Establishment of a Panel of Human Cell Lines to Identify Cellular Receptors Used by Enteroviruses to Infect Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
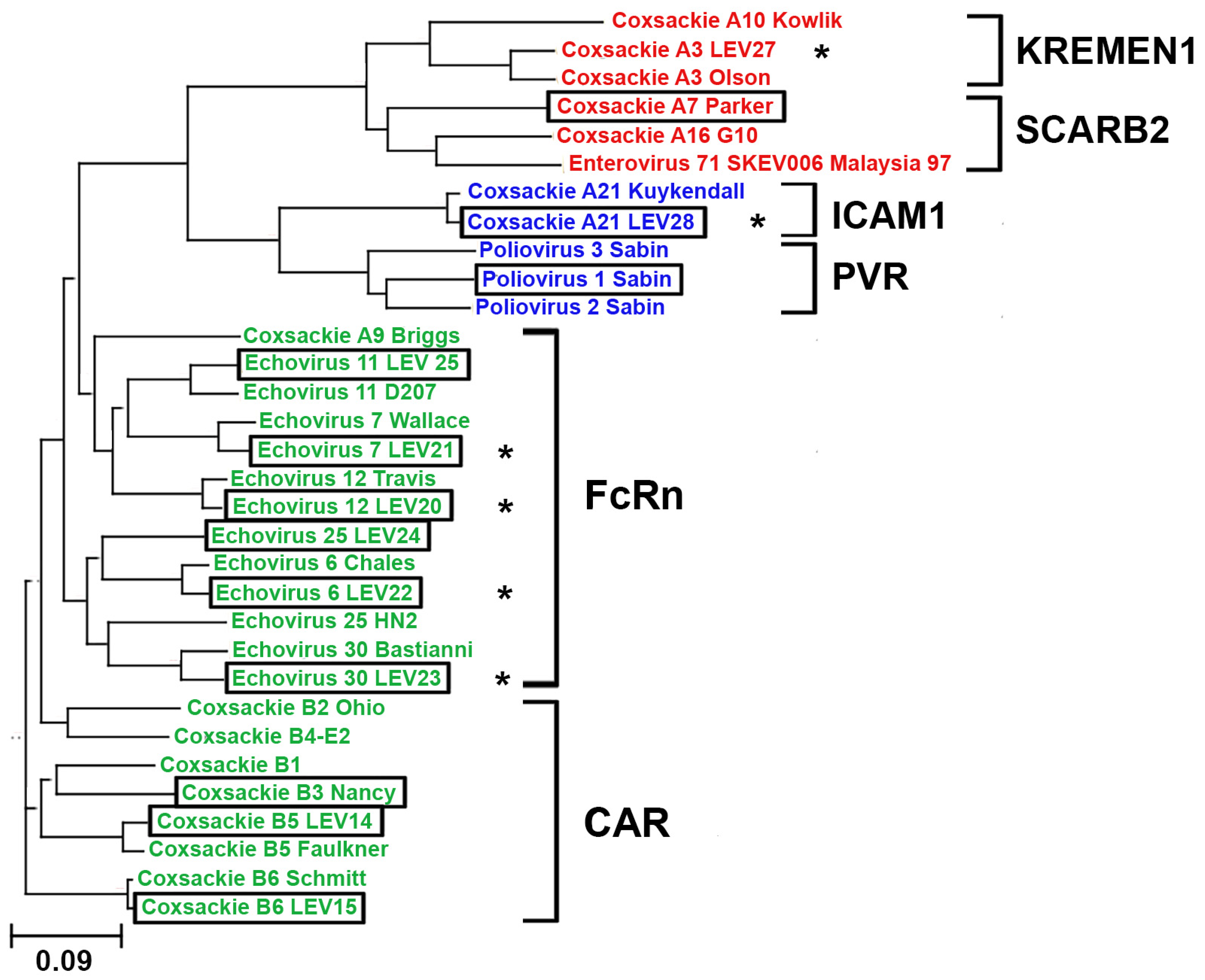
2.1. Phylogenetic Analysis of Enterovirus Structural Proteins
2.2. Obtaining a Panel of Cell Lines with Knockouts of Different Enterovirus Receptors
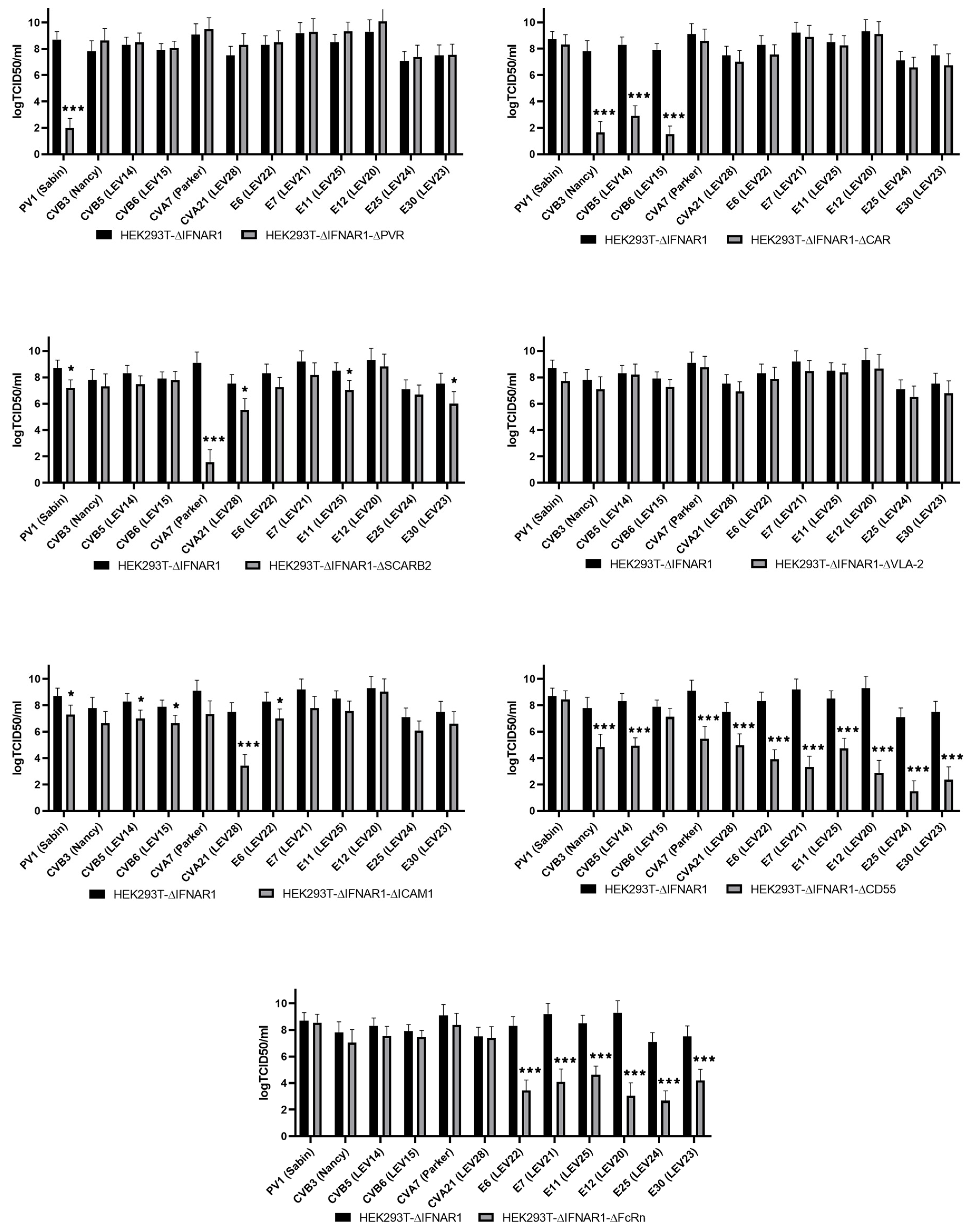
2.3. Evaluation of Enterovirus Production in a Panel of Cells with Viral Receptor Knockouts
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Phylogenetic Analysis of the Enteroviruses
4.2. Cell Lines and Viral Strains
4.3. The HEK293T Cell Lines with Viral Receptor Gene Knockouts
4.4. Enterovirus RNA Purification and Genome Sequencing
4.5. Determination of Enterovirus Production
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Jartti, M.; Flodstrom-Tullberg, M.; Hankaniemi, M.M. Enteroviruses: Epidemic potential, challenges and opportunities with vaccines. J. Biomed. Sci. 2024, 31, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikonov, O.S.; Chernykh, E.S.; Garber, M.B.; Nikonova, E.Y. Enteroviruses: Classification, Diseases They Cause and Approaches to Development of Antiviral Drugs. Biochemistry 2017, 82, 1615–1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alekseeva, O.N.; Hoa, L.T.; Vorobyev, P.O.; Kochetkov, D.V.; Gumennaya, Y.D.; Naberezhnaya, E.R.; Chuvashov, D.O.; Ivanov, A.V.; Chumakov, P.M.; Lipatova, A.V. Receptors and Host Factors for Enterovirus Infection: Implications for Cancer Therapy. Cancers 2024, 16, 3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergelson, J.M.; Coyne, C.B. Picornavirus entry. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2013, 790, 24–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, M.K.; Seth, S.; Czeloth, N.; Qiu, Q.; Ravens, I.; Kremmer, E.; Ebel, M.; Muller, W.; Pabst, O.; Forster, R.; et al. The adhesion receptor CD155 determines the magnitude of humoral immune responses against orally ingested antigens. Eur. J. Immunol. 2007, 37, 2214–2225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, J.; Zheng, Q.; Xin, N.; Wang, W.; Zhao, C. CD155, an onco-immunologic molecule in human tumors. Cancer Sci. 2017, 108, 1934–1938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergelson, J.M.; Cunningham, J.A.; Droguett, G.; Kurt-Jones, E.A.; Krithivas, A.; Hong, J.S.; Horwitz, M.S.; Crowell, R.L.; Finberg, R.W. Isolation of a common receptor for Coxsackie B viruses and adenoviruses 2 and 5. Science 1997, 275, 1320–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomko, R.P.; Xu, R.; Philipson, L. HCAR and MCAR: The human and mouse cellular receptors for subgroup C adenoviruses and group B coxsackieviruses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 3352–3356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamayoshi, S.; Iizuka, S.; Yamashita, T.; Minagawa, H.; Mizuta, K.; Okamoto, M.; Nishimura, H.; Sanjoh, K.; Katsushima, N.; Itagaki, T.; et al. Human SCARB2-dependent infection by coxsackievirus A7, A14 and A16 and enterovirus 71. J. Virol. 