Downregulation of the CCK-B Receptor in Pancreatic Stellate Cells Blocks Molecular Proliferative Pathways and Increases Apoptosis to Decrease Pancreatic Cancer Growth In Vitro
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Effects of CCK-BR Knockout on Migration, Proliferation, and Growth of Pancreatic Cancer
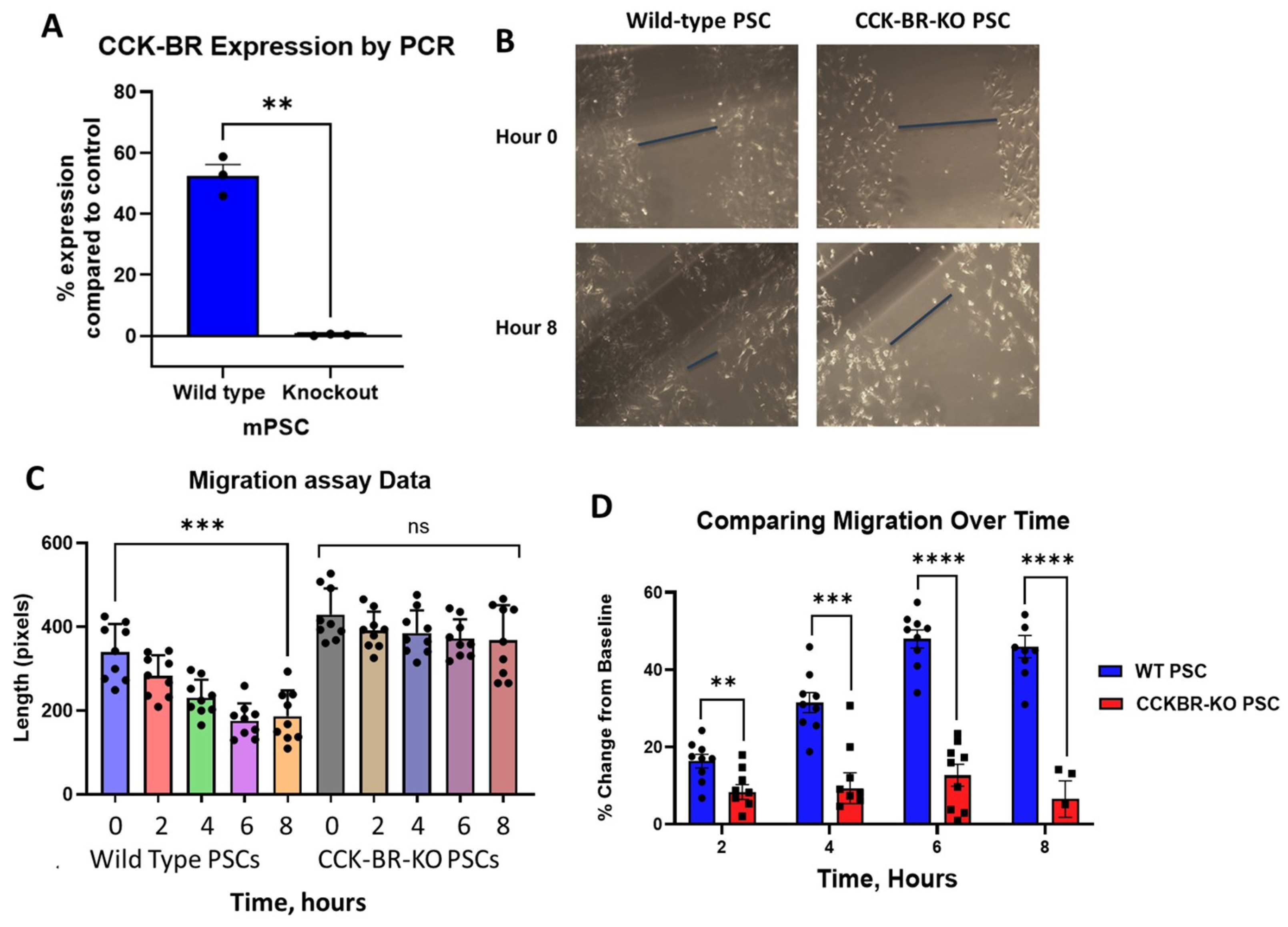
2.1.1. Effects of CCK-BR-KO on Migration of PSCs
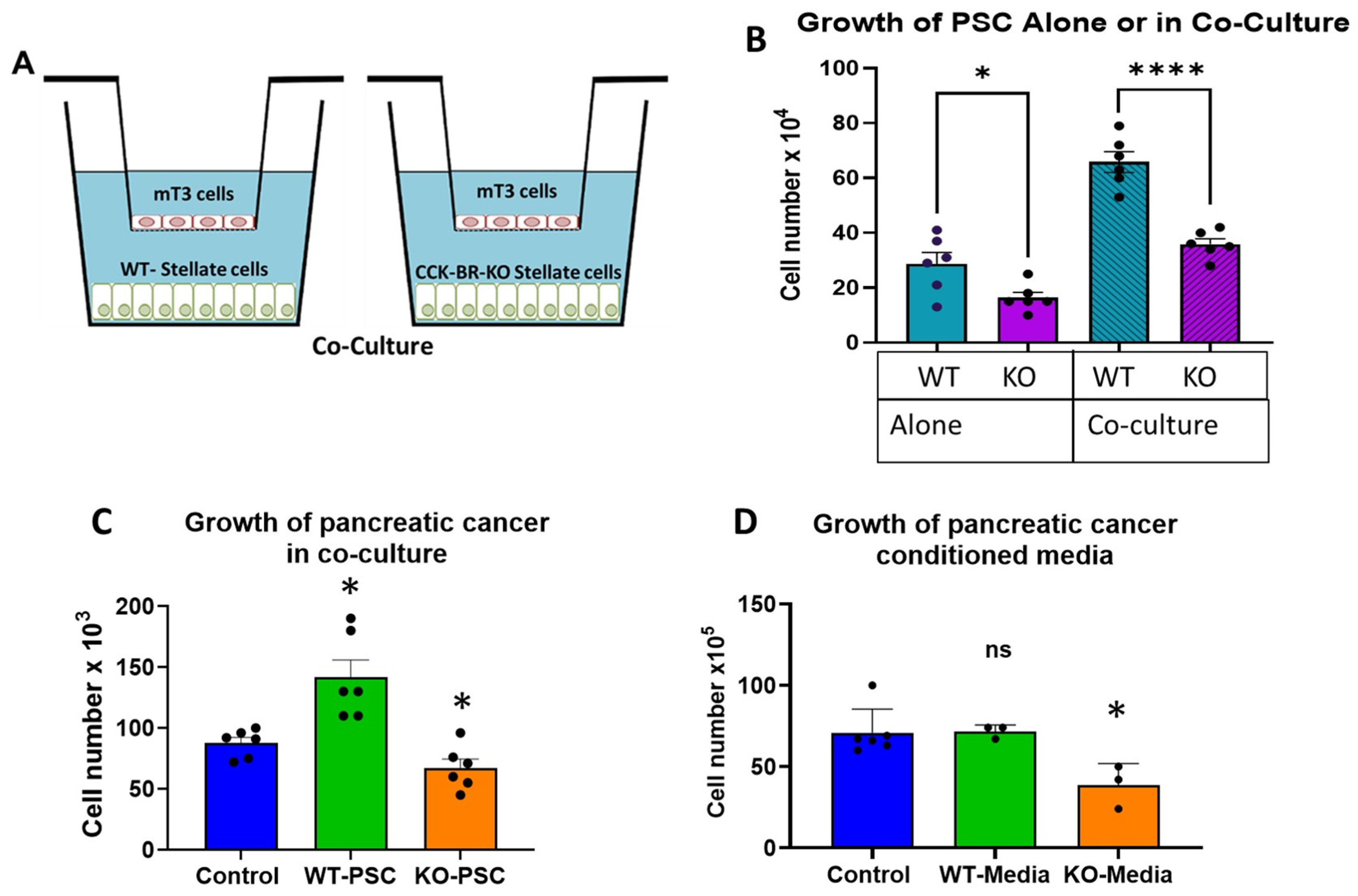
2.1.2. Effects of CCK-BR-KO on Proliferation of Pancreatic Stellate Cells and Cancer Cells
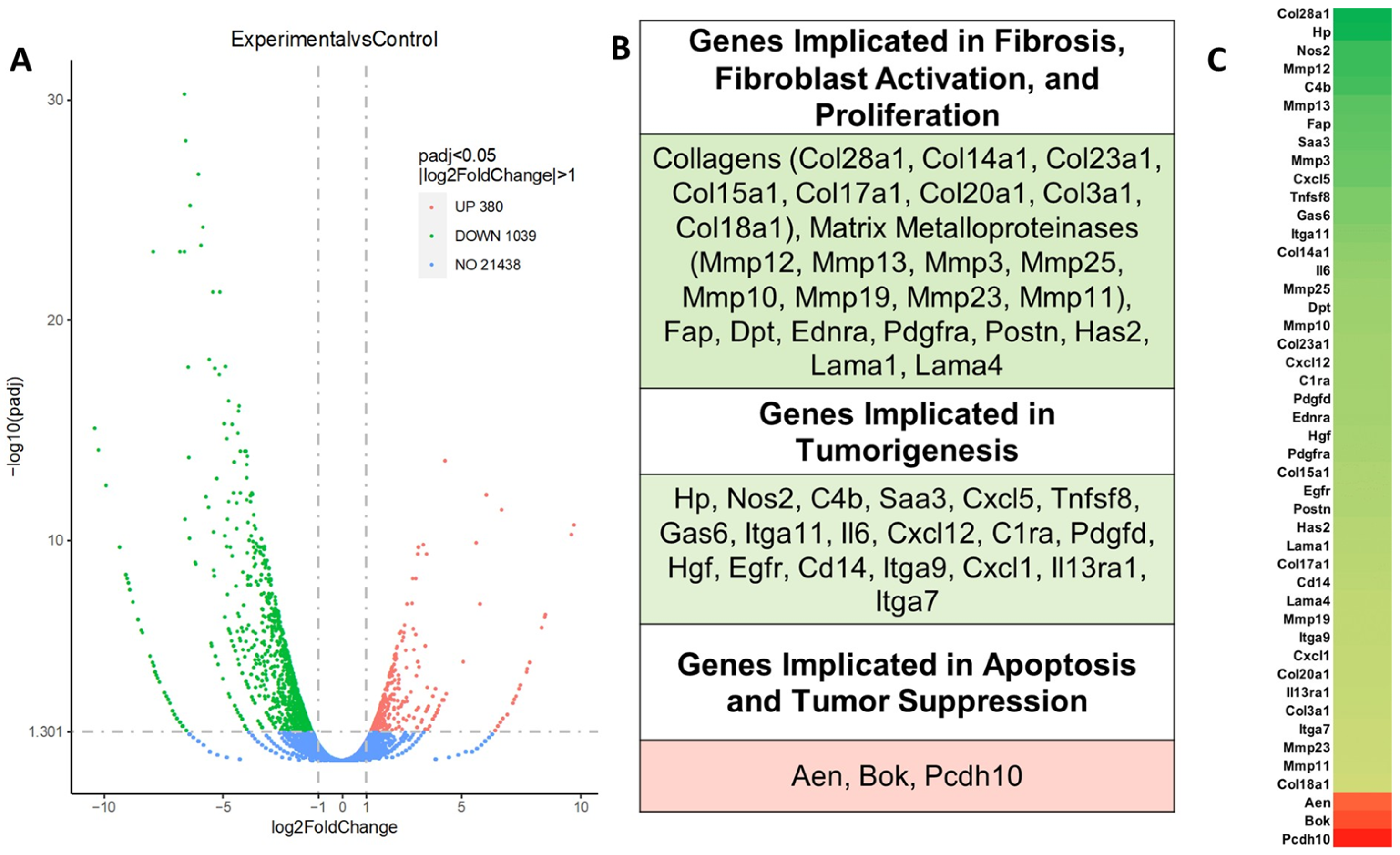
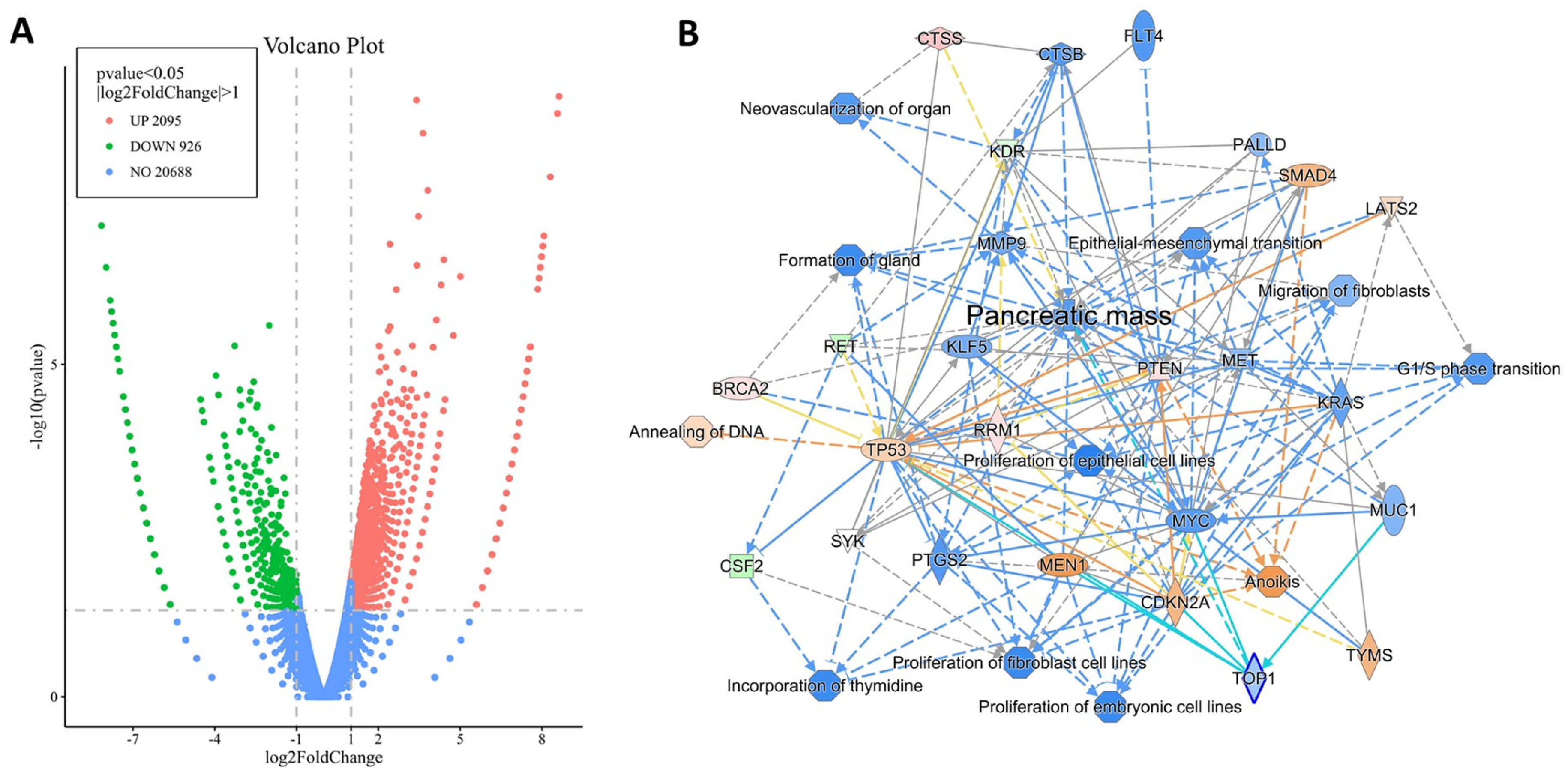
2.2. Differentially Expressed Genes by RNA Sequencing
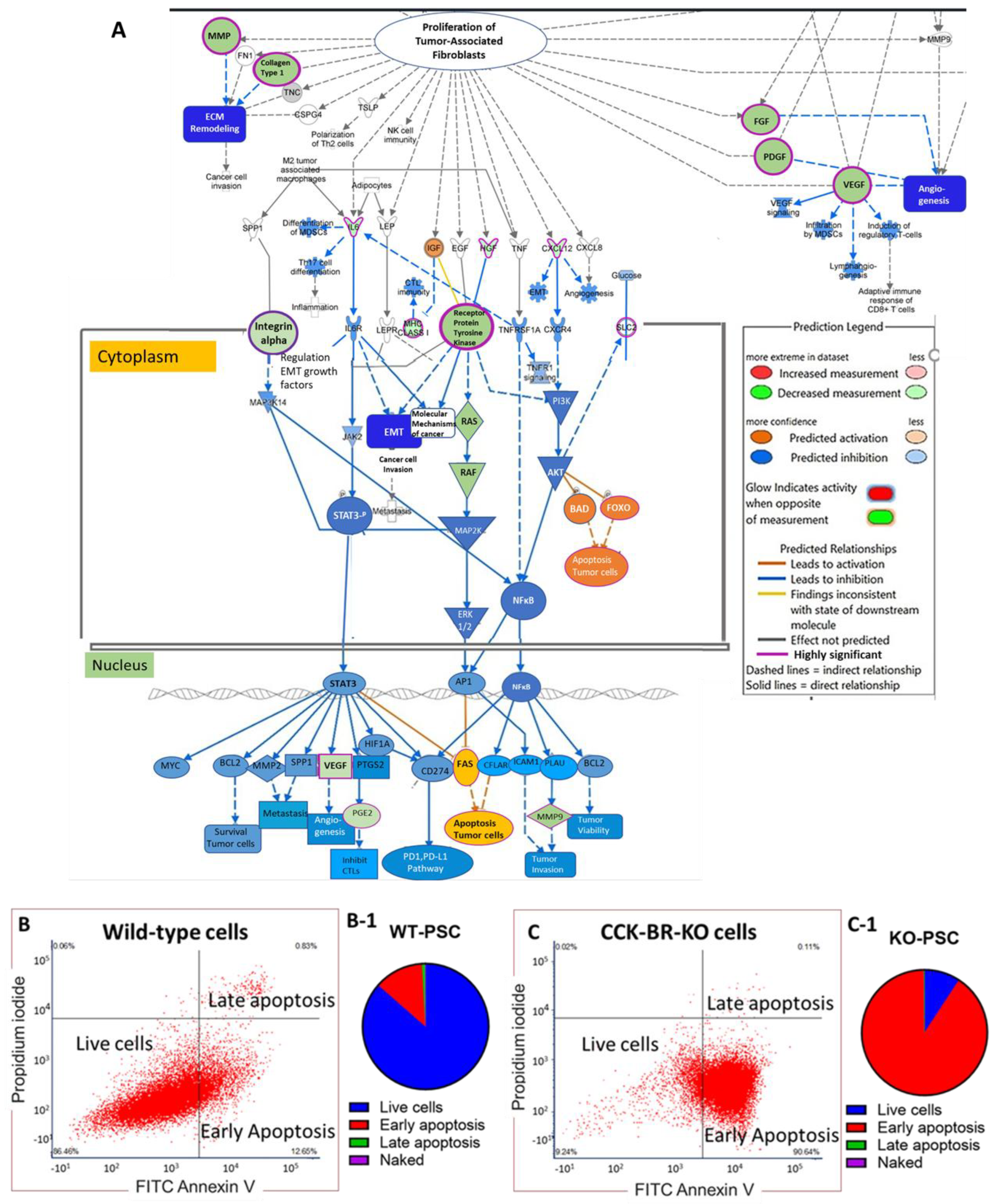
2.3. CCK-BR-KO Increases Markers of Apoptosis on PSCs
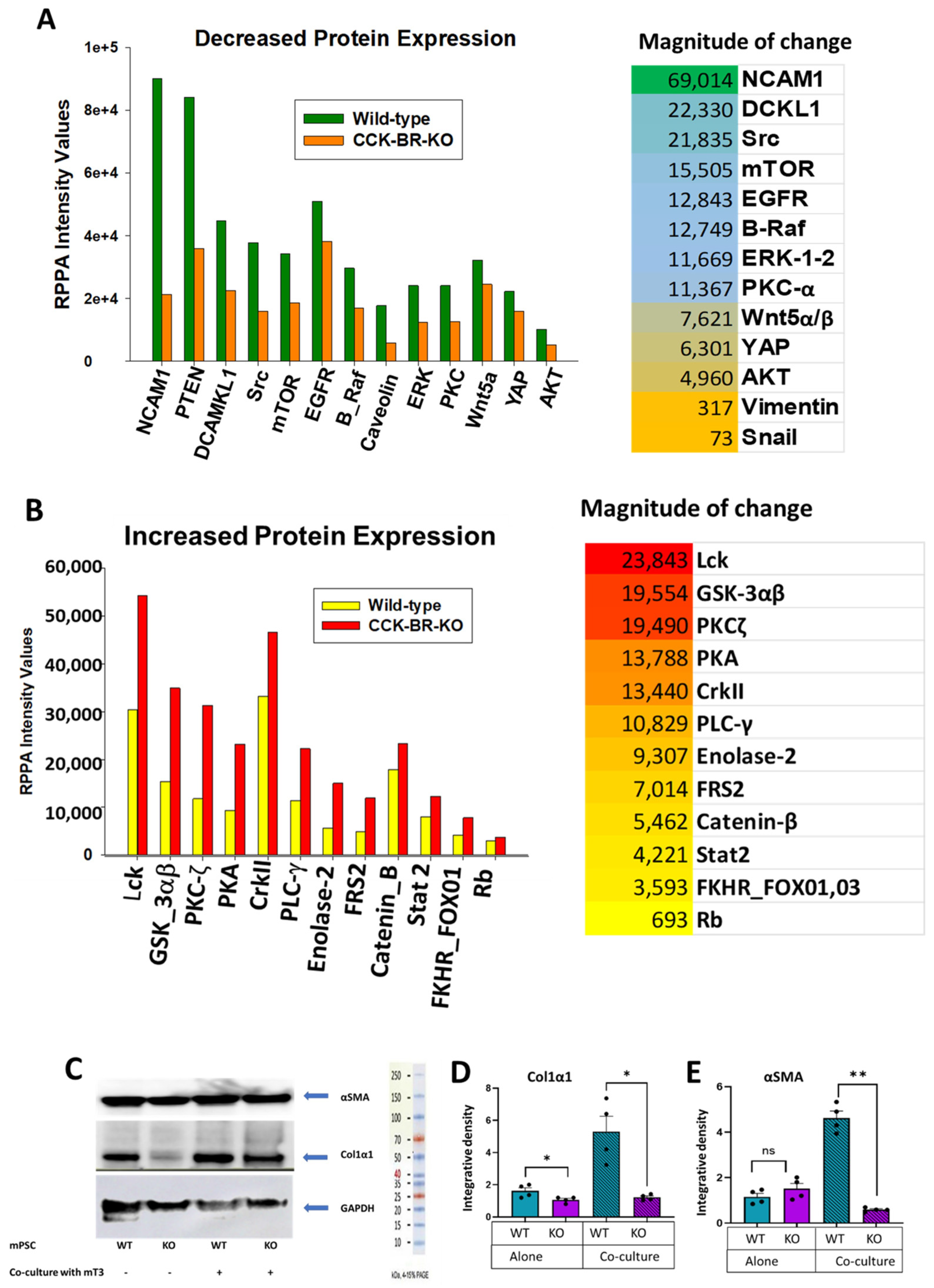
2.4. Evaluation of Differentially Expressed Proteins by Reverse Phase Protein Array (RPPA) and Western Blot Analysis
2.5. CCK-BR Pharmacologic Blockade in Human PSC (hPSCs) with Proglumide
2.6. Common Genes in Mouse and Human PSCs That Are Affected by Interference of CCK-BR Signaling
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Cell Lines and Culture Conditions
4.2. Downregulation of the CCK-BR with CRISPR Technology and Confirmation by PCR
4.3. Migration Assay
4.4. Proliferation Assay
4.5. Crosstalk Cell Counts with Murine PSC and Pancreatic Cancer Cells
4.6. Western Immunoblotting
4.7. RNA Sequencing
4.8. Reverse Phase Protein Array (RPPA)
4.9. Flow Cytometry
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| αSMA | alpha smooth muscle actin |
| CCK-BR | Cholecystokinin-B receptors |
| CAFs | cancer-associated fibroblasts |
| DEGs | differentially expressed genes |
| ECM | extracellular matrix |
| EMT | epithelial to mesenchymal transition |
| IPA | Ingenuity Pathway Analysis |
| KO | knockout |
| MMPs | matrix metalloproteinases |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide |
| PDAC | pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma |
| PSC | pancreatic stellate cells |
| qRT-PCR | quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction |
| RIN | RNA integrity numbers |
| RPPA | Reverse Phase Protein Array |
| TME | tumor microenvironment |
| WT | wild-type |
References
- Apte, M.; Pirola, R.C.; Wilson, J.S. Pancreatic stellate cell: Physiologic role, role in fibrosis and cancer. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2015, 31, 416–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biffi, G.; Tuveson, D.A. Diversity and Biology of Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Physiol. Rev. 2021, 101, 147–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, G.; Hong, W.; Guo, Y.; Bai, Y.; Chen, B. Molecular Mechanism of Pancreatic Stellate Cells Activation in Chronic Pancreatitis and Pancreatic Cancer. J. Cancer 2020, 11, 1505–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elyada, E.; Bolisetty, M.; Laise, P.; Flynn, W.F.; Courtois, E.T.; Burkhart, R.A.; Teinor, J.A.; Belleau, P.; Biffi, G.; Lucito, M.S.; et al. Cross-Species Single-Cell Analysis of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Reveals Antigen-Presenting Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts. Cancer Discov. 2019, 9, 1102–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sigirli, S.; Karakas, D. Fibrotic Fortresses and Therapeutic Frontiers: Pancreatic Stellate Cells and the Extracellular Matrix in Pancreatic Cancer. Cancer Med. 2025, 14, e70788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolm, L.; Cigolla, S.; Wittel, U.A.; Hopt, U.T.; Keck, T.; Rades, D.; Bronsert, P.; Wellner, U.F. The Role of Fibroblasts in Pancreatic Cancer: Extracellular Matrix Versus Paracrine Factors. Transl. Oncol. 