Restoring Sight: The Journey of AIPL1 from Discovery to Therapy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. AIPL1 Gene and Protein
2.1. Evolution and Orthologs
2.2. Gene Structure and Transcript Variants
2.3. Expression Pattern
2.4. Protein Structure
2.4.1. FKBP
2.4.2. TPR
2.4.3. PRD
3. Interacting Partners
3.1. HSP70 and HSP90
3.2. NUB1 and FAT10
3.3. PDE6 Maturation
4. AIPL1 Dysfunction in Retinal Disorders
4.1. Pathogenic Mechanism
4.2. AIPL1 Mutations Identified in the IRDs
5. Model Systems
6. AAV-Mediated Gene Therapy in AIPL1-Caused Retinal Disorders
7. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AIPL1 | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor interacting protein-like 1 |
| AIP | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor interacting protein |
| AhR | Aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| LCA | Leber congenital amaurosis |
| LCA4 | Leber congenital amaurosis type 4 |
| EOSRD | Early-onset severe retinal dystrophy |
| RP | Retinitis pigmentosa |
| IRD | Inherited retinal diseases |
| RPE | Retinal pigment epithelium |
| ONL | Outer nuclear layer |
| AAV | Adeno-associated virus |
| FKBP | FK506-binding protein |
| TPR | Tetratricopeptide repeat |
| PRD | Proline-rich domain |
| HSP70 | 70 kilodalton heat shock proteins |
| HSP90 | 90 kilodalton heat shock proteins |
| PDE6 | Phosphodiesterase 6 |
| PDE6α | Phosphodiesterase 6 subunit α |
| PDE6α′ | Phosphodiesterase 6 subunit α′ |
| PDE6β | Phosphodiesterase 6 subunit β |
| PDE6γ | Phosphodiesterase 6 subunit γ |
| PDE6γ’ | Phosphodiesterase 6 subunit γ’ |
| Pγ | Phosphodiesterase 6 subunit γ |
| Pγ’ | Phosphodiesterase 6 subunit γ |
| NUB1 | NEDD8 ultimate buster 1 |
| FAT10 | Human leukocyte antigen F adjacent transcript 10 |
| CDS | Coding sequence |
| RT-PCR | Reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| OCT | Optical coherence tomography |
| ERG | Electroretinography |
| iPSC | Induced pluripotent stem cell |
| UTR | Untranslated region |
| cryo-EM | Cryogenic electron microscopy |
| NMR | Nuclear magnetic resonance |
| BLI | Bio-layer interferometry |
| SPR | Surface plasmon resonance |
| ELISA | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay |
References
- Stone, E.M. Leber Congenital Amaurosis-A Model for Efficient Genetic Testing of Heterogeneous Disorders: LXIV Edward Jackson Memorial Lecture. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2007, 144, 791–811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenekoop, R.K. An Overview of Leber Congenital Amaurosis: A Model to Understand Human Retinal Development. Surv. Ophthalmol. 2004, 49, 379–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sherwin, J.C.; Hewitt, A.W.; Ruddle, J.B.; Mackey, D.A. Genetic Isolates in Ophthalmic Diseases. Ophthalmic Genet. 2008, 29, 149–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, D.; Pediatric, E.T. Leber Congenital Amaurosis: Clinical Correlations with Genotypes, Gene Therapy Trials Update, and Future Directions. J. Am. Assoc. Pediatr. Ophthalmol. Strabismus 2009, 13, 587–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Available online: https://www.aao.org/education/disease-review/leber-congenital-amaurosis-4 (accessed on 3 December 2025).
- Sather, R., III; Ihinger, J.; Simmons, M.; Lobo, G.P.; Montezuma, S.R. The Clinical Findings, Pathogenic Variants, and Gene Therapy Qualifications Found in a Leber Congenital Amaurosis Phenotypic Spectrum Patient Cohort. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumaran, N.; Moore, A.T.; Weleber, R.G.; Michaelides, M. Leber Congenital Amaurosis/Early-Onset Severe Retinal Dystrophy: Clinical Features, Molecular Genetics and Therapeutic Interventions. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 101, 1147–1154, Correction in Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 103, 862. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjophthalmol-2016-309975corr1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RetNet-Retinal Information Network. Available online: https://web.sph.uth.edu/RetNet/ (accessed on 17 November 2023).
- Thompson, J.A.; De Roach, J.N.; McLaren, T.L.; Montgomery, H.E.; Hoffmann, L.H.; Campbell, I.R.; Chen, F.K.; Mackey, D.A.; Lamey, T.M. The Genetic Profile of Leber Congenital Amaurosis in an Australian Cohort. Mol. Genet. Genom. Med. 2017, 5, 652–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacristan-Reviriego, A.; van der Spuy, J. The Leber Congenital Amaurosis-Linked Protein AIPL1 and Its Critical Role in Photoreceptors. In Retinal Degenerative Diseases; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; Volume 1074, pp. 381–386. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.; Zoldak, G.; Kriehuber, T.; Soroka, J.; Schmid, F.X.; Richter, K.; Buchner, J. Unique Proline-Rich Domain Regulates the Chaperone Function of AIPL1. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 2089–2096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michaelides, M.; Laich, Y.; Wong, S.C.; Oluonye, N.; Zaman, S.; Kumaran, N.; Kalitzeos, A.; Petrushkin, H.; Georgiou, M.; Tailor, V.; et al. Gene Therapy in Children with AIPL1-Associated Severe Retinal Dystrophy: An Open-Label, First-in-Human Interventional Study. Lancet 2025, 405, 648–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, A.L.; Du, S.W.; Palczewski, K. Genome Editing, a Superior Therapy for Inherited Retinal Diseases. Vision Res. 2023, 206, 108192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohocki, M.M.; Sullivan, L.S.; Tirpak, D.L.; Daiger, S.P. Comparative Analysis of Aryl-Hydrocarbon Receptor Interacting Protein-like 1 (Aipl1), a Gene Associated with Inherited Retinal Disease in Humans. Mamm. Genome 2001, 12, 566–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhalla, D.; van Noort, V. Molecular Evolution of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Signaling Pathway Genes. J. Mol. Evol. 2023, 91, 628–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iribarne, M.; Nishiwaki, Y.; Nakamura, S.; Araragi, M.; Oguri, E.; Masai, I. Aipl1 Is Required for Cone Photoreceptor Function and Survival through the Stability of Pde6c and Gc3 in Zebrafish. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 45962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyons, L.A.; Creighton, E.K.; Alhaddad, H.; Beale, H.C.; Grahn, R.A.; Rah, H.C.; Maggs, D.J.; Helps, C.R.; Gandolfi, B. Whole Genome Sequencing in Cats, Identifies New Models for Blindness in AIPL1 and Somite Segmentation in HES7. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacristan-Reviriego, A.; Le, H.M.; Georgiou, M.; Meunier, I.; Bocquet, B.; Roux, A.F.; Prodromou, C.; Bainbridge, J.; Michaelides, M.; van der Spuy, J. Clinical and Functional Analyses of AIPL1 Variants Reveal Mechanisms of Pathogenicity Linked to Different Forms of Retinal Degeneration. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 17520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohocki, M.M.; Malone, K.A.; Sullivan, L.S.; Daiger, S.P. Localization of Retina/Pineal-Expressed Sequences: Identification of Novel Candidate Genes for Inherited Retinal Disorders. Genomics 1999, 58, 29–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohocki, M.; Blackshaw, S.; Cepko, C.; Sullivan, L.; Daiger, S. Human Aryl-hydrocarbon Interacting Protein-like 1 Gene (AIPL1), a Candidate for Inherited Retinal Disorders: Mapping to 17p13, Characterization and Mutation Testing. In Proceedings of the ASHG Annual Meeting 65, San Francisco, CA, USA, 19–23 October 1999; p. 569. [Google Scholar]
- McHale, J.C.; McKie, A.B.; Tarttelin, E.E.; Inglehearn, C.F. Expression Map of Human Chromosome Region 17p13. 3, Spanning the RP13 Dominant Retinitis Pigmentosa Locus, the Miller-Dieker Lissencephaly Syndrome (MDLS). Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 2000, 88, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohocki, M.M.; Bowne, S.J.; Sullivan, L.S.; Blackshaw, S.; Cepko, C.L.; Payne, A.M.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Khaliq, S.; Mehdi, S.Q.; Birch, D.G.; et al. Mutations in a New Photoreceptor-Pineal Gene on 17p Cause Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Nat. Genet. 2000, 24, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AIPL1 AIP like 1 HSP90 Co-Chaperone [Homo Sapiens (Human)]-Gene-NCBI. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/gene/23746 (accessed on 21 November 2025).
