Changes in the Protein Composition of the Aqueous Humor in Patients with Glaucoma: An Update Review
Abstract
1. Introduction
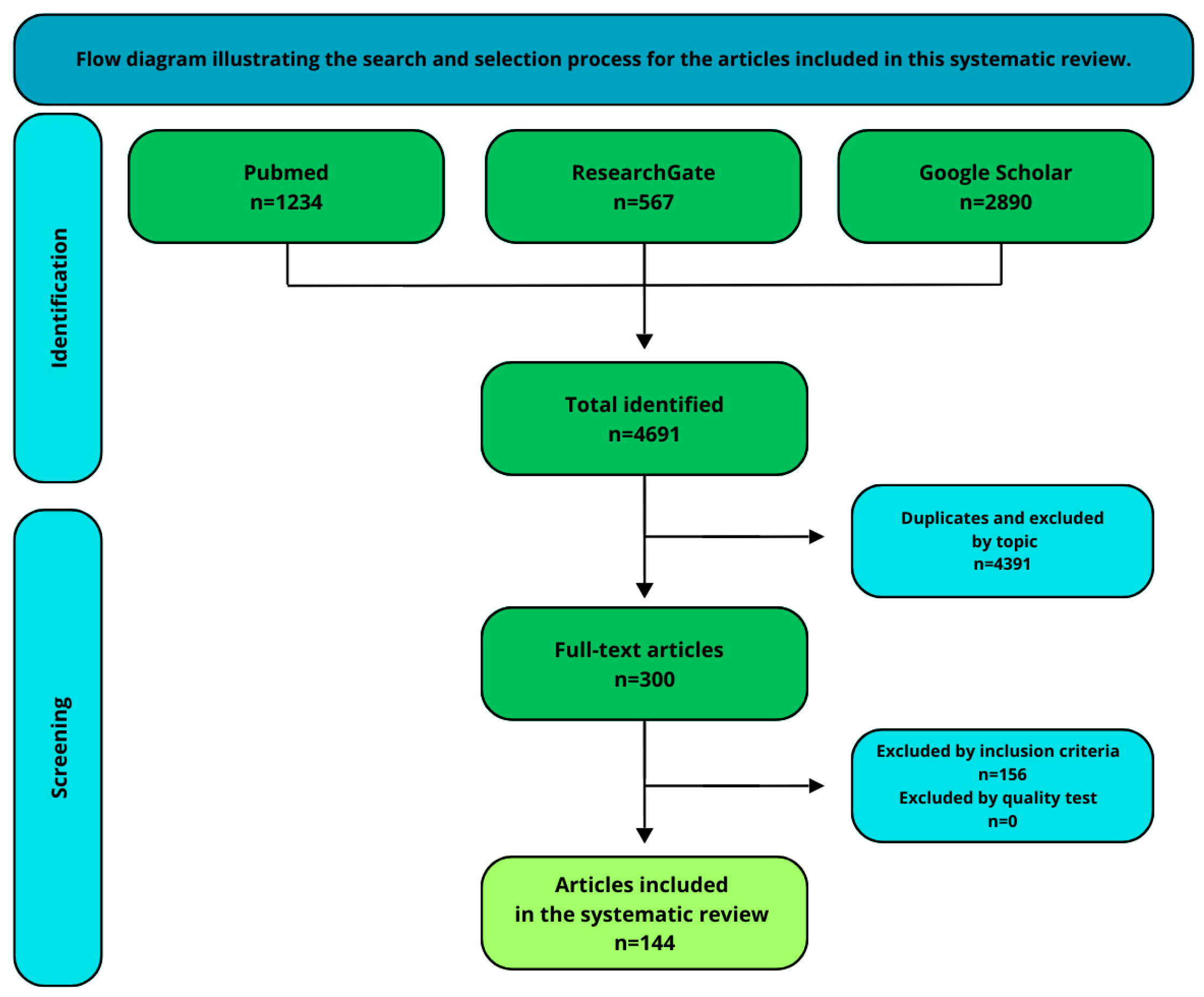
2. Materials and Methods
3. Pathomechanism
4. Methods for Determining the Protein Composition of the Aqueous Humor
5. Protein Composition of Aqueous Humor in Different Types of Glaucoma
5.1. Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma
5.2. Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma
5.3. Secondary Glaucoma
5.3.1. Pseudoexfoliation Glaucoma
5.3.2. Neovascular Glaucoma
5.3.3. Pigmentary Open-Angle Glaucoma
5.3.4. Steroid-Induced Open-Angle Glaucoma
5.3.5. Post-Traumatic Glaucoma
5.4. Pathways Implicated in Glaucoma
6. Conclusions
7. Limitations
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Alphabetical Order | Abbreviations | Meaning |
| A | AACG | acute angle-closure glaucoma |
| ACG | angle-closure glaucoma | |
| AFM | afamin | |
| AH | aqueous humor | |
| B | BDNF | brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| C | CACG | chronic angle-closure glaucoma |
| CCT8 | T-complex protein 1 subunit theta | |
| CLANs | cross-linked actin networks | |
| CPACG | chronic primary angle-closure glaucoma | |
| D | DKK3 | Dickkopf-related protein 3 |
| G | GPx | glutathione peroxidase |
| H | HRM-MS | hyper-response monitoring mass spectrometry |
| HSPB1 | heat shock protein beta-1 | |
| I | IL-1β | interleukin-1β |
| IOP | intraocular pressure | |
| L | LDH | lactate dehydrogenase |
| LOXL1 | lysyl oxidase | |
| M | MMP | matrix metalloproteinase |
| N | NEDD4 | neural precursor cell-expressed, developmentally downregulated protein 4 |
| NfL | neurofilament 158 light chain | |
| NVG | neovascular glaucoma | |
| O | OAG | open-angle glaucoma |
| OCT | optical coherence tomography | |
| OGI | open-globe injuries | |
| OHT | ocular hypertension | |
| P | PAACG | primary acute angle-closure glaucoma |
| PACG | primary angle-closure glaucoma | |
| PACS | primary angle-closure suspects | |
| PAI-1 | plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 | |
| PCACG | primary chronic angle-closure glaucoma | |
| PDGF | platelet-derived growth factor | |
| PDR | proliferative diabetic retinopathy | |
| PDS | pigment dispersion syndrome | |
| PEBP1 | phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 1 | |
| PEDF | pigment epithelium-derived factor | |
| PEG | pseudoexfoliative glaucoma | |
| PEX | pseudoexfoliation syndrome | |
| PGK1 | phosphoglycerate kinase 1 | |
| POAG | primary open-angle glaucoma | |
| R | RGCS | retinal ganglion cells |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species | |
| S | SFRP1 | secreted frizzled--related protein-1 |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase | |
| SOD | superoxide dismutase | |
| SPP1 | osteopontin 1 | |
| SDS-PAGE | sodium dodecyl sulfate–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis | |
| SWATH | Sequential Window Acquisition of all Theoretical Mass Spectra | |
| T | TAC | total antioxidant capacity |
| TGF-β2 | transforming growth factor-β2 | |
| TIMP-1 | tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases | |
| TNF-α | tumor necrosis factor-alpha | |
| U | UBM | ultrasound biomicroscopy |
| URSG | uveitis-related secondary glaucoma | |
| V | VEGF | vascular endothelial growth factor |
| VIM | vimentin | |
| VTN | vitronectin | |
| W | WIF1 | Wnt inhibitory factor 1 |
| X | XFG | exfoliation glaucoma |
| XFS | exfoliation syndrome |
References
- Leske, M.C.; Heijl, A.; Hussein, M.; Bengtsson, B.; Hyman, L.; Komaroff, E. Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial Group Factors for Glaucoma Progression and the Effect of Treatment: The Early Manifest Glaucoma Trial. Arch. Ophthalmol. Chic. Ill 1960 2003, 121, 48–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reina-Torres, E.; Boussommier-Calleja, A.; Sherwood, J.M.; Overby, D.R. Aqueous Humor Outflow Requires Active Cellular Metabolism in Mice. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, X.; Wang, Y.; Sun, H.; Guo, Z.; Tang, X.; Li, J.; Xiao, X.; Zheng, S.; Yu, M.; et al. Proteome Characterization of Glaucoma Aqueous Humor. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2021, 20, 100117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quigley, H.A.; Friedman, D.S.; Congdon, N.G. Possible Mechanisms of Primary Angle-Closure and Malignant Glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2003, 12, 167–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AGIS Investigators. The Advanced Glaucoma Intervention Study (AGIS): 12. Baseline Risk Factors for Sustained Loss of Visual Field and Visual Acuity in Patients with Advanced Glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2002, 134, 499–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, J.B.; Aung, T.; Bourne, R.R.; Bron, A.M.; Ritch, R.; Panda-Jonas, S. Glaucoma. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2017, 390, 2183–2193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omodaka, K.; Kikawa, T.; Kabakura, S.; Himori, N.; Tsuda, S.; Ninomiya, T.; Takahashi, N.; Pak, K.; Takeda, N.; Akiba, M.; et al. Clinical Characteristics of Glaucoma Patients with Various Risk Factors. BMC Ophthalmol. 2022, 22, 373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, S.; Stankowska, D.L.; Ellis, D.Z.; Krishnamoorthy, R.R.; Yorio, T. Targets of Neuroprotection in Glaucoma. J. Ocul. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 34, 85–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayaram, H.; Kolko, M.; Friedman, D.S.; Gazzard, G. Glaucoma: Now and Beyond. Lancet Lond. Engl. 2023, 402, 1788–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Glaucoma Society Terminology and Guidelines for Glaucoma, 5th Edition. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 1–169. [CrossRef]
