Control of Conformational Transitions by the Conserved GX9P Motif in the Fifth Transmembrane Domain of Neurotransmitter Sodium Symporters
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Sequence Alignment of the NSS Members and Structural Comparison of the GX9P Motif in SERT
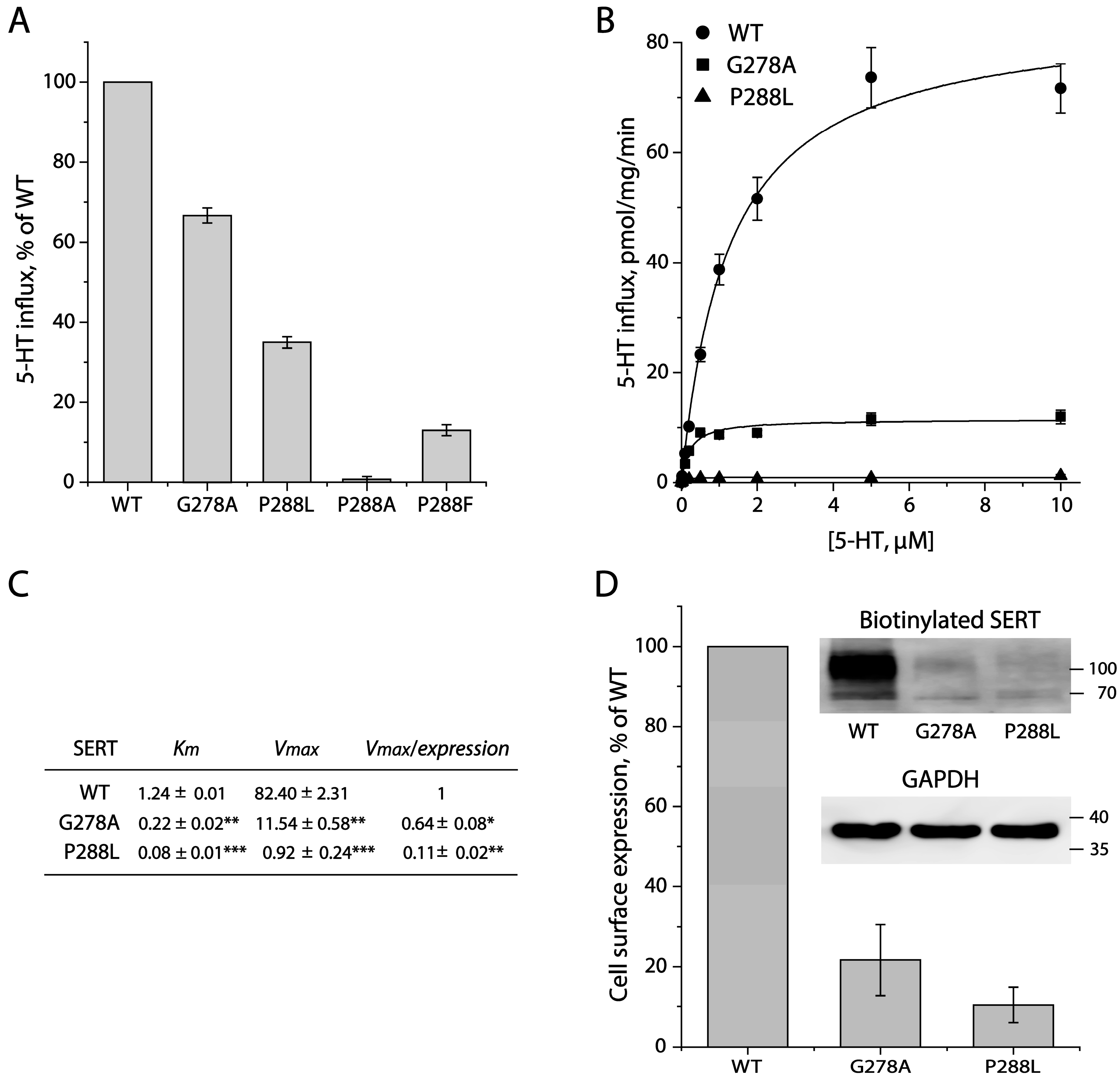
2.2. Mutational Analysis for the GX9P Motif
2.3. Effects of the GX9P Mutations on SERT Conformation
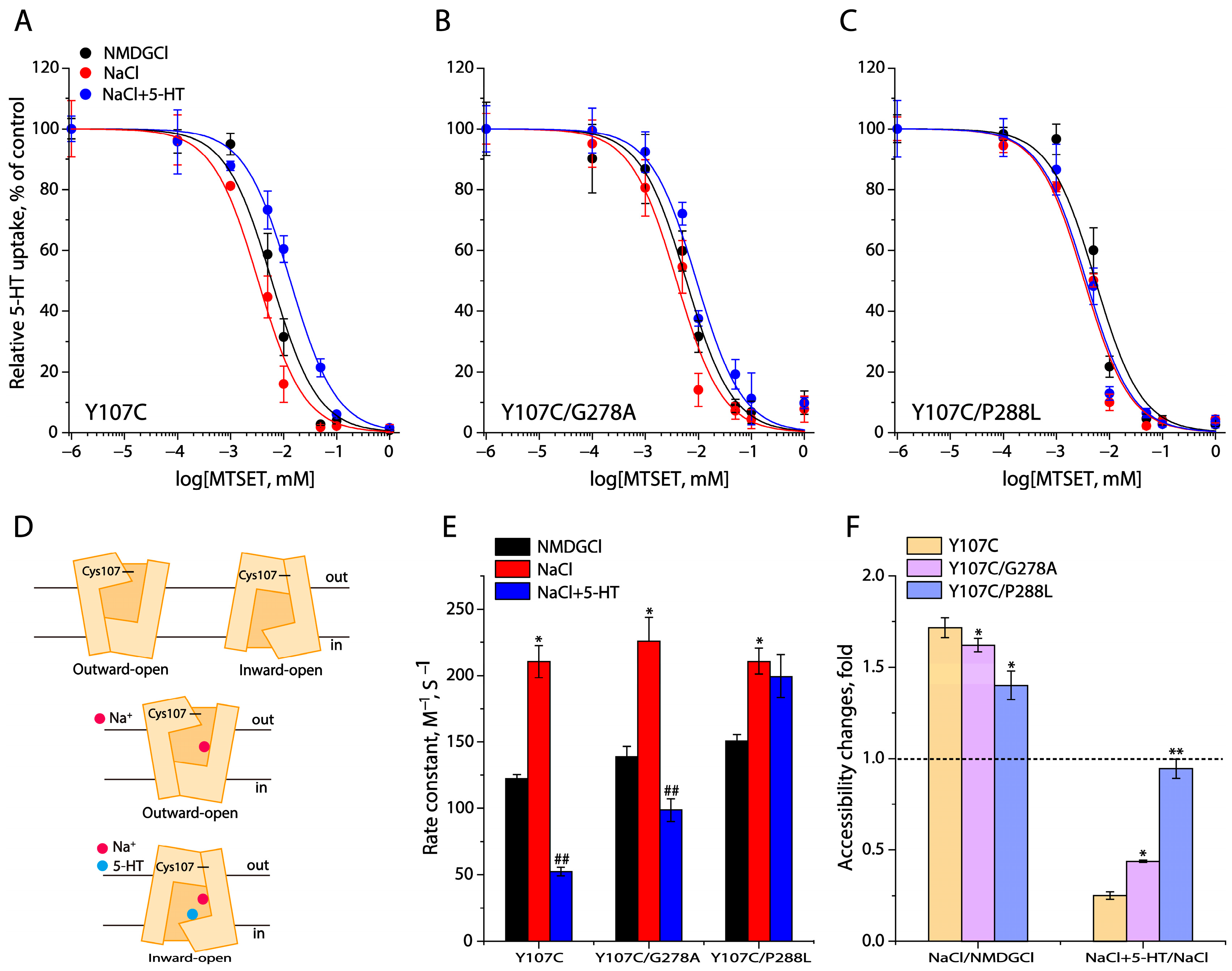
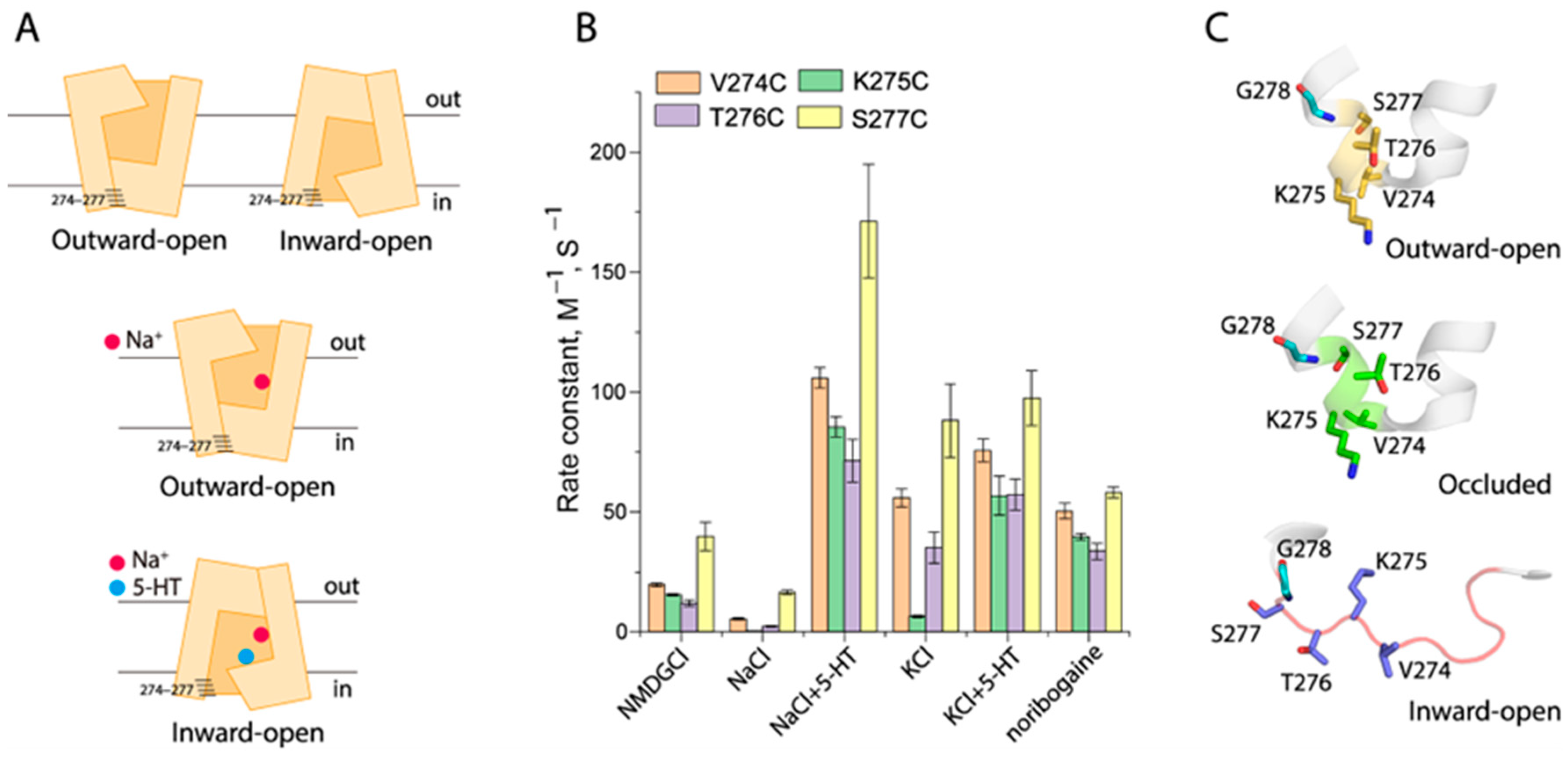
2.4. Conformational Analysis for Unwinding in the Middle of TM5
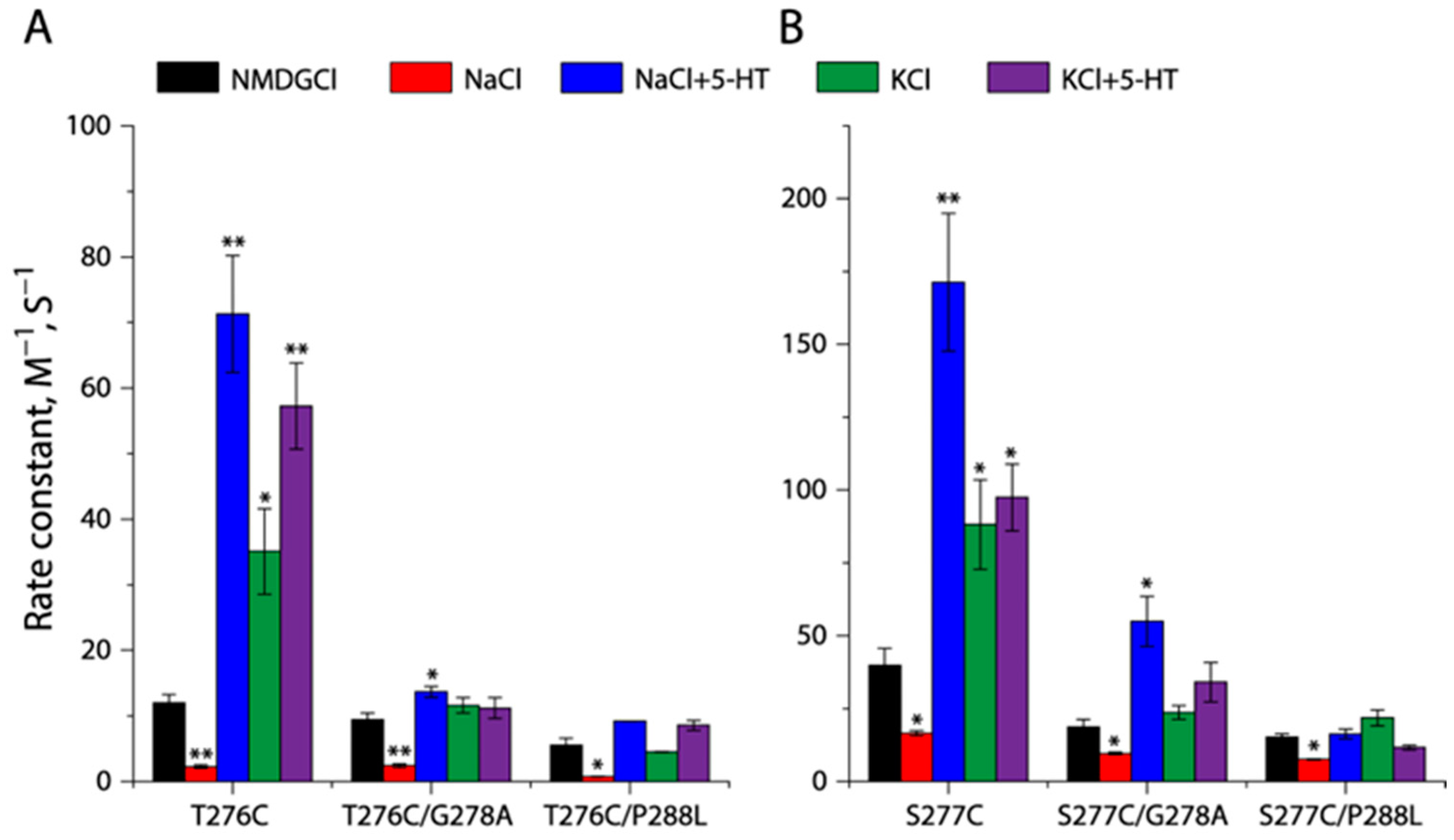
2.5. Effects of the GX9P Mutations on Unwinding in the Middle of TM5
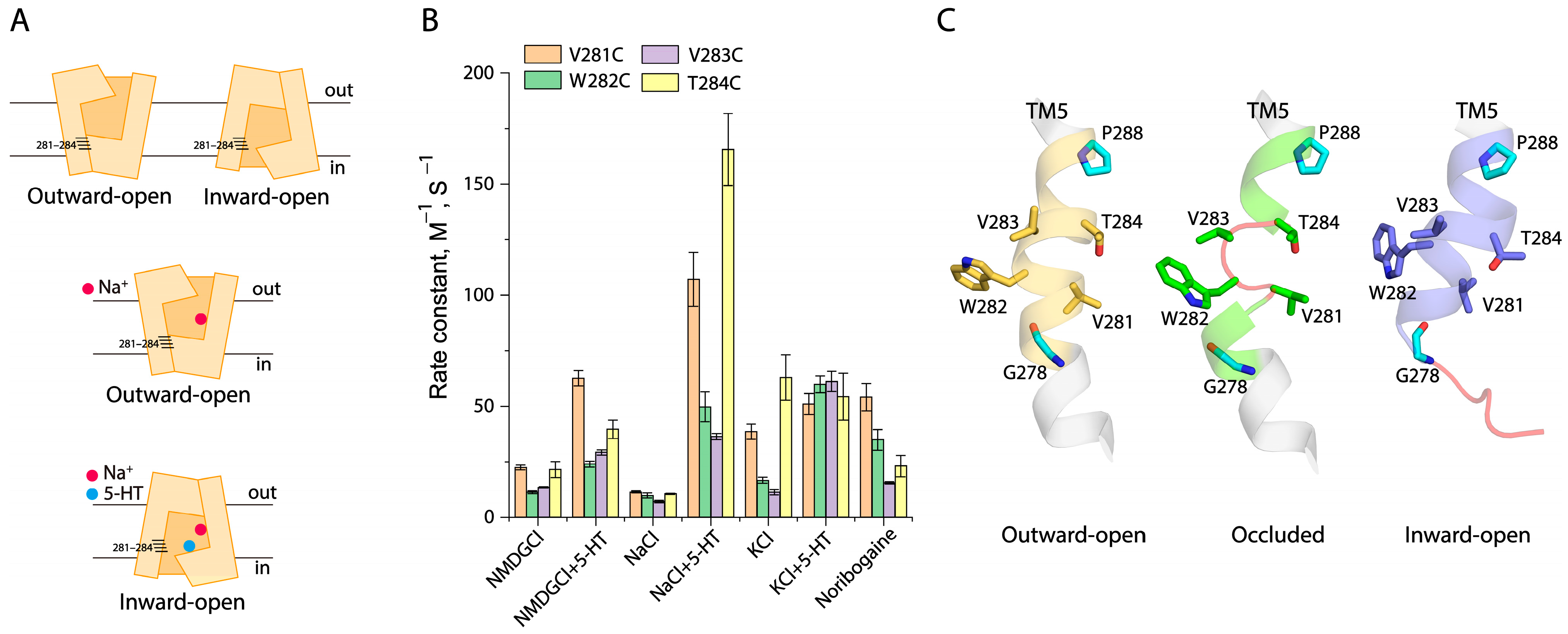
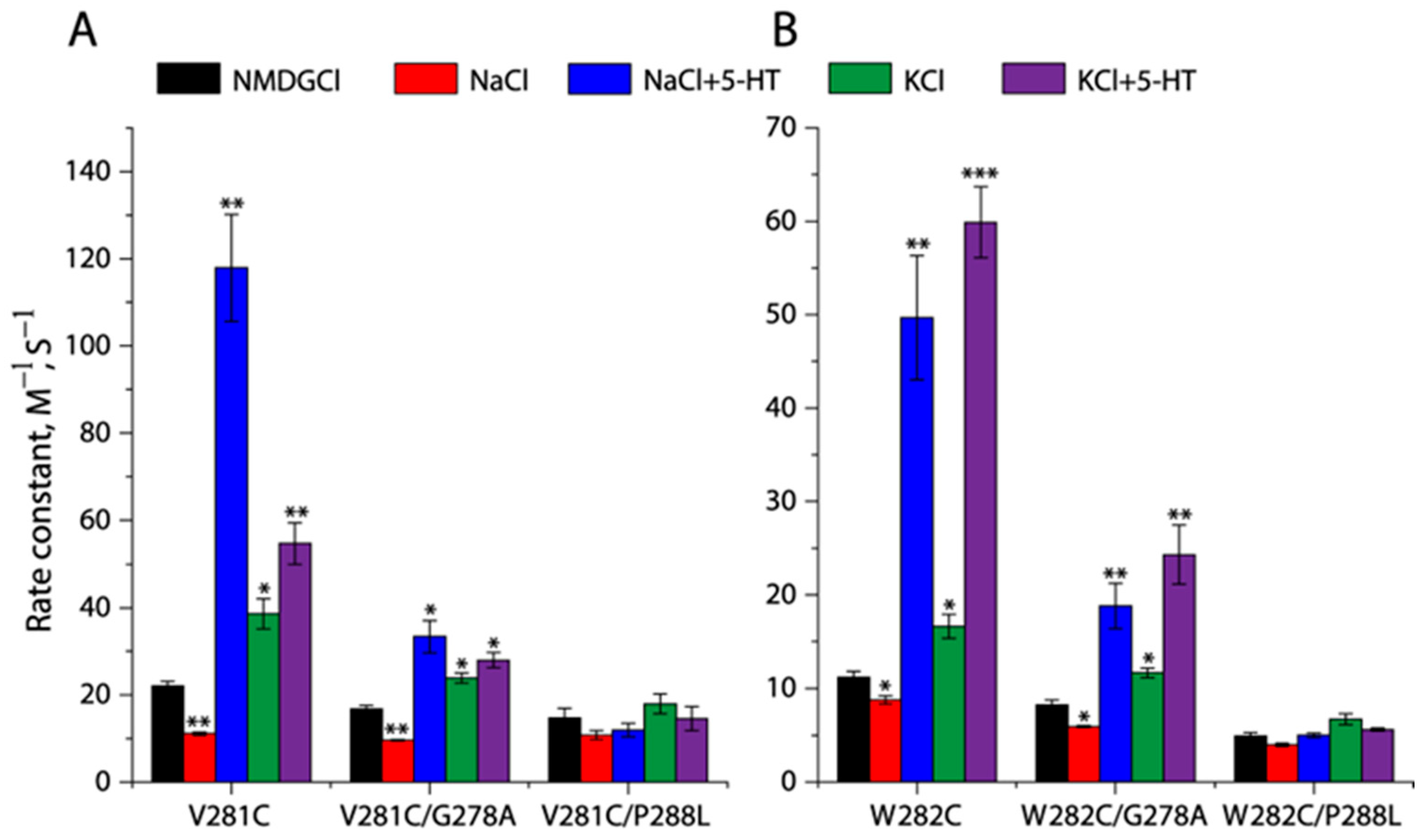
2.6. Conformational Analysis for Unwinding of the Intracellular End of TM5
2.7. Effects of the GX9P Mutations on Unwinding at the Intracellular End of TM5
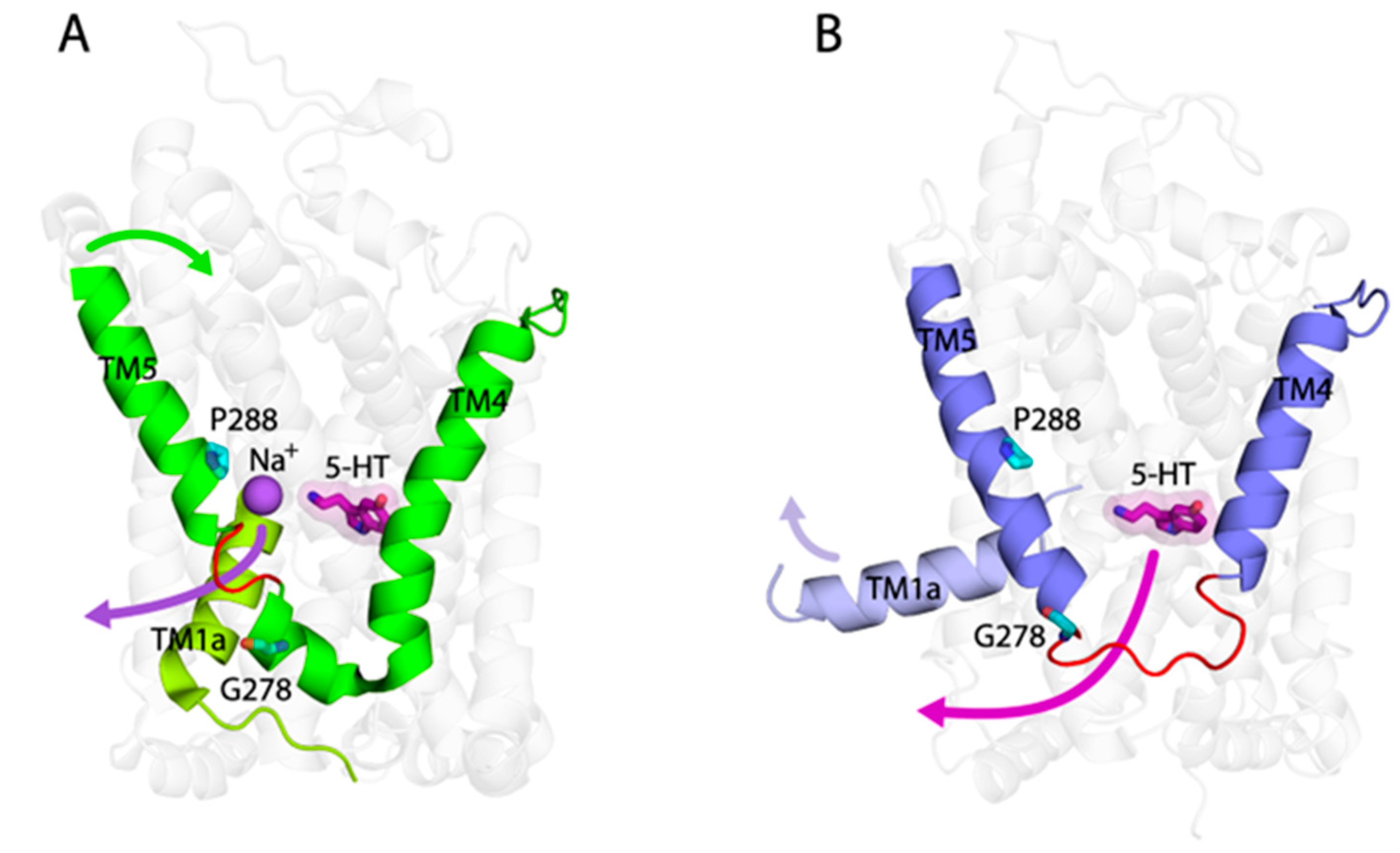
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials
4.2. Mutagenesis and Stable Cell Line Generation
4.3. 5-HT Transport Assay
4.4. Cell Surface Biotinylation
4.5. Cysteine Accessibility Measurements
4.6. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kristensen, A.S.; Andersen, J.; Jørgensen, T.N.; Sørensen, L.; Eriksen, J.; Loland, C.J.; Strømgaard, K.; Gether, U. SLC6 neurotransmitter transporters: Structure, function, and regulation. Pharmacol. Rev. 2011, 63, 585–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, N.-H.; Reith, M.E.A.; Quick, M.W. Synaptic uptake and beyond: The sodium- and chloride-dependent neurotransmitter transporter family SLC6. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2004, 447, 519–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurian, M.A.; Gissen, P.; Smith, M.; Heales, S., Jr.; Clayton, P.T. The monoamine neurotransmitter disorders: An expanding range of neurological syndromes. Lancet Neurol. 2011, 10, 721–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, G.; Krämer, R.; Blakely, R.D.; Murphy, D.L.; Verrey, F. The SLC6 transporters: Perspectives on structure, functions, regulation, and models for transporter dysfunction. Pflugers Arch. Eur. J. Physiol. 