Modulating Whiteleg Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) Health from the Inside out: Effects of Xylooligosaccharides from Salicornia ramosissima on Gut Metabolites and Microbial Community
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Growth Performance and Survival
2.2. Hepatopancreas Gene Expression
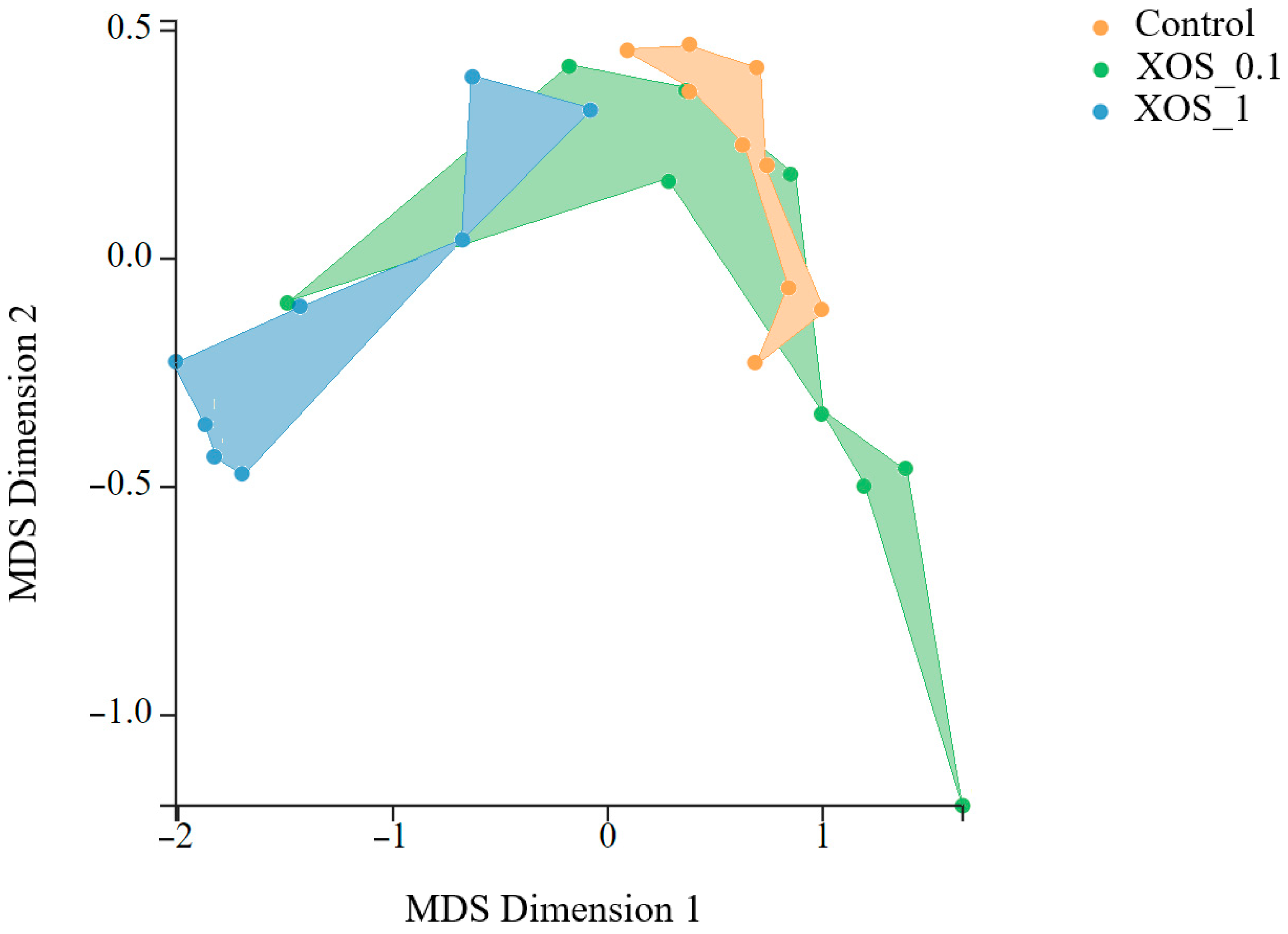
2.3. Microbial Composition of the Gut
2.4. Gut Proteome Profile
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Salicornia Ramosissima Biomass and Xylooligosaccharides Production
4.2. Dietary Treatment
4.3. Experiment Design and Animal Sampling
4.4. Bacterial Challenge with Vibrio Harveyi
4.5. Production Efficiency and Growth Performance
4.6. Gene Expression Analysis
4.7. Microbiota Studies
4.7.1. gDNA Extraction and Preparation of 16S Sequencing
4.7.2. Analysis of 16S Sequencing
4.8. Proteome Gut Profile
4.9. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- The State of World Fisheries and Aquaculture 2022; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Villarreal, H. Shrimp farming advances, challenges, and opportunities. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2023, 54, 1092–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, S.; Kim, A.; Lee, W.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Yoon, D.; Bae, J.S.; Park, C., II; Kim, S. Vibrio harveyi infection significantly alters amino acid and carbohydrate metabolism in whiteleg shrimp, litopenaeus vannamei. Metabolites 2020, 10, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amatul-Samahah, M.A.; Wan Omar, W.H.H.; Mohd Ikhsan, N.F.; Amal Azmai, M.N.; Zamri-Saad, M.; Ina-Salwany, M.Y. Vaccination trials against vibriosis in shrimp: A review. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibay-Valdez, E.; Martínez-Córdova, L.R.; López-Torres, M.A.; Almendariz-Tapia, F.J.; Martínez-Porchas, M.; Calderón, K. The implication of metabolically active Vibrio spp. in the digestive tract of Litopenaeus vannamei for its post-larval development. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 11428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Angthong, P.; Uengwetwanit, T.; Uawisetwathana, U.; Koehorst, J.J.; Arayamethakorn, S.; Schaap, P.J.; Dos Santos, V.M.; Phromson, M.; Karoonuthaisiri, N.; Chaiyapechara, S.; et al. Investigating host-gut microbial relationship in Penaeus monodon upon exposure to Vibrio harveyi. Aquaculture 2023, 567, 739252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gufe, C.; Merrifield, D.L.; Hoseinifar, S.H.; Rattanarojpong, T.; Khunrae, P.; Abdel-Tawwab, M. Prebiotic effects of dietary xylooligosaccharides on fish gut microbiota, growth, and immunological parameters—A review. Ann. Anim. Sci. 2023, 24, 331–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali, R.; Nwamaioha, N.; Fiagbor, R.; Zimmerman, T.; Newman, R.H.; Ibrahim, S.A. The Role of Prebiotics in Disease Prevention and Health Promotion. In Dietary Interventions in Gastrointestinal Diseases; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.H.; Chou, L.M.; Chien, Y.W.; Chang, J.S.; Lin, C.I. Prebiotic Effects of Xylooligosaccharides on the Improvement of Microbiota Balance in Human Subjects. Gastroenterol. Res. Pract. 2016, 2016, 5789232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Probert, H.M.; Van Loo, J.; Rastall, R.A.; Roberfroid, M.B. Dietary modulation of the human colonic microbiota: Updating the concept of prebiotics. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2004, 17, 259–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, A.P.; Bhardwaj, S.