- Michels, T.C.; Ivan, O. Glaucoma: Diagnosis and Management. Am. Fam. Physician 2023, 107, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wolfram, C. The Epidemiology of Glaucoma—An Age-Related Disease. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 2024, 241, 154–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Höhn, R.; Nickels, S.; Schuster, A.K.; Wild, P.S.; Münzel, T.; Lackner, K.J.; Schmidtmann, I.; Beutel, M.; Pfeiffer, N. Prevalence of Glaucoma in Germany: Results from the Gutenberg Health Study. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2018, 256, 1695–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, A.; Zou, M.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, L.; Li, Y.; Zheng, D.; Jin, G.; Congdon, N. Time Trends, Associations and Prevalence of Blindness and Vision Loss Due to Glaucoma: An Analysis of Observational Data from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. BMJ Open 2022, 12, e053805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.A.; Higginbotham, E.J. Glaucoma and Its Treatment: A Review. Am. J. Health-Syst. Pharm. 2005, 62, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, V.; Swamidoss, I.N.; Aquino, M.C.D.; Chew, P.T.; Sng, C. Novel Automated Approach to Predict the Outcome of Laser Peripheral Iridotomy for Primary Angle Closure Suspect Eyes Using Anterior Segment Optical Coherence Tomography. J. Med. Syst. 2018, 42, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, D.S.; Trobe, J.; Park, L. Open-angle glaucoma: Epidemiology, clinical presentation, and diagnosis. In UpToDate; Wolters Kluwer Health: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Schuster, A.K.; Wagner, F.M.; Pfeiffer, N.; Hoffmann, E.M. Risk Factors for Open-Angle Glaucoma and Recommendations for Glaucoma Screening. Ophthalmol. Z. Dtsch. Ophthalmol. Ges. 2021, 118, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Dai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yu, D.-Y.; Cringle, S.J.; Chen, J.; Kong, X.; Wang, X.; Jiang, C. Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma: What We Know and What We Don’t Know. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2017, 57, 26–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beutgen, V.M.; Graumann, J. Advances in Aqueous Humor Proteomics for Biomarker Discovery and Disease Mechanisms Exploration: A Spotlight on Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2024, 17, 1397461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahabadi, N.; Zeppieri, M.; Tripathy, K. Open Angle Glaucoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Kaeslin, M.A.; Killer, H.E.; Fuhrer, C.A.; Zeleny, N.; Huber, A.R.; Neutzner, A. Changes to the Aqueous Humor Proteome during Glaucoma. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0165314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buffault, J.; Labbé, A.; Hamard, P.; Brignole-Baudouin, F.; Baudouin, C. The Trabecular Meshwork: Structure, Function and Clinical Implications. A Review of the Literature. J. Fr. Ophtalmol. 2020, 43, e217–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietze, J.; Blair, K.; Zeppieri, M.; Havens, S.J. Glaucoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Greslechner, R.; Helbig, H. Secondary Glaucoma in the Context of Retinal Disease. Klin. Monatsbl. Augenheilkd. 2022, 239, 1111–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakazawa, T. Ocular Blood Flow and Influencing Factors for Glaucoma. Asia-Pac. J. Ophthalmol. Phila. Pa. 2016, 5, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein, J.D.; Khawaja, A.P.; Weizer, J.S. Glaucoma in Adults-Screening, Diagnosis, and Management: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langbøl, M.; Saruhanian, A.; Saruhanian, S.; Tiedemann, D.; Baskaran, T.; Vohra, R.; Rives, A.S.; Moreira, J.; Prokosch, V.; Liu, H.; et al. Proteomic and Cytokine Profiling in Plasma from Patients with Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2024, 44, 59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Yu, M.; Baig, N.; Chan, P.P.; Tang, F.Y.; Cheung, C.Y.; Tham, C.C.Y. Association of Ultra-Short-Term Intraocular Pressure Fluctuation with Disease Progression in Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma: The CUPAL Study. J. Glaucoma 2022, 31, 874–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terelak-Borys, B.; Czechowicz-Janicka, K. Investigation into the Vasospastic Mechanisms in the Pathogenesis of Glaucomatous Neuropathy. Klin. Ocz. 2011, 113, 201–208. [Google Scholar]
