Inflammatory Transformation of Skin Basal Cells as a Key Driver of Cutaneous Aging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
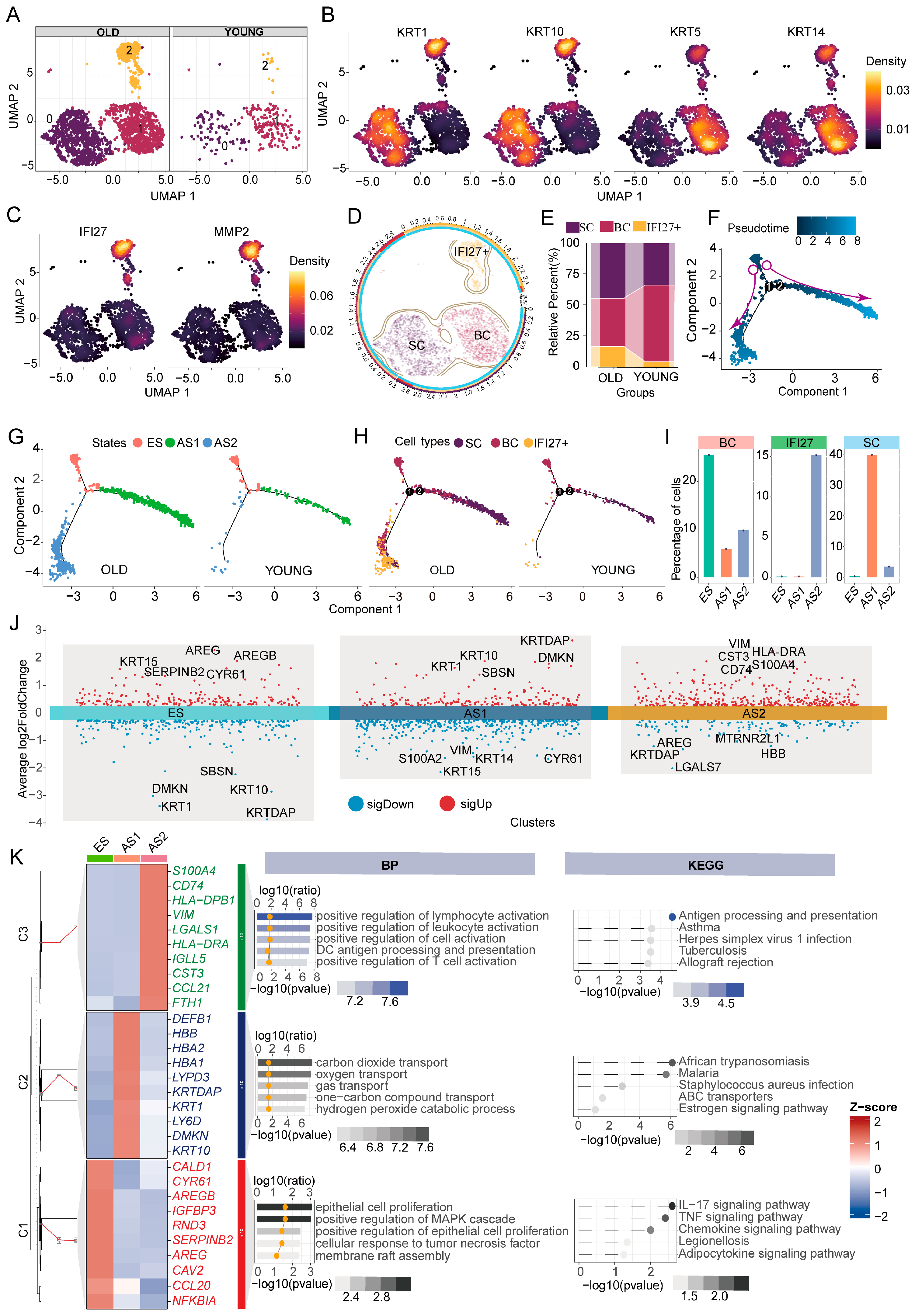
2.1. Keratinocyte Subpopulations and Developmental Trajectories in Young and Aged Skin
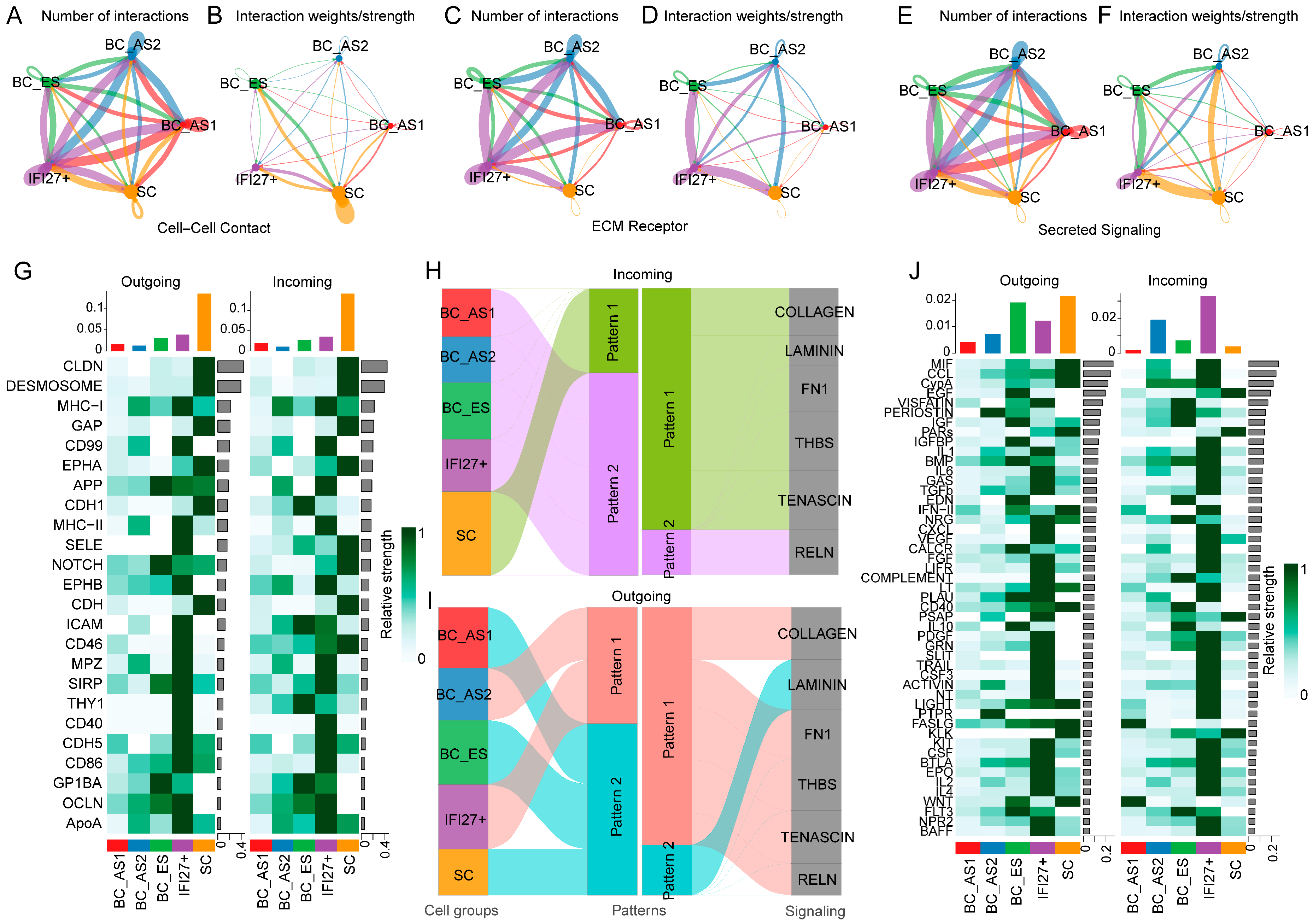
2.2. Keratinocyte Subpopulation Interactions in Young and Aged Skin
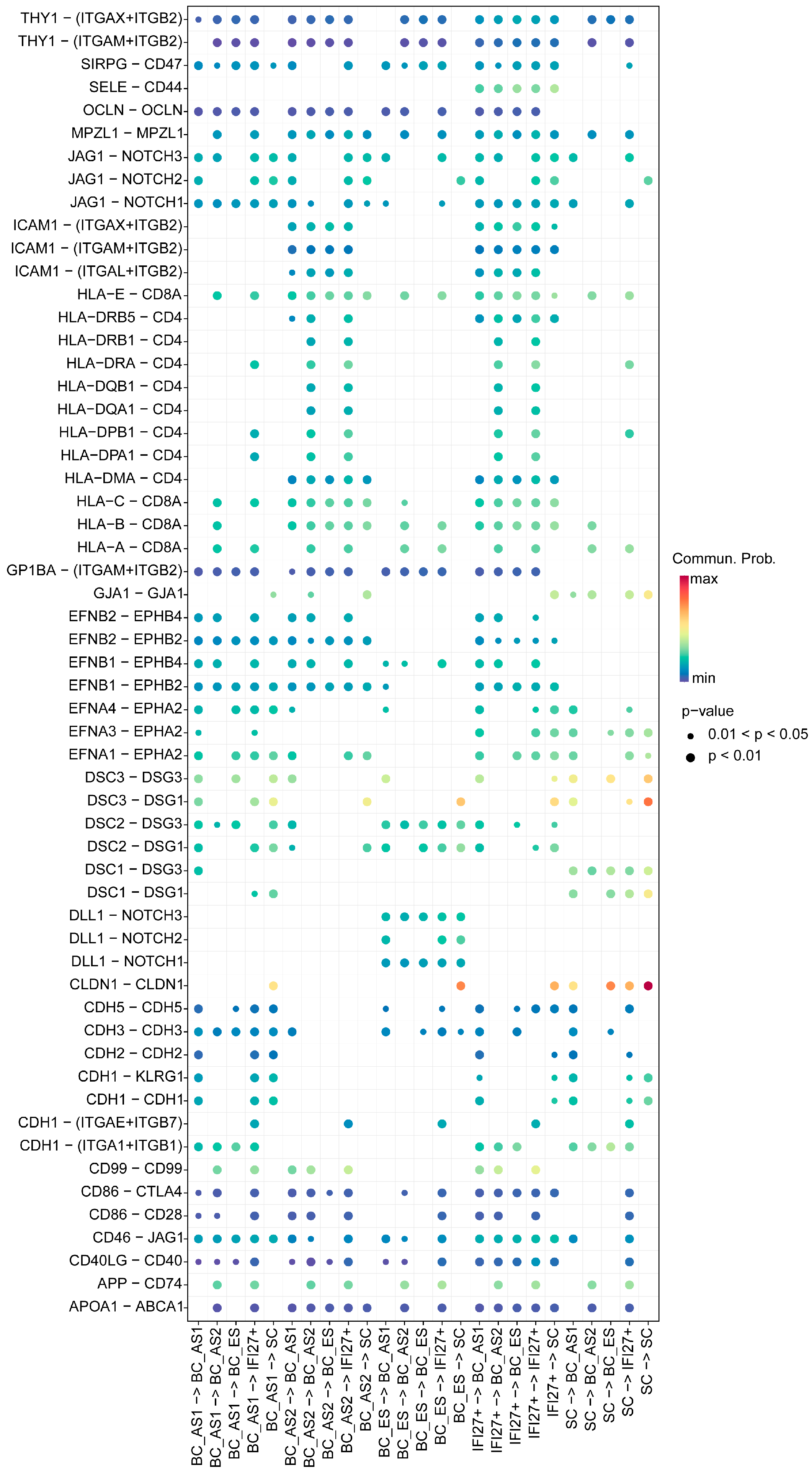
2.3. Keratinocyte Cell–Cell Interaction Features in Young and Aged Skin
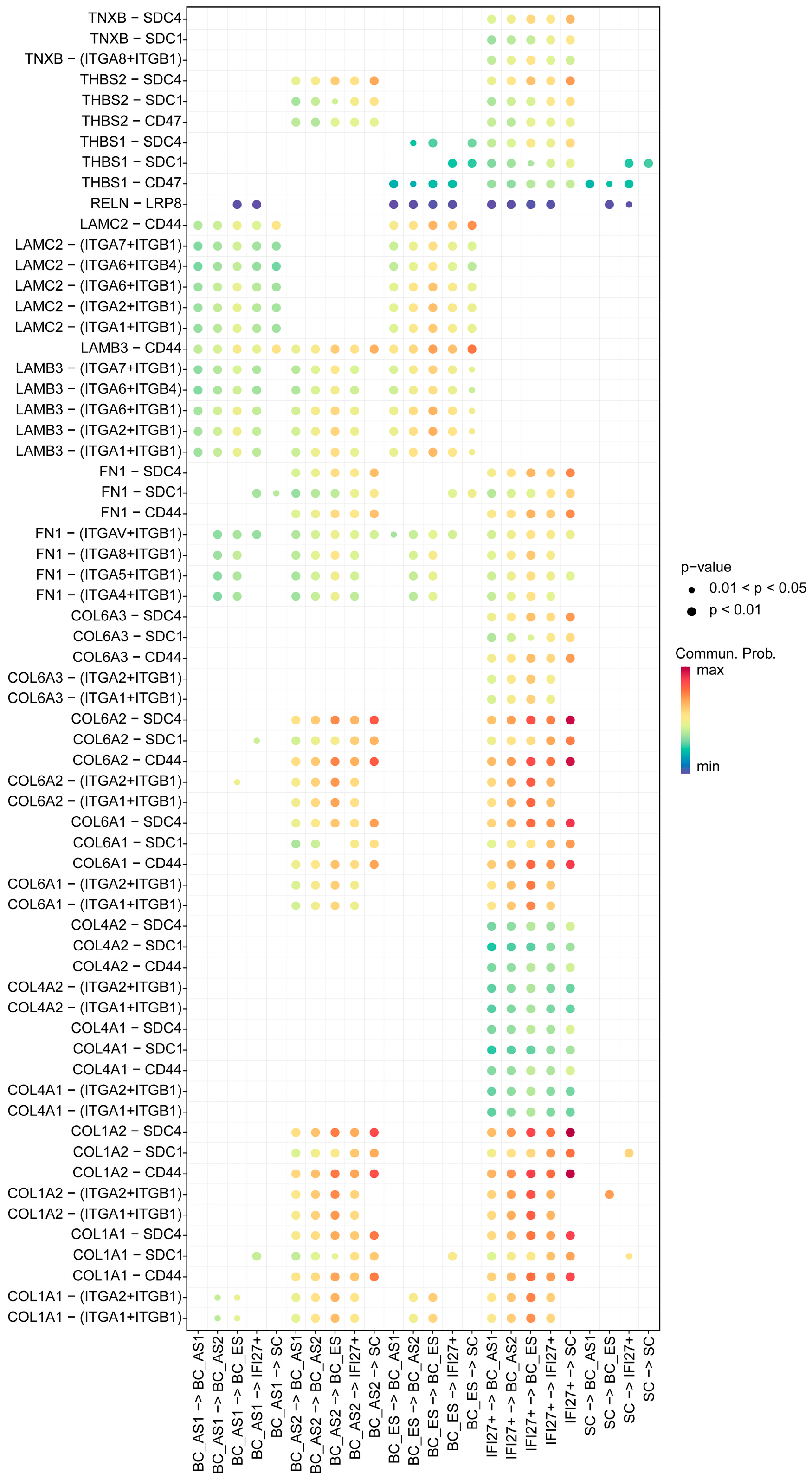
2.4. ECM Receptor Characteristics of Keratinocyte Subpopulations in Young and Aged Skin
2.5. Secreted Signaling Features Among Keratinocyte Subpopulations in Young and Aged Skin
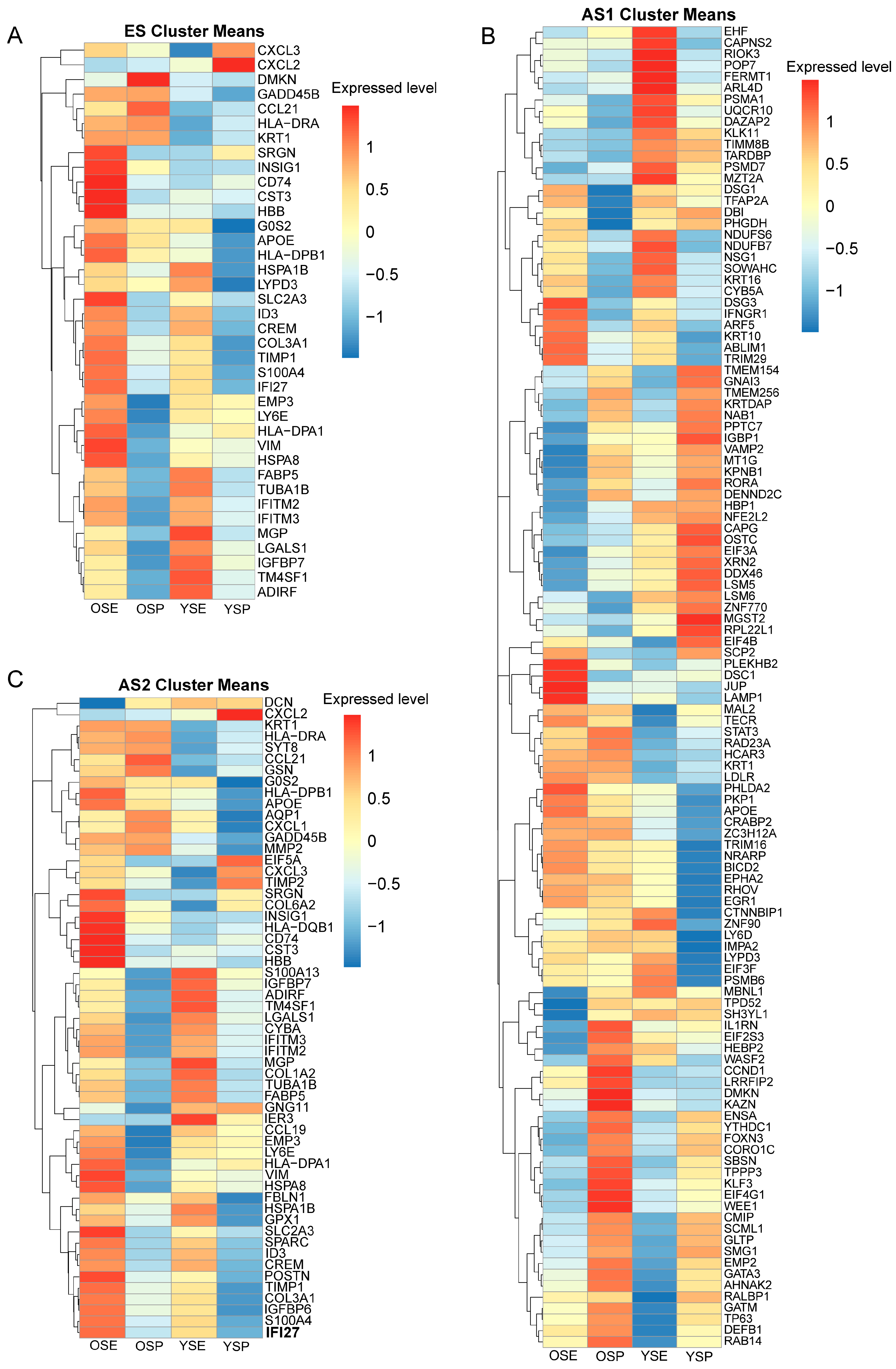
2.6. Transcriptomic Characteristics of Trajectory-Specific Genes in Keratinocyte Subpopulations of Young and Aged Skin
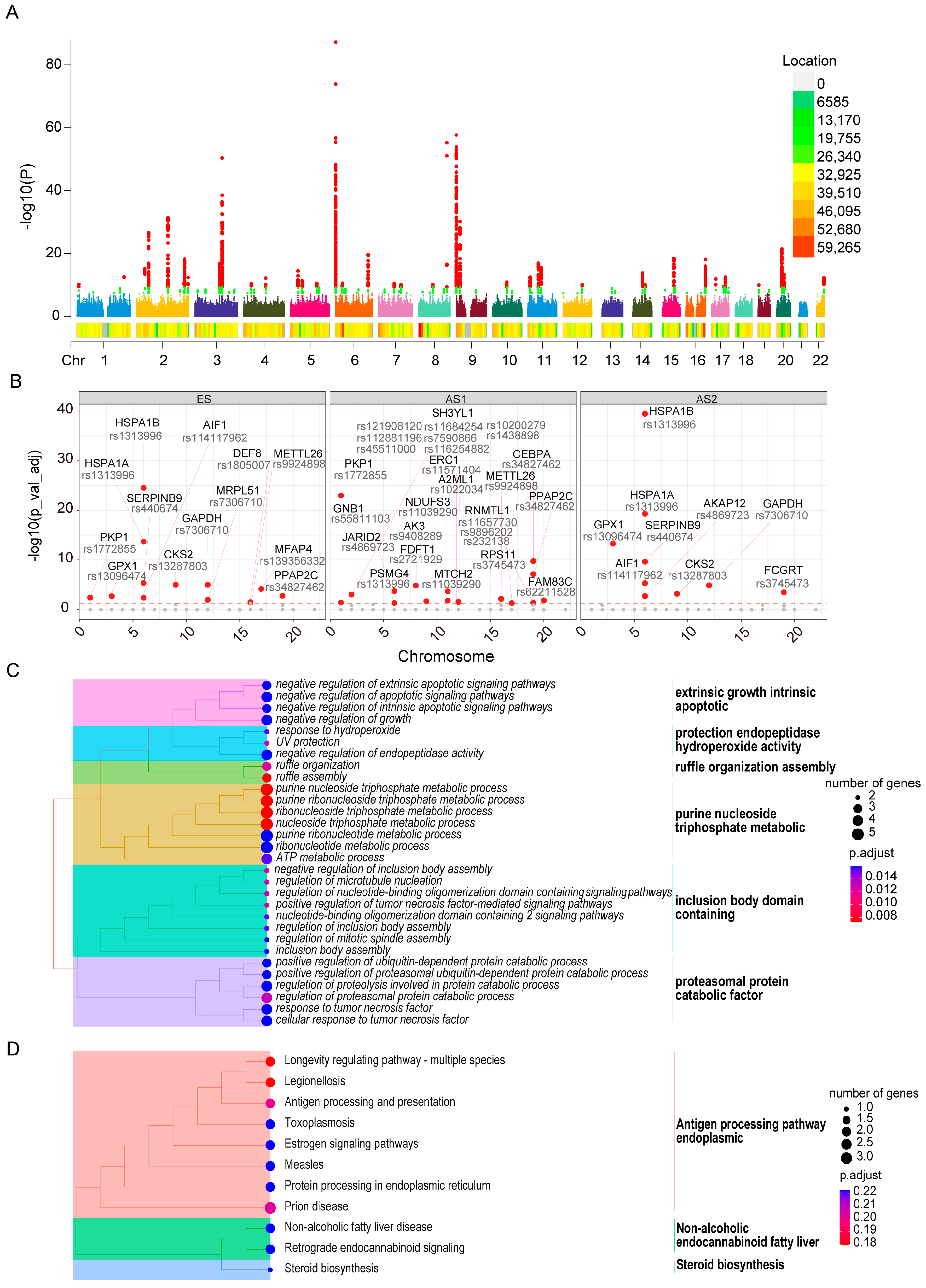
2.7. Genetic Loci Associated with Skin Aging and Their Influence on Developmental Trajectory Genes
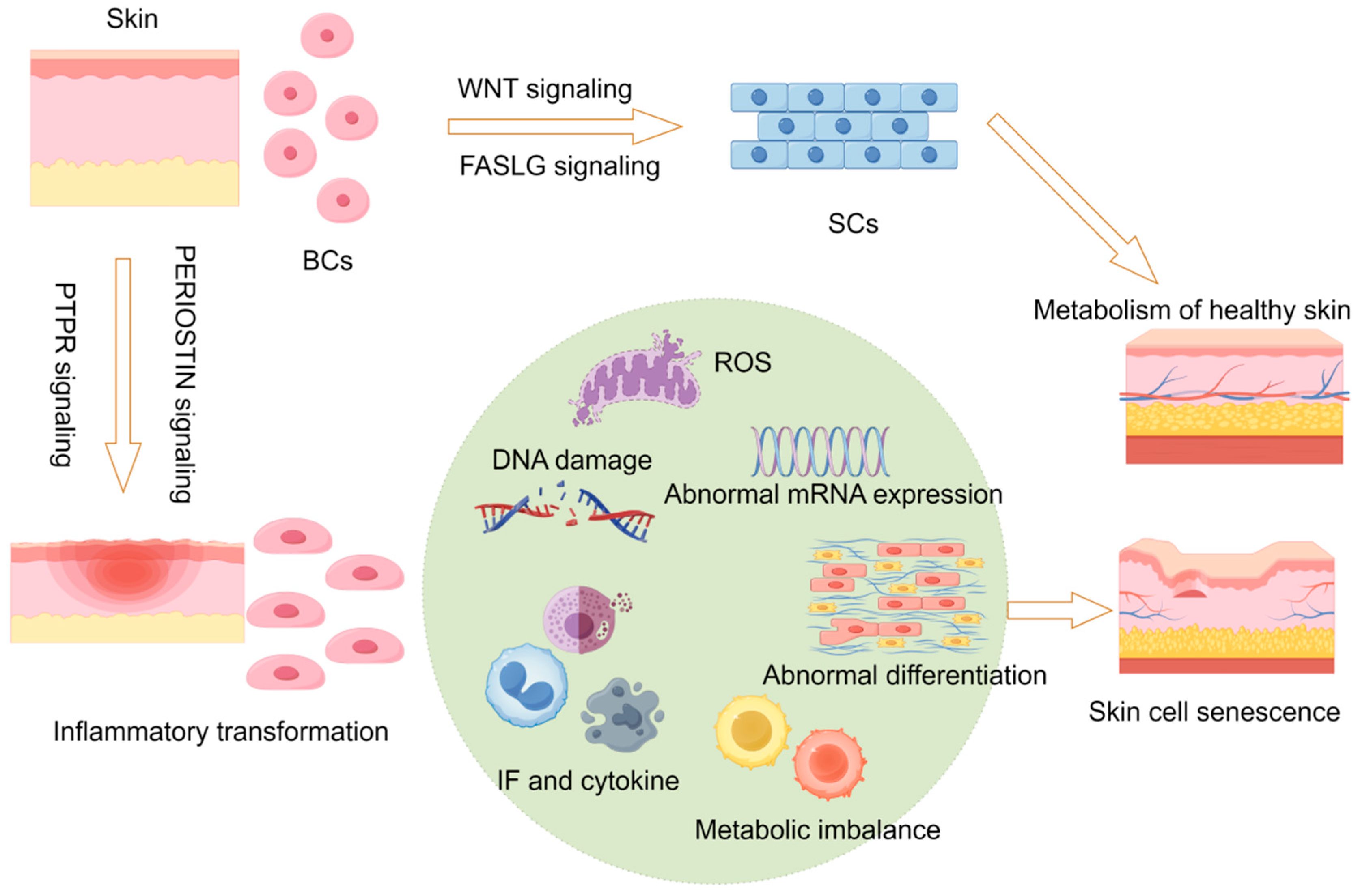
2.8. Hypothetical Molecular Model of Skin Aging
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Single-Cell Sequencing Data Acquisition and Keratinocyte Subgroup Identification
4.2. Developmental Trajectory Analysis of Skin Keratinocytes
4.3. Cell–Cell Communication Network Analysis
4.4. Transcriptome Data Validation
4.5. Genetic Variation and Skin Aging Association Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kammeyer, A.; Luiten, R.M. Oxidation events and skin aging. Ageing Res. Rev. 2015, 21, 16–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, L.; Yue, L.; Huang, Y.; Wang, B.; Liu, P. Uncovering key mechanisms and intervention therapies in aging skin. