New Perspectives in Studying Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility Biomarkers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Markers of Humoral Autoimmunity
3. Type 1 Diabetes Is an Immune-Mediated Disorder
4. Type 1 Diabetes Is a Genetic Disease
5. Importance of HLA in Determining Genetic Susceptibility
6. Multiple Genes Outside HLA
7. Type 1 Diabetes in Asia Is Also a Genetic Disease
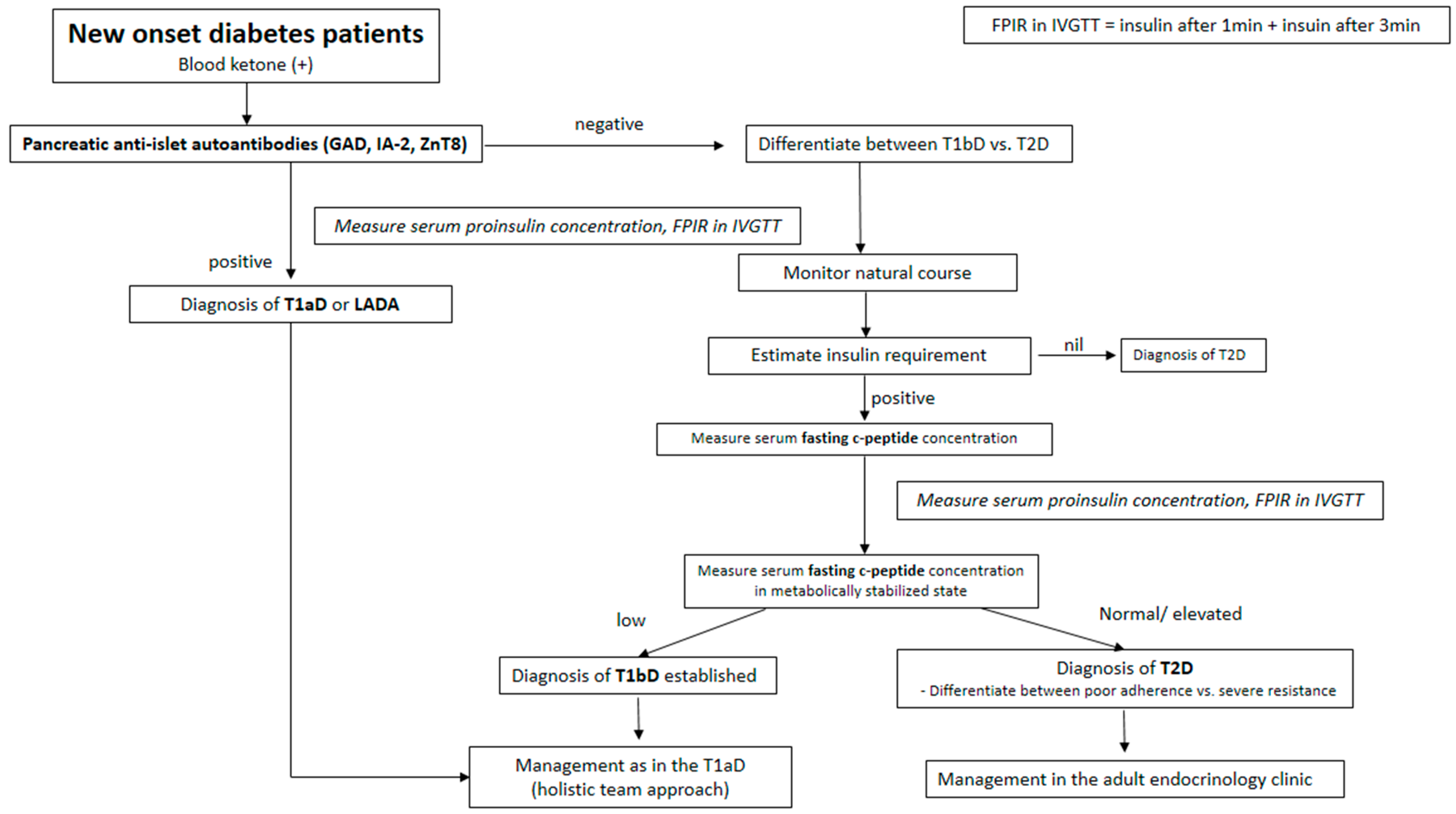
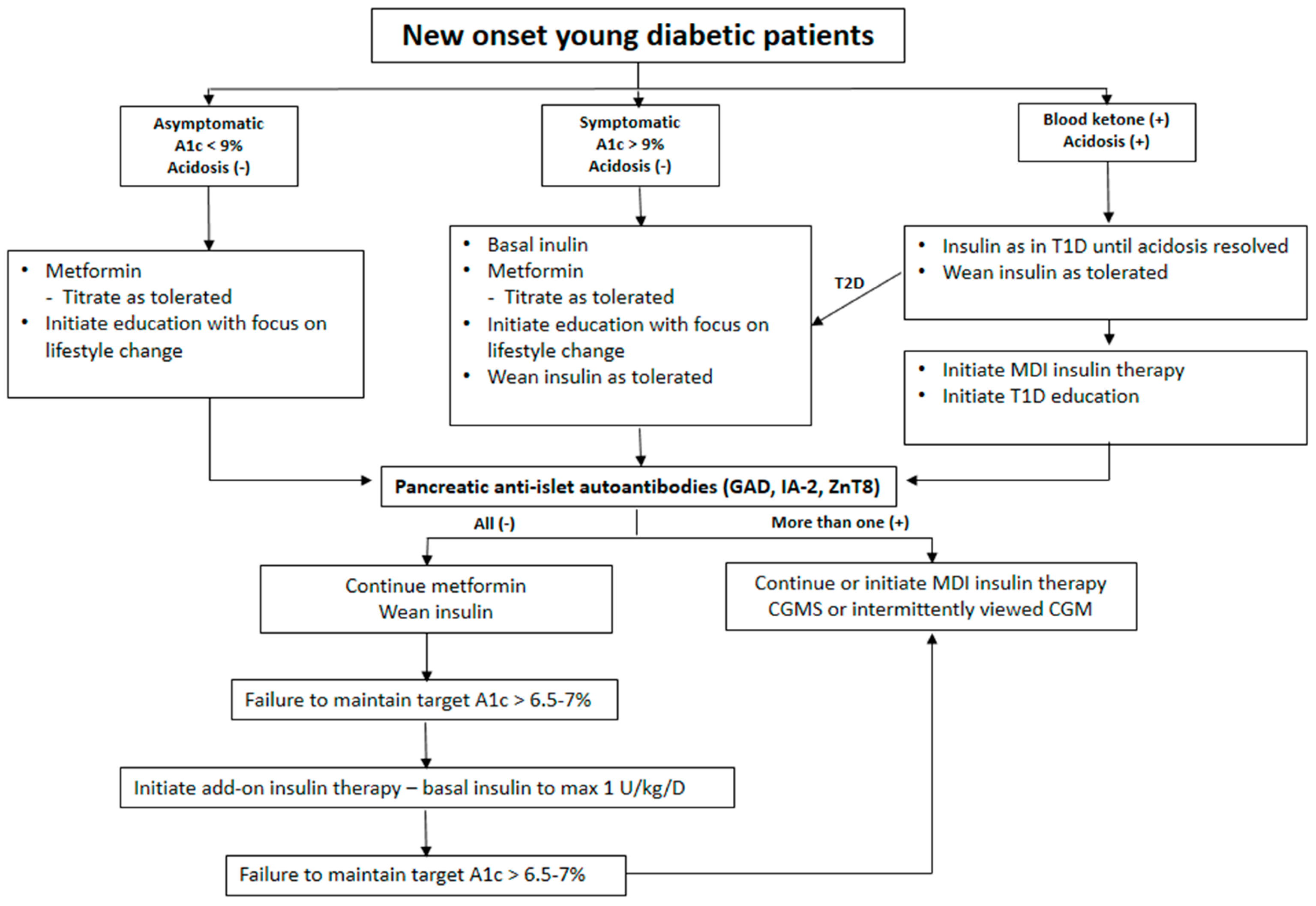
8. Adult-Onset Type 1 Diabetes
9. Ambiguous Autoimmune Pathogenesis
10. T1D as a β-Cell Disease
11. Role of Diet and Microbiota
12. Etiologic Heterogeneity and Future Prospect (Beyond Utilizing Biomarkers)
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Expert Committee on the Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Report of the expert committee on the diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care 2003, 26 (Suppl. 1), S5–S20.
- Tuomi, T.; Groop, L.C.; Zimmet, P.Z.; Rowley, M.J.; Knowles, W.J.; Mackay, I.R. Antibodies to glutamic acid decarboxylase reveal latent autoimmune diabetes in adults with a non-insulin-dependent onset of diabetes. Diabetes 1993, 42, 359–362. [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo, G.F.; Florin-Christensen, A.; Doniach, D. Islet cell antibodies in diabetes mellitus with autoimmune polyendocrine deficiencies. Lancet 1974, 2, 1279–1282. [Google Scholar]
- Verge, C.F.; Gianani, R.; Kawasaki, E.; Yu, L.; Pietropaolo, M.; Chase, H.P.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Jackson, R.A. Prediction of type 1 diabetes in first-degree relatives using a combination of insulin, GAD, and ICA512bdc/IA-2 autoantibodies. Diabetes 1996, 45, 926–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bingley, P.J.; Christie, M.R.; Bonifacio, E.; Bonfanti, R.; Shattock, M.; Fonte, M.; Bottazzo, G.F.; Gale, E.A. Combined analysis of autoantibodies improves prediction of IDDM in islet cell antibody-positive relatives. Diabetes 1994, 43, 1304–1310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bingley, P.J.; Bonifacio, E.; Williams, A.J.K.; Genovese, S.; Bottazzo, G.F.; Gale, E.A.M. Prediction of IDDM in the general population: Strategies based on combination of autoantibody markers. Diabetes 1997, 46, 1701–1710. [Google Scholar]
- Gepts, W. Islet changes suggesting a possible immune aetiology of human diabetes mellitus. Acta Endocrinol. 1976, 205, 95–106. [Google Scholar]
- Rohane, P.W.; Shimada, A.; Kim, D.T.; Edwards, C.T.; Charlton, B.; Shultz, L.D.; Fathman, C.G. Islet-infiltrating lymphocytes from prediabetic NOD mice rapidly transfer diabetes to NOD-scid/scid mice. Diabetes 1995, 44, 550–554. [Google Scholar]
- Wegmann, D.R.; Norbury-Glaser, M.; Daniel, D. Insulin-specific T cells are a predominant component of islet infiltrates in pre-diabetic NOD mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 1994, 24, 1853–1857. [Google Scholar]
- Castano, L.; Ziegler, A.G.; Ziegler, R.; Shoelson, S.; Eisenbarth, G.S. Characterization of insulin autoantibodies in relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 1993, 42, 1202–1209. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, D.; Gill, R.G.; Schloot, N.; Wegmann, D. Epitope specificity, cytokine production profile and diabetogenic activity of insulin-specific T cell clones isolated from NOD mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 1995, 25, 1056–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, M.B.; Allison, J.; Cram, D.S.; Thomas, H.E.; Demsey-Collier, M.; Silva, A.; Georgiou, H.M.; Kay, T.W.; Harrison, L.C.; Lew, A.M. Transgenic expression of mouse proinsulin II prevents diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice. Diabetes 1996, 46, 34–39. [Google Scholar]
- Nikoopour, E.; Cheung, R.; Bellemore, S.; Krougly, O.; Lee-Chan, E.; Stridsberg, M.; Singh, B. Vasostatin-1 antigenic epitope mapping for induction of cellular and humoral immune responses to chromogranin A autoantigen in NOD mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 1170–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckle, I.; Loaiza Naranjo, J.D.; Bergot, A.S.; Zhang, V.; Talekar, M.; Steptoe, R.J.; Thomas, R.; Hamilton-Williams, E.E. Tolerance induction by liposomes targeting a single CD8 epitope IGRP (206–214) in a model of type 1 diabetes is impeded by co-targeting a CD4(+) islet epitope. Immunol. Cell Biol. 2022, 100, 33–48. [Google Scholar]