- Zaidi, M.; Jilani, A.; Bhattacharya, P.; Islam, N.; Alam, S. A Study of Aqueous Humour Proteins in Patients of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. Adv. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2010, 1, 110–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Tabatabaei, M.S.; Ahmed, M. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA). Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2022, 2508, 115–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Igarashi, T.; Nakamoto, K.; Kobayashi, M.; Suzuki, H.; Arima, T.; Tobita, Y.; Takao, K.; Igarashi, T.; Okuda, T.; Okada, T.; et al. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor in the Aqueous Humor of Glaucoma Patients. J. Nippon Med. Sch. Nippon Ika Daigaku Zasshi 2021, 88, 128–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woltsche, N.; Valentin, K.; Hoeflechner, L.; Guttmann, A.; Horwath-Winter, J.; Schneider, M.R.; Ivastinovic, D.; Lindner, M.; Schmetterer, L.; Singh, N.; et al. Neurofilament Light Chain: A New Marker for Neuronal Decay in the Anterior Chamber Fluid of Patients with Glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 107, 1432–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hubens, W.H.G.; Mohren, R.J.C.; Liesenborghs, I.; Eijssen, L.M.T.; Ramdas, W.D.; Webers, C.A.B.; Gorgels, T.G.M.F. Aqueous Humor Proteome of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma: A Combined Dataset of Mass Spectrometry Studies. Data Brief 2020, 32, 106327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wang, D.; Li, H.; Ma, X.; Zou, Y.; Mu, D.; Yu, S.; Cheng, X.; Qiu, L. Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry in Clinical Laboratory Protein Measurement. Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 2024, 562, 119846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussmann, D.; Hansen, L.L. Methylation-Sensitive High Resolution Melting (MS-HRM). Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2018, 1708, 551–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draht, M.X.G.; Smits, K.M.; Jooste, V.; Tournier, B.; Vervoort, M.; Ramaekers, C.; Chapusot, C.; Weijenberg, M.P.; van Engeland, M.; Melotte, V. Analysis of RET Promoter CpG Island Methylation Using Methylation-Specific PCR (MSP), Pyrosequencing, and Methylation-Sensitive High-Resolution Melting (MS-HRM): Impact on Stage II Colon Cancer Patient Outcome. Clin. Epigenetics 2016, 8, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Määttä, M.; Tervahartiala, T.; Vesti, E.; Airaksinen, J.; Sorsa, T. Levels and Activation of Matrix Metalloproteinases in Aqueous Humor Are Elevated in Uveitis-Related Secondary Glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2006, 15, 229–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balaiya, S.; Edwards, J.; Tillis, T.; Khetpal, V.; Chalam, K.V. Tumor Necrosis Factor-Alpha (TNF-α) Levels in Aqueous Humor of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. Clin. Ophthalmol. Auckl. NZ 2011, 5, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohira, S.; Inoue, T.; Shobayashi, K.; Iwao, K.; Fukushima, M.; Tanihara, H. Simultaneous Increase in Multiple Proinflammatory Cytokines in the Aqueous Humor in Neovascular Glaucoma with and without Intravitreal Bevacizumab Injection. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 3541–3548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dursun, F.; Vural Ozec, A.; Aydin, H.; Topalkara, A.; Dursun, A.; Toker, M.I.; Erdogan, H.; Arici, M.K. Total Oxidative Stress, Paraoxonase and Arylesterase Levels at Patients with Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome and Pseudoexfoliative Glaucoma. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2015, 8, 985–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bojikian, K.D.; Stein, A.L.; Slabaugh, M.A.; Chen, P.P. Incidence and Risk Factors for Traumatic Intraocular Pressure Elevation and Traumatic Glaucoma after Open-Globe Injury. Eye 2015, 29, 1579–1584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetikoğlu, M.; Sağdik, H.M.; Aktas, S.; Uçar, F.; Özcura, F. Serum Prolidase Activity and Oxidative Stress in Patients with Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2016, 254, 1339–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, T.; Guo, L.; Fan, Y.; Fang, L.; Wei, J.; Tan, Y.; Chen, Y.; Fan, X. Aqueous Humor Levels of TGFβ2 and SFRP1 in Different Types of Glaucoma. BMC Ophthalmol. 2019, 19, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikhalashree, S.; George, R.; Shantha, B.; Lingam, V.; Vidya, W.; Panday, M.; Sulochana, K.N.; Coral, K. Detection of Proteins Associated with Extracellular Matrix Regulation in the Aqueous Humour of Patients with Primary Glaucoma. Curr. Eye Res. 2019, 44, 1018–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.; Zhang, H.; Jiang, J.; Li, Y.; Nie, C.; Gu, J.; Luo, L.; Wang, Z. Angiogenic and Inflammatory Biomarker Levels in Aqueous Humor and Vitreous of Neovascular Glaucoma and Proliferative Diabetic Retinopathy. Int. Ophthalmol. 2020, 40, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaur, I.; Kaur, J.; Sooraj, K.; Goswami, S.; Saxena, R.; Chauhan, V.S.; Sihota, R. Comparative Evaluation of the Aqueous Humor Proteome of Primary Angle Closure and Primary Open Angle Glaucomas and Age-Related Cataract Eyes. Int. Ophthalmol. 2019, 39, 69–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adav, S.S.; Wei, J.; Qian, J.; Gan, N.Y.; Yip, L.W.L.; Sze, S.K. Aqueous Humor Protein Dysregulation in Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma. Int. Ophthalmol. 2019, 39, 861–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.-L.; Song, X.-Y.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Nguyen, T.H.A.; Zhang, J.-Y.; Bao, S.-S.; Zhang, Y.-Y. Novel Inflammatory Cytokines (IL-36, 37, 38) in the Aqueous Humor from Patients with Chronic Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2019, 71, 164–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Anders, F.; Funke, S.; Mercieca, K.; Grus, F.; Prokosch, V. Proteome Alterations in Aqueous Humour of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma Patients. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 13, 176–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, S.; Lee, D.; Kang, S.; Kim, D.W.; Kim, Y.; Cho, J.