Heart Failure—Focus on Kidney Replacement Therapy: Why, When, and How?
Abstract
1. Introduction
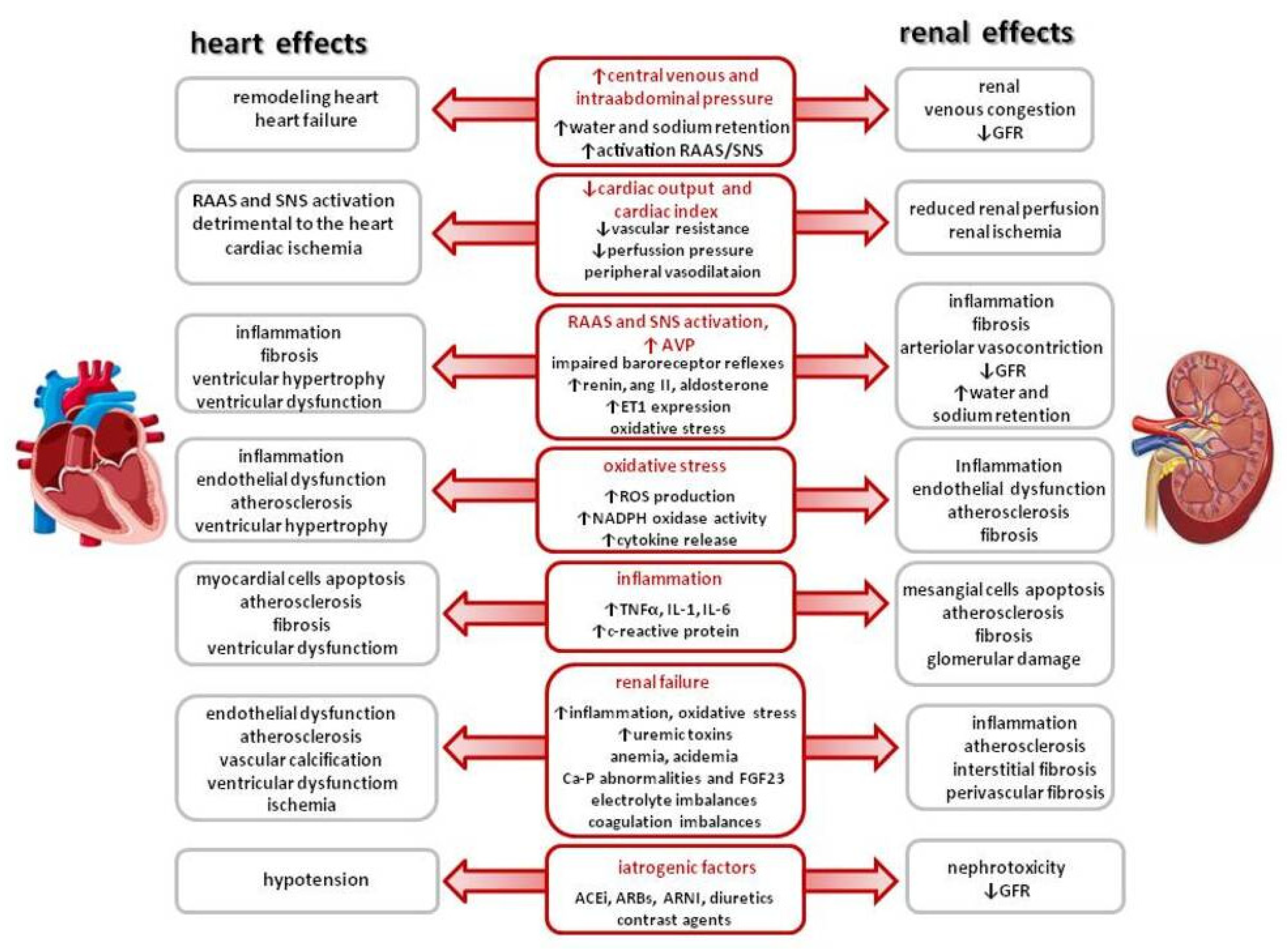
1.1. Cardiorenal Syndrome
1.2. New Concept of Cardiovascular–Kidney–Metabolic (CKM) Syndrome
2. Kidney Replacement Therapy
3. Extracorporeal Ultrafiltration
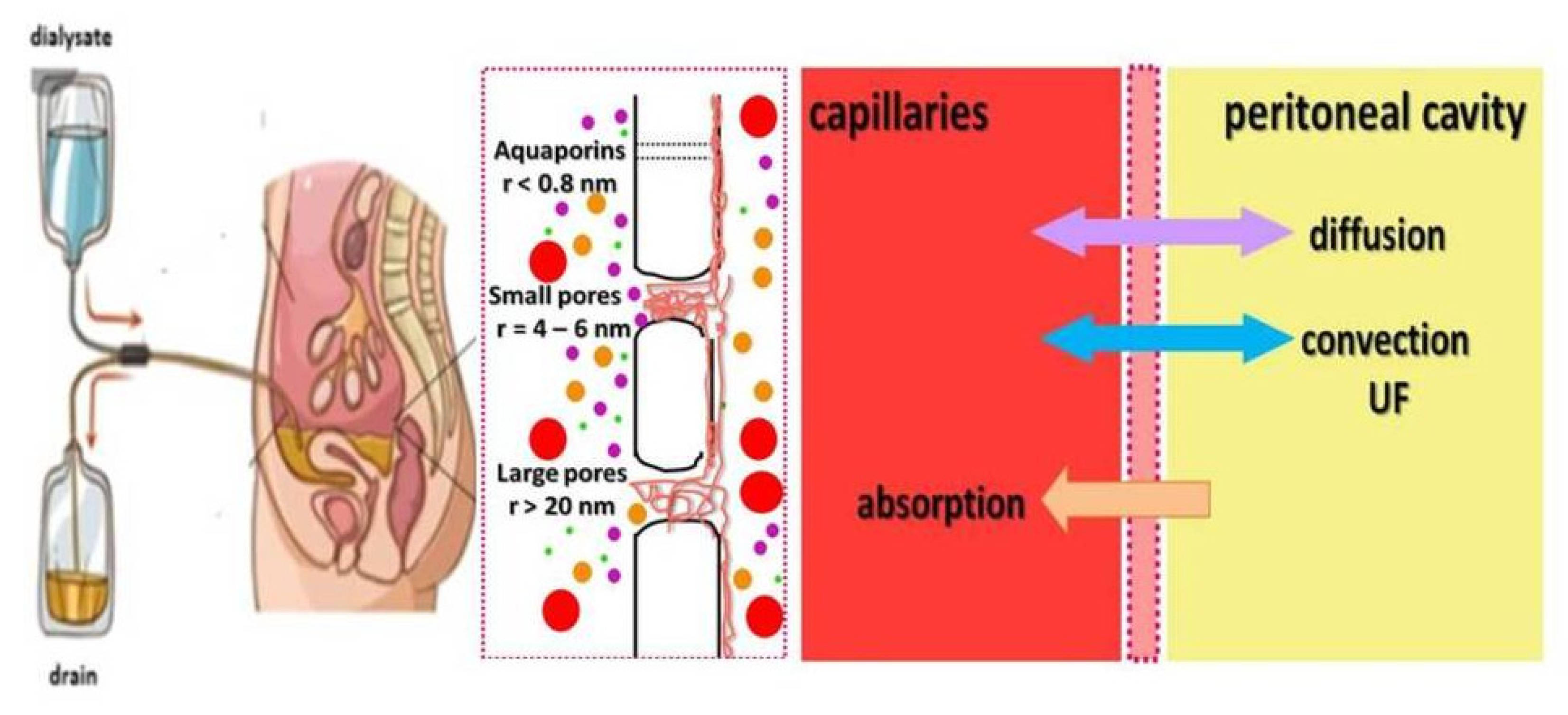
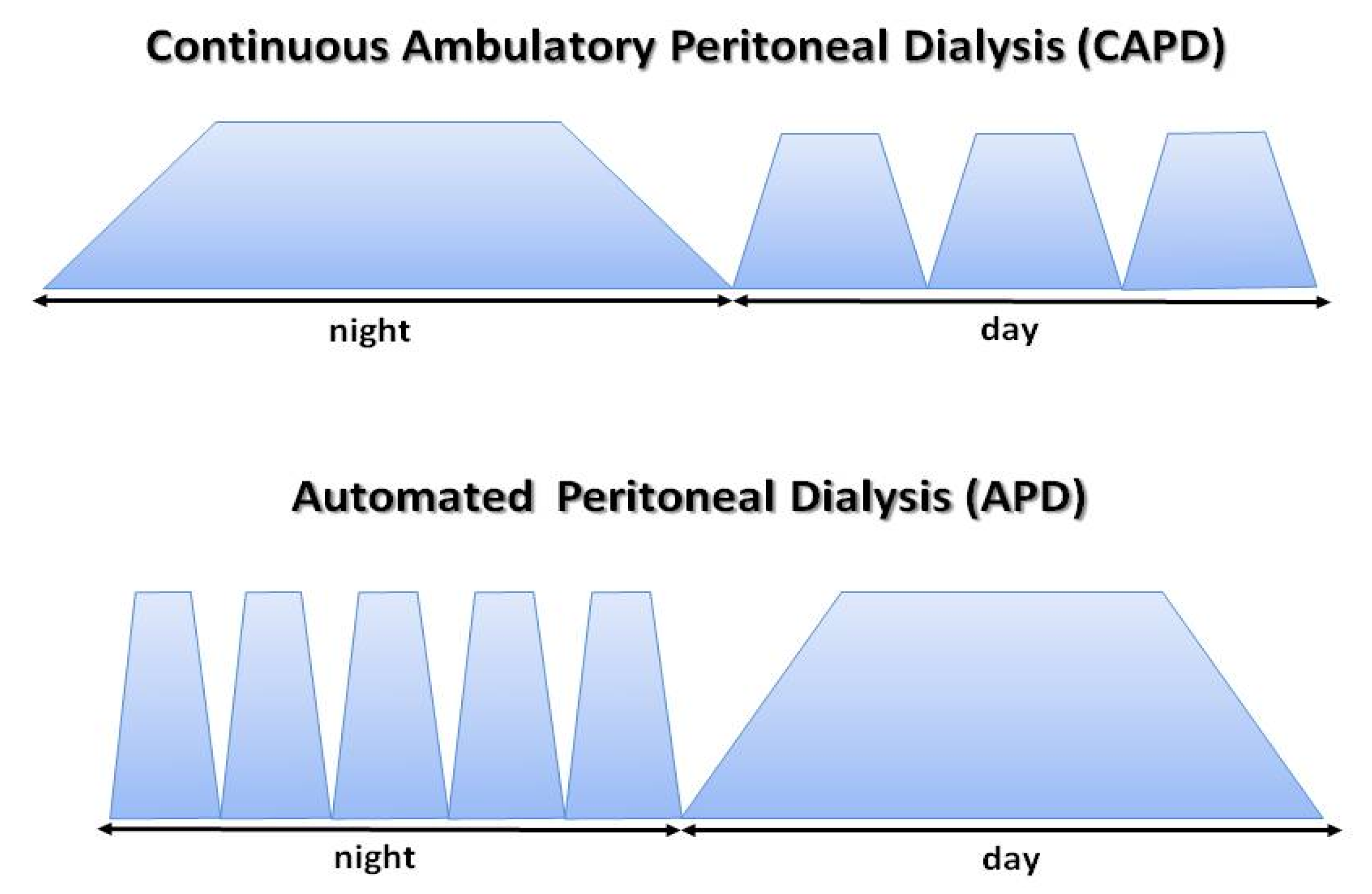
4. Peritoneal Dialysis
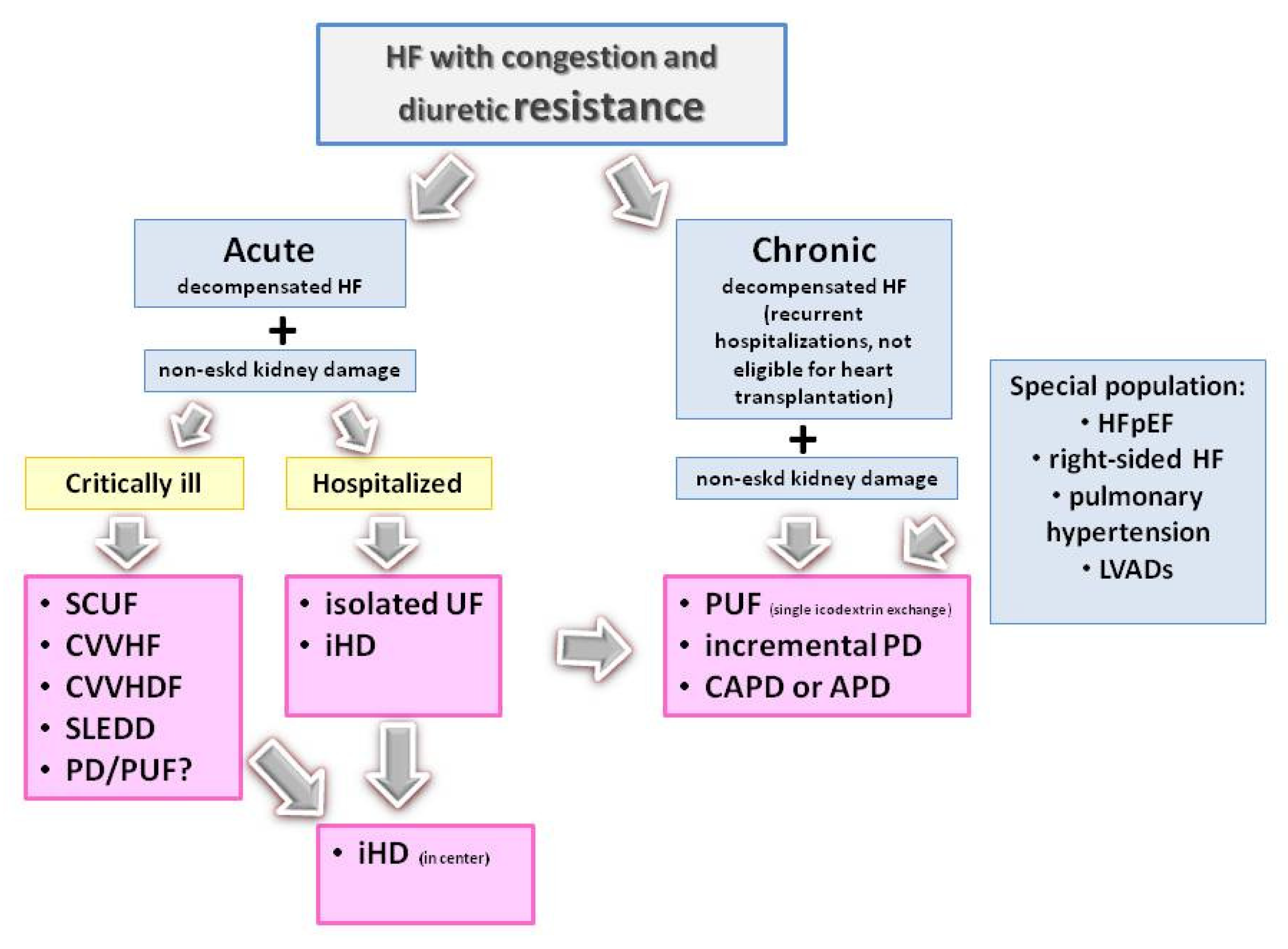
5. When Should Ultrafiltration Be Considered in HF Patients?
6. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Savarese, G.; Becher, P.M.; Lund, L.H.; Seferovic, P.; Rosano, G.M.C.; Coats, A.J.S. Global burden of heart failure: A comprehensive and updated review of epidemiology. Cardiovasc. Res. 2022, 118, 3272–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lippi, G.; Sanchis-Gomar, F. Global epidemiology and future trends of heart failure. AME Med. J. 2020, 5, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harjola, V.-P.; Mullens, W.; Banaszewski, M.; Bauersachs, J.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Chioncel, O.; Collins, S.P.; Doehner, W.; Filippatos, G.S.; Flammer, A.J.; et al. Organ dysfunction, injury and failure in acute heart failure: From pathophysiology to diagnosis and management. A review on behalf of the Acute Heart Failure Committee of the Heart Failure Association (HFA) of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC). Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 821–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cowger, J.A.; Radjef, R. Advanced heart failure therapies and cardiorenal syndrome. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2018, 25, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chioncel, O.; Lainscak, M.; Seferovic, P.M.; Anker, S.D.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Harjola, V.; Parissis, J.; Laroche, C.; Piepoli, M.F.; Fonseca, C.; et al. Epidemiology and one-year outcomes in patients with chronic heart failure and preserved, mid-range and reduced ejection fraction: An analysis of the ESC Heart Failure Long-Term Registry. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 1574–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emmons-Bell, S.; Johnson, C.; Roth, G. Prevalence, incidence and survival of heart failure: A systematic review. Heart 2022, 108, 1351–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cotter, G.; Davison, B.A.; Lam, C.S.P.; Metra, M.; Ponikowski, P.; Teerlink, J.R.; Mebazaa, A. Acute Heart Failure Is a Malignant Process: But We Can Induce Remission. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2023, 12, e031745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazory, A. Fluid overload as a major target in management of cardiorenal syndrome: Implications for the practice of peritoneal dialysis. World J. Nephrol. 2017, 6, 168–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Metra, M.; Davison, B.; Bettari, L.; Sun, H.; Edwards, C.; Lazzarini, V.; Piovanelli, B.; Carubelli, V.; Bugatti, S.; Lombardi, C.; et al. Is Worsening Renal Function an Ominous Prognostic Sign in Patients With Acute Heart Failure? The Role of Congestion and Its Interaction With Renal Function. Circ. Heart Fail. 2012, 5, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mullens, W.; Damman, K.; Testani, J.M.; Martens, P.; Mueller, C.; Lassus, J.; Tang, W.W.; Skouri, H.; Verbrugge, F.H.; Orso, F.; et al. Evaluation of kidney function throughout the heart failure trajectory—A position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2020, 22, 584–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bedo, D.; Beaudrey, T.; Florens, N. Unraveling chronic cardiovascular and kidney disorder through the butterfly effect. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaswami, J.; Bhalla, V.; Blair, J.E.A.; Chang, T.I.; Costa, S.; Lentine, K.L.; Lerma, E.V.; Mezue, K.; Molitch, M.; Mullens, W.; et al. Cardiorenal syndrome: Classification, pathphysiology, diagnosis, and treatment strategies. A scientific statement from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e840–e878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendez, A.B.; Azancot, M.A.; Olivella, A.; Soler, M.A. New aspects in cardiorenal syndrome and HFpEF. Clinical Kidney J. 2022, 15, 1807–1815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronco, C.; Haapio, M.; House, A.A.; Anavekar, N.; Bellomo, R. Cardiorenal Syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 1527–1539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prastaro, M.; Nardi, E.; Paolillo, S.; Santoro, C.; Parlati, A.L.M.; Gargiulo, P.; Basile, C.; Buonocore, D.; Esposito, G.; Filardi, P.P. Cardiorenal syndrome: Pathphysiology as a key to the therapeutic approach in an under-diagnosed disease. J. Clin. Ultrasound. 2022, 50, 1110–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabucanon, T.; Tang, W.H.W. Right heart failure and cardiorenal syndrome. Cardiol. Clin. 2020, 38, 185–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husain-Syed, F.; Gröne, H.; Assmus, B.; Bauer, P.; Gall, H.; Seeger, W.; Ghofrani, A.; Ronco, C.; Birk, H. Congestive nephropathy: A neglected entity? Proposal for diagnostic criteria and future perspectives. ESC Heart Fail. 2021, 8, 183–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallo, G.; Lanza, O.; Savoia, C. New insight in cardiorenal syndrome: From biomarkers to therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5089. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, W.; Wu, L.; Mei, Y.; Cui, S.; Feng, Z.; Chen, X. New insights into the pathophysiological mechanisms underlying cardiorenal syndrome. Aging 2020, 12, 12422–12431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damman, K.; van Deursen, V.M.; Navis, G.; Voors, A.A.