Concomitant Pathologies and Their Impact on Parkinson Disease: A Narrative Overview of Current Evidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
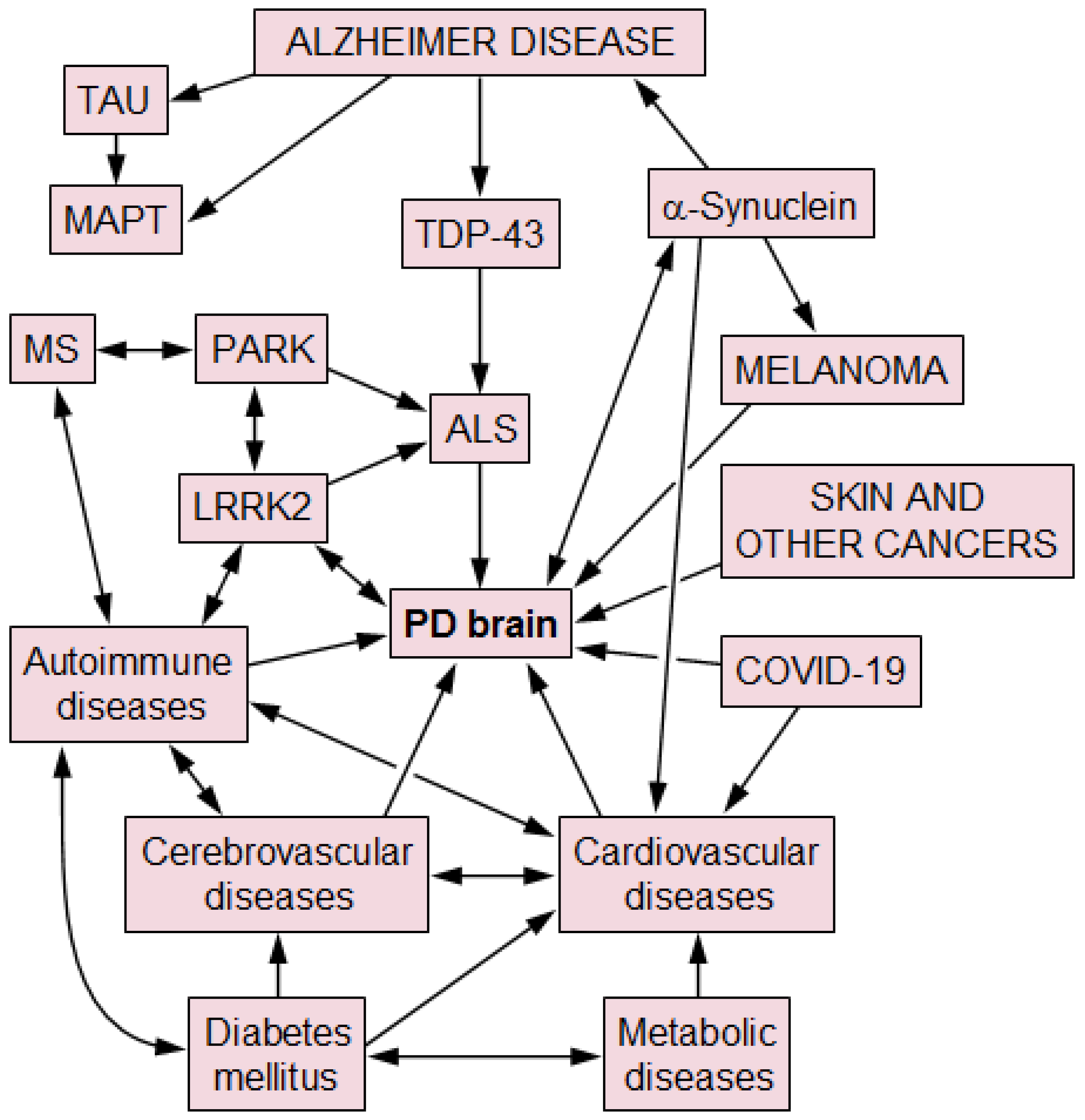
2. PD- and AD-Related Co-Pathology
3. PD and TDP-43 Pathology
4. Cerebrovascular Disease
5. Prevalence of Other Comorbidities
6. Diabetes Mellitus and Metabolic Syndrome
7. Autoimmune Diseases (Table 1)
| Type of Disorder | References |
|---|---|
| Allergic rhinitis | [112] |
| Autoimmune hepatitis | [111] |
| Bullous pemphigoid | [109] |
| Celiac disease | [109] |
| Crohn’s disease | [109,113] |
| Graves’ disease | [109] |
| Hashimoto thyroiditis | [114] |
| Inflammatory bowel disease/syndrome | [109,115,116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126] |
| Multiple sclerosis | [109,127,128,129,130,131,132,133,134] |
| Myasthenia gravis | [135,136,137,138,139,140,141,142,143] |
| Osteoarthritis | [144,145] |
| Polymyalgia rheumatica | [110] |
| Rheumatoid arthritis | [109,110] |
| Sjögren’s syndrome | [111,146,147,148,149,150,151,152,153,154,155] |
| Systemic lupus erythematosus | [109] |
| Ulcerative colitis | [109] |
7.1. Sjögren’s Syndrome
7.2. Rheumatoid Arthritis
7.3. Myasthenia Gravis
7.4. Inflammatory Bowel Disease
7.5. Hashimoto Thyroiditis
8. PD and Multiple Sclerosis
9. PD and Other Pathologies
10. PD and COVID-19
11. PD and Cancer Risk/Incidence
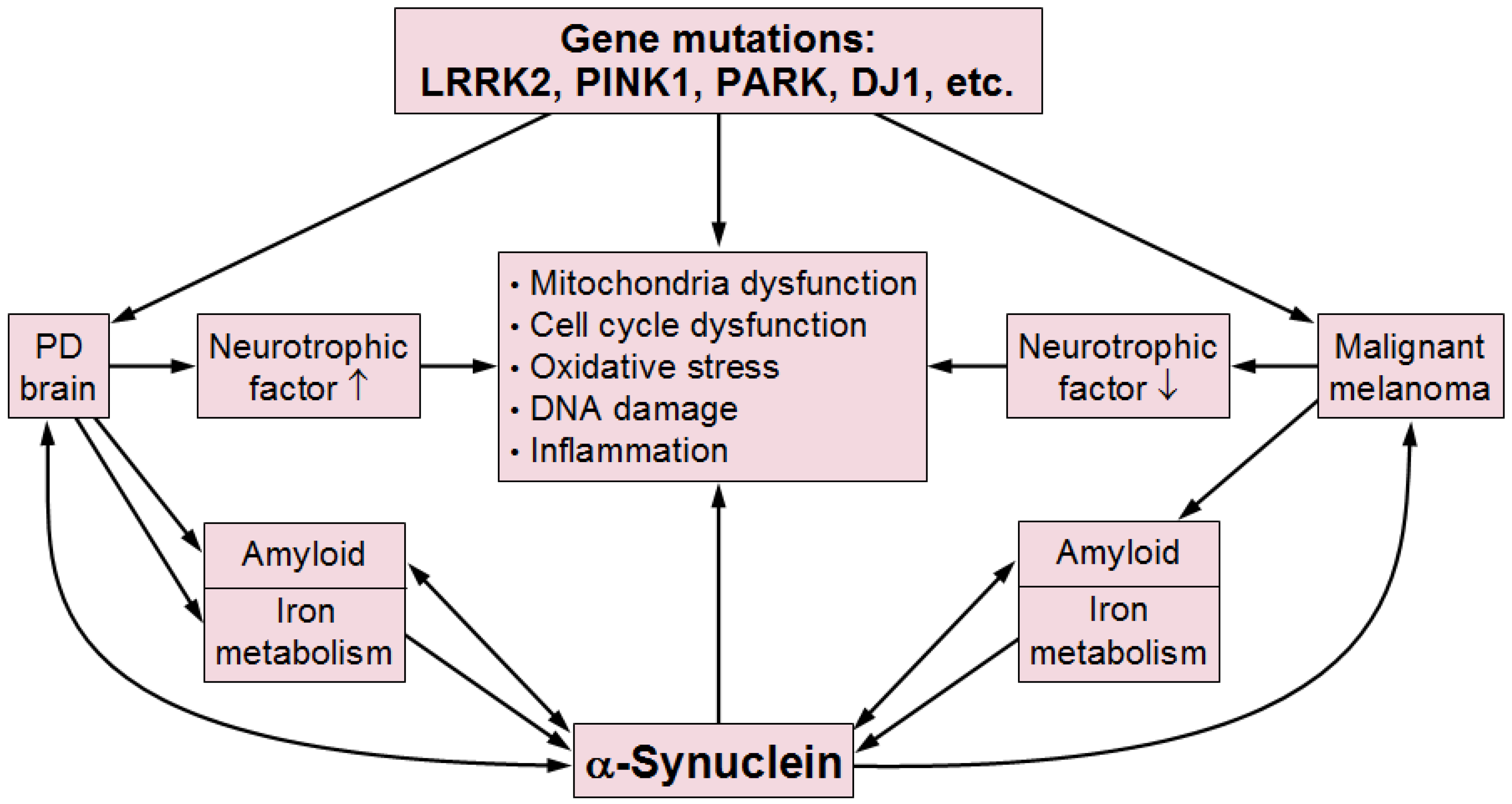
12. Role of Genetic Risk Factors
13. Linking PD and Malignancies—Possible Pathogenic Mechanisms
14. Conclusions and Outlook
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer disease |
| ADNC | Alzheimer disease-related pathology |
| AiDs | autoimmune disorders |
| ALS | amyotrophic lateral sclerosis |
| ARTAG | aging-related tau astrogliopathy |
| Aβ | β-amyloid |
| αSyn | α-synuclein |
| CAA | cerebral amyloid angiopathy |
| CD | Crohn’s disease |
| CJD | Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease |
| CSVD | cerebral small vessel disease |
| CVP | cerebrovascular pathology |
| DLB | dementia with Lewy bodies |
| FD | Fabry disease |
| GWAS | genome-wide association studies |
| IBD | inflammatory bowel disease |
| LATE | limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy |
| LBs | Lewy bodies |
| MG | myasthenia gravis |
| Mr | Mendelian randomization |
| MS | multiple sclerosis |
| OS | oxidative stress |
| PD | Parkinson disease |
| pSS | primary Sjögren’s syndrome |
| RA | rheumatoid arthritis |
| RLS | restless leg syndrome |
| SN | substantia nigra |
| SN | substantia nigra |
| SS | Sjögren’s syndrome |
| T2DM | type 2 diabetes mellitus |
| WM | white matter |
| WM | white matter |
References
- Braak, H.; Del Tredici, K.; Rüb, U.; de Vos, R.A.; Jansen Steur, E.N.; Braak, E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2003, 24, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beach, T.G.; Adler, C.H.; Lue, L.; Sue, L.I.; Bachalakuri, J.; Henry-Watson, J.; Sasse, J.; Boyer, S.; Shirohi, S.; Brooks, R.; et al. Unified staging system for Lewy body disorders: Correlation with nigrostriatal degeneration, cognitive impairment and motor dysfunction. Acta Neuropathol. 2009, 117, 613–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borghammer, P.; Horsager, J.; Andersen, K.; Van Den Berge, N.; Raunio, A.; Murayama, S.; Parkkinen, L.; Myllykangas, L. Neuropathological evidence of body-first vs. brain-first Lewy body disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2021, 161, 105557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chu, Y.; Hirst, W.D.; Federoff, H.J.; Harms, A.S.; Stoessl, A.J.; Kordower, J.H. Nigrostriatal tau pathology in parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease. Brain 2024, 147, 444–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchman, A.S.; Yu, L.; Oveisgharan, S.; Farfel, J.M.; Schneider, J.A.; Bennett, D.A. Person-specific contributions of brain pathologies to progressive parkinsonism in older adults. J. Gerontol. A Biol. Sci. Med. Sci. 2021, 76, 615–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, S.L.; Kovacs, G.G. Current concepts of mixed pathologies in neurodegenerative diseases. Can. J. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 50, 329–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spires-Jones, T.L.; Attems, J.; Thal, D.R. Interactions of pathological proteins in neurodegenerative diseases. Acta Neuropathol. 2017, 134, 187–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, H.; Chen, H.; Zhang, M.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y. Cerebral microbleeds is associated with dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2023, 123, 407–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchman, A.S.; Yu, L.; Wilson, R.S.; Leurgans, S.E.; Nag, S.; Shulman, J.M.; Barnes, L.L.; Schneider, J.A.; Bennett, D.A. Progressive parkinsonism in older adults is related to the burden of mixed brain pathologies. Neurology 2019, 92, e1821–e1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, Y.; Hirst, W.D.; Kordower, J.H. Mixed pathology as a rule, not exception: Time to reconsider disease nosology. Handb. Clin. Neurol. 2023, 192, 57–71. [Google Scholar]
- Smith, C.; Malek, N.; Grosset, K.; Cullen, B.; Gentleman, S.; Grosset, D.G. Neuropathology of dementia in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review of autopsy studies. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2019, 90, 1234–1243. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, L.L.; Zhang, X.L.; Hu, H.Y. Co-aggregation of TDP-43 with other pathogenic proteins and their co-pathologies in neurodegenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kovacs, G.G.; Milenkovic, I.; Wöhrer, A.; Höftberger, R.; Gelpi, E.; Haberler, C.; Hönigschnabl, S.; Reiner-Concin, A.; Heinzl, H.; Jungwirth, S.; et al. Non-Alzheimer neurodegenerative pathologies and their combinations are more frequent than commonly believed in the elderly brain: A community-based autopsy series. Acta Neuropathol. 2013, 126, 365–384. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dugger, B.N.; Adler, C.H.; Shill, H.A.; Caviness, J.; Jacobson, S.; Driver-Dunckley, E.; Beach, T.G. Concomitant pathologies among a spectrum of parkinsonian disorders. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 525–529. [Google Scholar]
- Beach, T.G.; Serrano, G.E.; Driver-Dunckley, E.D.; Sue, L.I.; Shill, H.A.; Mehta, S.H.; Belden, C.M.; Lorenzini, I.; Tremblay, C.; Choudhury, P.; et al. Parkinson disease neuropathological comorbidities: Prevalences from younger-old to older-old, with comparison to non-demented, non-parkinsonian subjects [PREPRINT]. medRxiv 2025. [Google Scholar]
- Jellinger, K.A. Behavioral disorders in Parkinson disease: Current view. J. Neural Transm. 2024, 132, 169–201. [Google Scholar]
- Jellinger, K.A. The pathobiological basis of depression in Parkinson disease: Challenges and outlooks. J. Neural Transm. 2022, 129, 1397–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jellinger, K.A. Morphological basis of Parkinson disease-associated cognitive impairment: An update. J. Neural Transm. 2022, 129, 977–999. [Google Scholar]
- Han, Y.; He, Z. Concomitant protein pathogenesis in Parkinson’s disease and perspective mechanisms. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2023, 15, 1189809. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, L.; Attems, J. Prevalence of concomitant pathologies in Parkinson’s disease: Implications for prognosis, diagnosis, and insights into common pathogenic mechanisms. J. Park. Dis. 2024, 14, 35–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, J.; Tang, J.; Kang, F.; Ye, J.; Cui, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, J.; Wu, S.; Ye, K. Gut-induced alpha-synuclein and tau propagation initiate Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s disease co-pathology and behavior impairments. Neuron 2024, 112, 3585–3601.e3585. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, K.A.; Seppi, K.; Wenning, G.K.; Poewe, W. Impact of coexistent Alzheimer pathology on the natural history of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2002, 109, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Winer, J.R.; Maass, A.; Pressman, P.; Stiver, J.; Schonhaut, D.R.; Baker, S.L.; Kramer, J.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Jagust, W.J. Associations between tau, beta-amyloid, and cognition in Parkinson disease. JAMA Neurol. 2018, 75, 227–235. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Gao, F.; Wang, D.; Li, C.; Fu, Y.; He, W.; Zhang, J. Tau pathology in Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurol. 2018, 9, 809. [Google Scholar]
- Kurosinski, P.; Guggisberg, M.; Götz, J. Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s disease—Overlapping or synergistic pathologies? Trends Mol. Med. 2002, 8, 3–5. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, L.; Meng, L.; He, M.; Zhang, Z. Tau in the pathophysiology of Parkinson’s disease. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2021, 71, 2179–2191. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, W.R.W.; Younce, J.R.; Campbell, M.C.; Racette, B.A.; Norris, S.A.; Ushe, M.; Criswell, S.; Davis, A.A.; Alfradique-Dunham, I.; Maiti, B.; et al. Neocortical Lewy body pathology parallels Parkinson’s dementia, but not always. Ann. Neurol. 2023, 93, 184–195. [Google Scholar]
- Tropea, T.F.; Albuja, I.; Cousins, K.A.Q.; Irwin, D.J.; Lee, E.B.; Chen-Plotkin, A.S. Concomitant Alzheimer disease pathology in Parkinson disease dementia. Ann. Neurol. 2023, 93, 1045–1046. [Google Scholar]
- Jellinger, K.A. Morphological characteristics differentiate dementia with Lewy bodies from Parkinson disease with and without dementia. J. Neural Transm. 2023, 130, 891–904. [Google Scholar]
- Lloyd, G.M.; Dhillon, J.S.; Gorion, K.M.; Riffe, C.; Fromholt, S.E.; Xia, Y.; Giasson, B.I.; Borchelt, D.R. Collusion of alpha-synuclein and Abeta aggravating co-morbidities in a novel prion-type mouse model. Mol. Neurodegener. 2021, 16, 63. [Google Scholar]
- Nalls, M.A.; Pankratz, N.; Lill, C.M.; Do, C.B.; Hernandez, D.G.; Saad, M.; DeStefano, A.L.; Kara, E.; Bras, J.; Sharma, M.; et al. Large-scale meta-analysis of genome-wide association data identifies six new risk loci for Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 989–993. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Simón-Sánchez, J.; Schulte, C.; Bras, J.M.; Sharma, M.; Gibbs, J.R.; Berg, D.; Paisan-Ruiz, C.; Lichtner, P.; Scholz, S.W.; Hernandez, D.G.; et al. Genome-wide association study reveals genetic risk underlying Parkinson’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 1308–1312. [Google Scholar]