-Y.; Seo, K. Proteomic Analysis of Aqueous Humor in Canine Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma in American Cocker Spaniel Dogs. Vet. Ophthalmol. 2021, 24, 520–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubens, W.H.G.; Beckers, H.J.M.; Gorgels, T.G.M.F.; Webers, C.A.B. Increased Ratios of Complement Factors C3a to C3 in Aqueous Humor and Serum Mark Glaucoma Progression. Exp. Eye Res. 2021, 204, 108460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mok, J.-H.; Park, D.Y.; Han, J.C. Differential Protein Expression and Metabolite Profiling in Glaucoma: Insights from a Multi-Omics Analysis. BioFactors 2024, 50, 1220–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Q.; Shen, J.; Zhang, L.; Wang, Q.; Luo, S.; Luo, M.; Chen, W. Expression of IL-4 and IL-12 in the Aqueous Humor of Patients with Chronic Primary Angle-Closure Glaucoma. Front. Med. 2024, 11, 1323829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, J.H.; Chung, Y.K.; Son, J.S. Apolipoprotein B: Novel Indicator of Elevated Intraocular Pressure. Eye 2015, 29, 1315–1320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Darzi, N.; Mast, N.; Petrov, A.M.; Dao, T.; Astafev, A.A.; Saadane, A.; Prendergast, E.; Schwarz, E.; Bederman, I.; Pikuleva, I.A. Studies of ApoD-/- and ApoD-/-ApoE-/- Mice Uncover the APOD Significance for Retinal Metabolism, Function, and Status of Chorioretinal Blood Vessels. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. CMLS 2021, 78, 963–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulhaq, Z.S.; Bittencourt, G.B.; Soraya, G.V.; Istifiani, L.A.; Pamungkas, S.A.; Ogino, Y.; Nurputra, D.K.; Tse, W.K.F. Association between Glaucoma Susceptibility with Combined Defects in Mitochondrial Oxidative Phosphorylation and Fatty Acid Beta Oxidation. Mol. Asp. Med. 2024, 96, 101238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Wei, X. Exosome-Based Crosstalk in Glaucoma Pathogenesis: A Focus on Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1202704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rim, E.Y.; Clevers, H.; Nusse, R. The Wnt Pathway: From Signaling Mechanisms to Synthetic Modulators. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2022, 91, 571–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallée, A.; Vallée, J.-N.; Lecarpentier, Y. Lithium and Atypical Antipsychotics: The Possible WNT/β Pathway Target in Glaucoma. Biomedicines 2021, 9, 473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, R.; Nosie, A.; Walker, T.; Faralli, J.A.; Filla, M.S.; Barrett-Wilt, G.; Peters, D.M. Comparative Genomic and Proteomic Analysis of Cytoskeletal Changes in Dexamethasone-Treated Trabecular Meshwork Cells. Mol. Cell. Proteom. MCP 2013, 12, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bermudez, J.Y.; Montecchi-Palmer, M.; Mao, W.; Clark, A.F. Cross-Linked Actin Networks (CLANs) in Glaucoma. Exp. Eye Res. 2017, 159, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benoist d’Azy, C.; Pereira, B.; Chiambaretta, F.; Dutheil, F. Oxidative and Anti-Oxidative Stress Markers in Chronic Glaucoma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0166915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goyal, A.; Srivastava, A.; Sihota, R.; Kaur, J. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress Markers in Aqueous Humor of Primary Open Angle Glaucoma and Primary Angle Closure Glaucoma Patients. Curr. Eye Res. 2014, 39, 823–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.H.; Lim, S.-H. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Glaucoma. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Han, R.; Xu, S.; Chen, J.; Zhong, Y. Matrix Metalloproteinases in Glaucoma: An Updated Overview. Semin. Ophthalmol. 2023, 38, 703–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Icer, M.A.; Gezmen-Karadag, M. The Multiple Functions and Mechanisms of Osteopontin. Clin. Biochem. 2018, 59, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ridge, K.M.; Eriksson, J.E.; Pekny, M.; Goldman, R.D. Roles of Vimentin in Health and Disease. Genes Dev. 2022, 36, 391–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Bolten, Z.T.; Wagner, D.R.; Hsieh, A.H. Deformability of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Is Dependent on Vimentin Intermediate Filaments. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 45, 1365–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michael, I.; Walton, D.S.; Levenberg, S. Infantile Aphakic Glaucoma: A Proposed Etiologic Role of IL-4 and VEGF. J. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2011, 48, 98–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Huang, Z.; Li, H.; Liu, X.; Zheng, S.; Su, W. IL-38: A New Player in Inflammatory Autoimmune Disorders. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.; Todorovic, V. Interleukin-36: Structure, Signaling and Function. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2021, 21, 191–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, B.; Chen, W.; Jiang, R.; Zhang, R.; Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Gordon, L.; Chen, L. Expression Profile of IL-1 Family Cytokines in Aqueous Humor and Sera of Patients with HLA-B27 Associated Anterior Uveitis and Idiopathic Anterior Uveitis. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 138, 80–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, M.; Ma, L.; Jiang, H.; Gu, Y.; Yang, X.; Liu, R.; Sun, C.; Li, Y. Interleukin-37 Is Involved in the Immunopathogenesis of Infectious Mononucleosis. Ital. J. Pediatr. 