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Hillege, H.L. Increased central venous pressure is associated with impaired renal function and mortality in a broad spectrum of patients with cardiovascular disease. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 582–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullens, W.; Abrahams, Z.; Francis, G.S.; Sokos, G.; Taylor, D.O.; Starling, R.C.; Young, J.B.; Tang, W.W. Importance of venous congestion for worsening of renal function in advanced decompensated heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2009, 53, 589–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Bottiglieri, T.; McCullough, P.A. The central role of endothelial dysfunction in cardiorenal syndrome. Cardiorenal Med. 2017, 7, 104–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peesapati, V.S.R.; Sadik, M.; Verma, S.; Attallah, M.A.; Khan, S. Panoramic dominance of the immune system in cardiorenal syndrome type I. Cureus 2020, 12, e9869. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Georgopoulou, T.; Petrakis, I.; Dermitzaki, K.; Pleros, C.; Drosataki, E.; Aletras, G.; Foukarakis, E.; Lioudaki, E.; Androulakis, E.; Stylianou, K. Cardiorenal syndrome: Challenges in everyday clinical practice and key points towards a better management. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellison, D.H. Diuretic resistance: Physiology and therapeutics. Semin. Nephrol. 1999, 19, 581–5971. [Google Scholar]
- Almeshari, K.; Ahlstrom, N.G.; Capraro, F.E.; Wilcox, C.S. A volume-independent component to postdiuretic sodium retention in humans. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1993, 3, 1878–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Virzi, G.M.; Clementi, A.; Battaglia, G.G.; Ronco, C. Multi-Omics Approach: New potential key mechanisms implicated in cardiorenal syndromes. Cardiorenal Med. 2019, 9, 201–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gembillo, G.; Visconti, L.; Giusti, M.A.; Siligato, R.; Gallo, A.; Santoro, D.; Mattina, A. Cardiorenal Syndrome: New pathways and novel biomarkers. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandramohan, D.; Simhadri, P.K.; Jena, N.; Palleti, S.K. Strategies for the Management of Cardiorenal Syndrome in the Acute Hospital Setting. Hearts 2024, 5, 329–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voors, A.A.; Angermann, C.E.; Teerlink, J.R.; Collins, S.P.; Kosiborod, M.; Biegus, J.; Ferreira, J.P.; Nassif, M.E.; Psotka, M.A.; Tromp, J.; et al. The SGLT2 inhibitor empagliflozin in patients hospitalized for acute heart failure: A multinational randomized trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 568–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavalle, C.; Mariani, M.V.; Severino, P.; Palombi, M.; Trivigno, S.; D’Amato, A.; Silvetti, G.; Pierucci, N.; Di Lullo, L.; Chimenti, C.; et al. Efficacy of Modern Therapies for Heart Failure with Reduced Ejection Fraction in Specific Population Subgroups: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cardiorenal Med. 2024, 14, 570–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullens, W.; Damman, K.; Harjola, V.; Mebazaa, A.; Rocca, H.B.; Martens, P.; Testani, J.M.; Tang, W.W.; Orso, F.; Rossignol, P.; et al. The use of diuretics in heart failure with congestion—A position statement from the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2019, 21, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Felker, G.M.; Ellison, D.H.; Mullens, W.; Cox, Z.L.; Testani, J.M. Diuretic therapy for patients with heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 75, 1178–1195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ter Maaten, J.M.; Beldhuis, I.E.; van der Meer, P.; Krikken, J.A.; Postmus, D.; Coster, J.E.; Nieuwland, W.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Voors, A.A.; Damman, K. Natriuresis-guided diuretic therapy in acute heart failure: A pragmatic randomized trial. Nat. Med. 2023, 29, 2625–2632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salah, K.; Kok, W.E.; Eurlings, L.W.; Bettencourt, P.; Pimenta, J.M.; Metra, M.; Verdiani, V.; Tijssen, J.G.; Pinto, Y.M. Competing risk of cardiac status and renal function during hospitalization for acute decompensated heart failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2015, 3, 751–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Griffin, M.; Rao, V.S.; Fleming, J.; Raghavendra, P.; Turner, J.; Mahoney, D.; Wettersten, N.; Maisel, A.; Ivey-Miranda, J.B.; Inker, L.; et al. Effect on survival of concurrent hemoconcentration and increase in creatinine during treatment of acute decompensated heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2019, 124, 1707–1711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McCallum, W.; Tighiouart, H.; Testani, J.M.; Griffin, M.; Konstam, M.A.; Udelson, J.E.; Sarnak, M.J. Rates of reversal of volume overload in hospitalized acute heart failure: Association with lng-term kidney function. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 80, 65–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, C.S.; Testani, J.M.; Pitt, B. The pathophysiology of diuretic resistance and its implications for the management of chronic heart failure. Hypertension 2020, 76, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lameire, N. Renal mechanisms of diuretic resistance in congestive heart failure. Kidney Dial. 2023, 3, 56–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Fu, B.; Liu, Y.; Hao, N.; Ji, Y.; Yang, H. Diuretic resistance in patients with kidney disease: Challenges and opportunities. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 57, 114058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martens, P.; Testani, J.; Damman, K. Prevention and treatment of diuretic resistance in acute heart failure: When to use which combination of diuretics? Eur. Heart J. 2023, 44, 2978–2981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuthbert, J.J.; Clark, A.L. Diuretic treatment in patients with heart failure: Current evidence and future directions—Part I: Looop diuretics. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2024, 21, 101–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cuthbert, J.J.; Cleland, J.G.F.; Clark, A.L. Diuretic treatment in patients with heart failure: Current evidence and future directions-Part II: Combination therapy. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2024, 21, 115–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandenberghe, W.; Gevaert, S.; Kellum, J.A.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Peperstraete, H.; Herck, I.; Decruyenaere, J.; Hoste, E.A. Acute kidney injury in cardiorenal syndrome type I patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiorenal Med. 2016, 6, 116–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Correa, A.; Patel, A.; Chauhan, K.; Shah, H.; Saha, A.; Dave, M.; Poojary, P.; Mishra, A.; Annapureddy, N.; Dalal, S.; et al. National trends and outcomes in dialysis requiring acute kidney injury in heart failure: 2002–2013. J. Cardiac Fail. 2018, 24, 442–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ndumele, C.E.; Rangaswami, J.; Chow, S.L.; Neeland, I.J.; Tuttle, K.R.; Khan, S.S.; Coresh, J.; Mathew, R.O.; Baker-Smith, C.M.; Carnethon, M.R.; et al. American Heart Association. Cardiovascular-Kidney-Metabolic Health: A Presidential Advisory From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2023, 148, 1606–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khayyat-Kholghi, M.; Oparil, S.; Davis, B.R.; Tereshchenko, L.G. Worsening kidney function is the major mechanism of heart failure in hypertension: The ALLHAT study. JACC Heart Fail. 2021, 9, 100–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perl, J.; Brown, E.A.; Chan, C.T.; Couchoud, C.; Davies, S.J.; Kazancioğlu, R.; Klarenbach, S.; Liew, A.; Weiner, D.E.; Cheung, M. Home dialysis: Conclusions from a Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) controversies conference. Kidney Int. 2023, 103, 842–858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarnak, M.J.; Auguste, B.L.; Brown, E.; Chang, A.R.; Chertow, G.M.; Hannan, M.; Herzog, C.A.; Nadeau-Fredette, A.-C.; Tang, W.H.W.; Wang, A.Y.-M.; et al. Cardiovascular Effects of Home Dialysis Therapies: A Scientific Statement From the American Heart Association. Circulation 2022, 146, e146–e164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaswami, J.; McCullough, P.A. Heart failure in end-stage kidney disease: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and therapeutic strategies. Semin. Nephrol. 2018, 38, 600–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jentzer, J.C.; Bihorac, A.; Brusca, S.B.; Del Rio-Pertuz, G.; Kashani, K.; Kazory, A.; Kellum, J.A.; Mao, M.; Moriyama, B.; Morrow, D.A.; et al. Contemporary management of severe acute kidney injury and refractory cardiorenal syndrome. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2020, 76, 1084–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ricci, Z.; Romagnoli, S.; Ronco, C. Renal Replacement Therapy. F1000Research 2016, 5, F1000 Rev-103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gaudry, S.; Palevsky, P.M.; Dreyfus, D. Extracorporeal Kidney-Replacement Therapy for Acute Kidney Injury. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 964–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, J.P.; Neyra, J.A.; Tolwani, A. Continuous KRT: A Contemporary Review. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 18, 256–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nash, D.M.; Przech, S.; Wald, R.; O’Reilly, D. Systematic review and meta-analysis of renal replacement therapy modalities for acute kidney injury in the intensive care unit. J. Crit. Care 2017, 41, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chander, S.; Luhana, S.; Sadarat, F.; Parkash, O.; Rahaman, Z.; Wang, H.Y.; Kiran, F.; Lohana, A.C.; Sapna, F.; Kumari, R. Mortality and mode of dialysis: Meta-analysis and systematic review. BMC Nephrol. 2024, 25, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wald, R.; Gaudry, S.; da Costa, B.R.; Adhikari, N.K.J.; Bellomo, R.; Du, B.; Gallagher, M.P.; Hoste, E.A.; Lamontagne, F.; Joannidis, M.; et al. Initiation of continuous renal replacement therapy versus intermittent hemodialysis in critically ill patients with severe acute kidney injury: A secondary analysis of STARRT-AKI trial. Intensive Care Med. 2023, 49, 1305–1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yang, J.; Eastwood, G.M.; Zhu, G.; Tanaka, A.; Bellomo, R. Extended Daily Dialysis Versus Continuous Renal Replacement Therapy for Acute Kidney Injury: A Meta-analysis. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 322–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Libetta, C.; Sepe, V.; Zucchi, M.; Pisacco, P.; Cosmai, L.; Meloni, F.; Campana, C.; Rampino, T.; Monti, C.; Tavazzi, L.; et al. Intermittent haemodiafiltration in refractory congestive heart failure: BNP and balance of inflammatory cytokines. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2007, 22, 2013–2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Premuzic, V.; Basic-Jukic, N.; Jelakocic, B.; Kes, P. Continuous Veno-Venous Hemofiltration Improves Survival of Patients With Congestive Heart Failure and Cardiorenal Syndrome Compared to Slow Continuous Ultrafiltration. Ther. Apher. Dial. 2017, 21, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leskovar, B.; Furlan, T.; Poznic, S.; Potisek, M.; Adamlje, A. Hemodialysis treatment of cardiorenal syndrome. Clin. Nephrol. 