2012, 86, 5686–5696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonzalez, A.; Valeiras, M.; Sidransky, E.; Tayebi, N. Lysosomal integral membrane protein-2: A new player in lysosome-related pathology. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2014, 111, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergelson, J.M.; Shepley, M.P.; Chan, B.M.; Hemler, M.E.; Finberg, R.W. Identification of the integrin VLA-2 as a receptor for echovirus 1. Science 1992, 255, 1718–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergelson, J.M.; St John, N.; Kawaguchi, S.; Chan, M.; Stubdal, H.; Modlin, J.; Finberg, R.W. Infection by echoviruses 1 and 8 depends on the alpha 2 subunit of human VLA-2. J. Virol. 1993, 67, 6847–6852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roivainen, M.; Piirainen, L.; Hovi, T.; Virtanen, I.; Riikonen, T.; Heino, J.; Hyypia, T. Entry of coxsackievirus A9 into host cells: Specific interactions with alpha v beta 3 integrin, the vitronectin receptor. Virology 1994, 203, 357–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, C.H.; Kajander, T.; Hyypia, T.; Jackson, T.; Sheppard, D.; Stanway, G. Integrin alpha v beta 6 is an RGD-dependent receptor for coxsackievirus A9. J. Virol. 2004, 78, 6967–6973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafren, D.R.; Dorahy, D.J.; Ingham, R.A.; Burns, G.F.; Barry, R.D. Coxsackievirus A21 binds to decay-accelerating factor but requires intercellular adhesion molecule 1 for cell entry. J. Virol. 1997, 71, 4736–4743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, C.; Bator, C.M.; Bowman, V.D.; Rieder, E.; He, Y.; Hebert, B.; Bella, J.; Baker, T.S.; Wimmer, E.; Kuhn, R.J.; et al. Interaction of coxsackievirus A21 with its cellular receptor, ICAM-1. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 2444–2451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto, A.; Inoue, H.; Miyamoto, S.; Ito, S.; Soda, Y.; Tani, K. Coxsackievirus A11 is an immunostimulatory oncolytic virus that induces complete tumor regression in a human non-small cell lung cancer. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 5924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, G.; Liu, S.; Chen, X.; Peng, R.; Dai, L.; Qu, X.; Li, S.; Song, H.; Gao, Z.; et al. Human Neonatal Fc Receptor Is the Cellular Uncoating Receptor for Enterovirus B. Cell 2019, 177, 1553–1565.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shafren, D.R.; Bates, R.C.; Agrez, M.V.; Herd, R.L.; Burns, G.F.; Barry, R.D. Coxsackieviruses B1, B3 and B5 use decay accelerating factor as a receptor for cell attachment. J. Virol. 