- Janke, B.; Lorenz, B.; Preising, M.N. Alternative Splicing in AIPL1—Implications On Function And The Mutational Spectrum. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 2481. [Google Scholar]
- Farkas, M.H.; Grant, G.R.; White, J.A.; Sousa, M.E.; Consugar, M.B.; Pierce, E.A. Transcriptome Analyses of the Human Retina Identify Unprecedented Transcript Diversity and 3.5 Mb of Novel Transcribed Sequence via Significant Alternative Splicing and Novel Genes. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellingham, J.; Davidson, A.E.; Aboshiha, J.; Simonelli, F.; Bainbridge, J.W.; Michaelides, M.; Van Der Spuy, J. Investigation of Aberrant Splicing Induced by AIPL1 Variations as a Cause of Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 7784–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janke, B.; Lorenz, B.; Preising, M.N. Alternative Splicing of LCA Gene AIPL1 Is Conserved in Mammals. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 3101. [Google Scholar]
- Sohocki, M.M.; Perrault, I.; Leroy, B.P.; Payne, A.M.; Dharmaraj, S.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Kaplan, J.; Maumenee, I.H.; Koenekoop, R.; Meire, F.M.; et al. Prevalence of AIPL1 Mutations in Inherited Retinal Degenerative Disease. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2000, 70, 142–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sacristan-Reviriego, A.; Bellingham, J.; Prodromou, C.; Kumaran, N.; Bainbridge, J.; Michaelides, M.; van der Spuy, J. The Integrity and Organization of the Human AIPL1 Functional Domains Is Critical for Its Role as a HSP90-Dependent Co-Chaperone for Rod PDE6. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 4465–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.P.; Gakhar, L.; Yu, L.; Artemyev, N.O. Unique Structural Features of the AIPL1–FKBP Domain That Support Prenyl Lipid Binding and Underlie Protein Malfunction in Blindness. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2017, 114, E6536–E6545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hidalgo-de-Quintana, J.; Evans, R.J.; Cheetham, M.E.; Van Der Spuy, J. The Leber Congenital Amaurosis Protein AIPL1 Functions as Part of a Chaperone Heterocomplex. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 2878–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivellin, G.; Korbonits, M. AIP and Its Interacting Partners. J. Endocrinol. 2011, 210, 137–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norrie, J.L.; Nityanandam, A.; Lai, K.; Chen, X.; Wilson, M.; Stewart, E.; Griffiths, L.; Jin, H.; Wu, G.; Orr, B.; et al. Retinoblastoma from Human Stem Cell-Derived Retinal Organoids. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 4535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Spuy, J.; Chapple, J.P.; Clark, B.J.; Luthert, P.J.; Sethi, C.S.; Cheetham, M.E. The Leber Congenital Amaurosis Gene Product AIPL1 Is Localized Exclusively in Rod Photoreceptors of the Adult Human Retina. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 823–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Der Spuy, J.; Kim, J.H.; Yu, Y.S.; Szel, A.; Luthert, P.J.; Clark, B.J.; Cheetham, M.E. The Expression of the Leber Congenital Amaurosis Protein AIPL1 Coincides with Rod and Cone Photoreceptor Development. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 5396–5403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrickson, A.; Bumsted-O’Brien, K.; Natoli, R.; Ramamurthy, V.; Possin, D.; Provis, J. Rod Photoreceptor Differentiation in Fetal and Infant Human Retina. Exp. Eye Res. 2008, 87, 415–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spuy, J.; van der Kim, J.; Luthert, P.J.; Chapple, J.P.; Cheetham, M.E. Spatial and Temporal Expression of AIPL1 and NUB1 Protein in Human Retina. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 2039. [Google Scholar]
- Kolandaivelu, S.; Ramamurthy, V. AIPL1 Protein and Its Indispensable Role in Cone Photoreceptor Function and Survival. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 801, 43–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Spuy, J.; Munro, P.M.G.; Luthert, P.J.; Preising, M.N.; Bek, T.; Heegaard, S.; Cheetham, M.E. Predominant Rod Photoreceptor Degeneration in Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Mol. Vis. 2005, 11, 542–553. [Google Scholar]
- Dharmaraj, S.; Leroy, B.P.; Sohocki, M.M.; Koenekoop, R.K.; Perrault, I.; Anwar, K.; Khaliq, S.; Devi, R.S.; Birch, D.G.; De Pool, E.; et al. The Phenotype of Leber Congenital Amaurosis in Patients With AIPL1 Mutations. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 1029–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Booij, J.C.; Florijn, R.J.; ten Brink, J.B.; Loves, W.; Meire, F.; van Schooneveld, M.J.; de Jong, P.T.; Bergen, A.A. Identification of Mutations in the AIPL1, CRB1, GUCY2D, RPE65, and RPGRIP1 Genes in Patients with Juvenile Retinitis Pigmentosa. J. Med. Genet. 2005, 42, e67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirschman, L.T.; Kolandaivelu, S.; Frederick, J.M.; Dang, L.; Goldberg, A.F.X.; Baehr, W.; Ramamurthy, V. The Leber Congenital Amaurosis Protein, AIPL1, Is Needed for the Viability and Functioning of Cone Photoreceptor Cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2010, 19, 1076–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Léveillard, T.; Mohand-Saïd, S.; Lorentz, O.; Hicks, D.; Fintz, A.C.; Clérin, E.; Simonutti, M.; Forster, V.; Cavusoglu, N.; Chalmel, F.; et al. Identification and Characterization of Rod-Derived Cone Viability Factor. Nat. Genet. 2004, 36, 755–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Mohand-Said, S.; Danan, A.; Simonutti, M.; Fontaine, V.; Clerin, E.; Picaud, S.; Léveillard, T.; Sahel, J.A. Functional Cone Rescue by RdCVF Protein in a Dominant Model of Retinitis Pigmentosa. Mol. Ther. 2009, 17, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krizaj, D.; Copenhagen, D.R. Calcium Regulation in Photoreceptors. Front. Biosci. 2002, 7, d2023–d2044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takemoto, N.; Tachibanaki, S.; Kawamura, S. High cGMP Synthetic Activity in Carp Cones. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 11788–11793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michalovicz, L.T.; Kolandaivelu, S.; Ramamurthy, V. The Leber Congenital Amaurosis (LCA) Protein, AIPL1, Is Essential for Cone Photoreceptor Cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2009, 50, 4144. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.H.; Smith, A.J.; Pawlyk, B.; Xu, X.; Liu, X.; Bainbridge, J.B.; Basche, M.; McIntosh, J.; Tran, H.V.; Nathwani, A.; et al. Gene Therapy for Retinitis Pigmentosa and Leber Congenital Amaurosis Caused by Defects in AIPL1: Effective Rescue of Mouse Models of Partial and Complete Aipl1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2009, 18, 2099–2114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.L.; Pezzella, F.; Harris, A.; Acuto, O. NUB1 as a Prognostic Marker in Breast Cancer: A Retrospective, Integrated Genomic, Transcriptomic, and Protein Analysis. In Proceedings of the ESMO Open; Elsevier BV: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 3, pp. A417–A418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.-L. Translational Relevance of AIPL1 and NUB1 in Cancer. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Oxford, Oxford, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishna, K.N.; Boyd, K.; Yadav, R.P.; Artemyev, N.O. Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Interacting Protein-like 1 Is an Obligate Chaperone of Phosphodiesterase 6 and Is Assisted by the γ-Subunit of Its Client. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 16282–16291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.P.; Majumder, A.; Gakhar, L.; Artemyev, N.O. Extended Conformation of the Proline-Rich Domain of Human Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Interacting Protein-like 1: Implications for Retina Disease. J. Neurochem. 2015, 135, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.P.; Artemyev, N.O. AIPL1: A Specialized Chaperone for the Phototransduction Effector. Cell. Signal. 2017, 40, 183–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wayne, N.; Bolon, D.N. Charge-Rich Regions Modulate the Anti-Aggregation Activity of Hsp90. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 401, 931–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.P.; Boyd, K.; Yu, L.; Artemyev, N.O. Interaction of the TPR-Domain of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Interacting Protein-like 1 with the Regulatory P [Gamma] Subunit of Phosphodiesterase 6. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 15795–15807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abramson, J.; Adler, J.; Dunger, J.; Evans, R.; Green, T.; Pritzel, A.; Ronneberger, O.; Willmore, L.; Ballard, A.J.; Bambrick, J.; et al. Accurate Structure Prediction of Biomolecular Interactions with AlphaFold 3. Nature 2024, 630, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziaka, K.; van der Spuy, J. The Role of Hsp90 in Retinal Proteostasis and Disease. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linnert, M.; Lin, Y.J.; Manns, A.; Haupt, K.; Paschke, A.K.; Fischer, G.; Weiwad, M.; Lücke, C. The FKBP-Type Domain of the Human Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Interacting Protein Reveals an Unusual Hsp90 Interaction. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 2097–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, D.; Yadav, R.P.; Singh, S.; Boyd, K.; Artemyev, N.O. Unique Interface and Dynamics of the Complex of HSP90 with a Specialized Cochaperone AIPL1. Structure 2023, 31, 309–317.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruszczyk, J.; Grandvuillemin, L.; Lai-Kee-Him, J.; Paloni, M.; Savva, C.G.; Germain, P.; Grimaldi, M.; Boulahtouf, A.; Kwong, H.S.; Bous, J.; et al. Cryo-EM Structure of the Agonist-Bound Hsp90-XAP2-AHR Cytosolic Complex. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, R.P.; Boyd, K.; Artemyev, N.O. Molecular Insights into the Maturation of Phosphodiesterase 6 by the Specialized Chaperone Complex of HSP90 with AIPL1. J. Biol. Chem. 2022, 298, 101620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Majumder, A.; Gopalakrishna, K.N.; Cheguru, P.; Gakhar, L.; Artemyev, N.O. Interaction of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Interacting Protein-like 1 with the Farnesyl Moiety. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 21320–21328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramamurthy, V.; Niemi, G.A.; Reh, T.A.; Hurley, J.B. Leber Congenital Amaurosis Linked to AIPL1: A Mouse Model Reveals Destabilization of cGMP Phosphodiesterase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13897–13902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yadav, R.P.; Artemyev, N.O. NMR Resonance Assignments of the TPR Domain of Human Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Interacting Protein-like 1 (AIPL1). Biomol. NMR Assign. 2019, 13, 79–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uversky, V.N. Unreported Intrinsic Disorder in Proteins: Building Connections to the Literature on IDPs. Intrinsically Disord. Proteins 2014, 2, e970499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, C.A.; Chiodo, V.A.; Boye, S.L.; Hayes, A.; Goldberg, A.F.X.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Ramamurthy, V. Viral-Mediated Vision Rescue of a Novel AIPL1 Cone-Rod Dystrophy Model. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 24, 670–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolandaivelu, S.; Singh, R.K.; Ramamurthy, V. AIPL1, a Protein Linked to Blindness, Is Essential for the Stability of Enzymes Mediating cGMP Metabolism in Cone Photoreceptor Cells. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parise, B. Splicing Pattern of Aryl Hydrocarbon Interacting Protein like 1 (AIPL1) in Relation to Centromere Protein F. Ph.D. Thesis, Justus Liebig University Giessen, Giessen, Germany, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Hidalgo-De-Quintana, J.; Schwarz, N.; Meschede, I.P.; Stern-Schneider, G.; Powner, M.B.; Morrison, E.E.; Futter, C.E.; Wolfrum, U.; Cheetham, M.E.; Van Der Spuy, J. The Leber Congenital Amaurosis Protein AIPL1 and EB Proteins Co-Localize at the Photoreceptor Cilium. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0121440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akey, D.T.; Zhu, X.; Dyer, M.; Li, A.; Sorensen, A.; Fukada-Kamitani, T.; Daiger, S.P.; Craft, C.; Kamitani, T.; Sohocki, M.M. Functional Studies of AIPL1: Potential Role of AIPL1 in Cell Cycle Exit and/or Differentiation of Photoreceptors. In Retinal Degenerations: Mechanisms and Experimental Therapy; LaVail, M.M., Hollyfield, J.G., Anderson, R.E., Eds.; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2003; Volume 533, pp. 287–295. [Google Scholar]