2014, 466, 25–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, G. Bioenergetics of neurotransmitter transport. J. Bioenerg. Biomembr. 1998, 30, 173–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, G. How do transporters couple solute movements? Mol. Membr. Biol. 2013, 30, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stolzenberg, S.; Quick, M.; Zhao, C.; Gotfryd, K.; Khelashvili, G.; Gether, U.; Loland, C.J.; Javitch, J.A.; Noskov, S.; Weinstein, H.; et al. Mechanism of the association between Na+ binding and conformations at the intracellular gate in neurotransmitter: Sodium symporters. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 13992–14003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Terry, D.S.; Shi, L.; Quick, M.; Weinstein, H.; Blanchard, S.C.; Javitch, J.A. Substrate-modulated gating dynamics in a Na+-coupled neurotransmitter transporter homologue. Nature 2011, 474, 109–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Noskov, S.Y. The molecular mechanism of ion-dependent gating in secondary transporters. PLoS Comput. Biol. 2013, 9, e1003296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burtscher, V.; Schicker, K.; Freissmuth, M.; Sandtner, W. Kinetic Models of secondary active transporters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, L.R.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Jacobs, M.T.; Gesmonde, J.; Xie, L.; Honig, B.H.; Rudnick, G. Mechanism for alternating access in neurotransmitter transporters. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10338–10343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merkle, P.S.; Gotfryd, K.; Cuendet, M.A.; Leth-Espensen, K.Z.; Gether, U.; Loland, C.J.; Rand, K.D. Substrate-modulated unwinding of transmembrane helices in the NSS transporter LeuT. Sci. Adv. 2018, 4, eaar6179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-W.; Tavoulari, S.; Sinning, S.; Aleksandrova, A.A.; Forrest, L.R.; Rudnick, G. Structural elements required for coupling ion and substrate transport in the neurotransmitter transporter homolog LeuT. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2018, 115, E8854–E8862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terry, D.S.; Kolster, R.A.; Quick, M.; LeVine, M.V.; Khelashvili, G.; Zhou, Z.; Weinstein, H.; Javitch, J.A.; Blanchard, S.C. A partially-open inward-facing intermediate conformation of LeuT is associated with Na+ release and substrate transport. Nat. Commun. 2018, 9, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotfryd, K.; Boesen, T.; Mortensen, J.S.; Khelashvili, G.; Quick, M.; Terry, D.S.; Missel, J.W.; LeVine, M.V.; Gourdon, P.; Blanchard, S.C.; et al. X-ray structure of LeuT in an inward-facing occluded conformation reveals mechanism of substrate release. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krishnamurthy, H.; Gouaux, E. X-ray structures of LeuT in substrate-free outward-open and apo inward-open states. Nature 2012, 481, 469–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavoulari, S.; Margheritis, E.; Nagarajan, A.; DeWitt, D.C.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Rosado, E.; Ravera, S.; Rhoades, E.; Forrest, L.R.; Rudnick, G. Two Na+ sites control conformational change in a neurotransmitter transporter homolog. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 1456–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claxton, D.P.; Quick, M.; Shi, L.; de Carvalho, F.D.; Weinstein, H.; Javitch, J.A.; Mchaourab, H.S. Ion/substrate-dependent conformational dynamics of a bacterial homolog of neurotransmitter:sodium symporters. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010, 17, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Noskov, S.Y. The role of local hydration and hydrogen-bonding dynamics in ion and solute release from ion-coupled secondary transporters. Biochemistry 2011, 50, 1848–1856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnick, G.; Nelson, P.J. Platelet 5-hydroxytryptamine transport, an