Utility of Optical Genome Mapping for Accurate Detection and Fine-Mapping of Structural Variants in Elusive Rare Diseases
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Detailed Case Description
2.1. Brief Description of Patient 1
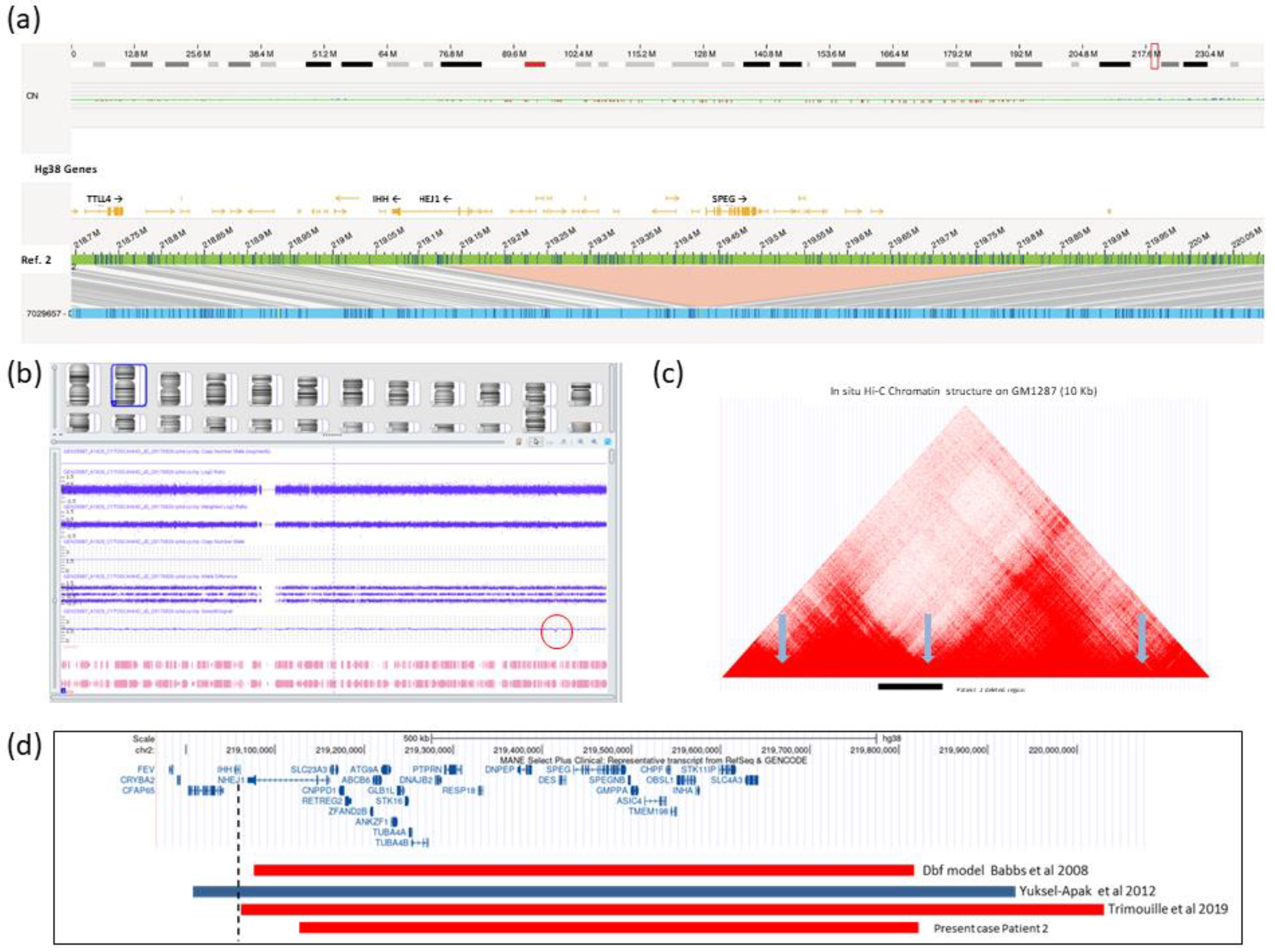
2.2. Brief Description of Patient 2
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Optical Genome Mapping
4.2. Exome Sequencing
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CGH-Array | Array comparative genomic hybridization |
| HbF | Fetal hemoglobin |
| OGM | Optical genome mapping |
| RDs | Rare diseases |
| SVs | Structural variants |
| TADs | Topologically Associated Domains |
References
- Clark, M.M.; Stark, Z.; Farnaes, L.; Tan, T.Y.; White, S.M.; Dimmock, D.; Kingsmore, S.F. Meta-analysis of the diagnostic and clinical utility of genome and exome sequencing and chromosomal microarray in children with suspected genetic diseases. Genom. Med. 2018, 3, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Liang, F.; Cheng, D.; Zhang, Z.; Yu, G.; Zha, J.; Wang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Yuan, D.; Tan, Y.; et al. Location of Balanced Chromosome-Translocation Breakpoints by Long-Read Sequencing on the Oxford Nanopore Platform. Front. Genet. 2020, 10, 1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gribble, S.M.; Prigmore, E.; Burford, D.C.; Porter, K.M.; Ng, B.L.; Douglas, E.J.; Fiegler, H.; Carr, P.; Kalaitzopoulos, D.; Clegg, S.; et al. The complex nature of constitutional de novo apparently balanced translocations in patients presenting with abnormal phenotypes. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadlubowska, M.K.; Schrauwen, I. Methods to Improve Molecular Diagnosis in Genomic Cold Cases in Pediatric Neurology. Genes 2022, 13, 333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, P.A.; Browne, C.; Gregson, N.; Joyce, C.; White, H. Estimates of the frequency of chromosome abnormalities detectable in unselected newborns using moderate levels of banding. J. Med. Genet. 1992, 29, 103–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villar, J.; Ismail, L.C.; Victora, C.G.; Ohuma, E.O.; Bertino, E.; Altman, D.G.; Lambert, A.; Papageorghiou, A.T.; Carvalho, M.; Jaffer, Y.A. International standards for newborn weight, length, and head circumference by gestational age and sex: The Newborn Cross-Sectional Study of the INTERGROWTH-21st Project. Lancet 2014, 384, 857–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dias, C.; Estruch, S.B.; Graham, S.A.; McRae, J.; Sawiak, S.J.; Hurst, J.A.; Joss, S.K.; Holder, S.E.; Morton, J.E.V.; Turner, C.; et al. BCL11A Haploinsufficiency Causes an Intellectual Disability Syndrome and Dysregulates Transcription. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2016, 99, 253–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchis, A.; Cervero, L.; Martinez, A.; Valverde, C. Duplication of hands and feet, multiple joint dislocations, absence of corpus callosum and hypsarrhythmia: Acrocallosal syndrome? Am. J. Med. Genet. 1985, 20, 123–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, S.S.P.; Huntley, M.H.; Durand, N.C.; Stamenova, E.K.; Bochkov, I.D.; Robinson, J.T.; Sanborn, A.L.; Machol, I.; Omer, A.D.; Sander, E.S.; et al. A 3D map of the human genome at kilobase resolution reveals principles of chromatin looping. Cell 2014, 159, 1665–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuksel-Apak, M.; Bögershausen, N.; Pawlik, B.; Li, Y.; Apak, S.; Uyguner, O.; Milz, E.; Nürnberg, G.; Karaman, B.; Gülgören, A.; et al. A large duplication involving the IHH locus mimics acrocallosal syndrome. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2012, 20, 639–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babbs, C.; Furniss, D.; Morriss-Kay, G.M.; Wilkie, A.O.M. Polydactyly in the mouse mutant Doublefoot involves altered Gli3 processing and is caused by a large deletion in cis to Indian hedgehog. Mech. Dev. 2008, 125, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trimouille, A.; Tingaud-Sequeira, A.; Pennamen, P.; André, G.; Bouron, J.; Boucher, C.; Fergelot, P.; Lacombe, D.; Arveiler, B.; Rooryck, C. Deletion in 2q35 excluding the IHH gene leads to fetal severe limb anomalies and suggests a disruption of chromatin architecture. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2019, 27, 384–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sokpor, G.; Xie, Y.; Rosenbusch, J.; Tuoc, T. Chromatin remodeling BAF (SWI/SNF) complexes in neural development and disorders. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2017, 10, 243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, R.; Wiegreffe, C.; Britsch, S. Bcl11 Transcription Factors Regulate Cortical Development and Function. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayo, S.; Monfort, S.; Roselló, M.; Orellana, C.; Oltra, S.; Caro-Llopis, A.; Martínez, F. Chimeric Genes in Deletions and Duplications Associated to Intellectual Disability. Int. J. Genom. 2017, 2017, 4798474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scott, S.A.; Cohen, N.; Brandt, T.; Toruner, G.; Desnick, R.J.; Edelmann, L. Detection of low-level mosaicism and placental mosaicism by oligonucleotide array comparative genomic hybridization. Genet. Med. 2010, 12, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gudmundsson, S.; Singer-Berk, M.; Watts, N.A.; Phu, W.; Goodrich, J.K.; Solomonson, M.; Genome Aggregation Database Consortium; Rehm, H.L.; MacArthur, D.G.; O’Donnell-Luria, A. Variant interpretation using population databases: Lessons from gnomAD. Hum. Mutat. 