Development and Evaluation of a New Measles Detection Assay Using Real-Time RT-PCR
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
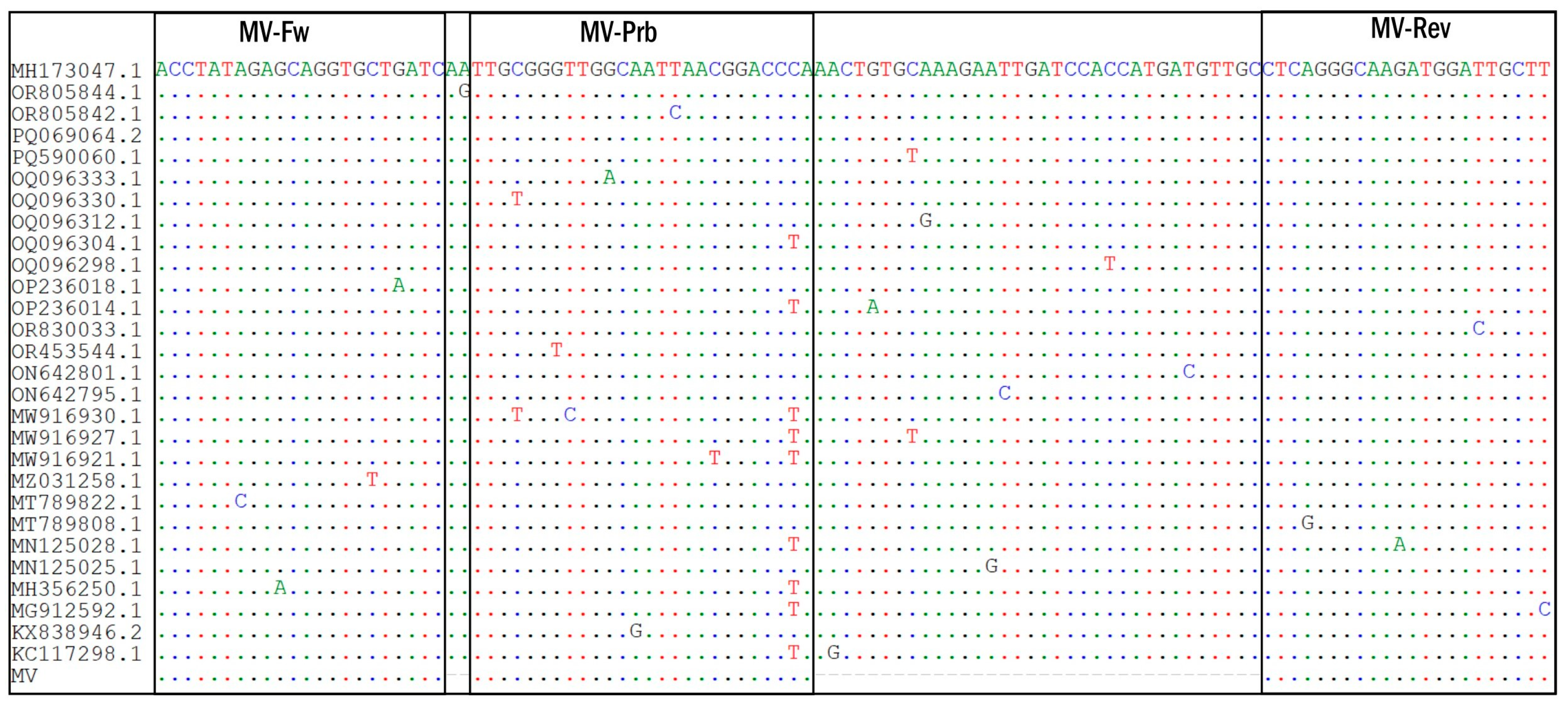
2.1. MV AmpPS Assay Design
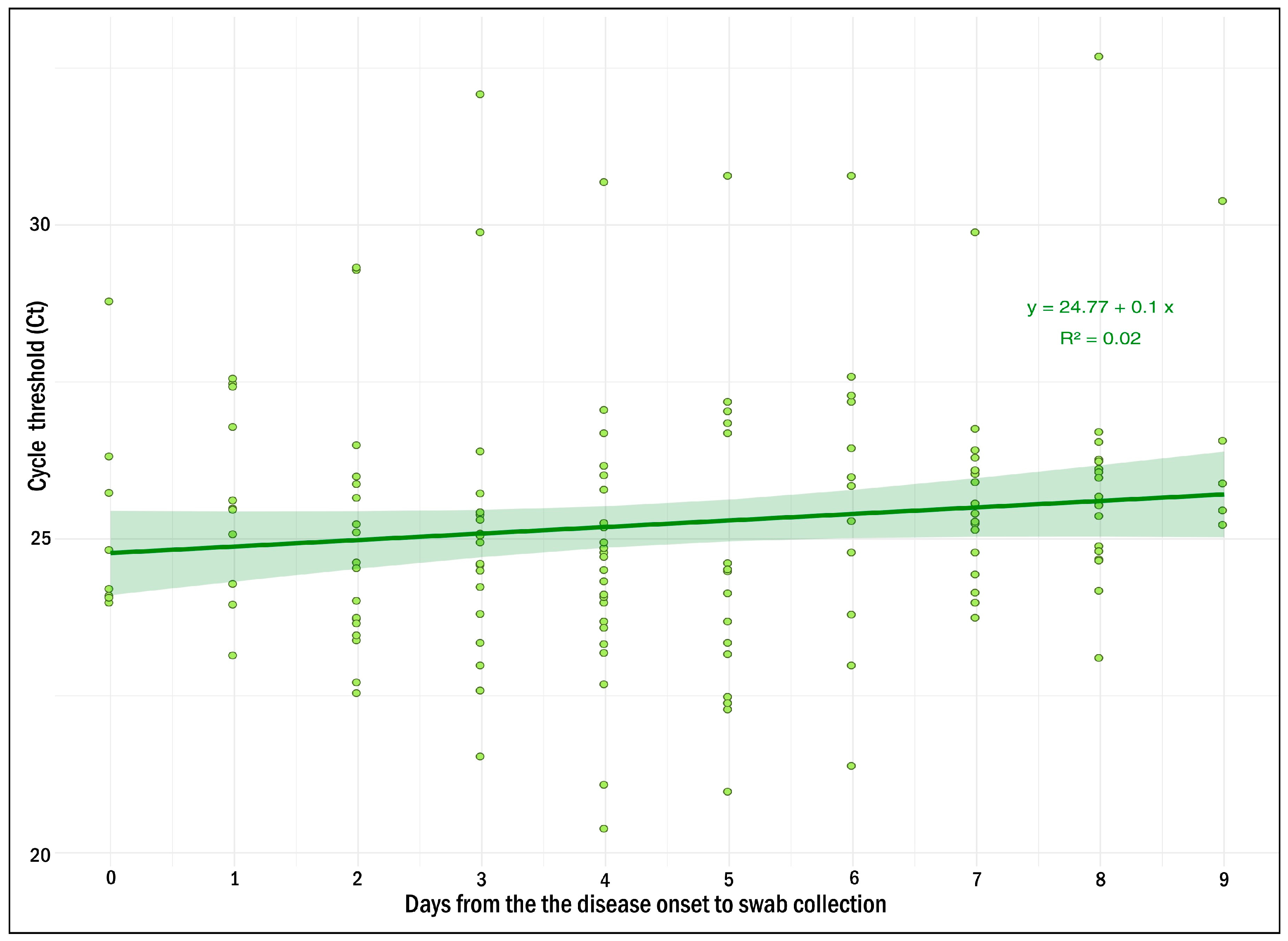
2.2. Clinical Evaluation of the MV AmpPS Assay
3. Discussion
4. Methods and Materials
4.1. Development of the MV AmpPS Assay
4.1.1. Identification of Conserved Sites
4.1.2. Positive and Internal Control Preparation
4.1.3. Reaction Mixture and Amplification Conditions
4.2. Limit of Detection
4.3. Analytical Specificity
4.4. Clinical Evaluation of the MV AmpPS Assay
4.4.1. Sample Collection
4.4.2. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay
4.4.3. RNA Extraction
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kuba, Y.; Kyan, H.; Iha, Y.; Kato, T.; Oyama, M.; Miyahira, M.; Kakita, T.; Takara, T.; Yamauchi, M.; Kamiya, H.; et al. Emergent Measles-Containing Vaccination Recommendation for Aged 6–11 Months and Detection of Vaccine-Associated Measles during a Large Measles Outbreak in Okinawa, Japan, in 2018. Vaccine 2020, 38, 2361–2367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, S.; Ding, Y.; Yan, R.; He, H. Measles in Zhejiang, China, 2004–2017: Population Density and Proportion of Floating Populations Effects on Measles Epidemic. Health Secur. 2019, 17, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremer, J.R.; Brown, K.E.; Jin, L.; Santibanez, S.; Shulga, S.V.; Aboudy, Y.; Demchyshyna, I.V.; Djemileva, S.; Echevarría, J.E.; Featherstone, D.; et al. High Genetic Diversity of Measles Virus, World Health Organization European Region, 2005–2006. Emerg. Infect. Dis. 2008, 14, 107–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gogoi, M.; Martin, C.A.; Bird, P.W.; Wiselka, M.J.; Gardener, J.; Ellis, K.; Renals, V.; Lewszuk, A.J.; Hargreaves, S.; Pareek, M. Risk