2017, 88, 57–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koev, I.; Bloch, A.; Ouzan, E.; Zwas, D.R.; Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Gotsman, I. Dialysis therapy for volume overload: A feasible option to reduce heart failure hospitalizations in advanced heart failure. Isr. Med. Assoc. J. 2022, 24, 475–479. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kazory, A.; Sgarabotto, L.; Ronco, C. Extracorporeal ultrafiltration for acute heart failure. Cardiorenal Med. 2023, 13, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somaschini, A.; Casirati, A.; Cornara, S.; Demarchi, A.; Mandurino-Mirizzi, A.; Androulakis, E.; Lioudaki, E. Extracorporeal veno-venous ultrafiltration in patients with acute heart failure. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 22, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbani, A.; Pensotti, F.; Provera, A.; Galassi, A.; Guazzi, M.; Castini, D. Extracorporeal veno-venous ultrafiltration in congestive heart failure: What’s the state of the art? A mini-review. World J. Cardiol. 2023, 15, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khine, S.K.; Lam, E.; Dholakia, K.; Scheinerman, S.J.; DeVita, M. Aquapheresis: An institutional experience. Heart Surg. Forum. 2020, 23, E632–E635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, A.; Alvi, M.J.; Afif, J.; Elsayegh, S.; Sahra, S.; El-Charabaty, E. Is Aquapheresis ready for prime time yet for congestive heart failure? A systemic review of the literature. Ren. Replace Ther. 2023, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez-Guerrero, G.; Ronco, C.; Lorenzin, A.; Brendolan, A.; Sgarabotto, L.; Zanella, M.; Reis, T. Development of a new miniaturized system for ultrafiltration. Heart Fail. Rev. 2024, 29, 615–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pourafshar, N.; Karimi, A.; Kazory, A. Extracorporeal ultrafiltration therapy for acute decompensated heart failure. Expert. Rev. Cardiovasc. Ther. 2016, 14, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bart, B.A.; Boyle, A.; Bank, A.J.; Anand, I.; Olivari, M.T.; Kraemer, M.; Mackedanz, S.; Sobotka, P.A.; Schollmeyer, M.; Goldsmith, S.R. Ultrafiltration versus usual care for hospitalized patients with heart failure: The Relief for Acutely Fluid-Overloaded Patients With Decompensated Congestive Heart Failure (RAPID-CHF) trial. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 2043–2046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, M.R.; Saltzberg, M.; O’Sullivan, J.; Sobotka, P. Early ultrafiltration in patients with decompensated heart failure and diuretic resistance. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2005, 46, 2047–2051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Costanzo, M.R.; Guglin, M.E.; Saltzberg, M.T.; Jessup, M.L.; Bart, B.A.; Teerlink, J.R.; Jaski, B.E.; Fang, J.C.; Feller, E.D.; Haas, G.J.; et al. Ultrafiltration versus intravenous diuretics for patients hospitalized for acute decompensated heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2007, 49, 675–683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giglioli, C.; Landi, D.; Cecchi, E.; Chiostri, M.; Gensini, G.F.; Valente, S.; Ciaccheri, M.; Castelli, G.; Romano, S.M. Effects of ULTRAfiltration vs. DIureticS on clinical, biohumoral and haemodynamic variables in patients with deCOmpensated heart failure: The ULTRADISCO study. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2011, 13, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bart, B.A.; Goldsmith, S.R.; Lee, K.L.; Givertz, M.M.; O’Connor, C.M.; Bull, D.A.; Redfield, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Rouleau, J.L.; LeWinter, M.M.; et al. Ultrafiltration in decompensated heart failure with cardiorenal syndrome. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 367, 2296–2304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marenzi, G.; Muratori, M.; Cosentino, E.R.; Rinaldi, E.R.; Donghi, V.; Milazzo, V.; Ferramosca, E.; Borghi, C.; Santoro, A.; Agostoni, P. Continuous ultrafiltration for congestive heart failure: The CUORE trial. J. Card. Fail. 2014, 20, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanzo, M.R.; Negoianu, D.; Jaski, B.E.; Bart, B.A.; Heywood, J.T.; Anand, I.S.; Smelser, J.M.; Kaneshige, A.M.; Chomsky, D.B.; Adler, E.D.; et al. Aquapheresis Versus Intravenous Diuretics and Hospitalizations for Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2016, 4, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanna, M.A.; Tang, W.W.; Teo, B.W.; O’neill, J.O.; Weinstein, D.M.; Lau, S.M.; Van Lente, F.; Starling, R.C.; Paganini, E.P.; Taylor, D.O. Extracorporeal ultrafiltration vs. conventional diuretic therapy in advanced decompensated heart failure. Congest. Heart Fail. 2012, 18, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Wan, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, J.; Li, M.; Jiang, L.; Yuan, F. Efficacy and safety of early ultrafiltration in patients with acute decompensated heart failure with volume overload: A prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2020, 20, 447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ultrafiltration Versus IV Diuretics in Worsening Heart Failure (REVERSE-HF). Available online: https://clinicaltrials.gov/ct2/show/NCT05318105 (accessed on 25 February 2025).