- Duda, J.E.; Giasson, B.I.; Mabon, M.E.; Miller, D.C.; Golbe, L.I.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Concurrence of alpha-synuclein and tau brain pathology in the Contursi kindred. Acta Neuropathol. 2002, 104, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kotzbauer, P.T.; Giasson, B.I.; Kravitz, A.V.; Golbe, L.I.; Mark, M.H.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Lee, V.M. Fibrillization of alpha-synuclein and tau in familial Parkinson’s disease caused by the A53T alpha-synuclein mutation. Exp. Neurol. 2004, 187, 279–288. [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi, K.; Cochran, E.J.; Murrell, J.R.; Polymeropoulos, M.H.; Shannon, K.M.; Crowther, R.A.; Goedert, M.; Ghetti, B. Abundant neuritic inclusions and microvacuolar changes in a case of diffuse Lewy body disease with the A53T mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene. Acta Neuropathol. 2005, 110, 298–305. [Google Scholar]
- Hadi, F.; Akrami, H.; Totonchi, M.; Barzegar, A.; Nabavi, S.M.; Shahpasand, K. Alpha-synuclein abnormalities trigger focal tau pathology, spreading to various brain areas in Parkinson disease. J. Neurochem. 2021, 157, 727–751. [Google Scholar]
- Milber, J.M.; Noorigian, J.V.; Morley, J.F.; Petrovitch, H.; White, L.; Ross, G.W.; Duda, J.E. Lewy pathology is not the first sign of degeneration in vulnerable neurons in Parkinson disease. Neurology 2012, 79, 2307–2314. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, P.T.; Dickson, D.W.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Jack, C.R.; Boyle, P.A.; Arfanakis, K.; Rademakers, R.; Alafuzoff, I.; Attems, J.; Brayne, C.; et al. Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy (LATE): Consensus working group report. Brain 2019, 142, 1503–1527. [Google Scholar]
- Abner, E.L.; Kryscio, R.J.; Schmitt, F.A.; Santacruz, K.S.; Jicha, G.A.; Lin, Y.; Neltner, J.M.; Smith, C.D.; Van Eldik, L.J.; Nelson, P.T. “End-stage” neurofibrillary tangle pathology in preclinical Alzheimer’s disease: Fact or fiction? J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2011, 25, 445–453. [Google Scholar]
- Josephs, K.A.; Murray, M.E.; Whitwell, J.L.; Tosakulwong, N.; Weigand, S.D.; Petrucelli, L.; Liesinger, A.M.; Petersen, R.C.; Parisi, J.E.; Dickson, D.W. Updated TDP-43 in Alzheimer’s disease staging scheme. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 131, 571–585. [Google Scholar]
- Kokoulina, P.; Rohn, T.T. Caspase-cleaved transactivation response DNA-binding protein 43 in Parkinson’s disease and dementia with Lewy bodies. Neurodegener. Dis. 2010, 7, 243–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakashima-Yasuda, H.; Uryu, K.; Robinson, J.; Xie, S.X.; Hurtig, H.; Duda, J.E.; Arnold, S.E.; Siderowf, A.; Grossman, M.; Leverenz, J.B.; et al. Co-morbidity of TDP-43 proteinopathy in Lewy body related diseases. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokota, O.; Davidson, Y.; Arai, T.; Hasegawa, M.; Akiyama, H.; Ishizu, H.; Terada, S.; Sikkink, S.; Pickering-Brown, S.; Mann, D.M. Effect of topographical distribution of alpha-synuclein pathology on TDP-43 accumulation in Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2010, 120, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, L.; Wang, C.; Chen, L.; Leung, K.L.; Lo, E.; Lakso, M.; Wong, G. TDP-1/TDP-43 potentiates human alpha-Synuclein (HASN) neurodegeneration in Caenorhabditis elegans. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2020, 1866, 165876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, T.; Huang, C.; Tong, J.; Yang, M.; Zhou, H.; Xia, X.G. TDP-43 potentiates alpha-synuclein toxicity to dopaminergic neurons in transgenic mice. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2011, 7, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masuda-Suzukake, M.; Nonaka, T.; Hosokawa, M.; Kubo, M.; Shimozawa, A.; Akiyama, H.; Hasegawa, M. Pathological alpha-synuclein propagates through neural networks. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaweda-Walerych, K.; Sitek, E.J.; Narozanska, E.; Buratti, E. Parkin beyond Parkinson’s disease-a functional meaning of parkin downregulation in TDP-43 proteinopathies. Cells 2021, 10, 3389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, H.; Holton, J.L.; Lees, A.J.; Revesz, T. TDP-43 pathology is present in most post-encephalitic parkinsonism brains. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2014, 40, 654–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuboi, Y.; Mishima, T.; Fujioka, S. Perry disease: Concept of a new disease and clinical diagnostic criteria. J. Mov. Disord. 2021, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsumata, Y.; Wu, X.; Aung, K.Z.; Gauthreaux, K.; Mock, C.; Forrest, S.L.; Kovacs, G.G.; Nelson, P.T. Pathologic correlates of aging-related tau astrogliopathy: ARTAG is associated with LATE-NC and cerebrovascular pathologies, but not with ADNC. Neurobiol. Dis. 2024, 191, 106412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grau-Rivera, O.; Gelpi, E.; Rey, M.J.; Valldeoriola, F.; Tolosa, E.; Compta, Y.; Martí, M.J. Prominent psychiatric symptoms in patients with Parkinson’s disease and concomitant argyrophilic grain disease. J. Neurol. 2013, 260, 3002–3009. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Homma, T.; Mochizuki, Y.; Takahashi, K.; Komori, T. Medial temporal regional argyrophilic grain as a possible important factor affecting dementia in Parkinson’s disease. Neuropathology 2015, 35, 441–451. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, K.A. Prevalence of cerebrovascular lesions in Parkinson’s disease. A postmortem study. Acta Neuropathol. 2003, 105, 415–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, A.J.; Daniel, S.E.; Kilford, L.; Lees, A.J. Accuracy of clinical diagnosis of idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: A clinico-pathological study of 100 cases. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 1992, 55, 181–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastaglia, F.L.; Johnsen, R.D.; Kakulas, B.A. Prevalence of stroke in Parkinson’s disease: A postmortem study. Mov. Disord. 2002, 17, 772–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasimhan, M.; Schwartz, R.; Halliday, G. Parkinsonism and cerebrovascular disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 433, 120011. [Google Scholar]
- van der Horn, H.J.; Vakhtin, A.A.; Julio, K.; Nitschke, S.; Shaff, N.; Dodd, A.B.; Erhardt, E.; Phillips, J.P.; Pirio Richardson, S.; Deligtisch, A.; et al. Parkinson’s disease cerebrovascular reactivity pattern: A feasibility study. J. Cereb. Blood Flow. Metab. 2024, 44, 1774–1786. [Google Scholar]
- Jacob, M.A.; Cai, M.; Bergkamp, M.; Darweesh, S.K.L.; Gelissen, L.M.Y.; Marques, J.; Norris, D.G.; Duering, M.; Esselink, R.A.J.; Tuladhar, A.M.; et al. Cerebral small vessel disease progression increases risk of incident parkinsonism. Ann. Neurol. 2023, 93, 1130–1141. [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz, R.S.; Halliday, G.M.; Soh, D.; Cordato, D.J.; Kril, J.J. Impact of small vessel disease on severity of motor and cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2018, 58, 70–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Li, H.; Jia, J.; Shao, X.; Li, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, H.; Jin, L. Progressive cerebrovascular reactivity reduction occurs in Parkinson’s disease: A longitudinal study. Mov. Disord. 2024, 39, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.; Wu, H.; Zhou, C.; Guan, X.; Guo, T.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Wen, J.; Qin, J.; Tan, S.; et al. Neurovascular coupling alteration in drug-naive Parkinson’s disease: The underlying molecular mechanisms and levodopa’s restoration effects. Neurobiol. Dis. 2024, 191, 106406. [Google Scholar]
- Wan, H.; Wang, G.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Y. Effect of cerebral small vessel disease on cognitive impairment in Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann. Transl. Med. 2022, 10, 288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalaker, T.O.; Larsen, J.P.; Dwyer, M.G.; Aarsland, D.; Beyer, M.K.; Alves, G.; Bronnick, K.; Tysnes, O.B.; Zivadinov, R. White matter hyperintensities do not impact cognitive function in patients with newly diagnosed Parkinson’s disease. Neuroimage 2009, 47, 2083–2089. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chen, K.; Jin, Z.; Fang, J.; Qi, L.; Liu, C.; Wang, R.; Su, Y.; Yan, H.; Liu, A.; Xi, J.; et al. Lacunes may worsen cognition but not motor function in Parkinson’s disease. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e2880. [Google Scholar]
- Donahue, E.K.; Foreman, R.P.; Duran, J.J.; Jakowec, M.W.; O’Neill, J.; Petkus, A.J.; Holschneider, D.P.; Choupan, J.; Van Horn, J.D.; Venkadesh, S.; et al. Increased perivascular space volume in white matter and basal ganglia is associated with cognition in Parkinson’s Disease. Brain Imaging Behav. 2023, 18, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Compta, Y.; Parkkinen, L.; O’Sullivan, S.S.; Vandrovcova, J.; Holton, J.L.; Collins, C.; Lashley, T.; Kallis, C.; Williams, D.R.; de Silva, R.; et al. Lewy- and Alzheimer-type pathologies in Parkinson’s disease dementia: Which is more important? Brain 2011, 134, 1493–1505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elabi, O.; Gaceb, A.; Carlsson, R.; Padel, T.; Soylu-Kucharz, R.; Cortijo, I.; Li, W.; Li, J.Y.; Paul, G. Human alpha-synuclein overexpression in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease leads to vascular pathology, blood brain barrier leakage and pericyte activation. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 1120. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, G.; Elabi, O.F. Microvascular changes in Parkinson’s disease—Focus on the neurovascular unit. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 853372. [Google Scholar]
- Agrawal, S.; Leurgans, S.E.; Nag, S.; Oveisgharan, S.; Barnes, L.L.; Bennett, D.A.; Buchman, A.S.; Schneider, J.A. Effects of cerebrovascular and Lewy body pathology on parkinsonian signs in community-dwelling older adults. Neurology 2023, 101, e754–e763. [Google Scholar]
