Extremely Rare Flavonoid Glycosides Identified in the Stems of Ephedra gerardiana by HPLC-MS and Their Antioxidant Activity
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Afzelin and Its Conjugates
2.2. Other Flavonoid O-Glycosides
2.3. Apigenin-6,8-di-C-Glycosides and Their Malonylated Conjugates
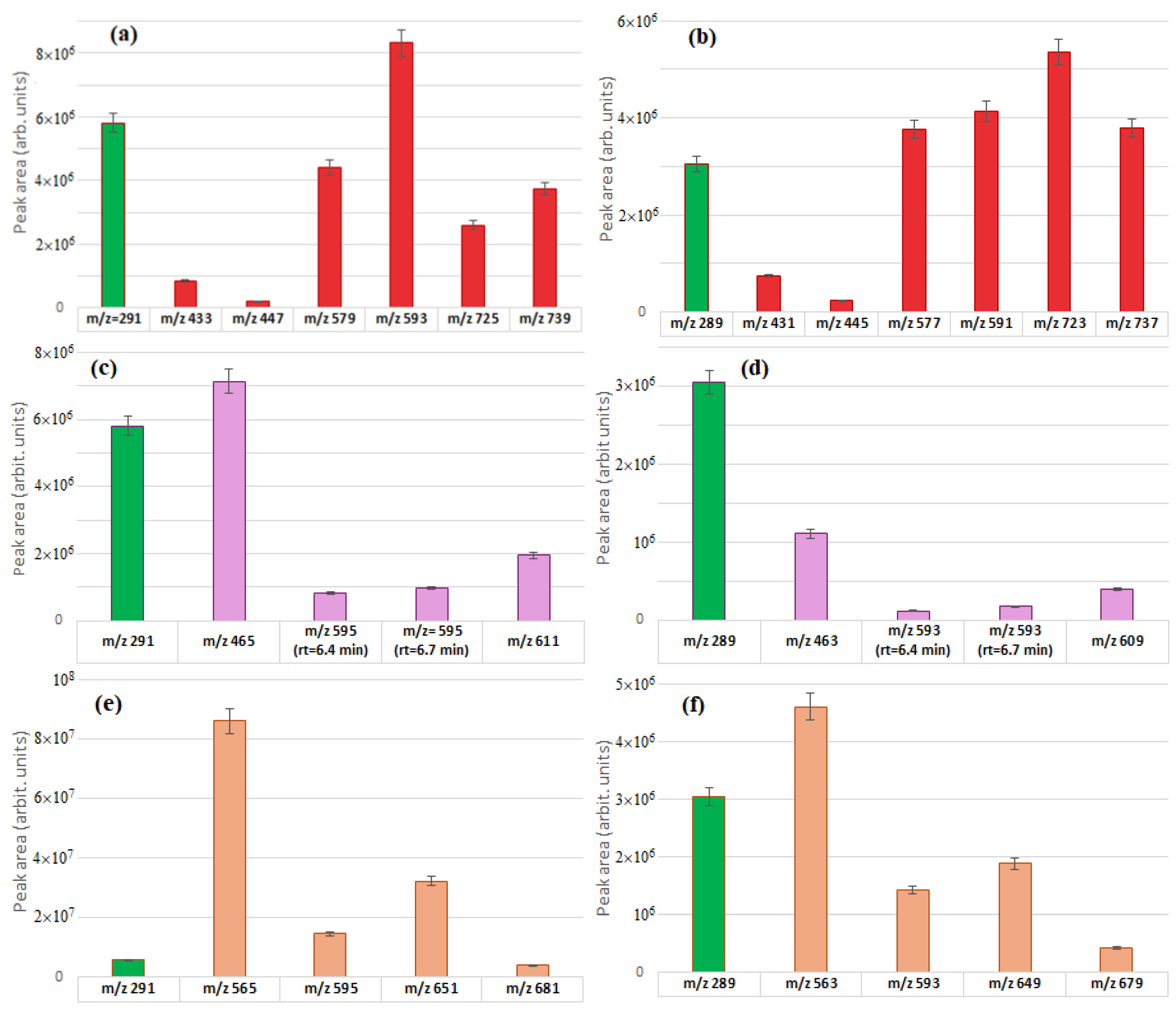
2.4. Relative Abundances of the Identified Flavonoid Glycosides
2.5. Antioxidant Activity and Total Flavonoid Content
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Preparation of the Extract for HPLC-MS Analysis
3.2. HPLC-MS Analysis
3.3. Preparation of the Extract for Determination of Antioxidant Activity and Total Flavonoid Content
3.4. Antioxidant Activity Assay
3.5. Total Flavonoid Content
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Elhadef, K.; Smaoui, S.; Fourati, M.; Ben Hlima, H.; Chakchouk Mtibaa, A.; Sellem, I.; Ennouri, K.; Mellouli, L. A review on worldwide Ephedra history and story: From fossils to natural products mass spectroscopy characterization and biopharmacotherapy potential. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2020, 2020, 1540638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Juárez, D.E.; Escobedo-Moratilla, A.; Flores, J.; Hidalgo-Figueroa, S.; Martínez-Tagüeña, N.; Morales-Jiménez, J.; Muñiz-Ramírez, A.; Pastor-Palacios, G.; Sandra Pérez-Miranda, S.; Ramírez-Hernández, A.; et al. A review of the Ephedra genus: Distribution, ecology, ethnobotany, phytochemistry and pharmacological properties. Molecules 2020, 25, 3283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.; Kumar, P.; Kaur, A.; Kaur, S.; Kaur, S. Bioactive phytochemicals from Ephedra: An updated review. Thai J. Pharm. Sci. 2024, 47, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Ren, J.; Kong, L.; Yan, G.; Liu, C.; Han, Y.; Sun, H.; Wang, X.J. Ephedrae herba: A review of its phytochemistry, pharmacology, clinical application, and alkaloid toxicity. Molecules 2023, 28, 663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Mu, X.; Pan, S.; Luan, R.; Zhao, P. Ephedrae herba: A comprehensive review of its traditional uses, phytochemistry, pharmacology, and toxicology. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2023, 307, 116153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibragic, S.; Barbini, S.; Oberlerchner, J.T.; Potthast, A.; Rosenau, T.; Böhmdorfer, S. Antioxidant properties and qualitative analysis of phenolic constituents in Ephedra spp. by HPTLC together with injection port derivatization GC-MS. J. Chromatogr. B 2021, 1180, 122877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazar, H.; Amar, A.; Younus, M.; Shaheen, G.; Asif, H.M.; Zafar, F.; Ayaz, S. Review of pharmacological activity of Ephedra Gerardiana. Sci. Inq. Rev. 2023, 7, 81–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uttra, A.M.; Shahzad, M.; Shabbir, A.; Jahan, S. Ephedra gerardiana aqueous ethanolic extract and fractions attenuate Freund Complete Adjuvant induced arthritis in Sprague Dawley rats by downregulating PGE2, COX2, IL-1?, IL-6, TNF-?, NF-kB and upregulating IL-4 and IL-10. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 224, 482–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Badere, R.; Singh, S.B. Antibacterial and antioxidant activities of ethanol extracts from trans Himalayan medicinal plants. Pharmacogn. J. 2010, 2, 66–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Jan, G.; Khan, A.; Gul Jan, F.; Bahadur, A.; Danish, M. In vitro antioxidant and antimicrobial activities of Ephedra gerardiana (root and stem) crude extract and fractions. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat. Med. 2017, 2017, 4040254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osmic, N.; Culum, D.; Ibragic, S. Catechins and other phenolic compounds in herb of eight Ephedra species in comparison to Camellia sinensis. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 38, 1457–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, M.; He, W.; Xu, Z.; Lu, Y.; Crabbe, M.J.C.; De, J. The effect of high altitude on ephedrine content and metabolic variations in two species of Ephedra. Front. Plant Sci. 2023, 14, 1236145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domon, B.; Costello, C.E. A systematic nomenclature for carbohydrate fragmentations in FAB-MS/MS spectra of glycoconjugates. Glycoconj. J. 1988, 5, 397–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawwar, M.A.; El-Sissi, H.I.; Barakat, H.H. Flavonoid constituents of Ephedra alata. Phytochemistry 1984, 23, 2937–2939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuo, Y.; Sasaki, M.; Fukaya, H.; Miyake, K.; Takeuchi, R.; Kumata, H.; Mimaki, Y. Chemical constituents of the terrestrial stems of Ephedra sinica and their PPAR-γ ligand-binding activity. Planta Med. Int. Open 2020, 7, e12–e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yahagi, H.; Yahagi, T.; Matsumura, M.; Igarashi, K.; Yokoyama, N.; Matsuzaki, K. Inhibitory activity of flavonoids from Ephedrae Herba on hypoxia signaling in PANC-1 cells and the evaluation of their mechanisms. J. Nat. Med. 2021, 75, 612–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, S.; Gaglione, R.; Masi, M.; Padhi, S.; Rai, A.K.; Omar, G.; Cimmino, A.; Arciello, A. Ephedra foeminea as a novel source of antimicrobial and anti-biofilm compounds to fight multidrug resistance phenotype. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 3284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- March, R.E.; Lewars, E.G.; Stadey, C.J.; Miao, X.-S.; Zhao, X.; Metcalfe, C.D. A comparison of flavonoid glycosides by electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. Int. J. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 248, 61–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beszterda, M.; Frański, R. Elucidation of glycosylation sites of kaempferol di-O-glycosides from methanolic extract of the leaves of Prunus domestica subsp. syriaca. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2021, 35, e9100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.-Z.; Qiao, X.; Bo, T.; Wang, Q.; Guo, D.-A.; Ye, M. Low energy induced homolytic fragmentation of flavonol 3-O-glycosides by negative electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2014, 28, 385–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilia, A.R.; Palme, E.; Marsili, A.; Pistelli, L.; Morelli, I. A flavanol glycoside from Agrimonia eupatoria. Phytochemistry 1993, 32, 1078–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rifai, Y.; Arai, M.A.; Sadhu, S.K.; Ahmed, F.; Ishibashi, M. New Hedgehog/GLI signaling inhibitors from Excoecaria agallocha. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 718–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, T.; Lou, Y.; Ge, Y.; Lu, X.; Zhang, P.; Shu, P. A new monoterpene rhamnoside from Cercis glabra legumes. Rec. Nat. Prod. 2023, 17, 335–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.-C.; Yang, C.-P.; Wang, S.-Y.; Chang, C.-I.; Sung, P.-J.; Huang, G.-J.; Chien, S.-C.; Kuo, Y.-H. Anti-inflammatory flavonol acylglycosides from the aerial part of Lindera akoensis Hayata. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 50868–50874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Kongstad, K.T.; Staerk, D. Identification of α-glucosidase inhibitors in Machilus litseifolia by combined use of high-resolution α-glucosidase inhibition profiling and HPLC-PDA-HRMS-SPE-NMR. J. Nat. Prod. 2019, 82, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhao, Z.; Zhong, R.; Tan, X. A comprehensive review of herbacetin: From chemistry to pharmacological activities. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2021, 279, 114356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyuga, S.; Hyuga, M.; Yoshimura, M.; Amakura, Y.; Goda, Y.; Hanawa, T. Herbacetin, a constituent of ephedrae herba, suppresses the HGF-induced motility of human breast cancer MDA-MB-231 cells by inhibiting c-Met and Akt phosphorylation. Planta Med. 2013, 79, 1525–1530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amakura, Y.; Yoshimura, M.; Yamakami, S.; Yoshida, T.; Wakana, D.; Hyuga, M.; Hyuga, S.; Hanawa, T.; Goda, Y. Characterization of phenolic constituents from Ephedra herb extract. Molecules 2013, 18, 5326–5334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, S.A.; Barakat, H.H.; Nawar, M.A.; Willuhn, G. Flavonoids from Ephedra aphylla. Phytochemistry 1997, 45, 1529–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Tang, W.; Zeng, J.; Tang, C. Screening of terpene lactones and flavonoid glycosides in Gingko biloba capsule by UPLC-Orbitrap high resolution MS, with emphasis on isomer differentiation. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2014, 2, 369–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.-H.; Guo, H.; Xu, W.-B.; Ge, J.; Li, X.; Alimu, M.; He, D.-J. Rapid identification of flavonoid constituents directly from PTP1B inhibitive extract of raspberry (Rubus idaeus L.) leaves by HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS-MS. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 805–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamagaki, T.; Watanabe, T.; Tanaka, M.; Sugahara, K. Laser-induced hydrogen radical removal in UV MALDI-MS allows for the differentiation of flavonoid monoglycoside isomers. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 25, 88–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuyckens, F.; Claeys, M. Determination of the glycosylation site in flavonoid mono-O-glycosides by collision-induced dissociation of electrospray-generated deprotonated and sodiated molecules. J. Mass Spectrom. 2005, 40, 364–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ablajan, K.; Tuoheti, A. Fragmentation characteristics and isomeric differentiation of flavonol O-rhamnosides using negative ion electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2013, 27, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ablajan, K.; Abliz, Z.; Shang, X.-Y.; He, J.-M.; Zhang, R.-P.; Shi, J.