of vaccine preventable diseases in UK migrants: A serosurvey and concordance analysis. J. Migr. Health 2024, 9, 100217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knights, F.; Carter, J.; Deal, A.; Crawshaw, A.; Bouaddi, O.; Sanchez-Clemente, N.; Seedat, F.; Vanderslott, S.; Eagan, R.; Holt, D.E.; et al. Strengthening life-course immunisation in migrant populations: Access, equity, and inclusion. Lancet Reg. Health Eur. 2024, 41, 100806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/measles-and-rubella-strategic-framework-2021-2030 (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- European Center for Disease Prevention and Control. Available online: https://www.ecdc.europa.eu/sites/default/files/documents/measles-eu-threat-assessment-brief-february-2024.pdf (accessed on 1 February 2025).
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news/item/23-11-2022-nearly-40-million-children-are-dangerously-susceptible-to-growing-measles-threat (accessed on 30 January 2025).
- Benecke, O.; DeYoung, S.E. Anti-Vaccine Decision-Making and Measles Resurgence in the United States. Glob. Pediatr. Health 2019, 6, 2333794X1986294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaméogo, K.R.; Perry, R.T.; Yaméogo, A.; Kambiré, C.; Kondé, M.K.; Nshimirimana, D.; Kezaala, R.; Hersh, B.S.; Cairns, K.L.; Strebel, P. Migration as a Risk Factor for Measles after a Mass Vaccination Campaign, Burkina Faso, 2002†. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2005, 34, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mat Daud, M.R.H.; Yaacob, N.A.; Ibrahim, M.I.; Wan Muhammad, W.A.R. Five-Year Trend of Measles and Its Associated Factors in Pahang, Malaysia: A Population-Based Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- W/Kidan, F.; Getachew, D.; Mekonnen, B.; Woldeselassie Hammeso, W. Risk Factors of Measles Outbreak among Students of Mizan-Tepi University, Tepi Campus, Southwest Ethiopia. Infect. Drug Resist. 