Enhanced Anti-Tumor Effects of Natural Killer Cell-Derived Exosomes Through Doxorubicin Delivery to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells: Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Study
Abstract
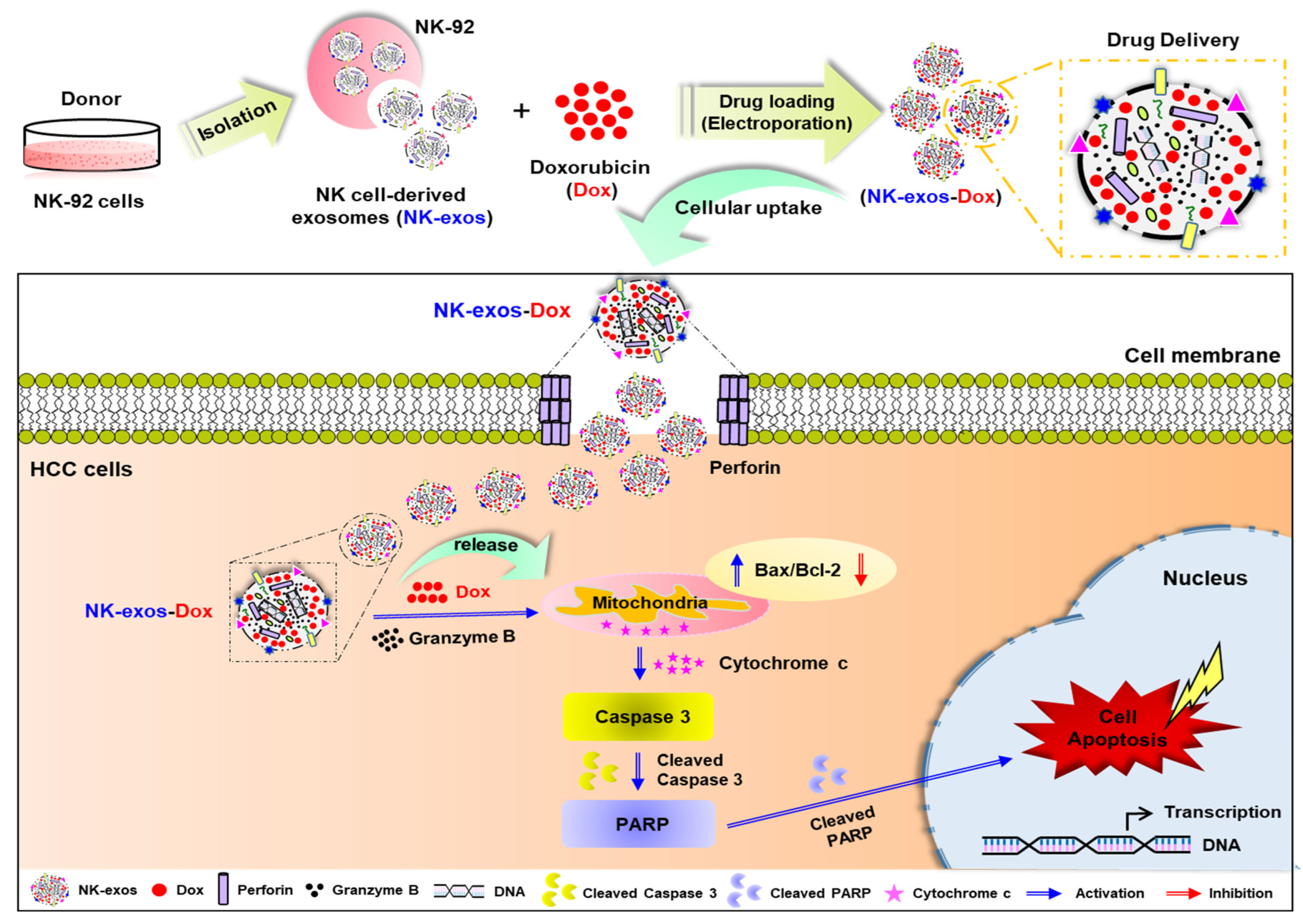
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Characterization of NK-exos-Dox
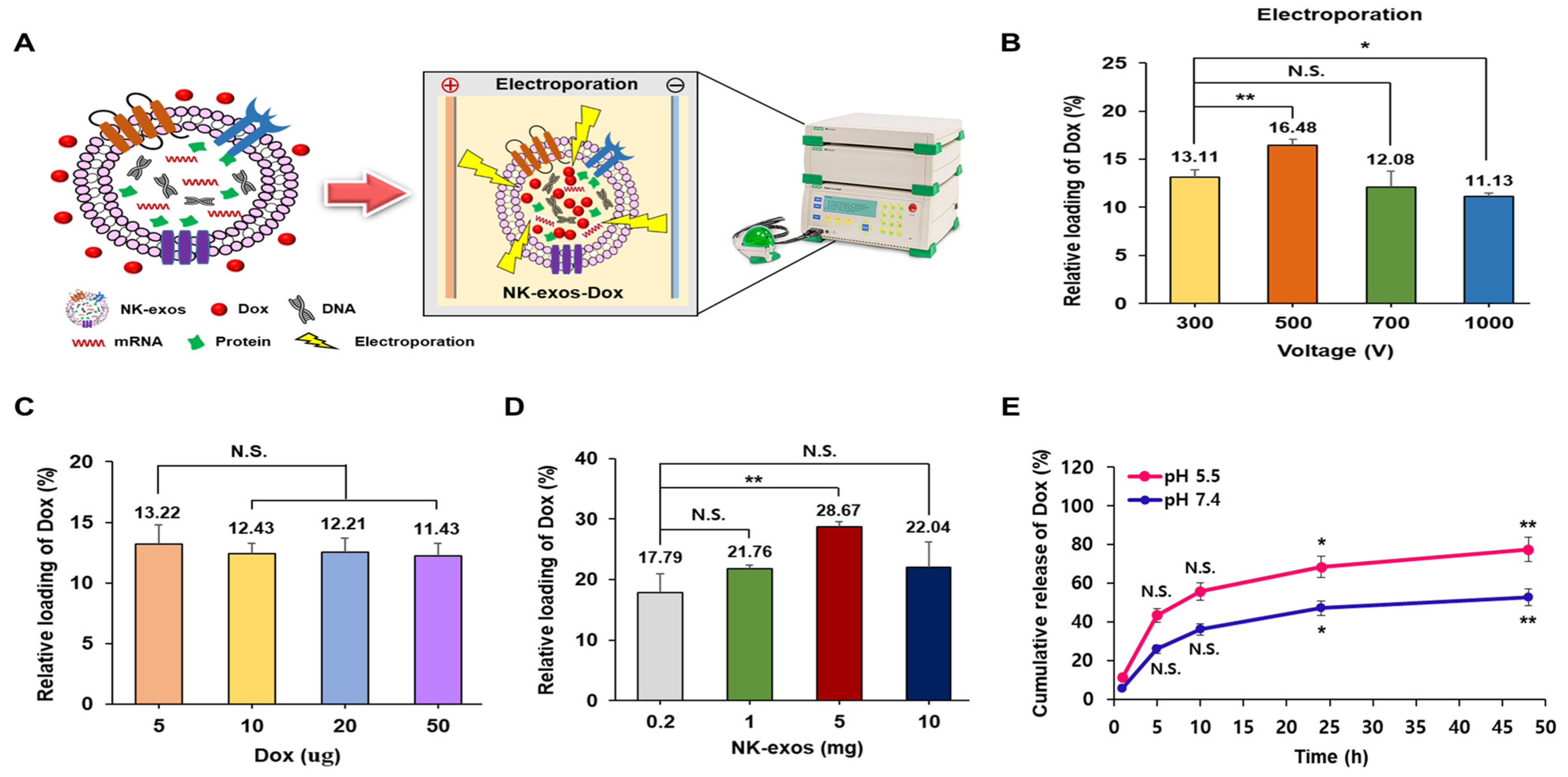
2.2. Loading and Release Efficiency of Dox into NK-exos as a Drug Delivery Carrier
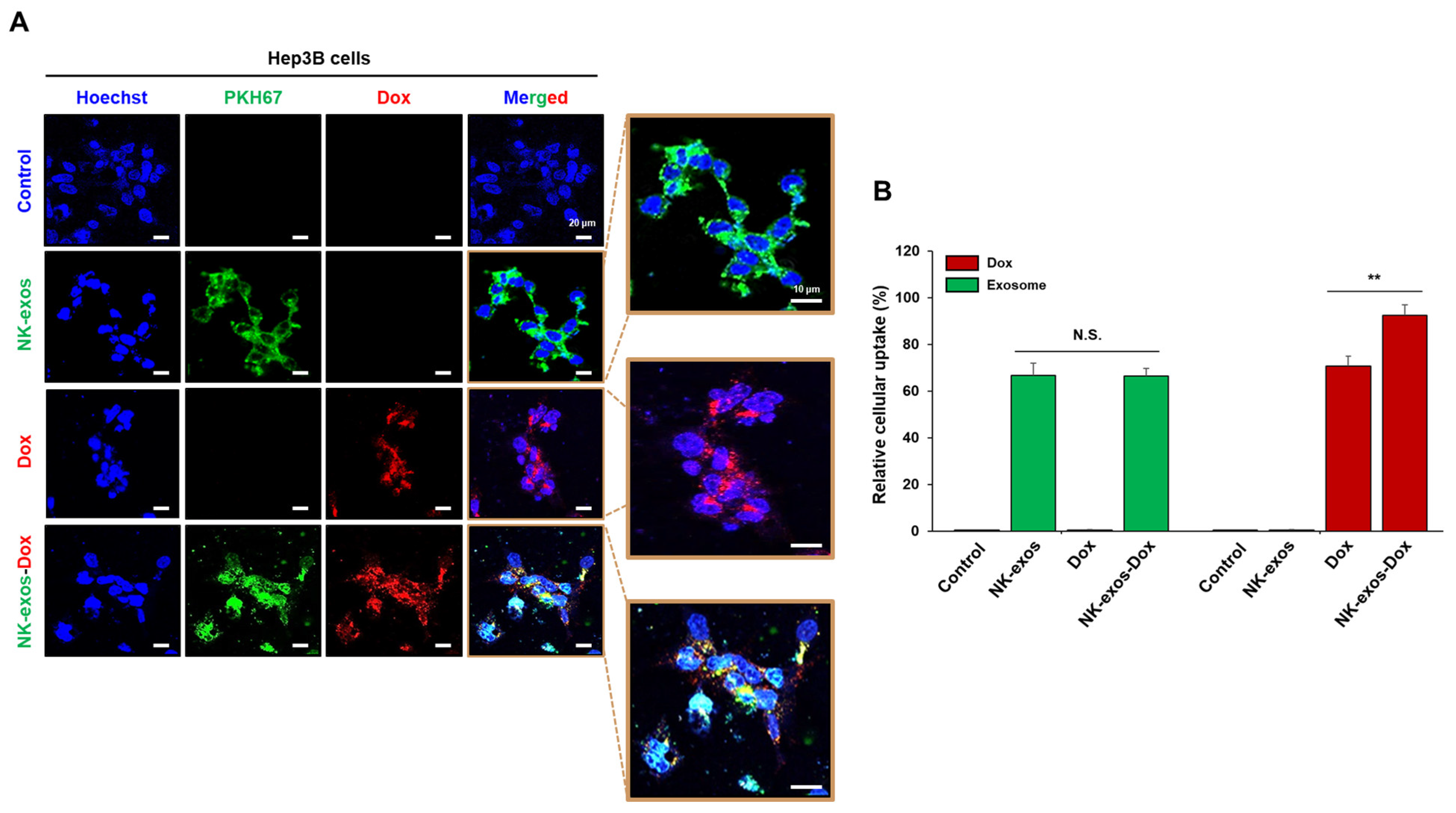
2.3. Uptake of NK-exos-Dox by HCC Cells
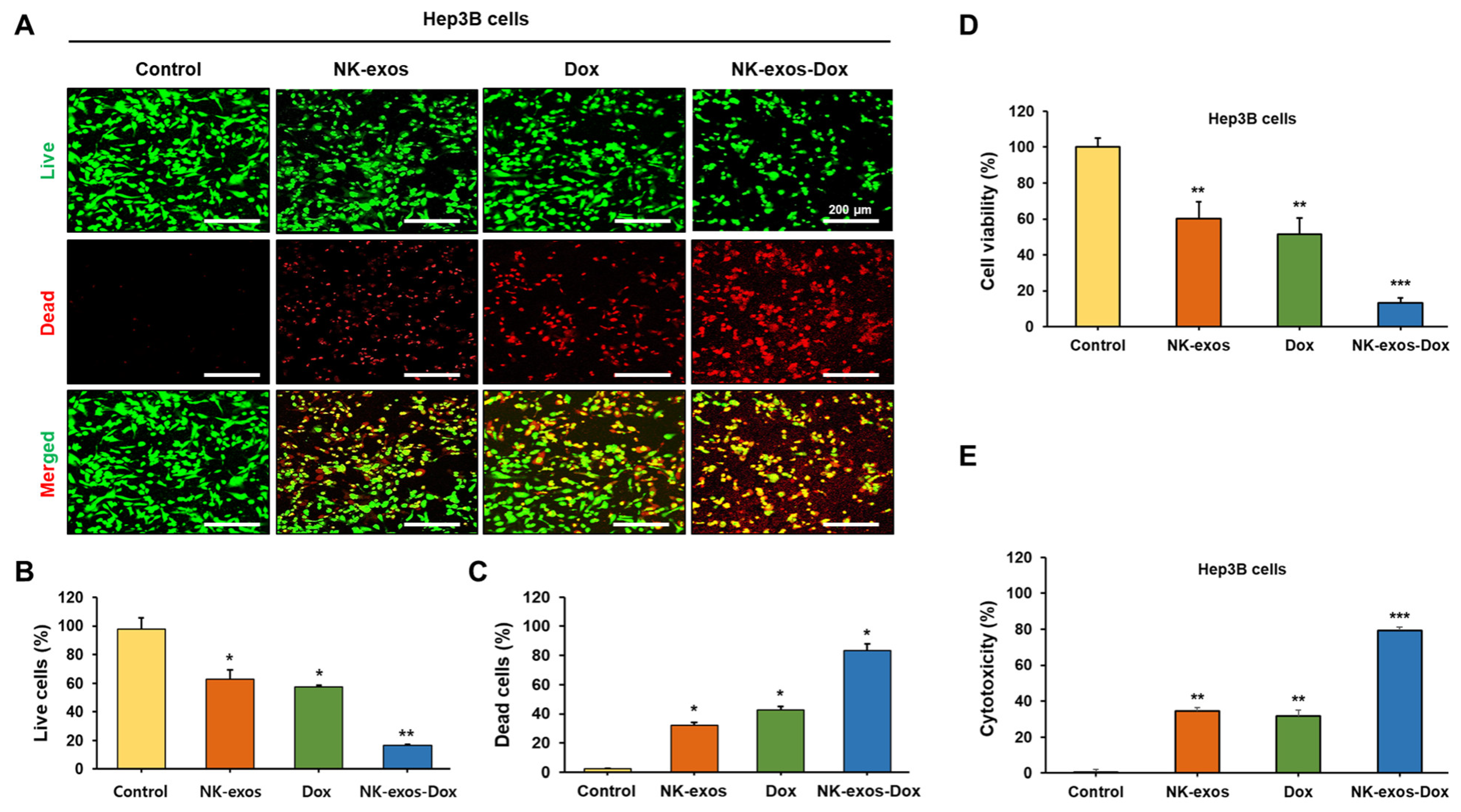
2.4. Improvement of Cytotoxicity and Reduction in Cell Viability by NK-exos-Dox in HCC Cells
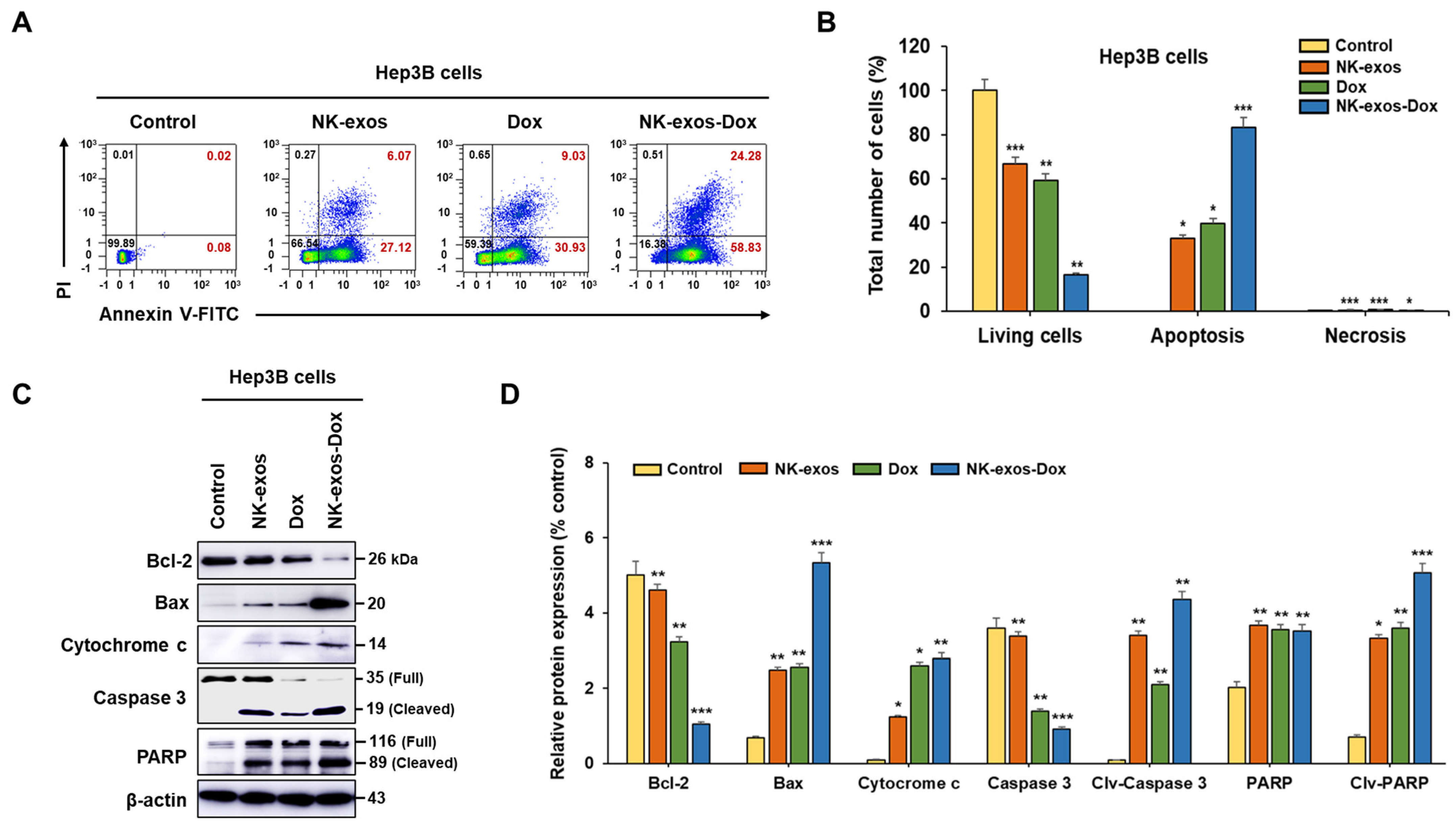
2.5. Enhancement of Apoptotic Activity Induced by NK-exos-Dox in HCC Cells
2.6. Potential Signaling Mechanism of NK-exos-Dox Linked to Apoptosis in HCC Cells
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Cell Culture
4.2. Exosome Isolation
4.3. Exosome Characterization
4.4. Drug Loading and Release
4.5. Exosome Uptake Assay
4.6. Live and Dead Assay
4.7. Cell Cytotoxicity Assay
4.8. Cell Viability Assay
4.9. Apoptosis Analysis
4.10. Western Blot Analysis
Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| HCC | Hepatocellular carcinoma |
| NK-exos | NK cell-derived exosomes |
| NK-exos-Dox | NK-exos loaded with doxorubicin |
| Dox | Doxorubicin |
| PTX | Paclitaxel |
| DDP | Cisplatin |
| CTX | Cyclophosphamide |
| FasL | Fas ligand |
| TNF | Tumor necrosis factor |
| TME | Tumor microenvironment |
| TEM | Transmission electron microscopy |
| DLS | Dynamic light scattering |
| NTA | Nanoparticle tracking analysis |
| SPION | Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticle |
| CCK-8 | Cell counting kit-8 |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| LDH | Lactate dehydrogenase |
| Bax | Bcl-2-associated X protein |
| Bcl-2 | B-cell lymphoma 2 |
| Caspase 3 | Cysteine-aspartic acid protease 3 |
| PARP | Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase |
| Clv | Cleaved |
References
- Balogh, J.; Victor, D., 3rd; Asham, E.H.; Burroughs, S.G.; Boktour, M.; Saharia, A.; Li, X.; Ghobrial, R.M.; Monsour, H.P., Jr. Hepatocellular carcinoma: A review. J. Hepatocell. Carcinoma 2016, 3, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Craig, A.J.; von Felden, J.; Garcia-Lezana, T.; Sarcognato, S.; Villanueva, A. Tumour evolution in hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2020, 17, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Llovet, J.M.; Kelley, R.K.; Villanueva, A.; Singal, A.G.; Pikarsky, E.; Roayaie, S.; Lencioni, R.; Koike, K.; Zucman-Rossi, J.; Finn, R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2021, 7, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fong, Z.V.; Tanabe, K.K. The clinical management of hepatocellular carcinoma in the United States, Europe, and Asia: A comprehensive and evidence-based comparison and review. Cancer 2014, 120, 2824–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimasaki, N.; Coustan-Smith, E.; Kamiya, T.; Campana, D. Expanded and armed natural killer cells for cancer treatment. Cytotherapy 2016, 18, 1422–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leavy, O. Maturation and function of NK cells. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2012, 12, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voskoboinik, I.; Smyth, M.J.; Trapani, J.A. Perforin-mediated target-cell death and immune homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2006, 6, 940–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.; Lu, M.; Petersen, S.; Ashkenazi, A. Apoptosis initiation through the cell-extrinsic pathway. Methods Enzymol. 2014, 544, 99–128. [Google Scholar]