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2024, 79, 66–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris-Tryon, T.A.; Grice, E.A. Microbiota and maintenance of skin barrier function. Science 2022, 376, 940–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Driskell, R.R.; Lichtenberger, B.M.; Hoste, E.; Kretzschmar, K.; Simons, B.D.; Charalambous, M.; Ferron, S.R.; Herault, Y.; Pavlovic, G.; Ferguson-Smith, A.C.; et al. Distinct fibroblast lineages determine dermal architecture in skin development and repair. Nature 2013, 504, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Byrd, A.L.; Belkaid, Y.; Segre, J.A. The human skin microbiome. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2018, 16, 143–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, S.C. Skin of color: Biology, structure, function, and implications for dermatologic disease. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2002, 46, S41–S62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Matsumura, H.; Kato, T.; Ichinose, S.; Takada, A.; Namiki, T.; Asakawa, K.; Morinaga, H.; Mohri, Y.; De Arcangelis, A.; et al. Stem cell competition orchestrates skin homeostasis and ageing. Nature 2019, 568, 344–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.M.; Liu, Y.X.; Liu, Y.D.; Ho, C.K.; Tsai, Y.T.; Wen, D.S.; Huang, L.; Zheng, D.N.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, Y.F.; et al. Salvianolic acid B protects against UVB-induced skin aging via activation of NRF2. Phytomed. Int. J. Phytother. Phytopharm. 2024, 130, 155676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.; Plazyo, O.; Billi, A.C.; Tsoi, L.C.; Xing, X.; Wasikowski, R.; Gharaee-Kermani, M.; Hile, G.; Jiang, Y.; Harms, P.W.; et al. Single cell and spatial sequencing define processes by which keratinocytes and fibroblasts amplify inflammatory responses in psoriasis. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 3455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, Z.; Long, X.; Zhao, Q.; Zheng, Y.; Song, M.; Ma, S.; Jing, Y.; Wang, S.; He, Y.; Esteban, C.R.; et al. A Single-Cell Transcriptomic Atlas of Human Skin Aging. Dev. Cell 2021, 56, 383–397.