- Edouard, P.; Hiserodt, J.C.; Plamondon, C.; Poussier, P. CD8+ T cells are required for adoptive transfer of the BB rat diabetic syndrome. Diabetes 1993, 42, 390–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Presa, M.; Chen, Y.G.; Grier, A.E.; Leiter, E.H.; Brehm, M.A.; Greiner, D.L.; Shultz, L.D.; Serreze, D.V. The presence and preferential activation of regulatory T cells diminish adoptive transfer of autoimmune diabetes by polyclonal nonobese diabetic (NOD) T cell effectors into NSG versus NOD-scid mice. J. Immunol. 2015, 195, 3011–3019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Z.; Diz, R.; Martin, A.J.; Morillon, Y.M.; Kline, D.E.; Li, L.; Wang, B.; Tisch, R. Long-term remission of diabetes in NOD mice is induced by nondepleting anti-CD4 and anti-CD8 antibodies. Diabetes 2012, 61, 2871–2880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, Y.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Twells, R.C.; Muxworthy, C.; Hunter, K.M.; Wilson, A.; Merriman, M.E.; Cox, R.D.; Merriman, T.; Cucca, F.; et al. Fine mapping of the diabetes-susceptibility locus, IDDM4, on chromosome 11q13. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1998, 63, 547–556. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hawkes, C.H. Twin studies in diabetes mellitus. Diabet. Med. 1997, 17, 347–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nilsen, E.M.; Gjertsen, H.A.; Jensen, K.; Brandzaeg, P.; Lundin, K.E. Gluten activation of peripheral blood T cells induces a Th0-like cytokine pattern in both coeliac patients and controls. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 1996, 103, 295–303. [Google Scholar]
- Kyvik, K.O.; Green, A.; Beck-Nielsen, H. Concordance rates of insulin dependent diabetes mellitus: A population based study of young Danish twins. BMJ 1995, 311, 913–917. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Redondo, M.J.; Jeffrey, J.; Fain, P.R.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Orban, T. Concordance for islet autoimmunity among monozygotic twins. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 2849–2850. [Google Scholar]
- Bottazzo, G.F.; Dean, B.M.; McNally, J.M.; MacKay, E.H.; Swift, P.G.; Gamble, D.R. In situ characterization of autoimmune phenomena and expression of HLA molecules in the pancreas in diabetic insulitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 1985, 313, 353–360. [Google Scholar]
- Nerup, J.; Platz, P.; Andersen, O.; Christy, M.; Lyngsøe, J.; Poulsen, J.; Ryder, L.; Thomsen, M.; Nielsen, L.; Svejgaard, A. HLA antigens and diabetes mellitus. Lancet 1974, 2, 864–866. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Todd, J.A.; Bell, J.I.; McDevitt, H.O. HLA-DQB gene contributes to susceptibility and resistance to insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Nature 1987, 329, 599–604. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Davies, J.L.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Bennett, S.T.; Copeman, J.B.; Cordell, H.J.; Pritchard, L.E.; Reed, P.W.; Gough, S.C.L.; Jenkins, S.C.; Palmer, S.M.; et al. A genome-wide search for human type 1 diabetes susceptibility genes. Nature 1994, 371, 130–136. [Google Scholar]
- Erlich, H.A.; Zeidler, A.; Chang, J.; Shaw, S.; Raffel, L.J.; Klitz, W.; Beshkov, Y.; Costin, G.; Pressman, S.; Bugawan, T.; et al. HLA class II alleles and susceptibility and resistance to insulin dependent diabetes mellitus in Mexican-American families. Nat. Genet. 1993, 3, 358–364. [Google Scholar]
- van Lummel, M.; Van Veelen, P.A.; De Ru, A.H.; Janssen, G.; Pool, J.; Laban, S.; Joosten, A.M.; Nikolic, T.; Drijfhout, J.W.; Mearin, M.L.; et al. Dendritic cells guide islet autoimmunity through a restricted and uniquely processed peptidome presented by high-risk HLA-DR. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 3253–3263. [Google Scholar]
- Wolf, E.; Spencer, K.M.; Cudworth, A.G. The genetic susceptibility of type1 (insulin-dependent) diabetes; analysis of the HLA-DR association. Diabetologia 1983, 24, 224–230. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, J.A.; Valdes, A.M.; Cook, M.; Klitz, W.; Thomson, G.; Erlich, H.A. The role of HLA class II genes in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus: Molecular analysis of 180 caucasian, multiplex families. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1996, 59, 1134–1148. [Google Scholar]
- Baisch, J.M.; Weeks, T.; Giles, R.; Hoover, M.; Stastny, P.; Capra, J.D. Analysis of HLA-DQ genotypes and susceptibility in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1990, 322, 1836–1841. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y. Why is type 1 diabetes uncommon in Asia? Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2006, 1079, 31–40. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.; She, J.X.; Wang, C.-Y.; Lee, H.; Babu, S.; Erlich, H.A.; Noble, J.A.; Eisenbarth, G.S. Common susceptibility and transmission pattern of HLA DRB1-DQB1 haplotypes to Korean and Caucasian patients with type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2000, 85, 4538–4542. [Google Scholar]