- Akey, D.T.; Zhu, X.; Dyer, M.; Li, A.; Sorensen, A.; Blackshaw, S.; Fukuda-Kamitani, T.; Daiger, S.P.; Craft, C.M.; Kamitani, T.; et al. The Inherited Blindness Associated Protein AIPL1 Interacts with the Cell Cycle Regulator Protein NUB1. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2002, 11, 2723–2733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanaya, K.; Sohocki, M.M.; Kamitani, T. Abolished Interaction of NUB1 with Mutant AIPL1 Involved in Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 317, 768–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bett, J.S.; Kanuga, N.; Richet, E.; Schmidtke, G.; Groettrup, M.; Cheetham, M.E.; van der Spuy, J. The Inherited Blindness Protein AIPL1 Regulates the Ubiquitin-Like FAT10 Pathway. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boehm, A.N.; Bialas, J.; Catone, N.; Sacristan-Reviriego, A.; van der Spuy, J.; Groettrup, M.; Aichem, A. The Ubiquitin-like Modifier FAT10 Inhibits Retinal PDE6 Activity and Mediates Its Proteasomal Degradation. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 14402–14418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolandaivelu, S.; Huang, J.; Hurley, J.B.; Ramamurthy, V. AIPL1, a Protein Associated with Childhood Blindness, Interacts with α-Subunit of Rod Phosphodiesterase (PDE6) and Is Essential for Its Proper Assembly. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 30853–30861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Yadav, R.P.; Artemyev, N.O. NMR Resonance Assignments of the FKBP Domain of Human Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor-Interacting Protein-like 1 (AIPL1) in Complex with a Farnesyl Ligand. Biomol. NMR Assign. 2017, 11, 111–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spuy, J.; van der Cheetham, M.E. The Leber Congenital Amaurosis Protein AIPL1 Modulates the Nuclear Translocation of NUB1 and Suppresses Inclusion Formation by NUB1 Fragments. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 48038–48047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, D.; Poland, A. Binding of Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor (AhR) to AhR-Interacting Protein: The Role of Hsp90. J. Biol. 2000, 275, 36407–36414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Spuy, J.; Cheetham, M.E. The Chaperone Function of the LCA Protein AIPL1; Springer: Boston, MA, USA, 2006; Volume 572, pp. 471–476. [Google Scholar]
- Muthukumaran, S.; Umashankar, V.; Valliappan, M.R. Structural Studies on AIPL1 and Its Functional Interactions with NUB1 to Identify Key Interacting Residues in LCA4. J. Ocul. Biol. Dis. Inform. 2013, 5, 54–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Bulgakov, O.V.; Wen, X.H.; Woodruff, M.L.; Pawlyk, B.; Yang, J.; Fain, G.L.; Sandberg, M.A.; Makino, C.L.; Li, T. AIPL1, the Protein That Is Defective in Leber Congenital Amaurosis, Is Essential for the Biosynthesis of Retinal Rod cGMP Phosphodiesterase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 13903–13908, Correction in Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 515. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0408916101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramamurthy, V.; Roberts, M.; Van den Akker, F.; Niemi, G.; Reh, T.A.; Hurley, J.B. AIPL1, a Protein Implicated in Leber’s Congenital Amaurosis, Interacts with and Aids in Processing of Farnesylated Proteins. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 12630–12635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pannbacker, R.G.; Fleischman, D.E.; Reed, D.W. Cyclic Nucleotide Phosphodiesterase: High Activity in a Mammalian Photoreceptor. Science 1972, 175, 757–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashok, S.; Ramachandra Rao, S. Updates on Protein-Prenylation and Associated Inherited Retinopathies. Front. Ophthalmol. 2024, 4, 1410874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walia, S.; Fishman, G.A.; Jacobson, S.G.; Aleman, T.S.; Koenekoop, R.K.; Traboulsi, E.I.; Weleber, R.G.; Pennesi, M.E.; Heon, E.; Drack, A.; et al. Visual Acuity in Patients with Leber’s Congenital Amaurosis and Early Childhood-Onset Retinitis Pigmentosa. Ophthalmology 2010, 117, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallespin, E.; Cantalapiedra, D.; Riveiro-Alvarez, R.; Wilke, R.; Aguirre-Lamban, J.; Avila-Fernandez, A.; Lopez-Martinez, M.A.; Gimenez, A.; Trujillo-Tiebas, M.J.; Ramos, C.; et al. Mutation Screening of 299 Spanish Families with Retinal Dystrophies by Leber Congenital Amaurosis Genotyping Microarray. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 5653–5661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jacobson, S.G.; Cideciyan, A.V.; Aleman, T.S.; Sumaroka, A.; Roman, A.J.; Swider, M.; Schwartz, S.B.; Banin, E.; Stone, E.M. Human Retinal Disease from AIPL1 Gene Mutations: Foveal Cone Loss with Minimal Macular Photoreceptors and Rod Function Remaining. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 70–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, M.H.; Mackay, D.S.; Cowing, J.; Tran, H.V.; Smith, A.J.; Wright, G.A.; Dev-Borman, A.; Henderson, R.H.; Moradi, P.; Russell-Eggitt, I.; et al. Leber Congenital Amaurosis Associated with AIPL1: Challenges in Ascribing Disease Causation, Clinical Findings, and Implications for Gene Therapy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wiszniewski, W.; Lewis, R.A.; Stockton, D.W.; Peng, J.; Mardon, G.; Chen, R.; Lupski, J.R. Potential Involvement of More than One Locus in Trait Manifestation for Individuals with Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Hum. Genet. 2011, 129, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Xiao, X.; Li, S.; Jia, X.; Wang, P.; Guo, X.; Jiao, X.; Zhang, Q.; Hejtmancik, J.F. Detection of Variants in 15 Genes in 87 Unrelated Chinese Patients with Leber Congenital Amaurosis. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e19458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; Sun, J.; Liu, Z.; Wang, H.; Zhou, H.; Liu, W.; Jia, H.; Li, N.; Li, T.; Wang, F.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Characterization of AIPL1-Associated Leber Congenital Amaurosis/Early-Onset Severe Retinal Dystrophy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 266, 235–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Chen, Y.; Chen, H.; Ma, Y.; Chiang, P.W.; Zhong, J.; Liu, X.; Asan; Wu, J.; Su, Y.; et al. Systematic Evaluation of a Targeted Gene Capture Sequencing Panel for Molecular Diagnosis of Retinitis Pigmentosa. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0185237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, F.; Surace, E.M.; Rossi, S.; Marrocco, E.; Gargiulo, A.; Iorio, V.D.; Ziviello, C.; Nesti, A.; Fecarotta, S.; Bacci, M.L.; et al. Evaluation of Italian Patients with Leber Congenital Amaurosis Due to AIPL1 Mutations Highlights the Potential Applicability of Gene Therapy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 5618–5624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennesi, M.E.; Stover, N.B.; Stone, E.M.; Chiang, P.W.; Weleber, R.G. Residual Electroretinograms in Young Leber Congenital Amaurosis Patients with Mutations of AIPL1. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 8166–8173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahli, E.; Çavdarlı, B.; Kiziltunc, P.B.; Atilla, H. Clinical and Genetic Profile of Patients with Leber’s Congenital Amaurosis. Acta Ophthalmol. (Copenh.) 2025, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chacon-Camacho, O.F.; Zenteno, J.C. Review and Update on the Molecular Basis of Leber Congenital Amaurosis. World J. Clin. Cases 2015, 3, 112–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dyer, M.A.; Donovan, S.L.; Zhang, J.; Gray, J.; Ortiz, A.; Tenney, R.; Kong, J.; Allikmets, R.; Sohocki, M.M. Retinal Degeneration in Aipl1-Deficient Mice: A New Genetic Model of Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Mol. Brain Res. 2004, 132, 208–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pittler, S.J.; Baehr, W. Identification of a Nonsense Mutation in the Rod Photoreceptor cGMP Phosphodiesterase Beta-Subunit Gene of the Rd Mouse. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 8322–8326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farber, D.B.; Flannery, J.G.; Bowes-Rickman, C. The Rd Mouse Story: Seventy Years of Research on an Animal Model of Inherited Retinal Degeneration. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 1994, 13, 31–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pennesi, M.E.; Michaels, K.V.; Magee, S.S.; Maricle, A.; Davin, S.P.; Garg, A.K.; Gale, M.J.; Tu, D.C.; Wen, Y.; Erker, L.R.; et al. Long-Term Characterization of Retinal Degeneration in Rd1 and Rd10 Mice Using Spectral Domain Optical Coherence Tomography. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2012, 53, 4644–4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McLaughlin, M.E.; Sandberg, M.A.; Berson, E.L.; Dryja, T.P. Recessive Mutations in the Gene Encoding the β–Subunit of Rod Phosphodiesterase in Patients with Retinitis Pigmentosa. Nat. Genet. 1993, 4, 130–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, M.L.; Hurley, J.B.; Visvanathan, R. Biochemical Function of the LCA Linked Protien, Aryl Hydrocarbon Receptor Interacting Protein Like-1 (AIPL1). Role of AIPL1 in Retina. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2007, 6, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thiadens, A.A.H.J.; Hollander, A.I.; den Roosing, S.; Nabuurs, S.B.; Zekveld-Vroon, R.C.; Collin, R.W.J.; Baere, E.D.; Koenekoop, R.K.; Schooneveld, M.J.; van Strom, T.M.; et al. Homozygosity Mapping Reveals PDE6C Mutations in Patients with Early-Onset Cone Photoreceptor Disorders. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2009, 85, 240–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Chen, Y.; Sun, S.; Klein, M.; Birch, D.G. Mechanistic Studies of AIPL1-Rod cGMP Phosphodiesterase (PDE6) Interaction. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 164. [Google Scholar]