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, R.; Jin, S.; Sun, P.; Haensel, D.; Nguyen, Q.H.; Dragan, M.; Kessenbrock, K.; Nie, Q.; Dai, X. Wound healing in aged skin exhibits systems-level alterations in cellular composition and cell-cell communication. Cell Rep. 2022, 40, 111155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Talbott, H.E.; Mascharak, S.; Griffin, M.; Wan, D.C.; Longaker, M.T. Wound healing, fibroblast heterogeneity, and fibrosis. Cell Stem Cell 2022, 29, 1161–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezzani, R.; Favero, G.; Cominelli, G.; Pinto, D.; Rinaldi, F. Skin Aging and the Upcoming Role of Ferroptosis in Geroscience. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 8238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.D.; Watt, F.M. Fibroblast heterogeneity: Implications for human disease. J. Clin. Investig. 2018, 128, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, X.; Hu, Y.; Jiang, L.; Lei, L.; Fu, C.; Wu, S.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, L.; Zhang, F.; Chen, J.; et al. Decreased oxidative stress response and oxidant detoxification of skin during aging. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2023, 216, 111878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarate, R.M.; Hochstetter, J.; Valet, M.; Hallou, A.; Song, Y.; Bansaccal, N.; Ligare, M.; Aragona, M.; Engelman, D.; Bauduin, A.; et al. Dynamic regulation of tissue fluidity controls skin repair during wound healing. Cell 2024, 187, 5298–5315.e19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Gao, X.; Li, M.; Yu, X.; Huang, F.; Wang, Y.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, H.; Shi, Y.; He, X. The role of mitochondrial quality surveillance in skin aging: Focus on mitochondrial dynamics, biogenesis and mitophagy. Ageing Res. Rev. 2023, 87, 101917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydont, V.; Bernard, B.A.; Fortunel, N.O. Age-related evolutions of the dermis: Clinical