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Nepovimova, E.; Cruz-martins, N.; Kuča, K.; Chopra, C.; Singh, R.; Kumar, H.; Șen, F.; et al. Plant prebiotics and their role in the amelioration of diseases. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Wu, X.; Giovanni, V.; Meng, X. Effects of soybean oligosaccharides on intestinal microbial communities and immune modulation in mice. Saudi J. Biol. Sci. 2017, 24, 114–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neyrinck, A.M.; Possemiers, S.; Druart, C.; van de Wiele, T.; de Backer, F.; Cani, P.D.; Larondelle, Y.; Delzenne, N.M. Prebiotic effects of wheat Arabinoxylan related to the increase in bifidobacteria, roseburia and bacteroides/prevotella in diet-induced obese mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e20944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aachary, A.A.; Prapulla, S.G. Xylooligosaccharides (XOS) as an Emerging Prebiotic: Microbial Synthesis, Utilization, Structural Characterization, Bioactive Properties, and Applications. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2011, 10, 2–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, G.R.; Hutkins, R.; Sanders, M.E.; Prescott, S.L.; Reimer, R.A.; Salminen, S.J.; Scott, K.; Stanton, C.; Swanson, K.S.; Cani, P.D.; et al. Expert consensus document: The International Scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 14, 491–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, F.; Li, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yi, R.; Zhao, X. Effects of Xylooligosaccharides on Lipid Metabolism, Inflammation, and Gut Microbiota in C57BL/6J Mice Fed a High-Fat Diet. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12, 791614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, Y.; Debevere, S.; Bourgeois, H.; Ran, M.; Broeckx, B.J.G.; Vanhaecke, L.; Van de Wiele, T.; Hesta, M. Dose-Dependent Effects of Dietary Xylooligosaccharides Supplementation on Microbiota, Fermentation and Metabolism in Healthy Adult Cats. Molecules 2020, 25, 5030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broekaert, W.F.; Courtin, C.M.; Verbeke, K.; van de Wiele, T.; Verstraete, W.; Delcour, J.A. Prebiotic and other health-related effects of cereal-derived arabinoxylans, arabinoxylan-oligosaccharides, and xylooligosaccharides. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011, 51, 178–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Y.; Xie, Y.; Ajuwon, K.M.; Zhong, R.; Li, T.; Chen, L.; Zhang, H.; Beckers, Y.; Everaert, N. Xylo-Oligosaccharides, Preparation and Application to Human and Animal Health: A Review. Front. Nutr. 2021, 8, 731930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Forest Resources Assessment 2020; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Hameed, A.; Hussain, S.; Rasheed, A.; Ahmed, M.Z.; Abbas, S. Exploring the Potentials of Halophytes in Addressing Climate Change-Related Issues: A Synthesis of Their Biological, Environmental, and Socioeconomic Aspects. World 2024, 5, 36–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.R.; Cristofoli, N.L.; Rosa da Costa, A.M.; Saraiva, J.A.; Vieira, M.C. Comparative study of the production of cellulose nanofibers from agro-industrial waste streams of Salicornia ramosissima by acid and enzymatic treatment. Food Bioprod. Process. 