Protective Vaccination of Mice Against Blood-Stage Malaria Impacts Hepatic Expression of Genes Encoding Acute-Phase Proteins and IL-6 Family Members
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
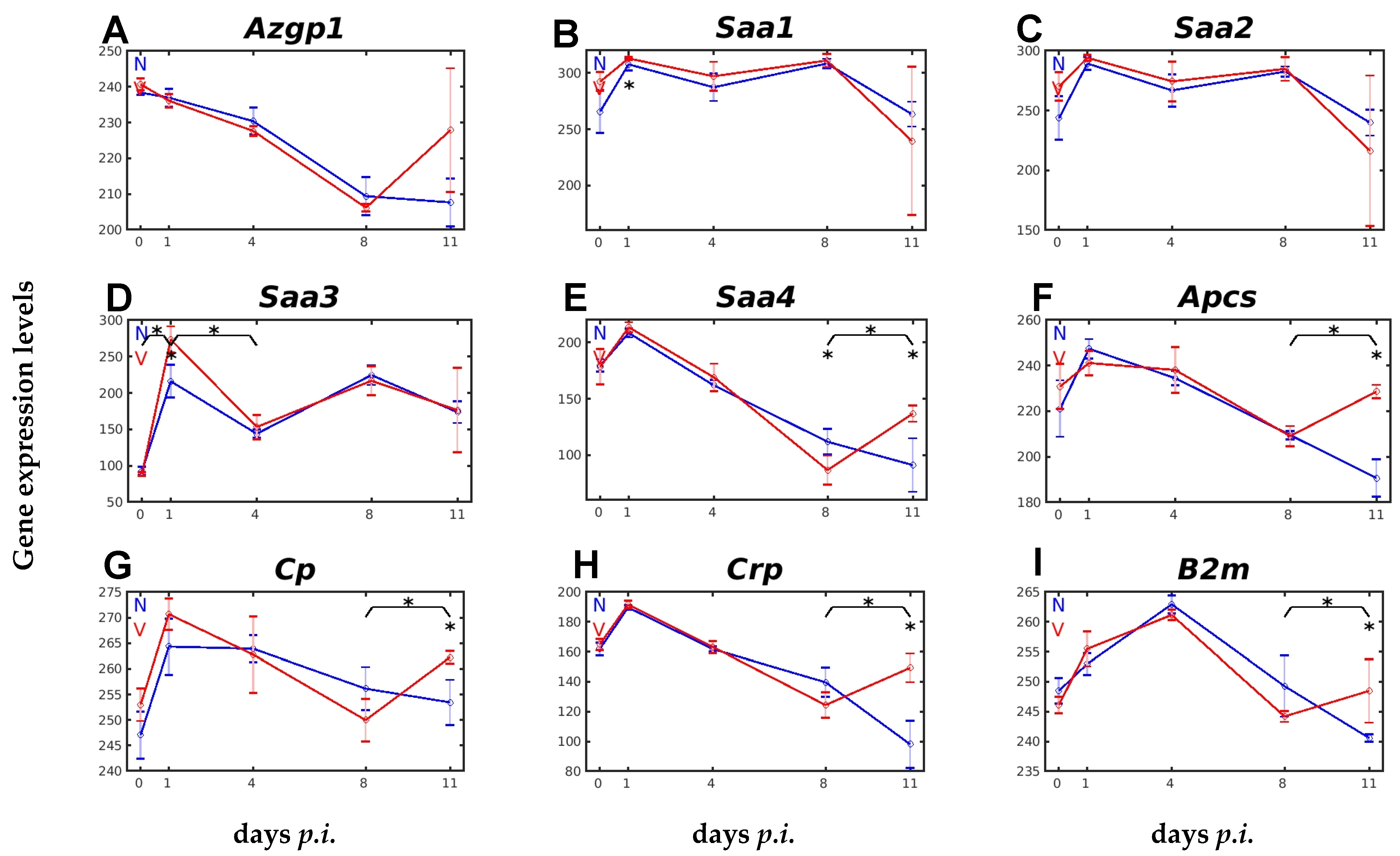
2.1. Responsiveness to Malaria and Vaccination of Hepatic Expression of Genes Encoding APPs
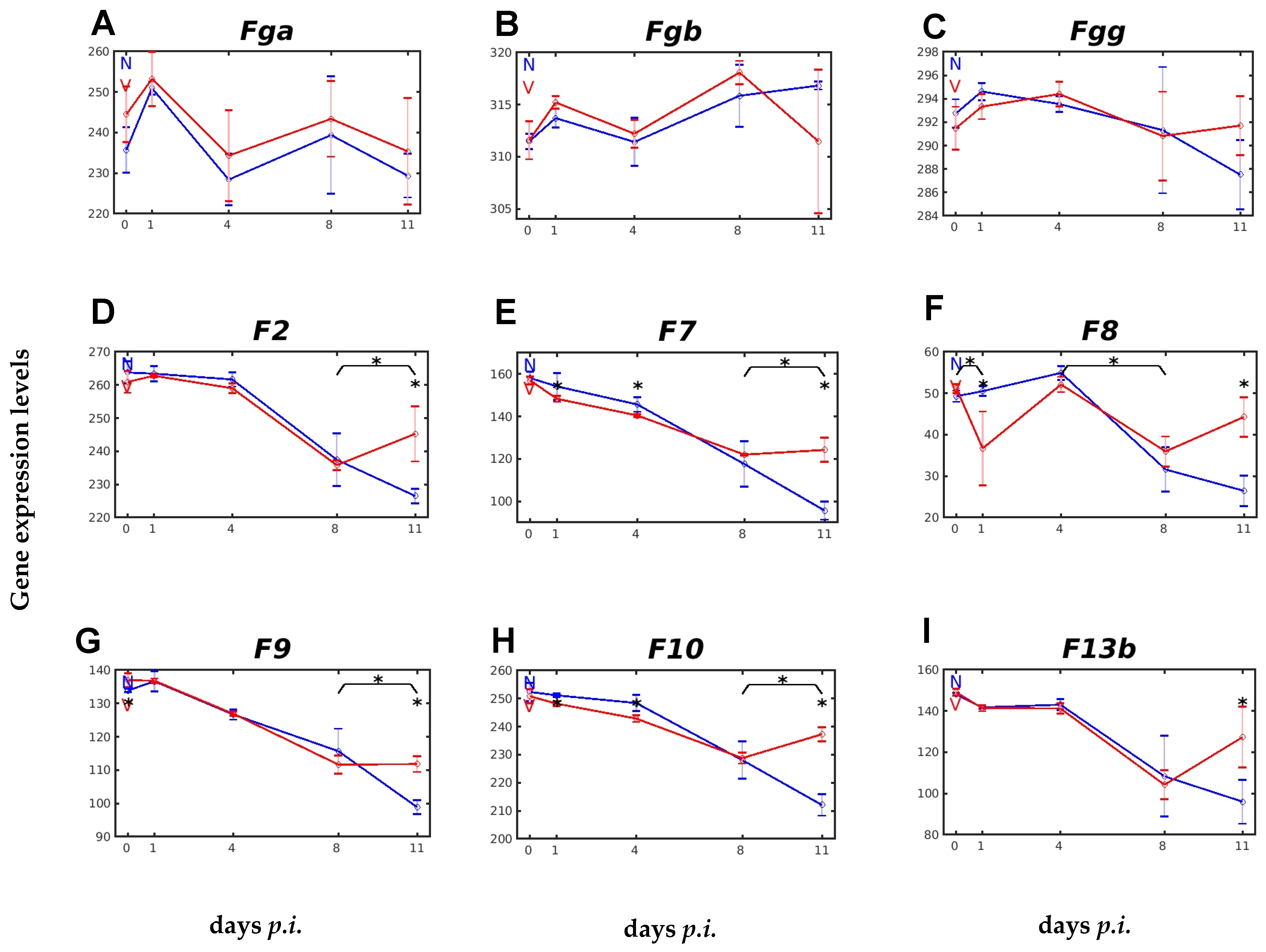
2.2. Vaccination Affects Expression of Genes Involved in Blood Coagulation and Fibrinolysis
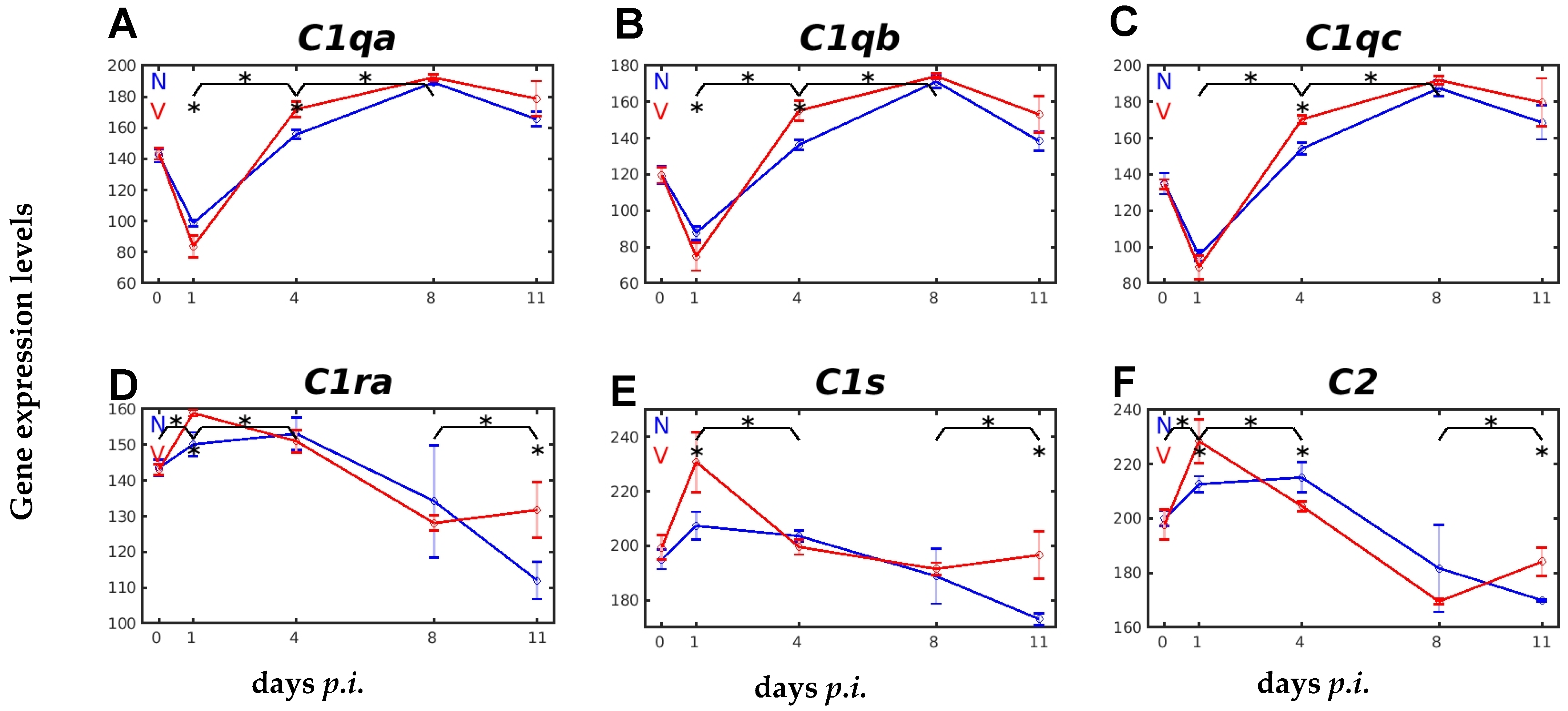
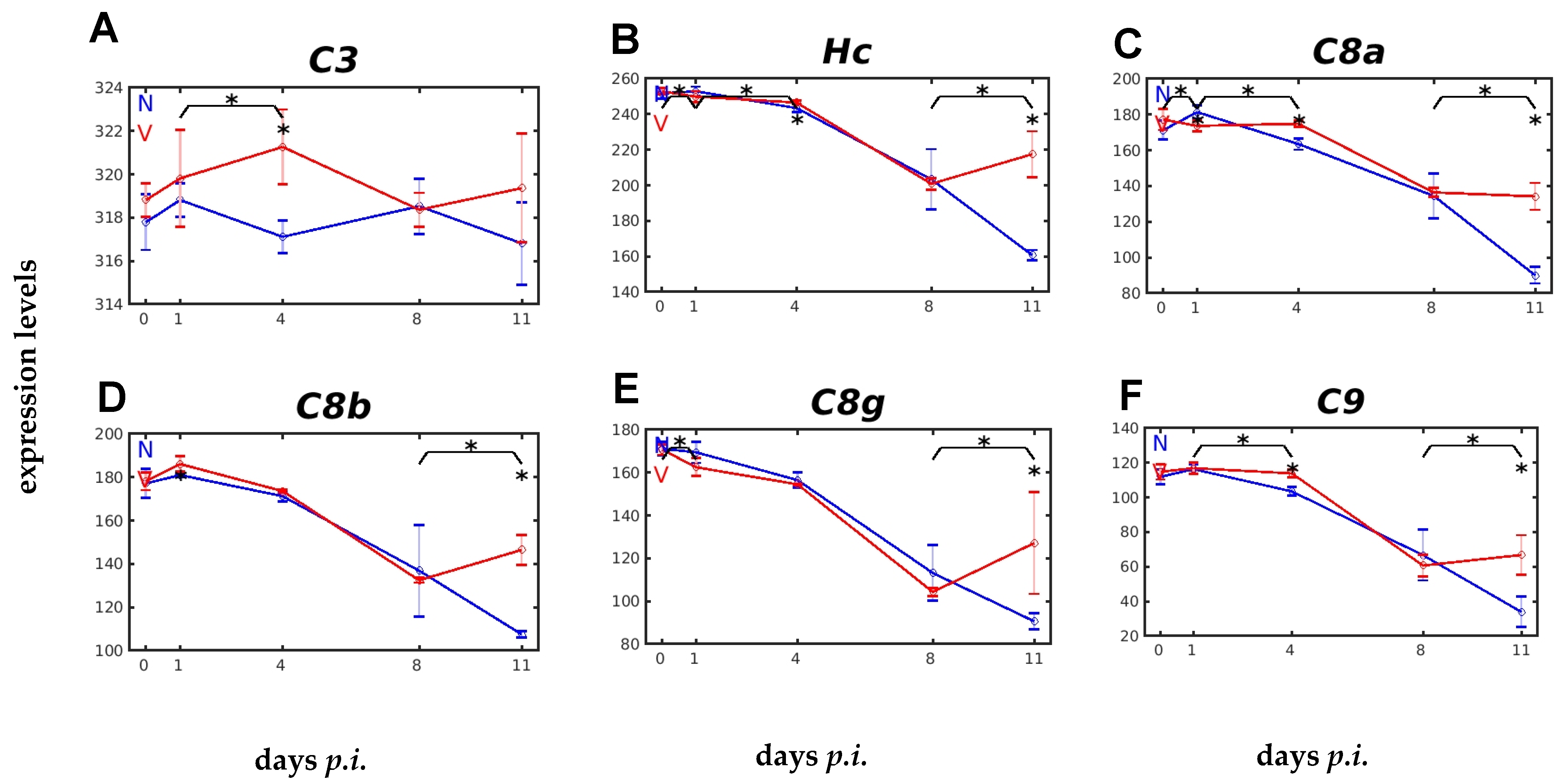
2.3. Vaccination Impacts Malaria-Responsive Expression of Genes Encoding C Components
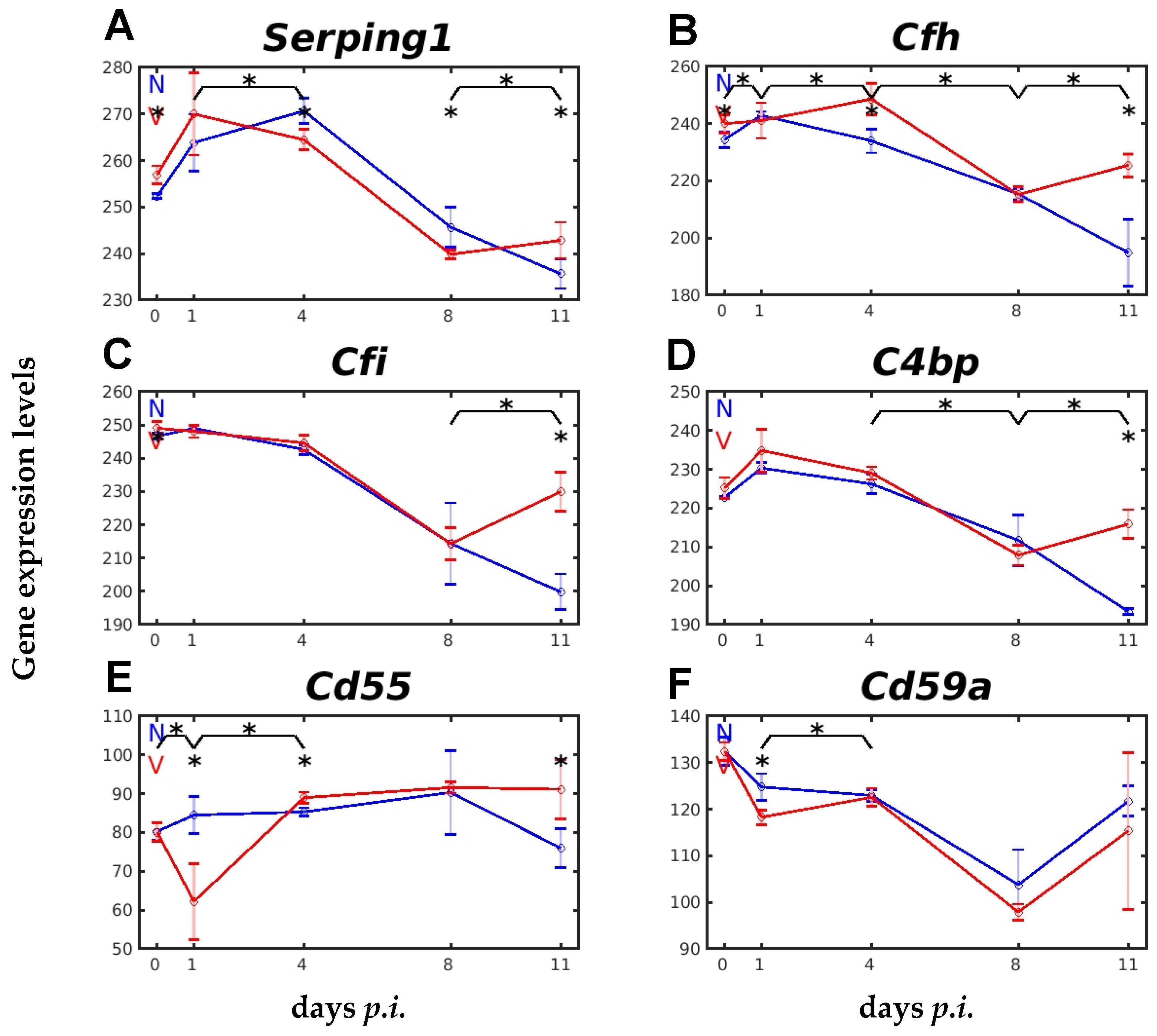
2.4. Vaccination Impacts Expression of Genes Encoding Complement Regulatory Proteins
2.5. Vaccination Affects Hepatic Gene Expression of IL-6 Family Members in Response to Blood-Stage Malaria
3. Discussion
4. Material and Methods
4.1. Blood-Stage Malaria of P. chabaudi
4.2. Protective Vaccination
4.3. Collection of Livers and RNA Preparation
4.4. Hybridization and Analyses of Mouse Whole-Genome Oligo Microarrays
4.5. Statistical Analysis
5. Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. World Malaria Report 2022; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Datoo, M.S. Immunogenicity of R21/Matrix-M vaccine against clinical malaria after 2 years’ follow-up in children in Burkina Faso: A phase 1/2b randomized clinical trial. Lancet Infect Dis. 2022, 22, 1728–1736. [Google Scholar]
- Ganley, M.; Holz, L.E.; Minnell, J.J.; deMenezes, M.N.; Burn, O.K.; Poa, K.C.Y.; Draper, S.L.; English, K.; Chan, S.T.S.; Anderson, R.J.; et al. mRNA vaccines against malaria tailored for liver-resident memory T cells. Nature Immunol. 2023, 24, 1487–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Wadman, M. First malaria vaccine slashes childhood deaths. Science 2023, 382, 357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, G. New hope against malaria. Science 2023, 382, 1232. [Google Scholar]
- Ogieuhi, I.J.; Ajekliigbe, V.O.; Kolo-Manna, K.; Akingbola, A.; Odeniyi, T.A.; Soyemi, T.S.; Ayomide, J.H.; Thiyagarajan, B.; Awolola, B.D. A narrative review of the RTS S AS01 malaria vaccine and its implementation in Africa to reduce the global malaria burden. Discover Public Health 2024, 21, 152. [Google Scholar]