1995, 69, 3873–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ward, T.; Pipkin, P.A.; Clarkson, N.A.; Stone, D.M.; Minor, P.D.; Almond, J.W. Decay-accelerating factor CD55 is identified as the receptor for echovirus 7 using CELICS, a rapid immuno-focal cloning method. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 5070–5074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shakeel, S.; Seitsonen, J.J.; Kajander, T.; Laurinmaki, P.; Hyypia, T.; Susi, P.; Butcher, S.J. Structural and functional analysis of coxsackievirus A9 integrin alphavbeta6 binding and uncoating. J. Virol. 2013, 87, 3943–3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nikolaidis, M.; Mimouli, K.; Kyriakopoulou, Z.; Tsimpidis, M.; Tsakogiannis, D.; Markoulatos, P.; Amoutzias, G.D. Large-scale genomic analysis reveals recurrent patterns of intertypic recombination in human enteroviruses. Virology 2019, 526, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambaro, F.; Perez, A.B.; Aguera, E.; Prot, M.; Martinez-Martinez, L.; Cabrerizo, M.; Simon-Loriere, E.; Fernandez-Garcia, M.D. Genomic surveillance of enterovirus associated with aseptic meningitis cases in southern Spain, 2015–2018. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 21523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyriakopoulou, Z.; Pliaka, V.; Amoutzias, G.D.; Markoulatos, P. Recombination among human non-polio enteroviruses: Implications for epidemiology and evolution. Virus Genes 2015, 50, 177–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, P.O.; Babaeva, F.E.; Panova, A.V.; Shakiba, J.; Kravchenko, S.K.; Soboleva, A.V.; Lipatova, A.V. Oncolytic Viruses in the Therapy of Lymphoproliferative Diseases. Mol. Biol. 2022, 56, 684–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, D.; Shen, Y.; Liang, T. Oncolytic virotherapy: Basic principles, recent advances and future directions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donina, S.; Strele, I.; Proboka, G.; Auzinš, J.; Alberts, P.; Jonsson, B.; Venskus, D.; Muceniece, A. Adapted ECHO-7 virus Rigvir immunotherapy (oncolytic virotherapy) prolongs survival in melanoma patients after surgical excision of the tumour in a retrospective study. Melanoma Res. 2015, 25, 421–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babiker, H.M.; Riaz, I.B.; Husnain, M.; Borad, M.J. Oncolytic virotherapy including Rigvir and standard therapies in malignant melanoma. Oncolytic Virother. 2017, 6, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, A.; Soboleva, A.V.; Vorobyev, P.O.; Mahmoud, M.; Vasilenko, K.V.; Chumakov, P.M.; Lipatova, A.V. Development of a recombinant oncolytic poliovirus type 3 strain with altered cell tropism. Bull. RSMU 2022, 2, 5–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podshivalova, E.S.; Semkina, A.S.; Kravchenko, D.S.; Frolova, E.I.; Chumakov, S.P. Efficient delivery of oncolytic enterovirus by carrier cell line NK-92. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics 2021, 21, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, W.J.; Burnett, D.M.; Parkman, G.; Ramstead, A.; Contreras, N.; Gravley, W.; Holmen, S.L.; Williams, M.A.; VanBrocklin, M.W. Prior Exposure to Coxsackievirus A21 Does Not Mitigate Oncolytic Therapeutic Efficacy. Cancers 2021, 13, 4462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Xing, M.; Zhang, C.; Yang, Y.; Chi, Y.; Tang, X.; Zhang, H.; Xiong, S.; Yu, L.; Zhou, D. Neutralizing antibody responses to enterovirus and adenovirus in healthy adults in China. Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2014, 3, e30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, T.H.; Lipatova, A.V.; Volskaya, M.A.; Tikhonova, O.A.; Chumakov, P.M. The state of the Jak/Stat pathway affects the sensitivity of tumor cells to oncolytic enteroviruses. Mol. Biol. 2020, 54, 634–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn, C.L.; Wimmer, E.; Racaniello, V.R. Cellular receptor for poliovirus: Molecular cloning, nucleotide sequence and expression of a new member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Cell 1989, 56, 855–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martino, T.A.; Petric, M.; Weingartl, H.; Bergelson, J.M.; Opavsky, M.A.; Richardson, C.D.; Modlin, J.F.; Finberg, R.W.; Kain, K.C.; Willis, N.; et al. The coxsackie-adenovirus receptor (CAR) is used by reference strains and clinical isolates representing all six serotypes of coxsackievirus group B and by swine vesicular disease virus. Virology 2000, 271, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipatova, A.V.; Le, T.H.; Sosnovtseva, A.O.; Babaeva, F.E.; Kochetkov, D.V.; Chumakov, P.M. Relationship between cell receptors and tumor cell sensitivity to oncolytic enteroviruses. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 2018, 166, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lea, S.M.; Powell, R.M.; McKee, T.; Evans, D.J.; Brown, D.; Stuart, D.I.; van der Merwe, P.A. Determination of the affinity and kinetic constants for the interaction between the human virus echovirus 11 and its cellular receptor, CD55. J. Biol. Chem. 1998, 273, 30443–30447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettigrew, D.M.; Williams, D.T.; Kerrigan, D.; Evans, D.J.; Lea, S.M.; Bhella, D. Structural and functional insights into the interaction of echoviruses and decay-accelerating factor. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 5169–5177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vandesande, H.; Laajala, M.; Kantoluoto, T.; Ruokolainen, V.; Lindberg, A.M.; Marjomaki, V. Early Entry Events in Echovirus 30 Infection. J. Virol. 2020, 94, e00592-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudnik-Jansen, I.; Howard, K.A. FcRn expression in cancer: Mechanistic basis and therapeutic opportunities. J. Control. Release 2021, 337, 248–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.H.; Lee, J.H.