Scutellarin Alleviates CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis by Regulating Intestinal Flora and PI3K/AKT Signaling Axis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
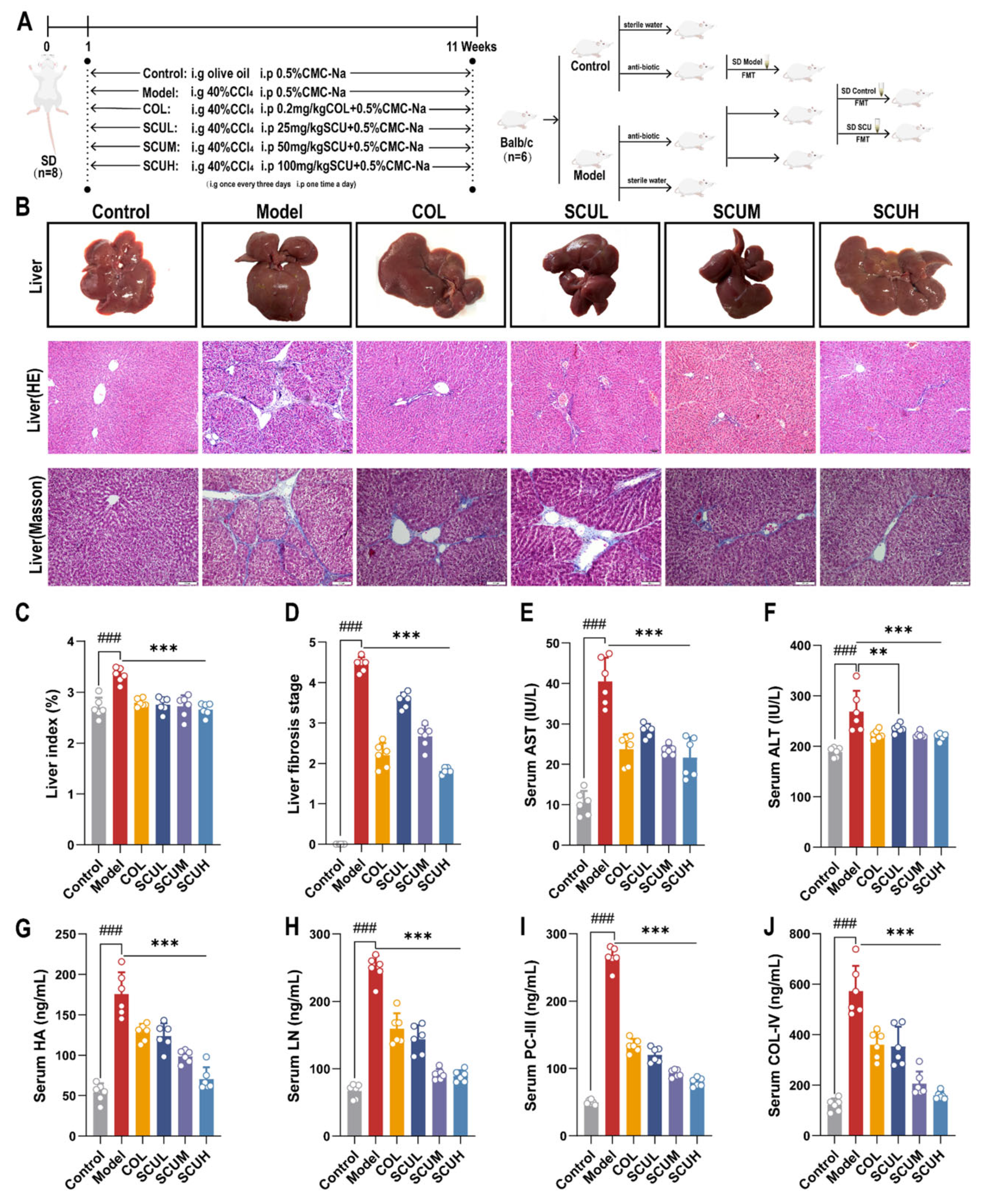
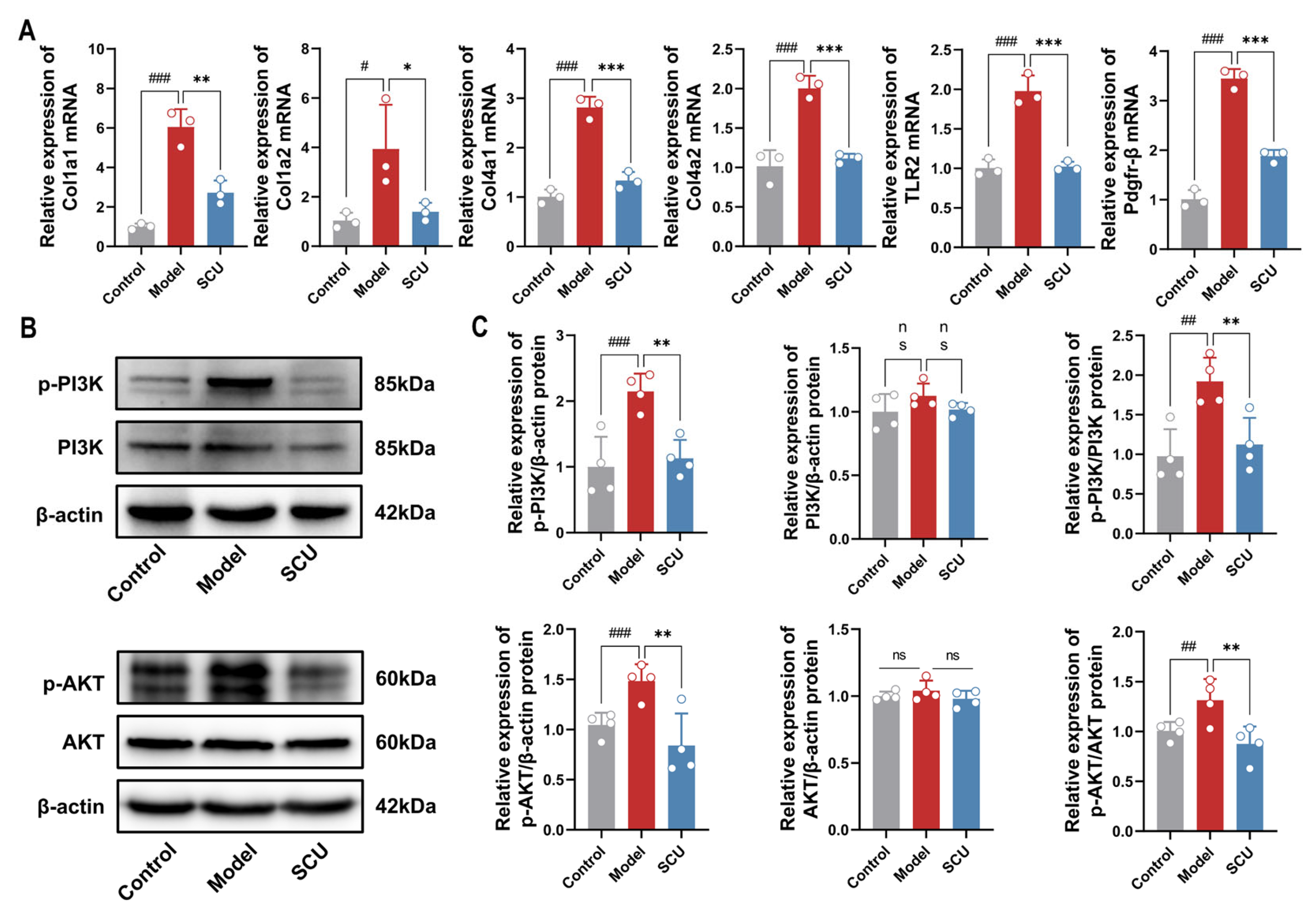
2.1. The Ameliorating Effect of SCU on Liver Fibrosis Rats Induced by CCl4
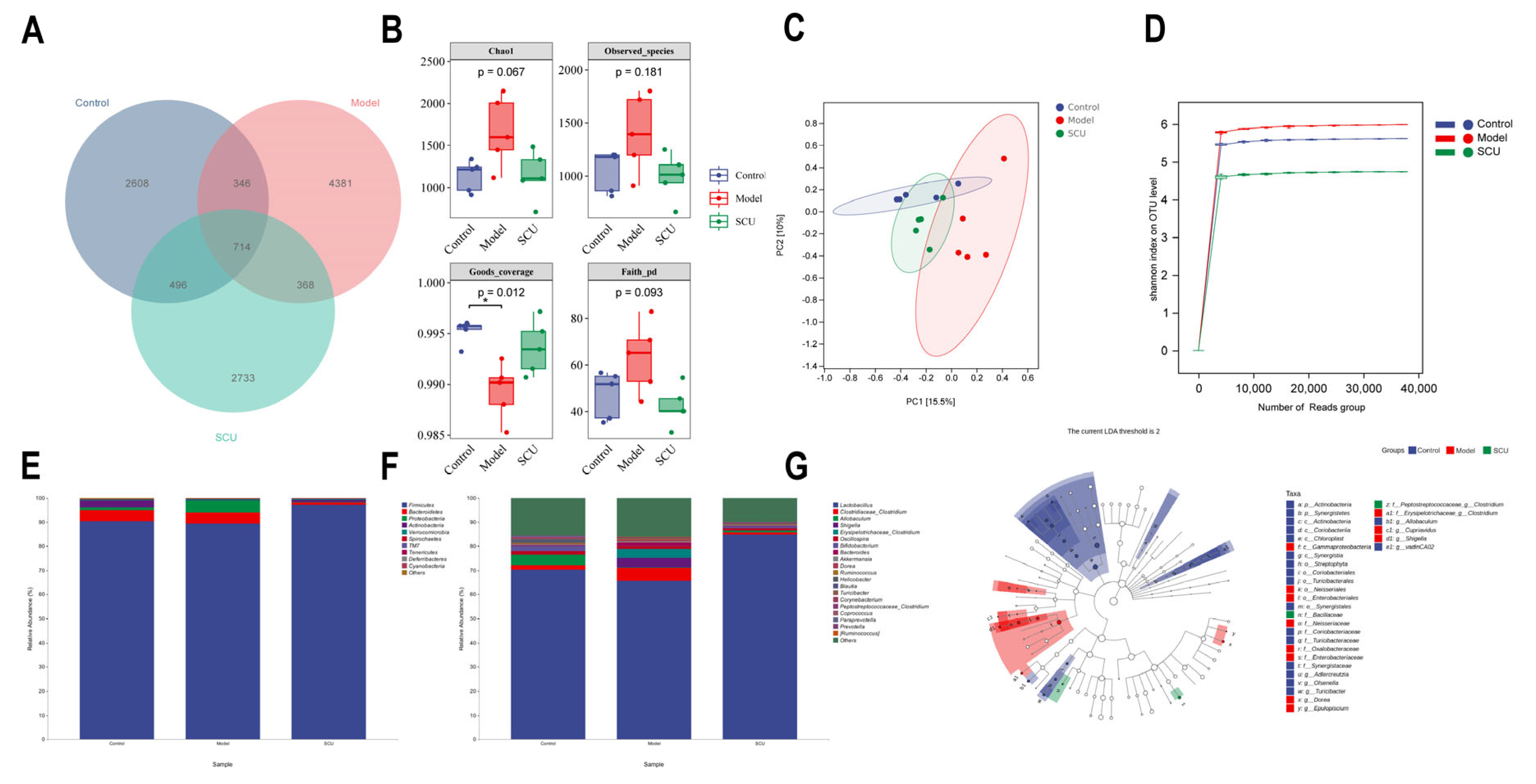
2.2. Effects of SCU on Intestinal Flora in CCl4-Induced-Liver-Fibrosis Rats
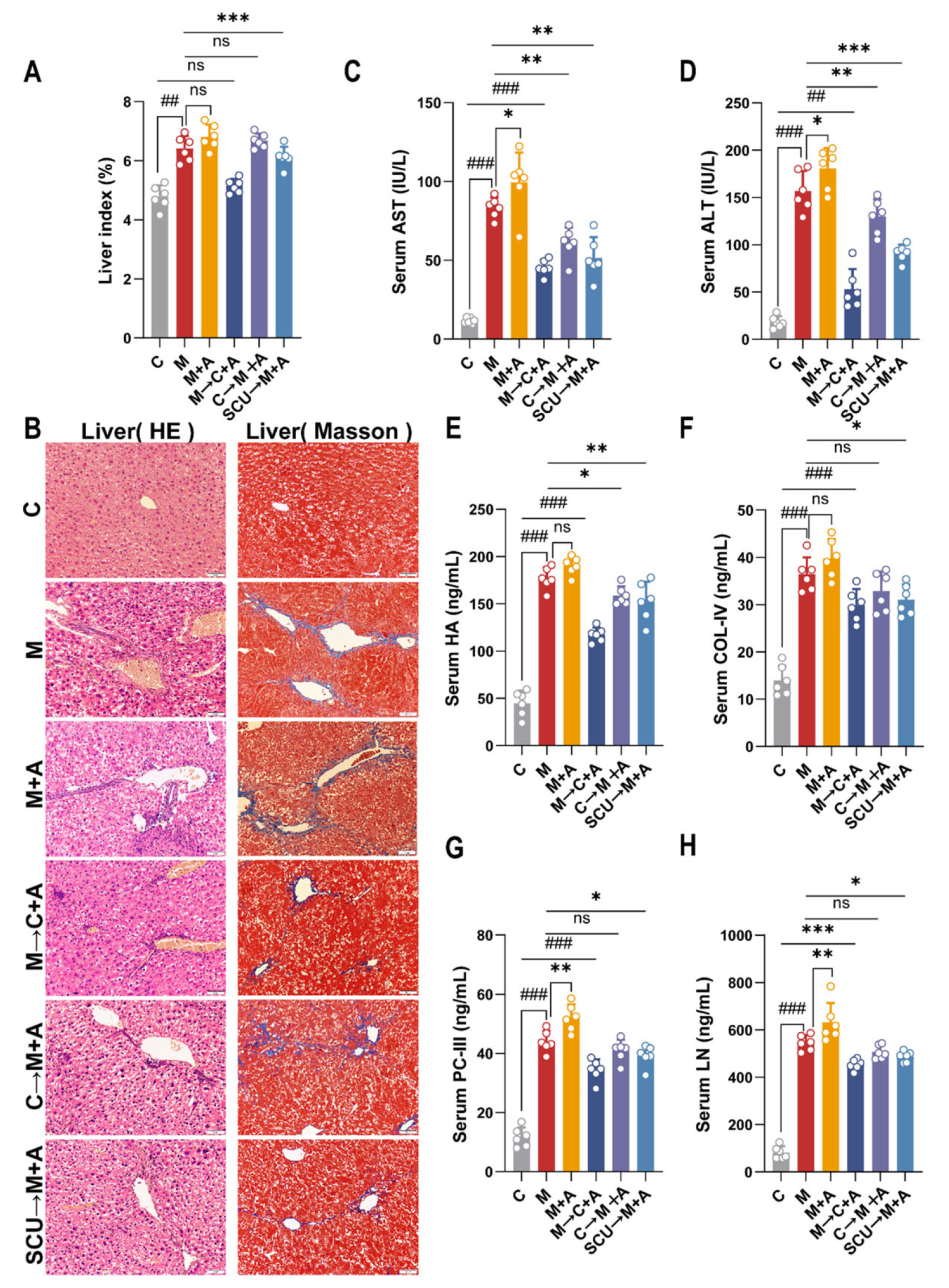
2.3. Fecal Microbiota Transplantation Verifies That Intestinal Flora Can Improve Liver Fibrosis in Mice
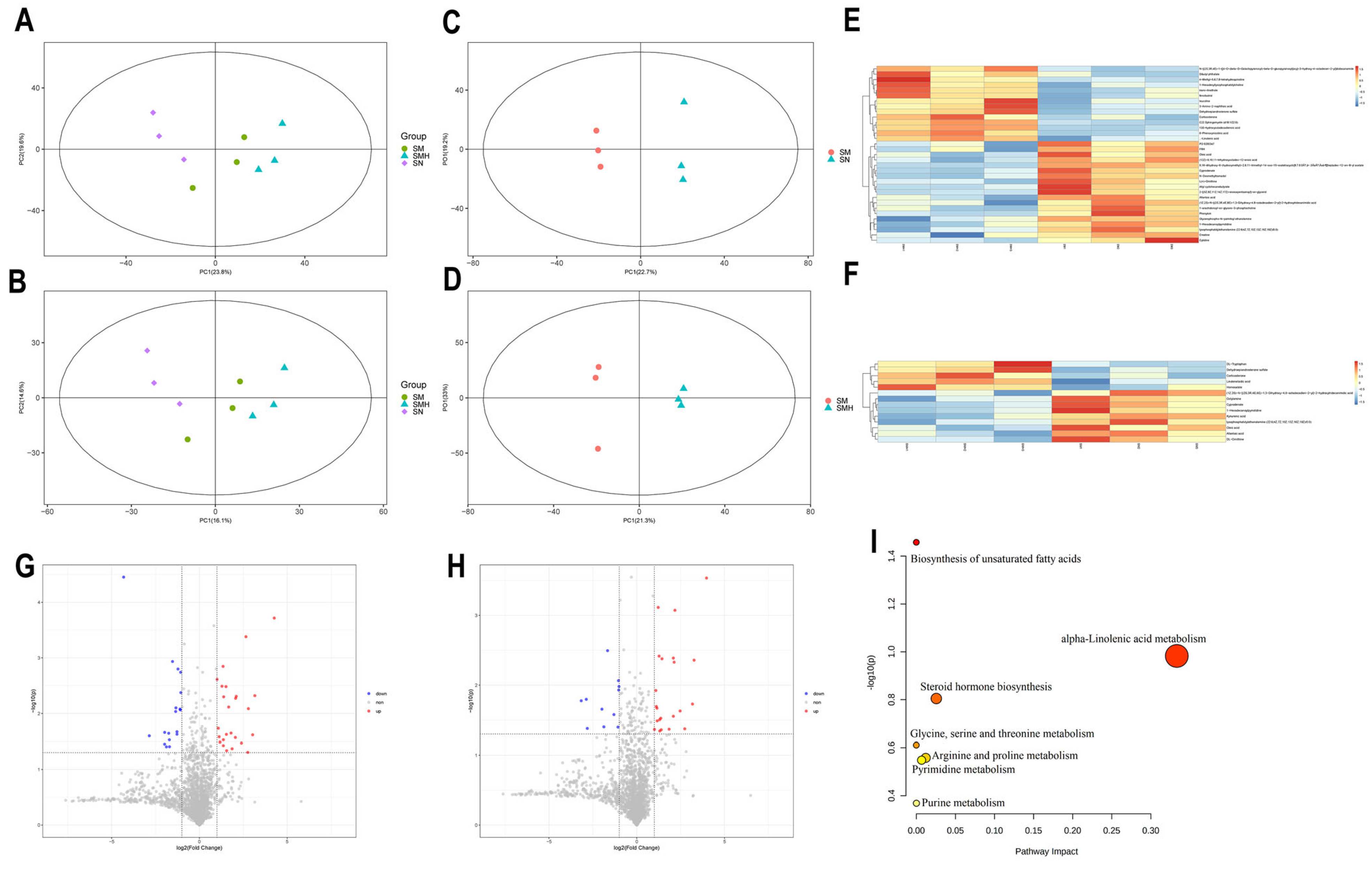
2.4. Effect of SCU on Serum Metabolites in Liver Fibrosis Rats
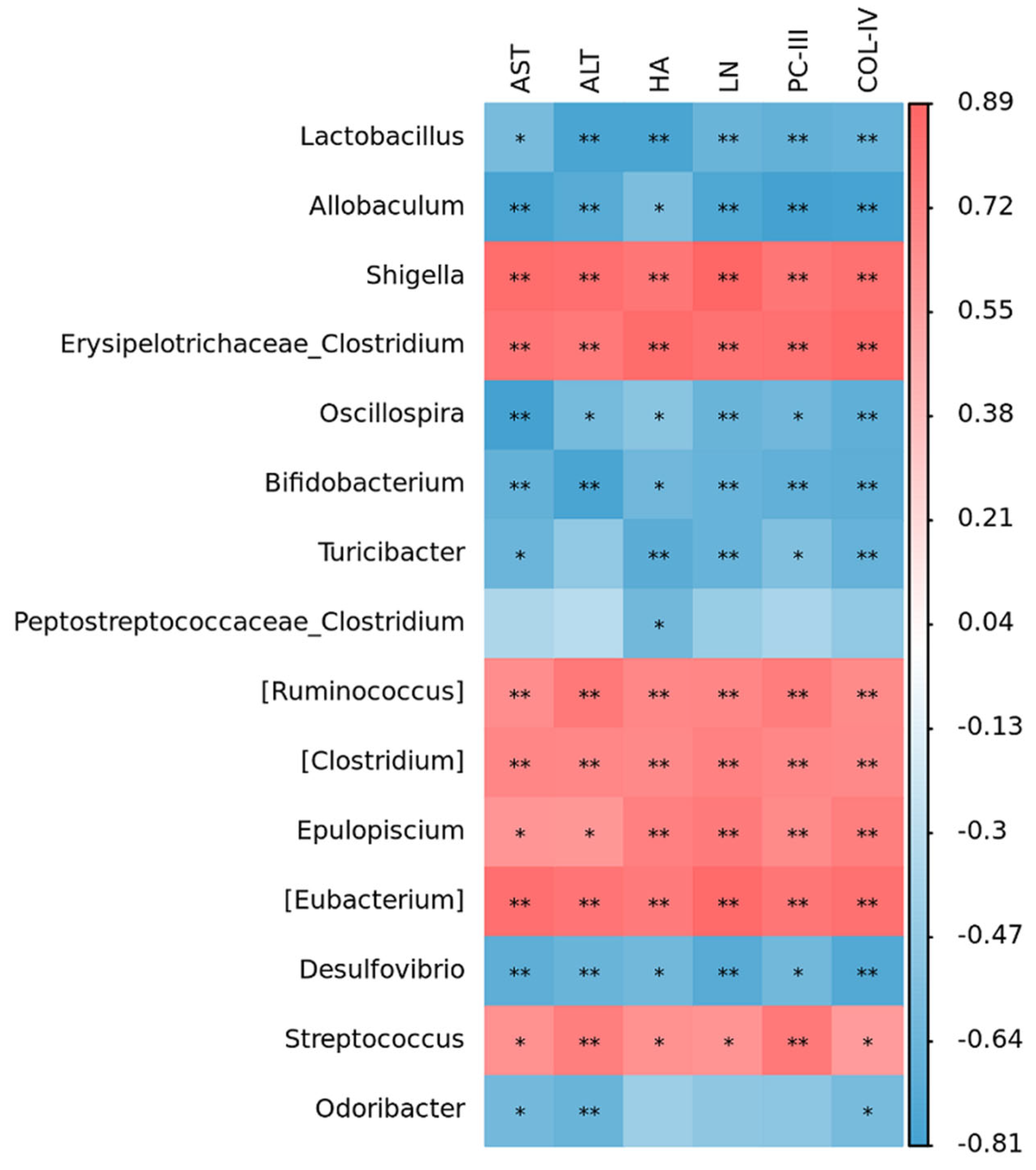
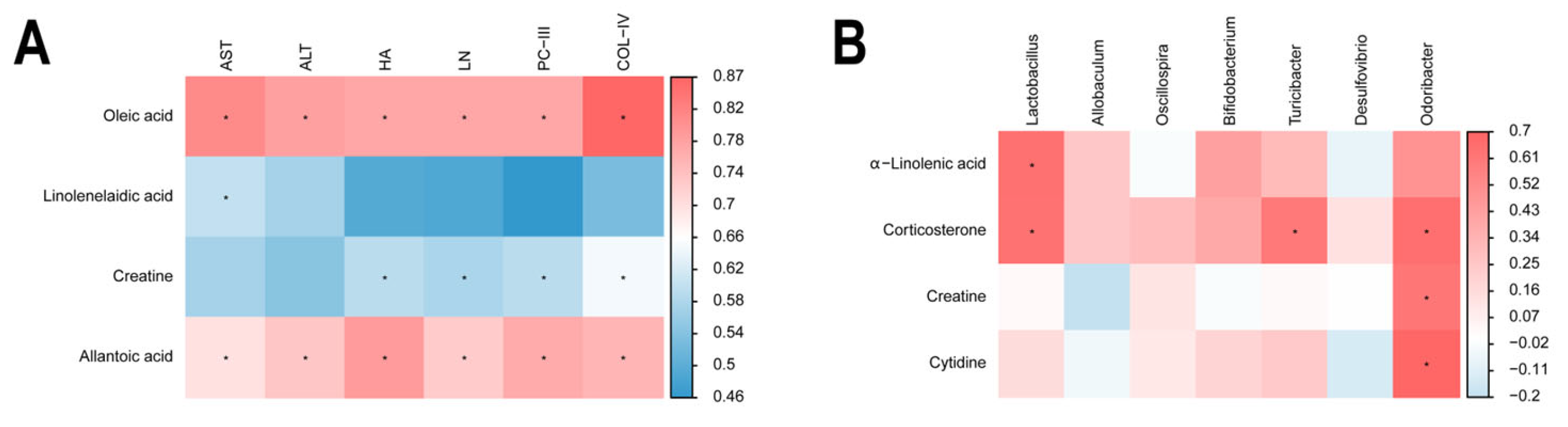
2.5. Correlation Within Metabolite–Liver Fibrosis–Intestinal Flora
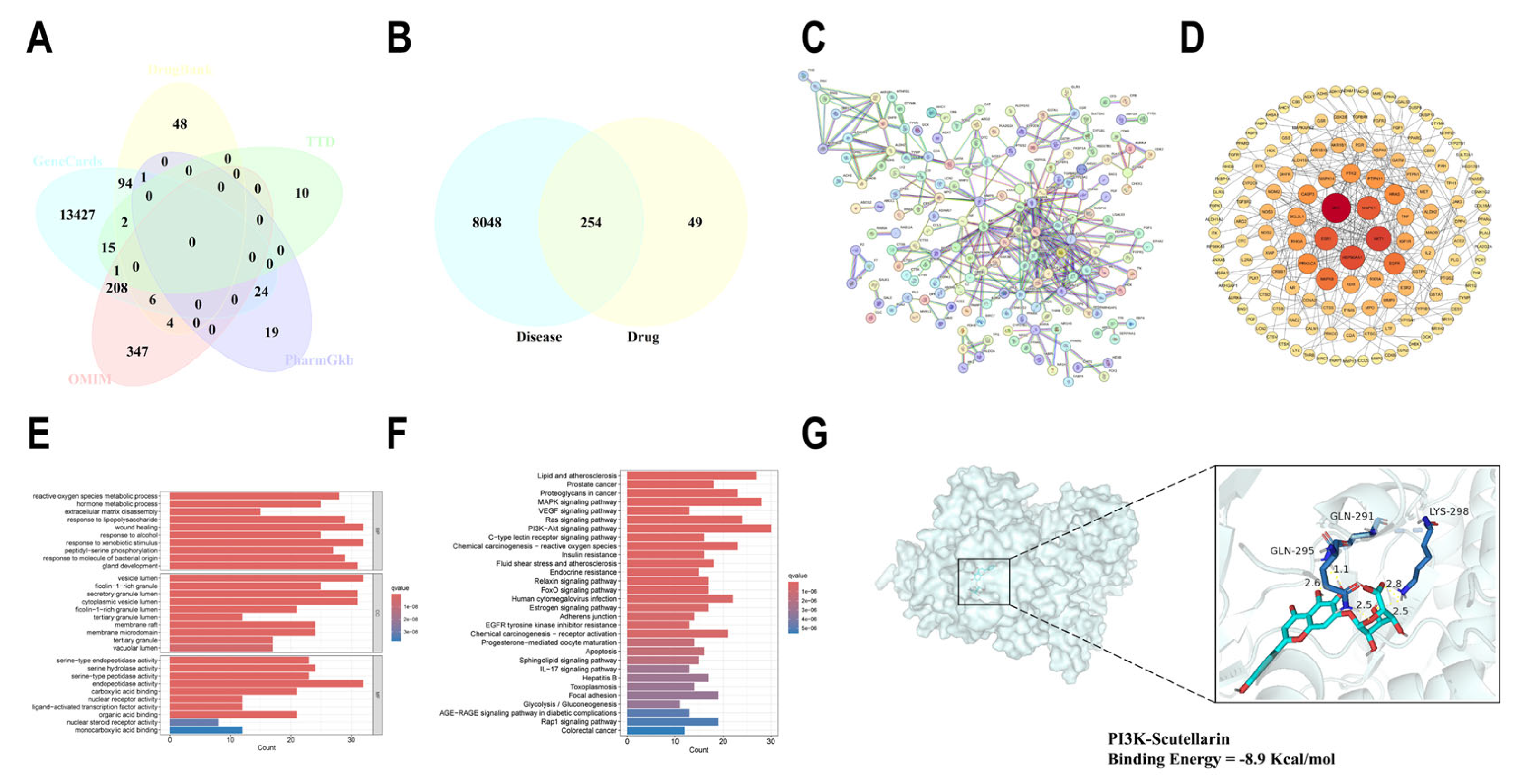
2.6. Network Pharmacological Analysis of SCU for the Treatment of Liver Fibrosis
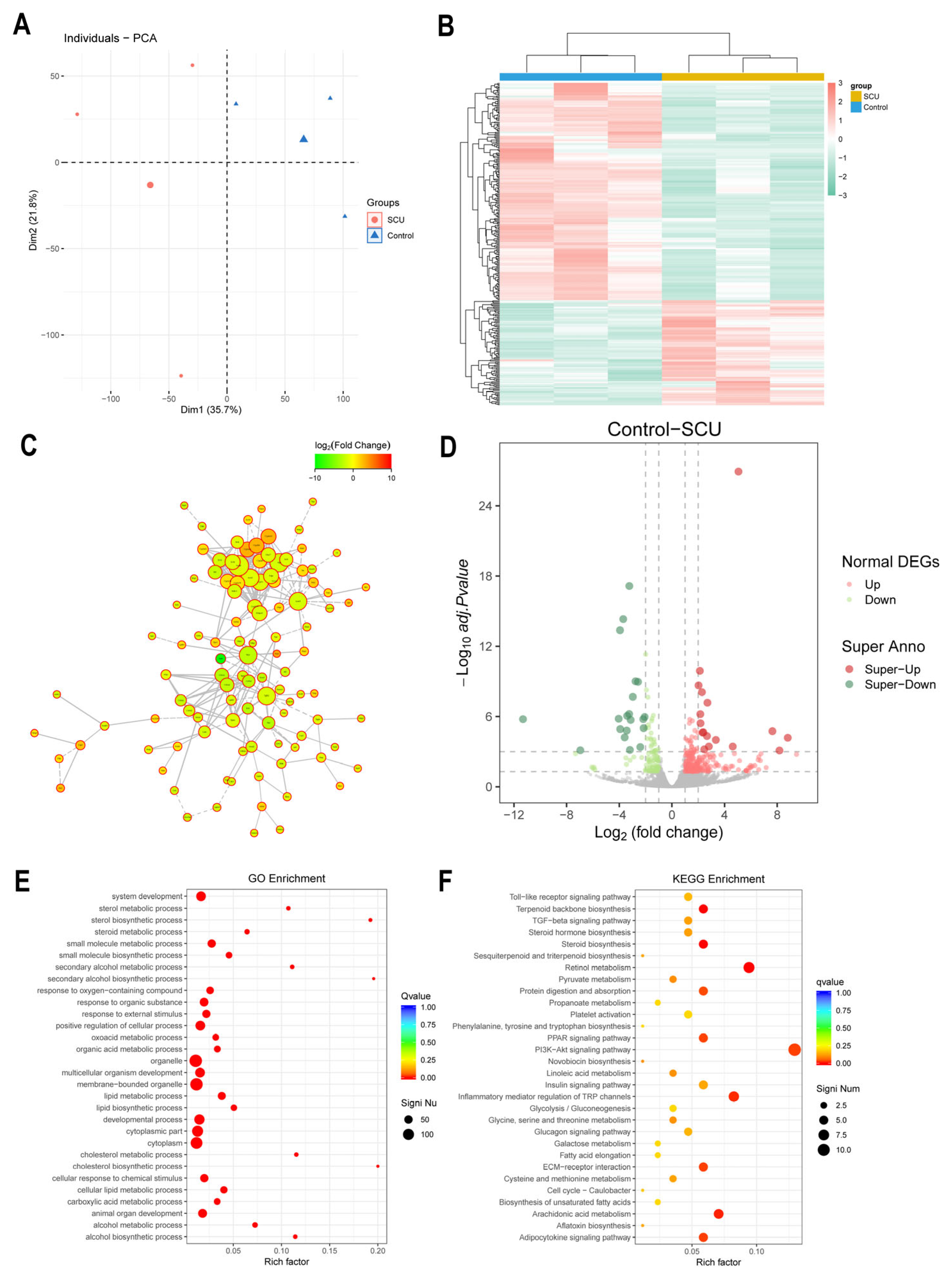
2.7. Effects of SCU on Transcriptomics in CCl4-Induced-Liver-Fibrosis Rats
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Materials and Reagents
4.2. Animal Study
4.3. Biochemical Assays
4.4. Histological Analysis
4.5. 16S rRNA Sequencing
4.6. Serum Metabolomics Analysis
4.6.1. Sample Preparation and Quality Control
4.6.2. Instrumental Analysis Methods
4.7. Metabolite Identification and Pathway Analysis
4.8. Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking
4.9. Transcriptome Sequencing of Liver Tissue
4.10. qRT-PCR Analysis
4.11. Western Blotting
4.12. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AKT (PKB) | Protein Kinase B |
| ALT | Alanine aminotransferase |
| AST | Aspartate aminotransferase |
| BP | Biological process |
| CC | Cell composition |
| CCl4 | Carbon tetrachloride |
| COL | Colchicine |
| Col1a1 | Collagen Type I Alpha 1 |
| Col1a2 | Collagen Type I Alpha 2 |
| Col4a1 | Collagen Type IV Alpha 1 |
| Col4a2 | Collagen Type IV Alpha 2 |
| COL-IV | Type IV collagen |
| DEGs | Differentially expressed genes |
| ECM | Extracellular matrix |
| FMT | Fecal microflora transplantation |
| GO | Gene Ontology |
| H&E | Haematoxylin and Eosin |
| HA | Hyaluronic acid |
| HSCs | Hepatic stellate cells |
| KEGG | Kyoto Encyclopedia of Gene and Genome |
| LDA | Linear discriminant analysis |
| LEfSe | Linear discriminant analysis Effect Size |
| LN | Layer adhesion protein |
| MF | Molecular function |