- Veselý, B.; Antonini, A.; Rektor, I. The contribution of white matter lesions to Parkinson’s disease motor and gait symptoms: A critical review of the literature. J. Neural Transm. 2016, 123, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wan, H.; Zhang, M.; Liu, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Ma, H.; Pan, Y.; Feng, T.; Wang, Y. Cerebral small vessel disease may worsen motor function, cognition, and mood in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2021, 83, 86–92. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wan, H.; Wu, D.; Gao, D.; Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Huang, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Shao, X. Disturbance of functional brain networks and cognitive decline in Parkinson’s disease: Severe cerebral small vessel disease aggravates this relationship. Park. Relat. Disord. 2023, 110, 105386. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, Z.; Zhang, M.; Fang, Q.; Huang, J. Relationship between Parkinson’s disease and cardio-cerebrovascular diseases: A Mendelian randomized study. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 20428. [Google Scholar]
- Potashkin, J.; Huang, X.; Becker, C.; Chen, H.; Foltynie, T.; Marras, C. Understanding the links between cardiovascular disease and Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2020, 35, 55–74. [Google Scholar]
- Minar, M.; Dragasek, J.; Valkovic, P. Psychiatric and somatic co-morbidities in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A STROBE-compliant national multi-center, cross-sectional, observational study COSMOS in Slovakia. Neuro Endocrinol. Lett. 2022, 43, 39–44. [Google Scholar]
- Carroll, C.; Clarke, C.E.; Grosset, D.; Rather, A.; Mohamed, B.; Parry, M.; Reddy, P.; Fackrell, R.; Chaudhuri, K.R. Addressing comorbidities in people with Parkinson’s disease: Considerations from an expert panel. J. Park. Dis. 2024, 14, 53–63. [Google Scholar]
- Chahine, L.M.; Dos Santos, C.; Fullard, M.; Scordia, C.; Weintraub, D.; Erus, G.; Rosenthal, L.; Davatzikos, C.; McMillan, C.T. Modifiable vascular risk factors, white matter disease and cognition in early Parkinson’s disease. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 246-e18. [Google Scholar]
- Gage, H.; Hendricks, A.; Zhang, S.; Kazis, L. The relative health related quality of life of veterans with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2003, 74, 163–169. [Google Scholar]
- Thomas, H.A.; Goudman, L.; DiMarzio, M.; Barron, G.; Pilitsis, J.G. Prevalence of pain phenotypes and co-morbidities of chronic pain in Parkinson’s Disease. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2024, 246, 108563. [Google Scholar]
- Patel, V.; Ts, J.; Kamble, N.; Yadav, R.; K, T.; Pal, P.K.; Reddy Yc, J. Prevalence and correlates of psychiatric comorbidity and multimorbidity in Parkinson’s disease and atypical parkinsonian syndromes. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry Neurol. 2023, 36, 155–163. [Google Scholar]
- Rai, N.K.; Goyal, V.; Kumar, N.; Shukla, G.; Srivastava, A.K.; Singh, S.; Behari, M. Neuropsychiatric co-morbidities in non-demented Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Indian. Acad. Neurol. 2015, 18, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Greten, S.; Wegner, F.; Jensen, I.; Krey, L.; Rogozinski, S.; Fehring, M.; Heine, J.; Doll-Lee, J.; Pötter-Nerger, M.; Zeitzschel, M.; et al. The comorbidity and co-medication profile of patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. J. Neurol. 2024, 271, 782–793. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Doi, Y.; Yokoyama, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Nagai, M.; Fujimoto, K.; Nakano, I. How can the national burden of Parkinson’s disease comorbidity and mortality be estimated for the Japanese population? J. Epidemiol. 2011, 21, 211–216. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, A.; Kumar, A.; Faruq, M.; Singh, V.K.; Dwivedi, N.; Singh, K.; Hussain, I.; Parida, S.; Kumar Jha, G.; Kumar, N.; et al. Co-occurrence of Parkinson’s disease and Retinitis Pigmentosa: A genetic and in silico analysis. Neuroscience 2025, 565, 519–526. [Google Scholar]
- Cheong, J.L.Y.; de Pablo-Fernandez, E.; Foltynie, T.; Noyce, A.J. The association between type 2 diabetes mellitus and Parkinson’s disease. J. Park. Dis. 2020, 10, 775–789. [Google Scholar]
- Chegão, A.; Guarda, M.; Alexandre, B.M.; Shvachiy, L.; Temido-Ferreira, M.; Marques-Morgado, I.; Fernandes Gomes, B.; Matthiesen, R.; Lopes, L.V.; Florindo, P.R.; et al. Glycation modulates glutamatergic signaling and exacerbates Parkinson’s disease-like phenotypes. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 51. [Google Scholar]
- De Pablo-Fernandez, E.; Goldacre, R.; Pakpoor, J.; Noyce, A.J.; Warner, T.T. Association between diabetes and subsequent Parkinson disease: A record-linkage cohort study. Neurology 2018, 91, e139–e142. [Google Scholar]
- Azami, M.; Moradkhani, A.; Afraie, M.; Khateri, S.; Sharifian, E.; Zamani, K.; Moradi, Y. The risk of Parkinson’s disease in diabetic people: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2024, 124, 775–790. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, X.; Lu, Y.; Gong, Z.; Huang, W.; Wang, Z. Prediabetes and the incidence of Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Biomol. Biomed. 2024, 24, 722–730. [Google Scholar]
- Biosa, A.; Outeiro, T.F.; Bubacco, L.; Bisaglia, M. Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease: A molecular point of view. Mol. Neurobiol. 2018, 55, 8754–8763. [Google Scholar]
- König, A.; Outeiro, T.F. Diabetes and Parkinson’s disease: Understanding shared molecular mechanisms. J. Park. Dis. 2024, 14, 917–924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duta, C.; Muscurel, C.; Dogaru, C.B.; Stoian, I. Ferroptosis-a shared mechanism for Parkinson’s disease and type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, S.; Lin, Y.; Jones, D.; Walker, D.I.; Duarte Folle, A.; Del Rosario, I.; Yu, Y.; Zhang, K.; Keener, A.M.; Bronstein, J.; et al. Untargeted serum metabolic profiling of diabetes mellitus among Parkinson’s disease patients. NPJ Park. Dis. 2024, 10, 100. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H. MicroRNAs, Parkinson’s disease, and diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De, S.; Banerjee, S.; Rakshit, P.; Kumar, S.K.A. Unraveling the ties: Type 2 diabetes and Parkinson’s disease—A nano-based targeted drug delivery approach. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 2024, 21, E130524229900. [Google Scholar]
- Dobbs, S.M.; Dobbs, R.J.; Weller, C.; Charlett, A.; Augustin, A.; Taylor, D.; Ibrahim, M.A.; Bjarnason, I. Peripheral aetiopathogenic drivers and mediators of Parkinson’s disease and co-morbidities: Role of gastrointestinal microbiota. J. Neurovirol 2016, 22, 22–32. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, Y.; Shimoga, D.; Sharma, A. Parkinson’s disease and diabetes mellitus: Synergistic effects on pathophysiology and GI motility. Curr. Gastroenterol. Rep. 2023, 25, 106–113. [Google Scholar]
- Bohnen, N.I.; Kotagal, V.; Müller, M.L.; Koeppe, R.A.; Scott, P.J.; Albin, R.L.; Frey, K.A.; Petrou, M. Diabetes mellitus is independently associated with more severe cognitive impairment in Parkinson disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2014, 20, 1394–1398. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Geng, C.; Meng, K.; Zhao, B.; Liu, X.; Tang, Y. Causal relationships between type 1 diabetes mellitus and Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2024, 29, 53. [Google Scholar]
- Mai, A.S.; Tan, B.J.; Sun, Q.Y.; Tan, E.K. Association between type 1 diabetes mellitus and Parkinson’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sääksjärvi, K.; Knekt, P.; Männistö, S.; Lyytinen, J.; Heliövaara, M. Prospective study on the components of metabolic syndrome and the incidence of Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meléndez-Flores, J.D.; Castillo-Torres, S.A.; Cerda-Contreras, C.; Chávez-Luévanos, B.; Estrada-Bellmann, I. Clinical features of metabolic syndrome in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 72, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Peng, Z.; Dong, S.; Tao, Y.; Huo, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Huang, W.; Qu, H.; Liu, J.; Chen, Y.; Xu, Z.; et al. Metabolic syndrome contributes to cognitive impairment in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2018, 55, 68–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, J.H.; Lee, S.; Yoon, J.H. Metabolic syndrome and Parkinson’s disease incidence: A nationwide study using propensity score matching. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2021, 19, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.H.; Nam, G.E.; Han, K.; Huh, Y.; Kim, W.; Lee, M.K.; Koh, E.S.; Kim, E.S.; Kim, M.K.; Kwon, H.S.; et al. Association of dynamic changes in metabolic syndrome status with the risk of Parkinson’s disease: A nationwide cohort study. J. Park. Dis. 2021, 11, 1751–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.Y.; Liu, S.F.; Zhuang, J.L.; Li, M.M.; Huang, Z.P.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, X.R.; Chen, C.N.; Lin, S.; Ye, L.C. Recent research progress on metabolic syndrome and risk of Parkinson’s disease. Rev. Neurosci. 2023, 34, 719–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Feng, Y.; Yue, Z. Association of metabolic syndrome and its components with Parkinson’s disease: A cross-sectional study. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2024, 24, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sundquist, J.; Sundquist, K. Subsequent risks of Parkinson disease in patients with autoimmune and related disorders: A nationwide epidemiological study from Sweden. Neurodegener. Dis. 2012, 10, 277–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Wan, J.; Xu, Z.; Tang, B. The association between Parkinson’s disease and autoimmune diseases: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1103053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Zhao, H.; Wang, F.; Guo, X. Inflammatory rheumatic diseases and the risk of Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 999820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pakpoor, J.; Noyce, A.; Goldacre, R.; Selkihova, M.; Mullin, S.; Schrag, A.; Lees, A.; Goldacre, M. Viral hepatitis and Parkinson disease: A national record-linkage study. Neurology 2017, 88, 1630–1633. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nam, J.Y.; Park, S.J.; Song, J.; Jeong, S.; Choi, S.; Park, S.M. Association of allergic disease with Parkinson’s disease: A nationally representative retrospective cohort study. Allergol. Int. 2024, 73, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jia, Y.; Xu, Q.; Yang, P.; Sun, L.; Liu, Y.; Chang, X.; He, Y.; Shi, M.; Guo, D.; et al. Association of Crohn’s disease and ulcerative colitis with the risk of neurological diseases: A large-scale Mendelian randomization study. J. Hum. Genet. 2024, 69, 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, S.; Dolatshahi, M.; Rahmani, F. Shedding light on thyroid hormone disorders and Parkinson disease pathology: Mechanisms and risk factors. J. Endocrinol. Invest. 2021, 44, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, X.; Ploner, A.; Wang, Y.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Williams, D.M.; Pedersen, N.L.; Wirdefeldt, K. Genetic overlap between Parkinson’s disease and inflammatory bowel disease. Brain Commun. 2023, 5, fcad002. [Google Scholar]