2021, 14, 963–970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hungerford, D.; Cleary, P.; Ghebrehewet, S.; Keenan, A.; Vivancos, R. Risk Factors for Transmission of Measles during an Outbreak: Matched Case–Control Study. J. Hosp. Infect. 2014, 86, 138–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nassar, A.A.H.; Al Amad, M.A.; Qasim, M.; Dureab, F. Risk Factors for Measles Outbreak in Ataq and Habban Districts, Shabwah Governorate, Yemen, February to May 2018. BMC Infect Dis. 2021, 21, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polonsky, J.A.; Singh, B.; Masiku, C.; Langendorf, C.; Kagoli, M.; Hurtado, N.; Berthelot, M.; Heinzelmann, A.; Puren, A.; Grais, R.F. Exploring HIV Infection and Susceptibility to Measles among Older Children and Adults in Malawi: A Facility-Based Study. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2015, 31, 61–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Wirth, K.E.; Wolf, E.R.; Goldfarb, D.M.; Ho-Foster, A.; Tolle, M.; Jacovides, C.; Kirk, B.; Chise, M.; Steenhoff, A.P. Risk Factors for Measles in HIV-Infected Children and Adolescents in Botswana. Pediatr. Infect. Dis. J. 2015, 34, 1093–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Moss, W.J. Measles. Lancet 2017, 390, 2490–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Donadel, M.; Stanescu, A.; Pistol, A.; Stewart, B.; Butu, C.; Jankovic, D.; Paunescu, B.; Zimmerman, L. Risk Factors for Measles Deaths among Children during a Nationwide Measles Outbreak—Romania, 2016–2018. BMC Infect Dis. 2021, 21, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/m/item/chapter-1-manual-for-the-laboratory-based-surveillance-of-measles-rubella-and-congenital-rubella-syndrome (accessed on 23 October 2023).