2017, 10, 578–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, R.; Xu, Z.; Perera, C.J.; Apte, M.V. Emerging role of pancreatic stellate cell-derived extracellular vesicles in pancreatic cancer. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2023, 93, 114–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barrera, L.N.; Ridley, P.M.; Bermejo-Rodriguez, C.; Costello, E.; Perez-Mancera, P.A. The role of microRNAs in the modulation of cancer-associated fibroblasts activity during pancreatic cancer pathogenesis. J. Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 79, 193–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebelo, R.; Xavier, C.P.R.; Giovannetti, E.; Vasconcelos, M.H. Fibroblasts in pancreatic cancer: Molecular and clinical perspectives. Trends Mol. Med. 2023, 29, 439–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.S.; Cwidak, N.; Awasthi, N.; von Holzen, U. Cytokine Interaction with Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts in Esophageal Cancer. Cancer Control 2022, 29, 10732748221078470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligorio, M.; Sil, S.; Malagon-Lopez, J.; Nieman, L.T.; Misale, S.; Di, P.M.; Ebright, R.Y.; Karabacak, M.N.; Kulkarni, A.S.; Liu, A.; et al. Stromal Microenvironment Shapes the Intratumoral Architecture of Pancreatic Cancer. Cell 2019, 178, 160–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ansardamavandi, A.; Tafazzoli-Shadpour, M. The functional cross talk between cancer cells and cancer associated fibroblasts from a cancer mechanics perspective. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Cell Res. 2021, 1868, 119103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.; Deng, Z.; Zang, L.; Shu, Y.; He, S.; Wu, X. Immune cells regulate matrix metalloproteinases to reshape the tumor microenvironment to affect the invasion, migration, and metastasis of pancreatic cancer. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2022, 14, 8437–8456. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.; Wu, Q.; Rajasekaran, S.; Wu, R. MMP3 at the crossroads: Linking molecular pathways to disease diagnosis and therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2025, 216, 107750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tjomsland, V.; Pomianowska, E.; Aasrum, M.; Sandnes, D.; Verbeke, C.S.; Gladhaug, I.P. Profile of MMP and TIMP Expression in Human Pancreatic Stellate Cells: Regulation by IL-1alpha and TGFbeta and Implications for Migration of Pancreatic Cancer Cells. Neoplasia 2016, 18, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalili-Tanha, G.; Radisky, E.S.; Radisky, D.C.; Shoari, A. Matrix metalloproteinase-driven epithelial-mesenchymal transition: Implications in health and disease. J. Transl. Med. 2025, 23, 436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jolly, G.; Duka, T.; Shivapurkar, N.; Chen, W.; Bansal, S.; Cheema, A.; Smith, J.P. Cholecystokinin Receptor Antagonist Induces Pancreatic Stellate Cell Plasticity Rendering the Tumor Microenvironment Less Oncogenic. Cancers 2023, 15, 2811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malchiodi, Z.X.; Cao, H.; Gay, M.D.; Safronenka, A.; Bansal, S.; Tucker, R.D.; Weinberg, B.A.; Cheema, A.; Shivapurkar, N.; Smith, J.P. Cholecystokinin Receptor Antagonist Improves Efficacy