- Sun, Q.; Li, Y.J.; Ning, S.B. Investigating the molecular mechanisms underlying the co-occurrence of Parkinson’s disease and inflammatory bowel disease through the integration of multiple datasets. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 17028. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H.S.; Lobbestael, E.; Vermeire, S.; Sabino, J.; Cleynen, I. Inflammatory bowel disease and Parkinson’s disease: Common pathophysiological links. Gut 2021, 70, 408–417. [Google Scholar]
- Herrick, M.K.; Tansey, M.G. Is LRRK2 the missing link between inflammatory bowel disease and Parkinson’s disease? NPJ Park. Dis. 2021, 7, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Kars, M.E.; Wu, Y.; Stenson, P.D.; Cooper, D.N.; Burisch, J.; Peter, I.; Itan, Y. The landscape of rare genetic variation associated with inflammatory bowel disease and Parkinson’s disease comorbidity. Genome Med. 2024, 16, 66. [Google Scholar]
- Lippai, R.; Veres-Székely, A.; Sziksz, E.; Iwakura, Y.; Pap, D.; Rokonay, R.; Szebeni, B.; Lotz, G.; Béres, N.J.; Cseh, Á.; et al. Immunomodulatory role of Parkinson’s disease 7 in inflammatory bowel disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 14582. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, Y.; Yuan, M.; Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; Chen, W.Z.; Xu, Z.Z.; Xiang, Z.B.; Xu, R.S. Association between inflammatory bowel diseases and Parkinson’s disease: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Neural. Regen. Res. 2022, 17, 344–353. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zeng, R.; Wang, J.; Zheng, C.; Jiang, R.; Tong, S.; Wu, H.; Zhuo, Z.; Yang, Q.; Leung, F.W.; Sha, W.; et al. Lack of causal associations of inflammatory bowel disease with Parkinson’s disease and other neurodegenerative disorders. Mov. Disord. 2023, 38, 1082–1088. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.L.; Wang, Z.Y.; Tian, J.; Ma, D.R.; Shi, C.H. Association between inflammatory bowel disease and Parkinson’s disease: A prospective cohort study of 468,556 UK biobank participants. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2024, 15, 1294879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freuer, D.; Meisinger, C. Association between inflammatory bowel disease and Parkinson’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. NPJ Park. Dis. 2022, 8, 55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-Oliva, A.M.; Ruiz, R.; Soto, M.S.; Boza-Serrano, A.; Rodriguez-Perez, A.I.; Roca-Ceballos, M.A.; García-Revilla, J.; Santiago, M.; Serres, S.; Economopoulus, V.; et al. Inflammatory bowel disease induces pathological Alpha-synuclein aggregation in the human gut and brain. Neuropathol. Appl. Neurobiol. 2024, 50, e12962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zong, J.; Yang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, H.; Yang, X. The two-directional prospective association between inflammatory bowel disease and neurodegenerative disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis based on longitudinal studies. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1325908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valkovic, P.; Krastev, G.; Mako, M.; Leitner, P.; Gasser, T. A unique case of coincidence of early onset Parkinson’s disease and multiple sclerosis. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 2278–2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katunina, E.A.; Boyko, O.V.; Shipilova, N.N.; Kabaeva, A.R.; Boyko, A.N. A rare clinical case of comorbidity of early-onset Parkinson’s disease and remitting multiple sclerosis. Zhurnal Nevrol. I Psikhiatrii Im. SS Korsakova 2021, 121, 99–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damásio, J.; Ramos, C.; Valdemar, L.; da Silva, A.M.; Magalhães, M. A coincidental case of young-onset Parkinson disease and multiple sclerosis. Neurologist 2011, 17, 286–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadnicka, A.; Sheerin, U.M.; Kaplan, C.; Molloy, S.; Muraro, P.A. Primary progressive multiple sclerosis developing in the context of young onset Parkinson’s disease. Mult. Scler. 2013, 19, 123–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wise, A.; Ortega, R.A.; Raymond, D.; Cervera, A.; Thorn, E.; Leaver, K.; Russell, D.S.; Bressman, S.B.; Crary, J.F.; Saunders-Pullman, R. Multiple sclerosis in LRRK2 G2019S Parkinson’s disease and isolated nigral degeneration in a homozygous variant carrier. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1450654. [Google Scholar]
- O’Hara, D.M.; Pawar, G.; Kalia, S.K.; Kalia, L.V. LRRK2 and alpha-synuclein: Distinct or synergistic players in Parkinson’s disease? Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, J.Q.; Fan, Y.; Mitha, A.P.; Bell, R.; Metz, L.; Moore, G.R.; Yong, V.W. Association of alpha-synuclein immunoreactivity with inflammatory activity in multiple sclerosis lesions. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Carmona, A.; Carboni, E.; Gomes, L.C.; Roudeau, S.; Maass, F.; Lenz, C.; Ortega, R.; Lingor, P. Metal dyshomeostasis in the substantia nigra of patients with Parkinson’s disease or multiple sclerosis. J. Neurochem. 2024, 168, 128–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albassam, M.S.; Thabet, S.A.; Hmoud, M.; Makkawi, S. Anti-muscle specific kinase (Anti-MuSK) positive myasthenia gravis overlapping with Parkinson’s disease: A challenging diagnosis. Cureus 2021, 13, e14839. [Google Scholar]
- Alshaikh, J.T.; Mills, K. Coincident parkinsonism and myasthenia gravis: A case series. Park. Relat. Disord. 2021, 89, 4–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gamez, J.; Carmona, F.; Lorenzo-Bosquet, C.; Cuberas-Borrós, G.; de Fabregues, O.; Gamez, A. Myasthenia gravis concurrent with Parkinson’s disease in a Spanish cohort. Causation or correlation? Neurol. Sci. 2024, 45, 3183–3189. [Google Scholar]
- Iori, E.; Mazzoli, M.; Ariatti, A.; Salviato, T.; Rispoli, V.; Valzania, F.; Galassi, G. Myasthenia Gravis crossing Parkinson’s disease: A 20 year study from single Italian center. Int. J. Neurosci. 2024, 134, 429–435. [Google Scholar]
- Mangiardi, M.; Magliozzi, A.; Colosimo, C.; Marsili, L. Dropped head syndrome: The importance of neurophysiology in distinguishing myasthenia gravis from Parkinson’s disease. Biomedicines 2024, 12, 1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uludag, I.F.; Korucuk, M.; Sener, U.; Zorlu, Y. Myasthenia gravis as a cause of head drop in Parkinson disease. Neurologist 2011, 17, 144–146. [Google Scholar]
- Fasano, A.; Evoli, A.; Piano, C.; Tonali, P.A.; Bentivoglio, A.R. Myasthenia gravis: An unrecognized cause of head drop in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2008, 14, 164–165. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Xu, E.; Li, H.F.; Chan, P.; Zhao, Z.; Ma, J. Parkinson’s disease and comorbid myasthenia gravis: A case report and literature review. Front. Neurol. 2024, 14, 1303434. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Liu, Y.; Schmidt, C.; Chien, J.H.; Wang, C. Therapeutic effect and side effects of pharmacotherapy in patients with Parkinson disease and myasthenia gravis: A systematic review of case reports and case series studies. Clin. Ther. 2024, 46, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roper, J.A.; Schmitt, A.C.; Gao, H.; He, Y.; Wu, S.; Schmidt, P.; Okun, M.S.; Hass, C.J.; Cubillos, F. Coexistent osteoarthritis and Parkinson’s disease: Data from the Parkinson’s Foundation outcomes project. J. Park. Dis. 2020, 10, 1601–1610. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, S.H.; Chuang, H.J.; Yeh, K.C.; Pan, S.L. Association of osteoarthritis with increased risk of Parkinson’s disease: A population-based, longitudinal follow-up study. Arthritis Care Res. 2022, 74, 1842–1848. [Google Scholar]
- Walker, R.H.; Spiera, H.; Brin, M.F.; Olanow, C.W. Parkinsonism associated with Sjögren’s syndrome: Three cases and a review of the literature. Mov. Disord. 1999, 14, 262–268. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.Z.; Liu, M.S.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, X.L.; Zhang, M.L.; Xiong, K.; Zhou, F. Risk of dementia or Parkinson’s disease in the presence of Sjögren’s syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 1027044. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, M.C.; Xu, X.; Chen, S.M.; Tyan, Y.S.; Chiou, J.Y.; Wang, Y.H.; Lin, L.C.; Chen, C.M.; Wei, J.C. Impact of Sjogren’s syndrome on Parkinson’s disease: A nationwide case-control study. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0175836. [Google Scholar]
- Hsu, H.C.; Hou, T.Y.; Lin, T.M.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, W.S.; Kuo, P.I.; Lin, Y.C.; Chang, C.C.; Chen, J.H. Higher risk of Parkinson disease in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin. Rheumatol. 2020, 39, 2999–3007. [Google Scholar]
- Sandhya, P.; Danda, D. Exploring the connection between Parkinson’s disease and Sjögren’s syndrome: The aquaporin link. Park. Relat. Disord. 2023, 117, 105863. [Google Scholar]
- Chivasso, C.; D’Agostino, C.; Parisis, D.; Soyfoo, M.S.; Delporte, C. Involvement of aquaporin 5 in Sjögren’s syndrome. Autoimmun. Rev. 2023, 22, 103268. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zong, Y.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, J.; Li, L.; Luo, D.; Hu, J.; Gao, Y.; Xie, X.; Shen, L.; Chen, S.; et al. Identification of key mitochondria-related genes and their relevance to the immune system linking Parkinson’s disease and primary Sjögren’s syndrome through integrated bioinformatics analyses. Comput. Biol. Med. 2024, 175, 108511. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, H.; Qi, J.; Gu, Q.; Sun, Q.; Chen, L.; Jiang, Z.; Liu, A.; et al. Causal relationships between Sjögren’s syndrome and Parkinson’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2024, 27, e15128. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, X.; Wang, M.; Li, F.; Wang, Z.; Gao, Z. Sjögren’s syndrome and Parkinson’s disease: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Front. Genet. 2024, 15, 1370245. [Google Scholar]