- Komabayashi, K.; Seto, J.; Tanaka, S.; Suzuki, Y.; Ikeda, T.; Onuki, N.; Yamada, K.; Ahiko, T.; Ishikawa, H.; Mizuta, K. The Largest Measles Outbreak, Including 38 Modified Measles and 22 Typical Measles Cases in Its Elimination Era in Yamagata, Japan, 2017. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 71, 413–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chua, K.Y.L.; Thapa, K.; Yapa, C.M.; Somerville, L.K.; Chen, S.C.-A.; Dwyer, D.E.; Sheppeard, V.; Kok, J. What Assay Is Optimal for the Diagnosis of Measles Virus Infection? An Evaluation of the Performance of a Measles Virus Real-Time Reverse Transcriptase PCR Using the Cepheid SmartCycler ® and Antigen Detection by Immunofluorescence. J. Clin. Virol. 2015, 70, 46–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, K.B.; Lowe, L.; Bellini, W.J.; Rota, P.A. Development of Quantitative Gene-Specific Real-Time RT-PCR Assays for the Detection of Measles Virus in Clinical Specimens. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 132, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.S.; Lopareva, E.N.; Hwang, H.; Hart, D.; de Almeida, M.; Anderson, R.; Rota, P.A.; Bankamp, B. Evaluation of the Sensitivity of a Measles Diagnostic Real-Time RT-PCR Assay Incorporating Recently Observed Priming Mismatch Variants, 2024. Eurosurveillance 2024, 29, 2400410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/europe/news/item/14-12-2023-a-30-fold-rise-of-measles-cases-in-2023-in-the-who-european-region-warrants-urgent-action (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- World Health Organization. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/measles (accessed on 25 October 2023).
- Onishchenko, G.; Ezhlova, E.; Gerasimova, A.; Tsvirkun, O.; Shulga, S.; Lipskaya, G.; Mamayeva, T.; Aleshkin, V.; Tikhonova, N. Progress toward Measles Elimination in the Russian Federation, 2003–2009. J. Infect. Dis. 2011, 204, S366–S372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramov, I.A.; Chernyavskaya, O.P.; Abramov, A.A. Procedure for Assessing Risks of an Infectious Disease Being Imported and Spread in the RF Regions Exemplified with Measles in 2018. Health Risk Anal. 2020, 108–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnaout, R.; Lee, R.A.; Lee, G.R.; Callahan, C.; Yen, C.F.; Smith, K.P.; Arora, R.; Kirby, J.E. SARS-CoV2 Testing: The Limit of Detection Matters. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, B.; Gopez, A.; Servellita, V.; Arevalo, S.; Ho, C.; Deucher, A.; Thornborrow, E.; Chiu, C.; Miller, S. Direct Comparison of SARS-CoV-2 Analytical Limits of Detection across Seven Molecular Assays. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2020, 58, e01535-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pinchon, E.; Henry, S.; Leon, F.; Fournier-Wirth, C.; Foulongne, V.; Cantaloube, J.