2023, 137, 214–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monção, M.; Thoresen, P.P.; Wretborn, T.; Lange, H.; Rova, U.; Christakopoulos, P.; Matsakas, L. A novel biorefinery concept based on marginally used halophyte biomass. Sustain. Energy Fuels 2023, 7, 3902–3918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Rodríguez, M.; Pereiro, P.; Reyes-López, F.E.; Tort, L.; Figueras, A.; Novoa, B. Analysis of the long-lived responses induced by immunostimulants and their effects on a viral infection in Zebrafish (Danio rerio). Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, G.; Peng, K.; Huang, Y.; Cao, J.; Huang, W.; Chen, B.; Hu, J. Effects of dietary xylooligosaccharides on growth performance, immunity and Vibrio alginolyticus resistance of juvenile Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Res. 2019, 50, 358–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazuń, B.; Kazuń, K.; Małaczewska, J.; Kamiński, R.; Adamek-Urbańska, D.; Sikorska, J.; Wolnicki, J.; Szudrowicz, H. Effects of long-term administration of various dietary prebiotic supplements on the growth, immune cell activity and digestive tract histology of juvenile vimba (Vimba vimba). J. Vet. Res. 2023, 67, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Jin, M.; Fang, F.; Tocher, D.R.; Betancor, M.B.; Jiao, L.; Hong, Y.; Zhou, Q. New Insight Into the Molting and Growth in Crustaceans: Regulation of Energy Homeostasis Through the Lipid Nutrition. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 914590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Li, W.; Chen, F.; Zhu, X.; Chen, H.Y.; Hao, H.; Wang, K.J. Metabolomic and transcriptomic analysis reveals immune and hormone modulation at the molting stage of juvenile mud crabs challenged with Staphylococcus aureus and Vibrio alginolyticus. Aquaculture 2023, 575, 739775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, R.; Barker, P.L. The decapod hepatopancreas. Oceanogr. Mar. Biol. 1979, 17, 285–346. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, F.; Tian, S.; Chen, H.; Gao, S.; Dong, X.; Du, K. Advances in xylooligosaccharides from grain byproducts: Extraction and prebiotic effects. Grain Oil Sci. Technol. 2022, 5, 98–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callac, N.; Giraud, C.; Boulo, V.; Wabete, N.; Pham, D. Microbial biomarker detection in shrimp larvae rearing water as putative bio-surveillance proxies in shrimp aquaculture. PeerJ 2023, 11, e15201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, P.; Guo, H.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D.; Wang, K. Glucose addition improves the culture performance of Pacific white shrimp by regulating the assembly of Rhodobacteraceae taxa in gut bacterial community. Aquaculture 2023, 567, 739254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.; Fu, X.; He, J.; Wang, R.; Yan, M.; Wang, J.; Dong, P.; Huang, L.; Zhang, D. Gut bacterial consortium enriched in a biofloc system protects shrimp against Vibrio parahaemolyticus infection. Microbiome 2023, 11, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Wen, M.; Xiang, L.; Shen, H.; Jiang, G.; Cheng, J.; Hu, Y.; Qian, J. Segmental variations in intestinal microbiota composition and functional capacity along the digestive tract of Litopenaeus vannamei. Aquac. Rep. 2024, 34, 101922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Guo, H.; Liu, Z.; Chen, C.; Wang, K.; Huang, X.; Chen, W.; Zhu, Y.; Yan, M.; Zhang, D. Contrasting patterns of bacterial communities in the rearing water and gut of Penaeus vannamei in response to exogenous glucose addition. Mar. Life Sci. Technol. 