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, D.C.; Yang, J.W.; An, H.J.; Na, J.M.; Shin, M.C.; Song, D.H. Fc Receptor Expression as a Prognostic Factor in Patients with Non-small-cell Lung Cancer. In Vivo 2022, 36, 2708–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nyström, K.; Waldenström, J.; Tang, K.-W.; Lagging, M. Ribavirin: Pharmacology, Multiple Modes of Action and Possible Future Perspectives. Future Virol. 2019, 14, 153–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, P. Development of Approaches to Glioblastoma Therapy with Oncolytic Viruses. Ph.D. Thesis, Engelhardt Insitute of Molecular Biology, Moscow, Russia, 2023. Available online: https://www.eimb.ru/ru1/zashita/vorobyev/vorobyev_autoref.pdf (accessed on 16 January 2025).
- Sievers, F.; Higgins, D.G. Clustal Omega for making accurate alignments of many protein sequences. Protein Sci. 2018, 27, 135–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huerta-Cepas, J.; Serra, F.; Bork, P. ETE 3: Reconstruction, Analysis and Visualization of Phylogenomic Data. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2016, 33, 1635–1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vorobyev, P.O.; Kochetkov, D.V.; Vasilenko, K.V.; Lipatova, A.V. Comparative efficiency of accessible transfection methods in model cell lines for biotechnological applications. Bull. Russ. State Med. Univ. 2022, 3, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bankevich, A.; Nurk, S.; Antipov, D.; Gurevich, A.A.; Dvorkin, M.; Kulikov, A.S.; Lesin, V.M.; Nikolenko, S.I.; Pham, S.; Prjibelski, A.D.; et al. SPAdes: A new genome assembly algorithm and its applications to single-cell sequencing. J. Comput. Biol. 2012, 19, 455–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galaxy, C. The Galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2022 update. Nucleic Acids Res. 2022, 50, W345–W351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Viral Receptor Target Gene | Oligonucleotides Used for Cloning of sgRNA Spacers | Oligonucleotides Used for Amplification of CRISPR/Cas9 Targeted Gene Regions | An Antibody Used Against a Viral Receptor |
|---|---|---|---|
| PVR | 5′-phospho-GATCGcgggatgcccaatacgagccG | CCATGCCATCCTGTACCCTT | Abcam (ab205304) |
| 5′-phospho-AAAACggctcgtattgggcatcccgC | GAAGCAATGCCTACAGTGCC | ||
| CXADR | 5′-phospho-GATCGtacgcttagtcccgaagaccG | TTCTGAATGGCTGCGGGG | Abcam (ab126250) |
| 5′-phospho-AAAACggtcttcgggactaagcgtaC | ATGTGACTGGCAAGGTGATG | ||
| CD55 | 5′-phospho-GATCGattggagagcactctattG | CCAGCACCACCACAAATTGA | Abcam (ab253284) |
| 5′-phospho-AAAACaatagagtgctctccaatC | AGACCCTTCTGAGAAGCTGT | ||
| SCARB2 | 5′-phospho-GATCGacagttgacgaattgctctggG | ATCGAGGCCATGTTGAAAGC | Abcam (ab176317) |
| 5′-phospho-AAAACccagagcaattcgtcaactgtC | GTTAATCTGGCTTGGGGTGC | ||
