Distribution and Characteristics of Oral Pathogens According to Blood Glucose Levels in South Korean Health Examinees
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
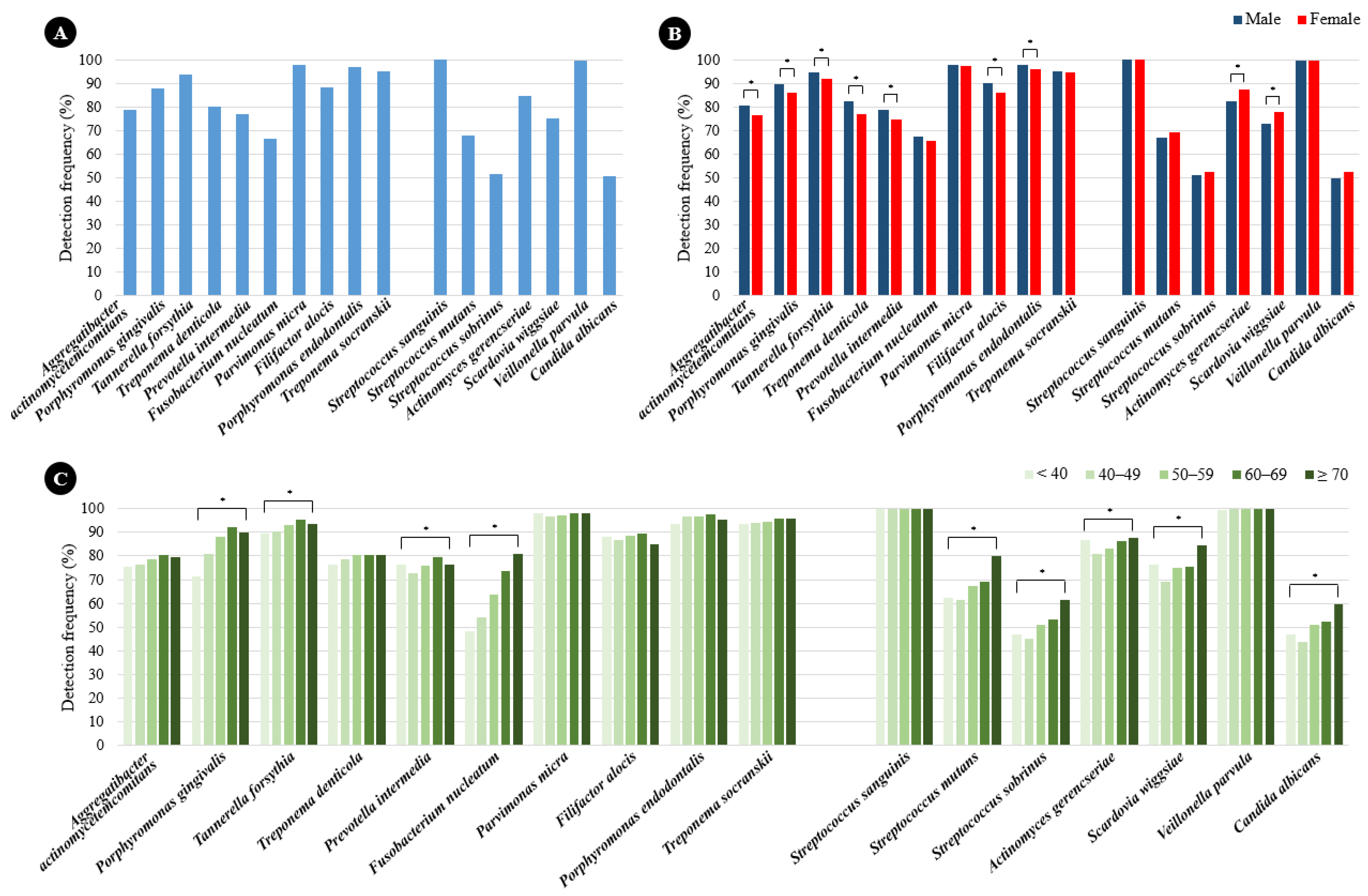
2.1. Prevalence of Periodontitis and Dental Caries Pathogens According to Sex and Age
2.2. Quantification of Periodontitis and Dental Caries Pathogens According to Sex and Age
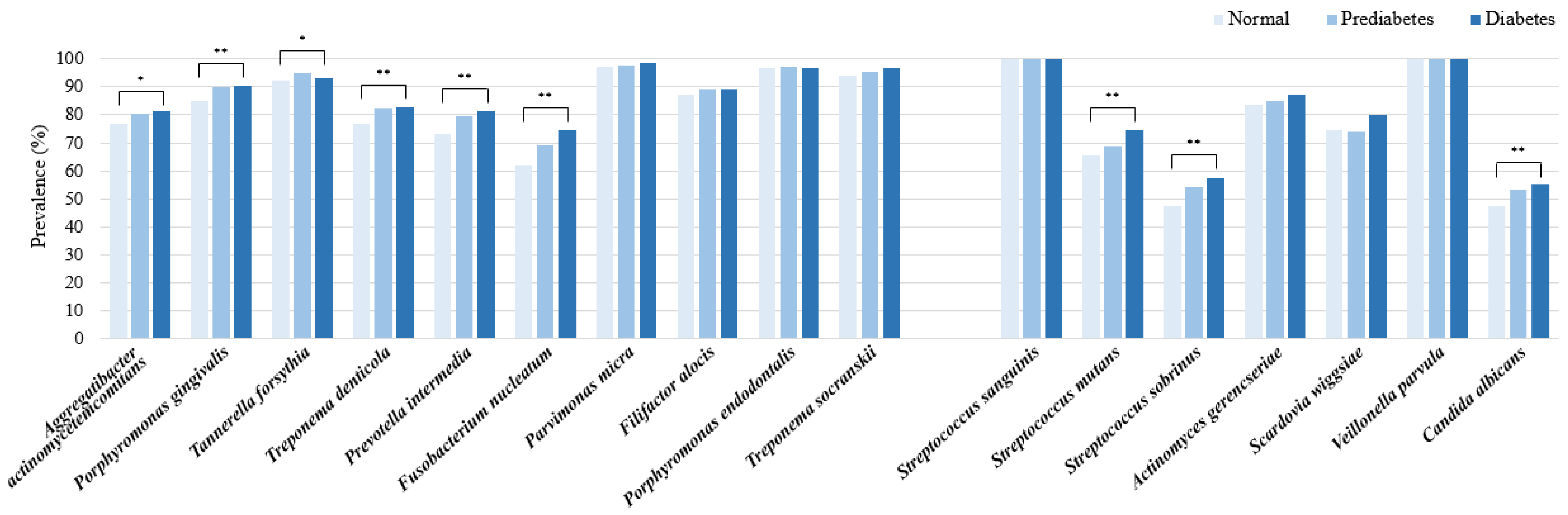
2.3. Prevalence Rates and Percentage Contents of Periodontitis and Dental Caries Pathogens According to Blood Glucose Levels
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Subjects
4.2. Laboratory Measurements
4.3. Sample Collection and DNA Extraction
4.4. Multiplex Real-Time PCR
4.5. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sharma, N.; Bhatia, S.; Sodhi, A.S.; Batra, N. Oral microbiome and health. AIMS Microbiol. 2018, 4, 42–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nath, S.G.; Raveendran, R. Microbial dysbiosis in periodontitis. J. Indian Soc. Periodontol. 2013, 17, 543–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woelber, J.P.; Bremer, K.; Vach, K.; König, D.; Hellwig, E.; Ratka-Krüger, P.; Al-Ahmad, A.; Tennert, C. An oral health optimized diet can reduce gingival and periodontal inflammation in humans—A randomized controlled pilot study. BMC Oral Health 2016, 17, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haffajee, A.D.; Japlit, M.; Bogren, A.; Kent, R.L.; Goodson, J.M.; Socransky, S.S. Differences in the subgingival microbiota of Swedish and USA subjects who were periodontally healthy or exhibited minimal periodontal disease. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2005, 32, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, S.; Aoki, Y.; Tamahara, T.; Goto, M.; Matsui, H.; Kawashima, J.; Danjoh, I.; Hozawa, A.; Kuriyama, S.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Oral Microbiome Analysis in Prospective Genome Cohort Studies of the Tohoku Medical Megabank Project. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 604596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, V.K.; Paul, S.; Dutta, C. Geography, Ethnicity or Subsistence-Specific Variations in Human Microbiome Composition and Diversity. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajishengallis, G.; Chavakis, T. Local and systemic mechanisms linking periodontal disease and inflammatory comorbidities. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2021, 21, 426–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, H.; Li, G.; Xu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhong, W.; Xu, S.; Yin, Y.; Song, J. The role of oral microbiome in periodontitis under diabetes mellitus. J. Oral Microbiol. 2022, 14, 2078031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, D.N.A.; Casarin, M.; Monajemzadeh, S.; Bezerra, B.B.; Lux, R.; Pirih, F.Q. The Microbiome in Periodontitis and Diabetes. Front. Oral Health 2022, 3, 859209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Liu, Y.; Yang, X.; Li, C.; Song, Z. The Oral Microbiota: Community Composition, Influencing Factors, Pathogenesis, and Interventions. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 895537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lalla, E.; Papapanou, P.N. Diabetes mellitus and periodontitis: A tale of two common interrelated diseases. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2011, 7, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffey, J.; Choudhry, M.; Shlossman, M.; Makin, I.R.S.; Singh, V.K. Multiplex real-time PCR detection and relative quantification of periodontal pathogens. Clin. Exp. Dent. Res. 2016, 2, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lochman, J.; Zapletalova, M.; Poskerova, H.; Izakovicova Holla, L.; Borilova Linhartova, P. Rapid Multiplex Real-Time PCR Method for the Detection and Quantification of Selected Cariogenic and Periodontal Bacteria. Diagnostics 2019, 10, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.; Kim, E.; Kang, J.; Kim, H.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Choi, J.; Joo, J.Y. Real-time PCR quantification of 9 periodontal pathogens in saliva samples from periodontally healthy Korean young adults. J. Periodontal Implant Sci. 2018, 48, 261–271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arenas Rodrigues, V.A.; de Avila, E.D.; Nakano, V.; Avila-Campos, M.J. Qualitative, quantitative and genotypic evaluation of Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans and Fusobacterium nucleatum isolated from individuals with different periodontal clinical conditions. Anaerobe 2018, 52, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Liu, X.; Li, J.; Aprecio, R.M.; Zhang, W.; Li, Y. Real-time PCR quantification of six periodontal pathogens in saliva samples from healthy young adults. Clin. Oral Investig. 2015, 19, 937–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvärinen, K.; Laitinen, S.; Paju, S.; Hakala, A.; Suominen-Taipale, L.; Skurnik, M.; Könönen, E.; Pussinen, P.J. Detection and quantification of five major periodontal pathogens by single copy gene-based real-time PCR. Innate Immun. 2009, 15, 195–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nonnenmacher, C.; Dalpke, A.; Rochon, J.; Flores-de-Jacoby, L.; Mutters, R.; Heeg, K. Real-time polymerase chain reaction for detection and quantification of bacteria in periodontal patients. J. Periodontol. 2005, 76, 1542–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, W.; Gizani, S.; Haffajee, A.D.; Quirynen, M.; Mamai-Homata, E.; Papagiannoulis, L. The microbiota on different oral surfaces in healthy children. Oral Microbiol. Immunol. 2009, 24, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papapanou, P.N.; Neiderud, A.M.; Papadimitriou, A.; Sandros, J.; Dahlén, G. “Checkerboard” assessments of periodontal microbiota and serum antibody responses: A case-control study. J. Periodontol. 