of cerebrospinal fluid metabolites in mediating the impact of lipids on Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease: A two-step mendelian randomization analysis. J. Transl. Med. 2024, 22, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, B.; Ouyang, J.; Wang, P.; Peng, X. Mendelian randomization study of causal link from Cerebrospinal fluid metabolomics to neurodegenerative diseases. Neurogenetics 2024, 26, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emdin, C.A.; Khera, A.V.; Kathiresan, S. Mendelian Randomization. JAMA 2017, 318, 1925–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Harbord, R.M.; Sterne, J.A.; Timpson, N.; Davey Smith, G. Mendelian randomization: Using genes as instruments for making causal inferences in epidemiology. Stat. Med. 2008, 27, 1133–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davey Smith, G.; Hemani, G. Mendelian randomization: Genetic anchors for causal inference in epidemiological studies. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, R89–R98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheehan, N.A.; Didelez, V.; Burton, P.R.; Tobin, M.D. Mendelian randomisation and causal inference in observational epidemiology. PLoS Med. 2008, 5, e177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hannun, Y.A.; Obeid, L.M. Principles of bioactive lipid signalling: Lessons from sphingolipids. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2008, 9, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.A.; London, E. Structure and function of sphingolipid- and cholesterol-rich membrane rafts. J. Biol. Chem. 2000, 275, 17221–17224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaaraj, N.; Soliman, A.; Hamed, N.; Alyafei, F.; De Sanctis, V. Understanding the complex role of mTORC as an intracellular critical mediator of whole-body metabolism in anorexia nervosa: A mini review. Acta Biomed. 2021, 92, e2021170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oldershaw, A.; Hambrook, D.; Stahl, D.; Tchanturia, K.; Treasure, J.; Schmidt, U. The socio-emotional processing stream in Anorexia Nervosa. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2011, 35, 970–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzman, D.K.; Christensen, B.; Young, A.R.; Zipursky, R.B. Starving the brain: Structural abnormalities and cognitive impairment in adolescents with anorexia nervosa. Semin. Clin. Neuropsychiatry 2001, 6, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaye, W.H.; Fudge, J.L.; Paulus, M. New insights into symptoms and neurocircuit function of anorexia nervosa. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2009, 10, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uher, R.; Murphy, T.; Brammer, M.J.; Dalgleish, T.; Phillips, M.L.; Ng, V.W.; Andrew, C.M.; Williams, S.C.; Campbell, I.C.; Treasure, J. Medial prefrontal cortex activity associated with symptom provocation in eating disorders. Am. J. Psychiatry 2004, 161, 1238–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kojima, S.; Nagai, N.; Nakabeppu, Y.; Muranaga, T.; Deguchi, D.; Nakajo, M.; Masuda, A.; Nozoe, S.; Naruo, T. Comparison of regional cerebral blood flow in patients with anorexia nervosa before and after weight gain. Psychiatry Res. 2005, 140, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabir, F.; Atkinson, R.; Cook, A.L.; Phipps, A.J.; King, A.E. The role of altered protein acetylation in neurodegenerative disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 1025473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshikawa, T.; Nakamura, T.; Shibakusa, T.; Sugita, M.; Naganuma, F.; Iida, T.; Miura, Y.; Mohsen, A.; Harada, R.; Yanai, K. Insufficient intake of L-histidine reduces brain histamine and causes anxiety-like behaviors in male mice. J. Nutr. 2014, 144, 1637–1641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ermer, T.; Nazzal, L.; Tio, M.C.; Waikar, S.; Aronson, P.S.; Knauf, F. Oxalate homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2023, 19, 123–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouquegneau, A.; Dubois, B.E.; Krzesinski, J.M.; Delanaye, P. Anorexia nervosa and the kidney. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2012, 60, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reungjui, S.; Roncal, C.A.; Sato, W.; Glushakova, O.Y.; Croker, B.P.; Suga, S.; Ouyang, X.; Tungsanga, K.; Nakagawa, T.; Johnson, R.J.; et al. Hypokalemic nephropathy is associated with impaired angiogenesis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2008, 19, 125–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wada, S.; Nagase, T.; Koike, Y.; Kugai, N.; Nagata, N. A case of anorexia nervosa with acute renal failure induced by rhabdomyolysis; possible involvement of hypophosphatemia or phosphate depletion. Intern. Med. 1992, 31, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonoda, M.; Wakabayashi, K.; Tamura, N. Renal dysfunction in patients with eating disorders. Jpn. J. Psychosom. Med. 2016, 56, 453–459. [Google Scholar]
- Herzog, W.; Deter, H.C.; Fiehn, W.; Petzold, E. Medical findings and predictors of long-term physical outcome in anorexia nervosa: A prospective, 12-year follow-up study. Psychol. Med. 1997, 27, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, S.; Surapaneni, A.; Zheng, Z.; Rhee, E.P.; Coresh, J.; Hung, A.M.; Nadkarni, G.N.; Yu, B.; Boerwinkle, E.; Tin, A.; et al. NAT8 Variants, N-Acetylated Amino Acids, and Progression of CKD. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2020, 16, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silber, T.J.; Kass, E.J. Anorexia nervosa and nephrolithiasis. J. Adolesc. Health Care 1984, 5, 50–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heller, A.; Coffman, S.S.; Jarvis, K. Potentially Pathogenic Calcium Oxalate Dihydrate and Titanium Dioxide Crystals in the Alzheimer’s Disease Entorhinal Cortex. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 77, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yap, H.-M.; Lye, K.-L. An insight of vitamin E as neuroprotective agents. Prog. Microbes Mol. Biol. 2020, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zielińska, A.; Nowak, I. Tocopherols and tocotrienols as vitamin E. Chemik 2014, 68, 585–591. [Google Scholar]