of Chemotherapy in Murine Models of Pancreatic Cancer by Altering the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancers 2021, 13, 4949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doneparthi, P.S.; Cao, H.; Chen, W.; Dou, W.; Fang, H.B.; Smith, J.P. Mechanistic Insights into Proglumide’s Role in Immune Cell Efficacy and Response to Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2025, 17, 2998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.P.; Wang, S.; Nadella, S.; Jablonski, S.A.; Weiner, L.M. Cholecystokinin receptor antagonist alters pancreatic cancer microenvironment and increases efficacy of immune checkpoint antibody therapy in mice. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2018, 67, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Gan, Y.; Shen, Y.; Cai, X.; Song, Y.; Zhao, F.; Yao, M.; Gu, J.; Tu, H. Leptin signaling enhances cell invasion and promotes the metastasis of human pancreatic cancer via increasing MMP-13 production. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 16120–16134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Zhu, Y.; Xie, K.L.; Peng, Y.P.; Tao, J.Q.; Tang, J.; Li, Z.; Xu, Z.K.; Dai, C.C.; Qian, Z.Y.; et al. Yin Yang-1 suppresses invasion and metastasis of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by downregulating MMP10 in a MUC4/ErbB2/p38/MEF2C-dependent mechanism. Mol. Cancer 2014, 13, 130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, A.; Li, J.; Weng, S.; Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, L.; Xing, Z.; Luo, P.; Cheng, Q.; Li, J.; et al. Integrated Exploration of Epigenetic Dysregulation Reveals a Stemness/EMT Subtype and MMP12 Linked to the Progression and Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Proteome Res. 2024, 23, 1821–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawase, T.; Ichikawa, H.; Ohta, T.; Nozaki, N.; Tashiro, F.; Ohki, R.; Taya, Y. p53 target gene AEN is a nuclear exonuclease required for p53-dependent apoptosis. Oncogene 2008, 27, 3797–3810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shalaby, R.; Flores-Romero, H.; Garcia-Saez, A.J. The Mysteries around the BCL-2 Family Member BOK. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, C.; Bu, X.; Jiang, Z. Protocadherin-10 acts as a tumor suppressor gene, and is frequently downregulated by promoter methylation in pancreatic cancer cells. Oncol. Rep. 2016, 36, 383–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasparini, G.; Pellegatta, M.; Crippa, S.; Lena, M.S.; Belfiori, G.; Doglioni, C.; Taveggia, C.; Falconi, M. Nerves and Pancreatic Cancer: New Insights into a Dangerous Relationship. Cancers 2019, 11, 893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, L.L.; Qu, D.; Sureban, S.; Mitchell, S.; Pitts, K.; Cooper, N.; Fazili, J.; Harty, R.; Oseini, A.; Ding, K.; et al. From Inflammation to Oncogenesis: Tracing Serum DCLK1 and miRNA Signatures in Chronic Liver Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kagawa, K.; Sato, S.; Koyama, K.; Imakura, T.; Murakami, K.; Yamashita, Y.; Naito, N.; Ogawa, H.; Kawano, H.; Nishioka, Y. The lymphocyte-specific protein tyrosine kinase-specific inhibitor A-770041 attenuates lung fibrosis via the suppression of TGF-beta production in regulatory T-cells. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0275987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, H.; Yang, Z.; Xin, Z.