Screening and Application of DNA Markers for Novel Quality Consistency Evaluation in Panax ginseng
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
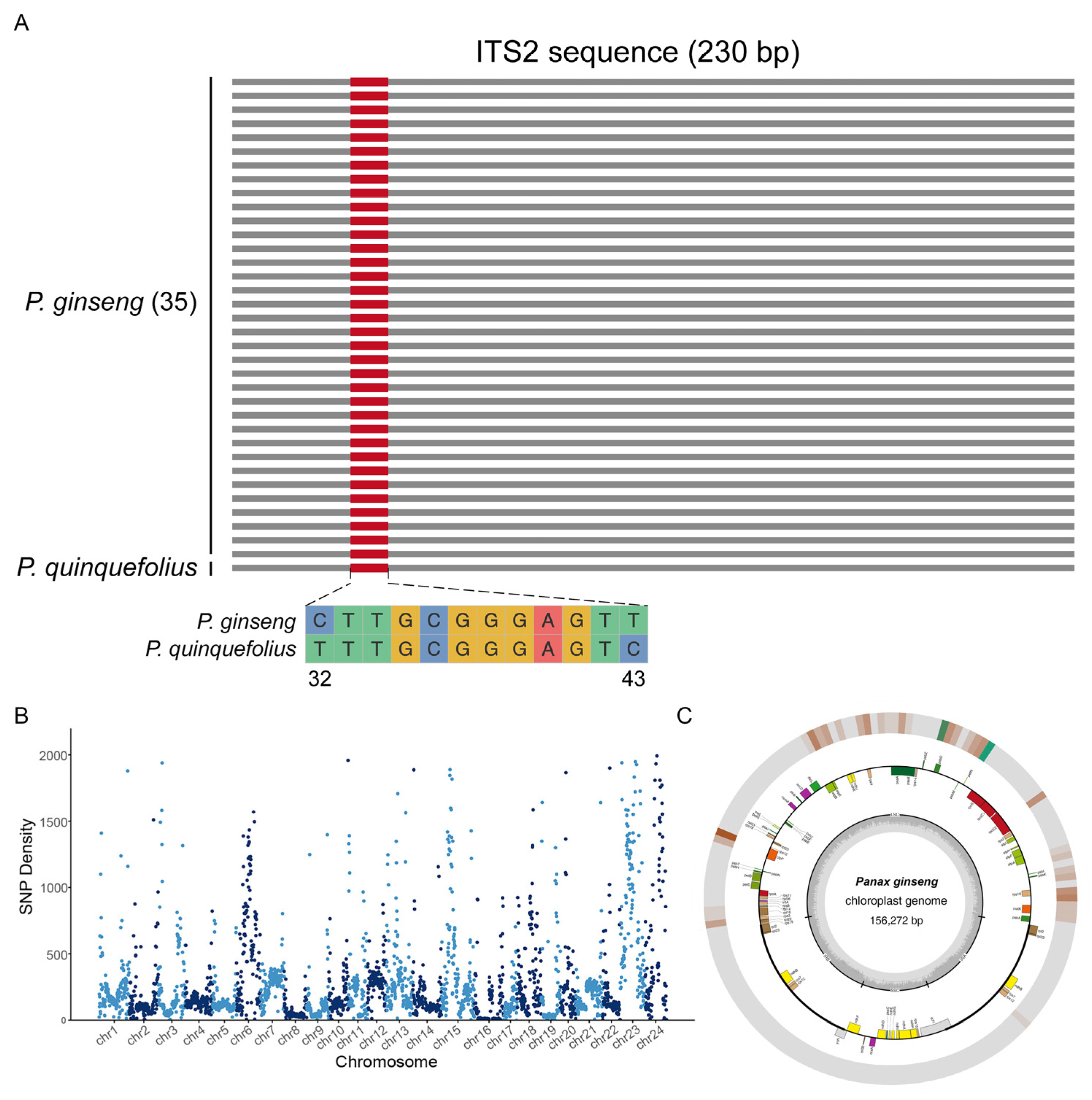
2.1. Screening of DNA Markers and Sequence Analysis
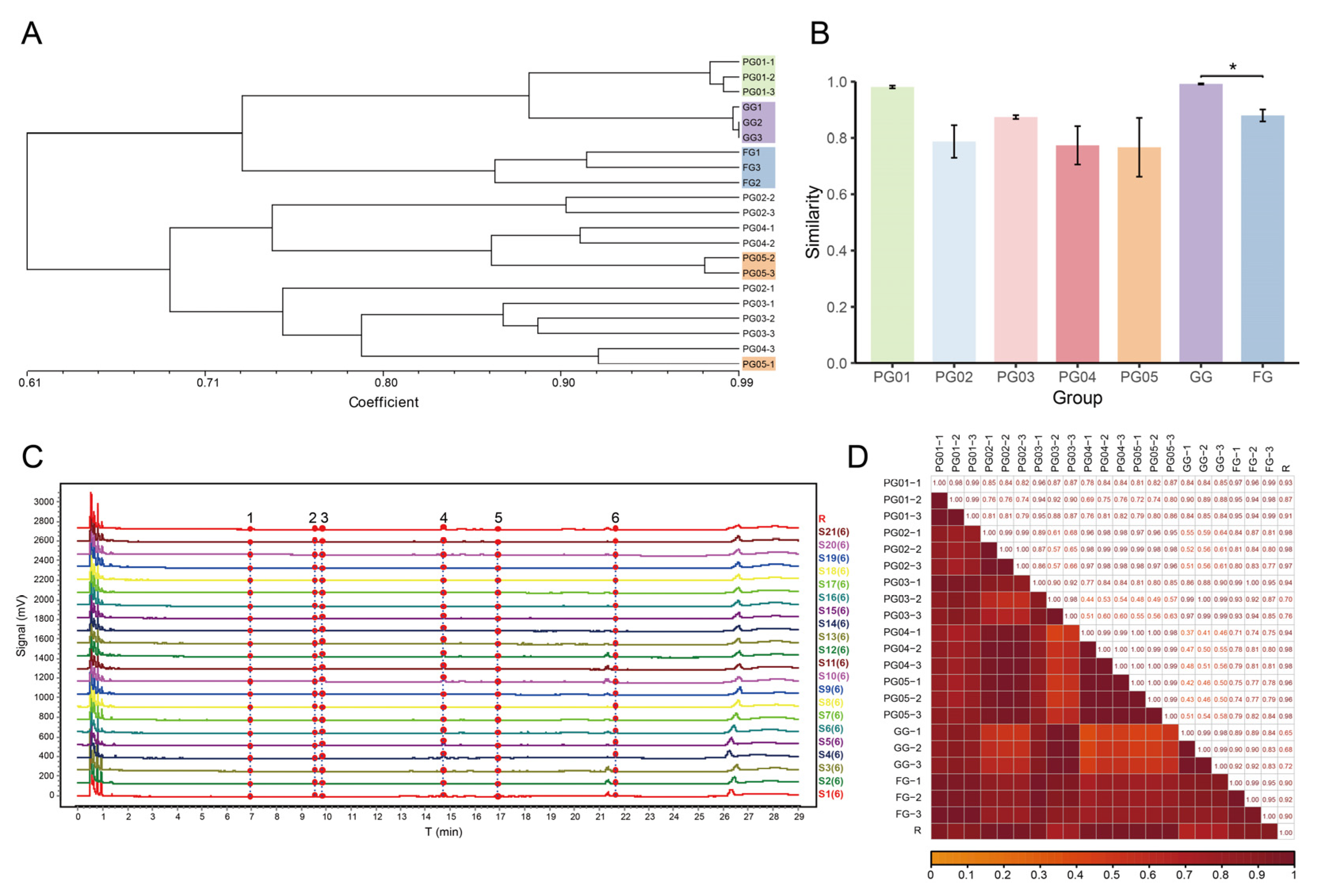
2.2. ISSR Analysis of Genetic Diversity in Ginseng
2.3. Genetic Similarity Coefficient and Cluster Analysis
2.4. Analysis of UPLC Fingerprint
2.4.1. Method Validation
2.4.2. UPLC Analysis and Similarity Evaluation
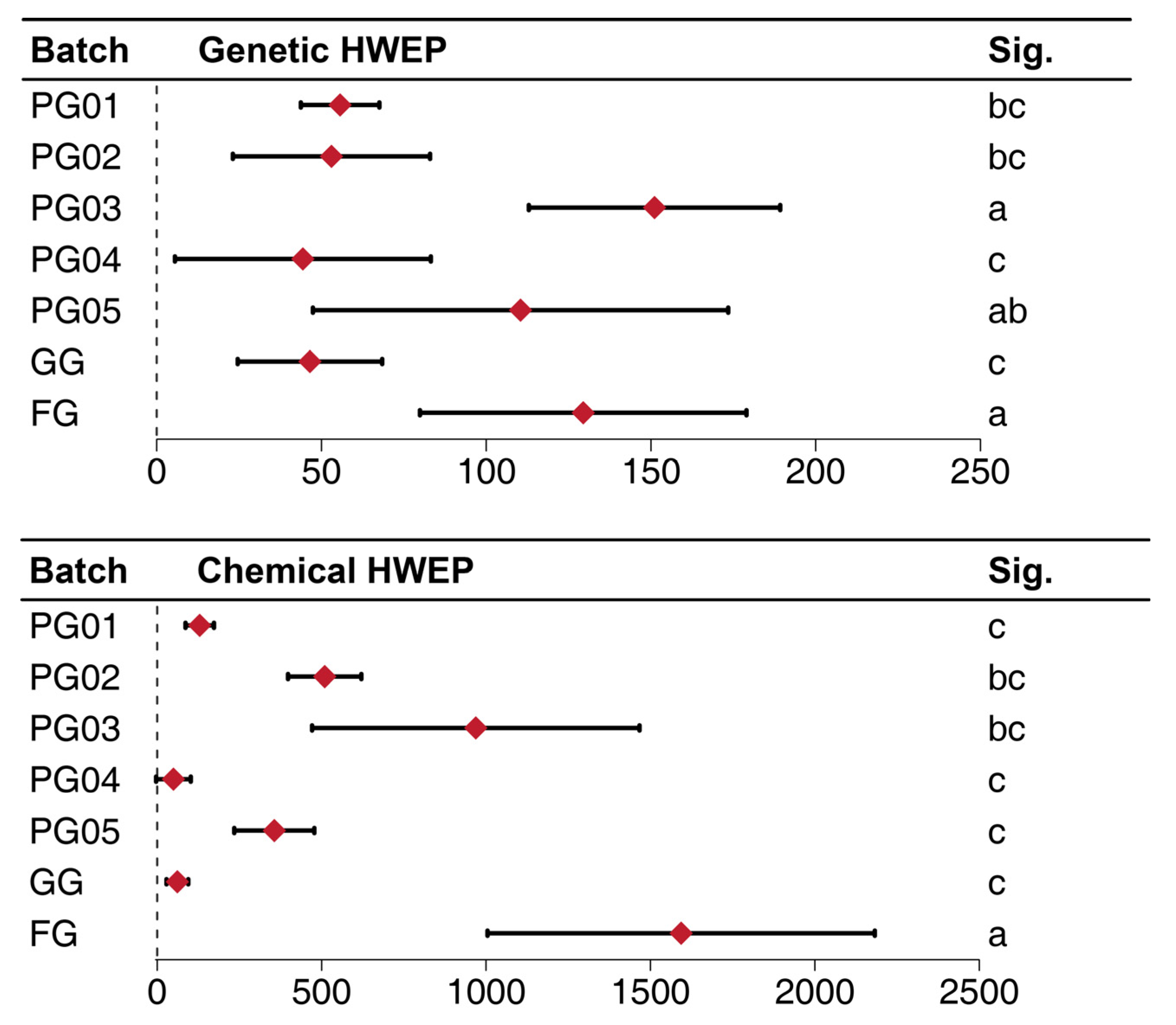
2.5. The HWEP Study Based on the Information Entropy
2.5.1. The Information Entropy and the MQS (Minimum Quantity for One Sampling) Determined by the ISSR Amplified Bands
2.5.2. The Information Entropy and the MQS Determined by Fingerprint Analysis
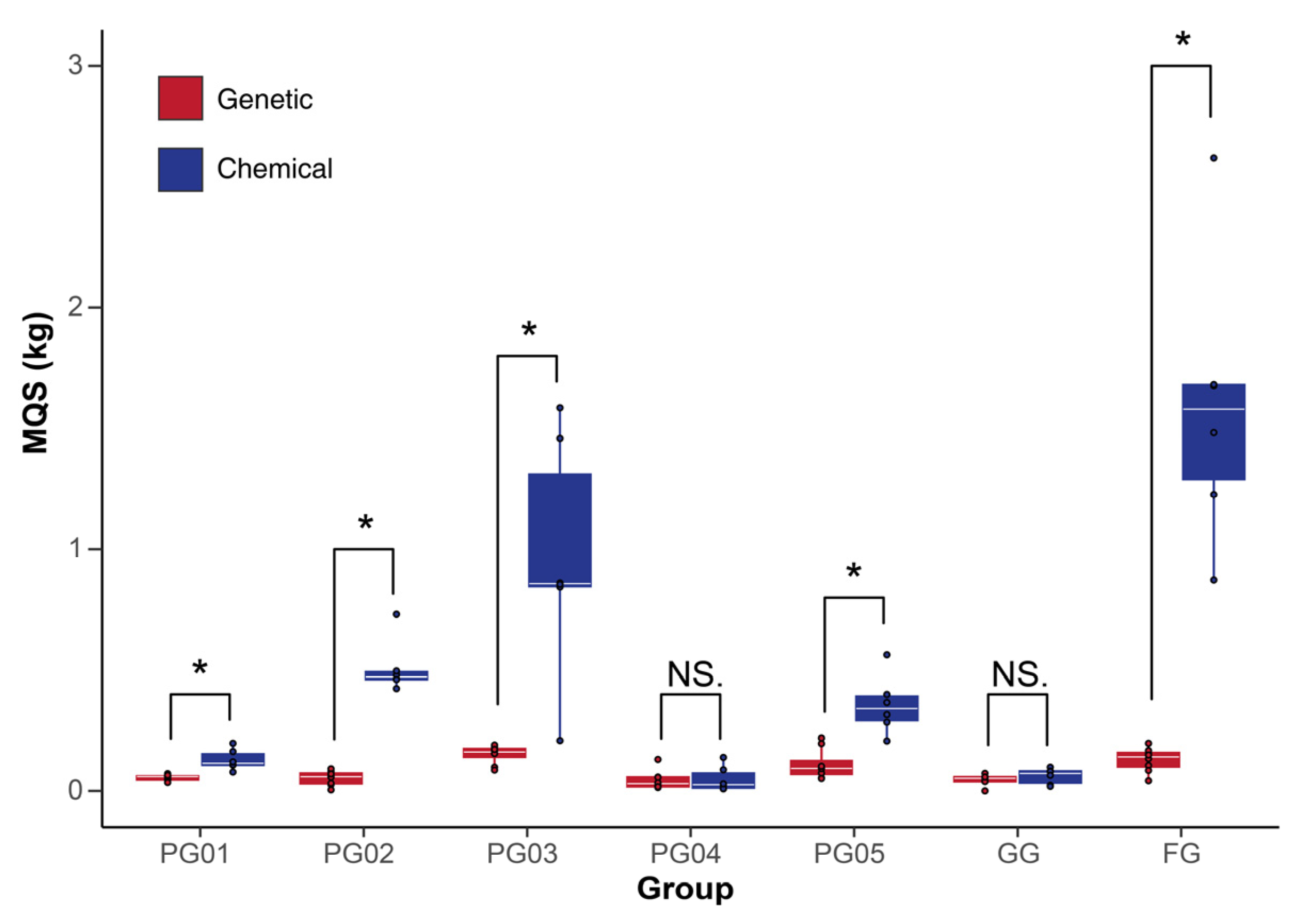
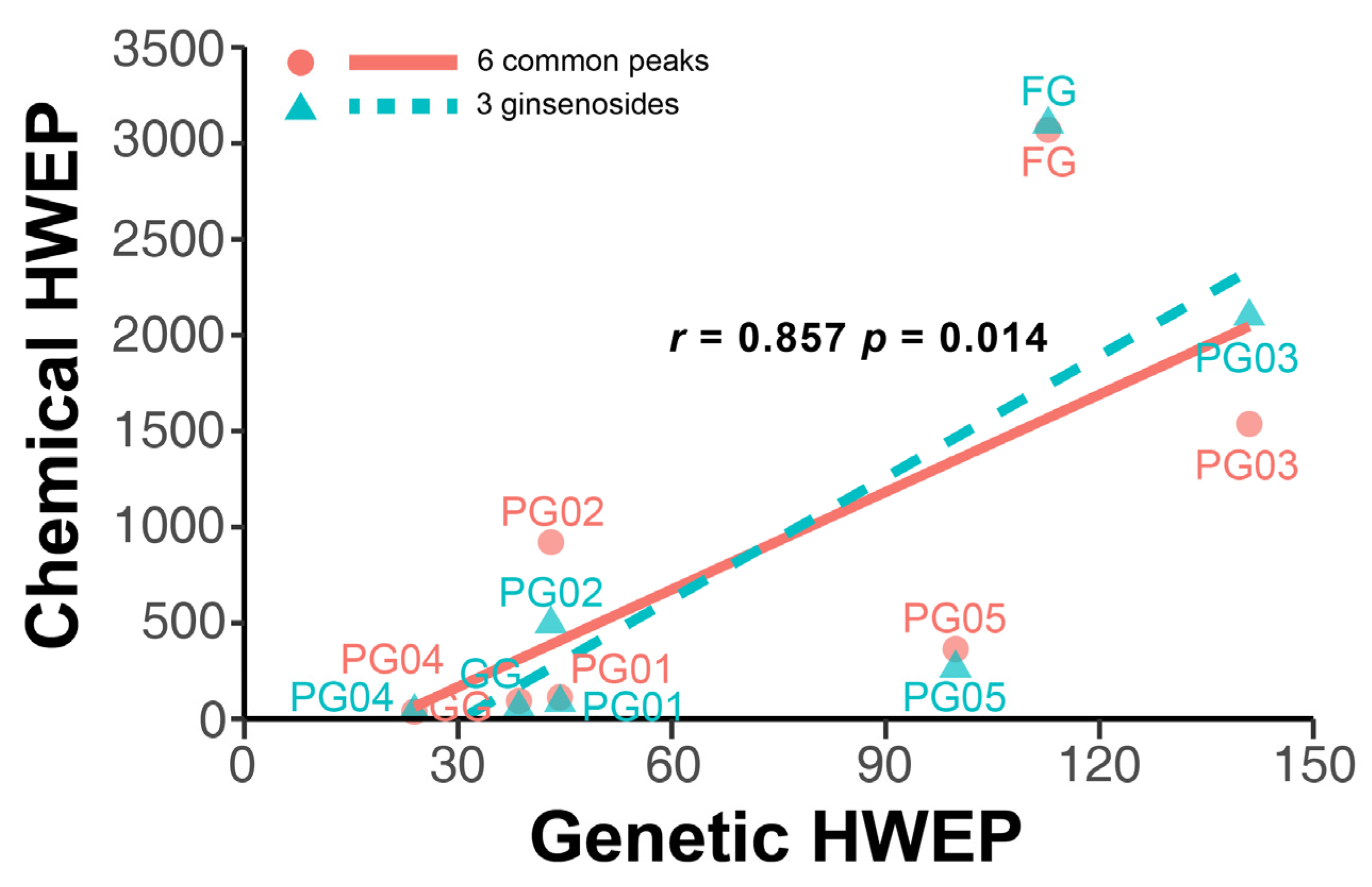
2.5.3. Correlation Analysis Between Chemical Composition Fluctuations and Genetic Diversity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Sample Collection and Reagents
4.2. ITS2 Sequences Analysis
4.3. ISSR Analysis
4.4. Genome Sequencing and SNP Calling
4.5. Preparation of Samples for UPLC Analysis
4.6. UPLC Analysis
4.7. HWEP Evaluation Based on ISSR and Chromatographic Fingerprint
4.8. Data Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, Y.; Shen, Y.; Yao, C.L.; Guo, D.A. Quality assessment of herbal medicines based on chemical fingerprints combined with chemometrics approach: A review. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2020, 185, 113215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.L.; Jiang, Y.; Li, H.J. Quality consistency evaluation of traditional Chinese medicines: Current status and future perspectives. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2024, 54, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, R.; Yu, L.H.; Wang, C.H.; Zhong, S.H.; Gu, R. Quality assessment of traditional Chinese medicine based on data fusion combined with machine learning: A review. Crit. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2024, 54, 2618–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, M.R.; He, Y.; Shi, S.M. Development of chromatographic technologies for the quality control of traditional Chinese medicine in the Chinese Pharmacopoeia. J. Pharm. Anal. 2021, 11, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhang, Q.Y.; Xin, H.L.; Qin, L.P.; Lu, B.R.; Rahman, K.; Zheng, H.C. Association between chemical and genetic variation of Vitex rotundifolia populations from different locations in China: Its implication for quality control of medicinal plants. Biomed. Chromatogr. 2007, 21, 967–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, D.Y.Q.; Lau, A.J.; Yeo, C.L.; Liu, X.K.; Yang, C.R.; Koh, H.L.; Hong, Y. Genetic diversity and variation of saponin contents in Panax notoginseng roots from a single farm. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2005, 53, 8460–8467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amom, T.; Tikendra, L.; Potshangbam, A.M.; Bidyananda, N.; Devi, R.S.; Dey, A.; Sahoo, M.R.; Vendrame, W.A.; Jamir, I.; Nongdam, P. Conservation strategies for endemic Dendrocalamus manipureanus: A study on genetic diversity and population structure based on molecular and phytochemical markers. S. Afr. J. Bot. 2023, 152, 106–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, H.; Sun, J.; Chen, M.Y.; Dong, Y.; Wang, P.; Xu, J.Z.; Shao, Q.S.; Wang, Z. The impact of non-environmental factors on the chemical variation of Radix Scrophulariae. Heliyon 2024, 10, e24468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, H.; Shen, X.; Liao, B.; Luo, L.; Xu, J.; Chen, S. Herbgenomics: A stepping stone for research into herbal medicine. Sci. China