- WHO. World Malaria Report 2024; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Longley, R.; Smith, C.; Fortin, A.; Berghout, J.; McMorran, B.; Burgio, G.; Foote, S.; Gros, P. Host resistance to malaria: Using mouse models to explore the host response. Mamm. Genome 2011, 22, 32–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stephens, R.; Culleton, R.I.; Lamb, T.J. The contribution of Plasmodium chabaudi to our understanding of malaria. Trends Parasitol. 2012, 28, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wunderlich, F.; Brenner, H.; Helwig, M. Plasmodium chabaudi malaria: Protective immunization with surface membranes of erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium chabaudi. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 3326–3328. [Google Scholar]
- Krücken, J.; Delic, D.; Pauen, H.; Wojtalla, A.; El-Khadragy, M.; Dkhil, M.A. Augmented particle trapping and attenuated inflammation in the liver by protective vaccination against Plasmodium chabaudi malaria. Malar. J. 2009, 8, 54–64. [Google Scholar]
- Dkhil, M.A.; Al-Quraishy, S.A.; Abdel-Baki, A.S.; Delic, D.; Wunderlich, F. Differential miRNA expression in the liver of Balb/c protected by vaccination during crisis of Plasmodium chabaudi blood-stage malaria. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 7, 2155. [Google Scholar]
- Delic, D.; Wunderlich, F.; Al-Quraishy, A.; Abdel-Baki, A.-A.; Dkhil, M.; Araúzo-Bravo, M.J. Vaccination accelerates hepatic erythroblastosis induced by blood-stage malaria. Malar. J. 2020, 19, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, F.; Delic, D.; Gerovska, D.; Arauzo-Bravo, M.J. Vaccination accelerates liver-intrinsic expression of megakaryote-related genes in response to blood-stage malaria. Vaccines 2022, 10, 287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Arauzo-Bravo, M.J.; Delic, D.; Gerovska, D.; Wunderlich, F. Protective vaccination reshapes hepatic response to blood-stage malaria of genes preferentially expressed by NK cells. Vaccines 2020, 8, 677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunderlich, F.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Dkhil, M. Liver-inherent immune system: Its role in blood-stage malaria. Front. Microbiol. 2014, 5, 559. [Google Scholar]