- Cai, X.; Jin, Z.; Zhang, S.; Liu, J.; Jiang, Z.; Tang, F.; Lan, T. Sjögren’s syndrome and Parkinson’s disease: A bidirectional two-sample Mendelian randomization study. PLoS ONE 2024, 19, e0298778. [Google Scholar]
- Barba, C.; Alexopoulos, H. Parkinsonism in autoimmune diseases. Int. Rev. Neurobiol. 2019, 149, 419–452. [Google Scholar]
- Witoelar, A.; Jansen, I.E.; Wang, Y.; Desikan, R.S.; Gibbs, J.R.; Blauwendraat, C.; Thompson, W.K.; Hernandez, D.G.; Djurovic, S.; Schork, A.J.; et al. Genome-wide pleiotropy between Parkinson disease and autoimmune diseases. JAMA Neurol. 2017, 74, 780–792. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, J.; Lin, W.; Ma, Y.; Song, H.; Mu, C.; Wu, Q.; Han, C.; Zhang, J.; Liu, X. Investigation of the causal association between Parkinson’s disease and autoimmune disorders: A bidirectional Mendelian randomization study. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1370831. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, C.C.; Lin, T.M.; Chang, Y.S.; Chen, W.S.; Sheu, J.J.; Chen, Y.H.; Chen, J.H. Autoimmune rheumatic diseases and the risk of Parkinson disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study in Taiwan. Ann. Med. 2018, 50, 83–90. [Google Scholar]
- Slouma, M.; Hajji, H.; Rahmouni, S.; Dhahri, R.; Metoui, L.; Gharsallah, I. Rheumatic manifestations of Parkinson’s disease: An overview. Curr. Rheumatol. Rev. 2023, 19, 294–302. [Google Scholar]
- Bes, C.; Altunrende, B.; Yilmaz Türkoglu, S.; Yildiz, N.; Soy, M. Parkinsonism in elderly rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin. Ter. 2014, 165, 19–21. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tang, G.; Pan, H.; Xu, L.; Feng, R.; Jiang, Y.; Kong, F.; Hu, S. A comparison of co-methylation relationships between rheumatoid arthritis and Parkinson’s disease. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 12, 1001. [Google Scholar]
- Bacelis, J.; Compagno, M.; George, S.; Pospisilik, J.A.; Brundin, P.; Naluai, Å.T.; Brundin, L. Decreased risk of Parkinson’s disease after rheumatoid arthritis diagnosis: A nested case-control study with matched cases and controls. J. Park. Dis. 2021, 11, 821–832. [Google Scholar]
- Sung, Y.F.; Liu, F.C.; Lin, C.C.; Lee, J.T.; Yang, F.C.; Chou, Y.C.; Lin, C.L.; Kao, C.H.; Lo, H.Y.; Yang, T.Y. Reduced risk of Parkinson disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: A nationwide population-based study. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2016, 91, 1346–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Ou, R.; Shang, H. Rheumatoid arthritis decreases risk for Parkinson’s disease: A Mendelian randomization study. NPJ Park. Dis. 2021, 7, 17. [Google Scholar]
- Li, D.; Hong, X.; Chen, T. Association between rheumatoid arthritis and risk of Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis and systematic review. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 885179. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, X.; Chong, L.; Zhang, X.; Li, R. Immunosuppressants contribute to a reduced risk of Parkinson’s disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2022, 51, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar]
- Brudek, T. Inflammatory bowel diseases and Parkinson’s disease. J. Park. Dis. 2019, 9, S331–S344. [Google Scholar]
- Weimers, P.; Halfvarson, J.; Sachs, M.C.; Saunders-Pullman, R.; Ludvigsson, J.F.; Peter, I.; Burisch, J.; Olén, O. Inflammatory bowel disease and Parkinson’s disease: A nationwide Swedish cohort study. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2019, 25, 111–123. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, F.; Li, C.; Gong, J.; Zhu, W.; Gu, L.; Li, N. The risk of Parkinson’s disease in inflammatory bowel disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2019, 51, 38–42. [Google Scholar]
- Li, H.X.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, K.; Liu, Y.Z.; Peng, X.X.; Zong, Q. Inflammatory bowel disease and risk of Parkinson’s disease: Evidence from a meta-analysis of 14 studies involving more than 13.4 million individuals. Front. Med. 2023, 10, 1137366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, S.A.; Tschaidse, L.; Reisch, N. Thyroid disorders and movement disorders—A systematic review. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2023, 10, 360–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Choi, I.A.; Kim, A.; Kang, G. Clinical association between gout and Parkinson’s disease: A nationwide population-based cohort study in Korea. Medicina 2021, 57, 1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ungprasert, P.; Srivali, N.; Thongprayoon, C. Gout is not associated with a lower risk of Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Park. Relat. Disord. 2015, 21, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pou, M.A.; Orfila, F.; Pagonabarraga, J.; Ferrer-Moret, S.; Corominas, H.; Diaz-Torne, C. Risk of Parkinson’s disease in a gout Mediterranean population: A case-control study. Joint Bone Spine 2022, 89, 105402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bougea, A.; Kapaki, E.; Paraskevas, G.P.; Kilidireas, K.; Andreadou, E. Multiple sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease: The two faces of neurodegeneration. Report. of the first Greek case and review of the literature. Neurol. Sci. 2015, 36, 2281–2285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barun, B.; Brinar, V.V.; Zadro, I.; Lusic, I.; Radovic, D.; Habek, M. Parkinsonism and multiple sclerosis—Is there association? Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2008, 110, 958–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etemadifar, M.; Afshar, F.; Nasr, Z.; Kheradmand, M. Parkinsonism associated with multiple sclerosis: A report of eight new cases and a review on the literature. Iran. J. Neurol. 2014, 13, 88–93. [Google Scholar]
- Saidha, S.; Mok, T.H.; Butler, M.; Fanning, N.; Harrington, H. Multiple sclerosis exceptionally presenting as parkinsonism responds to intravenous methylprednisolone. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 17, 654–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delalic, S.; Rus, T.; Horvat Ledinek, A.; Kojovic, M.; Georgiev, D. Parkinson’s disease in a patient with multiple sclerosis and heterozygous glucocerebrosidase gene mutation. Clin. Park. Relat. Disord. 2020, 3, 100055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, S.L.; Kim, J.H.; De Sousa, C.; Cheong, R.; Crockford, D.R.; Sheedy, D.; Stevens, J.; McCrossin, T.; Tan, R.H.; McCann, H.; et al. Coexisting Lewy body disease and clinical parkinsonism in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Eur. J. Neurol. 2021, 28, 2192–2199. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Aslam, A.; Sarmad, E.; Nawaz, A.; Numan, A.; Ahmad, A.; Hassan, M.A. Brait-Fahn-Schwartz disease: A unique co-occurrence of Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Case Rep. Neurol. 2023, 15, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Monsalve, C.A.J.; Fornari, L.H.T.; Júnior, N.D.S.; Nakata, D.T.; Neto, E.G.C.; Rotta, F.T.; Rieder, C.R.M. Characterization of the nigroestriatal system in a sample of patients with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2022, 80, 806–811. [Google Scholar]
- van Es, M.A.; Schelhaas, H.J.; van Vught, P.W.; Ticozzi, N.; Andersen, P.M.; Groen, E.J.; Schulte, C.; Blauw, H.M.; Koppers, M.; Diekstra, F.P.; et al. Angiogenin variants in Parkinson disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 70, 964–973. [Google Scholar]
- Martin, L.J. Mitochondrial pathobiology in Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2010, 20 (Suppl. S2), S335–S356. [Google Scholar]
- Klemmensen, M.M.; Borrowman, S.H.; Pearce, C.; Pyles, B.; Chandra, B. Mitochondrial dysfunction in neurodegenerative disorders. Neurotherapeutics 2024, 21, e00292. [Google Scholar]
- Vermeiren, Y.; Janssens, J.; Van Dam, D.; De Deyn, P.P. Serotonergic dysfunction in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease: Similar mechanisms, dissimilar outcomes. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 185. [Google Scholar]
- Lualdi, M.; Casale, F.; Rizzone, M.G.; Zibetti, M.; Monti, C.; Colugnat, I.; Calvo, A.; De Marco, G.; Moglia, C.; Fuda, G.; et al. Shared and unique disease pathways in amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease unveiled in peripheral blood mononuclear cells. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 4240–4251. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Liu, Y.T.; Ren, Y.L.; Guo, X.Y.; Wang, Y. Association of peripheral immune activation with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Neuroimmunol. 2024, 388, 578290. [Google Scholar]
- He, X.; Zhang, L.; Yao, X.; Hu, J.; Yu, L.; Jia, H.; An, R.; Liu, Z.; Xu, Y. Association studies of MMP-9 in Parkinson’s disease and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73777. [Google Scholar]
- Wainberg, M.; Andrews, S.J.; Tripathy, S.J. Shared genetic risk loci between Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias, Parkinson’s disease, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2023, 15, 113. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, W.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Guo, Y.; Ren, Z.; Cai, L.; Wu, S.; Zhou, M. Different intensities of physical activity for amyotrophic lateral sclerosis and Parkinson disease: A Mendelian randomization study and meta-analysis. Medicine 2024, 103, e40141. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ferrari, C.; Ingannato, A.; Matà, S.; Ramat, S.; Caremani, L.; Bagnoli, S.; Bessi, V.; Sorbi, S.; Nacmias, B. Parkinson-ALS with a novel MAPT variant. Neurol. Sci. 2024, 45, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Galasko, D.; Salmon, D.P.; Craig, U.K.; Thal, L.J.; Schellenberg, G.; Wiederholt, W. Clinical features and changing patterns of neurodegenerative disorders on Guam, 1997–2000. Neurology 2002, 58, 90–97. [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar-Vázquez, C.A.; Gallardo-González, L.I.; Raymundo-Carrillo, A.D.; Reyes-Sosa, L.C.; Martínez-Romo, E.S. [Parkinson-dementia and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis association (complex of Guam). Diagnostic challenge, Mexican patient]. Rev. Med. Inst. Mex. Seguro. Soc. 2023, 61, 677–684. [Google Scholar]