- Yang, Y.; Shen, C.; Lu, J.; Xu, F.; Tong, J.; Jiang, J.; Fu, G. Early continuous ultrafiltration in Chinese patients with congestive heart failure (EUC-CHF): Study protocol for an open-label registry-based prospective clinical trial. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2019, 19, 249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabach, M.; Alkhawam, H.; Shah, S.; Joseph, G.; Donath, E.M.; Moss, N.; Rosenstein, R.S.; Chait, R. Ultrafiltration versus intravenous loop diuretics in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: A meta-analysis of clinical trias. Acta Cardiol. 2017, 72, 132–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siddiqui, W.J.; Kohut, A.R.; Hasni, S.F.; Goldman, J.M.; Silverman, B.; Kelepouris, E.; Eisen, H.J.; Aggarwal, S. Readmission rate after ultrafiltration in acute decompensated heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2017, 22, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wobbe, B.; Wagner, J.; Szabó, D.K.; Rostás, I.; Farkas, N.; Garami, A.; Balaskó, M.; Hartmann, P.; Solymár, M.; Tenk, J.; et al. Ultrafiltration is better than diuretic therapy for volume-overloaded acute heart failure patients: A meta-analysis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2021, 26, 577–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Srivastava, M.; Harrison, N.; Caetano, A.F.S.; Tan, A.R.; Law, M. Ultrafiltration for acute heart failure. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2022, 1, CD013593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, W.; Sana, M.K.; Mustafa, H.U.; Sandhyavenu, H.; Hajduczok, A.; Mir, T.; Fischman, D.L.; Shah, M.; Brailovsky, Y.; Rajapreyar, I.N. Safety and efficacy of ultrafiltration versus decompensated heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2022, 104, 41–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, H.; Ning, B. Efficacy and safety of early ultrafiltration in patients with acute decompensated heart failure: A meta-analysis. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1234092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, K.L.-Y.; Osman, A.R.; Yeoh, E.E.X.; Luangboriboon, J.; Lau, J.F.; Chan, J.J.A.; Yousif, M.; Tse, B.Y.H.; Horgan, G.; Gamble, D.T.; et al. Ultrafiltraion versus diuretics on prognostic cardiac and renal biomarkers in acute decompensated heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haas, D.C.; Hummel, M.; Barrella, P.; Ullah, W.; Yi, M.; Watson, I.I.I.R.A. Ten year real world experience with ultrafiltration for the management of acute decompensated heart failure. Am. Heart J. Plus 2022, 24, 100230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazory, A. Cardiorenal syndrome: Ultrafiltration therapy for heart failure—Trials and tribulations. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2013, 8, 1816–1828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradley, S.M.; Levy, W.C.; Veenstra, D.L. Cost-consequences of ultrafiltration for acute heart failure: A decision model analysis. Circ. Cardiovasc. Qual. Outc 2009, 2, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ross, E.A.; Bellamy, F.B.; Hawig, S.; Kazory, A. Ultrafiltration for Acute Decompensated Heart Failure: Cost, Reimbursement, and Financial Impact. Clin. Cardiol. 2011, 34, 273–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunin, M.; Beckerman, P. The peritoneal membrane—A potential mediator of fibrosis and inflammation among heart failure patients on peritoneal dialysis. Membranes 2022, 12, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blake, P.G.; Daugirdas, J.T. Physiology of Peritoneal Dialysis. In Handbook of Dialysis, 5th ed.; Daugirdas, J.T., Blake, P.G., Ing, T.S., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2015; pp. 392–407. [Google Scholar]
- Bansal, S.; Teitelbaum, I. Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment of Peritoneal Membrane Failure. In Principles and Practice of Dialysis, 5th ed.; Lerma, E.V., Weir, M.R., Eds.; Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; pp. 194–219. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, H.L.; Lu, X.H.; Su, C.Y.; Tang, W.; Wang, T. Potassium metabolism in continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis patients. Ren. Fail. 2014, 36, 748–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gomes, A.M.; Rodriguez-Carmona, A.; Perez Fontan, M.; Muniz, L.; Castro, B.; da Cunha, M.; Falcona, G. Correlates of potassium transport during peritoneal equilibration tests using different dialysate glucose concentrations. Nefrologia 2010, 30, 1–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borrelli, S.; La Milia, V.; De Nicola, L.; Cabiddu, G.; Russo, R.; Provenzano, M.; Minutolo, R.; Conte, G.; Garofalo, C. Sodium removal by peritoneal dialysis: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 231–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharjan, S.R.S.; Davenport, A. Comparison of sodium removal in peritoneal dialysis patients treated by continuous ambulatory and automated peritoneal dialysis. J. Nephrol. 2019, 32, 1011–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miñana, G.; González-Rico, M.; de la Espriella, R.; González-Sánchez, D.; Montomoli, M.; Núñez, E.; Fernández-Cisnal, A.; Villar, S.; Górriz, J.L.; Núñez, J. Peritoneal and urinary transport removal in refractory congestive heart failure patients included In an Ambulatory Peritoneal Dialysis Prograf: Valuable for monitoring the course of the disease. Cardiorenal Med. 2023, 13, 211–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fourtounas, C.; Hardalias, A.; Dousdampanis, P.; Papachristopoulos, B.; Savidaki, E.; Vlachojannis, J.G. Sodium removal in peritoneal dialysis: The role of icodextrin and peritoneal dialysis modalities. Adv. Perit. Dial. 2008, 24, 27–31. [Google Scholar]