signs, fibroblast and extracellular matrix dynamics. Mech. Ageing Dev. 2019, 177, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Zamudio, R.I.; Roux, P.F.; de Freitas, J.; Robinson, L.; Doré, G.; Sun, B.; Belenki, D.; Milanovic, M.; Herbig, U.; Schmitt, C.A.; et al. AP-1 imprints a reversible transcriptional programme of senescent cells. Nat. Cell Biol. 2020, 22, 842–855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Choi, S. Deciphering the molecular mechanisms of stem cell dynamics in hair follicle regeneration. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 110–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, C.; Xiao, Z.; Wu, Y.; Ge, C. Diet and Skin Aging-From the Perspective of Food Nutrition. Nutrients 2020, 12, 870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, Z.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, X.; Chen, B.; Yin, H.; Gu, C.; Fang, X.; Zhu, R.; Yu, T.; Mi, W.; et al. A dysregulated sebum-microbial metabolite-IL-33 axis initiates skin inflammation in atopic dermatitis. J. Exp. Med. 2022, 219, e20212397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elpa, D.P.; Chiu, H.Y.; Wu, S.P.; Urban, P.L. Skin Metabolomics. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2021, 32, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baron, R.; Kneissel, M. WNT signaling in bone homeostasis and disease: From human mutations to treatments. Nat. Med. 2013, 19, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nejak-Bowen, K.; Monga, S.P. Wnt-β-catenin in hepatobiliary homeostasis, injury, and repair. Hepatology 2023, 78, 1907–1921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebel, C.; Lendahl, U. Notch Signaling in Development, Tissue Homeostasis, and Disease. Physiol. Rev. 2017, 97, 1235–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wajant, H. The Fas signaling pathway: More than a paradigm. Science 2002, 296, 1635–1636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moulin, V.; Plamondon, M. Differential expression of collagen integrin receptor on fetal vs. adult skin fibroblasts: Implication in wound contraction during healing. Br. J. Dermatol. 