JQ1 Treatment and miR-21 Silencing Activate Apoptosis of CD44+ Oral Cancer Cells
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
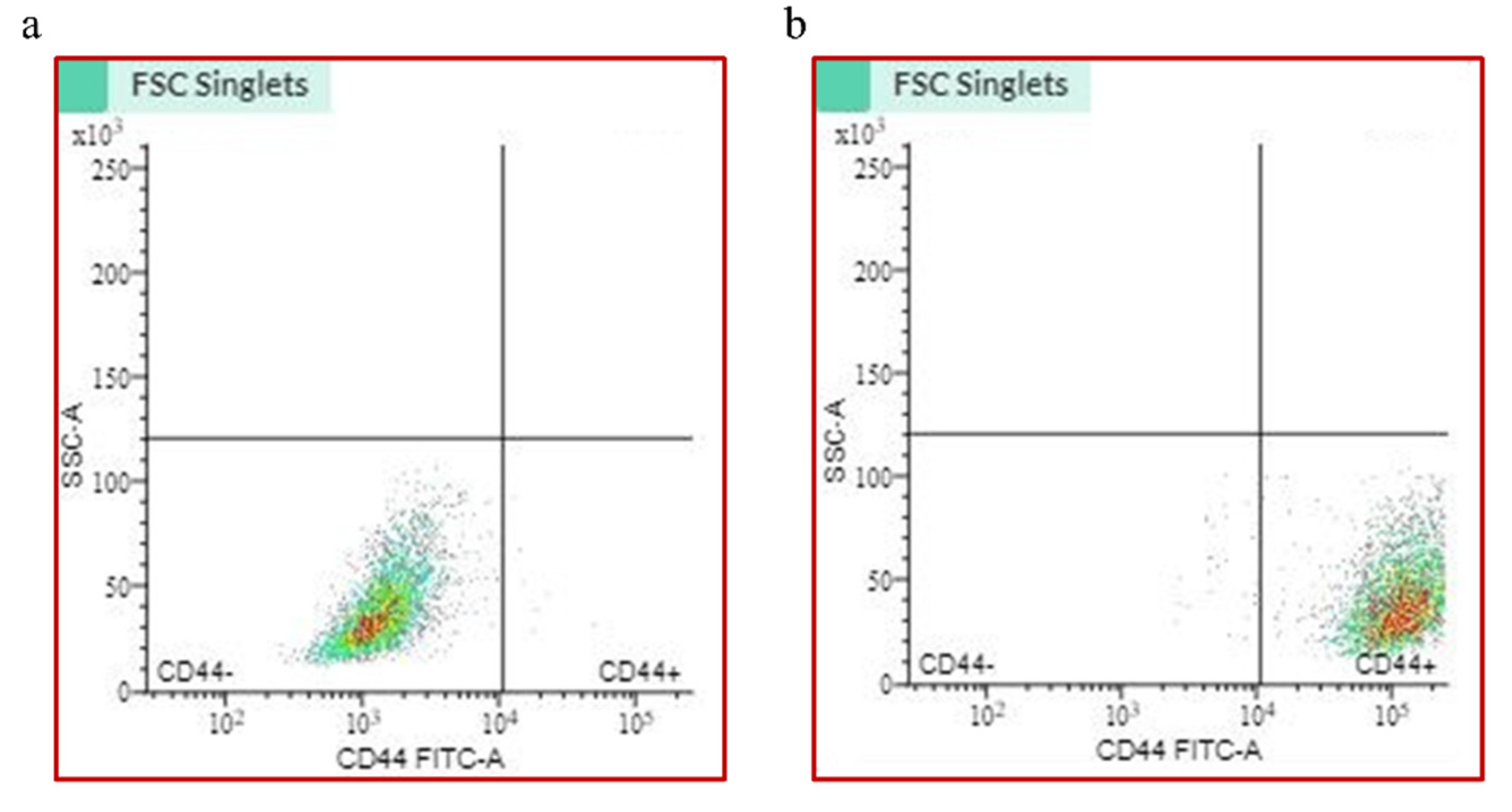
2.1. CD44+ Cell Sorting
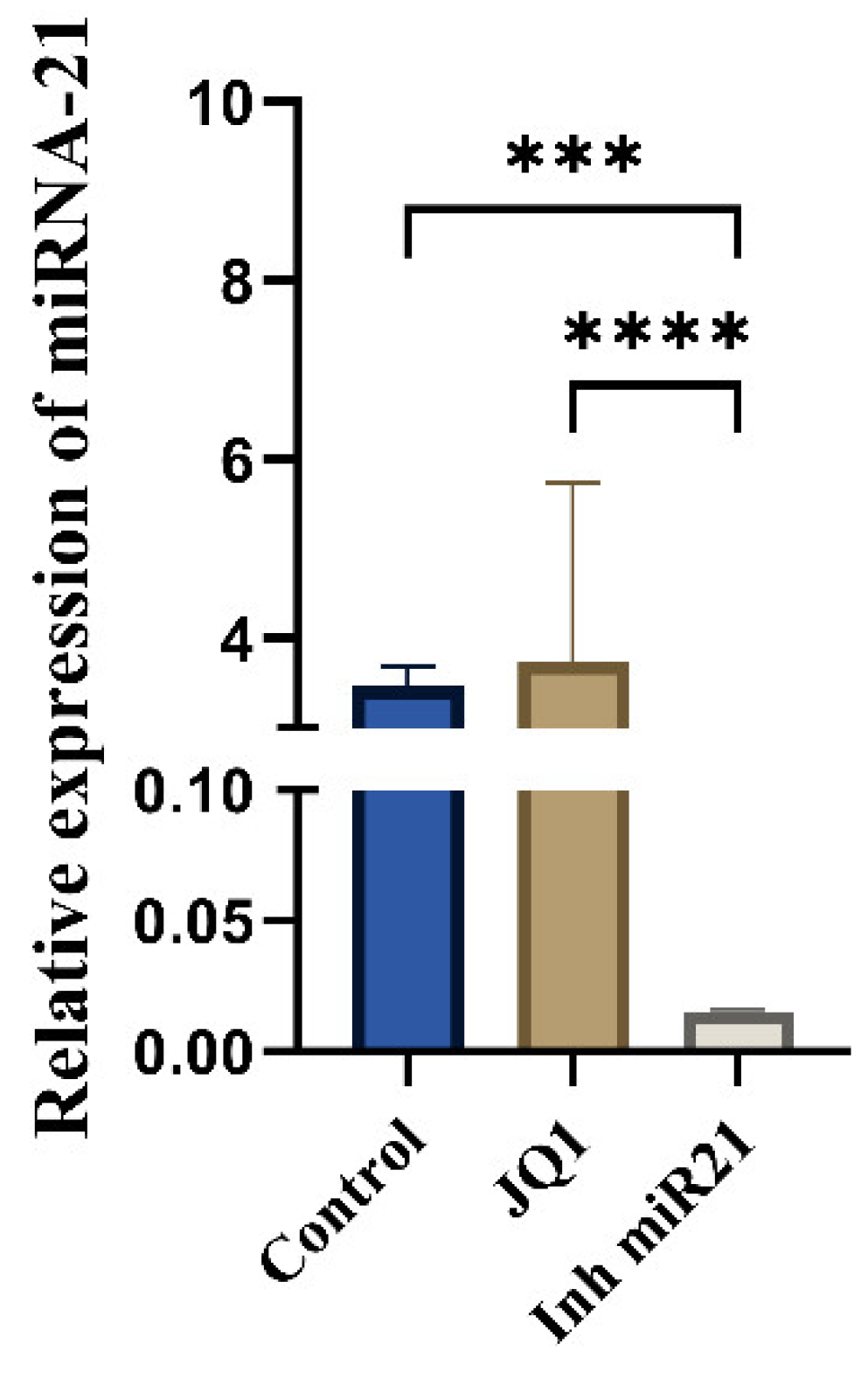
2.2. Expression on miR-21 in CSCs
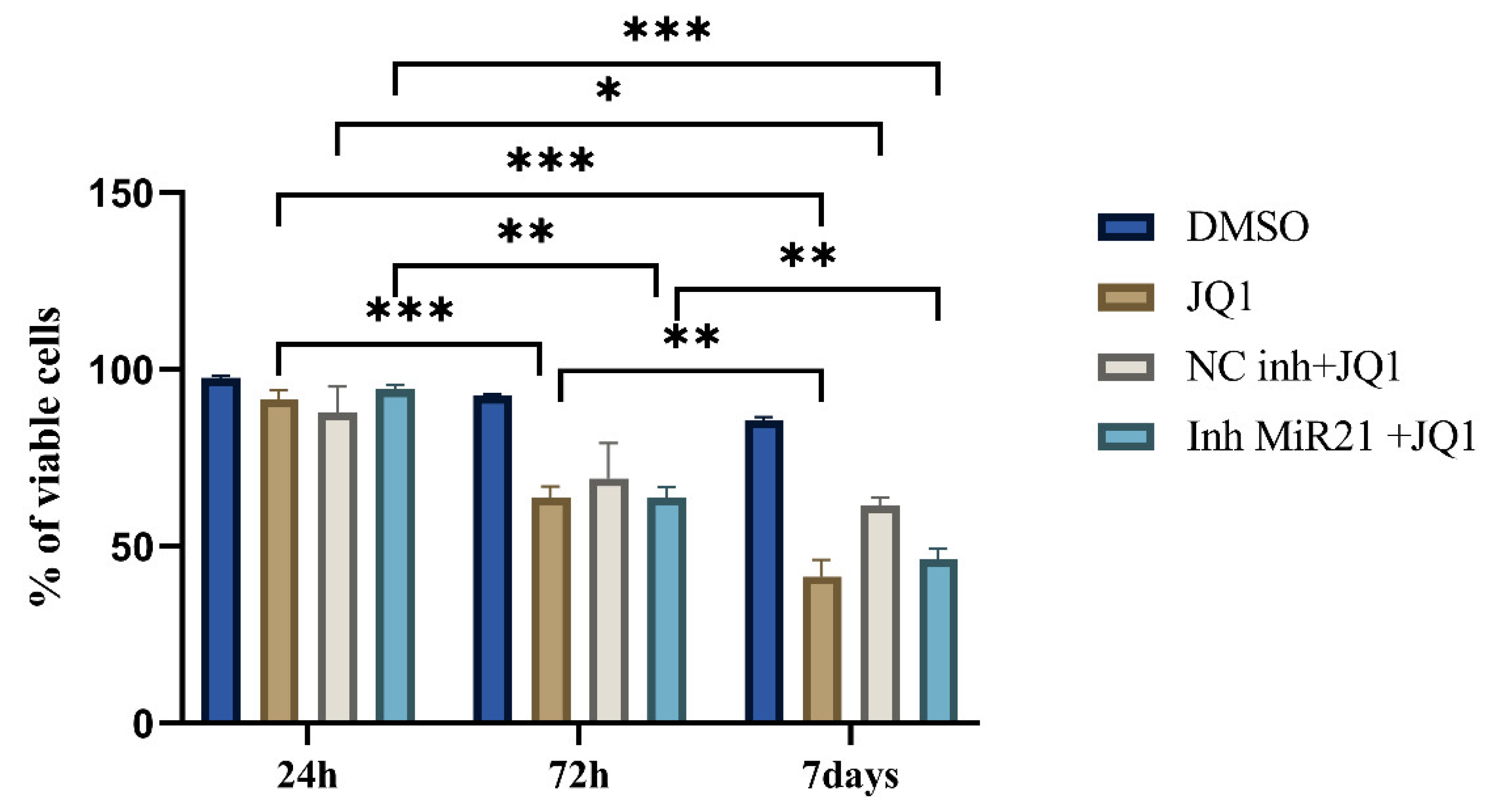
2.3. Effect of JQ1 Alone and JQ1 + miR-21 Inhibition on CD44+ Viability
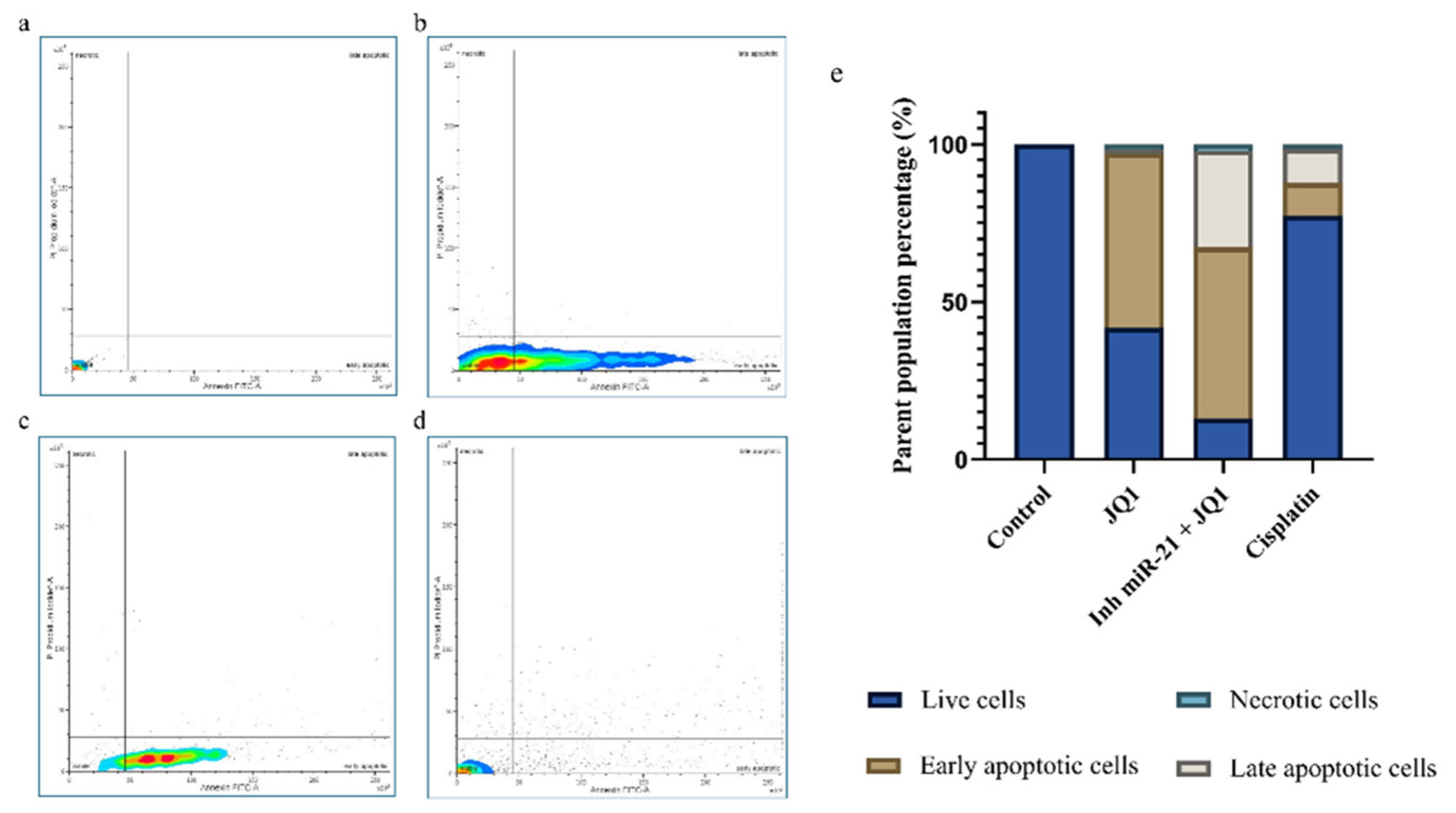
2.4. Effects of JQ1 Alone and JQ1 + miR-21 Inhibition on CD44+ Cell Apoptosis
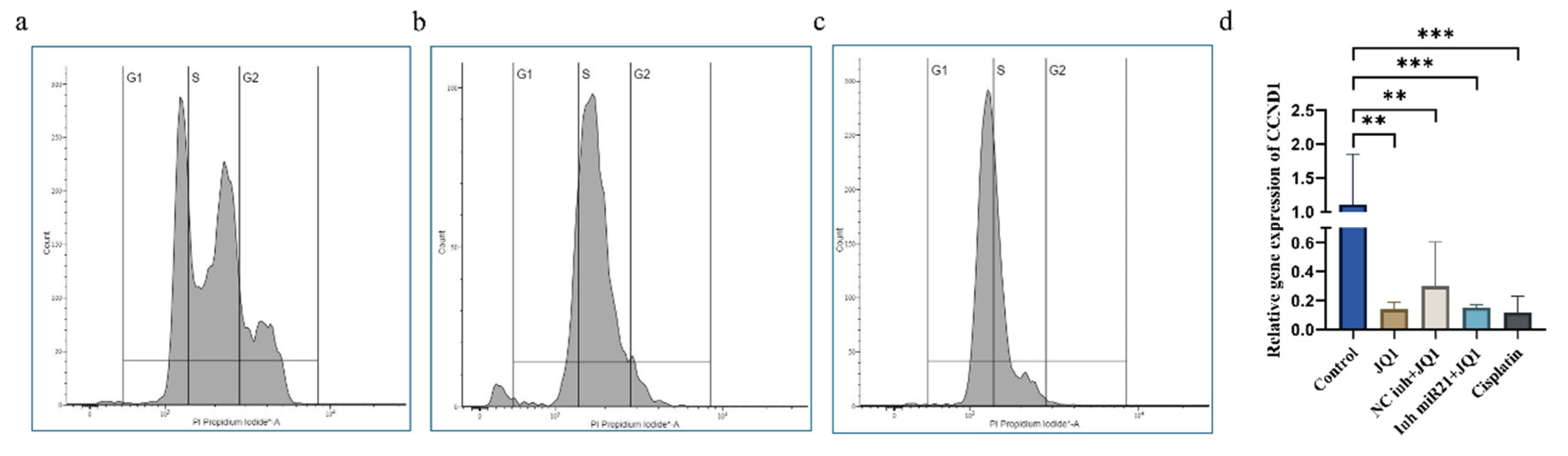
2.5. JQ1 and miR-21 Inhibition Effect on Cell Cycle of CD44+ Cells
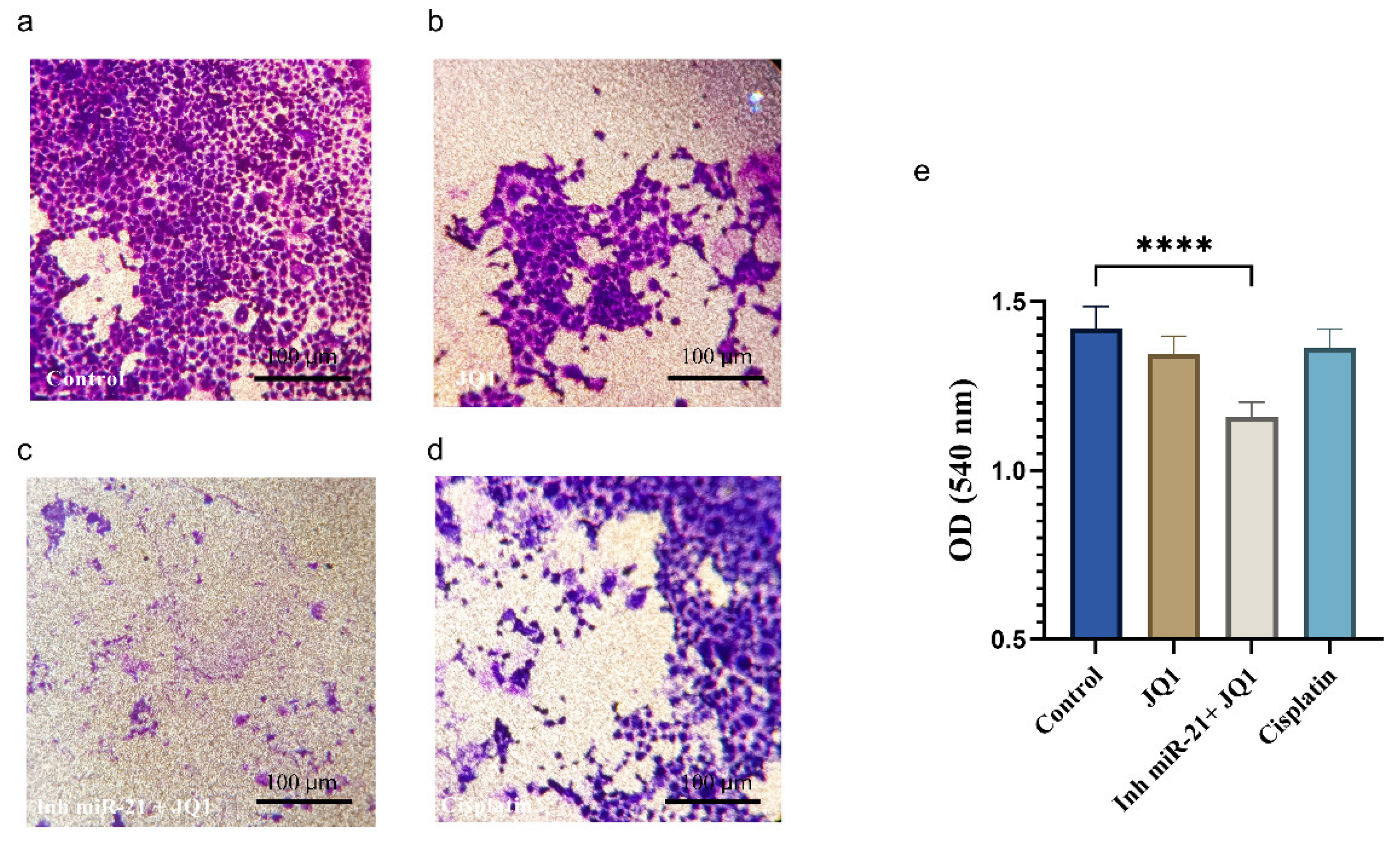
2.6. JQ1 Associated with miR-21 Inhibition Effect on Cancer Stem Cell Invasion
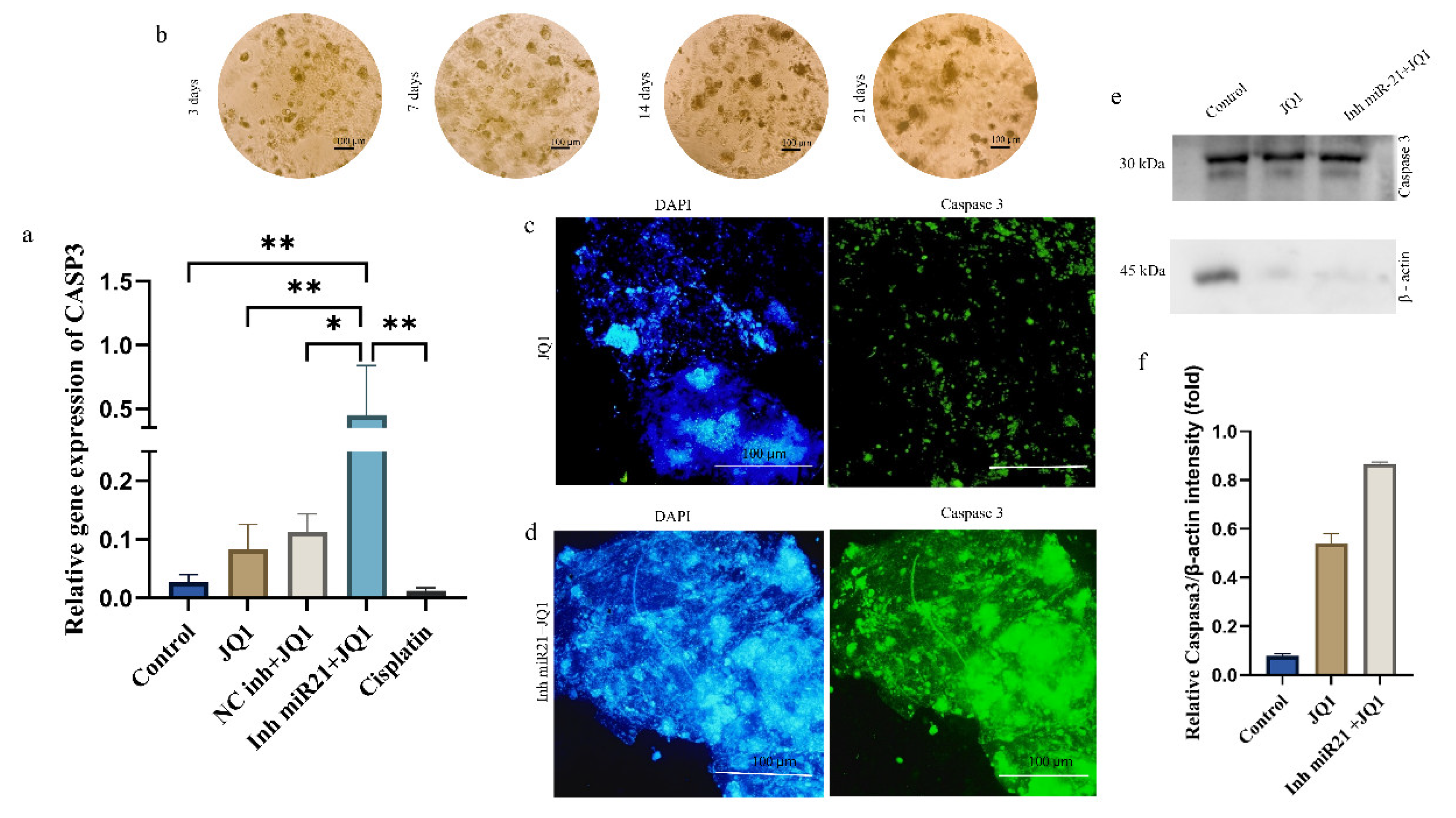
2.7. JQ1 and JQ1+ miR-21 Effect on Apoptosis Inhibition
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Cultures
4.2. Magnetic Cell Sorting and Flow Cytometry
4.3. MTT Assay
4.4. Transfection of miRNA-21 Inhibitor
4.5. Apoptosis Assay (Annexin V)
4.6. Transwell Cell Invasion Assay
4.7. Cell Cycle
4.8. Isolation of RNA and Reverse-Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.9. Real-Time Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction
4.10. Western Blot Assay
4.11. Immunofluorescence
4.12. Statistical Analysis