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Cui, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, F. Glycogen synthase kinase-3beta: A promising candidate in the fight against fibrosis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 11737–11753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Short, M.D.; Fox, S.M.; Lam, C.F.; Stenmark, K.R.; Das, M. Protein kinase Czeta attenuates hypoxia-induced proliferation of fibroblasts by regulating MAP kinase phosphatase-1 expression. Mol. Biol. Cell. 2006, 17, 1995–2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wettlaufer, S.H.; Penke, L.R.; Okunishi, K.; Peters-Golden, M. Distinct PKA regulatory subunits mediate PGE(2) inhibition of TGFbeta-1-stimulated collagen I translation and myofibroblast differentiation. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell. Mol. Physiol. 2017, 313, L722–L731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Wang, F.; Luo, F. The Role of JAK/STAT Pathway in Fibrotic Diseases: Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadot, E.; Conacci-Sorrell, M.; Zhurinsky, J.; Shnizer, D.; Lando, Z.; Zharhary, D.; Kam, Z.; Ben-Ze’ev, A.; Geiger, B. Regulation of S33/S37 phosphorylated beta-catenin in normal and transformed cells. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 2771–2780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carriere, C.; Gore, A.J.; Norris, A.M.; Gunn, J.R.; Young, A.L.; Longnecker, D.S.; Korc, M. Deletion of Rb accelerates pancreatic carcinogenesis by oncogenic Kras and impairs senescence in premalignant lesions. Gastroenterology 2011, 141, 1091–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sriram, G.; Birge, R.B. Emerging roles for crk in human cancer. Genes Cancer 2010, 1, 1132–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lax, I.; Wong, A.; Lamothe, B.; Lee, A.; Frost, A.; Hawes, J.; Schlessinger, J. The docking protein FRS2alpha controls a MAP kinase-mediated negative feedback mechanism for signaling by FGF receptors. Mol. Cell. 2002, 10, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coomans de, B.A.; Demoulin, J.B. FOXO transcription factors in cancer development and therapy. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 1159–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Wu, Y.; Ma, Y.; Liu, X. Interference with ENO2 promotes ferroptosis and inhibits glycolysis in clear cell renal cell carcinoma by regulating Hippo-YAP1 signaling. Oncol. Lett. 2024, 28, 443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Simons, M. Emerging roles of PLCgamma1 in endothelial biology. Sci. Signal. 2021, 14, eabc6612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhen, C.; Sun, P.; Liang, R.; Fei, S.; Chen, X.; Qian, J.; Xu, B.; Lin, Q.; Yao, G.; Zheng, B. Cadherin 23 is a prognostic marker of pancreatic cancer and promotes cell viability in floating culture conditions. Int. J. Med. Sci. 2025, 22, 101–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baumann, A.; Nier, A.; Hernandez-Arriaga, A.; Brandt, A.; Lorenzo Pisarello, M.J.; Jin, C.J.; Pilar, E.; Camarinha-Silva, A.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Bergheim, I. Toll-like receptor 1 as a possible target in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 17815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Samus, M.; Rot, A. Atypical chemokine receptors in cancer. Cytokine 2024, 176, 156504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayly-Jones, C.; Pang, S.S.; Spicer, B.A.; Whisstock, J.C.; Dunstone, M.A. Ancient but Not Forgotten: New Insights Into MPEG1, a Macrophage Perforin-Like Immune Effector. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 581906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Jiang, Q.; Gao, S.; Xia, Q.; Zhang, H.; Liu, B.; Zhao, R.; Jiang, H.; Li, X.; Xu, A.; et al. IL20Rb aggravates pulmonary fibrosis through enhancing bone marrow derived profibrotic macrophage activation. Pharmacol. Res. 2024, 203, 107178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Ouyang, Y.; Feng, Z.; Jiang, Z.; Ma, J.; Zhou, X.; Cai, C.; Han, Y.; Zeng, S.; Liu, S.; et al. RASGRP2 is a potential immune-related biomarker and regulates mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in lung adenocarcinoma. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1100231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pitarresi, J.R.; Norgard, R.J.; Chiarella, A.M.; Suzuki, K.; Bakir, B.; Sahu, V.; Li, J.; Zhao, J.; Marchand, B.; Wengyn, M.D.; et al. PTHrP Drives Pancreatic Cancer Growth and Metastasis and Reveals a New Therapeutic Vulnerability. Cancer Discov. 2021, 11, 1774–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Chen, Z.; Ni, X. Tissue transglutaminase-1 promotes stemness and chemoresistance in gastric cancer cells by regulating Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Exp. Biol. Med. 2017, 242, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, M.; Wang, H.; Liu, Z.; Guan, X.; Yang, R.; Huang, R.; Tang, Q.; Zou, C.; Wang, G.; et al. MEGF6 Promotes the Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via the TGFbeta/SMAD Signaling Pathway in Colorectal Cancer Metastasis. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 46, 1895–1906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Liu, F.; Jiang, Z.; Jiang, Z. TNFSF9 promotes metastasis of pancreatic cancer by regulating M2 polarization of macrophages through Src/FAK/p-Akt/IL-1beta signaling. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2022, 102, 108429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamidi, T.; Algul, H.; Cano, C.E.; Sandi, M.J.; Molejon, M.I.; Riemann, M.; Calvo, E.L.; Lomberk, G.; Dagorn, J.C.; Weih, F.; et al. Nuclear protein 1 promotes pancreatic cancer development and protects cells from stress by inhibiting apoptosis. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 2092–2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, S.; Lenchner, D.S.; Jaeger, E.; Hunihan, L.; DeSantis, D.F.; Fragkogianni, S.; Ronski, K.; Wilson, F.H. Genetic and oncogenic features of RASGRF fusions. NPJ Precis. Oncol. 2025, 9, 224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugea, A.; Waldron, R.T. Exosome-Mediated Intercellular Communication Between Stellate Cells and Cancer Cells in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma. Pancreas 2017, 46, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, W.; Ren, Y.; Lu, Z.; Zhao, X. The potential roles of exosomes in pancreatic cancer initiation and metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2020, 19, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brahmer, J.R.; Tykodi, S.S.; Chow, L.Q.; Hwu, W.J.; Topalian, S.L.; Hwu, P.; Drake, C.G.; Camacho, L.H.; Kauh, J.; Odunsi, K.; et al. Safety and activity of anti-PD-L1 antibody in patients with advanced cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2455–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Waghray, M.; Yalamanchili, M.; di Magliano, M.P.; Simeone, D.M. Deciphering the role of stroma in pancreatic cancer. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 2013, 29, 537–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, L.; Xue, J.; Jaffee, E.M.; Habtezion, A. Role of immune cells and immune-based therapies in pancreatitis and pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1230–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salmon, H.; Franciszkiewicz, K.; Damotte, D.; Dieu-Nosjean, M.C.; Validire, P.; Trautmann, A.; Mami-Chouaib, F.; Donnadieu, E. Matrix architecture defines the preferential localization and migration of T cells into the stroma of human lung tumors. J. Clin. Investig. 2012, 122, 899–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Owlia, A.; Espeijo, R.; Dai, B. Novel gastrin receptors mediate mitogenic effects of gastrin and processing intermediates of gastrin on Swiss 3T3 fibroblasts. Absence of detectable cholecystokinin (CCK)-A and CCK-B receptors. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 8429–8438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berna, M.J.; Seiz, O.; Nast, J.F.; Benten, D.; Blaker, M.; Koch, J.; Lohse, A.W.; Pace, A. CCK1 and CCK2 receptors are expressed on pancreatic stellate cells and induce collagen production. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 38905–38914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, M.V.; Park, S.; Phillips, P.A.; Santucci, N.; Goldstein, D.; Kumar, R.K.; Ramm, G.A.; Buchler, M.; Friess, H.; McCarroll, J.A.; et al. Desmoplastic reaction in pancreatic cancer: Role of pancreatic stellate cells. Pancreas 2004, 29, 179–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Apte, M.V.; Wilson, J.S.; Lugea, A.; Pandol, S.J. A starring role for stellate cells in the pancreatic cancer microenvironment. Gastroenterology 2013, 144, 1210–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, J.P.; Cooper, T.K.; McGovern, C.O.; Gilius, E.L.; Zhong, Q.; Liao, J.; Molinolo, A.A.; Gutkind, J.S.; Matters, G.L. Cholecystokinin receptor antagonist halts progression of pancreatic cancer precursor lesions and fibrosis in mice. Pancreas 2014, 43, 1050–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chan, Y.T.; Wang, N.; Tan, H.Y.; Li, S.; Feng, Y. Targeting Hepatic Stellate Cells for the Treatment of Liver Fibrosis by Natural Products: Is It the Dawning of a New Era? Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11, 548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefere, S.; Devisscher, L.; Tacke, F. Targeting CCR2/5 in the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and fibrosis: Opportunities and challenges. Expert. Opin. Investig. Drugs 2020, 29, 89–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amedei, A.; Niccolai, E.; Prisco, D. Pancreatic cancer: Role of the immune system in cancer progression and vaccine-based immunotherapy. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2014, 10, 3354–3368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, H.; Declerck, Y.A. Targeting the tumor microenvironment: From understanding pathways to effective clinical trials. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 4965–4977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sideras, K.; Braat, H.; Kwekkeboom, J.; van Eijck, C.H.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Sleijfer, S.; Bruno, M. Role of the immune system in pancreatic cancer progression and immune modulating treatment strategies. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 513–522, Erratum in Cancer Treat. Rev. 2014, 40, 892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strauss, J.; Alewine, C.; Figg, W.D.; Duffy, A. Targeting the microenvironment of pancreatic cancer: Overcoming treatment barriers and improving local immune responses. Clin. Transl. Oncol. 2016, 18, 653–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hingorani, S.R.; Harris, W.P.; Beck, J.T.; Berdov, B.A.; Wagner, S.A.; Pshevlotsky, E.M.; Tjulandin, S.A.; Gladkov, O.A.; Holcombe, R.F.; Korn, R.; et al. Phase Ib Study of PEGylated Recombinant Human Hyaluronidase and Gemcitabine in Patients with Advanced Pancreatic Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2016, 22, 2848–2854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van, C.E.; Tempero, M.A.; Sigal, D.; Oh, D.Y.; Fazio, N.; Macarulla, T.; Hitre, E.; Hammel, P.; Hendifar, A.E.; Bates, S.E.; et al. Randomized Phase III Trial of Pegvorhyaluronidase Alfa with Nab-Paclitaxel Plus Gemcitabine for Patients with Hyaluronan-High Metastatic Pancreatic Adenocarcinoma. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3185–3194. [Google Scholar]
- Signore, M.; Manganelli, V.; Hodge, A. Antibody Validation by Western Blotting. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1606, 51–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rabiee, A.; Gay, M.D.; Shivapurkar, N.; Cao, H.; Nadella, S.; Smith, C.I.; Lewis, J.H.; Bansal, S.; Cheema, A.; Kwagyan, J.; et al. Safety and Dosing Study of a Cholecystokinin Receptor Antagonist in Non-alcoholic Steatohepatitis. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 112, 1271–1279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciofoaia, V.; Chen, W.; Tarek, B.; Gay, M.; Shivapurkar, N.; Smith, J. The Role of a Cholecystokinin Receptor Antagonist in the Management of Chronic Pancreatitis: A Phase 1 Trial. Pharmaceutics 2024, 16, 611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boj, S.F.; Hwang, C.I.; Baker, L.A.; Chio, I.I.; Engle, D.D.; Corbo, V.; Jager, M.; Ponz-Sarvise, M.; Tiriac, H.; Spector, M.S.; et al. Organoid models of human and mouse ductal pancreatic cancer. Cell 2015, 160, 324–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Osborne, N.; Sundseth, R.; Gay, M.D.; Cao, H.; Tucker, R.D.; Nadella, S.; Wang, S.; Liu, X.; Kroemer, A.; Sutton, L.; et al. Vaccine against gastrin, a polyclonal antibody stimulator, decreases pancreatic cancer metastases. Am. J. Physiol. Gastrointest. Liver Physiol. 2019, 317, G682–G693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathison, A.; Liebl, A.; Bharucha, J.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Lomberk, G.; Shah, V.; Urrutia, R. Pancreatic stellate cell models for transcriptional studies of desmoplasia-associated genes. Pancreatology 2010, 10, 505–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanchard, C.E.; Gomeiz, A.T.; Avery, K.; Gazzah, E.E.; Alsubaie, A.M.; Sikaroodi, M.; Chiari, Y.; Ward, C.; Sanchez, J.; Espina, V.; et al. Signaling dynamics in coexisting monoclonal cell subpopulations unveil mechanisms of resistance to anti-cancer compounds. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pierobon, M.; Ramos, C.; Wong, S.; Hodge, K.A.; Aldrich, J.; Byron, S.; Anthony, S.P.; Robert, N.J.; Northfelt, D.W.; Jahanzeb, M.; et al. Enrichment of PI3K-AKT-mTOR Pathway Activation in Hepatic Metastases from Breast Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 23, 4919–4928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baldelli, E.; Calvert, V.; Hodge, A.; VanMeter, A.; Petricoin, E.F., III; Pierobon, M. Reverse Phase Protein Microarrays. Methods Mol. Biol. 2017, 1606, 149–169. [Google Scholar]