-G. Structural characterization of flavonol 3,7-di-O-glycosides and determination of the glycosylation position by using negative ion electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Mass Spectrom. 2006, 41, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuyckens, F.; Claeys, M. Mass spectrometry in the structural analysis of flavonoids. J. Mass Spectrom. 2004, 39, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.-L.; Vedernikova, I.; Van den Heuvel, H.; Claeys, M. Internal glucose residue loss in protonated O-diglycosyl flavonoids upon low-energy collision-induced dissociation. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2000, 11, 136–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oshima, N.; Maruyama, T.; Yamashita, T.; Uchiyama, N.; Amakura, Y.; Hyuga, S.; Hyuga, M.; Nakamori, S.; Takemoto, H.; Kobayashi, Y.; et al. Two flavone C-glycosides as quality control markers for the manufacturing process of ephedrine alkaloids-free Ephedra Herb extract (EFE) as a crude drug preparation. J. Nat. Med. 2018, 72, 73–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stobiecki, M.; Staszków, A.; Piasecka, A.; Garcia-Lopez, P.M.; Zamora-Natera, F.; Kachlicki, P. LC-MSMS profiling of flavonoid conjugates in wild Mexican lupine, Lupinus reflexus. J. Nat. Prod. 2010, 73, 1254–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, A.M.; Caulfield, J.C.; Hao, B.; Pickett, J.A.; Midega, C.A.O.; Khan, Z.R. Isolation and identification of desmodium root exudates from drought tolerant species used as intercrops against Striga hermonthica. Phytochemistry 2015, 117, 380–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beszterda, M.; Frański, R. Detection of flavone C-glycosides in the extracts from the bark of Prunus avium L. and Prunus cerasus L. Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. 2020, 26, 369–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gattuso, G.; Caristi, C.; Gargiuli, C.; Bellocco, E.; Toscano, G.; Leuzzi, U. Flavonoid glycosides in bergamot juice (Citrus bergamia risso). J. Agric. Food Chem. 2006, 54, 3929–3935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barreca, D.; Bellocco, E.; Caristi, C.; Leuzzi, U.G.O.; Gattuso, G. Flavonoid composition and antioxidant activity of juices from chinotto (Citrus × myrtifolia raf.) fruits at different ripening stages. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2010, 58, 3031–3036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, N.K.; Sharath Kumar, L.M.; Gajera, J.; Jadhav, A.N.; Muguli, G.; Babu, U.V. Isolation and characterization of flavonoid C-glycosides from Prosopis glandulosa Torr. leaves. Pharmacogn. Mag. 2018, 14, 451–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreres, F.; Gil-Izquierdo, A.; Vinholes, J.; Grosso, C.; Valentão, P.; Andrade, P.B. Approach to the study of C-glycosyl flavones acylated with aliphatic and aromatic acids from Spergularia rubra by high-performance liquid chromatography photodiode array detection/electrospray ionization multi-stage mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 2011, 25, 700–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chimichi, S.; Mercati, V.; Moneti, G.; Raffaelli, A.; Toja, E. Isolation and characterization of an unknown flavonoid in dry extracts from Passiflora incarnata. Nat. Prod. Lett. 1998, 11, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Z.; Chen, Z.; Xue, X.; He, C.; Yuan, X. A comparative study between Abrus cantoniensis and Abrus mollis: Flavonoids profiles by UPLC-Q-TOF-MS and anti-inflammatory mechanism by transcriptomics. Chem. Biodiversity 2023, 20, e202300204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreres, F.; Silva, B.M.; Andrade, P.B.; Seabra, R.M.; Ferreira, M.A. Approach to the study of C-glycosyl flavones by ion trap HPLC-PAD-ESI/MS/MS: Application to seeds of quince (Cydonia oblonga). Phytochem. Anal. 2003, 14, 352–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beszterda, M.; Frański, R. Isoflavones present in soybean seeds can be glycosylated at 4′-O position as indicated by the ratio of [Y0-H]− and [Y0]− fragment ions. J. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 50, 672–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donna, L.D.; Mazzotti, F.; Taverna, D.; Napoli, A.; Sindona, G. Structural characterisation of malonyl flavonols in leek (Allium porrum L.) using high-performance liquid chromatography and mass spectrometry. Phytochem. Anal. 2014, 25, 207–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stężycka, O.; Frańska, M. Comment on the “Response surface methodology optimization and HPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS analysis on ultrasonic-assisted extraction of phenolic compounds from okra (Abelmoschus esculentus) and their antioxidant activity”. Food Chem. 2023, 414, 135729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alamgir, K.M.; Kawashima, T.; Tebayashi, S.-I.; Kim, C.-S. Acylflavonoid C-glycosides from Eleusine coracana. Phytochem. Lett. 2008, 1, 111–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bylka, W.; Frański, R.; Stobiecki, M. Differentiation between isomeric acacetin-6-C-(6″-O-malonyl)glucoside and acacetin-8-C-(6’’-O-malonyl)glucoside by using low-energy CID mass spectra. J. Mass Spectrom. 