- Khalil, R.H.; Al-Humadi, N. Types of acute phase reactants and their importance in vaccination. Biomed. Rep. 2020, 12, 143–152. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ehlting, C.; Wolf, S.D.; Bode, J.G. Acute-phase protein synthesis: A key feature of innate immune functions of the liver. Biol. Chem. 2021, 402, 1129–1145. [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani, A.; Garlanda, C. Humoral innate immunity and acute phase proteins. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 439–452. [Google Scholar]
- Crispe, I.N. Hepatocytes as immunological agents. J. Immunol. 2016, 196, 17–21. [Google Scholar]
- Perez, L. Acute phase protein response to viral infection and vaccination. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2019, 671, 196–202. [Google Scholar]
- O’Donnell, A.; Fowkes, F.J.I.; Allen, S.J.; Imre, H.; Alpers, M.P.; Weatherall, D.J.; Day, K.P. The acute phase response in children with mild and severe malaria in Papua New Guinea. Trans. Roy. Soc. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2009, 103, 679–686. [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie, S.H.; Dow, C.; Raynes, J.G.; Behrens, R.H.; Chiodini, P.L.; McAdam, K.P.W.J. Measurement of acute phase proteins for assessing severity of Plasmodium falciparum malaria. J. Clin. Pathol. 1991, 44, 228–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reuterswärd, P.; Bergström, S.; Okikiiriza, E.; Lindquist, E.; Bergström, S.; Svahn, H.A.; Ayoglu, B.; Uhlen, M.; Wahlgren, M.; Normark, J.; et al. Levels of human proteins in plasma associated with acute paediatric malaria. Malar. J. 2018, 17, 426. [Google Scholar]
- Taylor-Robinson, A.W. Increased production of acute-phase proteins corresponds to the peak parasitaemia of primary malaria infection. Parasitol. Intern. 2000, 48, 297–301. [Google Scholar]
- Aggrey, A.A.; Srivastava, K.; Ture, S.; Field, D.J.; Morrell, C.N. Platelet induction of the acute-phase response is protective in murine experimental cerebral malaria. J. Immunol. 2013, 190, 4685–4691. [Google Scholar]
- Wilairatana, P.; Mahannop, P.; Tussato, T.; Hayeedoloh, I.; Boonhok, R.; Klangbud, W.K.; Mala, W.; Kotepui, K.U.; Kotepui, M. C-reactive protein as an early biomarker for malaria infection and monitoring of malaria severity: A meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 22033. [Google Scholar]