2023, 49, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Graaf, D.M.; Teufel, L.U.; Joosten, L.A.B.; Dinarello, C.A. Interleukin-38 in Health and Disease. Cytokine 2022, 152, 155824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greslechner, R.; Helbig, H.; Spiegel, D. Secondary open-angle glaucoma: Uveitic secondary glaucoma, steroid-induced glaucoma, posttraumatic and postoperative glaucoma, tumor-related glaucoma and glaucoma due to elevated episcleral venous pressure. Ophthalmol. Z. Dtsch. Ophthalmol. Ges. 2022, 119, 533–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greslechner, R.; Helbig, H.; Spiegel, D. [Secondary open-angle glaucoma: Pseudoexfoliative glaucoma, pigmentary glaucoma and neovascular glaucoma]. Ophthalmol. Z. Dtsch. Ophthalmol. Ges. 2022, 119, 425–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, A. Exfoliation Syndrome and Exfoliation Glaucoma: Current Perspectives and Clinical Paradigms. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 72, 938–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastronikolis, S.; Pagkalou, M.; Plotas, P.; Kagkelaris, K.; Georgakopoulos, C.D. Emerging Roles of Oxidative Stress in the Pathogenesis of Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome (Review). Exp. Ther. Med. 2022, 24, 602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuteja, S.; Zeppieri, M.; Chawla, H. Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome and Glaucoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Kurowska, A.K.; Kamińska, A.; Izdebska, J.; Szaflik, J.P.; Szaflik, J. [Pseudoexfoliation syndrome (PEX)—A systemic disorder]. Klin. Ocz. 2009, 111, 160–164. [Google Scholar]
- Tekin, K.; Inanc, M.; Elgin, U. Monitoring and Management of the Patient with Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome: Current Perspectives. Clin. Ophthalmol. Auckl. NZ 2019, 13, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiras, D.; Kitsos, G.; Petersen, M.B.; Skalidakis, I.; Kroupis, C. Oxidative Stress in Dry Age-Related Macular Degeneration and Exfoliation Syndrome. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2015, 52, 12–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastronikolis, S.; Pagkalou, M.; Baroutas, G.; Kyriakopoulou, K.; Makri, O.E.; Georgakopoulos, C.D. Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome: The Critical Role of the Extracellular Matrix in Pathogenesis and Treatment. IUBMB Life 2022, 74, 995–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, H.M.; Johnson, W.M.; Aboobakar, I.F.; Strickland, S.; Gomez-Caraballo, M.; Parker, M.; Finnegan, L.; Corcoran, D.L.; Skiba, N.P.; Allingham, R.R.; et al. Identification and Activity of the Functional Complex between hnRNPL and the Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome-Associated lncRNA, LOXL1-AS1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2020, 29, 1986–1995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; He, J.; Sun, J. LOXL1 Gene Polymorphisms Are Associated with Exfoliation Syndrome/Exfoliation Glaucoma Risk: An Updated Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0250772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumbrăveanu, L.; Cușnir, V.; Bobescu, D. A Review of Neovascular Glaucoma. Etiopathogenesis and Treatment. Rom. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 65, 315–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mishra, C.; Meyer, J.J. Neovascular Glaucoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Urbonavičiūtė, D.; Buteikienė, D.; Janulevičienė, I. A Review of Neovascular Glaucoma: Etiology, Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Med. Kaunas Lith. 2022, 58, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabral, T.; Mello, L.G.M.; Lima, L.H.; Polido, J.; Regatieri, C.V.; Belfort, R.; Mahajan, V.B. Retinal and Choroidal Angiogenesis: A Review of New Targets. Int. J. Retin. Vitr. 2017, 3, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, G.B.; Abe, R.Y.; Zangalli, C.; Sodre, S.L.; Donini, F.A.; Costa, D.C.; Leite, A.; Felix, J.P.; Torigoe, M.; Diniz-Filho, A.; et al. Neovascular Glaucoma: A Review. Int. J. Retin. Vitr. 2016, 2, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolshunov, A.V.; Poleva, R.P.; Ragozina, E.A.; Khderi, K. [Pigmentary glaucoma: Yesterday, today, tomorrow]. Vestn. Oftalmol. 2021, 137, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppieri, M. Pigment Dispersion Syndrome: A Brief Overview. J. Clin. Transl. Res. 2022, 8, 344–350. [Google Scholar]
- Scuderi, G.; Contestabile, M.T.; Scuderi, L.; Librando, A.; Fenicia, V.; Rahimi, S. Pigment Dispersion Syndrome and Pigmentary Glaucoma: A Review and Update. Int. Ophthalmol. 2019, 39, 1651–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okafor, K.; Vinod, K.; Gedde, S.J. Update on Pigment Dispersion Syndrome and Pigmentary Glaucoma. Curr. Opin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 28, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bustamante-Arias, A.; Ruiz-Lozano, R.E.; Carlos Alvarez-Guzman, J.; Gonzalez-Godinez, S.; Rodriguez-Garcia, A. Pigment Dispersion Syndrome and Its Implications for Glaucoma. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2021, 66, 743–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeppieri, M.; Tripathy, K. Pigment Dispersion Glaucoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Migliazzo, C.V.; Shaffer, R.N.; Nykin, R.; Magee, S. Long-Term Analysis of Pigmentary Dispersion Syndrome and Pigmentary Glaucoma. Ophthalmology 1986, 93, 1528–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phulke, S.; Kaushik, S.; Kaur, S.; Pandav, S.S. Steroid-Induced Glaucoma: An Avoidable Irreversible Blindness. J. Curr. Glaucoma Pract. 