- Bammens, B.; Evenepoel, P.; Verbeke, K.; Vanreterghem, Y. Removal of middle molecules and protein bound solutes by peritoneal dialysis and relation to uremic symptoms. Kidney Int. 2003, 64, 2238–2243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunin, M.; Carmon, V.; Arad, M.; Levin-Iaina, N.; Freimark, D.; Holtzman, E.J.; Dinour, D. Inflammatory biomarkers in refractory congestive heart failure patients treated with peritoneal dialysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 590851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtaszek, E.; Małyszko, J.; Matuszkiewicz-Rowuńska, J. Peritoneal ultrafiltration In end-stage congestive heart failure. Cardiol. J. 2014, 21, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Gotloib, L.; Fudin, R.; Yakubovich, M.; Vienken, J. Peritoneal dialysis in refractory end-stage congestive heart failure: A challenge facing a no-win situation. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2005, 20 (Suppl. S70), vii32–vii36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Diez Ojea, B.; Suarez, C.R.; Vidau, P.; Gago, E.; Diaz Molina, B.; Martin, M. Peritoneal dialysis role in heart failure treatment, experience in our center. Nefrologia 2007, 27, 605–611. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Basile, C.; Chimienti, D.; Bruno, A.; Cocola, S.; Libutti, P.; Teutonico, A.; Cazzato, F. Efficacy of peritoneal dialysis with icodextrin in the long-term treatment of refractory congestive heart failure. Perit. Dial. Int. 2009, 19, 116–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cnossen, T.T.; Kooman, J.P.; Konings, C.J.A.M.; Uszko-Lencer, N.H.M.K.; Leunissen, K.M.L.; van der Sande, F.M. Peritoneal dialysis in patients with primary cardiac failure complicated by renal failure. Blood Purif. 2010, 30, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakayama, M.; Nakano, H.; Nakayama, M. Novel therapeutic option for refractory heart failure in elderly patients with chronic kidney disease by incremental peritoneal dialysis. J. Cardiol. 2010, 55, 49–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, J.E.; Ortega, T.; Rodríguez, C.; Díaz-Molina, B.; Martín, M.; Garcia-Cueto, C.; Vidau, P.; Gago, E.; Ortega, F. Efficacy of peritoneal ultrafiltration in the treatment of refractory congestive heart failure. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2010, 25, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotirakopoulos, N.G.; Kalogiannidou, I.M.; Tersi, M.E.; Mavromatidis, K.S. Peritoneal dialysis for patients suffering from severe heart failure. Clin. Nephrology 2011, 76, 124–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Núñez, J.; González, M.; Miñana, G.; Garcia-Ramón, R.; Sanchis, J.; Bodí, V.; Núñez, E.; Puchades, M.J.; Palau, P.; Merlos, P.; et al. Continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis as a therapeutic alternative in patients with advanced congestive heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2012, 14, 540–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruhi, C.; Koçak, H.; Yavuz, A.; Suleymanlar, G.; Ersoy, F.F. Use of peritoneal ultrafiltration in the elderly refractory congestive heart failure patients. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2012, 44, 963–969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, M.; Haastert, B.; Kohnle, M.; Rump, L.C.; Kelm, M.; Trapp, R.; Aker, S. Peritoneal dialysis relives clinical symptoms an is well tolerated in patients with refractory heart failure and chronic kidney disease. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2012, 14, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bertoli, S.V.; Musetti, C.; Ciurlino, D.; Basile, C.; Galli, E.; Gambaro, G.; Iadarola, G.; Guastoni, C.; Carlini, A.; Fasciolo, F.; et al. Peritoneal ultrafiltration in refractory heart failure: A cohort study. Perit. Dial. Int. 2014, 34, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courivaud, C.; Kazory, A.; Crepin, T.; Azar, R.; Bresson-Vautrin, C.; Chalopin, J.M.; Ducloux, D. Peritoneal dialysis reduces the number of hospitalization days in heart failure patients refractory to diuretics. Perit. Dial. Int. 2014, 34, 100–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fröhlich, H.; Katus, H.A.; Täger, T.; Lossnitzer, N.; Grossekettler, L.; Kihm, L.; Zeier, M.; Remppis, A.; Frankenstein, L.; Schwenger, V. Peritoneal ultrafiltration in end-stage chronic heart failure. Clin. Kidney J. 2015, 8, 219–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedau, S.; Chakravarthi, R.; Reddy, V. Ultrafiltration by peritoneal route in refractory chronic congestive cardiac failure. Ind. J. Nephrol. 2018, 28, 298–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavo, N.; Yarragudi, R.; Puttinger, H.; Arfsten, H.; Strunk, G.; Bojic, A.; Hülsmann, M.; Vychytil, A. Parameters associated with therapeutic response Rusing peritoneal dialysis for therapy refraktory heart failure and congestive right ventricular dysfunction. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shao, Q.; Xia, Y.; Zhao, M.; Liu, J.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, B.; Xie, J.; Xu, B.; Gong, R.; Jiang, C. Effectiveness and safety of peritoneal dialysis treatment in patients with refractory congestive heart failure due to chronic cardiorenal syndrome. BioMed Res. Int. 2018, 2018, 6529283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojtaszek, E.; Grzejszczak, A.; Niemczyk, S.; Malyszko, J.; Matuszkiewicz-Rowińska, J. Peritoneal ultrafiltration in the long-term Treatment of chronic heart failure refractory to pharmacological therapy. Front. Physiol. 2019, 10, 310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grossekettler, L.; Schmack, B.; Meyer, K.; Brockmann, C.; Wanninger, R.; Kreusser, M.M.; Frankenstein, L.; Kihm, L.P.; Zeier, M.; Katus, H.A.; et al. Peritoneal dialysis as therapeutic option In heart failure patients. ESC Heart Fail. 2019, 6, 271–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehrotra, R.; Kathuria, P. Place of peritoneal dialysis in the management of treatment-resistant congestive heart failure. Kidney Int. 2006, 70, S67–S71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, R.; Muciño-Bermejo, M.