The Impact of Human Liver Transplantation on the Concentration of Fibroblast Growth Factors: FGF19 and FGF21
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
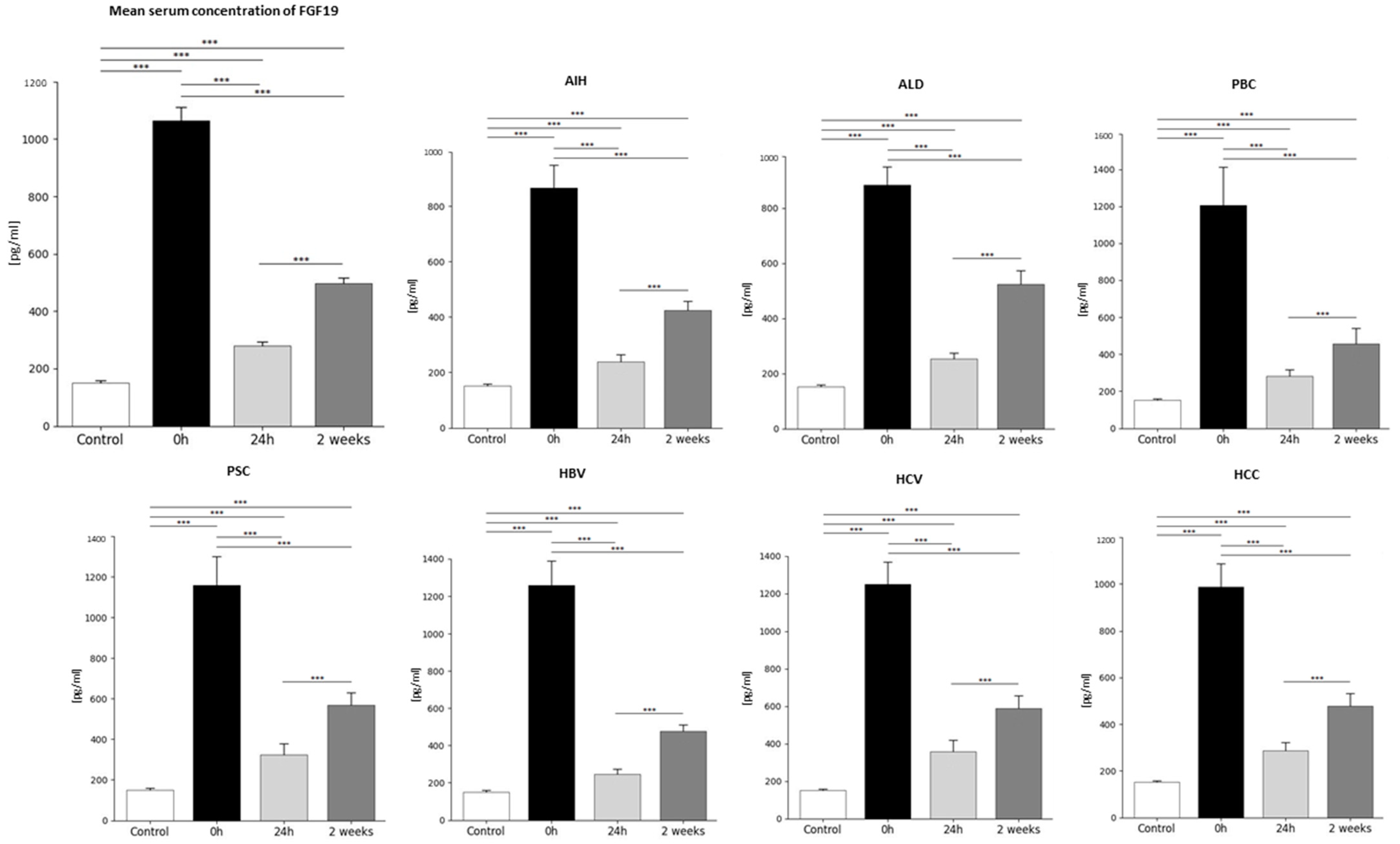
2.1. Analysis of Average FGF19 Concentration in Patients Before and After Liver Transplantation and in the Healthy Control Group—Statistics Data
2.2. FGF19 Concentration Before and After Liver Transplantation Depending on Primary Disease
2.3. Analysis of Average FGF21 Concentration in Patients Before and After Liver Transplantation and in the Healthy Control Group—Statistics Data
2.4. FGF21 Concentration Before and After Liver Transplantation Depending on the Primary Disease
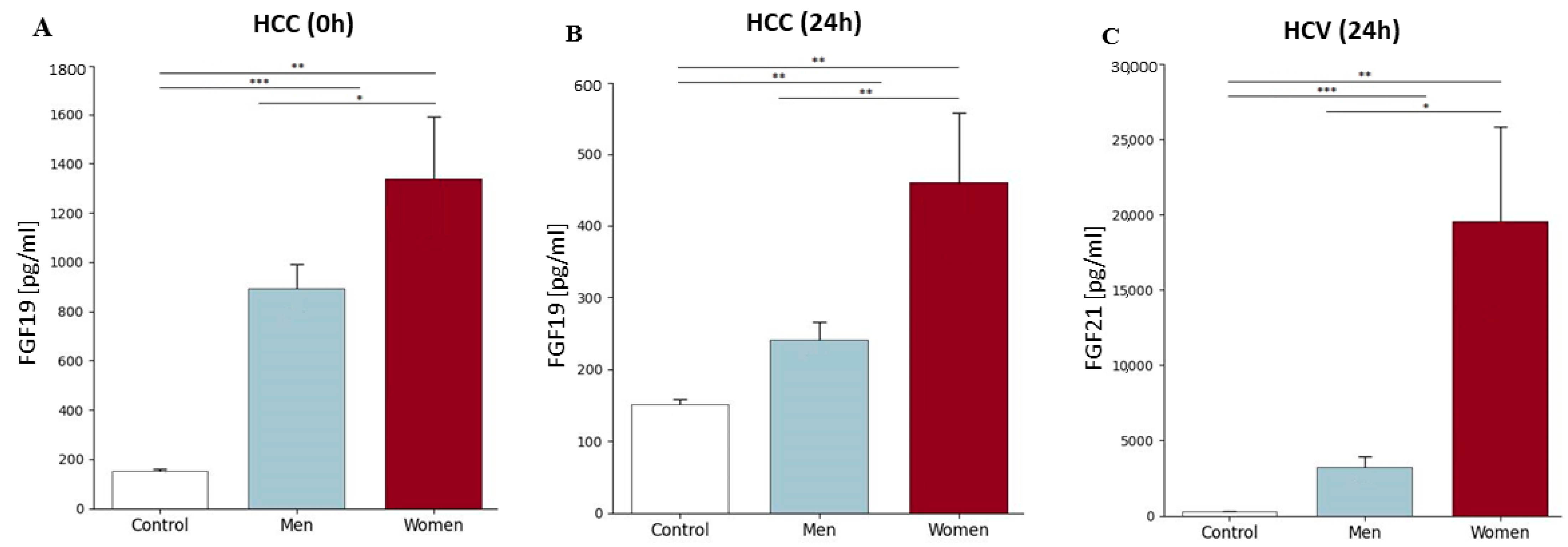
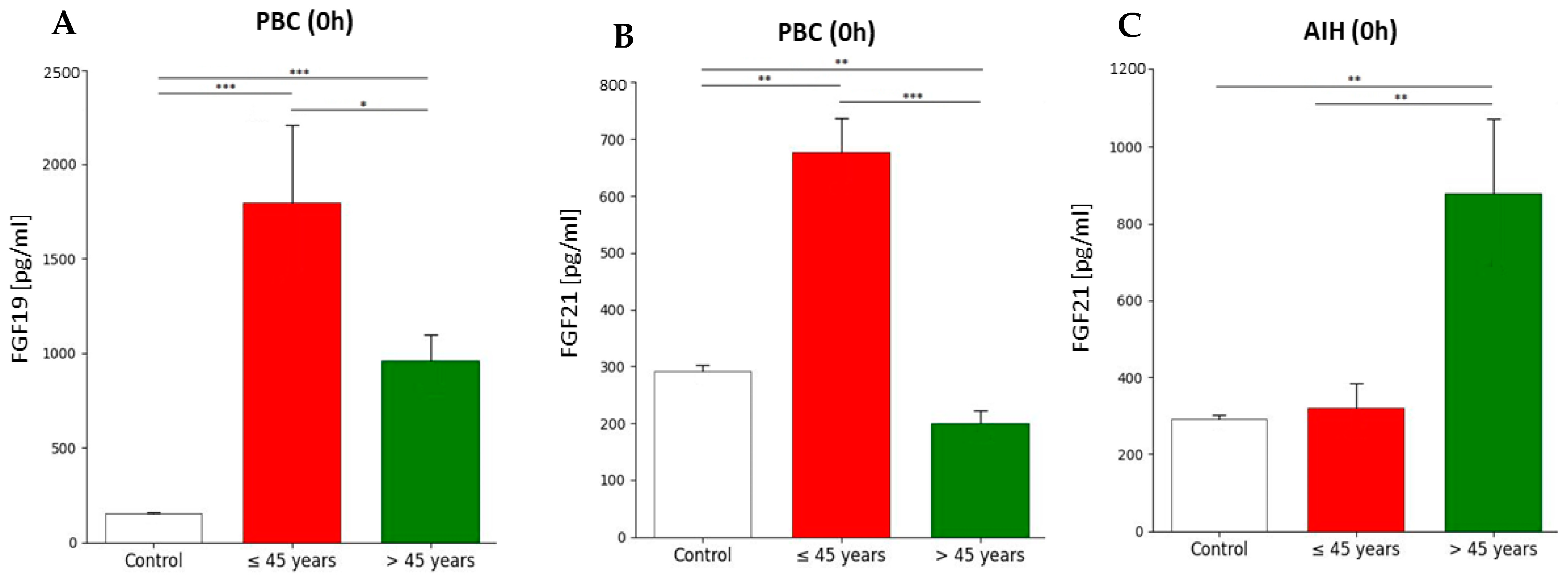
2.5. FGF19 and FGF21 Concentration Before and After Liver Transplantation Depending on the Primary Disease, Patient’s Gender, and Age Group
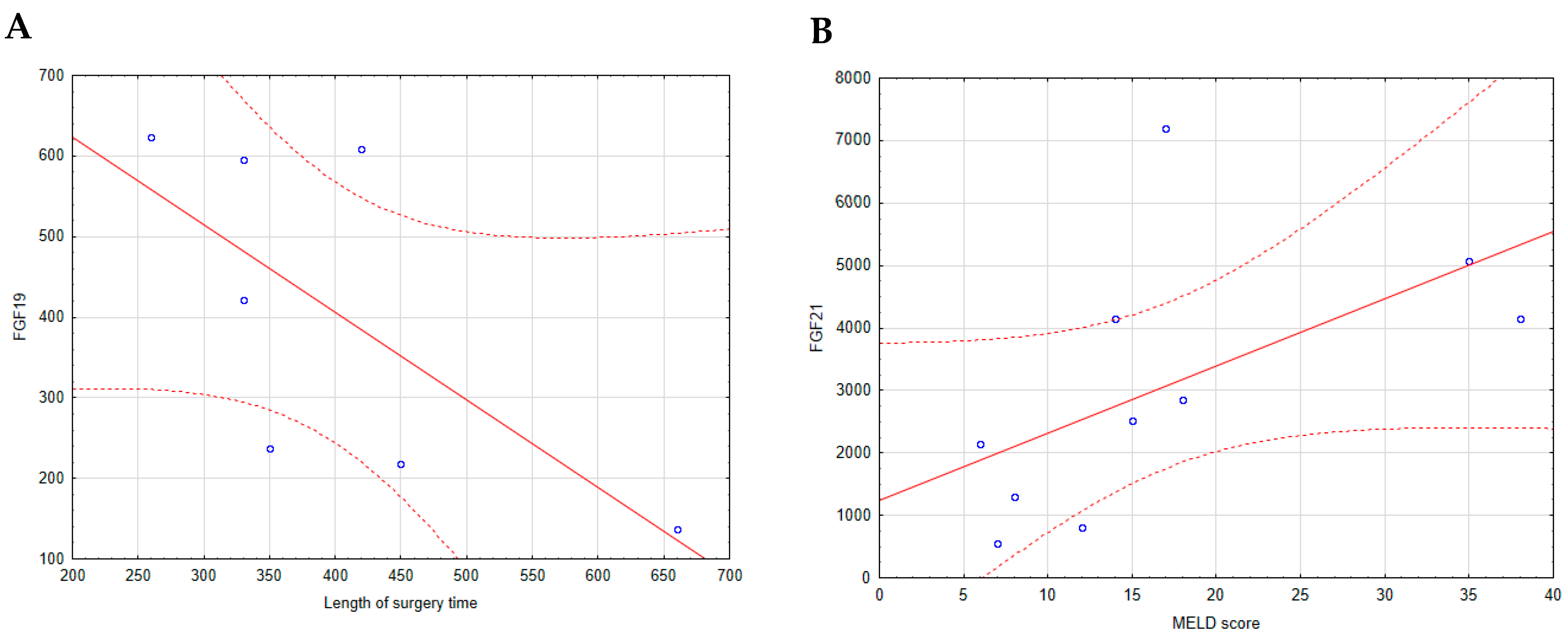
2.6. Correlations of Basic Laboratory Parameters with FGF19 and FGF21
3. Discussion
3.1. Changes in FGF19 Concentration in Patients Before and After Liver Transplantation (24 h, 2 Weeks) and Comparison in Those Changes with the Healthy Control Group
3.2. Changes in FGF21 Concentration in Patients Before and After Liver Transplantation (24 h, 2 Weeks) and Comparison in Those Changes with the Healthy Control Group
3.3. Conclusions
3.4. Limitations
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Group
4.2. Study Material
4.3. Assay Procedure
4.4. Statistical Analysis
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kalra, A.Y.E.; Wehrle, C.J.; Tuma, F. Physiology, Liver. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK535438/ (accessed on 1 May 2023).
- Adam, R.; Karam, V.; Delvart, V.; O’Grady, J.; Mirza, D.; Klempnauer, J.; Castaing, D.; Neuhaus, P.; Jamieson, N.; Salizzoni, M.; et al. Evolution of indications and results of liver transplantation in Europe. A report from the European Liver Transplant Registry (ELTR). J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 675–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, W.M.; Squires, R.H., Jr.; Nyberg, S.L.; Doo, E.; Hoofnagle, J.H. Acute liver failure: Summary of a workshop. Hepatology 2008, 47, 1401–1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, A.T.; Avelino-Silva, V.I.; Pecora, R.A.; Pugliese, V.; D’Albuquerque, L.A.; Abdala, E. Liver transplantation: Fifty years of experience. World J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 20, 5363–5374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Decker, K. Biologically active products of stimulated liver macrophages (Kupffer cells). Eur. J. Biochem. 1990, 192, 245–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meirelles Junior, R.F.; Salvalaggio, P.; Rezende, M.B.; Evangelista, A.S.; Guardia, B.D.; Matielo, C.E.; Neves, D.B.; Pandullo, F.L.; Felga, G.E.; Alves, J.A.; et al. Liver transplantation: History, outcomes and perspectives. Einstein 2015, 13, 149–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolf, M.; Molnar, M.Z.; Amaral, A.P.; Czira, M.E.; Rudas, A.; Ujszaszi, A.; Kiss, I.; Rosivall, L.; Kosa, J.; Lakatos, P.; et al. Elevated fibroblast growth factor 23 is a risk factor for kidney transplant loss and mortality. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2011, 22, 956–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prie, D.; Forand, A.; Francoz, C.; Elie, C.; Cohen, I.; Courbebaisse, M.; Eladari, D.; Lebrec, D.; Durand, F.; Friedlander, G. Plasma fibroblast growth factor 23 concentration is increased and predicts mortality in patients on the liver-transplant waiting list. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e66182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; Molnar, M.Z.; Kovesdy, C.P.; Mucsi, I.; Bunnapradist, S. Management of mineral and bone disorder after kidney transplantation. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2012, 21, 389–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, X.; Torregrosa, J.V. Role of FGF23 in Kidney Transplantation. J. Transplant. Technol. Res. 2011, S1, 002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchelek-Mysliwiec, M.; Dziedziejko, V.; Nowosiad-Magda, M.; Dolegowska, K.; Dolegowska, B.; Pawlik, A.; Safranow, K.; Wisniewska, M.; Stepniewska, J.; Domanski, M.; et al. Chronic Kidney Disease Is Associated with Increased Plasma Levels of Fibroblast Growth Factors 19 and 21. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2019, 44, 1207–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, D.; Li, H.; Wang, Y.; Jia, W.; Zhou, J.; Fan, J.; Man, K.; Lo, C.; Wong, C.; Wang, Y.; et al. Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Is A Sensitive Biomarker for Severe Ischemia/reperfusion Injury in Patients with Liver Transplantation. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 19776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miura, S.; Mitsuhashi, N.; Shimizu, H.; Kimura, F.; Yoshidome, H.; Otsuka, M.; Kato, A.; Shida, T.; Okamura, D.; Miyazaki, M. Fibroblast growth factor 19 expression correlates with tumor progression and poorer prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uriarte, I.; Fernandez-Barrena, M.G.; Monte, M.J.; Latasa, M.U.; Chang, H.C.; Carotti, S.; Vespasiani-Gentilucci, U.; Morini, S.; Vicente, E.; Concepcion, A.R.; et al. Identification of fibroblast growth factor 15 as a novel mediator of liver regeneration and its application in the prevention of post-resection liver failure in mice. Gut 2013, 62, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seeherunvong, W.; Wolf, M. Tertiary excess of fibroblast growth factor 23 and hypophosphatemia following kidney transplantation. Pediatr. Transplant. 2011, 15, 37–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, X.; Boney-Montoya, J.; Owen, B.M.; Bookout, A.L.; Coate, K.C.; Mangelsdorf, D.J.; Kliewer, S.A. betaKlotho is required for fibroblast growth factor 21 effects on growth and metabolism. Cell Metab. 2012, 16, 387–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kliewer, S.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Fibroblast growth factor 21: From pharmacology to physiology. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 254S–257S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolegowska, K.; Marchelek-Mysliwiec, M.; Nowosiad-Magda, M.; Slawinski, M.; Dolegowska, B. FGF19 subfamily members: FGF19 and FGF21. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 75, 229–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, M.C.; Shiizaki, K.; Kuro-o, M.; Moe, O.W. Fibroblast growth factor 23 and Klotho: Physiology and pathophysiology of an endocrine network of mineral metabolism. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2013, 75, 503–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Powers, C.J.; McLeskey, S.W.; Wellstein, A. Fibroblast growth factors, their receptors and signaling. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 2000, 7, 165–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Yu, L.; Lin, X.; Cheng, P.; He, L.; Li, X.; Lu, X.; Tan, Y.; Yang, H.; Cai, L.; et al. Minireview: Roles of Fibroblast Growth Factors 19 and 21 in Metabolic Regulation and Chronic Diseases. Mol. Endocrinol. 2015, 29, 1400–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, I.; Iwata, T.; Leung, H.Y. Mechanisms of FGFR-mediated carcinogenesis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2012, 1823, 850–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.; Garg, C.; Lahiri, S.S. Therapeutic potential of FGF 21 in diabetes. J. Med. Plants Stud. 2017, 5, 364–372. [Google Scholar]
- Johansson, H.; Mork, L.M.; Li, M.; Sandblom, A.L.; Bjorkhem, I.; Hoijer, J.; Ericzon, B.G.; Jorns, C.; Gilg, S.; Sparrelid, E.; et al. Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 in Portal and Systemic Blood. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2018, 8, 162–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dostalova, I.; Kavalkova, P.; Haluzikova, D.; Lacinova, Z.; Mraz, M.; Papezova, H.; Haluzik, M. Plasma concentrations of fibroblast growth factors 19 and 21 in patients with anorexia nervosa. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2008, 93, 3627–3632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Hanks, L.J.; Gutierrez, O.M.; Bamman, M.M.; Ashraf, A.; McCormick, K.L.; Casazza, K. Circulating levels of fibroblast growth factor-21 increase with age independently of body composition indices among healthy individuals. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2015, 2, 77–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeda, T.; Kanzaki, H.; Chiba, T.; Ao, J.; Kanayama, K.; Maruta, S.; Kusakabe, Y.; Saito, T.; Kobayashi, K.; Kiyono, S.; et al. Serum fibroblast growth factor 19 serves as a potential novel biomarker for hepatocellular carcinoma. BMC Cancer 2019, 19, 1088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelfat, K.V.K.; Svavarsson, B.I.; Neis, E.P.; Dejong, C.H.C.; Schaap, F.G.; Olde Damink, S.W.M. Elevated plasma levels of FGF19 is associated with repression of bile salt synthesis in patients with obstructive cholestasis. HPB J. 2008, 20, S331–S332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Hu, J.Y.; Zou, H.L.; Li, Y.H.; Nie, D.Y.; Chao, C.; Liu, J.H.; Ding, J.; Zhou, Z.G.; Xiao, Y. Serum fibroblast growth factor 19 (FGF19) levels are associated with atherogenic dyslipidemia in patients with type 2 diabetes. Chin. Med. J. 2021, 134, 2243–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wunsch, E.; Milkiewicz, M.; Wasik, U.; Trottier, J.; Kempinska-Podhorodecka, A.; Elias, E.; Barbier, O.; Milkiewicz, P. Expression of hepatic Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 is enhanced in Primary Biliary Cirrhosis and correlates with severity of the disease. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kir, S.; Kliewer, S.A.; Mangelsdorf, D.J. Roles of FGF19 in liver metabolism. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 2011, 76, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandez, M.; Semela, D.; Bruix, J.; Colle, I.; Pinzani, M.; Bosch, J. Angiogenesis in liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2009, 50, 604–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.S.; Semela, D.; Iredale, J.; Shah, V.H. Sinusoidal remodeling and angiogenesis: A new function for the liver-specific pericyte? Hepatology 2007, 45, 817–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bohm, F.; Kohler, U.A.; Speicher, T.; Werner, S. Regulation of liver regeneration by growth factors and cytokines. EMBO Mol. Med. 2010, 2, 294–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shan, Z.; Alvarez-Sola, G.; Uriarte, I.; Arechederra, M.; Fernandez-Barrena, M.G.; Berasain, C.; Ju, C.; Avila, M.A. Fibroblast growth factors 19 and 21 in acute liver damage. Ann. Transl. Med. 2018, 6, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.Y.; Xie, D.M.; Zhu, G.Q.; Huang, G.Q.; Lin, Y.Q.; Wang, L.R.; Shi, K.Q.; Hu, B.; Braddock, M.; Chen, Y.P.; et al. Targeting fibroblast growth factor 19 in liver disease: A potential biomarker and therapeutic target. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2015, 19, 675–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholes, K.; Guillet, S.; Tomlinson, E.; Hillan, K.; Wright, B.; Frantz, G.D.; Pham, T.A.; Dillard-Telm, L.; Tsai, S.P.; Stephan, J.P.; et al. A mouse model of hepatocellular carcinoma: Ectopic expression of fibroblast growth factor 19 in skeletal muscle of transgenic mice. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 2295–2307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- French, D.M.; Lin, B.C.; Wang, M.; Adams, C.; Shek, T.; Hotzel, K.; Bolon, B.; Ferrando, R.; Blackmore, C.; Schroeder, K.; et al. Targeting FGFR4 inhibits hepatocellular carcinoma in preclinical mouse models. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e36713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Sola, G.; Uriarte, I.; Latasa, M.U.; Jimenez, M.; Barcena-Varela, M.; Santamaria, E.; Urtasun, R.; Rodriguez-Ortigosa, C.; Prieto, J.; Corrales, F.J.; et al. Engineered fibroblast growth factor 19 protects from acetaminophen-induced liver injury and stimulates aged liver regeneration in mice. Cell Death Dis. 2017, 8, e3083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, A.L.; Coulter, S.; Liddle, C.; Wong, A.; Eastham-Anderson, J.; French, D.M.; Peterson, A.S.; Sonoda, J. FGF19 regulates cell proliferation, glucose and bile acid metabolism via FGFR4-dependent and independent pathways. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Lu, W.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Luo, Y. Targeting the FGF19-FGFR4 pathway for cholestatic, metabolic, and cancerous diseases. J. Intern. Med. 2024, 295, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manithody, C.S.; Van Nispen, J.; Murali, V.; Jain, S.; Samaddar, A.; Armstrong, A.; Jain, A. Role of Bile Acids and Gut Microbiota in Parenteral Nutrition Associated Injury. J. Hum. Nutr. 2020, 4, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiche, M.; Bachmann, A.; Lossner, U.; Bluher, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Fasshauer, M. Fibroblast growth factor 19 serum levels: Relation to renal function and metabolic parameters. Horm. Metab. Res. 2010, 42, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panek-Jeziorna, M.; Mulak, A. An Inverse Correlation of Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 with Abdominal Pain and Inflammatory Markers in Patients with Ulcerative Colitis. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2020, 2020, 2389312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Lin, B.; Lin, G.; Wu, Y.; Jie, Y.; Li, X.; Ko, B.; Chong, Y.; Luo, J. Circulating FGF19 closely correlates with bile acid synthesis and cholestasis in patients with primary biliary cirrhosis. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0178580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Massafra, V.; Milona, A.; Vos, H.R.; Burgering, B.M.; van Mil, S.W. Quantitative liver proteomics identifies FGF19 targets that couple metabolism and proliferation. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Yang, F.; Pang, J.; Wu, Y.; Chong, Y.; Li, X. Dysregulation of Circulating FGF19 and Bile Acids in Primary Biliary Cholangitis-Autoimmune Hepatitis Overlap Syndrome. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1934541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Learned, R.M.; Rossi, S.J.; DePaoli, A.M.; Tian, H.; Ling, L. Engineered fibroblast growth factor 19 reduces liver injury and resolves sclerosing cholangitis in Mdr2-deficient mice. Hepatology 2016, 63, 914–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milkiewicz, M.; Klak, M.; Kempinska-Podhorodecka, A.; Wiechowska-Kozlowska, A.; Urasinska, E.; Blatkiewicz, M.; Wunsch, E.; Elias, E.; Milkiewicz, P. Impaired Hepatic Adaptation to Chronic Cholestasis induced by Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 39573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, B.I.; Ince, V.; Bag, H.G.; Usta, S.; Ersan, V.; Isik, B.; Yilmaz, S. CRP is a superior and prognostically significant inflammation biomarker for hepatocellular cancer patients treated by liver transplantation. Clin. Pract. 2021, 18, 1626–1632. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, G.A.; Nashaat, E.H.; Fawzy, H.M.; ElGhandour, A.M. Assessment of fibroblast growth factor 19 as a non-invasive serum marker for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Hepatol. 2022, 14, 623–633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariello, M.; Piglionica, M.; Gadaleta, R.M.; Moschetta, A. The Enterokine Fibroblast Growth Factor 15/19 in Bile Acid Metabolism. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2019, 256, 73–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alvarez-Sola, G.; Uriarte, I.; Latasa, M.U.; Jimenez, M.; Barcena-Varela, M.; Santamaria, E.; Urtasun, R.; Rodriguez-Ortigosa, C.; Prieto, J.; Berraondo, P.; et al. Bile acids, FGF15/19 and liver regeneration: From mechanisms to clinical applications. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1326–1334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Kim, E.J.; Lee, J.G.; Kim, B.S.; Huh, K.H.; Kim, M.S.; Kim, S.I.; Kim, Y.S.; Joo, D.J. Clinical impact of serum bilirubin levels on kidney transplant outcomes. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 6889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kochhar, G.; Parungao, J.M.; Hanouneh, I.A.; Parsi, M.A. Biliary complications following liver transplantation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2013, 19, 2841–2846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferrell, J.M.; Dilts, M.; Pokhrel, S.; Stahl, Z.; Boehme, S.; Wang, X.; Chiang, J.Y.L. Fibroblast Growth Factor 19 Alters Bile Acids to Induce Dysbiosis in Mice with Alcohol-Induced Liver Disease. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2024, 18, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandl, K.; Hartmann, P.; Jih, L.J.; Pizzo, D.P.; Argemi, J.; Ventura-Cots, M.; Coulter, S.; Liddle, C.; Ling, L.; Rossi, S.J.; et al. Dysregulation of serum bile acids and FGF19 in alcoholic hepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2018, 69, 396–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louie, J.S.; Grandhe, S.; Matsukuma, K.; Bowlus, C.L. Primary Biliary Cholangitis: A Brief Overview. Clin. Liver Dis. 2020, 15, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weyand, C.M.; Goronzy, J.J. Aging of the Immune System. Mechanisms and Therapeutic Targets. Ann. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2016, 13 (Suppl. S5), S422–S428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galman, C.; Lundasen, T.; Kharitonenkov, A.; Bina, H.A.; Eriksson, M.; Hafstrom, I.; Dahlin, M.; Amark, P.; Angelin, B.; Rudling, M. The circulating metabolic regulator FGF21 is induced by prolonged fasting and PPARalpha activation in man. Cell Metab. 2008, 8, 169–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fazeli, P.K.; Lun, M.; Kim, S.M.; Bredella, M.A.; Wright, S.; Zhang, Y.; Lee, H.; Catana, C.; Klibanski, A.; Patwari, P.; et al. FGF21 and the late adaptive response to starvation in humans. J. Clin. Investig. 2015, 125, 4601–4611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Yeung, D.C.; Karpisek, M.; Stejskal, D.; Zhou, Z.G.; Liu, F.; Wong, R.L.; Chow, W.S.; Tso, A.W.; Lam, K.S.; et al. Serum FGF21 levels are increased in obesity and are independently associated with the metabolic syndrome in humans. Diabetes 2008, 57, 1246–1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taniguchi, H.; Tanisawa, K.; Sun, X.; Cao, Z.B.; Oshima, S.; Ise, R.; Sakamoto, S.; Higuchi, M. Cardiorespiratory fitness and visceral fat are key determinants of serum fibroblast growth factor 21 concentration in Japanese men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2014, 99, E1877–E1884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kralisch, S.; Tonjes, A.; Krause, K.; Richter, J.; Lossner, U.; Kovacs, P.; Ebert, T.; Bluher, M.; Stumvoll, M.; Fasshauer, M. Fibroblast growth factor-21 serum concentrations are associated with metabolic and hepatic markers in humans. J. Endocrinol. 2013, 216, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dushay, J.; Chui, P.C.; Gopalakrishnan, G.S.; Varela-Rey, M.; Crawley, M.; Fisher, F.M.; Badman, M.K.; Martinez-Chantar, M.L.; Maratos-Flier, E. Increased fibroblast growth factor 21 in obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 456–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.R.; Bando, Y.; Miyawaki, K.; Shikama, Y.; Kosugi, C.; Aki, N.; Funaki, M.; Noji, S. Correlation of fibroblast growth factor 21 serum levels with metabolic parameters in Japanese subjects. J. Med. Investig. 2014, 61, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bisgaard, A.; Sorensen, K.; Johannsen, T.H.; Helge, J.W.; Andersson, A.M.; Juul, A. Significant gender difference in serum levels of fibroblast growth factor 21 in Danish children and adolescents. Int. J. Pediatr. Endocrinol. 2014, 2014, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Gijbels, A.; Schutte, S.; Esser, D.; Michielsen, C.; Siebelink, E.; Mars, M.; Mensink, M.; Afman, L.A. Plasma FGF21 Levels Are Not Associated with Weight Loss or Improvements in Metabolic Health Markers upon 12 Weeks of Energy Restriction: Secondary Analysis of an RCT. Nutrients 2022, 14, 5061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gariani, K.; Drifte, G.; Dunn-Siegrist, I.; Pugin, J.; Jornayvaz, F.R. Increased FGF21 plasma levels in humans with sepsis and SIRS. Endocr. Connect. 