Life Sci. 2019, 62, 913–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Hu, H.; Xiao, S.; Zhou, G.; Sun, W.; Chu, Y.; Meng, X.; Wei, J.; Zhang, H.; Xu, J.; et al. Global Pharmacopoeia Genome Database is an integrated and mineable genomic database for traditional medicines derived from eight international pharmacopoeias. Sci. China Life Sci. 2022, 65, 809–817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chu, Y.; Liao, B.; Xiao, S.; Yin, Q.; Bai, R.; Su, H.; Dong, L.; Li, X.; Qian, J.; et al. Panax ginseng genome examination for ginsenoside biosynthesis. Gigascience 2017, 6, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, S.; Chu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Liao, B.; Zhang, J.; Gao, Y.; Xu, J.; Chen, S. Genome-wide identification and transcriptional profiling analysis of PIN/PILS auxin transporter gene families in Panax ginseng. Chin. Herb. Med. 2022, 14, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, W.; Jang, W.; Shim, H.; Kim, J.; Oh, Y.; Park, J.Y.; Kim, Y.C.; Lee, J.W.; Jo, I.H.; Lee, M.; et al. High-resolution genetic map and SNP chip for molecular breeding in Panax ginseng, a tetraploid medicinal plant. Hortic. Res. 2024, 11, uhae257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Guo, S.; Yin, X.; Li, M.; Su, H.; Liao, X.; Li, Q.; Le, L.; Chen, S.; Liao, B.; et al. Genomic, transcriptomic, and epigenomic analysis of a medicinal snake, Bungarus multicinctus, to provides insights into the origin of Elapidae neurotoxins. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2023, 13, 2234–2249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, B.; Shen, X.; Xiang, L.; Guo, S.; Chen, S.; Meng, Y.; Liang, Y.; Ding, D.; Bai, J.; Zhang, D.; et al. Allele-aware chromosome-level genome assembly of Artemisia annua reveals the correlation between ADS expansion and artemisinin yield. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 1310–1328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Liao, B.; Yuan, L.; Shen, X.; Liao, X.; Wang, J.; Hu, H.; Huang, Z.; Xiang, L.; Chen, S. 50th anniversary of artemisinin: From the discovery to allele-aware genome assembly of Artemisia annua. Mol. Plant 2022, 15, 1243–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Chen, J.; Dai, C.; Shi, P.; Pan, H.; Lin, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gong, L.; Chen, L.; Wu, W.; et al. Developing population identification tool based on polymorphism of rDNA for traditional Chinese medicine: Artemisia annua L. Phytomedicine 2023, 116, 154882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Q.W.; Guo, S.; Zheng, X.S.; Shen, X.F.; Zhang, T.Y.; Liao, B.S.; He, W.R.; Hu, H.Y.; Cheng, R.Y.; Xu, J. Licorice germplasm resources identification using DNA barcodes inner-variants. Plants 2021, 10, 2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, H.H.; Liu, Q.W.; Guo, S.; Qin, S.Y.; Xu, F.; Cao, G.; Xu, J.; Hu, H.Y.; Chen, S.L. Analysis of Ephedrae Herba-based promiscuous mixture based on high-throughput sequencing. Glob. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2022, 15, 2257–2265. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.Q.; Liu, W.L.; He, F.Y.; Chen, Z.H.; Zhang, X.L.; Xie, X.G.; Zeng, J.L.; Duan, X.P. Study on once sampling quantitation based on information entropy of ISSR amplified bands of Houttuynia cordata. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2012, 37, 288–292. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, W.; Chen, S.; Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.S.; Liu, A. Which one is more important, raw materials or productive technology?—A case study for quality consistency control of Gegen Qinlian decoction. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2016, 41, 1027–1032. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Sucher, N.J.; Carles, M.C. Genome-based approaches to the authentication of medicinal plants. Planta Med. 2008, 74, 603–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, O.T.; Bang, K.H.; In, D.S.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, Y.C.; Shin, Y.S.; Hyun, D.Y.; Lee, S.S.; Cha, S.W.; Seong, N.S. Molecular authentication of ginseng cultivars by comparison of internal transcribed spacer and 5.8S rDNA sequences. Plant Biotechnol. Rep. 2007, 1, 163–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.J.; Wang, X.Q.; Xiao, P.G.; Hong, D.Y. Comparison of ITS sequences between wild ginseng DNA and garden ginseng DNA. China J. Chin. Mater. Med. 2000, 25, 206–209. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ma, X.J.; Wang, X.Q.; Sun, S.S.; Xiao, P.G.; Hong, D.Y. A study on RAPD fingerprintings of wild mountain ginseng (Panax ginseng). Acta Pharm. Sin. 1999, 34, 312–316. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasyutkina, E.A.; Adrianova, I.Y.; Reunova, G.D.; Nguyen, T.P.T.; Zhuravlev, Y.N. A comparative analysis of genetic variability and differentiation in Panax vietnamensis Ha et Grushv. and P-ginseng CA Meyer using ISSR markers. Russ. J. Genet. 2018, 54, 262–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.; Zhao, J.X.; You, J.; Li, J.N.; Ma, H.; Chen, X. Factors influencing cultivated ginseng (Panax ginseng C. A. Meyer) bioactive compounds. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0223763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.Q.; Wang, Y.P.; Guo, J.; Zhao, Y.H.; Li, C.Y.; Tian, L. Genetic Diversity of Fuxing 01, Huangguo Ginseng and Five Land Races of Panax ginseng Based on RAMP and ISSR Markers. J. Jilin Agric. Univ. 2010, 32, 293–298+306. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.H.; Zhang, A.H.; Jin, H.; Fang, J.H.; Jin, Y.C.; Zhang, L.X. Genetic relationship analysis of ginseng by ISSR analysis. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2010, 41, 1164–1167. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Ling, J.; Cheng, Z.; Yang, X.L.; Li, S.; Gu, R.Q.; Wan, S.W.; Zhang, W.J. ISSR Analysis on genetic diversity of Panax ginseng landraces. Chin. Tradit. Herb. Drugs 2007, 38, 1392–1395. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, H.; Garrick, D.J.; Fernando, R.L. Efficient strategies for leave-one-out cross validation for genomic best linear unbiased prediction. J. Anim. Sci. Biotechnol. 2017, 8, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Primer ID | Primer Sequence (5′-3′) | TNB | NPB | PPB (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| UBC807 | AGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGT | 14 | 12 | 85.7 |
| UBC808 | AGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGC | 12 | 12 | 100 |
| UBC809 | AGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGG | 5 | 3 | 60.0 |
| UBC823 | TCTCTCTCTCTCTCTCC | 13 | 12 | 92.3 |
| UBC834 | AGAGAGAGAGAGAGAGYT | 13 | 10 | 76.9 |
| UBC840 | GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAYT | 10 | 9 | 90.0 |
| UBC842 | GAGAGAGAGAGAGAGAYG | 11 | 8 | 72.7 |
| UBC873 | GACAGACAGACAGACA | 14 | 14 | 100 |
| No. | TNB | ln m | H | RSD | n | MQS (kg) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PG01 | PG01-1 | 70 | −0.2733 | 0.3943 | 6.16% | 44.30 | 0.044 |
| PG01-2 | 72 | −0.2451 | 0.3536 | ||||
| PG01-3 | 70 | −0.2733 | 0.3943 | ||||
| PG02 | PG02-1 | 33 | −1.0253 | 1.4792 | 6.07% | 43.02 | 0.043 |
| PG02-2 | 37 | −0.9109 | 1.3141 | ||||
| PG02-3 | 34 | −0.9954 | 1.4361 | ||||
| PG03 | PG03-1 | 47 | −0.6716 | 0.9690 | 10.99% | 141.00 | 0.141 |
| PG03-2 | 41 | −0.8082 | 1.1660 | ||||
| PG03-3 | 47 | −0.6716 | 0.9690 | ||||