2002, 147, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuff, C.A.; Kothapalli, D.; Azonobi, I.; Chun, S.; Zhang, Y.; Belkin, R.; Yeh, C.; Secreto, A.; Assoian, R.K.; Rader, D.J.; et al. The adhesion receptor CD44 promotes atherosclerosis by mediating inflammatory cell recruitment and vascular cell activation. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 108, 1031–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weng, X.; Maxwell-Warburton, S.; Hasib, A.; Ma, L.; Kang, L. The membrane receptor CD44: Novel insights into metabolism. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. TEM 2022, 33, 318–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schikowski, T.; Hüls, A. Air Pollution and Skin Aging. Curr. Environ. Health Rep. 2020, 7, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrero-Navarro, L.; Jansen-Dürr, P.; Cavinato, M. Synergistic interplay of UV radiation and urban particulate matter induces impairment of autophagy and alters cellular fate in senescence-prone human dermal fibroblasts. Aging Cell 2024, 23, e14086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hernandez, D.F.; Cervantes, E.L.; Luna-Vital, D.A.; Mojica, L. Food-derived bioactive compounds with anti-aging potential for nutricosmetic and cosmeceutical products. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2021, 61, 3740–3755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Deng, Y.; Liu, H.; Fu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M.; Feng, Z. Causal Relationship between Meat Intake and Biological Aging: Evidence from Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 2433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janssen, P.; Kliesmete, Z.; Vieth, B.; Adiconis, X.; Simmons, S.; Marshall, J.; McCabe, C.; Heyn, H.; Levin, J.Z.; Enard, W.; et