- Preising, M.N.; Sitorus, R.S.; Rosenberg, T.; Kellner, U.; Lorenz, B. Screening of NUB1 in Patients With Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 2317. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, Y.; Kim, J.K.; Yoo, J.Y. NFκB and STAT3 Synergistically Activate the Expression of FAT10, a Gene Counteracting the Tumor Suppressor P53. Mol. Oncol. 2014, 8, 642–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Fernández de la Cámara, C.; Sequedo, M.D.; Gómez-Pinedo, U.; Jaijo, T.; Aller, E.; García-Tárraga, P.; García-Verdugo, J.M.; Millán, J.M.; Rodrigo, R. Phosphodiesterase Inhibition Induces Retinal Degeneration, Oxidative Stress and Inflammation in Cone-Enriched Cultures of Porcine Retina. Exp. Eye Res. 2013, 111, 122–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cote, R.H. Characteristics of Photoreceptor PDE (PDE6): Similarities and Differences to PDE5. Int. J. Impot. Res. 2004, 16, S28–S33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ripps, H. Cell Death in Retinitis Pigmentosa: Gap Junctions and the ‘Bystander’ Effect. Exp. Eye Res. 2002, 74, 327–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fain, G.L. Why Photoreceptors Die (and Why They Don’t). BioEssays 2006, 28, 344–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newton, F.; Megaw, R. Mechanisms of Photoreceptor Death in Retinitis Pigmentosa. Genes 2020, 11, 1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, T.; Tsang, S.H.; Chen, J. Two Pathways of Rod Photoreceptor Cell Death Induced by Elevated cGMP. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2017, 26, 2299–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arango-Gonzalez, B.; Trifunović, D.; Sahaboglu, A.; Kranz, K.; Michalakis, S.; Farinelli, P.; Koch, S.; Koch, F.; Cottet, S.; Janssen-Bienhold, U.; et al. Identification of a Common Non-Apoptotic Cell Death Mechanism in Hereditary Retinal Degeneration. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e112142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sancho-Pelluz, J.; Arango-Gonzalez, B.; Kustermann, S.; Romero, F.J.; van Veen, T.; Zrenner, E.; Per, E.; François, P.-D. Photoreceptor Cell Death Mechanisms in Inherited Retinal Degeneration. Mol. Neurobiol. 2008, 38, 253–269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murakami, Y.; Matsumoto, H.; Roh, M.; Suzuki, J.; Hisatomi, T.; Ikeda, Y.; Miller, J.W.; Vavvas, D.G. Receptor Interacting Protein Kinase Mediates Necrotic Cone but Not Rod Cell Death in a Mouse Model of Inherited Degeneration. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 14598–14603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gallon, V.A.; Wilkie, S.E.; Deery, E.C.; Newbold, R.J.; Sohocki, M.M.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Hunt, D.M.; Warren, M.J. Purification, Characterisation and Intracellular Localisation of Aryl Hydrocarbon Interacting Protein-like 1 (AIPL1) and Effects of Mutations Associated with Inherited Retinal Dystrophies. Biochim. Biophys. Acta BBA-Mol. Basis Dis. 2004, 1690, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguila, M.; Bevilacqua, D.; McCulley, C.; Schwarz, N.; Athanasiou, D.; Kanuga, N.; Novoselov, S.S.; Lange, C.A.; Ali, R.R.; Bainbridge, J.W. Hsp90 Inhibition Protects against Inherited Retinal Degeneration. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2014, 23, 2164–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alibrandi, S.; Scimone, C.; Abate, G.; Scalinci, S.Z.; Sidoti, A.; Donato, L. Computational Evidence for Digenic Contribution of AIPL1 and BBS2 Rare Variants in Inherited Retinal Dystrophy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 9430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, J.; Chen, N.; Wang, L.; Zhang, F.; Ma, Z.; Li, G.; Yang, L. Application of Whole Exome and Targeted Panel Sequencing in the Clinical Molecular Diagnosis of 319 Chinese Families with Inherited Retinal Dystrophy And. Genes 2018, 9, 360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.F.; Huang, F.; Wu, K.C.; Wu, J.; Chen, J.; Pang, C.P.; Lu, F.; Qu, J.; Jin, Z.B. Genotype–Phenotype Correlation and Mutation Spectrum in a Large Cohort of Patients with Inherited Retinal Dystrophy Revealed by next-Generation Sequencing. Genet. Med. 2015, 17, 271–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Zou, X.; Xu, S.; Li, H.; Soens, Z.T.; Wang, K.; Li, Y.; Dong, F.; Chen, R.; et al. Comprehensive Molecular Diagnosis of a Large Chinese Leber Congenital Amaurosis Cohort. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 3642–3655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yücel-Yilmaz, D.; Tarlan, B.; Kiratli, H.; Özgül, R.K. Genome-Wide Homozygosity Mapping in Families with Leber Congenital Amaurosis Identifies Mutations in AIPL1 and RDH12 Genes. DNA Cell Biol. 2014, 33, 876–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, K.; Xie, Y.; Sun, T.; Zhang, X.; Chen, C.; Li, Y. Genetic and Clinical Findings in a Chinese Cohort with Leber Congenital Amaurosis and Early Onset Severe Retinal Dystrophy. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 104, 932–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppieters, F.; Casteels, I.; Meire, F.; De Jaegere, S.; Hooghe, S.; van Regemorter, N.; Van Esch, H.; Matulevičiene, A.; Nunes, L.; Meersschaut, V.; et al. Genetic Screening of LCA in Belgium: Predominance of CEP290 and Identification of Potential Modifier Alleles in AHI1 of CEP290-Related Phenotypes. Hum. Mutat. 2010, 31, E1709–E1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galvin, J.A.; Fishman, G.A.; Stone, E.M.; Koenekoop, R.K. Evaluation of Genotype–Phenotype Associations in Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Retina 2005, 25, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Jin, C.; Jiao, X.; Li, L.; Bushra, T.; Naeem, M.A.; Butt, N.H.; Husnain, T.; Sieving, P.A.; Riazuddin, S.; et al. AIPL1 Implicated in the Pathogenesis of Two Cases of Autosomal Recessive Retinal Degeneration. Mol. Vis. 2014, 20, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Rashid, M.; Qasim Id, M.; Ishaq, R.; Bukhari, S.A.; Sajid, Z.; Ashfaq, U.A.; Haque, A.; Ahmed, Z.M. Pathogenic Variants of AIPL1, MERTK, GUCY2D, and FOXE3 in Pakistani Families with Clinically Heterogeneous Eye Diseases. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0239748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aboshiha, J.; Dubis, A.M.; Van Der Spuy, J.; Nishiguchi, K.M.; Cheeseman, E.W.; Ayuso, C.; Ehrenberg, M.; Simonelli, F.; Bainbridge, J.W.; Michaelides, M. Preserved Outer Retina in AIPL1 Leber’s Congenital Amaurosis: Implications for Gene Therapy. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 862–864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalavar, M.; Lovett, E.A., Jr.; Nicholas, M.P.; Ross-Hirsch, A.; Nirwan, R.S.; Sridhar, J.; Patel, S.; Flynn, H.W., Jr.; Albini, T.A.; Kuriyan, A.E. Update on “Cell Therapy” Clinics Offering Treatments of Ocular Conditions Using Direct-To-Consumer Marketing Websites in the US. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2024, 267, 135–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seong, M.W.; Kim, S.Y.; Yu, Y.S.; Hwang, J.M.; Kim, J.Y.; Park, S.S. Molecular Characterization of Leber Congenital Amaurosis in Koreans. Mol. Vis. 2008, 14, 1429–1436. [Google Scholar]
- Zobor, D.; Brühwiler, B.; Zrenner, E.; Weisschuh, N.; Kohl, S. Genetic and Clinical Profile of Retinopathies Due to Disease-Causing Variants in Leber Congenital Amaurosis (LCA)-Associated Genes in a Large German Cohort. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 8915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sitorus, R.S.; Lorenz, B.; Preising, M.N. Analysis of Three Genes in Leber Congenital Amaurosis in Indonesian Patients. Vision Res. 2003, 43, 3087–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaliq, S.; Abid, A.; Hameed, A.; Anwar, K.; Mohyuddin, A.; Azmat, Z.; Shami, S.A.; Ismail, M.; Mehdi, S.Q. Mutation Screening of Pakistani Families with Congenital Eye Disorders. Exp. Eye Res. 2003, 76, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dev Borman, A. A Genotype-Phenotype Study of Childhood Onset Retinal Dystrophies. Ph.D. Thesis, University College London, London, UK, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Beryozkin, A.; Shevah, E.; Kimchi, A.; Mizrahi-Meissonnier, L.; Khateb, S.; Ratnapriya, R.; Lazar, C.H.; Blumenfeld, A.; Ben-Yosef, T.; Hemo, Y.; et al. Whole Exome Sequencing Reveals Mutations in Known Retinal Disease Genes in 33 out of 68 Israeli Families with Inherited Retinopathies. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, L.; Xiang, L.; Wang, H.; Shi, Y.; Jiang, D.; Hao, F.; Huang, L. A New Novel Nonsense Mutation in AIPL1 in a LCA4 Family. Ophthalmic Genet. 2019, 40, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Huang, L.; Xie, Y.; Liu, W.; Zhang, S.; Liu, L.; Lin, P.; Li, N. Clinical and Genetic Studies for a Cohort of Patients with Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2024, 262, 3029–3038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lukovic, D.; Artero Castro, A.; Kaya, K.D.; Munezero, D.; Gieser, L.; Davó-Martínez, C.; Corton, M.; Cuenca, N.; Swaroop, A.; Ramamurthy, V.; et al. Retinal Organoids Derived from hiPSCs of an AIPL1-LCA Patient Maintain Cytoarchitecture despite Reduced Levels of Mutant AIPL1. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weisschuh, N.; Feldhaus, B.; Khan, M.I.; Cremers, F.P.M.; Kohl, S.; Wissinger, B.; Zobor, D. Molecular and Clinical Analysis of 27 German Patients with Leber Congenital Amaurosis. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0205380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jespersgaard, C.; Fang, M.; Bertelsen, M.; Dang, X.; Jensen, H.; Chen, Y.; Bech, N.; Dai, L.; Rosenberg, T.; Zhang, J.; et al. Molecular Genetic Analysis Using Targeted NGS Analysis of 677 Individuals with Retinal Dystrophy. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.H. Development of Gene Therapy for the Treatment of Retinal Dystrophies Caused by Mutations in AIPL1; University College London: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Henderson, R.H.; Waseem, N.; Searle, R.; Van Der Spuy, J.; Russell-Eggitt, I.; Bhattacharya, S.S.; Thompson, D.A.; Holder, G.E.; Cheetham, M.E.; Webster, A.R.; et al. An Assessment of the Apex Microarray Technology in Genotyping Patients with Leber Congenital Amaurosis and Early-Onset Severe Retinal Dystrophy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 5684–5689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Hao, P.; Ying, M.; Han, R.; Wang, Y.; Gao, J.; Yuan, X.; Li, X. Identification of AIPL1 Gene Variants in Two Chinese Families with Cone-Rod Dystrophy. Honghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi 2019, 36, 1081–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, A.; Sacristan-Reviriego, A.; Perdigão, P.R.L.; Sai, H.; Georgiou, M.; Kalitzeos, A.; Carr, A.J.F.; Coffey, P.J.; Michaelides, M.; Bainbridge, J.; et al. Investigation of PTC124-Mediated Translational Readthrough in a Retinal Organoid Model of AIPL1-Associated Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Stem Cell Rep. 2022, 17, 2187–2202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zernant, J.; Külm, M.; Dharmaraj, S.; Den Hollander, A.I.; Perrault, I.; Preising, M.N.; Lorenz, B.; Kaplan, J.; Cremers, F.P.M.; Maumenee, I.; et al. Genotyping Microarray (Disease Chip) for Leber Congenital Amaurosis: Detection of Modifier Alleles. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 3052–3059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonelli, F.; Ziviello, C.; Testa, F.; Rossi, S.; Fazzi, E.; Bianchi, P.E.; Fossarello, M.; Signorini, S.; Bertone, C.; Galantuomo, S.; et al. Clinical and Molecular Genetics of Leber’s Congenital Amaurosis: A Multicenter Study of Italian Patients. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2007, 48, 4284–4290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Astuti, G.D.N.; Bertelsen, M.; Preising, M.N.; Ajmal, M.; Lorenz, B.; Faradz, S.M.H.; Qamar, R.; Collin, R.W.J.; Rosenberg, T.; Cremers, F.P.M. Comprehensive Genotyping Reveals RPE65 as the Most Frequently Mutated Gene in Leber Congenital Amaurosis in Denmark. Eur. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 24, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasadhika, S.; Fishman, G.A.; Stone, E.M.; Lindeman, M.; Zelkha, R.; Lopez, I.; Koenekoop, R.K.; Shahidi, M. Differential Macular Morphology in Patients with RPE65-, CEP290-, GUCY2D-, and AIPL1-Related Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 2608–2614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damji, K.F.; Sohocki, M.M.; Khan, R.; Gupta, S.K.; Rahim, M.; Loyer, M.; Hussein, N.; Karim, N.; Ladak, S.S.; Jamal, A.; et al. Leber’s Congenital Amaurosis with Anterior Keratoconus in Pakistani Families Is Caused by the Trp278X Mutation in the AIPL1 Gene on 17p. Can. J. Ophthalmol. 2001, 36, 252–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McKibbin, M.; Ali, M.; Mohamed, M.D.; Booth, A.P.; Bishop, F.; Pal, B.; Springell, K.; Raashid, Y.; Jafri, H.; Inglehearn, C.F. Genotype-Phenotype Correlation for Leber Congenital Amaurosis in Northern Pakistan. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2010, 128, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gumus, E.; Ozgur, A. A Novel AIPL1 Nonsense Mutation: Case Report of Three Siblings Diagnosed with Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Fetal Pediatr. Pathol. 2020, 39, 251–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sallum, J.M.F.; Kaur, V.P.; Shaikh, J.; Banhazi, J.; Spera, C.; Aouadj, C.; Viriato, D.; Fischer, M.D. Epidemiology of Mutations in the 65-kDa Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE65) Gene-Mediated Inherited Retinal Dystrophies: A Systematic Literature Review. Adv. Ther. 2022, 39, 1179–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanein, S.; Perrault, I.; Gerber, S.; Tanguy, G.; Barbet, F.; Ducroq, D.; Calvas, P.; Dollfus, H.; Hamel, C.; Lopponen, T.; et al. Leber Congenital Amaurosis: Comprehensive Survey of the Genetic Heterogeneity, Refinement of the Clinical Definition, and Genotype-Phenotype Correlations as a Strategy for Molecular Diagnosis. Hum. Mutat. 2004, 23, 306–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heegaard, S.; Rosenberg, T.; Preising, M.N.; Prause, J.U.; Bek, T. An Unusual Retinal Vascular Morphology in Connection with a Novel AIPL1 Mutation in Leber’s Congenital Amaurosis. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2003, 87, 980–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srikrupa, N.N.; Srilekha, S.; Sen, P.; Arokiasamy, T.; Meenakshi, S.; Bhende, M.; Kapur, S.; Soumittra, N. Genetic Profile and Mutation Spectrum of Leber Congenital Amaurosis in a Larger Indian Cohort Using High Throughput Targeted Re-Sequencing. Clin. Genet. 2018, 93, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perrault, I.; Delphin, N.; Hanein, S.; Gerber, S.; Dufier, J.L.; Roche, O.; Defoort-Dhellemmes, S.; Dollfus, H.; Fazzi, E.; Munnich, A.; et al. Spectrum of NPHP6/CEP290 Mutations in Leber Congenital Amaurosis and Delineation of the Associated Phenotype. Hum. Mutat. 2007, 28, 416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollander, A.I.; den Koenekoop, R.K.; Yzer, S.; Lopez, I.; Arends, M.L.; Voesenek, K.E.J.; Zonneveld, M.N.; Strom, T.M.; Meitinger, T.; Brunner, H.G.; et al. Mutations in the CEP290 (NPHP6) Gene Are a Frequent Cause of Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2006, 79, 556–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, T.A.; Mullins, R.F.; Wagner, A.H.; Andorf, J.L.; Johnston, R.M.; Bakall, B.B.; Deluca, A.P.; Fishman, G.A.; Lam, B.L.; Weleber, R.G.; et al. Non-Exomic and Synonymous Variants in ABCA4 Are an Important Cause of Stargardt Disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2013, 22, 5136–5145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yzer, S.; Leroy, B.P.; De Baere, E.; De Ravel, T.J.; Zonneveld, M.N.; Voesenek, K.; Kellner, U.; Martinez Ciriano, J.P.; De Faber, J.T.H.N.; Rohrschneider, K.; et al. Microarray-Based Mutation Detection and Phenotypic Characterization of Patients with Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2006, 47, 1167–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tatour, Y.; Ben-Yosef, T. Syndromic Inherited Retinal Diseases: Genetic, Clinical and Diagnostic Aspects. Diagnostics 2020, 10, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenekoop, R.K.; Wang, H.; Majewski, J.; Wang, X.; Lopez, I.; Ren, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, Y.; Fishman, G.A.; Genead, M.; et al. Mutations in NMNAT1 Cause Leber Congenital Amaurosis and Identify a New Disease Pathway for Retinal Degeneration. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 1035–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garafalo, A.V.; Cideciyan, A.V.; Héon, E.; Sheplock, R.; Pearson, A.; Yu, C.W.Y.; Sumaroka, A.; Aguirre, G.D.; Jacobson, S.G. Progress in Treating Inherited Retinal Diseases: Early Subretinal Gene Therapy Clinical Trials and Candidates for Future Initiatives. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2020, 77, 100827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dunn, K.C.; Aotaki-keen, A.E.; Putkey, F.R.; Hjelmeland, L.M. ARPE-19, A Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cell Line with Differentiated Properties. Exp. Eye Res. 1996, 62, 155–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hellinen, L.; Hagström, M.; Knuutila, H.; Ruponen, M.; Urtti, A.; Mika, R.; Reinisalo, M. Characterization of Artificially Re-Pigmented ARPE-19 Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cell Model. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 13761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nommiste, B.; Carr, A.-J.; Gias, C.; Coffey, P. Effects of Culture Medium and Surface Coatings on RPE Cell Differentiation. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2013, 54, 3744. [Google Scholar]
- Shafei, E.V.; Rzhanova, L.A.; Novikova, Y.P.; Kurinov, A.M.; Grigoryan, E.N.; Aleksandrova, M.A.; Kuznetsova, A.V. Response of Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells to the Effect of the Conditioned Media of Newt Retinal Regenerates. Tsitologiya 2021, 15, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, A.-J.; Vugler, A.A.; Yu, L.; Semo, M.; Coffey, P.; Moss, S.E.; Greenwood, J. The Expression of Retinal Cell Markers in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells and Their Augmentation by the Synthetic Retinoid Fenretinide. Mol. Vis. 2011, 17, 1701–1715. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, S.; Samuel, W.; Fariss, R.N.; Duncan, T.; Kutty, R.K.; Wiggert, B. Differentiation of Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells into Neuronal Phenotype by N-(4-Hydroxyphenyl)Retinamide. J. Neurochem. 2003, 84, 972–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gurtsieva, D.; Minskaia, E.; Zhuravleva, S.; Subcheva, E.; Sakhibgaraeva, E.; Brovin, A.; Tumaev, A.; Karabelsky, A. Engineered AAV2.7m8 Serotype Shows Significantly Higher Transduction Efficiency of ARPE-19 and HEK293 Cell Lines Compared to AAV5, AAV8 and AAV9 Serotypes. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, Y.; Imamura, K.; Oishi, A.; Kondo, T.; Suga, M.; Yada, Y.; Shibukawa, R.; Okanishi, Y.; Sagara, Y.; Tsukita, K.; et al. One-Step Induction of Photoreceptor-like Cells from Human iPSCs by Delivering Transcription Factors. iScience 2022, 25, 103987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perdigão, P.R.L.; Ollington, B.; Sai, H.; Leung, A.; Sacristan-Reviriego, A.; van der Spuy, J. Retinal Organoids from an AIPL1 CRISPR/Cas9 Knockout Cell Line Successfully Recapitulate the Molecular Features of LCA4 Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, B.D. Zebrafish Models of Inherited Retinal Dystrophies. J. Transl. Genet. Genom. 2022, 6, 95–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iribarne, M.; Hyde, D.R.; Masai, I. TNFα Induces Müller Glia to Transition From Non-Proliferative Gliosis to a Regenerative Response in Mutant Zebrafish Presenting Chronic Photoreceptor Degeneration. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 7, 494319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agarwal, D.; Do, H.; Mazo, K.W.; Chopra, M.; Wahlin, K.J. Restoring Vision and Rebuilding the Retina by Müller Glial Cell Reprogramming. Stem Cell Res. 2023, 66, 103006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundin, O.H. The Mouse’s Eye and Mfrp: Not Quite Human. Ophthalmic Genet. 2005, 25, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ku, C.A.; Chiodo, V.A.; Boye, S.L.; Goldberg, A.F.X.; Li, T.; Hauswirth, W.W.; Ramamurthy, V. Gene Therapy Using Self-Complementary Y733F Capsid Mutant AAV2/8 Restores Vision in a Model of Early Onset Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2011, 20, 4569–4581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, R.K.; Kolandaivelu, S.; Ramamurthy, V. Early Alteration of Retinal Neurons in Aipl1−/− Animals. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2014, 55, 3081–3092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Procyk, C.A.; Melati, A.; Ribeiro, J.; Liu, J.; Branch, M.J.; Delicata, J.D.; Tariq, M.; Kalarygrou, A.A.; Kapadia, J.; Khorsani, M.M.; et al. Human Cone Photoreceptor Transplantation Stimulates Remodeling and Restores Function in AIPL1 Model of End-Stage Leber Congenital Amaurosis. Stem Cell Rep. 2025, 20, 102470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kharisova, C.B.; Kitaeva, K.V.; Solovyeva, V.V.; Sufianov, A.A.; Sufianova, G.Z.; Akhmetshin, R.F.; Bulgar, S.N.; Rizvanov, A.A. Looking to the Future of Viral Vectors in Ocular Gene Therapy: Clinical Review. Biomedicines 2025, 13, 365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perdigao, P.R.L.; van der Spuy, J. Gene and Cell Therapy for AIPL1-Associated Leber Congenital Amaurosis: Challenges and Prospects. In Retinal Degenerative Diseases; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; Volume 1185, pp. 97–101. [Google Scholar]
- den Hollander, A.I.; Roepman, R.; Koenekoop, R.K.; Cremers, F.P.M. Leber Congenital Amaurosis: Genes, Proteins and Disease Mechanisms. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2008, 27, 391–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Caspi, R.R. Ocular Immune Privilege Introduction and Context. F1000 Biol. Rep. 2010, 2, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russell, S.; Bennett, J.; Wellman, J.A.; Chung, D.C.; Yu, Z.F.; Tillman, A.; Wittes, J.; Pappas, J.; Elci, O.; McCague, S.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Voretigene Neparvovec (AAV2-hRPE65v2) in Patients with RPE65-Mediated Inherited Retinal Dystrophy: A Randomised, Controlled, Open-Label, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2017, 390, 849–860, Erratum in Lancet. 2017, 390, 848. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(17)32235-3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, R.R.; Reichel, M.B.; Thrasher, A.J.; Levinsky, R.J.; Kinnon, C.; Kanuga, N.; Hunt, D.M.; Bhattacharya, S.S. Gene Transfer into the Mouse Retina Mediated by an Adeno-Associated Viral Vector. Hum. Mol. Genet. 1996, 5, 591–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Day, T.P.; Byrne, L.C.; Schaffer, D.V.; Flannery, J.G. Advances in AAV Vector Development for Gene Therapy in the Retina. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2014, 801, 687–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebner, L.J.A.; Grimm, C. AAV Serotypes and Their Suitability for Retinal Gene Therapy. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2023, 1415, 131–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, W.; Wu, D.M.; Xue, Y.; Wang, S.K.; Chung, M.J.; Ji, X.; Rana, P.; Zhao, S.R.; Mai, S.; Cepko, C.L. AAV Cis-Regulatory Sequences Are Correlated with Ocular Toxicity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2019, 116, 5785–5794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Samulski, R.J. Engineering Adeno-Associated Virus Vectors for Gene Therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2020, 21, 255–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galieva, A.; Egorov, A.; Malogolovkin, A.; Brovin, A.; Karabelsky, A. RNA-Seq Analysis of Trans-Differentiated ARPE-19 Cells Transduced by AAV9-AIPL1 Vectors. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sai, H.; Ollington, B.; Rezek, F.O.; Chai, N.; Lane, A.; Georgiadis, T.; Bainbridge, J.; Michaelides, M.; Sacristan-Reviriego, A.; Perdigão, P.R.L.; et al. Effective AAV-Mediated Gene Replacement Therapy in Retinal Organoids Modeling AIPL1-Associated LCA4. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2024, 35, 102148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MeiraGTx Reports Fourth Quarter and Full Year 2024 Financial and Operational Results and Recent Business Updates|MeiraGTx. Available online: https://investors.meiragtx.com/news-releases/news-release-details/meiragtx-reports-fourth-quarter-and-full-year-2024-financial-and (accessed on 4 December 2025).
