Flavonoids as Promising Natural Compounds for Combating Bacterial Infections
Abstract
1. Introduction
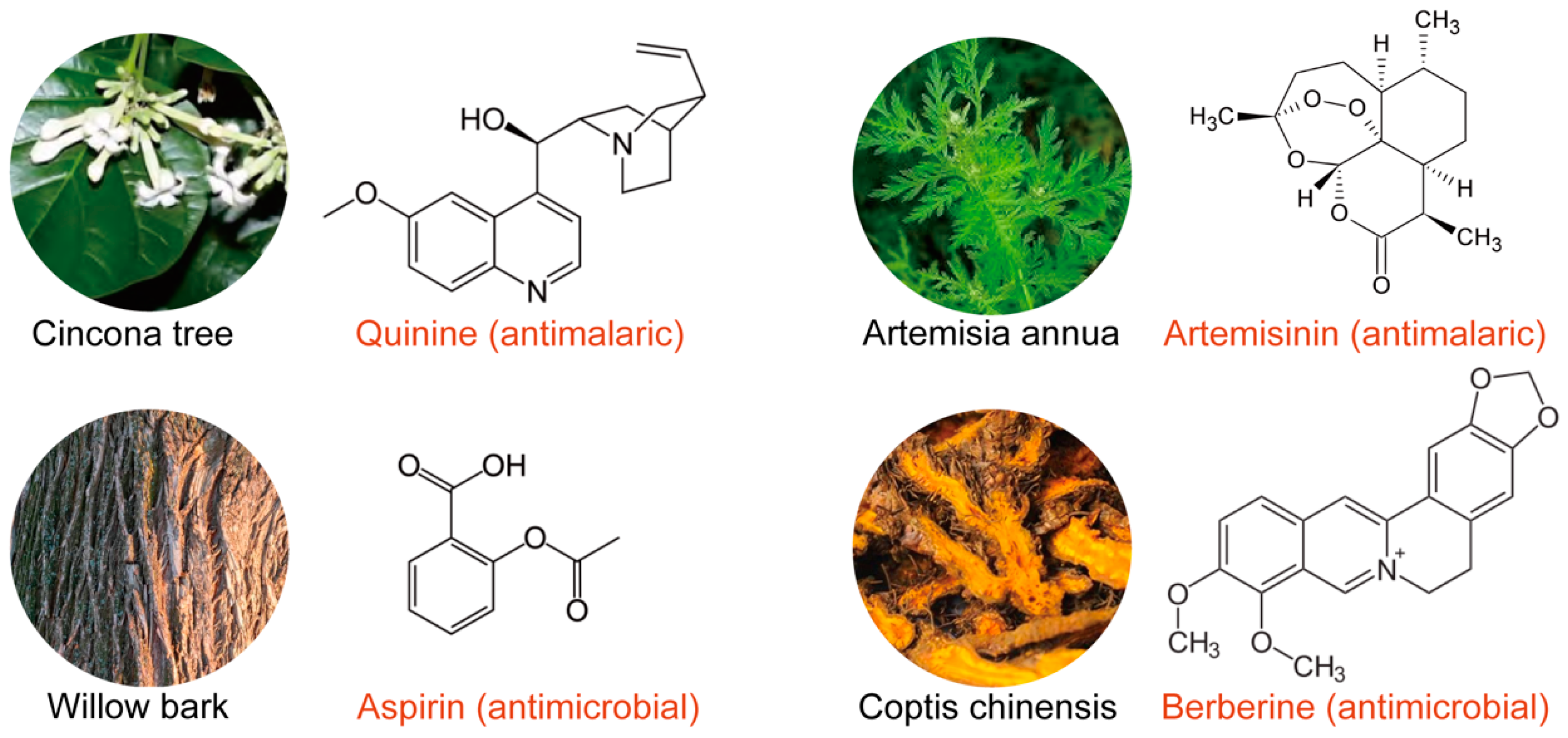
2. Plants as a Potential Source of Antimicrobial Agents
3. Overview of Flavonoids
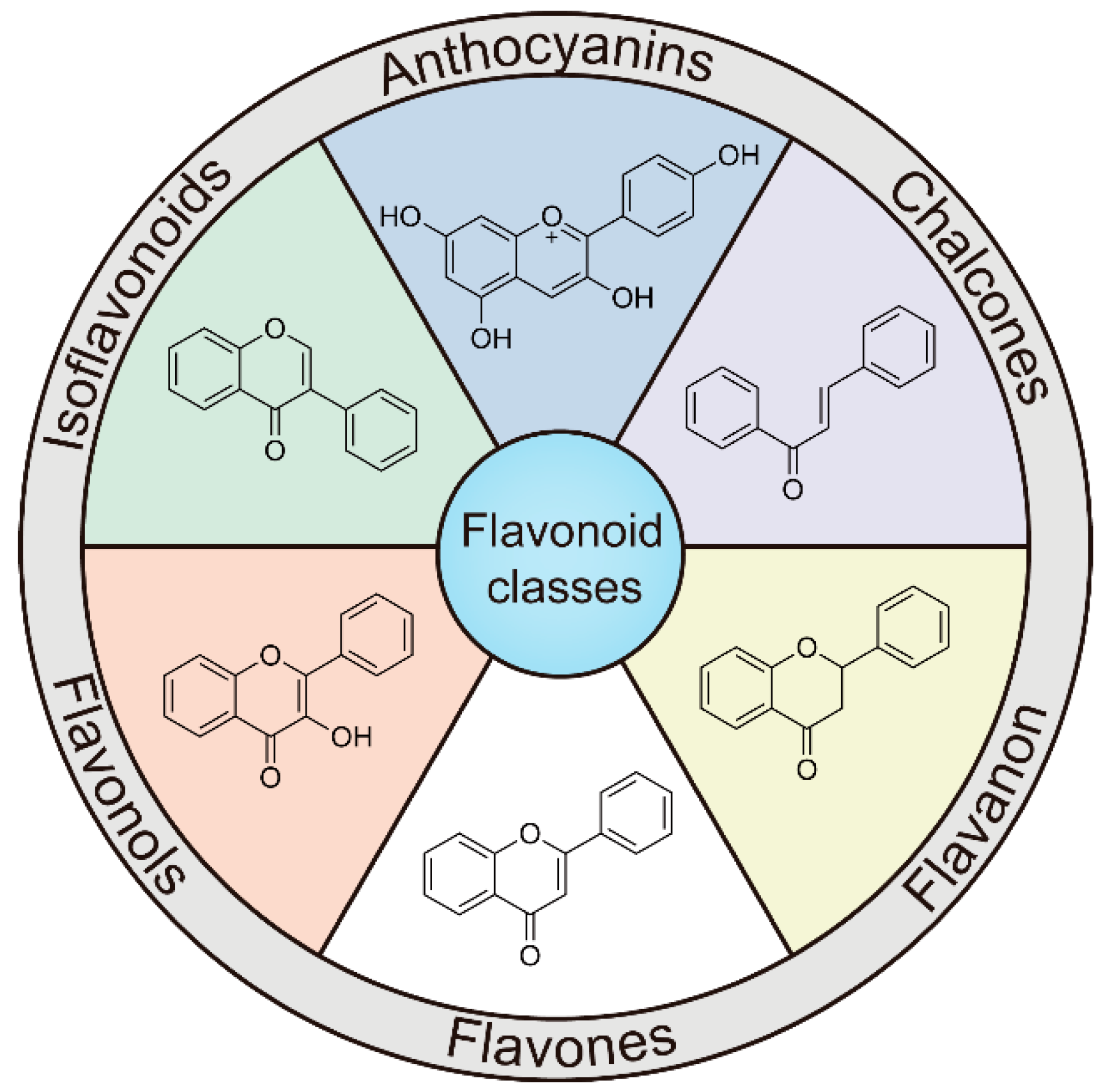
3.1. Introduction and Classification of Flavonoids
3.2. Biological Activities and Health Benefits Associated with Flavonoids
4. Antibacterial Potential of Flavonoids
4.1. Antibacterial Activity of Flavonoids Against Various Bacterial Strains
4.2. Potential Synergistic Combinations of Flavonoids with Antibiotics or Other Natural Compounds
4.3. Antibacterial Efficacy of Flavonoids in In Vivo Studies
4.4. Bioavailability and Strategies to Enhance the Efficacy of Flavonoids
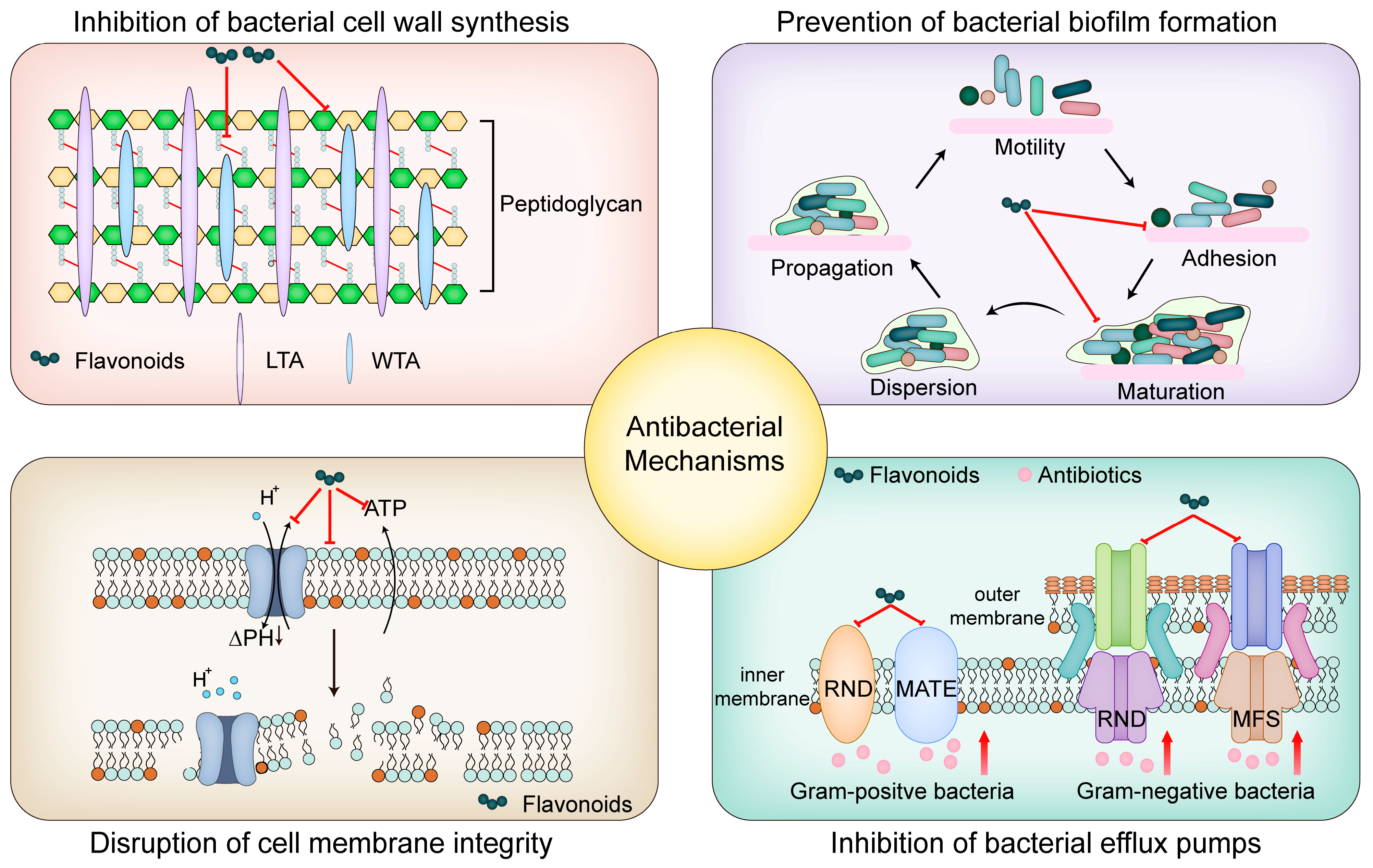
5. Antibacterial Mechanism of Flavonoids
5.1. Inhibition of Bacterial Cell Wall Synthesis
5.2. Inhibition of Bacterial Biofilm Formation
5.3. Disruption of Bacterial Cell Membrane Integrity
5.4. Flavonoids as Inhibitors of Bacterial Efflux Pumps
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad bugs, no drugs: No ESKAPE! An update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kupferschmidt, K. Resistance fighters. Science 2016, 352, 758–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambert, M.L.; Suetens, C.; Savey, A.; Palomar, M.; Hiesmayr, M.; Morales, I.; Agodi, A.; Frank, U.; Mertens, K.; Schumacher, M.; et al. Clinical outcomes of health-care-associated infections and antimicrobial resistance in patients admitted to European intensive-care units: A cohort study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2011, 11, 30–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.Y.; Wang, Y.; Walsh, T.R.; Yi, L.X.; Zhang, R.; Spencer, J.; Doi, Y.; Tian, G.; Dong, B.; Huang, X.; et al. Emergence of plasmid-mediated colistin resistance mechanism MCR-1 in animals and human beings in China: A microbiological and molecular biological study. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 161–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ding, S.; Shen, J.; Zhu, K. Nonribosomal antibacterial peptides that target multidrug-resistant bacteria. Nat. Prod. Rep. 2019, 36, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B. A New Golden Age of Natural Products Drug Discovery. Cell 2015, 163, 1297–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harvey, A.L.; Edrada-Ebel, R.; Quinn, R.J. The re-emergence of natural products for drug discovery in the genomics era. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2015, 14, 111–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, K. The Science of Antibiotic Discovery. Cell 2020, 181, 29–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.; Huang, H.; Xie, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, C.; Jia, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, T.; et al. Biosynthesis of ilamycins featuring unusual building blocks and engineered production of enhanced anti-tuberculosis agents. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janthawornpong, K.; Krasutsky, S.; Chaignon, P.; Rohmer, M.; Poulter, C.D.; Seemann, M. Inhibition of IspH, a [4Fe-4S]2+ enzyme involved in the biosynthesis of isoprenoids via the methylerythritol phosphate pathway. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2013, 135, 1816–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, H.H.; Kim, K.J.; Cha, J.D.; Kim, H.K.; Lee, Y.E.; Choi, N.Y.; You, Y.O. Antimicrobial activity of berberine alone and in combination with ampicillin or oxacillin against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Med. Food 2005, 8, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osbourn, A. Secondary metabolic gene clusters: Evolutionary toolkits for chemical innovation. Trends Genet. 2010, 26, 449–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.M.; Yang, Z.J.; Xie, Q.; Zhang, Z.K.; Zhang, H.; Ma, J.Y. Natural products for treating colorectal cancer: A mechanistic review. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2019, 117, 109142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand David, A.V.; Arulmoli, R.; Parasuraman, S. Overviews of Biological Importance of Quercetin: A Bioactive Flavonoid. Pharmacogn. Rev. 2016, 10, 84–89. [Google Scholar]