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bugshan, A.; Farooq, I. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Metastasis, Potentially Associated Malignant Disorders, Etiology and Recent Advancements in Diagnosis. F1000Research 2020, 9, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badwelan, M.; Muaddi, H.; Ahmed, A.; Lee, K.T.; Tran, S.D. Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma and Concomitant Primary Tumors, What Do We Know? A Review of the Literature. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 3721–3734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barsouk, A.; Aluru, J.S.; Rawla, P.; Saginala, K.; Barsouk, A. Epidemiology, Risk Factors, and Prevention of Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Med. Sci. 2023, 11, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, F.; Qiao, B.; Smith, R.A.; Gopalan, V.; Lam, A.K.-Y. Cancer Stem Cell: Fundamental Experimental Pathological Concepts and Updates. Exp. Mol. Pathol. 2015, 98, 184–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodini, C.O.; Lopes, N.M.; Lara, V.S.; Mackenzie, I.C. Oral Cancer Stem Cells—Properties and Consequences. J. Appl. Oral Sci. 2017, 25, 708–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-J.; Zhang, X.-Q.; Liu, Q.; Zhang, J.; Zhou, G. Nanotechnology: A Promising Method for Oral Cancer Detection and Diagnosis. J. Nanobiotechnol. 2018, 16, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Zuo, X.; Wei, D. Concise Review: Emerging Role of CD44 in Cancer Stem Cells: A Promising Biomarker and Therapeutic Target. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2015, 4, 1033–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Peng, Q.; Jiang, X.; Tan, S.; Yang, Y.; Yang, W.; Han, Y.; Chen, Y.; Oyang, L.; Lin, J.; et al. Metabolic Reprogramming and Epigenetic Modifications in Cancer: From the Impacts and Mechanisms to the Treatment Potential. Exp. Mol. Med. 2023, 55, 1357–1370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; He, C.; Wang, M.; Ma, X.; Mo, F.; Yang, S.; Han, J.; Wei, X. Targeting Epigenetic Regulators for Cancer Therapy: Mechanisms and Advances in Clinical Trials. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2019, 4, 1–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Ma, T.; Yu, B. Targeting Epigenetic Regulators to Overcome Drug Resistance in Cancers. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 1–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baldan, F.; Allegri, L.; Lazarevic, M.; Catia, M.; Milosevic, M.; Damante, G.; Milasin, J. Biological and Molecular Effects of Bromodomain and Extra-Terminal (BET) Inhibitors JQ1, IBET-151, and IBET-762 in OSCC Cells. J. Oral. Pathol. Med. 2019, 48, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Yang, P.; Guo, Z.; Yang, R.; Yang, H.; Yang, F.; Li, L.; Xiang, B. Overexpression of microRNA-21 Strengthens Stem Cell-like Characteristics in a Hepatocellular Carcinoma Cell Line. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2016, 14, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Zhang, B.; Pan, X.; Cobb, G.P.; Anderson, T.A. microRNAs as Oncogenes and Tumor Suppressors. Dev. Biol. 2007, 302, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, Q.; Chen, Y.; Zhou, X. The Roles of microRNAs in Epigenetic Regulation. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2019, 51, 11–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valeri, N.; Gasparini, P.; Braconi, C.; Paone, A.; Lovat, F.; Fabbri, M.; Sumani, K.M.; Alder, H.; Amadori, D.; Patel, T.; et al. MicroRNA-21 Induces Resistance to 5-Fluorouracil by down-Regulating Human DNA MutS Homolog 2 (hMSH2). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 21098–21103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheng, S.; Su, W.; Mao, D.; Li, C.; Hu, X.; Deng, W.; Yao, Y.; Ji, Y. MicroRNA-21 Induces Cisplatin Resistance in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asgar, M.A.; Senawong, G.; Sripa, B.; Senawong, T. Synergistic Anticancer Effects of Cisplatin and Histone Deacetylase Inhibitors (SAHA and TSA) on Cholangiocarcinoma Cell Lines. Int. J. Oncol. 2016, 48, 409–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, R.; Jiang, L. LINC00115 Promotes Stemness and Inhibits Apoptosis of Ovarian Cancer Stem Cells by Upregulating SOX9 and Inhibiting the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway through Competitively Binding to microRNA-30a. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, X.; Zhao, H.; Wang, R.; Chen, Y.; Ouyang, X.; Li, W.; Sun, Y.; Peng, A. Cancer Epigenetics: From Laboratory Studies and Clinical Trials to Precision Medicine. Cell Death Discov. 2024, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.C.; Gupta, A. MicroRNAs: Potential Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Prognosis of Different Cancers. Transl. Cancer Res. 2020, 9, 5798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, Y.; Hoyle, R.G.; Xie, N.; Wang, W.; Cai, H.; Zhang, M.; Ma, Z.; Xiong, G.; Xu, X.; Huang, Z.; et al. A Super-Enhancer Driven by FOSL1 Controls miR-21-5p Expression in Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 656628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muñoz, P.; Iliou, M.S.; Esteller, M. Epigenetic Alterations Involved in Cancer Stem Cell Reprogramming. Mol. Oncol. 2012, 6, 620–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaksic Karisik, M.; Lazarevic, M.; Mitic, D.; Nikolic, N.; Milosevic Markovic, M.; Jelovac, D.; Milasin, J. Osteogenic and Adipogenic Differentiation Potential of Oral Cancer Stem Cells May Offer New Treatment Modalities. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 4704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filippakopoulos, P.; Qi, J.; Picaud, S.; Shen, Y.; Smith, W.B.; Fedorov, O.; Morse, E.M.; Keates, T.; Hickman, T.T.; Felletar, I.; et al. Selective Inhibition of BET Bromodomains. Nature 2010, 468, 1067–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Guo, H.; Wu, Y.; Hu, Q.; Hu, G.; He, H.; Yin, Y.; Nan, X.; Lin, G.; Han, J.; et al. RCN1 Deficiency Inhibits Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma Progression and THP-1 Macrophage M2 Polarization. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 21488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaksic Karisik, M.; Lazarevic, M.; Mitic, D.; Milosevic Markovic, M.; Riberti, N.; Jelovac, D.; Milasin, J. MicroRNA-21 as a Regulator of Cancer Stem Cell Properties in Oral Cancer. Cells 2025, 14, 91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masamha, C.P.; Benbrook, D.M. Cyclin D1 Degradation Is Sufficient to Induce G1 Cell Cycle Arrest despite Constitutive Expression of Cyclin E2 in Ovarian Cancer Cells. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 6565–6572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murad, H.; Hawat, M.; Ekhtiar, A.; AlJapawe, A.; Abbas, A.; Darwish, H.; Sbenati, O.; Ghannam, A. Induction of G1-Phase Cell Cycle Arrest and Apoptosis Pathway in MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells by Sulfated Polysaccharide Extracted from Laurencia