2013, 2, 146–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantero, I.; Abete, I.; Bullon-Vela, V.; Crujeiras, A.B.; Casanueva, F.F.; Zulet, M.A.; Martinez, J.A. Fibroblast growth factor 21 levels and liver inflammatory biomarkers in obese subjects after weight loss. Arch. Med. Sci. 2022, 18, 36–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mai, K.; Andres, J.; Biedasek, K.; Weicht, J.; Bobbert, T.; Sabath, M.; Meinus, S.; Reinecke, F.; Mohlig, M.; Weickert, M.O.; et al. Free fatty acids link metabolism and regulation of the insulin-sensitizing fibroblast growth factor-21. Diabetes 2009, 58, 1532–1538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryan, K.K.; Packard, A.E.B.; Larson, K.R.; Stout, J.; Fourman, S.M.; Thompson, A.M.K.; Ludwick, K.; Habegger, K.M.; Stemmer, K.; Itoh, N.; et al. Dietary Manipulations That Induce Ketosis Activate the HPA Axis in Male Rats and Mice: A Potential Role for Fibroblast Growth Factor-21. Endocrinology 2018, 159, 400–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, M.S. FGF21 as a Stress Hormone: The Roles of FGF21 in Stress Adaptation and the Treatment of Metabolic Diseases. Diabetes Metab. J. 2014, 38, 245–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.H.; Lee, M.S. FGF21 as a mediator of adaptive responses to stress and metabolic benefits of anti-diabetic drugs. J. Endocrinol. 2015, 226, R1–R16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gomez-Samano, M.A.; Grajales-Gomez, M.; Zuarth-Vazquez, J.M.; Navarro-Flores, M.F.; Martinez-Saavedra, M.; Juarez-Leon, O.A.; Morales-Garcia, M.G.; Enriquez-Estrada, V.M.; Gomez-Perez, F.J.; Cuevas-Ramos, D. Fibroblast growth factor 21 and its novel association with oxidative stress. Redox Biol. 2017, 11, 335–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prida, E.; Alvarez-Delgado, S.; Perez-Lois, R.; Soto-Tielas, M.; Estany-Gestal, A.; Ferno, J.; Seoane, L.M.; Quinones, M.; Al-Massadi, O. Liver Brain Interactions: Focus on FGF21 a Systematic Review. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 13318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, M.; Morimoto, H.; Maruyama, R.; Inoue, J.; Sato, R. Selective Regulation of FGF19 and FGF21 Expression by Cellular and Nutritional Stress. J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2015, 61, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Falamarzi, K.; Malekpour, M.; Tafti, M.F.; Azarpira, N.; Behboodi, M.; Zarei, M. The role of FGF21 and its analogs on liver associated diseases. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 967375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Garza, U.; Torres-Oteros, D.; Yarritu-Gallego, A.; Marrero, P.F.; Haro, D.; Relat, J. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 and the Adaptive Response to Nutritional Challenges. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, Y.; He, J.; Li, S.; Song, L.; Guo, X.; Yao, W.; Zou, D.; Gao, X.; Liu, Y.; Bai, F.; et al. Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21) inhibits macrophage-mediated inflammation by activating Nrf2 and suppressing the NF-kappaB signaling pathway. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2016, 38, 144–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Q.; Martin, R.C.; Shi, X.; Pandit, H.; Yu, Y.; Liu, X.; Guo, W.; Tan, M.; Bai, O.; Meng, X.; et al. Lack of FGF21 promotes NASH-HCC transition via hepatocyte-TLR4-IL-17A signaling. Theranostics 2020, 10, 9923–9936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Zhao, T.T.; Li, S.M.; Sun, X.; Li, Z.C.; Li, Y.H.; Li, D.S.; Wang, W.F. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Exerts its Anti-inflammatory Effects on Multiple Cell Types of Adipose Tissue in Obesity. Obesity 2019, 27, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krautbauer, S.; Rein-Fischboeck, L.; Haberl, E.M.; Pohl, R.; Wiest, R.; Buechler, C. Circulating fibroblast growth factor 21 in patients with liver cirrhosis. Clin. Exp. Med. 2018, 18, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McLean Diaz, P.; Vannier, A.; Joshi, A.D.; Mahle, R.E.; Przybyszewski, E.M.; Corey, K.; Chung, R.T.; Luther, J.; Goodman, R.P.; Schaefer, E.A.K. Serum Fibroblast Growth Factor-21 Discriminates Between Decompensated Alcohol-Associated Cirrhosis and Severe Alcohol-Associated Hepatitis. Clin. Transl. Gastroenterol. 