| mTOR | Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin |
| OPLS-DA | Orthogonal Partial Least Squares Discriminant Analysis |
| PCA | Principal Component Analysis |
| PC-III | Type III pre-collagen |
| Pdgfr-β | Platelet-derived growth factor receptors-β |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase |
| PPI | Protein–protein interaction |
| qRT-PCR | Quantitative reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| SCFAs | Short-chain fatty acids |
| SCU | Scutellarin |
| TLR2 | Toll-like receptor 2 |
| VIP | Variable importance in the projection |
References
- Thiele, M.; Kamath, P.S.; Graupera, I.; Castells, A.; de Koning, H.J.; Serra-Burriel, M.; Lammert, F.; Ginès, P. Screening for liver fibrosis: Lessons from colorectal and lung cancer screening. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 21, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, J.; Huang, C.; Li, S.; Jiang, X.; Chang, H.; Li, M. Research Progress Regarding the Effect and Mechanism of Dietary Polyphenols in Liver Fibrosis. Molecules 2023, 29, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Liang, J.; Liu, J.; Dai, Y.; Leng, X.; Cheng, Y.; Chi, L. Anchang Yuyang Decoction inhibits experimental colitis-related carcinogenesis by regulating PPAR signaling pathway and affecting metabolic homeostasis of host and microbiota. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 326, 117995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chledzik, S.; Strawa, J.; Matuszek, K.; Nazaruk, J. Pharmacological Effects of Scutellarin, An Active Component of Genus Scutellaria and Erigeron: A Systematic Review. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2018, 46, 319–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Ma, Q. Clinical benefits and pharmacology of scutellarin: A comprehensive review. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 190, 105–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miao, Z.; Lai, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, L.; Zhou, J.; Li, C.; Wang, Y. Protective Property of Scutellarin Against Liver Injury Induced by Carbon Tetrachloride in Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 710692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.H.; Geng, L.; Li, H. Study on effect of scutellarin in resisting liver fibrosis in rats. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2015, 40, 1999–2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ashrafizadeh, M.; Ahmadi, Z.; Mohammadinejad, R.; Farkhondeh, T.; Samarghandian, S. Nano-soldiers Ameliorate Silibinin Delivery: A Review Study. Curr. Drug Deliv. 