2000, 71, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanz-Martin, I.; Doolittle-Hall, J.; Teles, R.P.; Patel, M.; Belibasakis, G.N.; Hämmerle, C.H.F.; Jung, R.E.; Teles, F.R.F. Exploring the microbiome of healthy and diseased peri-implant sites using Illumina sequencing. J. Clin. Periodontol. 2017, 44, 1274–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hurley, E.; Barrett, M.P.J.; Kinirons, M.; Whelton, H.; Ryan, C.A.; Stanton, C.; Harris, H.M.B.; O’Toole, P.W. Comparison of the salivary and dentinal microbiome of children with severe-early childhood caries to the salivary microbiome of caries-free children. BMC Oral Health 2019, 19, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, W.; Ma, T.; Ye, M.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Hao, P. Microbiota in the apical root canal system of tooth with apical periodontitis. BMC Genom. 2019, 20, 189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, W.; Rosier, B.T.; Artacho, A.; Paterson, M.; Piela, K.; Delaney, C.; Brown, J.L.; Ramage, G.; Mira, A.; Culshaw, S. Mechanical biofilm disruption causes microbial and immunological shifts in periodontitis patients. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lira-Junior, R.; Åkerman, S.; Klinge, B.; Boström, E.A.; Gustafsson, A. Salivary microbial profiles in relation to age, periodontal, and systemic diseases. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0189374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; He, J.; Xue, J.; Wang, Y.; Li, K.; Zhang, K.; Guo, Q.; Liu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Cheng, L.; et al. Oral cavity contains distinct niches with dynamic microbial communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2015, 17, 699–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeshita, T.; Kageyama, S.; Furuta, M.; Tsuboi, H.; Takeuchi, K.; Shibata, Y.; Shimazaki, Y.; Akifusa, S.; Ninomiya, T.; Kiyohara, Y.; et al. Bacterial diversity in saliva and oral health-related conditions: The Hisayama Study. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 22164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kinane, D.F.; Stathopoulou, P.G.; Papapanou, P.N. Periodontal diseases. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2017, 3, 17038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Wang, Z.; Wang, J.; Su, X.; Yang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, L. The oral microbiome profile and biomarker in Chinese type 2 diabetes mellitus patients. Endocrine 2020, 68, 564–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Long, J.; Cai, Q.; Steinwandel, M.; Hargreaves, M.K.; Bordenstein, S.R.; Blot, W.J.; Zheng, W.; Shu, X.O. Association of oral microbiome with type 2 diabetes risk. J. Periodont. Res. 2017, 52, 636–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeb, A.T.M.; Al-Rubeaan, K.A.; Aldosary, K.; Udaya Raja, G.K.; Mani, B.; Abouelhoda, M.; Tayeb, H.T. Relative reduction of biological and phylogenetic diversity of the oral microbiota of diabetes and pre-diabetes patients. Microb. Pathog. 