al. The effect of background noise and its removal on the analysis of single-cell expression data. Genome Biol. 2023, 24, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyar, B.; Palmer, D.; Kowald, A.; Murua Escobar, H.; Barrantes, I.; Möller, S.; Akalin, A.; Fuellen, G. Single-cell analyses of aging, inflammation and senescence. Ageing Res. Rev. 2020, 64, 101156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, K.; Korsunsky, I.; Marshall, J.L.; Gao, A.; Watts, G.F.M.; Major, T.; Croft, A.P.; Watts, J.; Blazar, P.E.; Lange, J.K.; et al. Notch signalling drives synovial fibroblast identity and arthritis pathology. Nature 2020, 582, 259–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunomura, S.; Uta, D.; Kitajima, I.; Nanri, Y.; Matsuda, K.; Ejiri, N.; Kitajima, M.; Ikemitsu, H.; Koga, M.; Yamamoto, S.; et al. Periostin activates distinct modules of inflammation and itching downstream of the type 2 inflammation pathway. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 111933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rikken, G.; Meesters, L.D.; Jansen, P.A.M.; Rodijk-Olthuis, D.; van Vlijmen-Willems, I.; Niehues, H.; Smits, J.P.H.; Oláh, P.; Homey, B.; Schalkwijk, J.; et al. Novel methodologies for host-microbe interactions and microbiome-targeted therapeutics in 3D organotypic skin models. Microbiome 2023, 11, 227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxberger, M.; Cenizo, V.; Cassir, N.; La Scola, B. Challenges in exploring and manipulating the human skin microbiome. Microbiome 2021, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solé-Boldo, L.; Raddatz, G.; Schütz, S.; Mallm, J.P.; Rippe, K.; Lonsdorf, A.S.; Rodríguez-Paredes, M.; Lyko, F. Single-cell transcriptomes of the human skin reveal age-related loss of fibroblast priming. Commun. Biol. 2020, 3, 188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hao, Y.; Hao, S.; Andersen-Nissen, E.; Mauck, W.M., 