| PG04 | PG04-1 | 37 | −0.9109 | 1.3141 | 4.52% | 23.86 | 0.024 |
| PG04-2 | 40 | −0.8329 | 1.2016 | ||||
| PG04-3 | 38 | −0.8842 | 1.2756 | ||||
| PG05 | PG05-1 | 36 | −0.9383 | 1.3536 | 9.25% | 99.80 | 0.998 |
| PG05-2 | 42 | −0.7841 | 1.1312 | ||||
| PG05-3 | 40 | −0.8329 | 1.2016 | ||||
| GG | GG1 | 81 | −0.1273 | 0.1837 | 5.75% | 38.53 | 0.039 |
| GG2 | 82 | −0.1151 | 0.1660 | ||||
| GG3 | 81 | −0.1273 | 0.1837 | ||||
| FG | FG1 | 50 | −0.6098 | 0.8797 | 9.83% | 112.79 | 0.113 |
| FG2 | 47 | −0.6716 | 0.9690 | ||||
| FG3 | 53 | −0.5515 | 0.7956 |
| No. | 6 Common Peaks | 3 Identified Ginsenosides | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Information Entropy | RSD | n | MQS (kg) | Information Entropy | RSD | n | MQS (kg) | |
| PG01 | 1.08 × 105 | 9.85% | 113.07 | 0.113 | 1.01 × 105 | 8.54% | 85.13 | 0.085 |
| 9.26 × 104 | 8.81 × 104 | |||||||
| 9.09 × 104 | 8.66 × 104 | |||||||
| PG02 | 2.44 × 105 | 28.10% | 920.99 | 0.921 | 1.61 × 105 | 20.62% | 495.83 | 0.496 |
| 2.05 × 105 | 1.88 × 105 | |||||||
| 1.36 × 105 | 1.23 × 105 | |||||||
| PG03 | 7.52 × 104 | 36.31% | 1537.46 | 1.537 | 7.39 × 104 | 42.41% | 2097.62 | 2.098 |
| 4.51 × 104 | 3.59 × 104 | |||||||
| 3.92 × 104 | 3.92 × 104 | |||||||
| PG04 | 1.73 × 105 | 5.66% | 37.37 | 0.037 | 1.57 × 105 | 5.79% | 39.15 | 0.039 |
| 1.57 × 105 | 1.42 × 105 | |||||||
| 1.57 × 105 | 1.43 × 105 | |||||||
| PG05 | 1.73 × 105 | 17.66% | 363.74 | 0.364 | 1.60 × 105 | 15.08% | 265.30 | 0.265 |
| 1.39 × 105 | 1.31 × 105 | |||||||
| 1.23 × 105 | 1.20 × 105 | |||||||
| GG | 2.54 × 104 | 8.97% | 93.85 | 0.094 | 1.84 × 104 | 7.06% | 58.17 | 0.058 |
| 2.48 × 104 | 2.09 × 104 | |||||||
| 2.15 × 104 | 1.88 × 104 | |||||||
| FG | 3.64 × 104 | 51.30% | 3070.03 | 3.070 | 3.33 × 104 | 51.54% | 3098.48 | 3.098 |
| 3.52 × 104 | 3.44 × 104 | |||||||
| 8.09 × 104 | 7.68 × 104 | |||||||