2022, 4, 222–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, X.; He, J.; Wang, J.; Shen, F.; Qiu, J.; Chen, C.; Zhang, D.; Guo, H. Specific gut bacterial taxa inhabited in healthy shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) confer protection against Vibrio parahaemolyticus challenge. Aquaculture 2024, 579, 740192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alvarez-Ruiz, S.A.P.; Luna-González, A.; Escamilla-Montes, R.; Fierro-Coronado, A.; Diarte-Plata, G.; García-Gutiérrez, C.; Peraza-Gómez, V. Gut bacterial profile associated with healthy and diseased (AHPND) shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Lat. Am. J. Aquat. Res. 2022, 50, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, C.; Wang, L.; Liu, M.; Jiang, K.; Wang, M.; Zhao, W.; Wang, B. Transcriptomic and morphological analyses of Litopenaeus vannamei intestinal barrier in response to Vibrio paraheamolyticus infection reveals immune response signatures and structural disruption. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2017, 70, 437–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, Y.; Wang, Y.; Huang, J.; Li, H.; Dong, H.; Zhang, J. Toxic effects of cadmium and lead exposure on intestinal histology, oxidative stress response, and microbial community of Pacific white shrimp Litopenaeus vannamei. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2021, 167, 112220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes, G.; Andrade, B.; Betancourt, I.; Panchana, F.; Preciado, C.; Bayot, B. Bacterial communities and signatures in the stomach and intestine of juvenile Penaeus (litopenaeus) vannamei shrimp affected by acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease. Heliyon 2024, 10, e33034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Luo, X.; Lin, H.; Han, F.; Qin, J.G.; Chen, L.; Xu, C.; Li, E. Growth, Health, and Gut Microbiota of Female Pacific White Shrimp, Litopenaeus vannamei Broodstock Fed Different Phospholipid Sources. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, X.; Gu, Y.; Zhou, H.; Xu, L.; Cao, H.; Gai, C. Acinetobacter venetianus, a potential pathogen of red leg disease in freshwater-cultured whiteleg shrimp Penaeus vannamei. Aquac. Rep. 2020, 18, 100543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasin, A.; Begum, K.; Eshik, M.E.; Punom, N.J.; Ahmmed, S.; Rahman, M.S. Molecular identification and antibiotic resistance patterns of diverse bacteria associated with shrimp PL nurseries of Bangladesh: Suspecting Acinetobacter venetianus as future threat. PeerJ 2022, 10, e12808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuebutornye, F.K.A.; Abarike, E.D.; Lu, Y. A review on the application of Bacillus as probiotics in aquaculture. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2019, 87, 820–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Proespraiwong, P.; Mavichak, R.; Imaizumi, K.; Hirono, I.; Unajak, S. Evaluation of Bacillus spp. as Potent Probiotics with Reduction in AHPND-Related Mortality and Facilitating Growth Performance of Pacific White Shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) Farms. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanjan, P.; Kimtun, A.; Chaimongkol, S.; Sakpetch, P. Probiotic Weissella cibaria KY10 derived from digestive tract of healthy shrimp exhibits strong antibacterial effects against Vibrio parahaemolyticus causing AHPND in shrimp. Aquac. Res. 2022, 53, 2597–2607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philippot, L.; Griffiths, B.S.; Langenheder, S. Microbial Community Resilience across Ecosystems and Multiple Disturbances. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2021, 85, e00026-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicholson, J.K.; Holmes, E.; Kinross, J.; Burcelin, R.; Gibson, G.; Jia, W.; Pettersson, S. Metabolic Interactions. Science 2012, 108, 1262–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legrand, T.P.R.A.; Catalano, S.R.; Wos-Oxley, M.L.; Stephens, F.; Landos, M.; Bansemer, M.S.; Stone, D.A.J.; Qin, J.G.; Oxley, A.P.A. The inner workings of the outer surface: Skin and gill microbiota as indicators of changing gut health in Yellowtail Kingfish. Front. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 2664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, S.; He, J.; Huang, Z. The intestine microbiota of shrimp and its impact on cultivation. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2024, 108, 362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, J.; Zhu, J.; Dai, W.; Dong, C.; Qiu, Q.; Li, C. Integrating Gut Microbiota Immaturity and Disease-Discriminatory Taxa to Diagnose the Initiation and Severity of Shrimp Disease. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 19, 1490–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornejo-Granados, F.; Lopez-Zavala, A.A.; Gallardo-Becerra, L.; Mendoza-Vargas, A.; Sánchez, F.; Vichido, R.; Brieba, L.G.; Viana, M.T.; Sotelo-Mundo, R.R.; Ochoa-Leyva, A. Microbiome of Pacific Whiteleg shrimp reveals differential bacterial community composition between Wild, Aquacultured and AHPND/EMS outbreak conditions. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 11783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, Y.-T.; Ko, H.-T.; Wu, P.-L.; Kumar, R.; Wang, H.-C.; Lu, H.-P. Gut microbiota of Pacific white shrimp (Litopenaeus vannamei) exhibits distinct responses to pathogenic and non-pathogenic Vibrio parahaemolyticus. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e01180-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tran, P.T.N.; Kumar, V.; Bossier, P. Do acute hepatopancreatic necrosis disease-causing PirABVP toxins aggravate vibriosis? Emerg. Microbes Infect. 2020, 9, 1919–1932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosas, C.; Cuzon, G.; Gaxiola, G.; Le Priol, Y.; Pascual, C.; Rossignyol, J.; Contreras, F.; Sanchez, A.; Van Wormhoudt, A. Metabolism and growth of juveniles of Litopenaeus vannamei: Effect of salinity and dietary carbohydrate levels. J. Exp. Mar. Bio. Ecol. 2001, 259, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lodish, H.; Berk, A.; Kaiser, C.; Krieger, M.; Bretscher, A.; Ploegh, H.; Martin, K.; Yaffe, M.; Amon, A. Molecular Cell Biology, 9th ed.; W. H. Freeman: New York, NY, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Den Besten, G.; Van Eunen, K.; Groen, A.K.; Venema, K.; Reijngoud, D.J.; Bakker, B.M. The role of short-chain fatty acids in the interplay between diet, gut microbiota, and host energy metabolism. J. Lipid Res. 2013, 54, 2325–2340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.; Gordon, J.I. Honor thy symbionts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 10452–10459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herigstad, B.; Hamilton, M.; Heersink, J. How to optimize the drop plate method for enumerating bacteria. J. Microbiol. Methods 2001, 44, 121–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shankregowda, A.M.; Siriyappagouder, P.; Kuizenga, M.; Bal, T.M.P.; Abdelhafiz, Y.; Eizaguirre, C.; Fernandes, J.M.O.; Kiron, V.; Raeymaekers, J.A.M. Host habitat rather than evolutionary history explains gut microbiome diversity in sympatric stickleback species. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14, 1232358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, T.; Kalxdorf, M.; Longuespée, R.; Kazdal, D.N.; Stenzinger, A.; Krijgsveld, J. Automated sample preparation with SP 3 for low-input clinical proteomics. Mol. Syst. Biol. 2020, 16, e9111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, D.R. Degust: Interactive RNA-seq analysis. Zenodo 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.W.; Sherman, B.T.; Lempicki, R.A. Bioinformatics enrichment tools: Paths toward the comprehensive functional analysis of large gene lists. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009, 37, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szklarczyk, D.; Kirsch, R.; Koutrouli, M.; Nastou, K.; Mehryary, F.; Hachilif, R.; Gable, A.L.; Fang, T.; Doncheva, N.T.; Pyysalo, S.; et al. The STRING database in 2023: Protein–protein association networks and functional enrichment analyses for any sequenced genome of interest. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023, 51, D638–D646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| CTRL | XOS_0.1 | XOS_1 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Initial weight (g) | 0.84 ± 0.01 | 0.85 ± 0.02 | 0.85 ± 0.01 |
| Final weight (g) | 3.09 ± 0.15 | 3.08 ± 0.10 | 3.13 ± 0.17 |
| RGR (% day−1) | 9.71 ± 0.40 | 9.65 ± 0.28 | 9.72 ± 0.38 |
| FCR | 0.86 ± 0.06 | 0.81 ± 0.03 | 0.83 ± 0.06 |
| Feed intake (% ABW day−1) | 7.06 ± 0.34 | 6.64 ± 0.30 | 6.94 ± 0.31 |
| Survival (%) | 96.5 ± 1.7 | 98.1 ± 1.6 | 94.2 ± 3.1 |
| Gene Acronym | Group | 0 h | 72 h | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Non-Infected | Infected | ||||||
| Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | Mean | SEM | ||
| IAP | Control | 1.00 | 0.60 | 0.24 | 0.17 | 0.27 | 0.11 |
| XOS_0.1 | 0.20 | 0.04 | 0.13 | 0.07 | |||
| XOS_1 | 1.86 | 1.69 | 0.18 | 0.05 | |||
| PEN3 | Control | 1.00 | 0.17 | 0.71 | 0.18 | 1.43 | 0.33 |
| XOS_0.1 | 1.05 | 0.30 | 0.84 | 0.23 | |||
| XOS_1 | 3.05 | 2.49 | 1.02 | 0.22 | |||
| LZC | Control | 1.00 | 0.58 | 12.50 | 8.56 | 5.60 | 1.35 |
| XOS_0.1 | 0.52 | 0.13 | 2.24 | 1.09 | |||
| XOS_1 | 16.42 | 15.80 | 3.52 | 1.80 | |||
| TRYP | Control | 1.00 | 0.25 | 0.27 | 0.06 | 0.55 | 0.11 |
| XOS_0.1 | 0.84 | 0.21 | 0.52 | 0.21 | |||
| XOS_1 | 2.02 | 0.98 | 0.44 | 0.16 | |||
| GPX2 | Control | 1.00 | 0.17 | 0.65 | 0.07 | 0.58 | 0.08 |
| XOS_0.1 | 0.75 | 0.08 | 0.66 | 0.09 | |||
| XOS_1 | 0.90 | 0.14 | 0.59 | 0.06 | |||
| LECTIN2 | Control | 1.00 | 0.23 | 0.17 | 0.03 | 0.46 | 0.12 |
| XOS_0.1 | 0.45 | 0.09 | 0.30 | 0.12 | |||
| XOS_1 | 0.53 | 0.11 | 0.21 | 0.04 | |||
| TRX2 | Control | 1.00 | 0.23 | 1.10 | 0.31 | 0.51 | 0.10 |
| XOS_0.1 | 0.56 | 0.08 | 0.53 | 0.10 | |||
| XOS_1 | 1.05 | 0.40 | 0.42 | 0.05 | |||
| HSP70 | Control | 1.00 | 0.38 | 4.62 | 3.19 | 3.39 | 1.05 |
| XOS_0.1 | 0.52 | 0.13 | 7.57 | 6.24 | |||
| XOS_1 | 13.52 | 13.22 | 2.15 | 0.60 | |||
| CASP3 | Control | 1.00 | 0.24 | 0.33 | 0.08 | 0.45 | 0.15 |
| XOS_0.1 | 0.52 | 0.09 | 0.75 | 0.27 | |||
| XOS_1 | 1.32 | 1.04 | 0.34 | 0.06 | |||
| GST | Control | 1.00 | 0.81 | 0.47 | 0.40 | 0.01 | 0.01 |
| XOS_0.1 | 0.14 | 0.11 | 0.78 | 0.73 | |||
| XOS_1 | 0.15 | 0.05 | 1.52 | 1.49 | |||
| Genus | vs. Control at 0 h | vs. Control at 72 h | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| XOS_0.1 | XOS_1 | XOS_0.1 | XOS_1 | |