3rd; Zheng, S.; Butler, A.; Lee, M.J.; Wilk, A.J.; Darby, C.; Zager, M.; et al. Integrated analysis of multimodal single-cell data. Cell 2021, 184, 3573–3587.e29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trapnell, C.; Cacchiarelli, D.; Grimsby, J.; Pokharel, P.; Li, S.; Morse, M.; Lennon, N.J.; Livak, K.J.; Mikkelsen, T.S.; Rinn, J.L. The dynamics and regulators of cell fate decisions are revealed by pseudotemporal ordering of single cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 381–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fagherazzi, G.; Aguayo, G.A.; Zhang, L.; Hanaire, H.; Picard, S.; Sablone, L.; Vergès, B.; Hamamouche, N.; Detournay, B.; Joubert, M.; et al. Heterogeneity of glycaemic phenotypes in type 1 diabetes. Diabetologia 2024, 67, 1567–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, T.; Hu, E.; Xu, S.; Chen, M.; Guo, P.; Dai, Z.; Feng, T.; Zhou, L.; Tang, W.; Zhan, L.; et al. clusterProfiler 4.0: A universal enrichment tool for interpreting omics data. Innovation 2021, 2, 100141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Gao, L.; Lu, Y.; He, X.; Xie, J. The potential contribution of aberrant cathepsin K expression to gastric cancer pathogenesis. Discover. Oncol. 2024, 15, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Zhang, L.; Chang, I.; Ramos, R.; Kuan, C.H.; Myung, P.; Plikus, M.V.; Nie, Q. Inference and analysis of cell-cell communication using CellChat. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandiver, A.R.; Irizarry, R.A.; Hansen, K.D.; Garza, L.A.; Runarsson, A.; Li, X.; Chien, A.L.; Wang, T.S.; Leung, S.G.; Kang, S.; et al. Age and sun exposure-related widespread genomic blocks of hypomethylation in nonmalignant skin. Genome Biol. 2015, 16, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hemani, G.; Zheng, J.; Elsworth, B.; Wade, K.H.; Haberland, V.; Baird, D.; Laurin, C.; Burgess, S.; Bowden, J.; Langdon, R.; et al. The MR-Base platform supports