2019, 128, 215–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilian, M.; Chapple, I.L.; Hannig, M.; Marsh, P.D.; Meuric, V.; Pedersen, A.M.; Tonetti, M.S.; Wade, W.G.; Zaura, E. The oral microbiome—An update for oral healthcare professionals. Br. Dent. J. 2016, 221, 657–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, M.R.; Preshaw, P.M.; Nagaraja, H.N.; Dabdoub, S.M.; Rahman, A.; Kumar, P.S. The subgingival microbiome of clinically healthy current and never smokers. ISME J. 2015, 9, 268–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomar-Vercher, S.; Cabrera-Rubio, R.; Mira, A.; Montiel-Company, J.M.; Almerich-Silla, J.M. Relationship of children’s salivary microbiota with their caries status: A pyrosequencing study. Clin. Oral Investig. 2014, 18, 2087–2094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.R.; Cheng, W.C.; Hsiao, Y.C.; Su, G.W.; Lin, S.J.; Wei, Y.S.; Chou, H.C.; Lin, H.P.; Lin, G.Y.; Chan, H.L. Links between oral microbiome and insulin resistance: Involvement of MAP kinase signaling pathway. Biochimie 2023, 214, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamont, R.J.; Koo, H.; Hajishengallis, G. The oral microbiota: Dynamic communities and host interactions. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 745–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Characteristic | Total (n = 3045) | Normal a (n = 1352) | Prediabetes b (n = 1305) | Diabetes c (n = 388) | p * | Multiple Comparisons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 57 ± 9.7 | 55.5 ± 10.3 | 57.9 ± 9.2 | 59.3 ± 8.6 | <0.001 | a < b < c |
| Sex, male | 1711 (56.2) | 656 (48.5) | 771 (59.1) | 284 (73.2) | <0.001 | a < b < c |
| Blood glucose, mg/dL | 107.2 ± 24.4 | 91.6 ± 6.2 | 108.8 ± 6.7 | 156 ± 33.9 | <0.001 | a < b < c |
| AST, U/L | 34 ± 21.6 | 31.9 ± 17.5 | 34.5 ± 21.5 | 39.9 ± 31.2 | <0.001 | a < b < c |
| ALT, U/L | 33 ± 51.3 | 28.7 ± 21.8 | 33.4 ± 25.2 | 46.8 ± 129 | <0.001 | a, b < c |
| γ-GTP, U/L | 44.9 ± 69.9 | 36.5 ± 63.4 | 48.8 ± 76.3 | 61.3 ± 64.5 | <0.001 | a < b < c |
| Total cholesterol, mg/dL | 207 ± 48.5 | 210.8 ± 40.6 | 208.1 ± 44.2 | 189.7 ± 76.3 | <0.001 | a, b > c |
| Triglycerides, mg/dL | 125.9 ± 99.8 | 105 ± 74.4 | 134.2 ± 86.8 | 170.4 ± 172.8 | <0.001 | a < b < c |
| HDL-cholesterol, mg/dL | 55.3 ± 14.1 | 58 ± 15 | 54.2 ± 13.1 | 49.7 ± 11.8 | <0.001 | a > b > c |
| LDL-cholesterol, mg/dL | 123.1 ± 40 | 127.2 ± 38.1 | 124.1 ± 40.1 | 105 ± 41.5 | <0.001 | a, b > c |
| Hemoglobin, g/dL | 14.6 ± 1.5 | 14.4 ± 1.5 | 14.7 ± 1.4 | 15 ± 1.5 | <0.001 | a < b < c |
| Bacterial Strain | Total (n = 3041) | Normal a (n = 1348) | Prediabetes b (n = 1305) | Diabetes c (n = 388) | p * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periodontitis pathogens | |||||
| Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans | 1.5% | 1.9% | 1.3% | 1.0% | 0.054 |
| Porphyromonas gingivalis | 12.1% | 11.6% | 12.6% | 12.1% | 0.227 |