2020, 17, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras, D.; Nistal, E.; Martínez-Flórez, S.; Pisonero-Vaquero, S.; Olcoz, J.L.; Jover, R.; González-Gallego, J.; García-Mediavilla, M.V.; Sánchez-Campos, S. Protective effect of quercetin on high-fat diet-induced non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice is mediated by modulating intestinal microbiota imbalance and related gut-liver axis activation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2017, 102, 188–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maslennikov, R.; Poluektova, E.; Zolnikova, O.; Sedova, A.; Kurbatova, A.; Shulpekova, Y.; Dzhakhaya, N.; Kardasheva, S.; Nadinskaia, M.; Bueverova, E.; et al. Gut Microbiota and Bacterial Translocation in the Pathogenesis of Liver Fibrosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 16502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, K.; Li, F.; Gu, Z.; Liu, Q.; He, L.; Shao, T.; Song, Q.; Zhu, F.; Zhang, L.; et al. Probiotic Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG Prevents Liver Fibrosis Through Inhibiting Hepatic Bile Acid Synthesis and Enhancing Bile Acid Excretion in Mice. Hepatology. 2020, 71, 2050–2066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, D.; Hao, X.; Xu, L.; Cui, J.; Xue, L.; Tian, Z. Intestinal flora imbalance promotes alcohol-induced liver fibrosis by the TGFβ/smad signaling pathway in mice. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 4511–4516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, R.; Tang, R.; Li, B.; Ma, X.; Schnabl, B.; Tilg, H. Gut microbiome, liver immunology, and liver diseases. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2021, 18, 4–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, X.; Lu, Q.; Zhang, C.; Tang, Z.; Chu, L. Clinical Application and Progress of Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Liver Diseases: A Review. Semin. Liver Dis. 2021, 41, 495–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Ma, C.; Fu, K.; Liu, Y.; Gong, L.; Peng, C.; Li, Y. Hepatoprotective effect of phillygenin on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis and its effects on short chain fatty acid and bile acid metabolism. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2022, 296, 115478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D'Argenio, G.; Cariello, R.; Tuccillo, C.; Mazzone, G.; Federico, A.; Funaro, A.; De Magistris, L.; Grossi, E.; Callegari, M.L.; Chirico, M.; et al. Symbiotic formulation in experimentally induced liver fibrosis in rats: Intestinal microbiota as a key point to treat liver damage? Liver Int. 2013, 33, 687–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koutoukidis, D.A.; Yen, S.; Gomez Castro, P.; Misheva, M.; Jebb, S.A.; Aveyard, P.; Tomlinson, J.W.; Mozes, F.E.; Cobbold, J.F.; Johnson, J.S.; et al. Changes in intestinal permeability and gut microbiota following diet-induced weight loss in patients with metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis and liver fibrosis. Gut Microbes 2024, 16, 2392864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, M.; Wang, L.; Wang, M.; Zhou, S.; Lu, Y.; Cui, H.; Racanelli, A.C.; Zhang, L.; Ye, T.; Ding, B.; et al. Targeting fibrosis, mechanisms and cilinical trials. Signal. Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, C.; Sampaio-Maia, B.; Araujo, R.; Nascimento, D.S.; Ferreira-Gomes, J.; Pestana, M.; Azevedo, M.J.; Alencastre, I.S. Gut Microbiome and Organ Fibrosis. Nutrients 2022, 14, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seki, E.; Schnabl, B. Role of innate immunity and the microbiota in liver fibrosis: Crosstalk between the liver and gut. J. Physiol. 2012, 590, 447–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, P.; Zhu, H.; Qian, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, G.; Chen, W. Consumption of Butylated Starch Alleviates the Chronic Restraint Stress-Induced Neurobehavioral and Gut Barrier Deficits Through Reshaping the Gut Microbiota. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 755481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bokoliya, S.C.; Dorsett, Y.; Panier, H.; Zhou, Y. Procedures for Fecal Microbiota Transplantation in Murine Microbiome Studies. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 711055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huyan, Z.; Pellegrini, N.; Steegenga, W.; Capuano, E. Insights into gut microbiota metabolism of dietary lipids: The case of linoleic acid. Food. Funct. 2022, 13, 4513–4526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Xue, H.; Fang, S.; Wang, G.; Wang, Y.; Wang, T.; Shi, R.; Wu, J.; Ma, Y. Time-series metabolomics insights into the progressive characteristics of 3,5-diethoxycarbonyl-1,4-dihydrocollidine-induced cholestatic liver fibrosis in mice. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2021, 198, 113986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Tabashsum, Z.; Patel, P.; Bernhardt, C.; Biswas, C.; Meng, J.; Biswas, D. Prevention of enteric bacterial infections and modulation of gut microbiota with conjugated linoleic acids producing Lactobacillus in mice. Gut Microbes 2020, 11, 433–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, Y.; Goh, B.; Bao, B.; Mello, S.S.; Sun, X.; Zheng, W.; Gazzaniga, F.S.; Wu, M.; et al. Gut microbial fatty acid isomerization modulates intraepithelial T cells. Nature 2023, 619, 837–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa Godinho, L.R.L.; Cella, P.S.; Guimarães, T.A.S.; Palma, G.H.D.; Nunes, J.H.C.; Deminice, R. Creatine Supplementation Potentiates Exercise Protective Effects against Doxorubicin-Induced Hepatotoxicity in Mice. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrescu, A.D.; Grant, S.; Frampton, G.; Kain, J.; Hadidi, K.; Williams, E.; McMillin, M.; DeMorrow, S. Glucocorticoids Cause Gender-Dependent Reversal of Hepatic Fibrosis in the MDR2-Knockout Mouse Model. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 2389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Zhong, H.; Chen, F.; Regenstein, J.; Hu, X.; Cai, L.; Feng, F. The gut microbiota as a target to control hyperuricemia pathogenesis: Potential mechanisms and therapeutic strategies. Crit. Rev. Food. Sci. Nutr. 2022, 62, 3979–3989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sari, D.C.R.; Soetoko, A.S.; Soetoko, A.S.; Romi, M.M.; Tranggono, U.; Setyaningsih, W.A.W.; Arfian, N. Uric acid induces liver fibrosis through activation of inflammatory mediators and proliferating hepatic stellate cell in mice. Med. J. Malaysia 2020, 75 (Suppl. 1), 14–18. [Google Scholar]
- Cansanção, K.; Silva Monteiro, L.; Carvalho Leite, N.; Dávalos, A.; Tavares do Carmo, M.D.G.; Arantes Ferreira Peres, W. Advanced Liver Fibrosis Is Independently Associated with Palmitic Acid and Insulin Levels in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nutrients 2018, 10, 1586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verma, S.; Ishteyaque, S.; Washimkar, K.R.; Verma, S.; Nilakanth Mugale, M. Mitochondrial-mediated nuclear remodeling and macrophage polarizations: A key switch from liver fibrosis to HCC progression. Exp. Cell. Res. 2024, 434, 113878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamazoe, T.; Mori, T.; Yoshio, S.; Kanto, T. Hepatocyte ploidy and pathological mutations in hepatocellular carcinoma: Impact on oncogenesis