systematic causal inference across the human phenome. eLife 2018, 7, e34408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyon, M.S.; Andrews, S.J.; Elsworth, B.; Gaunt, T.R.; Hemani, G.; Marcora, E. The variant call format provides efficient and robust storage of GWAS summary statistics. Genome Biol. 2021, 22, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Wang, Y.; Fu, Z.; Liao, J.; Liu, H.; Zhou, M. Exploring the Causal Effects of Mineral Metabolism Disorders on Telomere and Mitochondrial DNA: A Bidirectional Two-Sample Mendelian Randomization Analysis. Nutrients 2024, 16, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, D.; Feng, Z.; Zhou, M.; Ren, Z.; Zhang, F.; Li, Y. Bioinformatic Evidence Reveals that Cell Cycle Correlated Genes Drive the Communication between Tumor Cells and the Tumor Microenvironment and Impact the Outcomes of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. BioMed Res. Int. 2021, 2021, 4092635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Lu, S.; Pang, Z.; Li, J.; Zhou, M.; Ding, Z.; Feng, Z. Inflammatory Transformation of Skin Basal Cells as a Key Driver of Cutaneous Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062617
Liu S, Lu S, Pang Z, Li J, Zhou M, Ding Z, Feng Z. Inflammatory Transformation of Skin Basal Cells as a Key Driver of Cutaneous Aging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062617
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shupeng, Sheng Lu, Zhiping Pang, Jiacheng Li, Meijuan Zhou, Zhenhua Ding, and Zhijun Feng. 2025. "Inflammatory Transformation of Skin Basal Cells as a Key Driver of Cutaneous Aging" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062617
APA StyleLiu, S., Lu, S., Pang, Z., Li, J., Zhou, M., Ding, Z., & Feng, Z. (2025). Inflammatory Transformation of Skin Basal Cells as a Key Driver of Cutaneous Aging. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2617. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062617