- Gago, M.F.; Azevedo, O.; Guimarães, A.; Teresa Vide, A.; Lamas, N.J.; Oliveira, T.G.; Gaspar, P.; Bicho, E.; Miltenberger-Miltenyi, G.; Ferreira, J.; et al. Parkinson’s disease and Fabry disease: Clinical, biochemical and neuroimaging analysis of three pedigrees. J. Park. Dis. 2020, 10, 141–152. [Google Scholar]
- Perillo, S.; Palmieri, G.R.; Del Moral, M.O.; De Michele, G.; Giglio, A.; Cuomo, N.; Pane, C.; Bauer, P.; De Rosa, A. Screening for Fabry disease in a series of Parkinson’s disease patients and literature review. Neurol. Sci. 2023, 44, 1235–1241. [Google Scholar]
- Salcedo-Arellano, M.J.; Wolf-Ochoa, M.W.; Hong, T.; Amina, S.; Tassone, F.; Lechpammer, M.; Hagerman, R.; Martínez-Cerdeño, V. Parkinsonism versus concomitant Parkinson’s disease in fragile X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2020, 7, 413–418. [Google Scholar]
- Rigby, H.B.; Dugger, B.N.; Hentz, J.G.; Adler, C.H.; Beach, T.G.; Shill, H.A.; Driver-Dunckley, E.; Sabbagh, M.N.; Sue, L.I.; Caviness, J.N. Clinical features of patients with concomitant Parkinson’s disease and progressive supranuclear palsy pathology. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2014, 2, 33–38. [Google Scholar]
- Bliwise, D.L.; Karroum, E.G.; Greer, S.A.; Factor, S.A.; Trotti, L.M. Restless legs symptoms and periodic leg movements in sleep among patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Park. Dis. 2022, 12, 1339–1344. [Google Scholar]
- Moccia, M.; Erro, R.; Picillo, M.; Santangelo, G.; Spina, E.; Allocca, R.; Longo, K.; Amboni, M.; Palladino, R.; Assante, R.; et al. A four-year longitudinal study on restless legs syndrome in Parkinson disease. Sleep 2016, 39, 405–412. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nomura, T.; Nakashima, K. Prevalence of restless legs syndrome. Brain Nerve 2009, 61, 515–521. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Calzetti, S.; Negrotti, A.; Bonavina, G.; Angelini, M.; Marchesi, E. Absence of co-morbidity of Parkinson disease and restless legs syndrome: A case-control study in patients attending a movement disorders clinic. Neurol. Sci. 2009, 30, 119–122. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tan, E.K.; Lum, S.Y.; Wong, M.C. Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2002, 196, 33–36. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, K.; Okuma, Y.; Uchiyama, T.; Miyamoto, M.; Sakakibara, R.; Shimo, Y.; Hattori, N.; Kuwabara, S.; Yamamoto, T.; Kaji, Y.; et al. Characterizing restless legs syndrome and leg motor restlessness in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A multicenter case-controlled study. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2017, 44, 18–22. [Google Scholar]
- Maggi, G.; Barone, A.; Mastromarino, C.; Santangelo, G.; Vitale, C. Prevalence and clinical profile of patients with restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Sleep. Med. 2024, 121, 275–286. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, J.M.; Choi, S.M.; Cho, S.H.; Kim, B.C. Restless legs syndrome affects sleep in de novo Parkinson’s disease patients. Medicine 2023, 102, e35551. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Esteban, J.C.; Zarranz, J.J.; Tijero, B.; Velasco, F.; Barcena, J.; Rouco, I.; Lezcano, E.; Lachen, M.C.; Jauregui, A.; Ugarte, A. Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2007, 22, 1912–1916. [Google Scholar]
- Verbaan, D.; van Rooden, S.M.; van Hilten, J.J.; Rijsman, R.M. Prevalence and clinical profile of restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 2142–2147. [Google Scholar]
- Angelini, M.; Negrotti, A.; Marchesi, E.; Bonavina, G.; Calzetti, S. A study of the prevalence of restless legs syndrome in previously untreated Parkinson’s disease patients: Absence of co-morbid association. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 310, 286–288. [Google Scholar]
- Rajabally, Y.A.; Martey, J. No association between neuropathy and restless legs in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2013, 127, 216–220. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Akhmadulina, A.O.; Levin, O.S.; Poluektov, M.G. Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. Zhurnal Nevrol. I Psikhiatrii Im. SS Korsakova 2020, 120, 80–88. [Google Scholar]
- Iwaki, H.; Hughes, K.C.; Gao, X.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Ascherio, A. The association between restless legs syndrome and premotor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 394, 41–44. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wong, J.C.; Li, Y.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Ascherio, A.; Gao, X. Restless legs syndrome: An early clinical feature of Parkinson disease in men. Sleep 2014, 37, 369–372. [Google Scholar]
- Dragan, E.M.; Chen, Z.; Ondo, W.G. Does idiopathic restless legs syndrome delay onset and reduce severity of Parkinson’s disease: A pilot study. Int. J. Neurosci. 2015, 125, 526–530. [Google Scholar]
- Rijsman, R.M.; Schoolderman, L.F.; Rundervoort, R.S.; Louter, M. Restless legs syndrome in Parkinson’s disease. Park. Relat. Disord. 2014, 20 (Suppl. 1), S5–S9. [Google Scholar]
- Calzetti, S.; Bellanova, M.F.; Negrotti, A.; Saccani, E.; Capozzi, A.; Pietrini, V. Non-length-dependent somatosensory small fiber pathology presenting with restless legs syndrome in pre-motor Parkinson’s disease. Evidence from skin biopsy in four patients. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 69, 139–142. [Google Scholar]
- Estiar, M.A.; Senkevich, K.; Yu, E.; Varghaei, P.; Krohn, L.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Noyce, A.J.; Rouleau, G.A.; Gan-Or, Z. Lack of causal effects or genetic correlation between restless legs syndrome and Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1967–1972. [Google Scholar]
- Vignatelli, L.; Zenesini, C.; Belotti, L.M.B.; Baldin, E.; Bonavina, G.; Calandra-Buonaura, G.; Cortelli, P.; Descovich, C.; Fabbri, G.; Giannini, G.; et al. Risk of hospitalization and death for COVID-19 in people with Parkinson’s disease or parkinsonism. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- El-Qushayri, A.E.; Ghozy, S.; Reda, A.; Kamel, A.M.A.; Abbas, A.S.; Dmytriw, A.A. The impact of Parkinson’s disease on manifestations and outcomes of Covid-19 patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Rev. Med. Virol. 2022, 32, e2278. [Google Scholar]
- Khoshnood, R.J.; Zali, A.; Tafreshinejad, A.; Ghajarzadeh, M.; Ebrahimi, N.; Safari, S.; Mirmosayyeb, O. Parkinson’s disease and COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Neurol. Sci. 2022, 43, 775–783. [Google Scholar]
- Przytula, F.; Kasprzak, J.; Dulski, J.; Koziorowski, D.; Kwasniak-Butowska, M.; Soltan, W.; Roszmann, A.; Smilowska, K.; Schinwelski, M.; Slawek, J. Morbidity and severity of COVID-19 in patients with Parkinson’s disease treated with amantadine—A multicenter, retrospective, observational study. Park. Relat. Disord. 2023, 106, 105238. [Google Scholar]
- Sorrell, L.; Leta, V.; Barnett, A.; Stevens, K.; King, A.; Inches, J.; Kobylecki, C.; Walker, R.; Chaudhuri, K.R.; Martin, H.; et al. Clinical features and outcomes of hospitalised patients with COVID-19 and Parkinsonian disorders: A multicentre UK-based study. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0285349. [Google Scholar]
- Cavallieri, F.; Fioravanti, V.; Bove, F.; Del Prete, E.; Meoni, S.; Grisanti, S.; Zedde, M.; Pascarella, R.; Moro, E.; Valzania, F. COVID-19 and parkinsonism: A critical appraisal. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Polverino, P.; Cocco, A.; Albanese, A. Post-COVID parkinsonism: A scoping review. Park. Relat. Disord. 2024, 123, 106066. [Google Scholar]
- Mirsattari, S.M.; Power, C.; Nath, A. Parkinsonism with HIV infection. Mov. Disord. 1998, 13, 684–689. [Google Scholar]
- Hriso, E.; Kuhn, T.; Masdeu, J.C.; Grundman, M. Extrapyramidal symptoms due to dopamine-blocking agents in patients with AIDS encephalopathy. Am. J. Psychiatry 1991, 148, 1558–1561. [Google Scholar]
- Moulignier, A.; Gueguen, A.; Lescure, F.X.; Ziegler, M.; Girard, P.M.; Cardon, B.; Pialoux, G.; Molina, J.M.; Brandel, J.P.; Lamirel, C. Does HIV infection alter Parkinson disease? J. Acquir. Immune Defic. Syndr. 2015, 70, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Amod, F.H.; Bhigjee, A.I.; Moodley, A. Does antiretroviral therapy alter the course of Parkinson’s disease in people living with HIV? J. Neurovirol. 2021, 27, 595–600. [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Oehring, E.M.; Hong, J.Y.; Hughes, R.L.; Kwon, D.; Brontë-Stewart, H.M.; Poston, K.L.; Schulte, T. Alterations of brain signal oscillations in older individuals with HIV infection and Parkinson’s disease. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2021, 16, 289–305. [Google Scholar]
- Fama, R.; Müller-Oehring, E.M.; Levine, T.F.; Sullivan, E.V.; Sassoon, S.A.; Asok, P.; Brontë-Stewart, H.M.; Poston, K.L.; Pohl, K.M.; Pfefferbaum, A.; et al. Episodic memory deficit in HIV infection: Common phenotype with Parkinson’s disease, different neural substrates. Brain Struct. Funct. 2023, 228, 845–858. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Iida, T.; Doh-ura, K.; Kawashima, T.; Abe, H.; Iwaki, T. An atypical case of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with Parkinson’s disease. Neuropathology 2001, 21, 294–297. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kubo, S.I.; Matsubara, T.; Taguchi, T.; Sengoku, R.; Takeuchi, A.; Saito, Y. Parkinson’s disease with a typical clinical course of 17 years overlapped by Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease: An autopsy case report. BMC Neurol. 2021, 21, 480. [Google Scholar]
- Rus, T.; Mlakar, J.; Jamšek, J.; Trošt, M. Metabolic brain changes can predict the underlying pathology in neurodegenerative brain disorders: A case report of sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease with concomitant Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 13081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vital, A.; Fernagut, P.O.; Canron, M.H.; Joux, J.; Bezard, E.; Martin-Negrier, M.L.; Vital, C.; Tison, F. The nigrostriatal pathway in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2009, 68, 809–815. [Google Scholar]
- Woerman, A.L.; Tamgüney, G. Body-first Parkinson’s disease and variant Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease—Similar or different? Neurobiol. Dis. 2022, 164, 105625. [Google Scholar]
- Filippou, P.S.; Outeiro, T.F. Cancer and Parkinson’s disease: Common targets, emerging hopes. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 340–346. [Google Scholar]