- MeiraGTx Seeks UK Approval after Gene Therapy Restores Sight in Children Born Blind-Pharmaceutical Technology. Available online: https://www.pharmaceutical-technology.com/news/meiragtx-seeks-uk-approval-after-gene-therapy-restores-sight-in-children-born-blind/ (accessed on 29 October 2025).
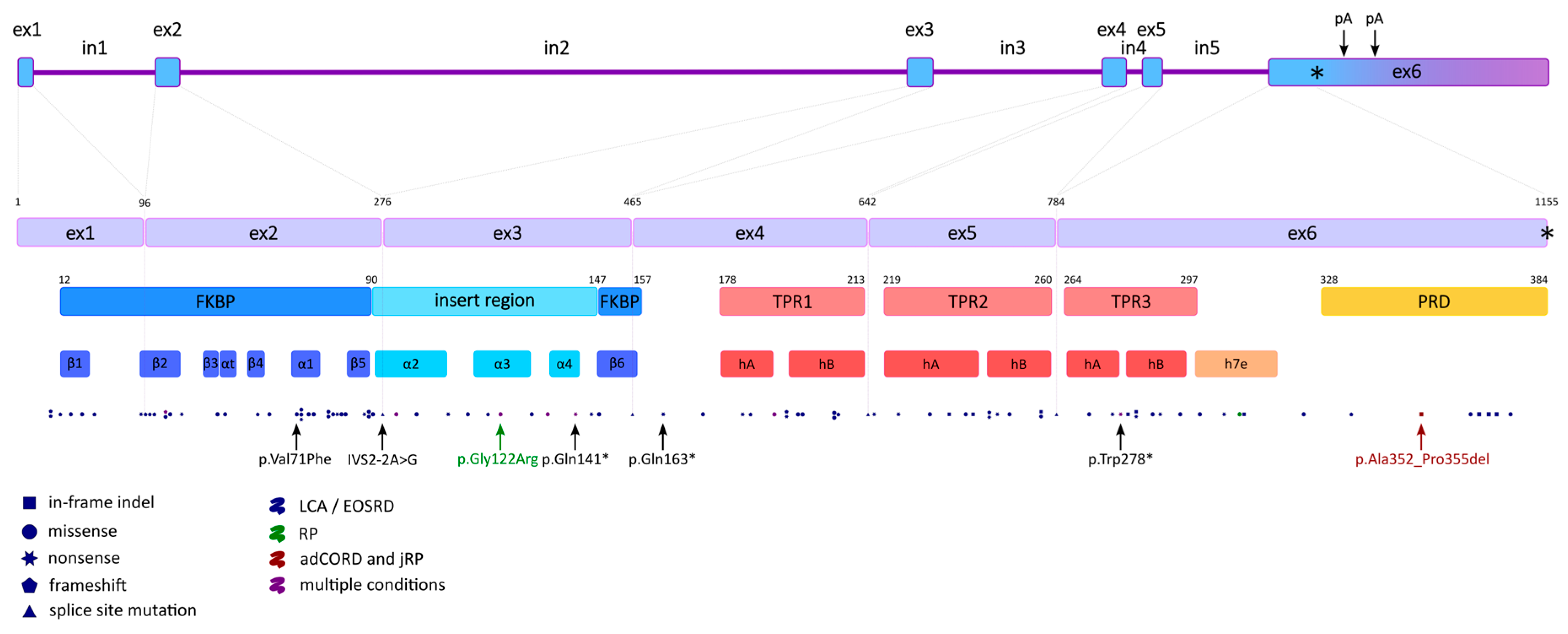
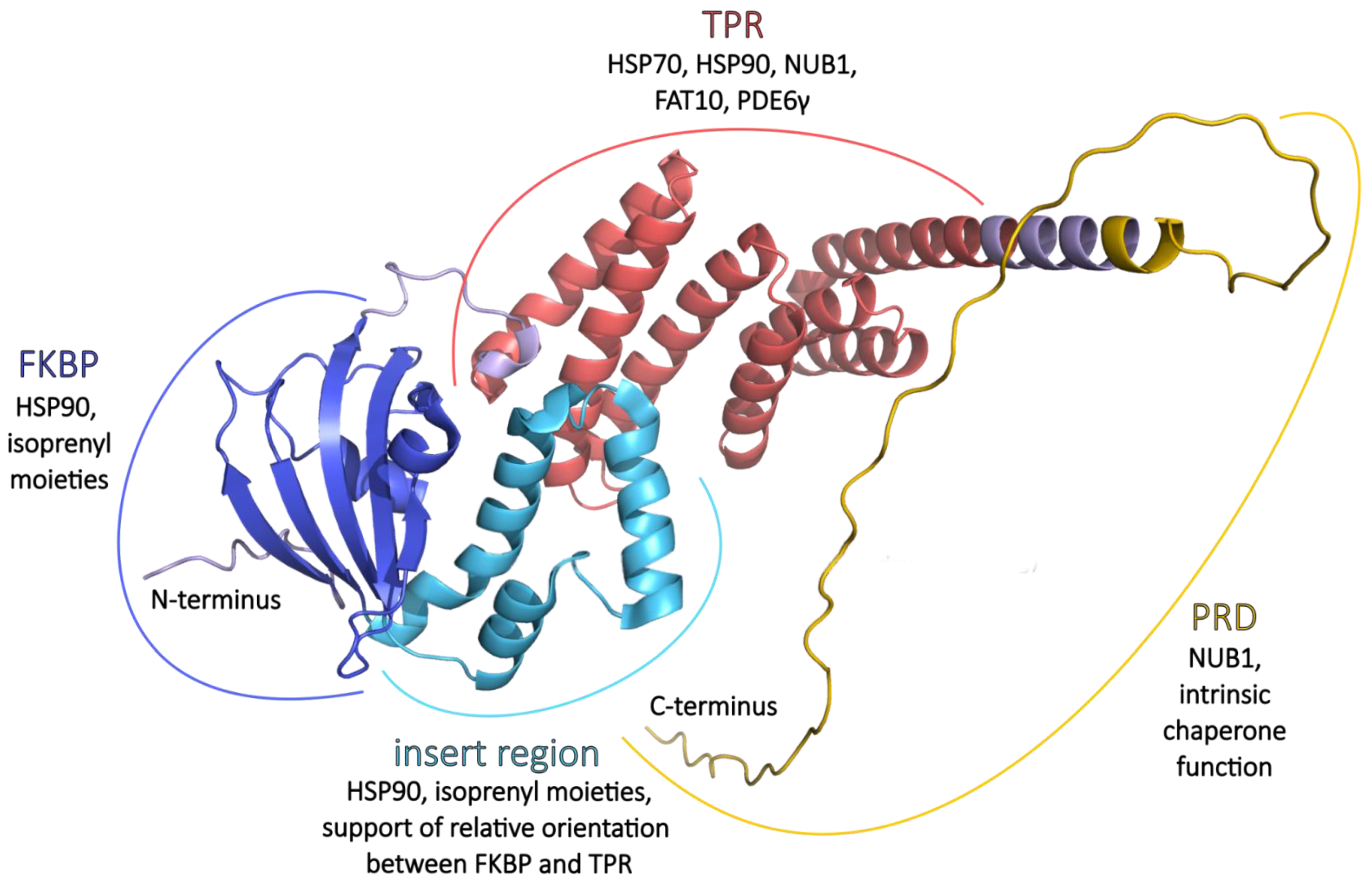
| Interactant | Method | Source |
|---|---|---|
| HSP70 | yeast two-hybrid system, in vitro biochemical assays | [31] |
| HSP90 | yeast two-hybrid system, in vitro biochemical assays | [31] |
| immunoprecipitation, quantitative ELISA | [29] | |
| bio-layer interferometry, cross-linking/SDS-PAGE, cross-linking/mass photometry | [61] | |
| NUB1 | yeast two-hybrid system, co-immunoprecipitation/immunoblot, immunohistochemistry | [71] |
| immunohistochemistry, subcellular fractionation/immunoblot | [35] | |
| yeast two-hybrid system | [31] | |
| yeast two-hybrid analysis, immunoprecipitation/immunoblot, GST pull-down/immunoblot | [72] | |
| FAT10 | immunocytochemistry, immunoprecipitation/immunoblot, GST pull-down/immunoblot | [73] |
| immunoprecipitation, in vitro biochemical assays | [74] | |
| rod PDE6α (PDE6A) | immunoprecipitation/immunoblot, mass spectrometry | [75] |
| rod PDE6β (PDE6B) | immunoprecipitation/mass spectrometry | [75] |
| cone PDE6α′ (PDE6C) | retinal extracts, immunoblotting, immunoprecipitation/immunoblotting | [67] |
| rod Pγ (PDE6G) | fluorescence binding assay | [52] |
| dynamic light scattering, biolayer interferometry, fluorescence binding assays, NMR spectroscopy | [55] |
| Inheritance Pattern | Allele 1 | Allele 2 | Cohort | Conditions | Reference | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| cDNA | Protein | Type | cDNA | Protein | Type | ||||
| n/s | c.26-delT | p.Val9-del1 | fs | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| n/s | [n/s] insGGAA | p.Val9-ins4 | fs | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| compHet | c.34dup | p.Val12Gly-fs*32 | fs | c.238C>T | p.Arg80Trp | mis | German | LCA | [131] |
| hom | c.40A>G | p.Lys14Glu | mis | c.40A>G | p.Lys14Glu | mis | Indonesian | LCA | [132] |
| compHet | n/s | p.Leu17Pro | mis | n/s | p.Lys214Asn | splVar | Vietnamese | LCA | [94] |
| compHet | c.59delG | p.Gly20Ala-fs*14 | fs | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | Chinese | LCA | [91] |
| compHet | c.94C>T | p.Arg32* | nons | c.276+2T>C | [IVS2+2T>C] | splVar | n/s | LCA | [128] |
| compHet | n/s | p.Val33-fs | fs | [c.834G>A] | p.Trp278* | nons | European | LCA | [87] |
| n/s | c.97insGTGATCTT | p.Val33ins8 | fs | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| compHet | n/s | p.Val33ins8bp | fs | [c.834G>A] | p.Trp278* | nons | U.S. American | LCA | [40] |
| compHet | c.97_104dup or c.96_97 insGTGATCTT | p.Gly31fs [p.Phe35-fs] | fs | c.IVS5-10_786del (c.785-10del12CTCCCCACAGGC) | [IVS5-10del12bp] | splVar | Italian | LCA | [93] |
| compHet | c.96_97insGTGATCTT | p.Phe35Leu-fs*2 | fs | c.785-10del12CTCCCCACAGGC | c.IVS5-10_786del [IVS5-10del12bp] | splVar | n/s | LCA | [128] |
| compHet | c.96_97insGTGATCTT | p.Phe35Leu-fs*2 | fs | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [128] |
| compHet | c.98_99 insTGATCTTG | p.Phe35-fs*36 | fs | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | Italian | LCA | [93] |
| compHet | c.98_99insTGATCTTG | p.Ile34Asp-fs*10 | fs | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [128] |
| het | c.111delC | p.Arg38-fs | fs | - | - | - | Spanish | LCA, non-early-onset RP | [86] |
| n/s | c.112C>T | p.Arg38Cys | mis | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| hom | c.116C>A | p.Thr39Asn | mis | c.116C>A | p.Thr39Asn | mis | Pakistani | LCA | [133] |
| n/s | LCA | [18] | |||||||
| compHet | n/s | p.Cys42* | nons | [c.784G>A] | p.Gly262Ser | U.S. American | LCA | [40] | |
| hom | c.152A>G | p.Asp51Gly | mis | c.152A>G | p.Asp51Gly | mis | Chinese | EOSRD | [91] |
| compHet | c.152A>G | p.Asp51Gly | mis | c.182delT | p.Ile61Thr-fs*43 | fs | Chinese | EOSRD | [91] |
| compHet | c.152A>G | p.Asp51Gly | mis | c.325C>T | p.Gln109* | nons | Chinese | EOSRD | [91] |
| compHet | c.152A>G | p.Asp51Gly | mis | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | Chinese | EOSRD | [91] |
| compHet | c.152A>G | p.Asp51Gly | mis | c.506 T>C | p.Leu169Pro | mis | Chinese | EOSRD | [91] |
| compHet | c.152A>G | p.Asp51Gly | mis | c.749T>C | p.Leu250Pro | mis | Chinese | EOSRD | [91] |
| compHet | c.152A>G | p.Asp51Gly | mis | c.826G>T | p.Glu276* | nons | Chinese | EOSRD | [91] |
| compHet | c.152A>G | p.Asp51Gly | mis | c.733_735delGAG | p.Glu245del | indel | Chinese | LCA | [121] |
| n/s | c.157C>T | p.Arg53Trp | mis | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [18] |
| compHet | c.190G>A | p.Gly64Arg | mis | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | White | LCA | [88] |
| compHet | c.190G>A | p.Gly64Arg | mis | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [128] |
| compHet | c.190G>A | p.Gly64Arg | mis | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | British Caucasian | EORD | [134] |
| hom | c.211G>T | p.Val71Phe | mis | c.211G>T | p.Val71Phe | mis | n/s | n/s | [85] |
| North African Jewish | LCA | [87] | |||||||
| Israeli | [135] | ||||||||
| n/s | [153] | ||||||||
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | [1] | ||||
| compHet | c.211G>T | p.Val71Phe | mis | c.216G>A | p.Trp72* | nons | n/s | [128] | |
| compHet | mis | nons | Mixed | LCA | [87] | ||||
| compHet | c.211G>T | p.Val71Phe | mis | c.733_735delGAG | [p.Glu245del] | indel | Chinese | LCA | [91] |
| compHet | [c.236T>C] | p.Met79Thr | mis | [c.834G>A] | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [125] |
| compHet | mis | nons | n/s | n/s | [85] | ||||
| n/s | c.214T>C | p.Trp72Arg | mis | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [18] | |||
| hom | c.215G>C | p.Trp72Ser | mis | c.215G>C | p.Trp72Ser | mis | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| compHet | c.214T>C | p.Trp72Arg | mis | c.265T>C | p.Cys89Arg | mis | Mixed | LCA | [87] |
| n/s | [18] | ||||||||
| compHet | c.221T>C | [p.Ile74Thr] | mis | c.616A>G | p.Ile206Val | mis | Chinese | EOSRD | [91] |
| compHet | c.224T>G | [p.Leu75Arg] | mis | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | Chinese | LCA | [91] |
| hom | c.236T>C | p.Met79Thr | mis | c.236T>C | p.Met79Thr | mis | Indian | LCA | [28,40] |
| compHet | c.237G>A | [p.Met79Ile] | mis | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | Chinese | LCA | [91] |
| hom | c.241C>T | p.Gly81* | nons | c.241C>T | p.Gly81* | nons | Chinese | LCA | [136] |
| n/s | c.244C>T | p.His82Tyr | mis | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| compHet | c.244C>T | p.His82Tyr | mis | c.286G>C | p.Asp90His | mis | n/s | LCA | [39,154] |
| hom | c.247G>A | p.Glu83Lys | mis | c.247G>A | p.Glu83Lys | mis | Indian | LCA | [155] |
| compHet | c.247G>A | p.Glu83Lys | mis | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | Chinese | LCA | [137] |
| hom | c.264G>A | p.Trp88* | nons | c.264G>A | p.Trp88* | nons | Pakistani | LCA | [88] |
| n/s | [128] | ||||||||
| Bangladeshi | [28,40] | ||||||||
| hom | c.265T>C | p.Cys89Arg | mis | c.265T>C | p.Cys89Arg | mis | n/s | LCA | [18,128] |
| Spanish | LCA | [138] | |||||||
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] | |||
| compHet | c.265T>C | p.Cys89Arg | mis | c.618_619dupCT | p.Cys207Ser-fs*3 | fs | n/s | LCA | [12] |
| hom | c.266G>A | p.Cys89Tyr | mis | c.266G>A | p.Cys89Tyr | mis | n/s | LCA | [89] |
| compHet | c.265T>C | p.Cys89Arg | mis | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [128] |