| Tannerella forsythia | 5.7% | 5.7% | 5.8% | 5.6% | 0.922 |
| Treponema denticola | 4.0% | 3.7% | 4.3% | 4.0% | 0.053 |
| Prevotella intermedia | 23.0% | 21.7% | 23.8% | 24.8% | 0.058 |
| Fusobacterium nucleatum | 6.2% | 5.9% | 6.7% | 5.8% | 0.168 |
| Parvimonas micra | 4.4% | 4.9% | 4.1% | 4.0% | 0.023 |
| Filifactor alocis | 4.7% | 4.7% | 4.6% | 4.8% | 0.964 |
| Porphyromonas endodontalis | 28.6% | 29.6% | 27.6% | 28.7% | 0.077 |
| Treponema socranskii | 9.8% | 10.3% | 9.2% | 9.2% | 0.114 |
| Dental caries pathogens | |||||
| Streptococcus sanguinis | 59.7% | 61.1% | 59.8% | 54.2% | <0.001 |
| Streptococcus mutans | 1.6% | 1.6% | 1.6% | 2.1% | 0.339 |
| Streptococcus sobrinus | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.2% | 0.974 |
| Actinomyces gerencseriae | 1.8% | 1.7% | 1.9% | 1.9% | 0.718 |
| Scardovia wiggsiae | 0.7% | 0.7% | 0.6% | 0.7% | 0.558 |
| Veillonella parvula | 35.9% | 34.6% | 35.8% | 40.8% | <0.001 |
| Candida albicans | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.1% | 0.735 |
| Bacterial Strain | Target Gene |
|---|---|
| Periodontitis pathogens | |
| Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans | fts I |
| Prohormonal gingivalis | waaA |
| Tannerella forsythia | fts Z |
| Treponema denticola | fts K |
| Prevotella intermedia | piACP |
| Fusobacterium nucleatum | rpoB |
| Parvimonas micra | fus A |
| Filifactor alocis | gyr B |
| Porphyromonas endodontalis | 16S |
| Treponema socranskii | 16S |
| Dental caries pathogens | |
| Streptococcus sanguinis | tuf |
| Streptococcus mutans | gtf B |
| Streptococcus sobrinus | gtf I |
| Actinomyces gerencseriae | 16S |
| Scardovia wiggsiae | 16S |
| Veillonella parvula | rpoB |
| Candida albicans | SAP3 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.J.; Park, J.; Shin, M.G.; Jung, B.-K.; Shin, H.; Cho, S.; Cho, H.-I.; Nah, E.-H. Distribution and Characteristics of Oral Pathogens According to Blood Glucose Levels in South Korean Health Examinees. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062638
Choi YJ, Park J, Shin MG, Jung B-K, Shin H, Cho S, Cho H-I, Nah E-H. Distribution and Characteristics of Oral Pathogens According to Blood Glucose Levels in South Korean Health Examinees. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062638
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Yong Jun, Jooheon Park, Myung Geun Shin, Bong-Kwang Jung, Hyejoo Shin, Seon Cho, Han-Ik Cho, and Eun-Hee Nah. 2025. "Distribution and Characteristics of Oral Pathogens According to Blood Glucose Levels in South Korean Health Examinees" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062638
APA StyleChoi, Y. J., Park, J., Shin, M. G., Jung, B.-K., Shin, H., Cho, S., Cho, H.-I., & Nah, E.-H. (2025). Distribution and Characteristics of Oral Pathogens According to Blood Glucose Levels in South Korean Health Examinees. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2638. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062638



.jpg)