- Suarez, B.K. The affected sib pair IBD distribution for HLA-linked disease susceptibility genes. Tissue Antigens 1978, 12, 87–93. [Google Scholar]
- The Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium; Nejentsev, S.; Howson, J.M.M.; Walker, N.M.; Szeszko, J.; Field, S.F.; Stevens, H.E.; Reynolds, P.; Hardy, M.; King, E.; et al. Localization of type 1 diabetes susceptibility to the MHC class I genes HLA-B, HLA-A. Nature 2007, 450, 887–892. [Google Scholar]
- Noble, J.A.; Erlich, H.A. Genetics of type 1 diabetes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a007732. [Google Scholar]
- Barratt, B.J.; Payne, F.; Lowe, C.E.; Hearmann, R.; Heally, B.C.; Harold, D.; Concannon, P.; Gharani, N.; McCarthy, M.I.; Olavesen, M.G.; et al. Remapping the insulin gene/ IDDM2 locus in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1884–1889. [Google Scholar]
- Bottini, N.; Musumeci, L.; Alonso, A.; Rahmouni, S.; Nika, K.; Rostamkhani, M.; MacMurray, T. A functional variant of lymphoid tyrosine phosphatase is associated with type 1 disease. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 337–338. [Google Scholar]
- Hakonarson, H.; Grant, S.F.; Bradfield, J.P.; Marchand, L.; Kim, C.E.; Glessner, J.T.; Grabs, R.; Casalunovo, T.; Taback, S.P.; Frackelton, E.C.; et al. A genome-wide association study identifies KIAA0350 as a type 1 diabetes gene. Nature 2007, 448, 591–594. [Google Scholar]
- Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium. Genome-wide association study of 14,000 cases of seven common diseases and 3,000 shared controls. Nature 2007, 447, 661–678. [Google Scholar]
- Barrett, J.C.; Clayton, D.G.; Concannon, P.; Akolkar, B.; Cooper, J.D.; Erlich, H.A.; Julier, C.; Morahan, G.; Nerup, J.; Nierras, C.; et al. Genome-wide association study and meta-analysis find that over 40 loci affect risk of type 1 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 703–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lowe, C.E.; Cooper, J.D.; Brusko, T.; Walker, N.M.; Smyth, D.J.; Bailey, R.; Bourget, K.; Plagnol, V.; Field, S.; Atkinson, M.; et al. Large-scale genetic fine mapping and genotype-phenotype associations implicate polymorphism in the IL2RA region in type 1 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 1074–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, Y.; Concannon, P. Molecular-genetic characterization of common, noncoding UBASH3A variants associated with type 1 diabetes. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2018, 26, 1060–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pociot, F.; McDermott, M.F. Genetics of type1 diabetes mellitus. Genes. Immun. 2002, 3, 235–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pugliese, A.; Zeller, M.; Fernandez, A., Jr.; Zalcberg, L.J.; Bartlett, R.J.; Ricordi, C.; Pietropaolo, M.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Bennett, S.T.; Patel, D.D. The insulin gene is transcribed in the human thymus and transcription levels correlated with allelic variation at the INS VNTR-IDDM2 susceptibility locus for type 1 diabetes. Nat. Genet. 1997, 15, 293–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vafiadis, P.; Bennett, S.T.; Todd, J.A.; Nadeau, J.; Grabs, R.; Goodyer, C.G.; Wickramasinghe, S.; Colle, E.; Polychronakos, C. Insulin expression in human thymus is modulated by INS VNTR alleles at the IDDM2 locus. Nat. Genet. 1997, 15, 289–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Kawasaki, E.; Kelemen, K.; Yu, L.; Schiller, M.R.; Rewers, M.; Mizuta, M.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Hutton, J.C. Humoral autoreactivity to an alternatively spliced variant of ICA512/IA-2 in Type I diabetes. Diabetologia 2000, 43, 1293–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diez, J.; Park, Y.; Zeller, M.; Brown, D.; Garza, D.; Ricordi, C.; Hutton, J.; Eisenbarth, G.S.; Pugliese, A. Differential splicing of the IA-2 mRNA in pancreas and lymphoid organs as a permissive genetic mechanism for autoimmunity against the IA-2 type 1 diabetes autoantigen. Diabetes 2001, 50, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierabracci, A. Type 1 diabetes in autoimmune polyendocrinopathy-candidiasis-ectodermal dystrophy syndrome (APECED): A “rare” manifestation in a “rare” disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016, 17, E1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barzaghi, F.; Passerini, L.; Bacchetta, R. Immune dysregulation, polyendocrinopathy, enteropathy, x-linked syndrome: A paradigm of immunodeficiency with autoimmunity. Front. Immunol. 2012, 3, 211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejentsev, S.; Walker, N.; Riches, D.; Egholm, M.; Todd, J.A. Rare variants of IFIH1, a gene implicated in antiviral responses, protect against type 1 diabetes. Science 2009, 324, 387–389. [Google Scholar]