- Rugbjerg, K.; Friis, S.; Lassen, C.F.; Ritz, B.; Olsen, J.H. Malignant melanoma, breast cancer and other cancers in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Cancer 2012, 131, 1904–1911. [Google Scholar]
- Peretz, C.; Gurel, R.; Rozani, V.; Gurevich, T.; El-Ad, B.; Tsamir, J.; Giladi, N. Cancer incidence among Parkinson’s disease patients in a 10-yrs time-window around disease onset: A large-scale cohort study. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 28, 68–72. [Google Scholar]
- Driver, J.A.; Logroscino, G.; Buring, J.E.; Gaziano, J.M.; Kurth, T. A prospective cohort study of cancer incidence following the diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2007, 16, 1260–1265. [Google Scholar]
- Bajaj, A.; Driver, J.A.; Schernhammer, E.S. Parkinson’s disease and cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Causes Control. 2010, 21, 697–707. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Olsen, J.H.; Friis, S.; Frederiksen, K. Malignant melanoma and other types of cancer preceding Parkinson disease. Epidemiology 2006, 17, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Gao, X.; Lu, Y.; Chen, H. Meta-analysis of the relationship between Parkinson disease and melanoma. Neurology 2011, 76, 2002–2009. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Walter, U.; Heilmann, E.; Voss, J.; Riedel, K.; Zhivov, A.; Schäd, S.G.; Gross, G.E.; Benecke, R.; Trcka, J. Frequency and profile of Parkinson’s disease prodromi in patients with malignant melanoma. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2016, 87, 302–310. [Google Scholar]
- Becker, C.; Brobert, G.P.; Johansson, S.; Jick, S.S.; Meier, C.R. Cancer risk in association with Parkinson disease: A population-based study. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2010, 16, 186–190. [Google Scholar]
- Wirdefeldt, K.; Weibull, C.E.; Chen, H.; Kamel, F.; Lundholm, C.; Fang, F.; Ye, W. Parkinson’s disease and cancer: A register-based family study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 179, 85–94. [Google Scholar]
- Tacik, P.; Curry, S.; Fujioka, S.; Strongosky, A.; Uitti, R.J.; van Gerpen, J.A.; Diehl, N.N.; Heckman, M.G.; Wszolek, Z.K. Cancer in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat. Disord. 2016, 31, 28–33. [Google Scholar]
- Bertoni, J.M.; Arlette, J.P.; Fernandez, H.H.; Fitzer-Attas, C.; Frei, K.; Hassan, M.N.; Isaacson, S.H.; Lew, M.F.; Molho, E.; Ondo, W.G.; et al. Increased melanoma risk in Parkinson disease: A prospective clinicopathological study. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 347–352. [Google Scholar]
- Flynn, M.S.; Robinson, C.; Patel, S.; Liu, B.; Green, C.; Pavlis, M. Clinicopathologic characteristics of melanoma in patients with Parkinson disease. JID Innov. 2023, 3, 100173. [Google Scholar]
- Inzelberg, R.; Rabey, J.M.; Melamed, E.; Djaldetti, R.; Reches, A.; Badarny, S.; Hassin-Baer, S.; Cohen, O.; Trau, H.; Aharon-Peretz, J.; et al. High prevalence of malignant melanoma in Israeli patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Neural Transm. 2011, 118, 1199–1207. [Google Scholar]
- Lerman, S.; Amichai, B.; Weinstein, G.; Shalev, V.; Chodick, G. Parkinson’s disease, melanoma, and keratinocyte carcinoma: A population-based study. Neuroepidemiology 2018, 50, 168–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ong, E.L.; Goldacre, R.; Goldacre, M. Differential risks of cancer types in people with Parkinson’s disease: A national record-linkage study. Eur. J. Cancer 2014, 50, 2456–2462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, C.F.; Lu, M.K.; Muo, C.H.; Tsai, C.H.; Kao, C.H. Increased risk of brain tumor in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A nationwide cohort study in Taiwan. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2016, 134, 148–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryu, H.J.; Park, J.H.; Choi, M.; Jung, J.H.; Han, K.; Kwon, D.Y.; Kim, D.H.; Park, Y.G. Parkinson’s disease and skin cancer risk: A nationwide population-based cohort study in Korea. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2020, 34, 2775–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, V.; Diakoumakou, S.C.; Kuroli, E.; Tóth, B.; Kuzmanovszki, D.; Szakonyi, J.; Lorincz, K.K.; Somlai, B.; Kárpáti, S.; Holló, P. Cutaneous malignancies in patients with Parkinson’s disease at a dermato-oncological university centre in Hungary. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1142170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, P.; Yang, X.D.; Chen, S.D.; Xiao, Q. The association between Parkinson’s disease and melanoma: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Neurodegener. 2015, 4, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, J.J.; Neutel, D.; Mestre, T.; Coelho, M.; Rosa, M.M.; Rascol, O.; Sampaio, C. Skin cancer and Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasowska, D.; Gerkowicz, A.; Mlak, R.; Leziak, M.; Malecka-Massalska, T. Risk of nonmelanoma skin cancers and Parkinson’s disease-meta-analysis and systematic review. Cancers 2021, 13, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Guarin, D.; Mohammadzadehhonarvar, N.; Chen, X.; Gao, X. Parkinson’s disease and cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis of over 17 million participants. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e046329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y.S.; Ng, J.H.; Saffari, S.E.; Tan, E.K. Parkinson’s disease and cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis on the influence of lifestyle habits, genetic variants, and gender. Aging 2022, 14, 2148–2173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, E.; Feuerman, H.; Peleg, I.; Pavlotsky, F.; Segal, Z.; Oberman, B.; Lev, N.; Hodak, E.; Djaldetti, R.; Hassin-Baer, S.; et al. Risk factors for actinic keratosis, non-melanoma skin cancer and cutaneous malignant melanoma in persons with and without Parkinson’s disease: A cross-sectional study. Skin. Health Dis. 2024, 4, e464. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Disse, M.; Reich, H.; Lee, P.K.; Schram, S.S. A review of the association between Parkinson disease and malignant melanoma. Dermatol. Surg. 2016, 42, 141–146. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Dai, M.; Mullins, C.S.; Schafmayer, C.; Linnebacher, M. Global association of cause-specific mortality between the major gastrointestinal cancers and Parkinson’s disease for the first two decades of the new millennium. Aging Dis. 2022, 13, 534–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Song, F.; Chen, H.; Gao, X.; Amos, C.I.; Lee, J.E.; Wei, Q.; Qureshi, A.A.; Han, J. No association between Parkinson disease alleles and the risk of melanoma. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2012, 21, 243–245. [Google Scholar]
- Senkevich, K.; Bandres-Ciga, S.; Yu, E.; Liyanage, U.E.; Noyce, A.J.; Gan-Or, Z. No evidence for a causal relationship between cancers and Parkinson’s disease. J. Park. Dis. 2021, 11, 801–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saunders-Pullman, R.; Barrett, M.J.; Stanley, K.M.; Luciano, M.S.; Shanker, V.; Severt, L.; Hunt, A.; Raymond, D.; Ozelius, L.J.; Bressman, S.B. LRRK2 G2019S mutations are associated with an increased cancer risk in Parkinson disease. Mov. Disord. 2010, 25, 2536–2541. [Google Scholar]
- Inzelberg, R.; Cohen, O.S.; Aharon-Peretz, J.; Schlesinger, I.; Gershoni-Baruch, R.; Djaldetti, R.; Nitsan, Z.; Ephraty, L.; Tunkel, O.; Kozlova, E.; et al. The LRRK2 G2019S mutation is associated with Parkinson disease and concomitant non-skin cancers. Neurology 2012, 78, 781–786. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, T.; Li, X.; Jankovic, J. The association between Parkinson’s disease and melanoma. Int. J. Cancer 2011, 128, 2251–2260. [Google Scholar]
- Koros, C.; Simitsi, A.M.; Bougea, A.; Papagiannakis, N.; Antonelou, R.; Pachi, I.; Angelopoulou, E.; Prentakis, A.; Zachou, A.; Chrysovitsanou, C.; et al. Double trouble: Association of malignant melanoma with sporadic and genetic forms of Parkinson’s disease and asymptomatic carriers of related genes: A brief report. Medicina 2023, 59, 1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, L.; Srour, S.; Gartner, J.; Kapitansky, O.; Qutob, N.; Dror, S.; Golan, T.; Dayan, R.; Brener, R.; Ziv, T.; et al. Parkin somatic mutations link melanoma and Parkinson’s disease. J. Genet. Genomics 2016, 43, 369–379. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, H.H.; Kannengiesser, C.; Lesage, S.; André, J.; Mourah, S.; Michel, L.; Descamps, V.; Basset-Seguin, N.; Bagot, M.; Bensussan, A.; et al. PARKIN inactivation links Parkinson’s disease to melanoma. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2016, 108, djv340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.X.; Zheng, H.; Deng, X.F.; Zhou, D.; Dai, J.G. Status of the Parkinson’s disease gene family expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 13, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, D.D.; Cai, W.; Chen, X. The associations between Parkinson’s disease and cancer: The plot thickens. Transl. Neurodegener. 2015, 4, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Flanagan, C.H.; Morais, V.A.; Wurst, W.; De Strooper, B.; O’Neill, C. The Parkinson’s gene PINK1 regulates cell cycle progression and promotes cancer-associated phenotypes. Oncogene 2015, 34, 1363–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ejma, M.; Madetko, N.; Brzecka, A.; Guranski, K.; Alster, P.; Misiuk-Hojlo, M.; Somasundaram, S.G.; Kirkland, C.E.; Aliev, G. The links between Parkinson’s disease and cancer. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dube, U.; Ibanez, L.; Budde, J.P.; Benitez, B.A.; Davis, A.A.; Harari, O.; Iles, M.M.; Law, M.H.; Brown, K.M.; Cruchaga, C. Overlapping genetic architecture between Parkinson disease and melanoma. Acta Neuropathol. 2020, 139, 347–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugier, P.E.; Lucotte, E.A.; Domenighetti, C.; Law, M.H.; Iles, M.M.; Brown, K.; Amos, C.; McKay, J.D.; Hung, R.J.; Karimi, M.; et al. Investigation of shared genetic risk factors between Parkinson’s disease and cancers. Mov. Disord. 2023, 38, 604–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bianchini, M.; Giambelluca, M.; Scavuzzo, M.C.; Di Franco, G.; Guadagni, S.; Palmeri, M.; Furbetta, N.; Gianardi, D.; Costa, A.; Gentiluomo, M.; et al. In pancreatic adenocarcinoma alpha-synuclein increases and marks peri-neural infiltration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruening, W.; Giasson, B.I.; Klein-Szanto, A.J.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Godwin, A.K. Synucleins are expressed in the majority of breast and ovarian carcinomas and in preneoplastic lesions of the ovary. Cancer 2000, 88, 2154–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, K.M.; Rorke, L.B.; Giasson, B.; Lee, V.M.; Trojanowski, J.Q. Expression of alpha-, beta-, and gamma-synuclein in glial tumors and medulloblastomas. Acta Neuropathol. 2003, 106, 167–175. [Google Scholar]