-F. Rapid Detection of Measles Virus Using Reverse Transcriptase/Recombinase Polymerase Amplification Coupled with CRISPR/Cas12a and a Lateral Flow Detection: A Proof-of-Concept Study. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, S.C.; Nadeau, K.; Abbasi, M.; Lachance, C.; Nguyen, M.; Fenrich, J. The Ultimate QPCR Experiment: Producing Publication Quality, Reproducible Data the First Time. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 761–774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Pelt-Verkuil, E.; Van Belkum, A.; Hays, J.P. Principles and Technical Aspects of PCR Amplification; Springer, Cop: Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; pp. 63–87. [Google Scholar]
- Kibbe, W.A. OligoCalc: An Online Oligonucleotide Properties Calculator. Nucleic Acids Res. 2007, 35, W43–W46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuker, M. Mfold Web Server for Nucleic Acid Folding and Hybridization Prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3406–3415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goncharova, E.A.; Dedkov, V.G.; Dolgova, A.S.; Kassirov, I.S.; Safonova, M.V.; Voytsekhovskaya, Y.; Totolian, A.A. One-Step Quantitative RT-PCR Assay with Armored RNA Controls for Detection of SARS-CoV-2. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 1694–1701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dolgova, A.; Kanaeva, O.; Antonov, S.; Shabalina, A.; Klyuchnikova, E.; Sbarzaglia, V.; Gladkikh, A.; Ivanova, O.; Kozlovskaya, L.; Dedkov, V. Qualitative Real-Time RT-PCR Assay for NOPV2 Poliovirus Detection. J. Virol. Methods. 2024, 329, 114984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolgova, A.S.; Stukolova, O.A. High-Fidelity PCR Enzyme with DNA-Binding Domain Facilitates de Novo Gene Synthesis. 3 Biotech. 2017, 7, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaida, A.; Kubo, H.; Sekiguchi, J.-I.; Ohyama, M.; Goto, K.; Hase, A.; Iritani, N. Detection of Five Rash-Associated Viruses Using Multiplex Real-Time PCR during 2006–2011. Jpn. J. Infect. Dis. 2012, 65, 430–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidi, S.S.Z.; Hameed, A.; Suleman Rana, M.; Alam, M.M.; Umair, M.; Aamir, U.B.; Hussain, M.; Sharif, S.; Shaukat, S.; Angez, M.; et al. Identification of Measles Virus Genotype B3 Associated with Outbreaks in Islamabad, Pakistan, 2013–2015. J. Infect. Public Health 2018, 11, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

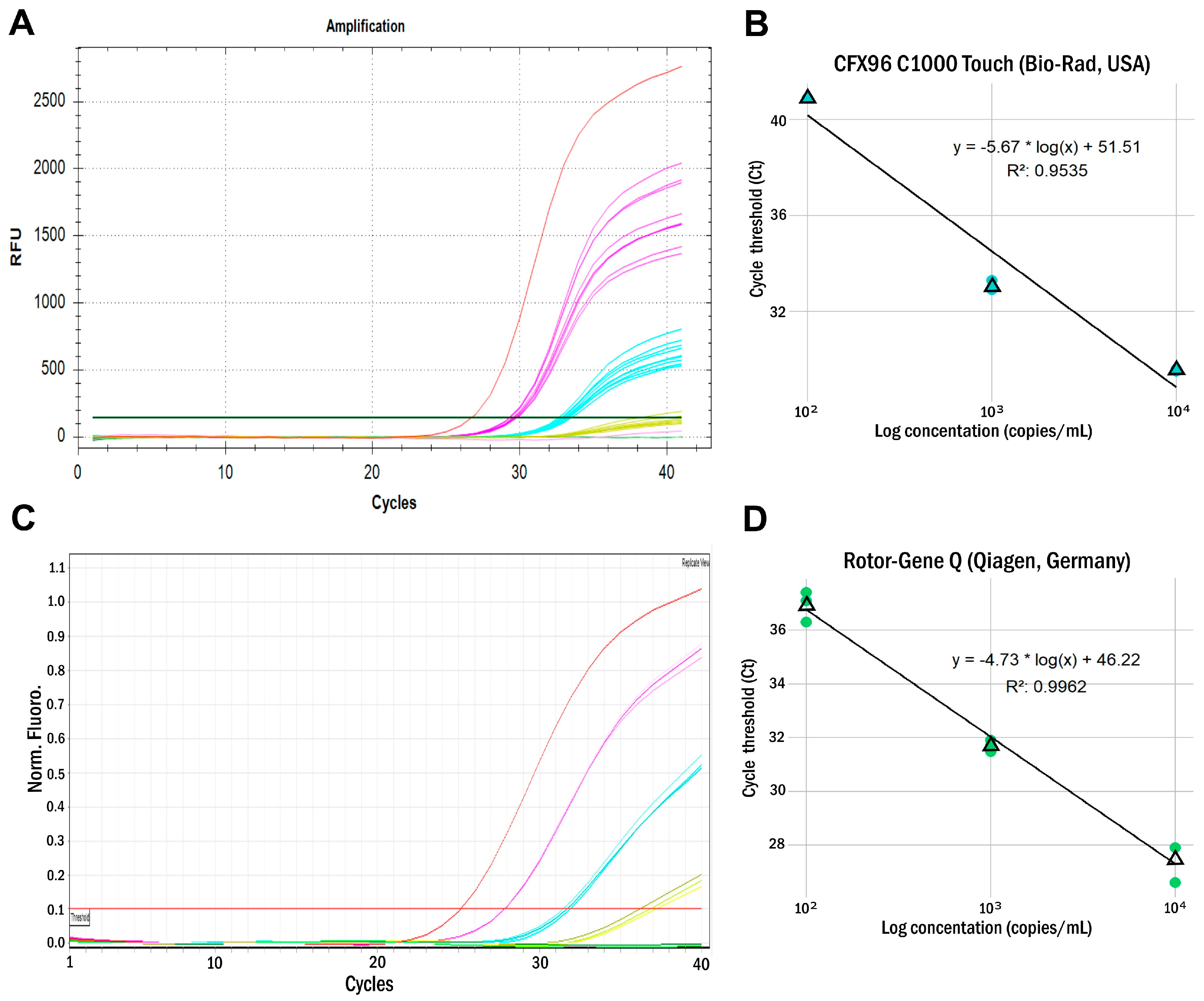
| ARC Concentration (Copies/mL) | CFX96 C1000 Touch (Bio-Rad, USA) | Rotor-Gene Q (Qiagen, Germany) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Replicate, Ct Values | Replicate, Ct Values | |||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | Median | 1 | 2 | 3 | Median | |
| 104 | 29.6 | 29.5 | 29.6 | 29.6 | 27.9 | 27.9 | 27.9 | 27.9 |
| 103 | 33.3 | 32.9 | 33.0 | 33.1 | 31.5 | 31.9 | 31.7 | 31.7 |