2023, 14, e00585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, S.N.; Reddy, K.R.; Keeffe, E.B.; Han, S.H.; Gaglio, P.J.; Perrillo, R.P.; Tran, T.T.; Pruett, T.L.; Lok, A.S. Comparison of clinical outcomes in chronic hepatitis B liver transplant candidates with and without hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transpl. 2007, 13, 334–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiang, W.; Shen, T.; Noman, M.; Guo, J.; Jin, Z.; Lin, D.; Pan, J.; Lu, H.; Li, X.; Gong, F. Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Augments Autophagy and Reduces Apoptosis in Damaged Liver to Improve Tissue Regeneration in Zebrafish. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 756743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.X.; Hu, Y.; French, S.W.; Gonzalez, F.J.; Wan, Y.J. Forced expression of fibroblast growth factor 21 reverses the sustained impairment of liver regeneration in hPPARalpha(PAC) mice due to dysregulated bile acid synthesis. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 9686–9700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Yu, C.; Jin, C.; Yang, C.; Xie, R.; Cao, D.; Wang, F.; McKeehan, W.L. Forced expression of hepatocyte-specific fibroblast growth factor 21 delays initiation of chemically induced hepatocarcinogenesis. Mol. Carcinog. 2006, 45, 934–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Schonke, M.; Spoorenberg, B.; Lambooij, J.M.; van der Zande, H.J.P.; Zhou, E.; Tushuizen, M.E.; Andreasson, A.C.; Park, A.; Oldham, S.; et al. FGF21 protects against hepatic lipotoxicity and macrophage activation to attenuate fibrogenesis in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Elife 2023, 12, e83075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.M.; Hale, C.; Stanislaus, S.; Xu, J.; Veniant, M.M. FGF21 acts as a negative regulator of bile acid synthesis. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 237, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbone, M.; Neuberger, J.M. Autoimmune liver disease, autoimmunity and liver transplantation. J. Hepatol. 2014, 60, 210–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heymann, F.; Tacke, F. Immunology in the liver--from homeostasis to disease. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2016, 13, 88–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Wang, L.; van der Laan, L.J.W.; Pan, Q.; Verstegen, M.M.A. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Oxidative Stress in Liver Transplantation and Underlying Diseases: New Insights and Therapeutics. Transplantation 2021, 105, 2362–2373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrielli, F.; Golfieri, L.; Nascimbeni, F.; Andreone, P.; Gitto, S. Metabolic Disorders in Liver Transplant Recipients: The State of the Art. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alkozai, E.M.; Lisman, T.; Porte, R.J.; Nijsten, M.W. Early elevated serum gamma glutamyl transpeptidase after liver transplantation is associated with better survival. F1000Res 2014, 3, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cazzagon, N.; Sarcognato, S.; Catanzaro, E.; Bonaiuto, E.; Peviani, M.; Pezzato, F.; Motta, R. Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: Diagnostic Criteria. Tomography 2024, 10, 47–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Pan, Q.; Wu, G.; Qian, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, L.; Fang, Q.; Zang, G.; Wang, Y.; Lau, G.; et al. Diverse Changes of Circulating Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Levels in Hepatitis B Virus-Related Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukla, M.; Berdowska, A.; Stygar, D.; Gabriel, A.; Mazur, W.; Logiewa-Bazger, B.; Sobala-Szczygiel, B.; Buldak, R.J.; Rokitka, M.; Zajecki, W.; et al. Serum FGF21 and RBP4 levels in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2012, 47, 1037–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ronca, V.; Mancuso, C.; Milani, C.; Carbone, M.; Oo, Y.H.; Invernizzi, P. Immune system and cholangiocytes: A puzzling affair in primary biliary cholangitis. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 108, 659–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritchie, M.; Hanouneh, I.A.; Noureddin, M.; Rolph, T.; Alkhouri, N. Fibroblast growth factor (FGF)-21 based therapies: A magic bullet for nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD)? Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannini, C.; Feldstein, A.E.; Santoro, N.; Kim, G.; Kursawe, R.; Pierpont, B.; Caprio, S. Circulating levels of FGF-21 in obese youth: Associations with liver fat content and markers of liver damage. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2013, 98, 2993–3000. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; He, B.W.; Yu, J.L.; Kang, H.M.; Zheng, T.T.; Chen, Z.Y.; Li, J.S. Clinical significance of serum FGF21 levels in diagnosing nonalcoholic fatty liver disease early. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 25191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| FGF19 [pg/mL] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease | Time of Blood Collection | p Value | |||
| Control Group | 0 h | 24 h | 2 Weeks | ||
| AIH | 151.0 ± 47.7 | 865.9 ± 286 | 237.8 ± 95 | 423.8 ± 118 | <0.0001 |
| ALD | 884.9 ± 214 | 252.6 ± 75 | 523.9 ± 162 | <0.0001 | |
| PBC | 1206.8 ± 580 | 280.9 ± 104 | 457.7 ± 235 | <0.0001 | |
| PSC | 1160.1 ± 396 | 325.4 ± 154 | 569.8 ± 173 | <0.0001 | |
| HBV | 1259.3 ± 430 | 245.3 ± 94 | 476.7 ± 120 | <0.0001 | |
| HCV | 1250 ± 352 | 356.5 ± 182 | 589.9 ± 201 | <0.0001 | |
| HCC | 986.5 ± 425 | 287.8 ± 142 | 479.4 ± 222 | <0.0001 | |
| FGF21 [pg/mL] | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Disease | Time of Blood Collection | p Value | |||
| Control Group | 0 h | 24 h | 2 Weeks | ||
| AIH | 290.59 ± 47.7 | 534.7 ± 387 | 2389.1 ± 1983 | 5897 ± 4808 | <0.0001 |
| ALD | 321.4 ± 205 | 781.8 ± 401 | 1892.2 ± 915 | <0.0001 | |
| PBC | 371.9 ± 226 | 3464.1 ± 2435 | 1165 ± 798 | <0.0001 | |
| PSC | 266 ± 108 | 2220.2 ± 992 | 449.1 ± 221 | <0.0001 | |
| HBV | 189 ± 65 | 2004.5 ± 2326 | 649.9 ± 485 | <0.0001 | |
| HCV | 973 ± 631 | 9758.3 ± 10,635 | 3073.4 ± 1979 | <0.0001 | |
| HCC | 561.7 ± 373 | 3182.6 ± 1960 | 1458.9 ± 762 | <0.0001 | |
| Time of Blood Collection | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | 0 h | 24 h | 2 Weeks |
| Gender (M/F) | 35/49 | 35/49 | 35/49 |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 50.9 ± 13 | 50.9 ± 13 | 50.9 ± 13 |
| CRP (mean ± SD NR < 5 mg/L) | 11.1 ± 12.3 | 41.7 ± 38.9 | 17.2 ± 19.6 |
| Hb (mean ± SD, NR 12–16 g/dL) | 11.9 ± 2.2 | 10.4 ± 1.25 | 10.2 ± 1.21 |
| Total bilirubin (mean ± SD, NR 0.2–1.1 mg/dL) | 6.2 ± 9.4 | 3.2 ± 3.3 | 1.9 ± 3.35 |
| ALP (mean ± SD, NR 40–120 IU/L) | 165 ± 125 | 272 ± 158 | 248 ± 216 |
| ALT (mean ± SD, NR 5–40 IU/L) | 91 ± 117.4 | 293 ± 226 | 123 ± 114 |
| AST (mean ± SD, NR 5–40 IU/L) | 105 ± 123 | 115 ± 161 | 47 ± 56 |
| GGTP (mean ± SD, NR 5–40 IU/L) | 152 ± 274 | 781 ± 520 | 567 ± 500 |
| Albumin (mean ± SD, NR 3.8–4.2 g/dL) | 3.6 ± 0.64 | 3.1 ± 0.42 | 3.3 ± 0.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Budkowska, M.; Ostrycharz-Jasek, E.; Cecerska-Heryć, E.; Dołęgowska, K.; Siennicka, A.; Nazarewski, Ł.; Rykowski, P.; Dołęgowska, B. The Impact of Human Liver Transplantation on the Concentration of Fibroblast Growth Factors: FGF19 and FGF21. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031299
Budkowska M, Ostrycharz-Jasek E, Cecerska-Heryć E, Dołęgowska K, Siennicka A, Nazarewski Ł, Rykowski P, Dołęgowska B. The Impact of Human Liver Transplantation on the Concentration of Fibroblast Growth Factors: FGF19 and FGF21. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031299
Chicago/Turabian StyleBudkowska, Marta, Ewa Ostrycharz-Jasek, Elżbieta Cecerska-Heryć, Katarzyna Dołęgowska, Aldona Siennicka, Łukasz Nazarewski, Paweł Rykowski, and Barbara Dołęgowska. 2025. "The Impact of Human Liver Transplantation on the Concentration of Fibroblast Growth Factors: FGF19 and FGF21" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031299
APA StyleBudkowska, M., Ostrycharz-Jasek, E., Cecerska-Heryć, E., Dołęgowska, K., Siennicka, A., Nazarewski, Ł., Rykowski, P., & Dołęgowska, B. (2025). The Impact of Human Liver Transplantation on the Concentration of Fibroblast Growth Factors: FGF19 and FGF21. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 1299. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031299