- Sordo-Bahamonde, C.; Lorenzo-Herrero, S.; Payer, A.R.; Gonzalez, S.; Lopez-Soto, A. Mechanisms of Apoptosis Resistance to NK Cell-Mediated Cytotoxicity in Cancer. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitale, M.; Cantoni, C.; Pietra, G.; Mingari, M.C.; Moretta, L. Effect of tumor cells and tumor microenvironment on NK-cell function. Eur. J. Immunol. 2014, 44, 1582–1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The biology, function, and biomedical applications of exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isaac, R.; Reis, F.C.G.; Ying, W.; Olefsky, J.M. Exosomes as mediators of intercellular crosstalk in metabolism. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1744–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, O.Y.; Lee, J.; Gho, Y.S. Extracellular vesicle mimetics: Novel alternatives to extracellular vesicle-based theranostics, drug delivery, and vaccines. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2017, 67, 74–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Su, Y.; Zhong, S.; Cong, L.; Liu, B.; Yang, J.; Tao, Y.; He, Z.; Chen, C.; Jiang, Y. Exosomes: Key players in cancer and potential therapeutic strategy. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2020, 5, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, L.; Kalimuthu, S.; Gangadaran, P.; Oh, J.M.; Lee, H.W.; Baek, S.H.; Jeong, S.Y.; Lee, S.W.; Lee, J.; Ahn, B.C. Exosomes Derived from Natural Killer Cells Exert Therapeutic Effect in Melanoma. Theranostics 2017, 7, 2732–2745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaban, K.; Hinterleitner, C.; Zhou, Y.J.; Salva, E.; Kantarci, A.G.; Salih, H.R.; Märklin, M. Therapeutic Silencing of BCL-2 Using NK Cell-Derived Exosomes as a Novel Therapeutic Approach in Breast Cancer. Cancers 2021, 13, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neviani, P.; Wise, P.M.; Murtadha, M.; Liu, C.W.; Wu, C.H.; Jong, A.Y.; Seeger, R.C.; Fabbri, M. Natural Killer-Derived Exosomal miR-186 Inhibits Neuroblastoma Growth and Immune Escape Mechanisms. Cancer Res. 2019, 79, 1151–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Hu, W.; Chen, H.; Shou, X.; Ye, T.; Xu, Y. Cocktail Strategy Based on NK Cell-Derived Exosomes and Their Biomimetic Nanoparticles for Dual