| 102 | neg. | neg. | 40.9 | neg. | 37.1 | 37.4 | 36.3 | 36.9 |
| 101 | neg. | neg. | neg. | neg. | neg. | neg. | neg. | neg. |
| LOD (copies/mL) | 103 | 102 | ||||||
| LOD* (copies/mL) | 1.2 × 103 | 2.7 × 102 | ||||||
| Parameter | Real-Time RT-PCR Assay |
|---|---|
| Reagent components | MeV super mix, RT-PCR enzyme mix, 2× RT-PCR buffer, armored internal control (IC), armored positive RNA control (ARC+), positive PCR control (C+), negative PCR control (C−), and negative extraction control (NEC) |
| Virus detected | Morbillivirus hominis (MeV) |
| Genetic target | RdRp gene |
| Real-time PCR platform | CFX96 C1000 Touch (Bio-Rad, USA), Rotor-Gene Q (Qiagen, Germany) |
| Nucleic acid extraction required | yes |
| Suitable specimens for testing | nasopharyngeal swabs |
| Sensitivity | 1–1.2 × 103 copies/mL (CFX96 C1000 Touch), 1–2.7 × 102 copies/mL (Rotor-Gene Q) |
| Duration of the analysis (excluding extraction time) | 90 min |
| Primer or Probe | Sequence (5′→3′) | Reference Sequence Nucleotide Position (GenBank OR290098) | 5′–3′ Modification | Amplicon Length (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MV-Fw | ACCTATAgAGCAggTgCTgATC | 15299–15320 | none | 106 |
| MV-Rev | AAgCAATCCATCTTGCCCTgAg | 15383–15404 | none | |
| MV-Prb | TTgCgggTTggCAATTAACggACCCA * | 15323–15348 | R6G—BHQ1 | - |
| IC-Fw | CCggATTgCgTATCTCCggACT | none | none | 122 |
| IC-Rev | CACggCggCATCTCTATCACgA | none | none | |
| IC-Prb1 | CTAgCTgggCgTCAggAATCCCAgg | none | FAM-BHQ1 | - |
| Name | Sequence (5′-3′) |
|---|---|
| MEV1 | AGTTATTAGAGGTGATATCAACCCTACTCTGAAAAAACTTACACCTATAGAGCAGGTG |
| MEV2 | GTTTGGGTCCGTTAATTGCCAACCCGCAATTGATCAGCACCTGCTCTATAGGTGTAAGTT |
| MEV3 | GGCAATTAACGGACCCAAACTGTGCAAAGAATTGATCCACCATGATGTTGCCTCAGGGCA |
| MEV4 | AACTCCCTGTAGAGGATGAGTATAGAATTAAGCAATCCATCTTGCCCTGAGGCAACATCA |
| Species | Acronym | Family | Genus | Type of Nucleic Acid | RT-PCR Kit | Ct Value | MV AmpS Assay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Influenza A/H1N3 | FLUAV (H1N3) | Orthomyxoviridae | Alphainfluenzavirus | RNA | AmpliSens® Influenza virus A-type-FRT PCR | 18.4 | negative |
| Influenza A/H3N2 | FLUAV (H3N2) | Orthomyxoviridae | Alphainfluenzavirus | RNA | 17.9 | negative | |
| Influenza B | FLUBV | Orthomyxoviridae | Betainfluenzavirus | RNA | AmpliSens® Influenza virus A/B-FRT PCR | 23.6 | negative |
| Human parainfluenza virus type 1 | HPIV-1 | Paramyxoviridae | Rubulavirus | RNA | AmpliSens® ARVI-screen-FRT | 20.4 | negative |
| Human parainfluenza virus type 4b | HPIV-4b | Paramyxoviridae | Rubulavirus | RNA | AmpliSens® ARVI-screen-FRT | 23.8 | negative |
| Human rhinovirus B (Type 17) | HRV-B | Picornaviridae | Enterovirus | RNA | AmpliSens® ARVI-screen-FRT | 24.4 | negative |
| Human adenovirus type 6 | HAdV-6 | Adenoviridae | Mastadenovirus | DNA | AmpliSens® All screen-FRT | 19.8 | negative |
| Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 | SARS-CoV-2 | Coronaviridae | Betacoronavirus | RNA | COVID-19Amp (St. Petersburg Pasteur Institute) [35] | 17.3 | negative |
| Rubella virus | RUBV | Matonaviridae | Rubivirus | RNA | NA | 22.7 | negative |
| Respiratory syncytial virus type B1 | RSV B1 | Pneumoviridae | Orthopneumovirus | RNA | AmpliSens® ARVI-screen-FRT | 21.9 | negative |
| Human parechovirus type 1 | HPeV-1 | Picornaviridae | Parechovirus | RNA | NA | - | negative |
| Human alphaherpesvirus 1 | HSV-1 | Herpesviridae | Alphaherpesvirus | DNA | AmpliSens® HSV I, II-FRT | 21.8 | negative |
| Human Rotavirus A | RVA | Reoviridae | Rotavirus | RNA | AmpliSens® Rotavirus/Norovirus/Astrovirus-FRT PCR | 19.9 | negative |
| Echovirus 4 | ECHOV-4 | Picornaviridae | Enterovirus | RNA | NA | - | negative |
| Human Cytomegalovirus 5 | HCMV-5 | Herpesviridae | Cytomegalovirus | DNA | AmpliSens® CMV-FRT PCR | 19.9 | negative |
| Human parvovirus B19 | B19 | Parvoviridae | Erythroparvovirus | DNA | AmpliSens® Parvovirus B19-FRT PCR | 22.1 | negative |
| Human Coxsackievirus B1 | CV-B1 | Picornaviridae | Enterovirus | RNA | NA | - | negative |
| Mumps orthorubulavirus | MuV | Paramyxoviridae | Orthorubulavirus | RNA | NA | - | negative |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chayeb, V.A.; Dolgova, A.S.; Popova, M.R.; Zheleznova, N.V.; Shirobokova, S.A.; Shabalina, A.V.; Sharova, A.A.; Gladkikh, A.S.; Antipova, A.Y.; Kirichenko, A.D.; et al. Development and Evaluation of a New Measles Detection Assay Using Real-Time RT-PCR. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051801
Chayeb VA, Dolgova AS, Popova MR, Zheleznova NV, Shirobokova SA, Shabalina AV, Sharova AA, Gladkikh AS, Antipova AY, Kirichenko AD, et al. Development and Evaluation of a New Measles Detection Assay Using Real-Time RT-PCR. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(5):1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051801
Chicago/Turabian StyleChayeb, Vera A., Anna S. Dolgova, Margarita R. Popova, Nina V. Zheleznova, Svetlana A. Shirobokova, Anna V. Shabalina, Alena A. Sharova, Anna S. Gladkikh, Anastasia Yu. Antipova, Anastasiia D. Kirichenko, and et al. 2025. "Development and Evaluation of a New Measles Detection Assay Using Real-Time RT-PCR" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 5: 1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051801
APA StyleChayeb, V. A., Dolgova, A. S., Popova, M. R., Zheleznova, N. V., Shirobokova, S. A., Shabalina, A. V., Sharova, A. A., Gladkikh, A. S., Antipova, A. Y., Kirichenko, A. D., Ramsay, E. S., & Dedkov, V. G. (2025). Development and Evaluation of a New Measles Detection Assay Using Real-Time RT-PCR. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(5), 1801. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26051801