- Silver, K.L.; Higgins, S.J.; McDonald, C.R.; Kain, K.C. Complement driven innate immune response to malaria: Fuelling severe malaria diseases. Cell. Microbiol. 2010, 12, 1036–1045. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kurtovic, L.; Boyle, M.J.; Opi, D.H.; Kennedy, A.T.; Tham, W.-H.; Reiling, L.; Chan, J.-A.; Beeson, J.G. Complement in malaria immunity and vaccines. Immunol. Rev. 2020, 293, 38–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahu, S.K.; Kulkarni, D.H.; Ozanturk, A.N.; Ma, L.; Kulkarni, H.S. Emerging roles of the complement system in host-pathogen interactions. Trends Microbiol. 2022, 30, 390–402. [Google Scholar]
- Biryukov, S.; Stoute, J.A. Complement activation in malaria: Friend or foe? Trends Mol. Med. 2014, 20, 293–301. [Google Scholar]
- Heissig, B.; Salama, Y.; Takahashi, S.; Osada, T.; Hattori, K. The multifaceted role of plasminogen in inflammation. Cell. Signal. 2020, 75, 109761. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, S.; Hu, D.; Wang, M.; Zipfel, P.F.; Hu, Y. Complement in hemolysis- and thrombosis-related diseases. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1212. [Google Scholar]
- Deroost, K.; Pham, T.-T.; Opdenakker, G.; Van den Steen, P.E. The immunological balance between host and parasite in malaria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2016, 40, 208–257. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heinrich, P.C.; Behrmann, I.; Hermanns, H.M.; Müller-Neven, G.; Schaper, F. Principles of interleukin (IL)-6-typew cytokine signalling and its regulation. Biochem. J. 2003, 374, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murakami, M.; Kamimura, D.; Hirano, T. Pleiotropy and specificity: Insights from the interleukin 6 family of cytokines. Immunity 2019, 50, 812–831. [Google Scholar]
- Wunderlich, C.M.; Delic, D.; Behnke, K.; Meryk, A.; Ströhle, P.; Chaurasia, B.; Al-Quraishy, S.; Wunderlich, F.; Brüning, J.C.; Wunderlich, F.T. Cutting edge: Inhibition of IL6 trans-signaling protects from malaria-induced lethality in mice. J. Immunol. 2012, 188, 4141–4144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pryzdial, E.L.G.; Leatherdale, A.; Conway, E.M. Coagulation and complement: Key innate defense participants in a seamless web. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 918775. [Google Scholar]