2022, 43, 1012–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupiáñez, D.G.; Kraft, K.; Heinrich, V.; Krawitz, P.; Brancati, F.; Klopocki, E.; Horn, D.; Kayserili, H.; Opitz, J.M.; Laxova, R.; et al. Disruptions of Topological Chromatin Domains Cause Pathogenic Rewiring of Gene-Enhancer Interactions. Cell 2016, 161, 1012–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibn-Salem, J.; Köhler, S.; Love, M.I.; Chung, H.R.; Huang, N.; Hurles, M.E.; Haendel, M.; Washington, N.L.; Smedley, D.; Mungall, C.J.; et al. Deletions of chromosomal regulatory boundaries are associated with congenital disease. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez, F.; Caro-Llopis, A.; Roselló, M.; Oltra, S.; Mayo, S.; Monfort, S.; Orellana, C. High diagnostic yield of syndromic intellectual disability by targeted next-generation sequencing. J. Med. Genet. 2017, 54, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richards, S.; Aziz, N.; Bale, S.; Bick, D.; Das, S.; Gastier-Foster, J.; Grody, W.W.; Hegde, M.; Lyon, E.; Spector, E.; et al. Standards and guidelines for the interpretation of sequence variants: A joint consensus recommendation of the American College of Medical Genetics and Genomics and the Association for Molecular Pathology. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 405–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Orellana, C.; Rosello, M.; Sanchis, A.; Pedrola, L.; Martín-Grau, C.; Gabaldón-Albero, A.; Senent, M.L.; Such, E.; García-Ruiz, C.; Avetisyan, G.; et al. Utility of Optical Genome Mapping for Accurate Detection and Fine-Mapping of Structural Variants in Elusive Rare Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031244
Orellana C, Rosello M, Sanchis A, Pedrola L, Martín-Grau C, Gabaldón-Albero A, Senent ML, Such E, García-Ruiz C, Avetisyan G, et al. Utility of Optical Genome Mapping for Accurate Detection and Fine-Mapping of Structural Variants in Elusive Rare Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031244
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrellana, Carmen, Monica Rosello, Amparo Sanchis, Laia Pedrola, Carla Martín-Grau, Alba Gabaldón-Albero, Maria Leonor Senent, Esperanza Such, Cristian García-Ruiz, Gayane Avetisyan, and et al. 2025. "Utility of Optical Genome Mapping for Accurate Detection and Fine-Mapping of Structural Variants in Elusive Rare Diseases" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031244
APA StyleOrellana, C., Rosello, M., Sanchis, A., Pedrola, L., Martín-Grau, C., Gabaldón-Albero, A., Senent, M. L., Such, E., García-Ruiz, C., Avetisyan, G., & Martínez, F. (2025). Utility of Optical Genome Mapping for Accurate Detection and Fine-Mapping of Structural Variants in Elusive Rare Diseases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 1244. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031244