electroneutral mechanism coupled to potassium. Biochemistry 1978, 17, 4739–4742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nelson, P.J.; Rudnick, G. Coupling between platelet 5-hydroxytryptamine and potassium transport. J. Biol. Chem. 1979, 254, 10084–10089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hellsberg, E.; Boytsov, D.; Chen, Q.; Niello, M.; Freissmuth, M.; Rudnick, G.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Sandtner, W.; Forrest, L.R. Identification of the potassium-binding site in serotonin transporter. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2024, 121, e2319384121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Billesbølle, C.B.; Mortensen, J.S.; Sohail, A.; Schmidt, S.G.; Shi, L.; Sitte, H.H.; Gether, U.; Loland, C.J. Transition metal ion FRET uncovers K+ regulation of a neurotransmitter/sodium symporter. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, S.G.; Nygaard, A.; Mindell, J.A.; Loland, C.J. Exploring the K+ binding site and its coupling to transport in the neurotransmitter: Sodium symporter LeuT. eLife 2024, 12, RP87985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, S.G.; Malle, M.G.; Nielsen, A.K.; Bohr, S.S.-R.; Pugh, C.F.; Nielsen, J.C.; Poulsen, I.H.; Rand, K.D.; Hatzakis, N.S.; Loland, C.J. The dopamine transporter antiports potassium to increase the uptake of dopamine. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 2446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.A.; Green, E.M.; Gouaux, E. X-ray structures and mechanism of the human serotonin transporter. Nature 2016, 532, 334–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coleman, J.A.; Yang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Wen, P.-C.; Yoshioka, C.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Gouaux, E. Serotonin transporter–ibogaine complexes illuminate mechanisms of inhibition and transport. Nature 2019, 569, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Wang, X.; Meng, Y.; Hu, T.; Zhao, J.; Li, R.; Bai, Q.; Yuan, P.; Han, J.; Hao, K.; et al. Dopamine