- Marroqui, L.; Dos Santos, R.S.; Fløyel, T.; Grieco, F.A.; Santin, I.; Op de Beeck, A.; Marselli, L.; Marchetti, P.; Pociot, F.; Eizirik, D.L. TYK2, a candidate gene for type 1 diabetes, modulates apoptosis and the innate immune response in human pancreatic β-cells. Diabetes 2015, 64, 3808–3817. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ram, R.; Morahan, G. Effects of type 1 diabetes risk alleles on immune cell gene expression. Genes 2017, 8, E167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y. Prediction of the risk of type 1 diabetes from polymorphisms in candidate genes. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2006, 66, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Luckett, A.M.; Weedon, M.N.; Hawkes, G.; Leslie, R.D.; Oram, R.A.; Grant, S.F.A. Utility of genetic risk scores in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 1589–1600. [Google Scholar]
- Ikegami, H.; Ogihara, T. Genetics of insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. Endocr. J. 1996, 43, 605–613. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.; Eisenbarth, G.S. Genetic susceptibility factor of type 1 diabetes in Asians and their functional evaluation. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2001, 17, 2–11. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.; Chun, M.Y.; Kim, Y.; Lee, I.; Kim, D.; Yang, S. Differential T1D susceptibility from polymorphisms in cytokine genes and genes associated with insulin secretion according to age of onset. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2011, 27, 844–848. [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita, H.; Awata, T.; Kawasaki, E.; Ikegami, H.; Tanaka, S.; Maruyama, T.; Shimada, A.; Nakanishi, K.; Takahashi, K.; Kobayashi, T.; et al. Analysis of the HLA and non-HLA susceptibility loci in Japanese type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2011, 27, 844–848. [Google Scholar]
- Jones, A.G.; Hattersley, A.T. The clinical utility of C-peptide measurement in the care of patients with diabetes. Diabet. Med. 2013, 30, 803–817. [Google Scholar]
- Shields, B.M.; Peters, J.L.; Cooper, C.; Lowe, J.; A Knight, B.; Powell, R.J.; Jones, A.; Hyde, C.J.; Hattersley, A.T. Can clinical features be used to differentiate type 1 from type 2 diabetes? A systematic review of the literature. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e009088. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Wintergerst, K.A.; Zhou, Z. Clinical heterogeneity of type 1 diabetes (T1D) found in Asia. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2017, 33, e2907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Hong, S.; Park, L.; Woo, J.; Baik, S.; Nam, M.; Lee, K.; Kim, Y.; KNDP collaboratory Group. LADA prevalence estimation and insulin dependency during follow-up. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2011, 27, 975–979. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Buzzetti, R.; Tuomi, T.; Mauricio, D.; Pietropaolo, M.; Zhou, Z.; Pozzilli, P.; Leslie, R.D. Management of Latent Autoimmune Diabetes in Adults: A Consensus Statement From an International Expert Panel. Diabetes 2020, 69, 2037–2047. [Google Scholar]
- Sharp, S.A.; Rich, S.S.; Wood, A.R.; Jones, S.E.; Beaumont, R.N.; Harrison, J.W.; Schneider, D.A.; Locke, J.M.; Tyrrell, J.; Weedon, M.N.; et al. Development and standardization of an improved type 1 diabetes genetic risk score for use in newborn screening and incident diagnosis. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 200–207. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roep, B.O.; Kallan, A.A.; Duinkerken, G.; Arden, S.D.; Hutton, J.C.; Bruining, G.J.; De Vries, R.R. T-cell reactivity to β-cell membrane antigens associated with β-cell destruction in IDDM. Diabetes 1995, 44, 278–283. [Google Scholar]
- Culina, S.; Lalanne, A.I.; Afonso, G.; Cerosaletti, K.; Pinto, S.; Sebastiani, G.; Kuranda, K.; Nigi, L.; Eugster, A.; Østerbye, T.; et al. Islet-reactive CD8(+) T cell frequencies in the pancreas, but not in blood, distinguish type 1 diabetic patients from healthy donors. Sci. Immunol. 2018, 3, eaao4013. [Google Scholar]
- Stamatouli, A.M.; Quandt, Z.; Perdigoto, A.L.; Clark, P.L.; Kluger, H.; Weiss, S.A.; Gettinger, S.; Sznol, M.; Young, A.; Rushakoff, R.; et al. Collateral damage: Insulin-dependent diabetes induced with checkpoint inhibitors. Diabetes 2018, 67, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar]