-J.; Ribeiro, L.C.; Tonini, E.; Estremadoyro, C.; Samoni, S.; Sharma, A.; Galván, J.d.J.Z.; Crepaldi, C.; Brendolan, A.; et al. Peritoneal dialysis in patients with refractory congestive heart failure: A systematic review. Cardiorenal Med. 2015, 5, 145–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chionh, C.Y.; Clementi, A.; Poh, C.B.; Finkelstein, F.O.; Cruz, D.N. The use of peritoneal dialysis in heart failure: A systematic review. Perit. Dial. Int. 2020, 40, 527–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales, R.O.; Barbosa, F.; Farre, N. Peritoneal dialysis in heart failure: Focus on kidney and ventricular dysfunction. Rev. Cardiovasc. Med. 2021, 22, 649–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Timόteo, A.T.; Branco Mano, T. Efficacy of peritoneal dialysis in patients with refractory congestive heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Fail. Rev. 2023, 28, 1053–1063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunin, M.; Mini, S.; Abu-Amer, N.; Beckerman, P. Regular at-home abdominal paraceteses via Tenckhoff catheter in patients with refractory congestive heart failure. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2021, 75, e14924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarragudi, R.; Pavo, N.; Bojic, A.; Hülsman, M.; Vychytil, A. Chronic peritoneal drainage in refractory right heart failure and ascites. Kindey Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 1703–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: Executive Summary: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022, 145, e876–e894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cullis, B. Peritoneal dialysis for acute kidney injury: Back on the front-line. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 210–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javaid, M.M.; Ekladious, A.; Khan, B.A. Is it time to give Peritoneal Dialysis its due place in managing acute kidney injury: Lessons learnt from COVID-19 pandemic. Bllod Purif. 2024, 53, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, M.; Cobo, M.; López-Sánchez, P.; García-Magallón, B.; Salazar, M.L.S.; López-Ibor, J.V.; Janeiro, D.; García, E.; Briales, P.S.; Montero, E.; et al. Multidisciplinary approach to patients with heart failure and kidney disease: Preliminary experience of an integrated cardiorenal unit. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 2100–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



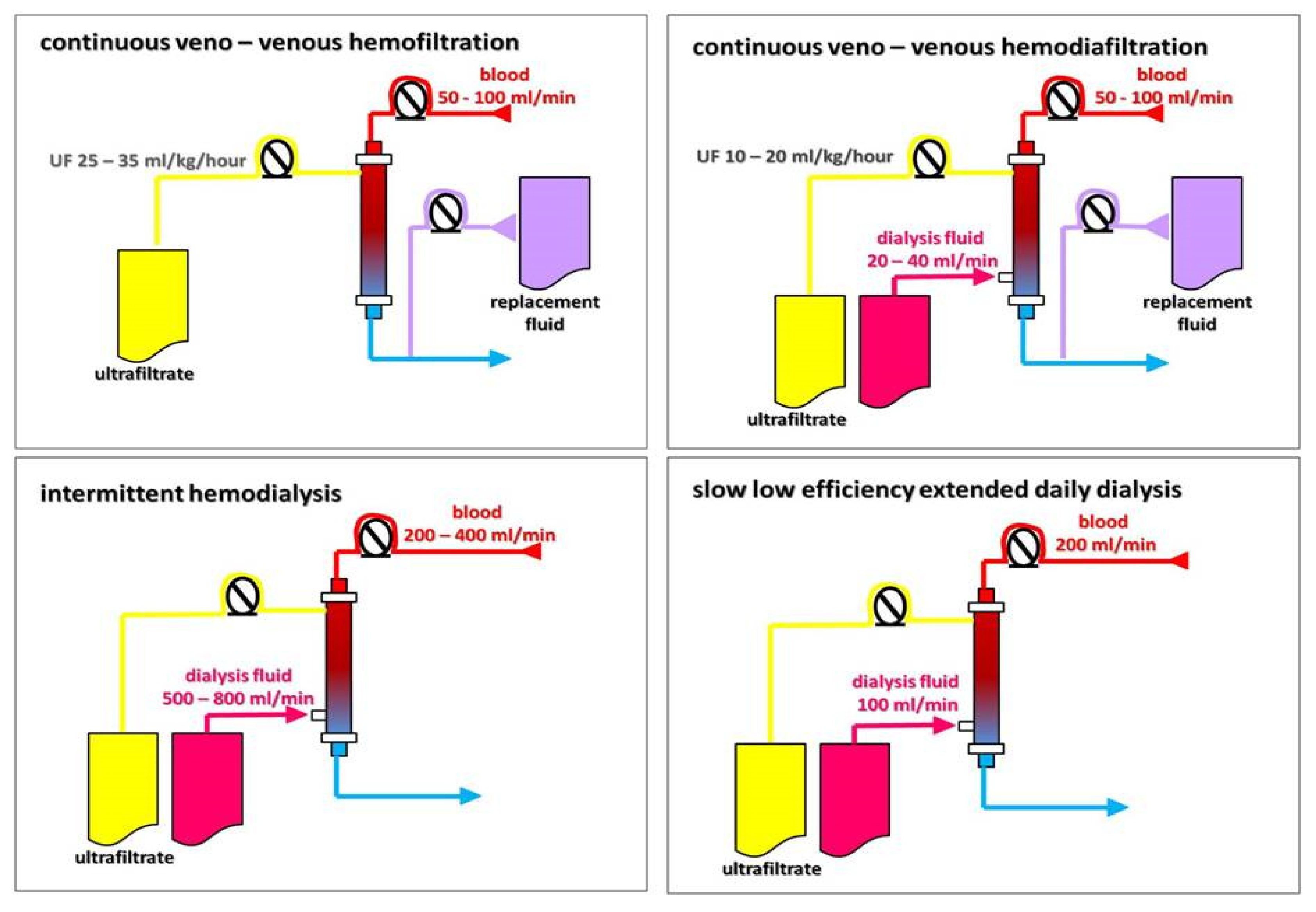

| Modality | Solute Transport | Duration (h) | Blood Flow (mL/min) | Dialysate Flow (mL/min) | Fluid Removal Rate (mL/h) | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCUF | Convection | ≥24 | 50–100 | - | 0–300 | Slow, sustained fluid removal; hemodynamic stability | Immobilization |
| IUF | Convection | 3–5 | 200–350 | - | 0–2000 | Shorter procedure | Higher risk of hemodynamic instability |
| IHD | Diffusion | 3–5 | 200–350 | 300–800 | 0–1000 | Fast small solute and fluid removal, effective control of toxemia and volemia | Higher risk of hemodynamic instability, fluctuating fluid balance |
| SLEDD | Diffusion | 6–16 | 100–300 | 200–300 | 0–500 | Slower solute and fluid removal, effective control of toxemia and volemia; hemodynamic stability | Worse than in convective techniques for large and mid-size molecule removal |
| CVVHF | Convection | ≥24 | 50–100 | - | 0–300 | Slow, sustained solute and fluid removal; large and mid-size molecule removal; hemodynamic stability | Immobilization, anticoagulation mandatory, high staff involvement, high costs |
| CVVHDF | Convection + diffusion | ≥24 | 50–100 | 20–40 | 0–300 | Slow, sustained solute and fluid removal; large and mid-size molecule removal + small solute removal; hemodynamic stability | Immobilization, anticoagulation mandatory, high staff involvement, high costs |
| Rapid and adjustable fluid removal and improvement in symptoms of congestion |
| Higher mass clearance of sodium |
| Lack of neurohormonal activation (SNS, RAAS, and AVP) with long-lasting beneficial effect on the neurohormonal axis |
| Decreased risk of electrolyte abnormalities, e.g., hypokalemia |
| Reduction in renal venous congestion with an improvement in renal hemodynamics |
| Improvement in diuretic resistance, urine output, and natriuresis |
| Decreased hospital length of stay and rate of HF-related hospitalizations |
| Study/ Reference | Pts | Intervention | Control | Follow-Up | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RAPID-CHF (RCT) 2005 [71] | 40 | Single, 8 h course of UF max rate 500 mL/h; diuretics held during the 8 h of UF | Standard CHF therapies | 30 days | ↔ weight loss at 24 h, ↓ dyspnea and CHF symptoms significantly improved, ↔ length of hospital stay |
| EUPHORIA (single arm) 2005 [72] | 20 ADHF, Scr ≥ 1.5 mg/dL, or diuretic resistance | UF max rate 500 mL/h; if SBP fell to ≤80 mm Hg, UF rate reduced to 200 mL/h | N/A | 90 days | Fluid removed 8654 ± 4205 mL; significant improvement in clinical signs and symptoms of volume overload ↓ NYHA class |
| UNLOAD (RCT) 2007 [73] | 200 ADFH, signs and symptoms of congestion | During the first 48 h UF ≤ 500 mL/h; no diuretics; sodium 2 g/d, fluid intake 2 L/d | Sodium 2 g/d, fluid intake 2 L/d; intravenous diuretics ending at 48 h after randomization | 90 days | greater weight loss; ↔ dyspnea score improvement ↓ patients’ rehospitalizations, rehospitalization days ↓ unscheduled visits |
| ULTRADISCO (RCT) 2011 [74] | 30 ADFH, signs and symptoms of congestion | UF 100–300 mL/h adjusted to SBP and HR; no diuretics and vasoactive drugs | Continuous infusion of furosemide 250 mg/24 h adjusted to SBP and HR; no vasoactive drugs | 36 h | ↑ stroke volume index cardiac index, cardiac power; ↓ systemic vascular resistance, NTproBNP, aldosterone ↓ sign and symptom score |