reuptake and inhibitory mechanisms in human dopamine transporter. Nature 2024, 632, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.K.; Navratna, V.; Tosh, D.K.; Chinn, A.; Sk, M.F.; Tajkhorshid, E.; Jacobson, K.A.; Gouaux, E. Structure of the human dopamine transporter and mechanisms of inhibition. Nature 2024, 632, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, T.; Yu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Meng, Y.; Salomon, K.; Bai, Q.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Dai, Q.; et al. Transport and inhibition mechanisms of the human noradrenaline transporter. Nature 2024, 632, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Xiao, Y.; Kong, F.; Zhang, X.; Xu, H.; Zhu, A.; Liu, Y.; Lei, J.; Tian, B.; Yuan, Y.; et al. Molecular basis of human noradrenaline transporter reuptake and inhibition. Nature 2024, 632, 921–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Yin, Y.-L.; Dai, A.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, C.; Wu, C.; Hu, W.; He, X.; Pan, B.; Jin, S.; et al. Dimerization and antidepressant recognition at noradrenaline transporter. Nature 2024, 630, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, W.; Miao, A.; Liang, K.; Liu, J.; Qi, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Duan, X.; Sun, J.; Lai, L.; Wu, J.-X. Substrate binding and inhibition mechanism of norepinephrine transporter. Nature 2024, 633, 473–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Motiwala, Z.; Aduri, N.G.; Shaye, H.; Han, G.W.; Lam, J.H.; Katritch, V.; Cherezov, V.; Gati, C. Structural basis of GABA reuptake inhibition. Nature 2022, 606, 820–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahsavar, A.; Stohler, P.; Bourenkov, G.; Zimmermann, I.; Siegrist, M.; Guba, W.; Pinard, E.; Sinning, S.; Seeger, M.A.; Schneider, T.R.; et al. Structural insights into the inhibition of glycine reuptake. Nature 2021, 591, 677–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.; Li, R.; Meng, Y.; Hu, T.; Zhao, J.; Gao, Y.; Bai, Q.; Li, N.; Zhao, Y. Transport mechanism