| Sample | Type | Place of Origin |
|---|---|---|
| PG01 | Decoction pieces | Market of Jilin Province, China |
| PG02 | Decoction pieces | Market of Jilin Province, China |
| PG03 | Decoction pieces | Market of Jilin Province, China |
| PG04 | Decoction pieces | Market of Jilin Province, China |
| PG05 | Decoction pieces | Market of Jilin Province, China |
| FG1 | Ginseng under forest | Tonghua City, Jilin Province, China |
| FG2 | Ginseng under forest | Tonghua City, Jilin Province, China |
| FG3 | Ginseng under forest | Tonghua City, Jilin Province, China |
| GG1 | Garden ginseng | Tonghua City, Jilin Province, China |
| GG2 | Garden ginseng | Tonghua City, Jilin Province, China |
| GG3 | Garden ginseng | Tonghua City, Jilin Province, China |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cai, S.; Liao, X.; Xi, Y.; Chu, Y.; Liu, S.; Su, H.; Dou, D.; Xu, J.; Xiao, S. Screening and Application of DNA Markers for Novel Quality Consistency Evaluation in Panax ginseng. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062701
Cai S, Liao X, Xi Y, Chu Y, Liu S, Su H, Dou D, Xu J, Xiao S. Screening and Application of DNA Markers for Novel Quality Consistency Evaluation in Panax ginseng. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062701
Chicago/Turabian StyleCai, Siyuan, Xuejiao Liao, Yidan Xi, Yang Chu, Shuang Liu, Hang Su, Deqiang Dou, Jiang Xu, and Shuiming Xiao. 2025. "Screening and Application of DNA Markers for Novel Quality Consistency Evaluation in Panax ginseng" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062701
APA StyleCai, S., Liao, X., Xi, Y., Chu, Y., Liu, S., Su, H., Dou, D., Xu, J., & Xiao, S. (2025). Screening and Application of DNA Markers for Novel Quality Consistency Evaluation in Panax ginseng. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2701. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062701