| Acinetobacter | − | − | −/+ | −/+ |
| Anaerococcus | − | − | ||
| Anaeromyxobacter | + | |||
| Aquabacterium | + | |||
| Bacillus | + | |||
| Bacteroides | − | − | ||
| Brevundimonas | + | |||
| Burkholderia-Caballeronia-Paraburkholderia | +++ | |||
| Congregibacter | − | − | ||
| Corynebacterium | −/+ | |||
| Corynebacterium_1 | + | − | ||
| Cupriavidus | − | |||
| Cutibacterium | − | − | ||
| Cytophaga | − | − | ||
| Delftia | − | |||
| Demequina | + | +++ | ||
| Devosia | + | + | ||
| Domibacillus | + | |||
| Enhydrobacter | − | − | ||
| Finegoldia | − | |||
| Flavobacterium | + | + | − | − |
| Fusibacter | − | − | ||
| Gilvimarinus | + | + | ||
| Haloferula | ++ | |||
| Hoeflea | − | |||
| Hwangdonia | + | + | ||
| Ilumatobacter | + | |||
| Kocuria | − | − | ||
| Labrenzia | ++ | |||
| Lawsonella | − | |||
| Leisingera | + | + | ||
| Lentimonas | − | |||
| Loktanella | + | |||
| Luteolibacter | + | + | ||
| Maritalea | ++ | |||
| Marmoricola | − | |||
| Massilia | + | |||
| Motilimonas | − | − | ||
| Muricauda | + | +++ | ||
| Nautella | + | |||
| Oceanobacter | − | − | ||
| Owenweeksia | + | + | ||
| Palleronia | + | − | ||
| Paracoccus | + | + | + | |
| Pelomonas | − | − | ||
| Peptoniphilus | − | − | ||
| Pseudomonas | −/+ | −/+ | + | |
| Qipengyuania | − | − | − | |
| Reyranella | ++ | |||
| Rheinheimera | + | |||
| Rhodoglobus | + | |||
| Rhodovulum | + | |||
| Romboutsia | + | |||
| Roseibacillus | + | |||
| Roseobacter | + | |||
| Roseovarius | + | |||
| Ruegeria | +++ | ++++ | ||
| Shewanella | − | − | ||
| Silicimonas | ++ | |||
| Sphingomonas | − | |||
| Staphylococcus | −− | −− | ||
| Streptococcus | ++ | |||
| Tamlana | + | + | ||
| Tenacibaculum | ++++ | ++++ | −− | |
| Terasakiella | − | − | ||
| Thermomonas | − | − | ||
| Thiothrix | + | |||
| Trichormus_HINDAK_2001–4 | − | − | ||
| Vibrio | + | − | + | |
| Weissella | + | |||
| Xanthomarina | + | + | ||
| Ingredients (%) | CTRL | XOS_0.1 | XOS_1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fishmeal 1 | 10.50 | 10.50 | 10.50 |
| Squid liver meal 2 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Poultry meal 3 | 6.00 | 6.00 | 6.00 |
| Corn gluten meal 4 | 3.90 | 3.90 | 3.90 |
| Soybean meal 5 | 34.00 | 34.00 | 34.00 |
| Wheat meal 6 | 28.40 | 28.40 | 28.40 |
| Wheat bran 7 | 7.00 | 7.00 | 7.00 |
| Vitamin and mineral premix 8 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Choline chloride 50% 9 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Antioxidant 10 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Sodium propionate 11 | 0.10 | 0.10 | 0.10 |
| Monoammonium phosphate 12 | 0.60 | 0.60 | 0.60 |
| Calcium carbonate 13 | 0.40 | 0.40 | 0.40 |
| Astaxanthin 14 | 0.05 | 0.05 | 0.05 |
| Binder 15 | 0.30 | 0.30 | 0.30 |
| L-Lysine HCl 99% 16 | 0.15 | 0.15 | 0.15 |
| DL-Methionine 17 | 0.20 | 0.20 | 0.20 |
| Soy lecithin 18 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Fish oil 19 | 2.00 | 2.00 | 2.00 |
| Soybean oil 20 | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| Salicornia XOS 21 | 0.10 | 1.00 |
| Proximate Composition (% Feed) | CTRL | XOS_0.1 | XOS_1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dry matter | 90.6 | 90.6 | 90.6 |
| Crude protein | 36.1 | 36.1 | 36.1 |
| Crude lipids | 7.1 | 7.1 | 7.1 |
| Ash | 6.8 | 6.8 | 6.8 |
| Energy (KJ g−1 DM) | 18.4 | 18.4 | 18.4 |
| Gene | Acronym | Primer Sequences (5′–3′) | Acc. No. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ribossomal protein L8 | RPL8 | F: AGCCAAGCAAGATGGGTCG | XM_027355167.1 |