2017, 11, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feroze, K.B.; Zeppieri, M.; Khazaeni, L. Steroid-Induced Glaucoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Roberti, G.; Oddone, F.; Agnifili, L.; Katsanos, A.; Michelessi, M.; Mastropasqua, L.; Quaranta, L.; Riva, I.; Tanga, L.; Manni, G. Steroid-Induced Glaucoma: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Clinical Management. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2020, 65, 458–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasetti, R.B.; Maddineni, P.; Patel, P.D.; Searby, C.; Sheffield, V.C.; Zode, G.S. Transforming Growth Factor Β2 (TGFβ2) Signaling Plays a Key Role in Glucocorticoid-Induced Ocular Hypertension. J. Biol. Chem. 2018, 293, 9854–9868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohd Nasir, N.A.; Agarwal, R.; Krasilnikova, A.; Sheikh Abdul Kadir, S.H.; Iezhitsa, I. Effect of Dexamethasone on the Expression of MMPs, Adenosine A1 Receptors and NFKB by Human Trabecular Meshwork Cells. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 2020, 31, 20190373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulig, S.; Krause, M. Anti-Aging of Our Optic Nerve-Dream or Reality?—Impact of Macrophage Activation and Resveratol on Optic Nerve Health. Open J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 14, 428–433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, K.; Shibata-Germanos, S.; Pahlitzsch, M.; Cordeiro, M.F. Current Perspective of Neuroprotection and Glaucoma. Clin. Ophthalmol. Auckl. NZ 2015, 9, 2109–2118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osman, E.A. Glaucoma after Open Globe Injury. Saudi J. Ophthalmol. Off. J. Saudi Ophthalmol. Soc. 2015, 29, 222–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ng, J.K.; Lau, O. Traumatic Glaucoma. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2025. [Google Scholar]
- De Leon-Ortega, J.E.; Girkin, C.A. Ocular Trauma-Related Glaucoma. Ophthalmol. Clin. N. Am. 2002, 15, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girkin, C.A.; McGwin, G.; Long, C.; Morris, R.; Kuhn, F. Glaucoma after Ocular Contusion: A Cohort Study of the United States Eye Injury Registry. J. Glaucoma 2005, 14, 470–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razeghinejad, R.; Lin, M.M.; Lee, D.; Katz, L.J.; Myers, J.S. Pathophysiology and Management of Glaucoma and Ocular Hypertension Related to Trauma. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2020, 65, 530–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Lei, F.; Zhou, C.; Chodosh, J.; Wang, L.; Huang, Y.; Dohlman, C.H.; Paschalis, E.I. Glaucoma after Ocular Surgery or Trauma: The Role of Infiltrating Monocytes and Their Response to Cytokine Inhibitors. Am. J. Pathol. 2020, 190, 2056–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohra, R.; Tsai, J.C.; Kolko, M. The Role of Inflammation in the Pathogenesis of Glaucoma. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2013, 58, 311–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levkovitch–Verbin, H.; Harris–Cerruti, C.; Groner, Y.; Wheeler, L.A.; Schwartz, M.; Yoles, E. RGC Death in Mice after Optic Nerve Crush Injury: Oxidative Stress and Neuroprotection. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 4169–4174. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, S.M.; Lerner, S.F.; Brunzini, R.; Evelson, P.A.; Llesuy, S.F. Oxidative Stress Markers in Aqueous Humor of Glaucoma Patients. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 137, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozdemir, G.; Tolun, F.I.; Gul, M.; Imrek, S. Retinal Oxidative Stress Induced by Intraocular Hypertension in Rats May Be Ameliorated by Brimonidine Treatment and N-Acetyl Cysteine Supplementation. J. Glaucoma 2009, 18, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghanem, A.A.; Arafa, L.F.; El-Baz, A. Oxidative Stress Markers in Patients with Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Curr. Eye Res. 2010, 35, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdurmuş, M.; Yağcı, R.; Atış, Ö.; Karadağ, R.; Akbaş, A.; Hepşen, İ.F. Antioxidant Status and Oxidative Stress in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma and Pseudoexfoliative Glaucoma. Curr. Eye Res. 2011, 36, 713–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majsterek, I.; Malinowska, K.; Stanczyk, M.; Kowalski, M.; Blaszczyk, J.; Kurowska, A.K.; Kaminska, A.; Szaflik, J.; Szaflik, J.P. Evaluation of Oxidative Stress Markers in Pathogenesis of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2011, 90, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagnis, A.; Izzotti, A.; Centofanti, M.; Saccà, S.C. Aqueous Humor Oxidative Stress Proteomic Levels in Primary Open Angle Glaucoma. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 103, 55–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Himori, N.; Yamamoto, K.; Maruyama, K.; Ryu, M.; Taguchi, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Nakazawa, T. Critical Role of Nrf2 in Oxidative Stress-induced Retinal Ganglion Cell Death. J. Neurochem. 