and pharmacology of the human GlyT1. Cell 2024, 187, 1719–1732.e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-W.; Rudnick, G. The cytoplasmic substrate permeation pathway of serotonin transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 36213–36220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malinauskaite, L.; Quick, M.; Reinhard, L.; Lyons, J.A.; Yano, H.; Javitch, J.A.; Nissen, P. A mechanism for intracellular release of Na+ by neurotransmitter/sodium symporters. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 1006–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weyand, S.; Shimamura, T.; Yajima, S.; Suzuki, S.; Mirza, O.; Krusong, K.; Carpenter, E.P.; Rutherford, N.G.; Hadden, J.M.; O’Reilly, J.; et al. Structure and Molecular Mechanism of a Nucleobase-Cation-Symport-1 Family Transporter. Science 2008, 322, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Chen, Q.; Zhang, Y.-W. Determining Ligand and Ion-Induced Conformational Changes in Serotonin Transporter with Its Fluorescent Substrates. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 10919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, M.T.; Zhang, Y.-W.; Campbell, S.D.; Rudnick, G. Ibogaine, a Noncompetitive Inhibitor of Serotonin Transport, Acts by Stabilizing the Cytoplasm-facing State of the Transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 29441–29447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavoulari, S.; Forrest, L.R.; Rudnick, G. Fluoxetine (Prozac) Binding to serotonin transporter is modulated by chloride and conformational changes. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 9635–9643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, D.; Gouaux, E. Illumination of serotonin transporter mechanism and role of the allosteric site. Sci. Adv. 2021, 7, eabl3857. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamashita, A.; Singh, S.K.; Kawate, T.; Jin, Y.; Gouaux, E. Crystal structure of a bacterial homologue of Na+/Cl--dependent neurotransmitter transporters. Nature 2005, 437, 215–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Penmatsa, A.; Wang, K.H.; Gouaux, E. X-ray structure of dopamine transporter elucidates antidepressant mechanism. Nature 2013, 503, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, Y.; Terry, D.; Shi, L.; Weinstein, H.; Blanchard, S.C.; Javitch, J.A. Single-molecule dynamics of gating in a neurotransmitter transporter homologue. Nature 2010, 465, 188–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazmier, K.; Sharma, S.; Quick, M.; Islam, S.M.; Roux, B.; Weinstein, H.; Javitch, J.A.; Mchaourab, H.S. Conformational dynamics of ligand-dependent alternating access in LeuT. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014, 21, 472–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fenollar-Ferrer, C.; Stockner, T.; Schwarz, T.C.; Pal, A.; Gotovina, J.; Hofmaier, T.; Jayaraman, K.; Adhikary, S.; Kudlacek, O.; Mehdipour, A.R.; et al. Structure and regulatory interactions of the cytoplasmic terminal domains of serotonin transporter. Biochemistry 2014, 53, 5444–5460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.-W.; Turk, B.E.; Rudnick, G. Control of serotonin transporter phosphorylation by conformational state. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E2776–E2783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elegheert, J.; Behiels, E.; Bishop, B.; Scott, S.; Woolley, R.E.; Griffiths, S.C.; Byrne, E.F.X.; Chang, V.T.; Stuart, D.I.; Jones, E.Y.; et al. Lentiviral transduction of mammalian cells for fast, scalable and high-level production of soluble and membrane proteins. Nat. Protoc. 2018, 13, 2991–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Androutsellis-Theotokis, A.; Ghassemi, F.; Rudnick, G. A conformationally sensitive residue on the cytoplasmic surface of serotonin transporter. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 45933–45938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, Y.; Mathewson, L.; Gesmonde, J.; Sato, Y.; Holy, M.; Sitte, H.H.; Rudnick, G. Involvement of serotonin transporter extracellular loop 1 in serotonin binding and transport. Mol. Membr. Biol. 2008, 25, 115–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Background | Mutants | Transport Activity (% of WT) |