- Petry, F.; McClive, P.J.; Botto, M.; Morley, B.J.; Morahan, G.; Loos, M. The mouse C1q genes are clustered on chromosome 4 and show conservation of gene organization. Immunogen. 1996, 43, 370–376. [Google Scholar]
- Kiyuka, P.K.; Meri, S.; Khattab, A. Complement in malaria: Immune evasion strategies and role in protective immunity. FEBS Letters 2020, 594, 2502–2517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santiago, V.F.; Dombrowski, J.G.; Kawahara, R.; Rosa-Fernandes, L.; Mule, S.N.; Murillo, O.; Santana, T.V.; Paccini Coutinho, J.V.; Macedo-da-Silva, J.; Cardoso Lazari, L.; et al. Complement system activation is a plasma biomarker signature during malaria in pregnancy. Genes 2023, 14, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liszewski, M.K.; Java, A.; Schramm, E.C.; Atkinson, J.P. Complement dysregulation and disease: Insights from contemporary genetics. Ann. Rev. Pathol. 2017, 12, 25–52. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L.; Chen, Z.; Yu, K.; Yan, J.; Li, T.; Ba, X.; Lin, W.; Huang, Y.; Shen, P.; Huang, Y.; et al. Interleukin 27 signaling in rheumatoid arthritis patients: Good or evil? Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 787252. [Google Scholar]
- Balmer, P.; McMonagle, F.A.; Alexander, J.; Phillips, R.S. Experimental erythrocytic malaria infection induces elevated serum amyloid P production in mice. Immunol. Lett. 2000, 72, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansar, W.; Bandyopadhyay, S.M.; Chowdhury, S.; Habib, S.H.; Mandal, C. Role of C-reactive protein in complement-mediated hemolysis in malaria. Glycoconj. J. 2006, 23, 233–240. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, J.; Mold, C.; DuClos, T.W.; Sun, P.D. Pentraxins and Fc receptor-mediated immune responses. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temming, A.R.; Buirs, M.T.; Bentlage, A.E.H.; Treffers, L.W.; Feringa, H.; de Taeye, S.W.; Kuijpers, T.W.; Nagelkerke, S.Q.; Brasser, G.; Mok, J.Y.; et al. C-reactive protein enhances cellular destruction through IgG-Fc receptors in vitro. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 594773. [Google Scholar]