Papillosa. Cancer Cell Int. 2016, 16, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Zhao, N. Generalized Anxiety Disorder, Depressive Symptoms and Sleep Quality during COVID-19 Outbreak in China: A Web-Based Cross-Sectional Survey. Psychiatry Res. 2020, 288, 112954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapor, S.; Vukotić, M.; Subotički, T.; Đikić, D.; Mitrović Ajtić, O.; Radojković, M.; Čokić, V.P.; Santibanez, J.F. Hydroxyurea Induces Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Senescence and Modifies Cell Functionality In Vitro. J. Pers. Med. 2021, 11, 1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Múnera, J.O.; Sundaram, N.; Rankin, S.A.; Hill, D.; Watson, C.; Mahe, M.; Vallance, J.E.; Shroyer, N.F.; Sinagoga, K.L.; Zarzoso-Lacoste, A.; et al. Differentiation of Human Pluripotent Stem Cells into Colonic Organoids via Transient Activation of BMP Signaling. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 21, 51–64.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bergdorf, K.N.; Phifer, C.J.; Bechard, M.E.; Lee, M.A.; McDonald, O.G.; Lee, E.; Weiss, V.L. Immunofluorescent Staining of Cancer Spheroids and Fine-Needle Aspiration-Derived Organoids. STAR Protoc. 