- de Filette, J.M.K.; Pen, J.J.; Decoster, L.; Vissers, T.; Bravenboer, B.; Van der Auwera, B.J.; Gorus, F.K.; Roep, B.O.; Aspeslagh, S.; Neyns, B.; et al. Immune checkpoint inhibitors and type 1 diabetes mellitus: A case report and systematic review. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2019, 181, 363–374. [Google Scholar]
- Claessens, L.A.; Wesselius, J.; van Lummel, M.; Laban, S.; Mulder, F.; Mul, D.; Nikolic, T.; Aanstoot, H.-J.; Koeleman, B.P.C.; Roep, B.O. Clinical and genetic correlates of islet-autoimmune signatures in juvenile-onset type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2019, 63, 351–361. [Google Scholar]
- Gibson, V.B.; Nikolic, T.; Pearce, V.; Demengeot, J.; O Roep, B.; Peakman, M. Proinsulin multi-peptide immunotherapy induces antigen-specific regulatory T cells and limits autoimmunity in a humanized model. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 182, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, S.; Li, Y.; Xia, J.; Jin, C.-H.; Hu, Z.; Duinkerken, G.; Li, Y.; Maharlooei, M.K.; Chavez, E.; Nauman, G.; et al. Type 1 diabetes induction in humanized mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, 10954–10959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roep, B.O.; Wheeler, D.C.S.; Peakman, M. Antigen-based immune modulation therapy for type 1 diabetes: The era of precision medicine. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ludvigsson, J.; Faresjö, M.; Hjorth, M.; Axelsson, S.; Chéramy, M.; Pihl, M.; Vaarala, O.; Forsander, G.; Ivarsson, S.; Johansson, C.; et al. GAD treatment and insulin secretion in recent-onset type 1 diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2008, 359, 1909–1920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thrower, S.L.; James, L.; Hall, W.; Green, K.M.; Arif, S.; Allen, J.S.; Van-Krinks, C.; Lozanoska-Ochser, B.; Marquesini, L.; Brown, S.; et al. Proinsulin peptide immunotherapy in type 1 diabetes: Report of a first-in-man phase I safety study. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2009, 155, 156–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jhala, G.; Chee, J.; Trivedi, P.M.; Selck, C.; Gurzov, E.N.; Graham, K.L.; Thomas, H.E.; Kay, T.W.; Krishnamurthy, B. Perinatal tolerance to proinsulin is sufficient to prevent autoimmune diabetes. JCI Insight 2016, 1, e86065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ludvigsson, J. Autoantigen Treatment in Type 1 Diabetes: Unsolved Questions on How to Select Autoantigen and Administration Route. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeun, R. Immunotherapies for prevention and treatment of type 1 diabetes. Immunotherapy 2025, 4, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atkinson, M.A.; Roep, B.O.; Posgai, A.; Wheeler, D.C.S.; Peakman, M. The challenge of modulating β-cell autoimmunity in type 1 diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2019, 7, 52–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenbaum, C.J.; Anderson, A.M.; Dolan, L.M.; Mayer-Davis, E.J.; Dabelea, D.; Imperatore, G.; Marcovina, S.; Pihoker, C.; SEARCH Study Group. Preservation of β-cell function in autoantibody-positive youth with diabetes. Diabetes Care 2009, 32, 1839–1844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosenko, J.M.; Skyler, J.S.; Beam, C.A.; Krischer, J.P.; Greenbaum, C.J.; Mahon, J.; Rafkin, L.E.; Matheson, D.; Herold, K.C.; Palmer, J.P. Acceleration of the loss of the first-phase insulin response during the progression to type 1 diabetes in diabetes prevention trial-type 1 participants. Diabetes 2013, 62, 4179–4183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baidal, D.A.; Warnock, M.; Xu, P.; Geyer, S.; Marks, J.B.; Moran, A.; Sosenko, J.; Evans-Molina, C. Oral glucose tolerance test measures of first-phase insulin response and their predictive ability for type 1 diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2022, 107, e3273–e3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Keenan, H.A.; Sun, J.K.; Levine, J.; Doria, A.; Aiello, L.P.; Eisenbarth, G.; Bonner-Weir, S.; King, G.L. Residual insulin production and pancreatic β-cell turnover after 50 years of diabetes: Joslin Medalist Study. Diabetes 2010, 59, 2846–2853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, C.J.; Jacobson, D.R.; Rankin, M.M.; Cox, A.R.; Kushner, J.A. β cells persist in T1D pancreata without evidence of ongoing β-cell turnover or neogenesis. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 2647–2659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, A.K.; DuBose, S.N.; Haller, M.J.; Miller, K.M.; DiMeglio, L.A.; Bethin, K.E.; Goland, R.S.; Greenberg, E.M.; Liljenquist, D.R.; Ahmann, A.J.; et al. Prevalence of detectable C-peptide according to age at diagnosis and duration of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 476–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oram, R.A.; McDonald, T.J.; Shields, B.M.; Hudson, M.M.; Shepherd, M.H.; Hammersley, S.; Pearson, E.R.; Hattersley, A.T.; on behalf of the UNITED Team. Most people with long-duration type 1 diabetes in a large population-based study are insulin microsecretors. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 323–328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bottazzo, G.F. Lawrence lecture. Death of a beta cell: Homicide or suicide? Diabet. Med. 1986, 3, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eizirik, D.L.; Colli, M.L.; Ortis, F. The role of inflammation in insulitis and β-cell loss in type 1 diabetes. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2009, 5, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, S.J.; Rodriguez-Calvo, T.; Gerling, I.C.; Mathews, C.E.; Kaddis, J.S.; Russell, M.A.; Zeissler, M.; Leete, P.; Krogvold, L.; Dahl-Jørgensen, K.; et al. Islet cell hyperexpression of HLA class I antigens: A defining feature in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2016, 59, 2448–2458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marhfour, I.; Lopez, X.M.; Lefkaditis, D.; Salmon, I.; Allagnat, F.; Richardson, S.J.; Morgan, N.G.; Eizirik, D.L. Expression of endoplasmic reticulum stress markers in the islets of patients with type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2012, 55, 2417–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tersey, S.A.; Nishiki, Y.; Templin, A.T.; Cabrera, S.M.; Stull, N.D.; Colvin, S.C.; Evans-Molina, C.; Rickus, J.L.; Maier, B.; Mirmira, R.G. Islet β-cell endoplasmic reticulum stress precedes the onset of type 1 diabetes in the nonobese diabetic mouse model. Diabetes 2012, 61, 818–827. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Eizirik, D.L.; Sammeth, M.; Bouckenooghe, T.; Bottu, G.; Sisino, G.; Igoillo-Esteve, M.; Ortis, F.; Santin, I.; Colli, M.L.; Barthson, J.; et al. The human pancreatic islet transcriptome: Expression of candidate genes for type 1 diabetes and the impact of pro-inflammatory cytokines. PLoS Genet. 2012, 8, e1002552. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.; Kim, H.; Park, L.; Chae, H. The protective ability of glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78) and Bax inhibitor 1 (BI-1) for improvement of alloimmunity in ß cell transplantation. Diabetes 2013, 62, 719–731. [Google Scholar]
- Teodoro-Morrison, T.; Schuiki, I.; Zhang, L.; Belsham, D.D.; Volchuk, A. GRP78 overproduction in pancreatic beta cells protects against high-fat-diet-induced diabetes in mice. Diabetologia 2013, 56, 1057–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Blanc, M.; Habbouche, L.; Xiao, P.; Lebeaupin, C.; Janona, M.; Vaillant, N.; Irondelle, M.; Gilleron, J.; Murcy, F.; Rousseau, D.; et al. Bax Inhibitor-1 preserves pancreatic beta-cell proteostasis by limiting proinsulin misfolding and programmed cell death. Cell Death Dis. 2024, 15, 334. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- DiMeglio, L.A.; Evans-Molina, C.; Oram, R.A. Type 1 diabetes. Lancet 2018, 391, 2449–2462. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell-Thompson, M.; Fu, A.; Kaddis, J.S.; Wasserfall, C.; Schatz, D.A.; Pugliese, A.; Atkinson, M.A. Insulitis and β-cell mass in the natural history of type 1 diabetes. Diabetes 2016, 65, 719–731. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell-Thompson, M.; Wasserfall, C.; Montgomery, E.L.; Atkinson, M.A.; Kaddis, J.S. Pancreas organ weight in individuals with disease-associated autoantibodies at risk for type 1 diabetes. JAMA 2012, 308, 2337–2339. [Google Scholar]
- Vehik, K.; Lynch, K.F.; Wong, M.C.; Tian, X.; Ross, M.C.; Gibbs, R.A.; Ajami, N.J.; Petrosino, J.F.; Rewers, M.; Toppari, J.; et al. Prospective virome analyses in young children at increased genetic risk for type 1 diabetes. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1865–1872. [Google Scholar]
- Ifie, E.; Russell, M.A.; Dhayal, S.; Leete, P.; Sebastiani, G.; Nigi, L.; Dotta, F.; Marjomäki, V.; Eizirik, D.L.; Morgan, N.G.; et al. Unexpected subcellular distribution of a specific isoform of the Coxsackie and adenovirus receptor, CAR-SIV, in human pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 2018, 61, 2344–2355. [Google Scholar]