- McGrath, F.D.G.; Brouwer, M.C.; Arlaud, G.J.; Daha, M.R.; Hack, C.E.; Roos, A. Evidence that complement protein C1q with C-reactive protein through its globular head region. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 46974–46982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidmann, H.; Heikaus, L.; Long, A.T.; Naudin, C.; Sclüter, H.; Renne, T. The plasma contact system, a protease cascade at the nexus of inflammation, coagulation and immunity. BBA-Mol. Cell Res. 2017, 1864, 2118–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krücken, J.; Dkhil, M.A.; Braun, J.V.; Schroetel, R.M.U.; El-Khadragy, M.; Carmeliet, P.; Mossmann, H.; Wunderlich, F. Testosterone suppresses protective responses of the liver to blood-stage malaria. Infect. Immun. 2005, 73, 436–443. [Google Scholar]
- Reiss, T.; Müller, F.; Pradel, G. The impact of human complement on the clinical outcome of malaria infection. Mol. Immunol. 2022, 151, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis III, A.E.; Lu, F.; Mejia, P. C1 Inhibitor, a multifunctional serine protease inhibitor. Thromb. Haemost. 2010, 104, 886–893. [Google Scholar]
- Hausburg, M.A.; Williams, J.S.; Banton, K.L.; Mains, C.W.; Roshon, M.; Bar-Or, D. C1 esterase inhibitor-mediated immunosuppression in Covid-19: Friend or foe? Clin. Immun. Comm. 2022, 2, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kennedy, A.T.; Wijeyewickrema, L.C.; Huglo, A.; Lin, C.; Pike, R.; Cowman, A.F.; Tham, W.H. Recruitment of human C1 esterase inhibitor controls complement activation on blood stage Plasmodium falciparum merozoites. J. Immunol. 2017, 198, 4728–4737. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mejia, P.; Diez-Silva, M.; Kamena, F.; Lu, F.; Fernandes, S.M.; Seeberger, P.H.; Davis, A.E., III; Mitchell, J.R. Human C1-inhibitor suppresses malaria parasite invasion and cytoadhesion via binding to parasite glycophosphatidylinositol and host cell receptors. J. Infect. Dis. 2016, 213, 80–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Richards, C.D.; Langdon, C.; Pennica, D.; Gauldie, J. Murine cardiotrophin-1 stimulates the acute phase response in rat hepatocytes and H35 hepatoma cells. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 1996, 16, 69–75. [Google Scholar]