| compHet | c.276+1G>A | [IVS2+1G>A] | splVar | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [128] |
| compHet | c.276+6T>C | [IVS2+6T>C] | splVar | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | German | LCA | [139] |
| compHet | [c.(276+1_277-1)del] | n/s | c.815G>C | p.Arg272Pro | mis | n/s | LCA | [140] | |
| het | c.277-2A>G | IVS2-2A>G | splVar | - | - | - | n/s | LCA | [125] |
| - | - | - | n/s | n/s | [85] | ||||
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] | |||
| compHet | c.277-2A>G | [in-frame ΔEx3] | splVar | c.784G>A | p.Gly262Ser | splVar | White | LCA | [88] |
| compHet | c.277-2A>G | [in-frame ΔEx3] | splVar | c.784G>A | p.Gly262Ser | splVar | n/s | LCA | [128] |
| compHet | c.277-2A>G | IVS2-2A>G | splVar | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | French | LCA | [28] |
| compHet | n/s | [128] | |||||||
| compHet | n/s | n/s | [85] | ||||||
| compHet | n/s | LCA | [153] | ||||||
| compHet | Australian | LCA | [9] | ||||||
| compHet | [c.834G>A] | Ireland, French | LCA | [40] | |||||
| compHet | European | [87] | |||||||
| hom | c.286G>A | p.Val96Ile | mis | c.286G>A | p.Val96Ile | mis | Belgian | LCA | [40] |
| het | - | - | - | Portuguese | LCA | [28] | |||
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | jRP | [41] | |||
| compHet | c.301T>C | [p.Ser101Pro] | mis | c.826G>T | p.Glu276* | nons | Chinese | LCA | [91] |
| compHet | c.325C>T | p.Gln109* | nons | c.421C>T | p.Q141* | mis | Chinese | LCA | [121] |
| het | c.341C>T | p.Thr114Ile | mis | - | - | - | n/s | LCA | [125] |
| - | - | - | n/s | [85] | |||||
| compHet | c.341C>T | p.Thr114I | mis | c.1126C>T | p.Pro376Ser | mis | U.S. American, French | LCA | [40] |
| n/s | n/s | [85] | |||||||
| n/s | LCA, LCA or EOSRD | [18] | |||||||
| African American | LCA | [28] | |||||||
| n/s | c.341C>T, c.1126C>T (cis-allelic) | p.Thr114Ile, p.Pro376Ser | mis | n/s | n/s | n/s | African | LCA | [124] |
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | EOSRD | [18] | ||||
| compHet | c.356_359del | p.His119Arg-fs*31 | fs | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | Australian | LCA | [9] |
| hom | c.364G>A | p.Gly122Arg | mis | c.364G>A | p.Gly122Arg | mis | n/s | RP | [18] |
| compHet | c.364G>A | p.Gly122Arg | mis | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | Chinese | RP/LCA/ CORD | [92] |
| compHet | c.364G>A | p.Gly122Arg | mis | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | Italian | LCA | [93] |
| compHet | c.364G>C | p.Gly122Arg | mis | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | European | late-onset retinal degeneration | [87] |
| compHet | n/s | LCA, mild RP, RP | [18] | ||||||
| compHet | c.364G>A | c.834G>A | Italian | LCA | [93] | ||||
| het | c.390C>A | p.His130Gln | mis | - | - | - | n/s | LCA or EOSRD (probably benign) | [88] |
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA or EOSRD | [18] | |||
| hom | c.401A>T | p.Tyr134Phe | mis | c.401A>T | p.Tyr134Phe | mis | French | LCA | [40] |
| het | - | - | - | Caucasian, Bangladeshi | LCA | [141] | |||
| compHet | c.1126C>T | p.Pro376Ser | mis | n/s | n/s | [142] | |||
| n/s | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | n/s | n/s | n/s | Chinese | LCA | [123] |
| hom | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | Turkish | LCA | [122] | |||
| Chinese | LCA | [91,120,121,137] | |||||||
| RP | [119] | ||||||||
| compHet | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | c.433C>T | p.Gln145* | nons | Chinese | LCA | [91] |
| compHet | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | c.465+1G>A | [IVS3+1G>A] | splVar | Chinese | LCA | [91] |
| compHet | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | c.572T>C | p.Leu191Pro | mis | Chinese | CORD | [143] |
| compHet | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | c.572T>C | p.Leu191Pro | mis | Chinese | LCA | [121] |
| compHet | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | c.572T>C | p.Leu191Pro | mis | Chinese | EOSRD | [91] |
| compHet | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | c.581_584delACGA | p.Tyr194Trp-fs*14 | fs | Chinese | LCA | [137] |
| compHet | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | c.602delA | p.Tyr201Ser-fs*7 | fs | Chinese | LCA | [91] |
| compHet | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | c.646A>T | [p.Lys216*] | nons | Chinese | LCA | [91] |
| compHet | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | c.703_705del | p.Asn235del | indel | Chinese | LCA | [91] |
| compHet | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | Chinese | LCA | [121] |
| compHet | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | Chinese | LCA | [91] |
| compHet | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | Chinese | LCA | [121] |
| compHet | c.421C>T | p.Gln141* | nons | c.923T>C | p.Leu308Pro | mis | Chinese | CORD | [143] |
| hom | c.440T>C | p.Leu147Pro | mis | c.440T>C | p.Leu147Pro | mis | Chinese | LCA | [91] |
| hom | c.465G>T | p.His93_Gln155del (ΔEx3) | splVar | c.465G>T | p.His93_Gln155del (ΔEx3) | splVar | Pakistani | n/s | [126] |
| hom | c.465G>T | p.Gln155His | splVar | c.465G>T | p.Gln155His | splVar | Pakistani | LCA | [127] |
| compHet | c.465G>T | p.Gln155His | splVar | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [140] |
| n/s | c.465+1G>A | IVS3+1 (IVS3+1G>A) | splVar | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| hom | c.465+1G>C | IVS3+1 (IVS3+1G>C) | splVar | c.465+1G>C | IVS3+1 (IVS3+1G>C) | splVar | n/s | LCA | [12] |
| het | c.466-2A>G | IVS3-2A>G | splVar | - | - | - | n/s | LCA | [141] |
| compHet | c.466-1G>C | [IVS3-1G>C] | splVar | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [144] |
| hom | c.487C>T | p.Gln163* | nons | c.487C>T | p.Gln163* | nons | Middle Eastern | LCA | [88] |
| Palestinian | [28,40] | ||||||||
| [145] | |||||||||
| n/s | [1,128] | ||||||||
| Emirati | [134] | ||||||||
| compHet | c.517G>A | [p.Gly173Lys] | mis | c.572T>C | p.Leu191Pro | mis | Chinese | EOSRD | [91] |
| hom | c.547G>T | p.Gly183* | nons | c.547G>T | p.Gly183* | nons | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| compHet | c.554delG | [p.Gly187Glu-fs*23] | fs | c.642G>C | p.Val156_Lys214del (ΔEx4) | splVar | Chinese | LCA | [91] |
| compHet | c.572T>C | p.Leu191Pro | mis | c.642G>C | p.Val156_Lys214del (ΔEx4) | splVar | Chinese | EOSRD | [91] |
| compHet | c.582C>G | p.Tyr194* | nons | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [18,128] |
| hom | c.589G>C | p.Ala197Pro | mis | c.589G>C | p.Ala197Pro | mis | Moroccan | LCA | [28,40] |
| North African | [153] | ||||||||
| het | c.593C>T | p.Ser198Phe | mis | - | - | - | n/s | LCA or EOSRD (probably benign) | [88] |
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA or EOSRD | [18] | |||
| n/s | c.617T>A | p.Ile206Asn | mis | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [18] |
| het | c.641A>G | p.Lys214Arg | mis | - | - | - | n/s | LCA or EOSRD | [141] |
| compHet | c.643-2A>G | [p.IVS4-2A>G] | c.741T>A | [p.Tyr247*] | nons | Chinese | LCA | [91] | |
| compHet | c.666G>A | p.Trp222* | nons | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [18] |
| het | c.672insC | [p.Lys224Asn-fs] | fs | - | - | - | n/s | LCA | [141] |
| hom | c.689A>G | p.Asn230Ser | mis | c.689A>G | p.Asn230Ser | mis | Indian | LCA | [155] |
| hom | c.715T>C | p.Cys239Arg | mis | c.715T>C | p.Cys239Arg | mis | U.S. American | LCA | [22,40] |
| n/s | [1] | ||||||||
| n/s | c.723_725del | p.Leu241del3 | indel | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| compHet | c.723_725del | p.Leu241del | [c.834G>A] | p.Trp278* | nons | European | LCA | [87] | |
| hom | c.733_735del | p.Glu245del | indel | c.733_735del | p.Glu245del | indel | n/s | LCA | [140] |