Tumor Therapy. Cancers 2019, 11, 1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y.T.; Niu, Z.; Hadlock, T.; Purcell, E.; Lo, T.W.; Zeinali, M.; Owen, S.; Keshamouni, V.G.; Reddy, R.; Ramnath, N.; et al. On-Chip Biogenesis of Circulating NK Cell-Derived Exosomes in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Exhibits Antitumoral Activity. Adv. Sci. 2021, 8, 2003747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.Y.; Min, H.K.; Song, H.W.; Yoo, A.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.P.; Park, J.O.; Choi, Y.H.; Choi, E. Delivery of human natural killer cell-derived exosomes for liver cancer therapy: An in vivo study in subcutaneous and orthotopic animal models. Drug Deliv. 2022, 29, 2897–2911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatami, Z.; Hashemi, Z.S.; Eftekhary, M.; Amiri, A.; Karpisheh, V.; Nasrollahi, K.; Jafari, R. Natural killer cell-derived exosomes for cancer immunotherapy: Innovative therapeutics art. Cancer Cell Int. 2023, 23, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reale, A.; Khong, T.; Spencer, A. Extracellular Vesicles and Their Roles in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunggulawa, E.J.; Wang, W.; Yin, T.Y.; Wang, N.; Durkan, C.; Wang, Y.Z.; Wang, G.X. Recent advancements in the use of exosomes as drug delivery systems. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.I.; Park, J.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X.; Han, Y.; Zhang, D. Recent advances in extracellular vesicles for therapeutic cargo delivery. Exp. Mol. Med. 2024, 56, 836–849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koh, H.B.; Kim, H.J.; Kang, S.W.; Yoo, T.H. Exosome-Based Drug Delivery: Translation from Bench to Clinic. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 2042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Wang, L.; Zeng, X.; Schwarz, H.; Nanda, H.S.; Peng, X.; Zhou, Y. Exosomes, a New Star for Targeted Delivery. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 751079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Long, S.; Lin, X.; Yang, A.; Duan, J.; Yang, N.; Yang, Z.; et al. NK cell-derived exosomes enhance the anti-tumor effects against ovarian cancer by delivering cisplatin and reactivating NK cell functions. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 1087689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, D.; Wang, K.; Zhang, T.; Gao, G.C.; Xu, H. Natural killer cell-derived exosome-entrapped paclitaxel can enhance its anti-tumor effect. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2020, 24, 5703–5713. [Google Scholar]
- Thery, C. Exosomes: Secreted vesicles and intercellular communications. F1000 Biol. Rep. 2011, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Wang, Y.; Jin, X.; Hu, D.; Xia, C.; Xu, H.; Hu, J. NK cell-derived exosomes carry miR-207 and alleviate depression-like symptoms in mice. J. Neuroinflamm. 2020, 17, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Pace, A.L.; Tumino, N.; Besi, F.; Alicata, C.; Conti, L.A.; Munari, E.; Maggi, E.; Vacca, P.; Moretta, L. Characterization of Human NK Cell-Derived Exosomes: Role of DNAM1 Receptor in Exosome-Mediated Cytotoxicity Against Tumor. Cancers 2020, 12, 661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, I.Y.; Kim, H.Y.; Song, H.W.; Park, J.O.; Choi, Y.H.; Choi, E. Functional enhancement of exosomes derived from NK cells by IL-15 and IL-21 synergy against hepatocellular carcinoma cells: The cytotoxicity and apoptosis in vitro study. Heliyon 2023, 9, e16962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schindler, C.; Collinson, A.; Matthews, C.; Pointon, A.; Jenkinson, L.; Minter, R.R.; Vaughan, T.J.; Tigue, N.J. Exosomal delivery of doxorubicin enables rapid cell entry and enhanced in vitro potency. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0214545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutlu, E.C.; Kaya, Ö.; Wood, M.; Mager, I.; Topkara, K.