2013, 127, 669–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, W.; Kuang, H. Oxidative Stress Induces Autophagy in Response to Multiple Noxious Stimuli in Retinal Ganglion Cells. Autophagy 2014, 10, 1692–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naguib, S.; Backstrom, J.R.; Gil, M.; Calkins, D.J.; Rex, T.S. Retinal Oxidative Stress Activates the NRF2/ARE Pathway: An Early Endogenous Protective Response to Ocular Hypertension. Redox Biol. 2021, 42, 101883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanz-Morello, B.; Ahmadi, H.; Vohra, R.; Saruhanian, S.; Freude, K.K.; Hamann, S.; Kolko, M. Oxidative Stress in Optic Neuropathies. Antioxidants 2021, 10, 1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Qi, Y.; Yang, X. Neuroprotective Effects of Crocin against Oxidative Stress Induced by Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury in Rat Retina. Ophthalmic Res 2015, 54, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hines-Beard, J.; Bond, W.S.; Backstrom, J.R.; Rex, T.S. Virus-Mediated EpoR76E Gene Therapy Preserves Vision in a Glaucoma Model by Modulating Neuroinflammation and Decreasing Oxidative Stress. J. Neuroinflammation 2016, 13, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Tang, L.; Zeng, J.; Chen, B. Adeno-Associated Virus Mediated SOD Gene Therapy Protects the Retinal Ganglion Cells from Chronic Intraocular Pressure Elevation Induced Injury via Attenuating Oxidative Stress and Improving Mitochondrial Dysfunction in a Rat Model. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2016, 8, 799–810. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, X.; Cho, K.; Thee, E.F.; Jager, M.J.; Chen, D.F. Neuroinflammation and Microglia in Glaucoma: Time for a Paradigm Shift. J. Neurosci. Res. 2019, 97, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, K.A.; Benowitz, L.I. Retinal Ganglion Cell Survival and Axon Regeneration after Optic Nerve Injury: Role of Inflammation and Other Factors. IJMS 2022, 23, 10179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Luo, C.; Cai, J.; Powell, D.W.; Yu, D.; Kuehn, M.H.; Tezel, G. Neurodegenerative and Inflammatory Pathway Components Linked to TNF-α/TNFR1 Signaling in the Glaucomatous Human Retina. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 8442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, G.N.; Inman, D.M.; Dengler-Crish, C.M.; Smith, M.A.; Crish, S.D. Early Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Elevations in the DBA/2J Mouse Model of Glaucoma. J. Neuroinflammation 2015, 12, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharma, R.; Grover, A. Myocilin-Associated Glaucoma: A Historical Perspective and Recent Research Progress. Mol. Vis. 2021, 27, 480–493. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pattabiraman, P.P.; Rao, P.V. Hic-5 Regulates Actin Cytoskeletal Reorganization and Expression of Fibrogenic Markers and Myocilin in Trabecular Meshwork Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 5656–5669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aroca-Aguilar, J.-D.; Sánchez-Sánchez, F.; Ghosh, S.; Fernández-Navarro, A.; Coca-Prados, M.; Escribano, J. Interaction of Recombinant Myocilin with the Matricellular Protein SPARC: Functional Implications. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gobeil, S.; Letartre, L.; Raymond, V. Functional Analysis of the Glaucoma-Causing TIGR/Myocilin Protein: Integrity of Amino-Terminal Coiled-Coil Regions and Olfactomedin Homology Domain Is Essential for Extracellular Adhesion and Secretion. Exp. Eye Res. 2006, 82, 1017–1029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vranka, J.A.; Kelley, M.J.; Acott, T.S.; Keller, K.E. Extracellular Matrix in the Trabecular Meshwork: Intraocular Pressure Regulation and Dysregulation in Glaucoma. Exp. Eye Res. 2015, 133, 112–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Marco, N.; Buono, M.; Troise, F.; Diez-Roux, G. Optineurin Increases Cell Survival and Translocates to the Nucleus in a Rab8-Dependent Manner upon an Apoptotic Stimulus. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 16147–16156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anborgh, P.H.; Godin, C.; Pampillo, M.; Dhami, G.K.; Dale, L.B.; Cregan, S.P.; Truant, R.; Ferguson, S.S.G. Inhibition of Metabotropic Glutamate Receptor Signaling by the Huntingtin-Binding Protein Optineurin. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 34840–34848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaie, T.; Child, A.; Hitchings, R.; Brice, G.; Miller, L.; Coca-Prados, M.; Héon, E.; Krupin, T.; Ritch, R.; Kreutzer, D.; et al. Adult-Onset Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma Caused by Mutations in Optineurin. Science 2002, 295, 1077–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forsman, E.; Lemmelä, S.; Varilo, T.; Kristo, P.; Forsius, H.; Sankila, E.-M.; Järvelä, I. The Role of TIGR and OPTN in Finnish Glaucoma Families: A Clinical and Molecular Genetic Study. Mol. Vis. 2003, 9, 217–222. [Google Scholar]
- Tovar-Vidales, T.; Clark, A.F.; Wordinger, R.J. Transforming Growth Factor-Beta2 Utilizes the Canonical Smad-Signaling Pathway to Regulate Tissue Transglutaminase Expression in Human Trabecular Meshwork Cells. Exp. Eye Res. 2011, 93, 442–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, J.M.; Vranka, J.; Colvis, C.M.; Conger, D.M.; Alexander, J.P.; Fisk, A.S.; Samples, J.R.; Acott, T.S. Effect of Matrix Metalloproteinases Activity on Outflow in Perfused Human Organ Culture. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1998, 39, 2649–2658. [Google Scholar]
- Keller, K.E.; Aga, M.; Bradley, J.M.; Kelley, M.J.; Acott, T.S. Extracellular Matrix Turnover and Outflow Resistance. Exp. Eye Res. 2009, 88, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuchshofer, R.; Tamm, E.R. The Role of TGF-β in the Pathogenesis of Primary Open-Angle Glaucoma. Cell Tissue Res. 2012, 347, 279–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Authors | Type of Study | Year | Country | Study Group | Control Group | Patient Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Määttä et al. [39] | Analytical study on MMP and TIMP levels and activation | 2006 | Finland | URSG | POAG, cataract | 13 URSG 10 POAG 10 cataract |