2021, 2, 100578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelica, S.; Diklić, M.; Đikić, D.; Kovačić, M.; Subotički, T.; Mitrović-Ajtić, O.; Radojković, M.; Čokić, V.; Santibanez, J.F. Hydroxyurea-Induced Senescent Peripheral Blood Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Inhibit Bystander Cell Proliferation of JAK2V617F-Positive Human Erythroleukemia Cells. FEBS J. 2019, 286, 3647–3663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jaksic Karisik, M.; Lazarevic, M.; Mitic, D.; Ajtic, O.M.; Damante, G.; Milasin, J. JQ1 Treatment and miR-21 Silencing Activate Apoptosis of CD44+ Oral Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031241
Jaksic Karisik M, Lazarevic M, Mitic D, Ajtic OM, Damante G, Milasin J. JQ1 Treatment and miR-21 Silencing Activate Apoptosis of CD44+ Oral Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(3):1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031241
Chicago/Turabian StyleJaksic Karisik, Milica, Milos Lazarevic, Dijana Mitic, Olivera Mitrovic Ajtic, Giuseppe Damante, and Jelena Milasin. 2025. "JQ1 Treatment and miR-21 Silencing Activate Apoptosis of CD44+ Oral Cancer Cells" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 3: 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031241
APA StyleJaksic Karisik, M., Lazarevic, M., Mitic, D., Ajtic, O. M., Damante, G., & Milasin, J. (2025). JQ1 Treatment and miR-21 Silencing Activate Apoptosis of CD44+ Oral Cancer Cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(3), 1241. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms26031241