- Hiemstra, H.S.; Schloot, N.C.; van Veelen, P.A.; Willemen, S.J.M.; Franken, K.L.M.C.; van Rood, J.J.; de Vries, R.R.P.; Chaudhuri, A.; Behan, P.O.; Drijfhout, J.W.; et al. Cytomegalovirus in autoimmunity: T cell crossreactivity to viral antigen and autoantigen glutamic acid decarboxylase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 3988–3991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- TIGI Study Team; Leete, P.; Oram, R.A.; McDonald, T.J.; Shields, B.M.; Ziller, C.; Hattersley, A.T.; Richardson, S.J.; Morgan, N.G. Studies of insulin and proinsulin in pancreas and serum support the existence of aetiopathological endotypes of type 1 diabetes associated with age at diagnosis. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 1258–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iida, H.; Kono, T.; Lee, C.C.; Krishnan, P.; Arvin, M.C.; Weaver, S.A.; Jarvela, T.S.; Branco, R.C.S.; McLaughlin, M.R.; Bone, R.N.; et al. SERCA2 regulates proinsulin processing and processing enzyme maturation in pancreatic beta cells. Diabetologia 2023, 66, 2042–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirmira, R.G.; Sims, E.K.; Syed, F.; Evans-Molina, C. Biomarkers of β-cell stress and death in type 1 diabetes. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans-Molina, C. The ailing β-cell in diabetes: Insights from a trip to the ER: The 2023 outstanding scientific achievement award lecture. Diabetes 2024, 73, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrannini, E.; Mari, A.; Nofrate, V.; Sosenko, J.M.; Skyler, J.S. Progression to diabetes in relatives of type 1 diabetic patients: Mechanisms and mode of onset. Diabetes 2010, 59, 679–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, H.; Li, Y.; Fang, J.; Liu, G.; Yin, J.; Li, T.; Yin, Y. Gut microbiota and type 1 diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 995–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morrison, D.J.; Preston, T. Formation of short chain fatty acids by the gut microbiota and their impact on human metabolism. Gut Microbes 2016, 7, 189–200. [Google Scholar]
- Miani, M.; Le Naour, J.; Waeckel-Enée, E.; chand Verma, S.; Straube, M.; Emond, P.; Ryffel, B.; Van Endert, P.; Sokol, H.; Diana, J. Gut microbiota-stimulated innate lymphoid cells support β-defensin 14 expression in pancreatic endocrine cells, preventing autoimmune diabetes. Cell Metab. 2018, 28, 557–572. [Google Scholar]
- Pingitore, A.; Gonzalez-Abuin, N.; Ruz-Maldonado, I.; Huang, G.C.; Frost, G.; Persaud, S.J. Short chain fatty acids stimulate insulin secretion and reduce apoptosis in mouse and human islets in vitro: Role of free fatty acid receptor 2. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 330–339. [Google Scholar]
- de Groot, P.F.; Nikolic, T.; Imangaliyev, S.; Bekkering, S.; Duinkerken, G.; Keij, F.M.; Herrema, H.; Winkelmeijer, M.; Kroon, J.; Levin, E.; et al. Oral butyrate does not affect innate immunity and islet autoimmunity in individuals with longstanding type 1 diabetes: A randomised controlled trial. Diabetologia 2020, 63, 597–610. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hansen, L.B.S.; Roager, H.M.; Søndertoft, N.B.; Gøbel, R.J.; Kristensen, M.; Vallès-Colomer, M.; Vieira-Silva, S.; Ibrügger, S.; Lind, M.V.; Mærkedahl, R.B.; et al. A low-gluten diet induces changes in the intestinal microbiome of healthy Danish adults. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 4630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Antvorskov, J.C.; Halldorsson, T.I.; Josefsen, K.; Svensson, J.; Granström, C.; O Roep, B.; Olesen, T.H.; Hrolfsdottir, L.; Buschard, K.; Olsen, S.F. Association between maternal gluten intake and type 1 diabetes in offspring: National prospective cohort study in Denmark. BMJ 2018, 362, k3547. [Google Scholar]
- Park, Y.; Lee, H.; Takino, H.; Abiru, N.; Kawasaki, E.; Eisenbarth, G.S. Evaluation of the efficacy of the combination of multiple autoantibodies to islet-specific antigens in Korean type 1 diabetic patients. Acta Diabetol. 2001, 38, 51–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Battelino, T.; Alexander, C.M.; Amiel, S.A.; Arreaza-Rubin, G.; Beck, R.W.; Bergenstal, R.M.; Buckingham, B.A.; Carroll, J.; Ceriello, A.; Chow, E.; et al. Continuous glucose monitoring and metrics for clinical trials: An international consensus statement. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2023, 11, 42–57. [Google Scholar]
- Uhl, S.; Choure, A.; Rouse, B.; Loblack, A.; Reaven, P. Effectiveness of continuous glucose monitoring on metrics of glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2024, 109, 1119–1131. [Google Scholar]
| Previous Designations | Etiological Distinctions | Clinical Distinctions | |
|---|---|---|---|
Type 1 DM:
| (a) Juvenile onset IDDM | Beta-cell destruction
| Both (a) and (b) result in insulin dependence with loss of β-cells |