| Balaiya et al. [40] | Observational study | 2011 | USA | POAG | cataract | 32 POAG 32 cataract |
| Ohira et al. [41] | Cross-sectional study with cytokine analysis | 2015 | Japan | NVG, POAG | cataract | 33 NVG 36 POAG 68 cataract |
| Dursun et al. [42] | Observational study with biochemical analysis | 2015 | Turkey | PEX syndrome, PEG | cataract | 26 PEX syndrome 26 PEG 26 cataract |
| Bojikian et al. [43] | Retrospective, observational case series | 2015 | USA | OGI | - | 515 OGI |
| Kaeslin et al. [22] | Case-control study with quantitative proteomic analysis | 2016 | Switzerland | POAG | cataract | 5 POAG 5 cataract |
| Tetikoğlu et al. [44] | Prospective clinical study with biochemical analysis | 2016 | Turkey | PEX syndrome | healthy subjects | 34 PEX syndrome 38 healthy subjects |
| Guo et al. [45] | Cross-sectional, observational study | 2019 | China | POAG, CACG, PACS | cataract | 21 POAG 19 CACG 9 PACS 24 cataract |
| Nikhalashree et al. [46] | Comparative, observational study with proteomic analysis | 2019 | India | POAG, PACG | cataract | 90 POAG 72 PACG 78 cataract |
| Sun et al. [47] | Observational study with biomarker analysis | 2019 | China | NVG, PDR | - | 15 NVG 17 PDR |
| Kaur et al. [48] | Comparative, cross-sectional study with proteomic analysis | 2019 | India | POAG, PACG, cataract | - | 9 POAG 9 PACG 9 cataract |
| Adav et al. [49] | Comparative, cross-sectional proteomics study | 2019 | Singapore | PACG | cataract | 2 PACG and cataract 3 cataract only |
| Zhang et al. [50] | Comparative, observational study | 2019 | China | CPACG | cataract | 22 CPACG 29 cataract |
| Liu H et al. [51] | Experimental study with proteomic analysis | 2020 | Germany | POAG | cataract | 23 POAG 12 cataract |
| Liu X et al. [3] | Observational study with proteomic analysis | 2021 | China | PAACG, PCACG, NVG, cataract | - | 57 PAACG 50 PCACG 35 NVG 33 cataract |
| Yun et al. [52] | Comparative, observational study with proteome analysis | 2021 | Republic of Korea | PACG | healthy subjects | 6 PACG 6 healthy subjects |
| Hubens et al. [53] | Comparative observational study | 2021 | Netherlands | progressive POAG, stable POAG | cataract | 10 progressive POAG 10 stable POAG 10 cataract patients |
| Mok et al. [54] | Multi-omics analysis | 2024 | Republic of Korea | POAG, XFS, XFG | cataract | 5 XFS 4 XFG 11 POAG 7 cataract |
| Feng et al. [55] | Comparative, cross-sectional, observational study | 2024 | China | CPACG | cataract | 31 CPACG 30 cataract |
| Authors | Year | Country | Patient Number | Cataract Proteins (Total Number) | Glaucoma Proteins (Total Number) | Comment |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kaeslin et al. [22] | 2016 | Switzerland | 5 POAG 5 cataract | 448 | 448 | Proteins different for both groups: 87 (in glaucoma, 34 were upregulated and 53 were downregulated). |
| Nikhalashree et al. [46] | 2019 | India | 90 POAG 72 PACG 78 cataract | 184 | POAG 190 PACG 299 | Unique proteins for cataract: 97; POAG: 87; PACG: 171. Proteins identified in every group: 58. Proteins identified in POAG and PACG: 43. |
| Kaur et al. [48] | 2019 | India | 9 POAG 9 PACG 9 cataract | 636 | POAG 594 PACG 625 | Unique proteins for cataract: 221; POAG: 206; PACG: 226. Proteins identified in every group: 246. Proteins identified in POAG and PACG: 55. |
| Liu H et al. [51] | 2020 | Germany | 23 POAG 12 cataract | 175 | 175 | No data for exact number of proteins upregulated or downregulated in glaucoma AH (6 proteins were described as with “significant up-regulation”). |
| Liu X et al. [3] | 2021 | China | 57 PAACG 50 PCACG 35 NVG 33 cataract | 315 | 315 | Differential proteins PAACG/cataract: 31. Differential proteins PCACG/cataract: 17. Differential proteins PCACG/cataract: 100. Differential proteins PAACG/PCACG: 202. |
| Mok et al. [54] | 2024 | Republic of Korea | 5 XFS 4 XFG 11 POAG 7 cataract | 329 | 329 | Differential proteins XFS/cataract: 15. Differential proteins XFG/cataract: 34. Differential proteins POAG/cataract: 51. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kiełbus, M.; Kuźmiuk, D.; Skrzyniarz, A.M.; Zynkowska, A.; Dolar-Szczasny, J.; Chorągiewicz, T.; Rejdak, R. Changes in the Protein Composition of the Aqueous Humor in Patients with Glaucoma: An Update Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073129
Kiełbus M, Kuźmiuk D, Skrzyniarz AM, Zynkowska A, Dolar-Szczasny J, Chorągiewicz T, Rejdak R. Changes in the Protein Composition of the Aqueous Humor in Patients with Glaucoma: An Update Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073129
Chicago/Turabian StyleKiełbus, Maria, Dominika Kuźmiuk, Aleksandra Magdalena Skrzyniarz, Aleksandra Zynkowska, Joanna Dolar-Szczasny, Tomasz Chorągiewicz, and Robert Rejdak. 2025. "Changes in the Protein Composition of the Aqueous Humor in Patients with Glaucoma: An Update Review" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073129
APA StyleKiełbus, M., Kuźmiuk, D., Skrzyniarz, A. M., Zynkowska, A., Dolar-Szczasny, J., Chorągiewicz, T., & Rejdak, R. (2025). Changes in the Protein Composition of the Aqueous Humor in Patients with Glaucoma: An Update Review. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3129. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073129