|---|---|---|
| hSERT WT | 100 | |
| C109A/Y107C | 69.32 ± 6.28 | |
| C109A/Y107C/G278A | 40.27 ± 7.63 ** | |
| C109A/Y107C/P288L | 9.79 ± 2.60 *** | |
| X5C | 74.53 ± 12.23 | |
| V281C | 80.04 ± 3.23 | |
| W282C | 75.01 ± 2.71 | |
| V283C | 76.26 ± 2.26 | |
| T284C | 78.06 ± 1.00 | |
| V281C/G278A | 48.60 ± 1.53 ** | |
| V281C/P288L | 11.98 ± 3.19 *** | |
| W282C/G278A | 8.51 ± 1.07 *** | |
| W282C/P288L | 1.12 ± 1.13 *** | |
| V274C | 74.08 ± 2.14 | |
| K275C | 75.28 ± 1.89 | |
| T276C | 70.46 ± 2.28 | |
| S277C | 72.38 ± 1.66 | |
| T276C/G278A | 6.62 ± 1.70 *** | |
| T276C/288L | 0.56 ± 0.46 *** | |
| S277C/G278A | 59.27 ± 2.07 * | |
| S277C/P288L | 13.20 ± 0.69 *** |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, X.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Li, C.; Zhang, Y.-W. Control of Conformational Transitions by the Conserved GX9P Motif in the Fifth Transmembrane Domain of Neurotransmitter Sodium Symporters. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073054
Zhang X, Xu Y, Chen Q, Li C, Zhang Y-W. Control of Conformational Transitions by the Conserved GX9P Motif in the Fifth Transmembrane Domain of Neurotransmitter Sodium Symporters. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073054
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Xintong, Yanhong Xu, Qingyang Chen, Chan Li, and Yuan-Wei Zhang. 2025. "Control of Conformational Transitions by the Conserved GX9P Motif in the Fifth Transmembrane Domain of Neurotransmitter Sodium Symporters" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073054
APA StyleZhang, X., Xu, Y., Chen, Q., Li, C., & Zhang, Y.-W. (2025). Control of Conformational Transitions by the Conserved GX9P Motif in the Fifth Transmembrane Domain of Neurotransmitter Sodium Symporters. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 3054. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26073054