| Type 2 DM | NIDDM | Insulin resistance plus relative insulin deficiency | Early in the disease oral hypoglycemic therapy is effective |
| Other specific types | Secondary diabetes | Specific genetic defects MODY* 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 Pancreatic disease Endocrinopathies Chemical-induced Infection-related Immune-mediated forms Genetic syndromes | |
| Gestational DM | Unchanged | Onset during pregnancy |
| Antigen | Sensitivity (Specificity) | Comment |
|---|---|---|
| Insulin * | 40–95% (99%) | Inversely age of diabetes onset related |
| GAD65 * | 70% (99%) | Glutamate decarboxylase 65, Predominantly age independent |
| IA-2 * | 60% (99%) | insulinoma antigen 2 (Islet protein tyrosine phosphatase) |
| Zinc transporter 8 * | 60% (99%) | |
| Chromogranin A | ||
| IGRP | islet-specific glucose 6 phosphatase catalytic subunit-related protein |
| High Risk | |||
| DR3 | DRB1*0301 | DQA1*0501 | DQB1*0201 |
| DR4 | DRB1*0401 | DQA1*0301 | DQB1*0302 |
| DRB1*0402 | DQA1*0301 | DQB1*0302 | |
| DRB1*0405 | DQA1*0301 | DQB1*0302 | |
| Moderate Risk | |||
| DR1 | DRB1*01 | DQA1*0101 | DQB1*0501 |
| DR8 | DRB1*0801 | DQA1*0401 | DQB1*0402 |
| DR9 | DRB1*0901 | DQA1*0301 | DQB1*0303 |
| DR10 | DRB1*1001 | DQA1*0301 | DQB1*0501 |
| Protective | |||
| Strong protection | |||
| DR2 | DRB1*1501 | DQA1*0102 | DQB1*0602 |
| DR5 | DRB1*1101 | DQA1*0501 | DQB1*0301 |
| Weak protection | |||
| DR4 | DRB1*0401 | DQA1*0301 | DQB1*0301 |
| DR4 | DRB1*0403 | DQA1*0301 | DQB1*0302 |
| DR7 | DRB1*0701 | DQA1*0201 | DQB1*0201 |
| Gene | SNP | Function | Allele | Others (Function/Onset Age/Replication in Asians) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| INS | rs3842753 | Insulin | G | Central immune tolerance, early onset, replication in Asians |
| PTPN22 | rs2476601 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase | A | Peripheral immune tolerance, not polymorphic in Asians |
| ERBB3 | rs2292239 | Erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 3 | A | Cytokine-induced β cell apoptosis, late onset, replication in Asians |
| PTPN2 | rs254215 | Protein tyrosine phosphatase, non-receptor type 2 | G | Innate immune response, early onset, replication in Asians |
| BACH2 | rs72928038 | BTB domain and CNC homolog 2, Basic leucine zipper transcription factor 2 | A | Immune-mediated β cell apoptosis, late onset, replication in Asians |
| UBASH3A | rs11203203 | Ubiquitin-associated and SH3 domain-containing protein A | C | Regulates NF-κB signaling in T cells, early onset, not replicated in Asians |
| C1QTNF6 | rs229541 | C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 6 | A | Enterovirus infection, innate immunity, not replicated in Asians |
| CLEC1 | rs10492166 | C-type lectin domain family 1 | A | Dendritic cell activation, Th17 immune response, not replicated in Asians |
| IFIH1 | rs2111485 | Interferon-induced helicase | A | Enterovirus infection, innate immunity, not replicated in Asians |
| CTLA4 | rs3087243 | Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-activated 4 | A | Regulatory T-cell, early onset, replication in Asians |
| CLEC16A | rs12708716 | C-type lectin domain family 16 A | G | Thymic epithelial cell autophagy, mitophagy, early onset, replication in Asians |
| TYK2 | rs2304256 | TYK2 kinase | T | Vulnerable Beta cells, late onset, not replicated in Asians |
| IL2RA | rs41295121 | Interleukin 2 receptor alpha, CD25 | T | Regulatory T-cell, early onset, replication in Asians |
| GLIS3 | rs7020673 | The transcription factor Gli-similar 3 | A | β cell development, insulin gene expression regulation, late onset, not replicated in Asians |
| IL27 | rs9924471 | Interleukin gene | A | Dendritic cell activation, Th17 immune response, not replicated in Asians |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Park, Y.; Ko, K.S.; Rhee, B.D. New Perspectives in Studying Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility Biomarkers. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073249
Park Y, Ko KS, Rhee BD. New Perspectives in Studying Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility Biomarkers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073249
Chicago/Turabian StylePark, Yongsoo, Kyung Soo Ko, and Byoung Doo Rhee. 2025. "New Perspectives in Studying Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility Biomarkers" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073249
APA StylePark, Y., Ko, K. S., & Rhee, B. D. (2025). New Perspectives in Studying Type 1 Diabetes Susceptibility Biomarkers. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3249. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073249