- Lopez-Yolgi, M.; Moreno-Aliaga, M.J.; Bustos, M. Cardiotrophin-1: A multifaceted cytokine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2015, 26, 523–532. [Google Scholar]
- Carneros, D.; Santamaria, E.M.; Larequi, E.; Velez-Ortiz, J.M.; Reboredo, M.; Mancheño, U.; Perugorria, M.J.; Navas, P.; Romero-Gómez, M.; Prieto, J.; et al. Cardiotrophin-1 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine and promotes IL-4-induced M2 macrophage polarization. Faseb J. 2019, 33, 7578–7587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kordula, T.; Rokita, H.; Koj, A.; Fiers, W.; Gauldie, J.; Baumann, H. Effects of interleukin-6 and leukemia inhibitory factor on the acute phase response and DNA synthesis in cultured rat hepatocytes. Lymphokine Cytokine Res. 1991, 10, 23–26. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, M.A.; Metcalf, D.; Gough, N.M. Leukemia inhibitory factor and interleukin 6 are expressed at very low levels in the normal adult mouse and are induced by inflammation. Cytokine 1994, 6, 300–309. [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf, D. The unsolved enigmas of leukemia inhibitory factor. Stem Cells 2003, 21, 5–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wang, J.; Chang, C.-Y.; Zhou, F.; Liu, J.; Xu, H.; Ibrahim, M.; Gomez, M.; Guo, G.L.; Liu, H.; et al. Leukemia inhibitory factor suppresses hepatic de novo lipogenesis and induces cachexia in mice. Nature Comm. 2024, 15, 627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widjaja, A.A.; Chothani, S.P.; Cook, S.A. Different roles of interleukin 6 and interleukin 11 in the liver: Implications for therapy. Hum. Vacc. Immunotherap. 2020, 16, 2357–2362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jostock, T.; Müllberg, J.; Özbek, S.; Atreya, R.; Blinn, G.; Voltz, N.; Fischer, M.; Neurath, M.F.; Rose-John, S. Soluble gp130 is the natural inhibitor of soluble interleukin-6 receptor transsignalling responses. Eur. J. Biochem. 2001, 268, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rose-John, S.; Jenkins, B.J.; Garbers, C.; Moll, J.M.; Scheller, J. Targeting IL-6 transsignalling: Past, present and future. Nature Rev. Immunol. 2023, 23, 666–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunderlich, F.; Mossmann, H.; Helwig, M.; Schillinger, G. Resistance to Plasmodium chabaudi in B10 mice: Influence of the H2-complex and testosterone. Infect. Immun. 