Ç.; Çamsari, Ç.; Yildirim, A.B.; Çetinkaya, A.; Acarel, D.; Bagci, J.O. Efficient Doxorubicin Loading to Isolated Dexosomes of Immature JAWSII Cells: Formulated and Characterized as the Bionanomaterial. Materials 2020, 13, 3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thery, C.; Zitvogel, L.; Amigorena, S. Exosomes: Composition, biogenesis and function. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2002, 2, 569–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, C.H.; Li, J.; Li, L.; Sun, J.; Fabbri, M.; Wayne, A.S.; Seeger, R.C.; Jong, A.Y. Extracellular vesicles derived from natural killer cells use multiple cytotoxic proteins and killing mechanisms to target cancer cells. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2019, 8, 1588538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huo, Z.J.; Wang, S.J.; Wang, Z.Q.; Zuo, W.S.; Liu, P.; Pang, B.; Liu, K. Novel nanosystem to enhance the antitumor activity of lapatinib in breast cancer treatment: Therapeutic efficacy evaluation. Cancer Sci. 2015, 106, 1429–1437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krylova, S.V.; Feng, D.R. The Machinery of Exosomes: Biogenesis, Release, and Uptake. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, M.H.; Kim, J.; Lim, S.A.; Kim, J.; Kim, S.J.; Lee, K.M. NK Cell-Based Immunotherapies in Cancer. Immune Netw. 2020, 20, e14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yang, L.; Chen, G.; Xu, F.; Yang, F.; Yu, H.; Li, L.; Dong, X.; Han, J.; Cao, C.; et al. A Review on Drug Delivery System for Tumor Therapy. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 735446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, E.; Zamora, P.; Feliu, J.; Gonzalez Baron, M. Classification of anticancer drugs—A new system based on therapeutic targets. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2003, 29, 515–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anand, U.; Dey, A.; Chandel, A.K.S.; Sanyal, R.; Mishra, A.; Pandey, D.K.; De Falco, V.; Upadhyay, A.; Kandimalla, R.; Chaudhary, A.; et al. Cancer chemotherapy and beyond: Current status, drug candidates, associated risks and progress in targeted therapeutics. Genes. Dis. 2023, 10, 1367–1401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Liu, H.; Tang, W.H. Exosomes: Biogenesis, biologic function and clinical potential. Cell Biosci. 2019, 9, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, W.P.; Wen, Z.B.; Chen, H.L.; Duan, Y.Y. Exosomes as Carriers for Drug Delivery in Cancer Therapy. Pharm. Res. 2023, 40, 873–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.H.; Wu, E.G.; Liao, J.W.; Wei, Z.Y.; Wang, J.; Chen, Z.H. Research Advances of Engineered Exosomes as Drug Delivery Carrier. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 43374–43387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, W.; Tang, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Y.; Rong, T.; Wang, H.; Chen, Y. Isolated cell-bound membrane vesicles (CBMVs) as a novel class of drug nanocarriers. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2020, 18, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKelvey, K.J.; Powell, K.L.; Ashton, A.W.; Morris, J.M.; McCracken, S.A. Exosomes: Mechanisms of Uptake. J. Circ. Biomark. 2015, 4, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munich, S.; Sobo-Vujanovic, A.; Buchser, W.J.; Beer-Stolz, D.; Vujanovic, N.L. Dendritic cell exosomes directly kill tumor cells and activate natural killer cells via TNF superfamily ligands. Oncoimmunology 2012, 1, 1074–1083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, J.; Weinman, S. Mechanisms of doxorubicin resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatic Oncol. 2016, 3, 57–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobb, R.J.; Becker, M.; Wen, S.W.; Wong, C.S.; Wiegmans, A.P.; Leimgruber, A.; Moller, A. Optimized exosome isolation protocol for cell culture supernatant and human plasma. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2015, 4, 27031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shelke, G.V.; Lasser, C.; Gho, Y.S.; Lotvall, J. Importance of exosome depletion protocols to eliminate functional and RNA-containing extracellular vesicles from fetal bovine serum. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2014, 3, 24783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Sample | Size by DLS (nm) | Size by NTA (nm) | Zeta Potential (mV) |
|---|---|---|---|
| NK-exos | 111.8 ± 69.44 | 136.8 ± 5.8 | −15.07 ± 2.88 |
| NK-exos-Dox | 183.5 ± 54.12 | 210.6 ± 1.4 | −27.90 ± 0.57 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, Y.H.; Kim, H.Y.; Park, J.-O.; Choi, E. Enhanced Anti-Tumor Effects of Natural Killer Cell-Derived Exosomes Through Doxorubicin Delivery to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells: Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 2234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052234
Choi YH, Kim HY, Park J-O, Choi E. Enhanced Anti-Tumor Effects of Natural Killer Cell-Derived Exosomes Through Doxorubicin Delivery to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells: Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):2234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052234
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, You Hee, Ho Yong Kim, Jong-Oh Park, and Eunpyo Choi. 2025. "Enhanced Anti-Tumor Effects of Natural Killer Cell-Derived Exosomes Through Doxorubicin Delivery to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells: Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Study" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 2234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052234
APA StyleChoi, Y. H., Kim, H. Y., Park, J.-O., & Choi, E. (2025). Enhanced Anti-Tumor Effects of Natural Killer Cell-Derived Exosomes Through Doxorubicin Delivery to Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cells: Cytotoxicity and Apoptosis Study. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 2234. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26052234