2002, 37, 648–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Zhou, Z.; Yao, S.; Li, S.; Yang, W.; Jiang, B.; Xuan Liu, X.; Wu, W.; Qv, H.; Guo, D.-A. Neutral loss ion mapping experiment combined with precursor mass list and dynamic exclusion for screening unstable malonyl glucoside conjugates. J. Am. Soc. Mass Spectrom. 2015, 27, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J.; Capanoglu, E.; Jassbi, A.R.; Miron, A. Advance on the flavonoid C-glycosides and health benefits. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2016, 56 (Suppl. 1), S29–S45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aidhen, I.S.; Srikanth, S.; Lal, H. The emerging promise with O/C-glycosides of important dietary phenolic compounds. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 2022, 2022, e202200758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, J. Dietary flavonoid aglycones and their glycosides: Which show better biological significance? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2017, 57, 1874–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Menezes, B.B.; Frescura, L.M.; Duarte, R.; Villetti, M.A.; Da Rosa, M.B. A critical examination of the DPPH method: Mistakes and inconsistencies in stoichiometry and IC50 determination by UV-Vis spectroscopy. Anal. Chim. Acta 2021, 1157, 338398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shraim, A.M.; Ahmed, T.A.; Rahman, M.M.; Hijji, Y.M. Determination of total flavonoid content by aluminum chloride assay: A critical evaluation. LWT 2021, 150, 111932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
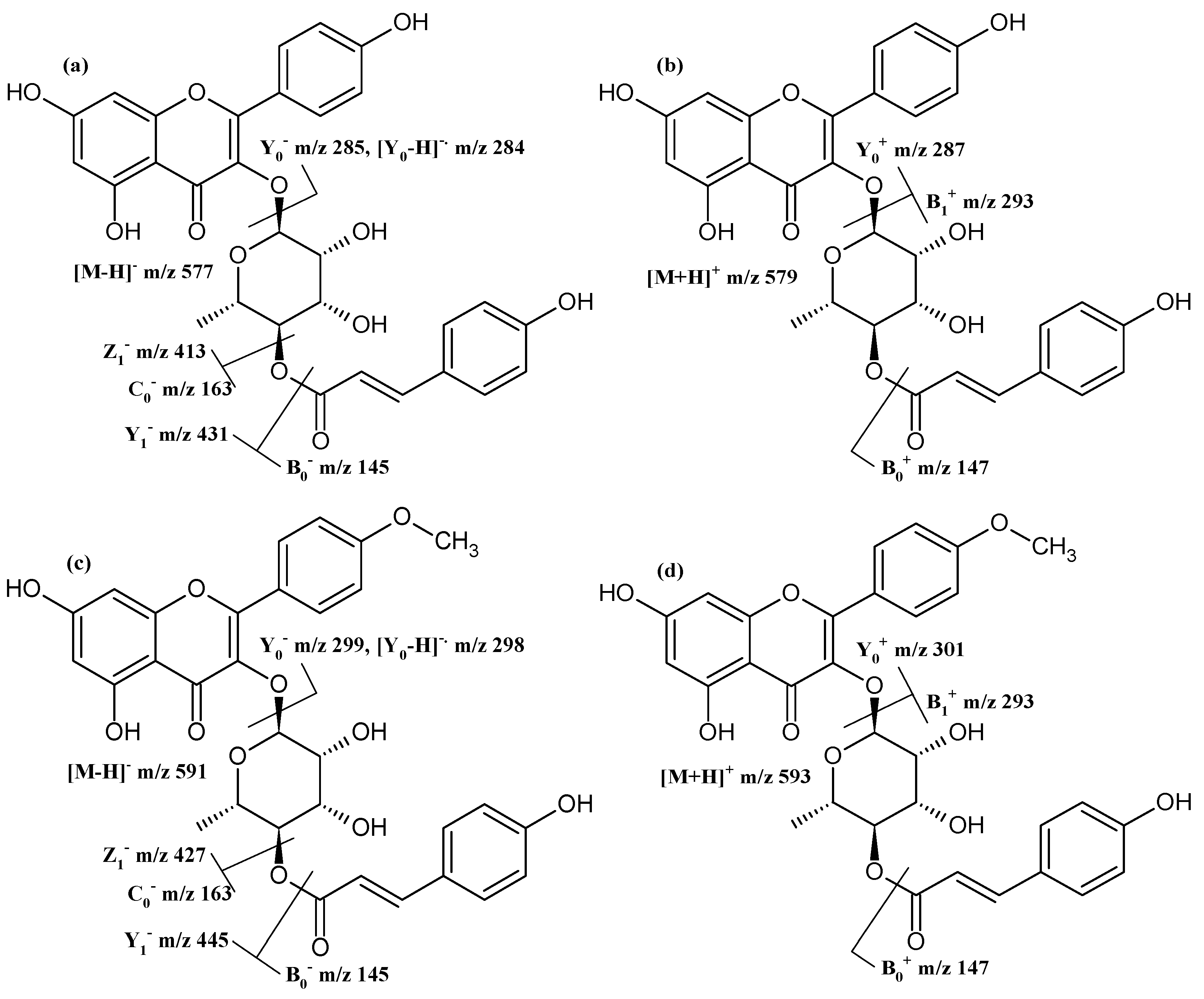
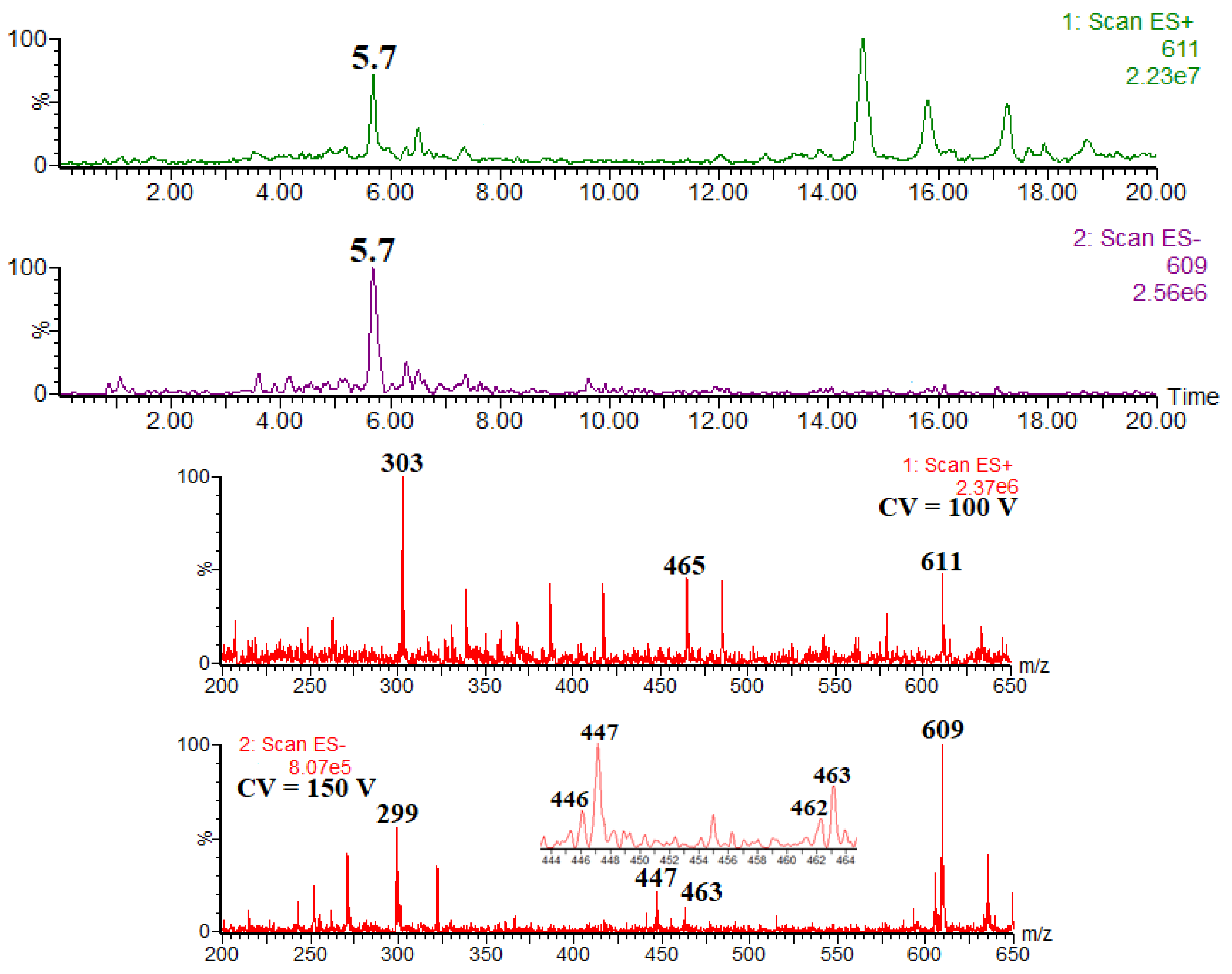
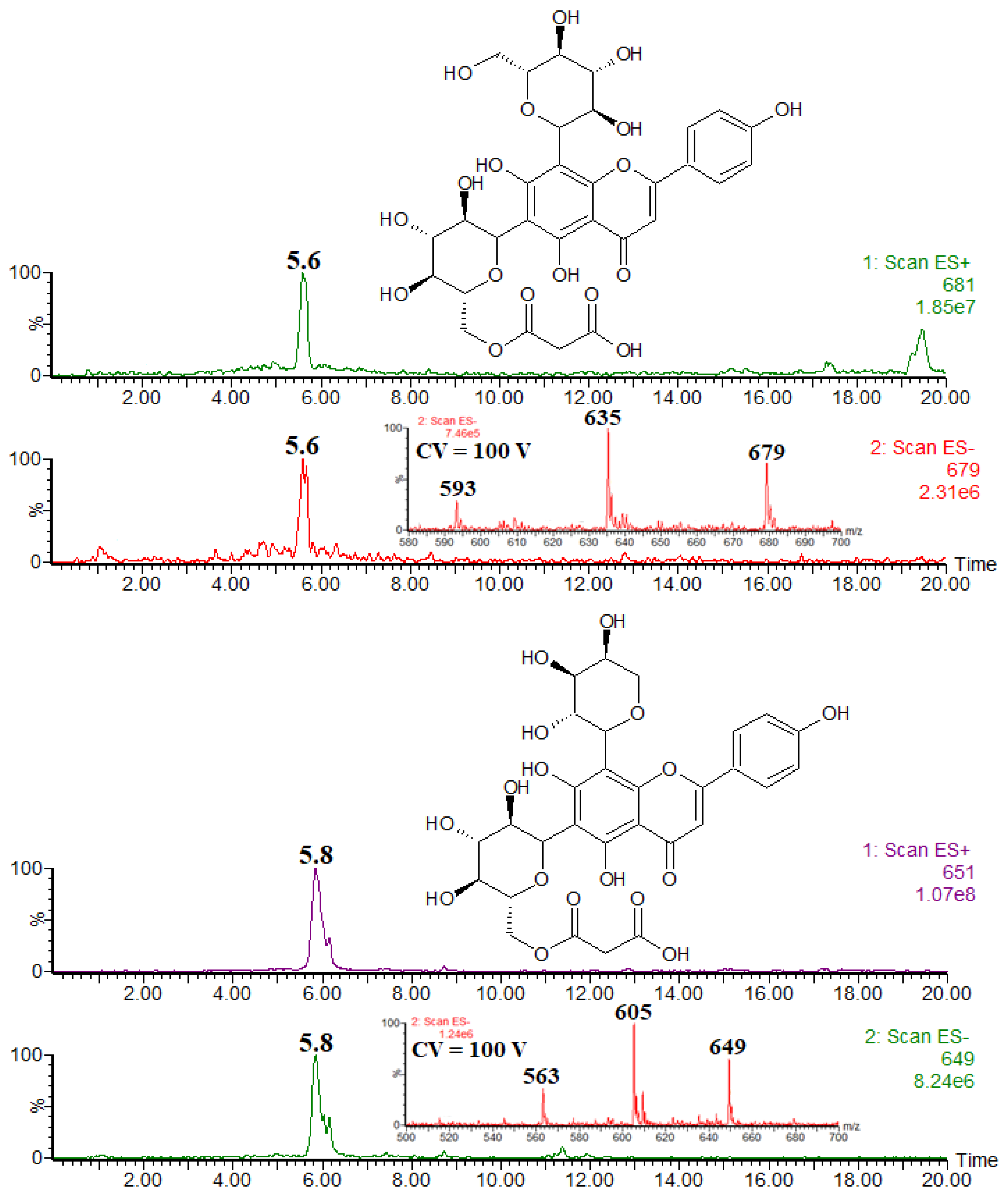
| Compound | rt | [M − H]− [M + H]+ | Product Ions (Type) |
|---|---|---|---|
| afzelin | 7.6 | 431 433 | 285 (Y0−), 284 ([Y0 − H]−•), 287 (Y0+) |
| (4″-[E]-p-coumaroyl)afzelin | 10.2 | 577 579 | 431 (Y1−), 413 (Z1−), 285 (Y0−), 284 ([Y0 − H]−•), 163 (C0−), 145 (B0−) 293 (B1+), 287 (Y0+), 147 (B0+) |
| (2″,4″-di-[E]-p-coumaroyl)afzelin | 12.2 | 723 725 | 577 (Y1−), 559 (Z1−), 437 (B1−), 285 (Y0−), 284 ([Y0 − H]−•), 163 (C0−), 145 (B0−) 439 (B1+), 147 (B0+) |
| 4′-O-methylafzelin | 8.5 | 445 447 | 299 (Y0−), 298 ([Y0 − H]−•) 301 (Y0+) |
| 4′-O-methyl-(4″-[E]-p-coumaroyl)afzelin | 11.1 | 591 593 | 445 (Y1−), 427 (Z1−), 299 (Y0−), 298 ([Y0 − H]−•), 163 (C0−), 145 (B0−) 293 (B1+), 301 (Y0+), 147 (B0+) |