and therapeutics. Glob. Health Med. 2020, 2, 273–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, A.; Yoshikawa, S.; Ikeda, Y.; Taniguchi, K.; Sawamura, H.; Morikawa, S.; Nakashima, M.; Asai, T.; Matsuda, S. Tactics with Prebiotics for the Treatment of Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease via the Improvement of Mitophagy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.T.; Liao, M.T.; Tsai, K.W.; Lu, K.C.; Hu, W.C. Interplay of Chemokines Receptors, Toll-like Receptors, and Host Immunological Pathways. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 2384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Dai, J.J.; Hu, W.F.; Wang, J. Expression of toll-like receptors in hepatic cirrhosis and hepatocellular carcinoma. Genet. Mol. Res. 2016, 15, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.; Damba, T.; Wu, Z.; Serna-Salas, S.; Buist-Homan, M.; Faber, K.N.; Moshage, H. Bioactive coumarin-derivative esculetin decreases hepatic stellate cell activation via induction of cellular senescence via the PI3K-Akt-GSK3β pathway. Food Biosci. 2022, 50, 102164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, X.; Fu, N.; Du, J.; Wang, R.; Wang, Y.; Zhao, S.; Du, H.; Wang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, D.; et al. miR-1273g-3p modulates activation and apoptosis of hepatic stellate cells by directly targeting PTEN in HCV-related liver fibrosis. FEBS Lett. 2016, 590, 2709–2724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, P.; Yin, K.; Luo, X.; Gu, J.; Tan, R.; Wu, Y.; Li, D. Tandem mass tag-based proteomics analysis reveals the multitarget mechanisms of Phyllanthus emblica against liver fibrosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 989995. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, W.; Wu, X.; Yan, X.; Xu, A.; Yang, A.; You, H. Multitranscriptome analyses reveal prioritized genes specifically associated with liver fibrosis progression independent of etiology. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 316, G744–G754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, A.; Sladowska, G.E.; Strzalka-Mrozik, B. The Role of the Gut Microbiota in Modulating Signaling Pathways and Oxidative Stress in Glioma Therapies. Cancers 2025, 17, 719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rakoff-Nahoum, S.; Paglino, J.; Eslami-Varzaneh, F.; Edberg, S.; Medzhitov, R. Recognition of commensal microflora by toll-like receptors is required for intestinal homeostasis. Cell 2004, 118, 229–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sha, M.; Gao, Y.; Deng, C.; Wan, Y.; Zhuang, Y.; Hu, X.; Wang, Y. Therapeutic effects of AdipoRon on liver inflammation and fibrosis induced by CCl(4) in mice. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 79, 106157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Miao, H.; Yan, H.; Sheng, Y.; Ji, L. Hepatoprotective effect of Forsythiae Fructus water extract against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver fibrosis in mice. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 218, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andruszkow, J.; Hartleben, B.; Schlué, J.; Ritz, T.; Knüchel, R.; Hasan, A.; Petersen, C.; Madadi-Sanjani, O. Staging of liver fibrosis in biliary atresia : Comparison of Chevallier and Ishak score as well as automated evaluation. Pathologe 2019, 40, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, S.; Liu, C.; Sun, L.; Wang, T.; Dai, H.; Wang, K.; Bao, L.; Li, H.; Wang, W.; Liu, S.J.; et al. Gut Parabacteroides merdae protects against cardiovascular damage by enhancing branched-chain amino acid catabolism. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 1271–1286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, C.; Lan, D.; Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Qi, S.; Liu, Y. Porphyromonas gingivalis is a risk factor for the development of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease via ferroptosis. Microbes Infect. 2023, 25, 105040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Metabolites | Formula | RT | Model vs. Control | SCU vs. Model | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Fold Change | Trend | VIP | Fold Change | Trend | VIP | |||
| Oleic acid | C18H34O2 | 9.00 | 1.15 | Up # | 1.34 | 0.82 | Down * | 1.36 |
| Linolenelaidic acid | C18H30O2 | 8.96 | 0.72 | Down # | 1.68 | 1.38 | Up * | 1.23 |
| Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate | C19H28O5S | 10.78 | 0.78 | Down ## | 1.19 | 1.48 | Up ** | 1.97 |
| Corticosterone | C21H30O4 | 6.65 | 0.14 | Down ## | 1.41 | 2.25 | Up ** | 1.76 |
| Creatine | C4H9N3O2 | 1.11 | 1.01 | Up # | 1.19 | 0.72 | Down * | 1.72 |
| Cytidine | C9H13N3O5 | 1.14 | 0.89 | Down # | 1.57 | 0.6 | Down * | 1.76 |
| Allantoic acid | C4H8N4O4 | 0.99 | 1.29 | Up # | 1.24 | 0.53 | Down * | 1.91 |
| Gene | Primer (5′ to 3′) | Product Length | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Col1a1 | FP | TGTTGGTCCTGCTGGCAAGAATG | 5843 bp |