- Sarbu, L.G.; Bahrin, L.G.; Babii, C.; Stefan, M.; Birsa, M.L. Synthetic flavonoids with antimicrobial activity: A review. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019, 127, 1282–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portincasa, P.; Calamita, G. Phytocompounds modulating Aquaporins: Clinical benefits are anticipated. Food Chem. 2019, 274, 642–650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raksat, A.; Maneerat, W.; Andersen, R.J.; Pyne, S.G.; Laphookhieo, S. Antibacterial Prenylated Isoflavonoids from the Stems of Millettia extensa. J. Nat. Prod. 2018, 81, 1835–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Chen, M.; Lam, P.Y.; Dini-Andreote, F.; Dai, L.; Wei, Z. Multifaceted roles of flavonoids mediating plant-microbe interactions. Microbiome 2022, 10, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behl, T.; Kumar, K.; Brisc, C.; Rus, M.; Nistor-Cseppento, D.C.; Bustea, C.; Aron, R.A.C.; Pantis, C.; Zengin, G.; Sehgal, A.; et al. Exploring the multifocal role of phytochemicals as immunomodulators. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 133, 110959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, B.S.; Claudie, D.J.; Smith, N.M.; Gerber, J.P.; McKinnon, R.A.; Semple, S.J. Flavonoids from the leaves and stems of Dodonaea polyandra: A Northern Kaanju medicinal plant. Phytochemistry 2011, 72, 1883–1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.B.; Ji, J.; Lei, C.; Wang, H.Y.; Zhao, Q.S.; Hou, A.J. Isoprenylated flavonoid and adipogenesis-promoting constituents of Dodonaea viscosa. J. Nat. Prod. 2012, 75, 699–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Yan, Y.; Zhu, J.; Xia, X.; Yuan, G.; Li, S.; Deng, B.; Luo, X. Quinone Pool, a Key Target of Plant Flavonoids Inhibiting Gram-Positive Bacteria. Molecules 2023, 28, 4972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, L.; Hu, X.; Ren, X.; Liu, J.; Liu, X. Antibacterial Modes of Herbal Flavonoids Combat Resistant Bacteria. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 873374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Su, T.; Qiu, Y.; Hua, X.; Ye, B.; Luo, H.; Liu, D.; Qu, P.; Qiu, Z. Novel Opportunity to Reverse Antibiotic Resistance: To Explore Traditional Chinese Medicine With Potential Activity Against Antibiotics-Resistance Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 610070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Culp, E.J.; Waglechner, N.; Wang, W.; Fiebig-Comyn, A.A.; Hsu, Y.P.; Koteva, K.; Sychantha, D.; Coombes, B.K.; Van Nieuwenhze, M.S.; Brun, Y.V.; et al. Evolution-guided discovery of antibiotics that inhibit peptidoglycan remodelling. Nature 2020, 578, 582–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zipperer, A.; Konnerth, M.C.; Laux, C.; Berscheid, A.; Janek, D.; Weidenmaier, C.; Burian, M.; Schilling, N.A.; Slavetinsky, C.; Marschal, M.; et al. Human commensals producing a novel antibiotic impair pathogen colonization. Nature 2016, 535, 511–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Meyer, K.J.; Iinishi, A.; Favre-Godal, Q.; Green, R.; Manuse, S.; Caboni, M.; Mori, M.; Niles, S.; Ghiglieri, M.; et al. A new antibiotic selectively kills Gram-negative pathogens. Nature 2019, 576, 459–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Liu, D.; Zhang, Q.; Guo, P.; Ding, S.; Shen, J.; Zhu, K.; Lin, W. A Marine Antibiotic Kills Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria without Detectable High-Level Resistance. ACS Infect. Dis. 2021, 7, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, L.L.; Schneider, T.; Peoples, A.J.; Spoering, A.L.; Engels, I.; Conlon, B.P.; Mueller, A.; Schäberle, T.F.; Hughes, D.E.; Epstein, S.; et al. A new antibiotic kills pathogens without detectable resistance. Nature 2015, 517, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brinster, S.; Lamberet, G.; Staels, B.; Trieu-Cuot, P.; Gruss, A.; Poyart, C. Type II fatty acid synthesis is not a suitable antibiotic target for Gram-positive pathogens. Nature 2009, 458, 83–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Zhao, Z.; Tang, B.Z. Natural products with aggregation-induced emission properties: From discovery to their multifunctional applications. Sci. Sin. Chim. 2022, 52, 1524–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tu, Y. The discovery of artemisinin (qinghaosu) and gifts from Chinese medicine. Nat. Med. 2011, 17, 1217–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meshnick, S.R. Artemisinin: Mechanisms of action, resistance and toxicity. Int. J. Parasitol. 2002, 32, 1655–1660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balint, G.A. Artemisinin and its derivatives: An important new class of antimalarial agents. Pharmacol. Ther. 2001, 90, 261–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, S.C.; Patchva, S.; Aggarwal, B.B. Therapeutic roles of curcumin: Lessons learned from clinical trials. Aaps J. 2013, 15, 195–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ai, X.; Yu, P.; Peng, L.; Luo, L.