| ICAM1 | 5′-phospho-GATCGgctattcaaactgccctgatgG | GCGCACATTCCCCTTGATGAA | Abcam (ab109361) |
| 5′-phospho-AAAACcatcagggcagtttgaatagcC | CAGTACACGGTGAGGAAGGT | ||
| ITGA2 | 5′-phospho-GATCGattggagagcactctattG | TGTAGCCACAAGACACTGATG | Abcam (ab181548) |
| 5′-phospho-AAAACgttggtacttcggctttctcC | ACAGCAAAAGGATTCCAGCA | ||
| FCGRT | 5′-phospho-GATCGctgagctacaatagcctgcgC | TTCTCCCTCCCTGGGTATCT | Abcam (ab228975) |
| 5′-phospho-AAAACaccggaatctcaccttttcccG | ACCGGAATCTCACCTTTTCCC |
| Name of Strain | Identified Virus | Strain from Gene Bank | Percent Identity |
|---|---|---|---|
| LEV14 | CVB5 | SPS68033 (CVB5 strain RO-14-5-70) | 97.27% |
| AF114383 (CVB5 strain Faulkner) | 96.02% | ||
| LEV15 | CVB6 | AFD32988.1 (CVB6 strain LEV15) | 100% |
| AAF12719 (CVB6 strain Schmitt) | 99.18% | ||
| LEV20 | E12 | AWX63811 (E12 strain K624/YN/CHN/2013) | 97.63% |
| Q66575 (E12 strain Travis) | 96.17% | ||
| LEV21 | E7 | AZT88545 (E7 strain Nigeria/AFP/2014) | 97.53% |
| AY302559 (E7 strain Wallace) | 94.2% | ||
| LEV22 | E6 | AXP11726 (E6 strain GHA:CEN:UDW/2017) | 99.10% |
| Q66474 (E6 strain Charles) | 95% | ||
| LEV23 | E30 | WGU13597 (E30 strain E30/USA/3E5/2009) | 93.69% |
| AF311938 (E30 strain Bastianni) | 92.45% | ||
| LEV24 | E25 | CAA62257 (E25 strain JV-4) | 98.13% |
| ADG63656 (E25 strain HN2) | 95.74% | ||
| LEV25 | E11 | QIZ12960 (E11 strain SD2003-478/SD/CHN/2003) | 97.53% |
| ABV00677 (E11 strain D207) | 91.80% | ||
| LEV28 | CVA21 | ABM54535 (CVA21 strain USA-Az94-10621) | 99.77% |
| AAQ04838 (CVA21 strain Kuykendall) | 97.69% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sosnovtseva, A.O.; Le, T.H.; Karpov, D.S.; Vorobyev, P.O.; Gumennaya, Y.D.; Alekseeva, O.N.; Chumakov, P.M.; Lipatova, A.V. Establishment of a Panel of Human Cell Lines to Identify Cellular Receptors Used by Enteroviruses to Infect Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26030923
Sosnovtseva AO, Le TH, Karpov DS, Vorobyev PO, Gumennaya YD, Alekseeva ON, Chumakov PM, Lipatova AV. Establishment of a Panel of Human Cell Lines to Identify Cellular Receptors Used by Enteroviruses to Infect Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26030923
Chicago/Turabian StyleSosnovtseva, Anastasiia O., Thi Hoa Le, Dmitry S. Karpov, Pavel O. Vorobyev, Yana D. Gumennaya, Olga N. Alekseeva, Peter M. Chumakov, and Anastasia V. Lipatova. 2025. "Establishment of a Panel of Human Cell Lines to Identify Cellular Receptors Used by Enteroviruses to Infect Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26030923
APA StyleSosnovtseva, A. O., Le, T. H., Karpov, D. S., Vorobyev, P. O., Gumennaya, Y. D., Alekseeva, O. N., Chumakov, P. M., & Lipatova, A. V. (2025). Establishment of a Panel of Human Cell Lines to Identify Cellular Receptors Used by Enteroviruses to Infect Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 923. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26030923