| CARRESS-HF (RCT) 2012 [75] | 188 ADHF, worsening kidney function, persistent congestion | UF rate 200 mL/h; no diuretics; vasoactive drugs only as rescue therapy | Stepped pharmacologic-therapy: diuretics to maintain urine output of 3–5 L/d, vasoactive therapy on the individual patient’s needs | 60 days | ↑ serum creatinine level in UF group; ↔ weight loss |
| CUORE (RCT) 2014 [76] | 56 HF—NYHA class III or IV, LVEF < 40%’ >4 kg weight gain/2 months | 1 or 2 sessions of UF 100–500 mL/h; cumulative fluid removal of >2 L (no more than 75% of the estimated weight increase | IV diuretics, standard of care | 1 year | ↓ rehospitalizations in UF group; ↑ freedom from rehospitalization for HF in UF group |
| AVOID-HF (RCT) 2016 [77] | 224 ADHF; fluid overload on oral loop diuretics | Adjustable UF (138 ± 47 mL/h); restriction in sodium and fluid intake; vasoactive drugs only as rescue therapy | Diuretics to maintain urine output of 3–5 L/d, restriction in sodium and fluid intake; vasoactive drugs only as rescue therapy | 90 days | ↔ days to first HF event |
| Hanna et al. (RCT) 2012 [78] | 36 ADHF, NYHA class III and IV, LVEF <40%, mean PCWP > 20 mm Hg | UF rate 400 mL/h for 6 h decreased to 200 mL/h; no diuretics, vasoactive medications at the physician’s discretion | IV diuretics designated by the treating clinician; vasoactive medications at the physician’s discretion | 90 days | ↓ time to primary endpoint in UF group |
| Hu et al. (RCT) 2020 [79] | 100 ADHF, volume overload | UF (200–300 mL/h) day 1–3; torasemide + tolvaptan days 4–7. | Torasemide + tolvaptan | 90 days | ↑ weight loss and ↑ urine in UF group |
| Reference |
Pts Age (y) |
eGFR/SCr (mL/min/mg/dL) |
NYHA Class | LVEF (%) |
Observation (Months) | 1-Year Survival | Key Findings |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gotloib 2005 [105] | 20 65.7 ± 7.6 | 14.8 ± 3.8 | IV | 31.2 ± 4.7 | 19.8 ± 7.37 | 90 | ↓ NYHA class, ↑ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Diez Ojea 2007 [106] | 5 60 ± 6.3 | 43.6 ± 27.07 | IV | 35 | 13.8 ± 5.6 | N/A | ↓ NYHA class, ↑ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Basile 2009 [107] | 4 71.5 ± 5.6 | Scr 3.55 ± 1.12 | IV | 45 ± 27.7 | 24.3 ± 15.6 | N/A | ↓ NYHA class, ↑ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Cnossen 2010 [108] | 24 67 ± 10 | 14.8 ± 12.1 | N/A | 33 ± 16 | 1.03 ± 0.84 years | N/A | ↔ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Nakayama 2010 [109] | 12 81 ± 6 | 10.5 ± 8.2 | III and IV | 56 ± 10 | Median 26.5 | N/A | ↓ NYHA class, ↔ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Sanchez 2010 [110] | 17 64 ± 9 | 35 ± 6 | III and IV | 33.3 | 15 ± 9 | 82 | ↓ NYHA class, ↑ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Sotirakopoulos 2011 [111] | 19 71.3 ± 8.1 | 23.8 ± 10.6 | III and IV | 28.6 ± 8.6 | median 16 | 68 | ↓ NYHA class, ↑ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Nunez 2012 [112] | 25 75.1 ± 8.2 | Median 33 | III and IV | 40 ± 14 | Median 14 | N/A | ↓ NYHA class, ↔ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Ruhi 2012 [113] | 6 72.8 ± 4.9 | 49 ± 14.6 | III and IV | 28.2 ± 4.5 | 6–36 | N/A | ↓ NYHA class, ↔LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Koch 2012 [114] | 118 73.2 ± 11.4 | 19.2 ± 13.3 | III and IV | Median 43.5 | 1.11 ± 1.17 years | 55 | ↓ NYHA class, ↑ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Bertoli 2014 [115] | 48 74 ± 9 | 21 ± 10 | II, III, and IV | 30 ± 11 | 24 | 85 | ↓ NYHA class, ↑ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Courivaud 2014 [116] | 126 72 ± 11 | 33.5 ± 15 | N/A | 38 ± 19 | 16 ± 16 | 58 | ↑ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Frolich 2015 [117] | 39 67 ± 11 | Median 22 | III and IV | 24 ± 7 | 9.5 | 67 | ↓ NYHA class, ↔ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Hedau 2018 [118] | 30 62.3 ± 7.5 | Scr 3.18 ± 0.98 | III and IV | 29.3 ± 7.4 | 6 | N/A | ↓ NYHA class, ↑ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Pavo 2018 [119] | 40 65 | Median 19.4 | N/A | Median 29 | 12.3 | 55 | ↓ hospitalization |
| Shao 2018 [120] | 14 53.6 ± 15.4 | 27.8 ± 9.87 | III and IV | 24.6 ± 3.78 | 6 | N/A | ↓ NYHA class, ↔ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Wojtaszek 2019 [121] | 15 72 ± 9 | 32 ± 11 | III and IV | 34.3 ± 12.4 | 24 | 93 | ↓ NYHA class, ↑ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
| Grossekettler 2019 [122] | 159 72.8 ± 12.1 | 24 ± 11.3 | II, III, and IV | 31 ± 13 | n.a. | 61 | ↓ NYHA class, ↑ LFEF, ↓ hospitalization |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wojtaszek, E.; Kwiatkowska-Stawiarczyk, M.; Sobieszczańska-Małek, M.; Głogowski, T.; Kaszyńska, A.; Markowski, M.; Małyszko, S.; Małyszko, J. Heart Failure—Focus on Kidney Replacement Therapy: Why, When, and How? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062456
Wojtaszek E, Kwiatkowska-Stawiarczyk M, Sobieszczańska-Małek M, Głogowski T, Kaszyńska A, Markowski M, Małyszko S, Małyszko J. Heart Failure—Focus on Kidney Replacement Therapy: Why, When, and How? International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(6):2456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062456
Chicago/Turabian StyleWojtaszek, Ewa, Marlena Kwiatkowska-Stawiarczyk, Małgorzata Sobieszczańska-Małek, Tomasz Głogowski, Aleksandra Kaszyńska, Michał Markowski, Sławomir Małyszko, and Jolanta Małyszko. 2025. "Heart Failure—Focus on Kidney Replacement Therapy: Why, When, and How?" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 6: 2456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062456
APA StyleWojtaszek, E., Kwiatkowska-Stawiarczyk, M., Sobieszczańska-Małek, M., Głogowski, T., Kaszyńska, A., Markowski, M., Małyszko, S., & Małyszko, J. (2025). Heart Failure—Focus on Kidney Replacement Therapy: Why, When, and How? International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(6), 2456. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26062456