- Fujita, M.; Sugama, S.; Nakai, M.; Takenouchi, T.; Wei, J.; Urano, T.; Inoue, S.; Hashimoto, M. alpha-Synuclein stimulates differentiation of osteosarcoma cells: Relevance to down-regulation of proteasome activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 5736–5748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, T.Z.; Yang, H.M.; Cheng, Y.Z.; Gu, L.; Zhang, J.N.; Zhang, H. The Parkinson’s disease-associated protein Alpha-synuclein inhibits hepatoma by exosome delivery. Mol. Carcinog. 2023, 62, 1163–1175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawashima, M.; Suzuki, S.O.; Doh-ura, K.; Iwaki, T. Alpha-synuclein is expressed in a variety of brain tumors showing neuronal differentiation. Acta Neuropathol. 2000, 99, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Matsuo, Y.; Kamitani, T. Parkinson’s disease-related protein, alpha-synuclein, in malignant melanoma. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e10481. [Google Scholar]
- Maitta, R.W.; Wolgast, L.R.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Bhattacharyya, P.; Gong, J.Z.; Sunkara, J.; Albanese, J.M.; Pizzolo, J.G.; Cannizzaro, L.A.; et al. Alpha- and beta-synucleins are new diagnostic tools for acute erythroid leukemia and acute megakaryoblastic leukemia. Am. J. Hematol. 2011, 86, 230–234. [Google Scholar]
- Turriani, E.; Lázaro, D.F.; Ryazanov, S.; Leonov, A.; Giese, A.; Schön, M.; Schön, M.P.; Griesinger, C.; Outeiro, T.F.; Arndt-Jovin, D.J.; et al. Treatment with diphenyl-pyrazole compound anle138b/c reveals that Alpha-synuclein protects melanoma cells from autophagic cell death. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E4971–E4977. [Google Scholar]
- Ye, Q.; Wang, T.F.; Peng, Y.F.; Xie, J.; Feng, B.; Qiu, M.Y.; Li, L.H.; Lu, A.G.; Liu, B.Y.; Zheng, M.H. Expression of alpha-, beta- and gamma-synuclein in colorectal cancer, and potential clinical significance in progression of the disease. Oncol. Rep. 2010, 23, 429–436. [Google Scholar]
- Zanotti, L.C.; Malizia, F.; Cesatti Laluce, N.; Avila, A.; Mamberto, M.; Anselmino, L.E.; Menacho-Márquez, M. Synuclein proteins in cancer development and progression. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.M.; Cheng, Y.Z.; Hou, T.Z.; Fan, J.K.; Gu, L.; Zhang, J.N.; Zhang, H. Upregulation of Parkinson’s disease-associated protein alpha-synuclein suppresses tumorigenesis via interaction with mGluR5 and gamma-synuclein in liver cancer. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2023, 744, 109698. [Google Scholar]
- Gajendran, N.; Rajasekaran, S.; Witt, S.N. Knocking out alpha-synuclein in melanoma cells downregulates L1CAM and decreases motility. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 9243. [Google Scholar]
- Niederberger, E.; Möller, M.; Mungo, E.; Hass, M.; Wilken-Schmitz, A.; Manderscheid, C.; Möser, C.V.; Geisslinger, G. Distinct molecular mechanisms contribute to the reduction of melanoma growth and tumor pain after systemic and local depletion of alpha-Synuclein in mice. FASEB J. 2023, 37, e23287. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rodriguez-Leyva, I.; Chi-Ahumada, E.; Mejía, M.; Castanedo-Cazares, J.P.; Eng, W.; Saikaly, S.K.; Carrizales, J.; Levine, T.D.; Norman, R.A.; Jimenez-Capdeville, M.E. The presence of alpha-synuclein in skin from melanoma and patients with Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. Clin. Pract. 2017, 4, 724–732. [Google Scholar]
- Shekoohi, S.; Rajasekaran, S.; Patel, D.; Yang, S.; Liu, W.; Huang, S.; Yu, X.; Witt, S.N. Knocking out alpha-synuclein in melanoma cells dysregulates cellular iron metabolism and suppresses tumor growth. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 5267. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Xia, C.; Zhang, C.; Tang, D.; Liu, F.; Ou, Y.; Gao, J.; Yi, H.; Yang, D.; Ma, K. Adeno-associated virus-delivered alpha synuclein inhibits bladder cancer growth via the p53/p21 signaling pathway. Cancer Gene Ther. 2022, 29, 1193–1206. [Google Scholar]
- Arnold, M.R.; Chen, S.; Unni, V.K. Alpha-synuclein knockout impairs melanoma development and alters DNA damage repair in the TG3 mouse model in a sex-dependent manner. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Rajasekaran, S.; Cheng, S.; Gajendran, N.; Shekoohi, S.; Chesnokova, L.; Yu, X.; Witt, S.N. Transcriptomic analysis of melanoma cells reveals an association of Alpha-synuclein with regulation of the inflammatory response. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 27140. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, D.N.; Lee, J.C. Defining an amyloid link Between Parkinson’s disease and melanoma. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 22671–22673. [Google Scholar]
- Dean, D.N.; Lee, J.C. Linking Parkinson’s disease and melanoma: Interplay between alpha-synuclein and Pmel17 amyloid formation. Mov. Disord. 2021, 36, 1489–1498. [Google Scholar]
- Horvath, I.; Mohamed, K.A.; Kumar, R.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Amyloids of alpha-synuclein promote chemical transformations of neuronal cell metabolites. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 12849. [Google Scholar]
- Horvath, I.; Wittung-Stafshede, P. Amyloid fibers of alpha-synuclein catalyze chemical reactions. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2023, 14, 603–608. [Google Scholar]
- Surguchov, A.; Surguchev, A.A. Association between Parkinson’s disease and cancer: New findings and possible mediators. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driver-Dunckley, E.D.; Zhang, N.; Adler, C.H.; Serrano, G.E.; Sue, L.I.; Shill, H.A.; Mehta, S.H.; Belden, C.M.; Zamrini, E.Y.; Davis, K.; et al. Brain Lewy-type synucleinopathy density is associated with a lower prevalence of atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease risk factors in patients with Parkinson’s disease. J. Park. Dis. 2019, 9, 543–552. [Google Scholar]
- Irwin, D.J.; Grossman, M.; Weintraub, D.; Hurtig, H.I.; Duda, J.E.; Xie, S.X.; Lee, E.B.; Van Deerlin, V.M.; Lopez, O.L.; Kofler, J.K.; et al. Neuropathological and genetic correlates of survival and dementia onset in synucleinopathies: A retrospective analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2017, 16, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jellinger, K.A.; Attems, J. Prevalence and impact of vascular and Alzheimer pathologies in Lewy body disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2008, 115, 427–436. [Google Scholar]
- Kulichikhin, K.Y.; Malikova, O.A.; Zobnina, A.E.; Zalutskaya, N.M.; Rubel, A.A. Interaction of proteins involved in neuronal proteinopathies. Life 2023, 13, 1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Reduced Risk/Incidence Smoking-Related/Non- Smoking | Increased Risk/Incidence | No Differences vs. Controls | Study Type | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lung, colorectal, bladder, prostate cancer | Malignant melanoma | Cohort analysis | [240] | |
| Smoking-related cancer | Melanoma, skin carcinoma (early PD) | Danish Hospital Register | [242] | |
| Hematologic malignancies | UK case–control | [245] | ||
| Melanoma 7 times higher | US cancer database | [248] | ||
| All cancers 31% ↓; after excluding skin tumors, 27% ↓ | Skin tumors | 29 studies (107,598 PD patients) | [241] | |
| Cancer | Melanoma, non-melanoma skin cancer, breast cancer | 26 studies | [257] | |
| Melanoma | Israel National Cancer Registry | [250] | ||
| Melanoma + PD vs. non-PD OR = 2.11 Melanoma after PD diagnosis not significantly increased | Non-melanoma skin tumors | 21 studies | [243] | |
| Melanoma 40% ↑ (before and after PD diagnosis) | Register-based | [246] | ||
| Overall cancer | Melanoma, non-melanoma skin cancer, breast cancer | Cancer (early PD) | Danish register | [238] |
| Melanoma (prodromal PD) | Prospective study | [244] | ||
| 11 cancers (lung, colon) | Six cancers (breast, uterus, melanoma, kidney, neurological) | UK nationwide | [252] | |
| Skin cancer (non-melanoma) preceding PD | Melanoma, breast and prostate cancer | Mayo Clinic Register | [247] | |
| Cancer | Melanoma, breast carcinoma | Minnesota | [262] | |
| Lung, colon cancer | Brain tumors | Taiwan cohort | [253] | |
| Basal cell carcinoma | Melanoma | South Israel cohort | [251] | |
| Lung, colon cancer | Most malignancies | Population-based cohort | [239] | |
| Melanoma, non-melanoma skin tumors (females over age 65) | Korea nationwide | [254] | ||
| Melanoma (after PD diagnosis), in Europe and North America: non-melanoma skin cancer slightly ↑ | 24 studies | [256] | ||
| Basal cell carcinoma ↑↑ | 16 studies | [258] | ||
| Total cancers, melanoma | Other skin cancers | 63 studies (n = 18 million) | [259] | |
| Lung, colon, rectal, colorectal cancer | Brain, breast, colon, hematological, melanoma LRRK2-G2019S carriers | 14 studies | [260] | |
| Pancreatic, colorectal cancer | Liver cancer | Global Health Observatory database | [263] | |
| Melanoma 2 times ↑ | Duke University study | [249] | ||
| All tumors | Melanoma | Hungary | [255] | |
| Melanoma | 141 PD patients | [261] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jellinger, K.A. Concomitant Pathologies and Their Impact on Parkinson Disease: A Narrative Overview of Current Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072942
Jellinger KA. Concomitant Pathologies and Their Impact on Parkinson Disease: A Narrative Overview of Current Evidence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(7):2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072942
Chicago/Turabian StyleJellinger, Kurt A. 2025. "Concomitant Pathologies and Their Impact on Parkinson Disease: A Narrative Overview of Current Evidence" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 7: 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072942
APA StyleJellinger, K. A. (2025). Concomitant Pathologies and Their Impact on Parkinson Disease: A Narrative Overview of Current Evidence. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(7), 2942. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26072942