1988, 56, 2400–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, F.; Helwig, M.; Schillinger, G.; Speth, V.; Wiser, M.F. Expression of the parasite protein Pc90 in plasma membranes of erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium chabaudi. Eur. J. Cell. Biol. 1988, 47, 157–164. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wunderlich, F.; Helwig, M.; Schillinger, G.; Speth, V. Cryptic disposition of antigenic parasite proteins in plasma membranes of erythrocytes infected with Plasmodium chabaudi. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 1988, 30, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wunderlich, F.; Maurin, W.; Benten, W.P.M.; Schmitt-Wrede, H.-P. Testosterone impairs efficacy of protective vaccination against P. chabaudi malaria. Vaccine 1993, 11, 1097–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kruskal, W.H.; Wallis, W.A. Use of ranks in one-criterion variance analysis. J. Amer. Statistic. Assoc. 1952, 47, 583–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wunderlich, F.; Gerovska, D.; Delic, D.; Araúzo-Bravo, M.J. Protective Vaccination of Mice Against Blood-Stage Malaria Impacts Hepatic Expression of Genes Encoding Acute-Phase Proteins and IL-6 Family Members. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073173
Wunderlich F, Gerovska D, Delic D, Araúzo-Bravo MJ. Protective Vaccination of Mice Against Blood-Stage Malaria Impacts Hepatic Expression of Genes Encoding Acute-Phase Proteins and IL-6 Family Members. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073173
Chicago/Turabian StyleWunderlich, Frank, Daniela Gerovska, Denis Delic, and Marcos J. Araúzo-Bravo. 2025. "Protective Vaccination of Mice Against Blood-Stage Malaria Impacts Hepatic Expression of Genes Encoding Acute-Phase Proteins and IL-6 Family Members" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073173
APA StyleWunderlich, F., Gerovska, D., Delic, D., & Araúzo-Bravo, M. J. (2025). Protective Vaccination of Mice Against Blood-Stage Malaria Impacts Hepatic Expression of Genes Encoding Acute-Phase Proteins and IL-6 Family Members. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3173. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073173