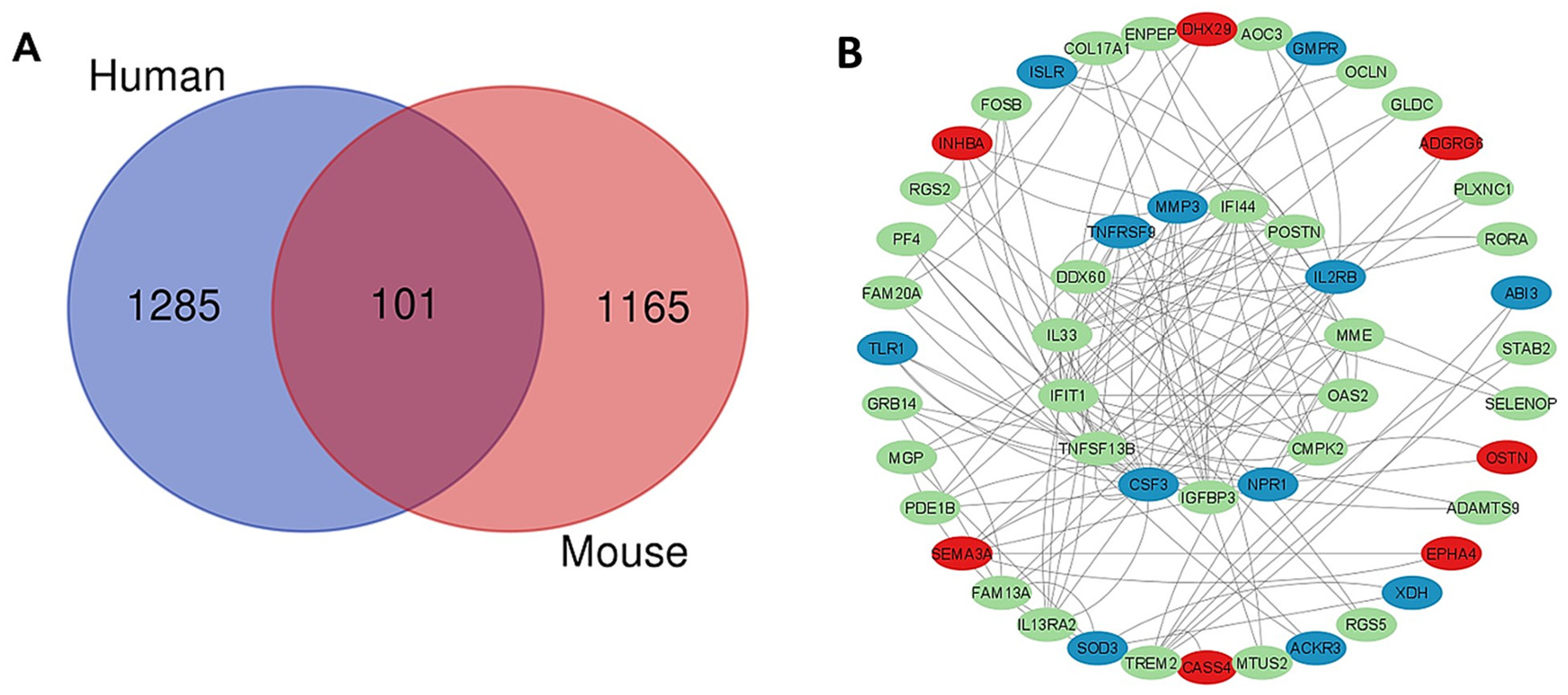
| Downregulated Genes | Human log2FoldChange | Mouse log2FoldChange | Function |
|---|---|---|---|
| CDH23 | −6.359513328 | −2.558595917 | High levels of cadherin 23, CDH23 expression, are correlated with a poor prognosis in pancreatic cancer [41]. |
| TLR1 | −6.359513328 | −2.289812863 | Toll-like receptors (TLRs) in the liver compartment have been attributed to the development of fatty liver disease [42]. |
| ACKR3 | −6.041971044 | −2.497630078 | Atypical chemokine receptors (ACKRs) [43]. |
| MPEG1 | −5.634213732 | −3.623322785 | Macrophage-expressed gene 1 codes for a pore-forming protein [44]. |
| IL2RB | −2.971465437 | −2.210742642 | β chain of the IL-2 receptor. Aggravates fibrosis by macrophage activation [45]. |
| MMP3 | −2.49685765 | −4.049810234 | Matrix metalloproteinase-3 promotes fibrosis and cancer development by remodeling the (ECM), stimulating (EMT) [14]. |
| RASGRP2 | −2.313596925 | −2.456959022 | Activates small GTPases like Rap1 and R-Ras and increases malignant progression [46]. |
| PTH1R | −2.149003603 | −1.735983328 | Parathyroid hormone receptor 1 (PTH1R or PTHR1) promotes Pancreatic cancer growth and metastasis [47]. |
| TGM1 | −2.069707582 | −2.817073954 | Transglutaminase-1 high expression can promote tumor progression, metastasis, and cancer stemness by cross-linking proteins [48]. |
| MEGF6 | −1.925472016 | −3.095780165 | Multiple epidermal growth factors: they are linked to promoting tumor growth, metastasis [49]. |
| TNFRSF9 | −1.72413648 | −1.811344963 | Tumor necrosis factor family promotes metastasis of pancreatic cancer by regulating M2 polarization of macrophages [50]. |
| NPR1 | −1.692027853 | −2.256071133 | Nuclear protein 1 is a human gene that promotes pancreatic cancer and confers drug resistance [51]. |
| RASGRF1 | −1.563551117 | −8.042302297 | Encodes the protein Ras-GRF1, a dual-function GEF that activates both Ras and Rac GTPases [52]. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ortega, M.; Agena, E.; Chen, W.; Cao, H.; Vasudevan, S.; Shivapurkar, N.; Pierobon, M.; Smith, J.P. Downregulation of the CCK-B Receptor in Pancreatic Stellate Cells Blocks Molecular Proliferative Pathways and Increases Apoptosis to Decrease Pancreatic Cancer Growth In Vitro. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311699
Ortega M, Agena E, Chen W, Cao H, Vasudevan S, Shivapurkar N, Pierobon M, Smith JP. Downregulation of the CCK-B Receptor in Pancreatic Stellate Cells Blocks Molecular Proliferative Pathways and Increases Apoptosis to Decrease Pancreatic Cancer Growth In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311699
Chicago/Turabian StyleOrtega, Miranda, Eri Agena, Wenqiang Chen, Hong Cao, Sona Vasudevan, Narayan Shivapurkar, Mariaelena Pierobon, and Jill P. Smith. 2025. "Downregulation of the CCK-B Receptor in Pancreatic Stellate Cells Blocks Molecular Proliferative Pathways and Increases Apoptosis to Decrease Pancreatic Cancer Growth In Vitro" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311699
APA StyleOrtega, M., Agena, E., Chen, W., Cao, H., Vasudevan, S., Shivapurkar, N., Pierobon, M., & Smith, J. P. (2025). Downregulation of the CCK-B Receptor in Pancreatic Stellate Cells Blocks Molecular Proliferative Pathways and Increases Apoptosis to Decrease Pancreatic Cancer Growth In Vitro. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11699. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311699