| R: TGTAACGATAAGGGTCACGGAAG | |||
| Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase | GADPH | F: AAAGGTAGGAATTGCCCCCG | XM_027372388.1 |
| R: AGGGATGAGACTAGCACGACT | |||
| Inhibitor of opoptosis protein | IAP | F: CAACACCTGCCTCAGGACAA | GQ293142.1 |
| R: CTTCCATTGCCTCCTCGTCT | |||
| Penaeidin 3 | PEN3 | F:ATACCCAGGCCACCACCCTT | XM_027360479.1 |
| R: TGACAGCAACGCCCTAACC | |||
| Lysozyme C-like | LZC | F: CGGGAAAGGCTATTCTGCCT | XM_027352840.1 |
| R: CCAGCACTCTGCCATGTACT | |||
| Trypsin | TRYP | F: CGGAGAGCTGCCTTACCAG | XM_027367621.1 |
| R: TCGGGGTTGTTCATGTCCTC | |||
| Glutathione peroxidase 2-like | GPX2 | F: AGGGACTTCCACCAGATG | XM_027372127.1 |
| R: CAACAACTCCCCTTCGGTA | |||
| C-type lectin 2-like | LECTIN2 | F: GCTTCTGTTGGTGCTGTTGGC | DQ858899.2 |
| R: GTTCCCTTCCCGTATGTGGC | |||
| Thioredoxin 2 | TRX2 | F: TTCCTGAAGGTGGATGTGGA | XM_027377405.1 |
| R: AGTTGGCACCAGACAAGCTG | |||
| Heath shock protein 70 | HSP70 | F: CAACGATTCTCAGCGTCAGG | XM_027369405.1 |
| R: ACCTTCTTGTCGAGGCCGTA | |||
| Caspase 3 | Casp3 | F: ACATTTCTGGGCGGAACACC | KC660103.1 |
| R: GTGACACCCGTGCTTGTACA | |||
| Glutathione S-transferase | GST | F: CACCTACGAACACTACGAAC | XM_027351980.1 |
| R: GGTTCTTGAAGCCGTCGAG | |||
| Rod shape-determining gene, subunit B | mreB | F: TGAAGCTGTGATCAACTACG | D0XAE4_VIBH1 |
| R: CCTGACAGTGGCTCTTGTAA | |||
| Transmembrane transcriptor regulator | toxR | F: GAAGCAGCACTCACCGAT | AY247418 |
| R: GGTGAAGACTCATCAGCA | |||
| Topoisomerase I | topA | F: TGGCGCAGCGTCTATACG | JF930499 |
| R: TATTTGTCACCGAACTCAGAACC |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Garcia, A.; Fernández-Boo, S.; Barreto, A.; Semedo, M.; Thomsen, M.H.; Stensballe, A.; Monção, M.; Matsakas, L.; Christakopoulos, P.; Kiron, V.; et al. Modulating Whiteleg Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) Health from the Inside out: Effects of Xylooligosaccharides from Salicornia ramosissima on Gut Metabolites and Microbial Community. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411978
Garcia A, Fernández-Boo S, Barreto A, Semedo M, Thomsen MH, Stensballe A, Monção M, Matsakas L, Christakopoulos P, Kiron V, et al. Modulating Whiteleg Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) Health from the Inside out: Effects of Xylooligosaccharides from Salicornia ramosissima on Gut Metabolites and Microbial Community. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(24):11978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411978
Chicago/Turabian StyleGarcia, Ana, Sergio Fernández-Boo, André Barreto, Miguel Semedo, Mette Hedegaard Thomsen, Allan Stensballe, Maxwel Monção, Leonidas Matsakas, Paul Christakopoulos, Viswanath Kiron, and et al. 2025. "Modulating Whiteleg Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) Health from the Inside out: Effects of Xylooligosaccharides from Salicornia ramosissima on Gut Metabolites and Microbial Community" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 24: 11978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411978
APA StyleGarcia, A., Fernández-Boo, S., Barreto, A., Semedo, M., Thomsen, M. H., Stensballe, A., Monção, M., Matsakas, L., Christakopoulos, P., Kiron, V., Rocha, R. J. M., & Costas, B. (2025). Modulating Whiteleg Shrimp (Penaeus vannamei) Health from the Inside out: Effects of Xylooligosaccharides from Salicornia ramosissima on Gut Metabolites and Microbial Community. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(24), 11978. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262411978