| RP | GTCACCTTGTTCGCCTGTCTCAC | ||
| Col1a2 | FP | GGGCAACAGCAGATTCACCTACAC | 4465 bp |
| RP | CAAGGAATGGCAGGCGAGATGG | ||
| Col4a1 | FP | ACAGCCAGGGATGCCAGGAAG | 6579 bp |
| RP | CACGACTACCAGGAAAGCCAACTC | ||
| Col4a2 | FP | GGGACCTGCCATTACTTCGCTAAC | 6382 bp |
| RP | GGATGGTGTGCTCTGGAAGTTCTG | ||
| TLR2 | FP | TCTGGAGTCTGCTGTGCCCTTC | 2614 bp |
| RP | GGAGCCACGCCCACATCATTC | ||
| Pdgfr-β | FP | CTTGTTCTGGGACGCACTCTTGG | 5405 bp |
| RP | GCTTCTCACTGCTTCTGGCTGTAG |
| Antibody | Host | Clonality | Dilution | Manufacturer | Cat. No. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phospho-PI3K (Tyr607) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 1:1000 | Abcam, Waltham, MA, USA | ab182651 |
| PI3K | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 1:1000 | Wanleibio, Shenyang, China | WL02240 |
| Phospho-AKT (Ser473) | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 1:1000 | Wanleibio, Shenyang, China | WLP001a |
| AKT | Rabbit | Polyclonal | 1:1000 | Zenbio, Chengdu, China | 342529 |
| β-actin | Rabbit | Monoclonal | 1:1000 | Cell Signaling Technology, Danvers, MA, USA | 4970 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, X.; Yang, W.; Weng, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Chen, H.; Chen, Y.; Qiu, J.; Jiang, B.; Li, C.; Lai, Y. Scutellarin Alleviates CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis by Regulating Intestinal Flora and PI3K/AKT Signaling Axis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072997
Li X, Yang W, Weng Y, Zhao Y, Chen H, Chen Y, Qiu J, Jiang B, Li C, Lai Y. Scutellarin Alleviates CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis by Regulating Intestinal Flora and PI3K/AKT Signaling Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072997
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Xin, Wanqi Yang, Ying Weng, Yingying Zhao, Haidong Chen, Yang Chen, Jishuang Qiu, Bei Jiang, Chunyan Li, and Yong Lai. 2025. "Scutellarin Alleviates CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis by Regulating Intestinal Flora and PI3K/AKT Signaling Axis" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072997
APA StyleLi, X., Yang, W., Weng, Y., Zhao, Y., Chen, H., Chen, Y., Qiu, J., Jiang, B., Li, C., & Lai, Y. (2025). Scutellarin Alleviates CCl4-Induced Liver Fibrosis by Regulating Intestinal Flora and PI3K/AKT Signaling Axis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2997. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072997