| 4′-O-methyl-(2″,4″-di-[E]-p-coumaroyl)afzelin | 13.0 | 737 739 | 591 (Y1−), 573 (Z1−), 437 (B1−), 299 (Y0−), 298 ([Y0 − H]−•), 163 (C0−), 145 (B0−) 439 (B1+), 147 (B0+) |
| Compound | rt | [M − H]− [M + H]+ | Product Ions (Type) |
|---|---|---|---|
| herbacetin 7-O-glucoside | 6.8 | 463 465 | 301 (Y0−) 303 (Y0+) |
| herbacetin-4′-O-rhamnoside-7-O-glucoside | 5.7 | 609 611 | 463 (Y4′0−), 447 (Y70−), 301 (Y0−), 299 ([Y0 − 2H]−) 465 (Y4′0+), 303 (Y0+) |
| kaempferol-4′-O-rhamnoside-7-O-glucoside | 6.4 | 593 595 | 447 (Y4′0−), 431 (Y70−), 285 (Y0−), 283 ([Y0 −2H]−) 449 (Y4′0+), 287 (Y0+) |
| kaempferol 7-O-neohesperidoside | 6.7 | 593 595 | 285 (Y0−), 284 ([Y0 − H]−•) 449 (Y1+, low abundance), 287 (Y0+) |
| Compound | rt | [M − H]− | Product Ions (Type) |
|---|---|---|---|
| apigenin 6,8-di-C-glucoside (vicenin-2) | 5.1 | 593 | 503 (0,3X−), 473 (0,2X−), 383 (0,3/0,2X−), 353 (0.2/0.2X−) |
| apigenin 6-C-glucoside-8-C-arabinoside (schaftoside) and its isomer | 5.4 | 563 | 503 (0,3X−), 473 (0,3X−), 443 (0,2X−), 383 (0,3/0,2X−), 353 (0,3/0,2X−) |
| malonyl conjugate of vicenin-2 | 5.6 | 679 | 635 ([M – H − CO2]−), 593 ([M – H − CO2 − CH2CO]−) |
| malonyl conjugate of schaftoside and its isomer | 5.8 | 649 | 605 ([M – H − CO2]−), 563 ([M − H-CO2 − CH2CO]−) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szymborska, K.; Frański, R.; Gierczyk, B.; Beszterda-Buszczak, M. Extremely Rare Flavonoid Glycosides Identified in the Stems of Ephedra gerardiana by HPLC-MS and Their Antioxidant Activity. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073097
Szymborska K, Frański R, Gierczyk B, Beszterda-Buszczak M. Extremely Rare Flavonoid Glycosides Identified in the Stems of Ephedra gerardiana by HPLC-MS and Their Antioxidant Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073097
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzymborska, Karolina, Rafał Frański, Błażej Gierczyk, and Monika Beszterda-Buszczak. 2025. "Extremely Rare Flavonoid Glycosides Identified in the Stems of Ephedra gerardiana by HPLC-MS and Their Antioxidant Activity" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073097
APA StyleSzymborska, K., Frański, R., Gierczyk, B., & Beszterda-Buszczak, M. (2025). Extremely Rare Flavonoid Glycosides Identified in the Stems of Ephedra gerardiana by HPLC-MS and Their Antioxidant Activity. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3097. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073097



_Kim.png)