| compHet | c.733G>T | p.Glu245* | nons | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [18,128] |
| compHet | n/s | p.Leu257del9bp | [c.834G>A] | p.Trp278* | nons | U.S. American | LCA | [40] | |
| hom | c.773G>C | p.Arg258Pro | mis | c.773G>C | p.Arg258Pro | mis | Pakistani | n/s | [126] |
| n/s | c.785-10delCTCCCCACAGGC | IVS5-10delCTCCCCACAGGC | splVar | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| n/s | c.784G>A | p.Gly262Ser | splVar | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| compHet | c.784G>A | p.Gly262Ser | splVar | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [28] |
| U.S. American | [40] | ||||||||
| European | [87] | ||||||||
| compHet | c.809G>A | p.Arg270His | mis | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | Italian | LCA | [93,146] |
| compHet | c.809G>A | p.Arg270His | mis | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [18] |
| compHet | c.809G>A | p.Arg270His | mis | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | LCA | [89] |
| monoallelic or compHet | c.815G>C | p.Arg272Pro | mis | n/s | n/s | n/s | Danish | LCA | [147] |
| hom | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | c.834G>A | p.Trp278* | nons | German | LCA | [131] |
| African, White | [88] | ||||||||
| Saudi Arabian, U.S. American, Pakistani, Portuguese, Belgian | [40] | ||||||||
| n/s | [12,125,128,142,144,148] | ||||||||
| Pakistani | [22] | ||||||||
| [149] | |||||||||
| [150] | |||||||||
| Belgian | [124] | ||||||||
| Danish | [147] | ||||||||
| Spanish, French | LCA, RP, RD | [28] | |||||||
| LCA | [153] | ||||||||
| Caucasian | LCA | [94] | |||||||
| Northwestern European | LCA | [159] | |||||||
| Italian | LCA | [93,146] | |||||||
| hom, monoallelic or compHet | n/s | LCA | [89] | ||||||
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] | |||
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | Danish | LCA | [147] | |||
| het | - | - | - | n/s | n/s | [85] | |||
| compHet | [c.834G>A] | p.Trp278* | nons | n/s | p.Ala336del2bp | fs | U.S. American | LCA | [40] |
| nons | fs | n/s | LCA | [22] | |||||
| n/s | insGAGGCC | p.Glu280-ins6 | indel | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| hom | c.844G>T | p.Glu282* | nons | c.844G>T | p.Glu282* | nons | Indian | LCA | [155] |
| hom | c.844_849dup | p.Glu282_Ala283-dup | indel | c.844_849dup | p.Glu282_Ala283-dup | indel | n/s | LCA | [128] |
| het | c.853G>A/c.854C>A | p.Arg285Gln | mis | - | - | - | n/s | LCA | [141] |
| hom | c.857A>T | p.Asp286Val | mis | c.857A>T | p.Asp286Val | mis | German | LCA | [139] |
| hom | c.862C>T | p.Gln288* | nons | c.862C>T | p.Gln288* | nons | Turkish | LCA | [151] |
| n/s | c.878T>C | p.Leu293Pro | mis | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [18] | |||
| het | c.894G>C | p.Gln298His | mis | - | - | - | n/s | LCA or EOSRD | [88] |
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA or EOSRD | [18] | |||
| hom | c.905G>T | p.Arg302Leu | mis | c.905G>T | p.Arg302Leu | mis | Indian | LCA | [28,40,145] |
| hom, het | Indian, Pakistani, Iranian | LCA or EOSRD, unaffected | [88] | ||||||
| het | - | - | - | n/s | n/s | [85] | |||
| - | - | - | Italian | LCA | [146] | ||||
| - | - | - | n/s | n/s | [142] | ||||
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [89] | ||||
| hom | c.910G>T | p.Glu304* | nons | c.910G>T | p.Glu304* | nons | Indian | LCA | [155] |
| hom | c.926_927insCCTGAACCGCAGGGAGCT | p.Glu309Asp-insLNRREL | indel | c.926_927insCCTGAACCGCAGGGAGCT | p.Glu309Asp-insLNRREL | indel | Chinese | LCA | [90] |
| n/s | LCA | [18] | |||||||
| het | c.971G>T | p.Arg324Leu | mis | - | - | - | n/s | LCA | [89] |
| hom | c.1003insG | [p.Pro335Ala-fs] | fs | c.1003insG | [p.Pro335Ala-fs] | fs | n/s | LCA | [141] |
| monoallelic het | c.1053_1064delTGCAGAGCCACC | p.Ala352_Pro355del (also known as. p.Pro351-del12bp) | indel | - | - | - | n/s | adCORD, juvenile RP | [18,28] |
| het | c.1076C>T | p.Ser359Phe | mis | - | - | - | n/s | LCA | [141] |
| n/s | c.1091C>G | p.Ala364Gly | mis | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA or EOSRD (probably benign) | [18] |
| het | c.1097C>G | p.Pro366Arg | mis | - | - | - | n/s | LCA or EOSRD (probably benign) | [88] |
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA or EOSRD | [18] | |||
| n/s | insCAGAGCCAGCCA | p.Ala368-ins12 | indel | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [1] |
| n/s | c.1103_1114dup | p.Glu369_Thr372-dup | indel | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [18] |
| het | c.1111_1122dup | p.Ala371_Pro374-dup | indel | - | - | - | n/s | LCA | [125] |
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA | [18] | |||
| het | c.1126C>T | p.Pro376Ser | mis | - | - | - | West African, African American, Caribbean | LCA (probably benign) | [88] |
| - | - | - | n/s | n/s | [142] | ||||
| hom | c.1126C>T | p.Pro376Ser | mis | West African, African American, Caribbean | LCA or EOSRD (probably benign) | [88] | |||
| n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | n/s | LCA or EOSRD (probably benign) | [18] | |||
| Therapy | Model | Outcomes | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| AAV2/2-CMV-hAIPL1-SV40, AAV2/8-CMV-hAIPL1-SV40, AAV2/2-CMV-mAipl1-SV40, AAV2/8-CMV-mAipl1-SV40 | AIPL1 null and hypomorphic mouse | increased production of AIPL1 in the photoreceptor inner segment, increased levels of PDE6 in the outer segment, slowdown of retinal degeneration, improved photoreceptor cell survival, preservation of outer segment morphology, stabilization of retinal function | [48] |
| scAAV-Y733F-RKp-hAipl1 | AIPL1 null mouse | scAAV variant induces earlier and higher expression of hAIPL1 compared to ssAAV, restoration of rod and cone PDE6 expression, and slowdown of photoreceptor degeneration, preservation of photoreceptor ultrastructure, functional vision rescue | [176] |
| scAAV2/8-Y733F-pRK-hAIPL1 | adCORD mouse | rescue of photopic cone-mediated ERG responses, improvement of visual acuity in photopic conditions, scotopic rod-mediated ERG responses did not improve | [66] |
| AAV9-AIPL1wt, AAV9-AIPL1co | ARPE-19 cells | AAV9-AIPL1co induced significantly less antiviral response compared to wtAIPL1 | [189] |
| rAAV2.7m8.hRK.AIPL1 | organoids | restored AIPL1 protein abundance, rescue of rod PDE6, and cGMP levels | [190] |
| rAAV8.hRKp.AIPL1 | patients | improvement of visual acuity, enhanced activity of the specific to the treated eye’s visual cortex, better preservation of retinal thickness and structural lamination of the outer retina in the treated eye than in the untreated eye, cystoid macular edema (treated eye of only one out of four patients) | [12] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galieva, A.; Karabelsky, A.; Egorov, A.D. Restoring Sight: The Journey of AIPL1 from Discovery to Therapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 12066. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412066
Galieva A, Karabelsky A, Egorov AD. Restoring Sight: The Journey of AIPL1 from Discovery to Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(24):12066. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412066
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalieva, Alima, Alexander Karabelsky, and Alexander D. Egorov. 2025. "Restoring Sight: The Journey of AIPL1 from Discovery to Therapy" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 24: 12066. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412066
APA StyleGalieva, A., Karabelsky, A., & Egorov, A. D. (2025). Restoring Sight: The Journey of AIPL1 from Discovery to Therapy. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(24), 12066. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262412066