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Lai, X.; Luan, F.; Meng, X. Berberine: A Review of its Pharmacokinetics Properties and Therapeutic Potentials in Diverse Vascular Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 762654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Liu, F.; Zhu, K.; Shen, J.Z. Natural Products That Target Virulence Factors in Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13195–13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Han, F.; Song, M.R.; Chen, S.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Zhu, K.; Shen, J.Z. Natural Flavones from Morus alba against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus via Targeting the Proton Motive Force and Membrane Permeability. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 10222–10234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, M.; Ingmer, H. Antibacterial and antifungal properties of resveratrol. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2019, 53, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.S.L.; Tan, L.T.; Chan, K.G.; Yap, W.H.; Pusparajah, P.; Chuah, L.H.; Ming, L.C.; Khan, T.M.; Lee, L.H.; Goh, B.H. Resveratrol-Potential Antibacterial Agent against Foodborne Pathogens. Front. Pharmacol. 2018, 9, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, N.; Usuki, T. Extraction of essential oils from tea tree (Melaleuca alternifolia) and lemon grass (Cymbopogon citratus) using betaine-based deep eutectic solvent (DES). Phytochem. Anal. 2022, 33, 831–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carson, C.F.; Hammer, K.A.; Riley, T.V. Melaleuca alternifolia (Tea Tree) oil: A review of antimicrobial and other medicinal properties. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 50–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fournier-Larente, J.; Morin, M.P.; Grenier, D. Green tea catechins potentiate the effect of antibiotics and modulate adherence and gene expression in Porphyromonas gingivalis. Arch. Oral. Biol. 2016, 65, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsudin, N.F.; Ahmed, Q.U.; Mahmood, S.; Ali Shah, S.A.; Khatib, A.; Mukhtar, S.; Alsharif, M.A.; Parveen, H.; Zakaria, Z.A. Antibacterial Effects of Flavonoids and Their Structure-Activity Relationship Study: A Comparative Interpretation. Molecules 2022, 27, 1149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Q.; Duan, G.; Yu, X. Bioconversion of Flavonoid Glycosides from Hippophae rhamnoides Leaves into Flavonoid Aglycones by Eurotium amstelodami. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panche, A.N.; Diwan, A.D.; Chandra, S.R. Flavonoids: An overview. J. Nutr. Sci. 2016, 5, e47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karsch-Völk, M.; Barrett, B.; Kiefer, D.; Bauer, R.; Ardjomand-Woelkart, K.; Linde, K. Echinacea for preventing and treating the common cold. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, 2014, Cd000530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Mnayer, D.; Morais-Braga, M.F.B.; Carneiro, J.N.P.; Bezerra, C.F.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Salehi, B.; Martorell, M.; Del Mar Contreras, M.; Soltani-Nejad, A.; et al. Echinacea plants as antioxidant and antibacterial agents: From traditional medicine to biotechnological applications. Phytother. Res. 2018, 32, 1653–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, G.Y.; Meng, X.; Gan, R.Y.; Zhao, C.N.; Liu, Q.; Feng, Y.B.; Li, S.; Wei, X.L.; Atanasov, A.G.; Corke, H.; et al. Health Functions and Related Molecular Mechanisms of Tea Components: An Update Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Nakkash, L.; Kubinski, A. Soy Isoflavones and Gastrointestinal Health. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2020, 9, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, J.; Deb, P.K.; Priya, S.; Medina, K.D.; Devi, R.; Walode, S.G.; Rudrapal, M. Dietary Flavonoids: Cardioprotective Potential with Antioxidant Effects and Their Pharmacokinetic, Toxicological and Therapeutic Concerns. Molecules 2021, 26, 4021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, A.; Khan, A.; Ahmad, I.; Alghamdi, S.; Rajab, B.S.; Babalghith, A.O.; Alshahrani, M.Y.; Islam, S.; Islam, M.R. Flavonoids a Bioactive Compound from Medicinal Plants and Its Therapeutic Applications. Biomed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5445291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, A.; Munir, S.; Badshah, S.L.; Khan, N.; Ghani, L.; Poulson, B.G.; Emwas, A.H.; Jaremko, M. Important Flavonoids and Their Role as a Therapeutic Agent. Molecules 2020, 25, 5243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mink, P.J.; Scrafford, C.G.; Barraj, L.M.; Harnack, L.; Hong, C.P.; Nettleton, J.A.; Jacobs, D.R., Jr. Flavonoid intake and cardiovascular disease mortality: A prospective study in postmenopausal women. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2007, 85, 895–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owona, B.A.; Abia, W.A.; Moundipa, P.F. Natural compounds flavonoids as modulators of inflammasomes in chronic diseases. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, J.; Fu, M.; Wang, J.; Huang, F.; Liu, H.; Huangfu, M.; Yu, D.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Guan, X.; et al. PTEN/AKT/mTOR signaling mediates anticancer effects of epigallocatechin-3-gallate in ovarian cancer. Oncol. Rep. 2020, 43, 1885–1896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, D.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; Zhang, Q.; Zhong, P.; Teng, T.; Chen, M.; Xie, Z.; Ji, A.; Li, Y. Epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits the growth and increases the apoptosis of human thyroid carcinoma cells through suppression of EGFR/RAS/RAF/MEK/ERK signaling pathway. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vingtdeux, V.; Dreses-Werringloer, U.; Zhao, H.; Davies, P.; Marambaud, P. Therapeutic potential of resveratrol in Alzheimer’s disease. BMC Neurosci. 2008, 9 (Suppl. S2), S6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.H.; Akter, R.; Bhattacharya, T.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Alkahtani, S.; Arafah, M.W.; Al-Johani, N.S.; Alhoshani, N.M.; Alkeraishan, N.; Alhenaky, A.; et al. Resveratrol and Neuroprotection: Impact and Its Therapeutic Potential in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 619024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.C.; Yang, Z.Q.; Liu, F.; Peng, W.J.; Qu, S.Q.; Li, Q.; Song, X.B.; Zhu, K.; Shen, J.Z. Antibacterial Effect and Mode of Action of Flavonoids From Licorice Against Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Liu, X.; Hao, Z.; Ding, S.; Panichayupakaranant, P.; Zhu, K.; Shen, J. Plant Natural Flavonoids Against Multidrug Resistant Pathogens. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, e2100749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboody, M.S.A.; Mickymaray, S. Anti-Fungal Efficacy and Mechanisms of Flavonoids. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, J.; Huang, Y.Y.; Zhou, Q.; Gao, Y.; Li, Z.; Wu, D.; Yu, S.; Guo, L.; Chen, Z.; Huang, L.; et al. Discovery and Optimization of α-Mangostin Derivatives as Novel PDE4 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Vascular Dementia. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 3370–3380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cushnie, T.P.; Lamb, A.J. Recent advances in understanding the antibacterial properties of flavonoids. Int. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2011, 38, 99–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eid, J.; Jraij, A.; Greige-Gerges, H.; Monticelli, L. Effect of quercetin on lipid membrane rigidity: Assessment by atomic force microscopy and molecular dynamics simulations. BBA Adv. 2021, 1, 100018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, W.H.; Hu, Z.Q.; Okubo, S.; Hara, Y.; Shimamura, T. Mechanism of synergy between epigallocatechin gallate and beta-lactams against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2001, 45, 1737–1742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, H.; Xun, H.; Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Yao, X.; Tang, F. Integrated Metabolomic and Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals the Underlying Antibacterial Mechanisms of the Phytonutrient Quercetin-Induced Fatty Acids Alteration in Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 27217. Molecules 2024, 29, 2266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudano Roccaro, A.; Blanco, A.R.; Giuliano, F.; Rusciano, D.; Enea, V. Epigallocatechin-gallate enhances the activity of tetracycline in staphylococci by inhibiting its efflux from bacterial cells. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 1968–1973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garg, S.; Kumar, R.; Kunimoto, D.; Rayat, G.R. Anti-Mycobacterial Activity of Flavonoid and Pyrimidine Compounds. Molecules 2022, 27, 6714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, D.; Singh, S.K.; Peng, L.; Kaushal, R.; Vílchez, J.I.; Shao, C.; Wu, X.; Zheng, S.; Morcillo, R.J.L.; Paré, P.W.; et al. Flavonoid-attracted Aeromonas sp. from the Arabidopsis root microbiome enhances plant dehydration resistance. ISME J. 2022, 16, 2622–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malczak, I.; Gajda, A. Interactions of naturally occurring compounds with antimicrobials. J. Pharm. Anal. 2023, 13, 1452–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Feng, S.; Liu, X.; Jia, X.; Qiao, F.; Guo, J.; Deng, S. Effects of Traditional Chinese Medicine and its Active Ingredients on Drug-Resistant Bacteria. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 837907. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guan, S.; Zhong, L.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Jin, Y.; Liu, J.; Xiang, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, L.; Wang, D. Molecular docking and proteomics reveals the synergistic antibacterial mechanism of theaflavin with β-lactam antibiotics against MRSA. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 993430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Porwal, P.; Sharma, S.K. Synergistic effect between vancomycin and Traditional Chinese Medicine (TCM) herbs against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) infections. Pharmacol. Res. Mod. Chin. Med. 2024, 13, 100538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Regmi, S.C.; Kim, J.A.; Cho, M.H.; Yun, H.; Lee, C.S.; Lee, J. Apple flavonoid phloretin inhibits Escherichia coli O157:H7 biofilm formation and ameliorates colon inflammation in rats. Infect. Immun. 2011, 79, 4819–4827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carević, T.; Kolarević, S.; Kolarević, M.K.; Nestorović, N.; Novović, K.; Nikolić, B.; Ivanov, M. Citrus flavonoids diosmin, myricetin and neohesperidin as inhibitors of Pseudomonas aeruginosa: Evidence from antibiofilm, gene expression and in vivo analysis. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2024, 181, 117642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Qi, Z.; Liu, Y.; He, W.; Yang, C.; Wang, Q.; Dong, J.; Deng, X. Baicalin Protects Mice from Lethal Infection by Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Brinsi, C.; Jedidi, S.; Sammari, H.; Selmi, H.; Sebai, H. Antidiarrheal, anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects of Anethum graveolens L. fruit extract on castor oil-induced diarrhea in rats. Neurogastroenterol. Motil. 2024, 36, e14892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivyna de Araújo Rêgo, R.; Guedes Silvestre, G.F.; Ferreira de Melo, D.; Albino, S.L.; Pimentel, M.M.; Silva Costa Cruz, S.B.; Silva Wurzba, S.D.; Rodrigues, W.F.; Goulart de Lima Damasceno, B.P.; Cançado Castellano, L.R. Flavonoids-Rich Plant Extracts Against Helicobacter pylori Infection as Prevention to Gastric Cancer. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13, 951125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowack, R.; Schmitt, W. Cranberry juice for prophylaxis of urinary tract infections--conclusions from clinical experience and research. Phytomedicine 2008, 15, 653–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Pandey, A.K. Chemistry and biological activities of flavonoids: An overview. Sci. World J. 2013, 2013, 162750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullen, W.; Edwards, C.A.; Crozier, A. Absorption, excretion and metabolite profiling of methyl-, glucuronyl-, glucosyl- and sulpho-conjugates of quercetin in human plasma and urine after ingestion of onions. Br. J. Nutr. 2006, 96, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rupasinghe, H.P.; Ronalds, C.M.; Rathgeber, B.; Robinson, R.A. Absorption and tissue distribution of dietary quercetin and quercetin glycosides of apple skin in broiler chickens. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1172–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anwar, A.; Masri, A.; Rao, K.; Rajendran, K.; Khan, N.A.; Shah, M.R.; Siddiqui, R. Antimicrobial activities of green synthesized gums-stabilized nanoparticles loaded with flavonoids. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 3122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nalini, T.; Basha, S.K.; Sadiq, A.M.; Kumari, V.S. In vitro cytocompatibility assessment and antibacterial effects of quercetin encapsulated alginate/chitosan nanoparticle. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2022, 219, 304–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Halevas, E.G.; Avgoulas, D.I.; Katsipis, G.; Pantazaki, A.A. Flavonoid-liposomes formulations: Physico-chemical characteristics, biological activities and therapeutic applications. Eur. J. Med. Chem. Rep. 2022, 5, 100059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Dai, T.; Chen, J.; Chen, M.; Liang, R.; Liu, C.; Du, L.; McClements, D.J. Modification of flavonoids: Methods and influences on biological activities. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2023, 63, 10637–10658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, H.L.; Lee, J.C.; Lee, K.; Lee, J.M.; Nam, H.J.; Bhoo, S.H.; Lee, T.H.; Lee, S.W.; Cho, M.H. Biochemical Characterization of a Flavonoid O-methyltransferase from Perilla Leaves and Its Application in 7-Methoxyflavonoid Production. Molecules 2020, 25, 4455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlowska, J.; Potaniec, B.; Zarowska, B.; Aniol, M. Synthesis and Biological Activity of Novel O-Alkyl Derivatives of Naringenin and Their Oximes. Molecules 2017, 22, 1485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, K.; Chauhan, D.N.; Chauhan, N.S.; Mishra, P. Recent Advancement in Prodrugs, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Brückner, M.; Westphal, S.; Domschke, W.; Kucharzik, T.; Lügering, A. Green tea polyphenol epigallocatechin-3-gallate shows therapeutic antioxidative effects in a murine model of colitis. J. Crohns Colitis 2012, 6, 226–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colombo, M.; Michels, L.R.; Teixeira, H.F.; Koester, L.S. Flavonoid delivery by solid dispersion: A systematic review. Phytochem. Rev. 2022, 21, 783–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- dos Santos Lima, B.; Shanmugam, S.; de Souza Siqueira Quintans, J.; Quintans-Júnior, L.J.; de Souza Araújo, A.A. Inclusion complex with cyclodextrins enhances the bioavailability of flavonoid compounds: A systematic review. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 1337–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, T.; Ji, M.; Sun, Y.; Yan, T.; Zhao, J.; Zhang, H.; Wang, Z. Preparation and characterization of baicalein/hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex for enhancement of solubility, antioxidant activity and antibacterial activity using supercritical antisolvent technology. J. Incl. Phenom. Macrocycl. Chem. 2020, 96, 285–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Górniak, I.; Bartoszewski, R.; Króliczewski, J. Comprehensive review of antimicrobial activities of plant flavonoids. Phytochem. Rev. 2019, 18, 241–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siti Aisiah, R.K.R. Wendy Alexander Tanod, Fatmawati Fatmawati, Noor Arida Fauzana, Olga Olga, Putut Har Riyadi, Metabolomic profiling of Jeruju (Acanthus ilicifolius) leaf extract with antioxidant and antibacterial activity on Aeromonas hydrophila growth. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2022, 12, 57–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, M.; Haque, M.A.; Kaur, P. Computational and Biophysical Approaches to Identify Cell Wall-Associated Modulators in Salmonella enterica serovar Typhi. In The Bacterial Cell Wall: Methods and Protocols; Ton-That, H., Ed.; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2024; pp. 35–55. [Google Scholar]
- Biharee, A.; Sharma, A.; Kumar, A.; Jaitak, V. Antimicrobial flavonoids as a potential substitute for overcoming antimicrobial resistance. Fitoterapia 2020, 146, 104720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pathak, D.; Mazumder, A. Potential of Flavonoids as Promising Phytotherapeutic Agents to Combat Multidrug-Resistant Infections. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2024, 25, 1664–1692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anek, P.; Kumpangcum, S.; Roytrakul, S.; Khanongnuch, C.; Saenjum, C.; Phannachet, K. Antibacterial Activities of Phenolic Compounds in Miang Extract: Growth Inhibition and Change in Protein Expression of Extensively Drug-Resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antibiotics 2024, 13, 536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unban, K.; Khatthongngam, N.; Shetty, K.; Khanongnuch, C. Nutritional biotransformation in traditional fermented tea (Miang) from north Thailand and its impact on antioxidant and antimicrobial activities. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2019, 56, 2687–2699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Wang, K.; Hou, C.; Cai, S.; Huang, Y.; Du, Z.; Huang, H.; Kong, J.; Chen, Y. Baicalein Inhibits Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation and the Quorum Sensing System In Vitro. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donlan, R.M.; Costerton, J.W. Biofilms: Survival mechanisms of clinically relevant microorganisms. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2002, 15, 167–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonincontro, G.; Scuderi, S.A.; Marino, A.; Simonetti, G. Synergistic Effect of Plant Compounds in Combination with Conventional Antimicrobials against Biofilm of Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Candida spp. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sathiya Deepika, M.; Thangam, R.; Sakthidhasan, P.; Arun, S.; Sivasubramanian, S.; Thirumurugan, R. Combined effect of a natural flavonoid rutin from Citrus sinensis and conventional antibiotic gentamicin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation. Food Control 2018, 90, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouyang, J.; Sun, F.; Feng, W.; Sun, Y.; Qiu, X.; Xiong, L.; Liu, Y.; Chen, Y. Quercetin is an effective inhibitor of quorum sensing, biofilm formation and virulence factors in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2016, 120, 966–974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Osonga, F.J.; Akgul, A.; Miller, R.M.; Eshun, G.B.; Yazgan, I.; Akgul, A.; Sadik, O.A. Antimicrobial Activity of a New Class of Phosphorylated and Modified Flavonoids. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 12865–12871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, S.; Wade, J.D.; Liu, S. De Novo Design of Flavonoid-Based Mimetics of Cationic Antimicrobial Peptides: Discovery, Development, and Applications. Acc. Chem. Res. 2021, 54, 104–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, J.J.; Lin, S.; Bai, Y.; Sin, W.W.L.; Aung, T.T.; Li, J.; Chandra, V.; Pervushin, K.; Beuerman, R.W.; Liu, S. Antimicrobial activity profiles of Amphiphilic Xanthone derivatives are a function of their molecular Oligomerization. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2018, 1860, 2281–2298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chi, X.Q.; Zi, C.T.; Li, H.M.; Yang, L.; Lv, Y.F.; Li, J.Y.; Hou, B.; Ren, F.C.; Hu, J.M.; Zhou, J. Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationships of mangostin analogs as cytotoxic agents. RSC Adv. 2018, 8, 41377–41388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Koh, J.J.; Aung, T.T.; Lim, F.; Li, J.; Zou, H.; Wang, L.; Lakshminarayanan, R.; Verma, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Symmetrically Substituted Xanthone Amphiphiles Combat Gram-Positive Bacterial Resistance with Enhanced Membrane Selectivity. J. Med. Chem. 2017, 60, 1362–1378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Quispe, C.; Imran, M.; Rauf, A.; Nadeem, M.; Gondal, T.A.; Ahmad, B.; Atif, M.; Mubarak, M.S.; Sytar, O.; et al. Genistein: An Integrative Overview of Its Mode of Action, Pharmacological Properties, and Health Benefits. Oxid. Med. Cell Longev. 2021, 2021, 3268136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamut, A.; Peterlin Mašič, L.; Kikelj, D.; Tomašič, T. Efflux pump inhibitors of clinically relevant multidrug resistant bacteria. Med. Res. Rev. 2019, 39, 2460–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Varela, M.F.; Stephen, J.; Bharti, D.; Lekshmi, M.; Kumar, S. Inhibition of Multidrug Efflux Pumps Belonging to the Major Facilitator Superfamily in Bacterial Pathogens. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rao, M.; Padyana, S.; Km, D.; Kumar, S.; Nayak, B.B.; Varela, M.F. Antimicrobial Compounds of Plant Origin as Efflux Pump Inhibitors: New Avenues for Controlling Multidrug Resistant Pathogens. J. Antimicrob. Agents 2018, 4, 1000159. [Google Scholar]
- Solnier, J.; Martin, L.; Bhakta, S.; Bucar, F. Flavonoids as Novel Efflux Pump Inhibitors and Antimicrobials Against Both Environmental and Pathogenic Intracellular Mycobacterial Species. Molecules 2020, 25, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weston, N.; Sharma, P.; Ricci, V.; Piddock, L.J.V. Regulation of the AcrAB-TolC efflux pump in Enterobacteriaceae. Res. Microbiol. 2018, 169, 425–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xu, H.; Huang, T.; Liu, G.; Cao, H.; Lin, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Yao, X. Fuzheng Touxie Jiedu Huayu Decoction inhibits the MexAB-OprM efflux pump and quorum sensing-mediated biofilm formation in difficult-to-treat multidrug resistance Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2024, 332, 118365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shriram, V.; Khare, T.; Bhagwat, R.; Shukla, R.; Kumar, V. Inhibiting Bacterial Drug Efflux Pumps via Phyto-Therapeutics to Combat Threatening Antimicrobial Resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 9, 2990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cisowska, A.; Wojnicz, D.; Hendrich, A.B. Anthocyanins as antimicrobial agents of natural plant origin. Nat. Prod. Commun. 2011, 6, 149–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.F.; Liu, J.; Yang, Y.A.; Zhu, H.L. A Review: The Anti-inflammatory, Anticancer and Antibacterial Properties of Four Kinds of Licorice Flavonoids Isolated from Licorice. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 1997–2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Hong, Z.; Qian, J.; Wang, Y.; Wang, S. Protective effect of Jie-Geng-Tang against Staphylococcus aureus induced acute lung injury in mice and discovery of its effective constituents. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 243, 112076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakar, N.S.; Zin, N.M.; Basri, D.F. Synergy of flavone with vancomycin and oxacillin against vancomycin-intermediate Staphyloccus aureus. Pak. J. Pharm. Sci. 2012, 25, 633–638. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Céliz, G.; Daz, M.; Audisio, M.C. Antibacterial activity of naringin derivatives against pathogenic strains. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2011, 111, 731–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, Z.J.; Li, C.; Dai, W.; Lou, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Khan, A.A.; Wan, C. The Anti-Biofilm Activity and Mechanism of Apigenin-7-O-Glucoside Against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Infect. Drug Resist. 2023, 16, 2129–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Periferakis, A.; Periferakis, K.; Badarau, I.A.; Petran, E.M.; Popa, D.C.; Caruntu, A.; Costache, R.S.; Scheau, C.; Caruntu, C.; Costache, D.O. Kaempferol: Antimicrobial Properties, Sources, Clinical, and Traditional Applications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 15054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, X. Antibacterial and anti-inflammatory effects of genistein in Staphylococcus aureus induced osteomyelitis in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 2023, 37, e23298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, J.; Zhang, D.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, S.; Yang, Y.; Xu, N.; Yang, Q.; Ai, X. Genistein Inhibits the Pathogenesis of Aeromonas hydrophila by Disrupting Quorum Sensing Mediated Biofilm Formation and Aerolysin Production. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 753581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Flavonoid Classes | General Structure of Flavonoid | Example | Natural Sources | Strains | MIC (μg/mL) | Target | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthocyanins | 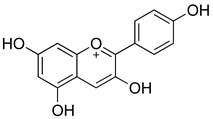 | Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside | Berries (e.g., blueberries, blackberries, raspberries), red cabbage, cherries, purple corn | S. aureus, E. coli, S. typhimurium, L. monocytogenes | 64–512 | Disruption of bacterial cell membrane integrity Inhibition of biofilm formation | [120] |
| Chalcones | 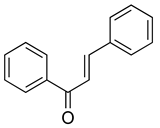 | Licochalcone A | Licorice root (Glycyrrhiza uralensis) | S. aureus, MRSA, B. subtilis, E. coli | 2–64 | Disruption of bacterial cell membrane integrity Inhibition of fatty acid synthesis Inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase | [121,122] |
| Isobavachalcone | Dorstenia barteri | S. aureus, MRSA, E. faecium | 1–8 | Disruption of bacterial cell membrane structure and function | [61] | ||
| Flavanones | 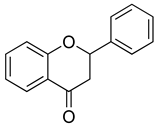 | Naringenin | Citrus fruits (e.g., grapefruits, oranges), tomatoes | B. subtilis, P. aeruginosa | 50–200 | Disruption of bacterial cell membrane integrity Inhibition of bacterial quorum sensing Interference with nucleic acid synthesis | [123,124] |
| Flavones |  | Apigenin | Parsley, celery, chamomile, thyme | S. aureus, B. subtilis, E. coli, L. monocytogenes | 25–100 | Disruption of bacterial cell membrane integrity Inhibition of nucleic acid synthesis | [125] |
| Flavonols | 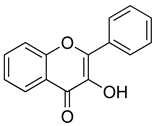 | Quercetin | Tea, broccoli, kale, beans, spinach | S. aureus, P. aeruginosa | 8–256 | Disruption of bacterial cell walls and cell membrane Reduction of expression of virulence factors | [44] |
| Kaempferol | Kale, beans, tea, spinach, broccoli | S. aureus, E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa | 0.5–625 | Disruption of bacterial cell membranes Inhibition of fatty acid biosynthesis and biofilm formation Suppression of DNA gyrase and helicase activity | [126] | ||
| Isoflavonoids | 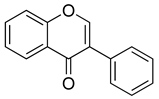 | Genistein | Soybeans, soy products, legumes (e.g., chickpeas, lentils) | S. aureus, A. hydrophila | 32–256 | Inhibition of bacterial DNA gyrase and topoisomerase IV Disruption of cell membrane integrity Inhibition of protein synthesis | [127,128] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Liu, Z.; Zhi, Y.; Mei, C.; Wang, H. Flavonoids as Promising Natural Compounds for Combating Bacterial Infections. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062455
Liu Y, Zhu J, Liu Z, Zhi Y, Mei C, Wang H. Flavonoids as Promising Natural Compounds for Combating Bacterial Infections. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062455
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Ying, Jiajia Zhu, Zhenyi Liu, Yan Zhi, Chen Mei, and Hongjun Wang. 2025. "Flavonoids as Promising Natural Compounds for Combating Bacterial Infections" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062455
APA StyleLiu, Y., Zhu, J., Liu, Z., Zhi, Y., Mei, C., & Wang, H. (2025). Flavonoids as Promising Natural Compounds for Combating Bacterial Infections. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2455. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062455