- Berman, K.; Brodaty, H. Tocopherol (vitamin E) in Alzheimer’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. CNS Drugs 2004, 18, 807–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzi, A. Tocopherols, tocotrienols and tocomonoenols: Many similar molecules but only one vitamin E. Redox Biol. 2019, 26, 101259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agnello, E.; Malfi, G.; Costantino, A.M.; Massarenti, P.; Pugliese, M.; Fortunati, N.; Catalano, M.G.; Palmo, A. Tumour necrosis factor alpha and oxidative stress as maintaining factors in the evolution of anorexia nervosa. Eat. Weight Disord. 2012, 17, e194–e199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stockwell, B.R.; Jiang, X. The Chemistry and Biology of Ferroptosis. Cell Chem. Biol. 2020, 27, 365–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costa, I.; Barbosa, D.J.; Benfeito, S.; Silva, V.; Chavarria, D.; Borges, F.; Remião, F.; Silva, R. Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and their involvement in brain diseases. Pharmacol. Ther. 2023, 244, 108373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La Torre, M.E.; Villano, I.; Monda, M.; Messina, A.; Cibelli, G.; Valenzano, A.; Pisanelli, D.; Panaro, M.A.; Tartaglia, N.; Ambrosi, A.; et al. Role of Vitamin E and the Orexin System in Neuroprotection. Brain Sci. 2021, 11, 1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitra, N.K.; Xuan, K.Y.; Teo, C.C.; Xian-Zhuang, N.; Singh, A.; Chellian, J. Evaluation of neuroprotective effects of alpha-tocopherol in cuprizone-induced demyelination model of multiple sclerosis. Res. Pharm. Sci. 2020, 15, 602–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ambrogini, P.; Betti, M.; Galati, C.; Di Palma, M.; Lattanzi, D.; Savelli, D.; Galli, F.; Cuppini, R.; Minelli, A. α-Tocopherol and Hippocampal Neural Plasticity in Physiological and Pathological Conditions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaisman, N.; Wolfhart, D.; Sklan, D. Vitamin A metabolism in plasma of normal and anorectic women. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 46, 873–878. [Google Scholar]
- Fitzsimons, P.E.; Alston, C.L.; Bonnen, P.E.; Hughes, J.; Crushell, E.; Geraghty, M.T.; Tetreault, M.; O’Reilly, P.; Twomey, E.; Sheikh, Y.; et al. Clinical, biochemical, and genetic features of four patients with short-chain enoyl-CoA hydratase (ECHS1) deficiency. Am. J. Med. Genet. A 2018, 176, 1115–1127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cost, J.; Krantz, M.J.; Mehler, P.S. Medical complications of anorexia nervosa. Clevel. Clin. J. Med. 2020, 87, 361–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, R.; Tian, L.; Pan, Y.; Sun, X.; Huang, Z.; Fan, J.; Chen, J.; Zhang, K.; Li, S.; et al. Novel Metabolites Associated With Blood Pressure After Dietary Interventions. Hypertension 2024, 81, 1966–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muratore, A.F.; Attia, E. Current Therapeutic Approaches to Anorexia Nervosa: State of the Art. Clin. Ther. 2021, 43, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pournajaf, S.; Dargahi, L.; Javan, M.; Pourgholami, M.H. Molecular Pharmacology and Novel Potential Therapeutic Applications of Fingolimod. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 807639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekula, P.; Del Greco, M.F.; Pattaro, C.; Köttgen, A. Mendelian Randomization as an Approach to Assess Causality Using Observational Data. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2016, 27, 3253–3265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Au Yeung, S.L.; Gill, D. Standardizing the reporting of Mendelian randomization studies. BMC Med. 2023, 21, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panyard, D.J.; Kim, K.M.; Darst, B.F.; Deming, Y.K.; Zhong, X.; Wu, Y.; Kang, H.; Carlsson, C.M.; Johnson, S.C.; Asthana, S.; et al. Cerebrospinal fluid metabolomics identifies 19 brain-related phenotype associations. Commun. Biol. 2021, 4, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, L.; Yilmaz, Z.; Gaspar, H.; Walters, R.; Goldstein, J.; Anttila, V.; Bulik-Sullivan, B.; Ripke, S.; Thornton, L.; Hinney, A.; et al. Significant Locus and Metabolic Genetic Correlations Revealed in Genome-Wide Association Study of Anorexia Nervosa. Am. J. Psychiatry 2017, 174, 850–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowden, J.; Davey Smith, G.; Haycock, P.C.; Burgess, S. Consistent Estimation in Mendelian Randomization with Some Invalid Instruments Using a Weighted Median Estimator. Genet. Epidemiol. 2016, 40, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartwig, F.P.; Davies, N.M.; Hemani, G.; Davey Smith, G. Two-sample Mendelian randomization: Avoiding the downsides of a powerful, widely applicable but potentially fallible technique. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 1717–1726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Dai, C.-L.; Bian, X.-W.; Yao, X.-H. Identification of Six Cerebrospinal Fluid Metabolites Causally Associated with Anorexia Nervosa Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073248
Dai C-L, Bian X-W, Yao X-H. Identification of Six Cerebrospinal Fluid Metabolites Causally Associated with Anorexia Nervosa Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073248
Chicago/Turabian StyleDai, Cheng-Liang, Xiu-Wu Bian, and Xiao-Hong Yao. 2025. "Identification of Six Cerebrospinal Fluid Metabolites Causally Associated with Anorexia Nervosa Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073248
APA StyleDai, C.-L., Bian, X.-W., & Yao, X.-H. (2025). Identification of Six Cerebrospinal Fluid Metabolites Causally Associated with Anorexia Nervosa Risk: A Mendelian Randomization Analysis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3248. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073248




