From Pathways to Patients in Atopic Dermatitis: Advanced Systemic Therapies
Abstract
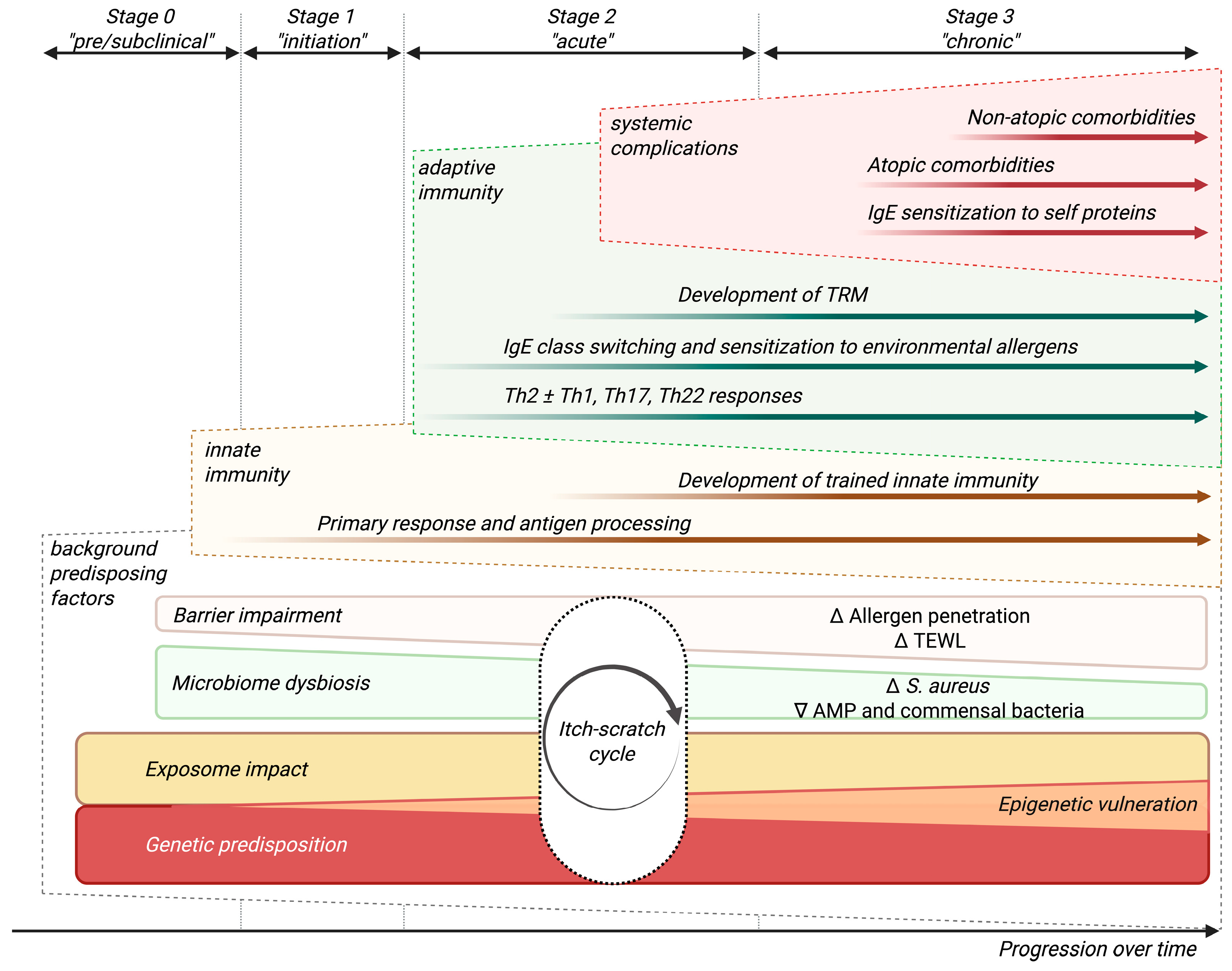
1. Introduction
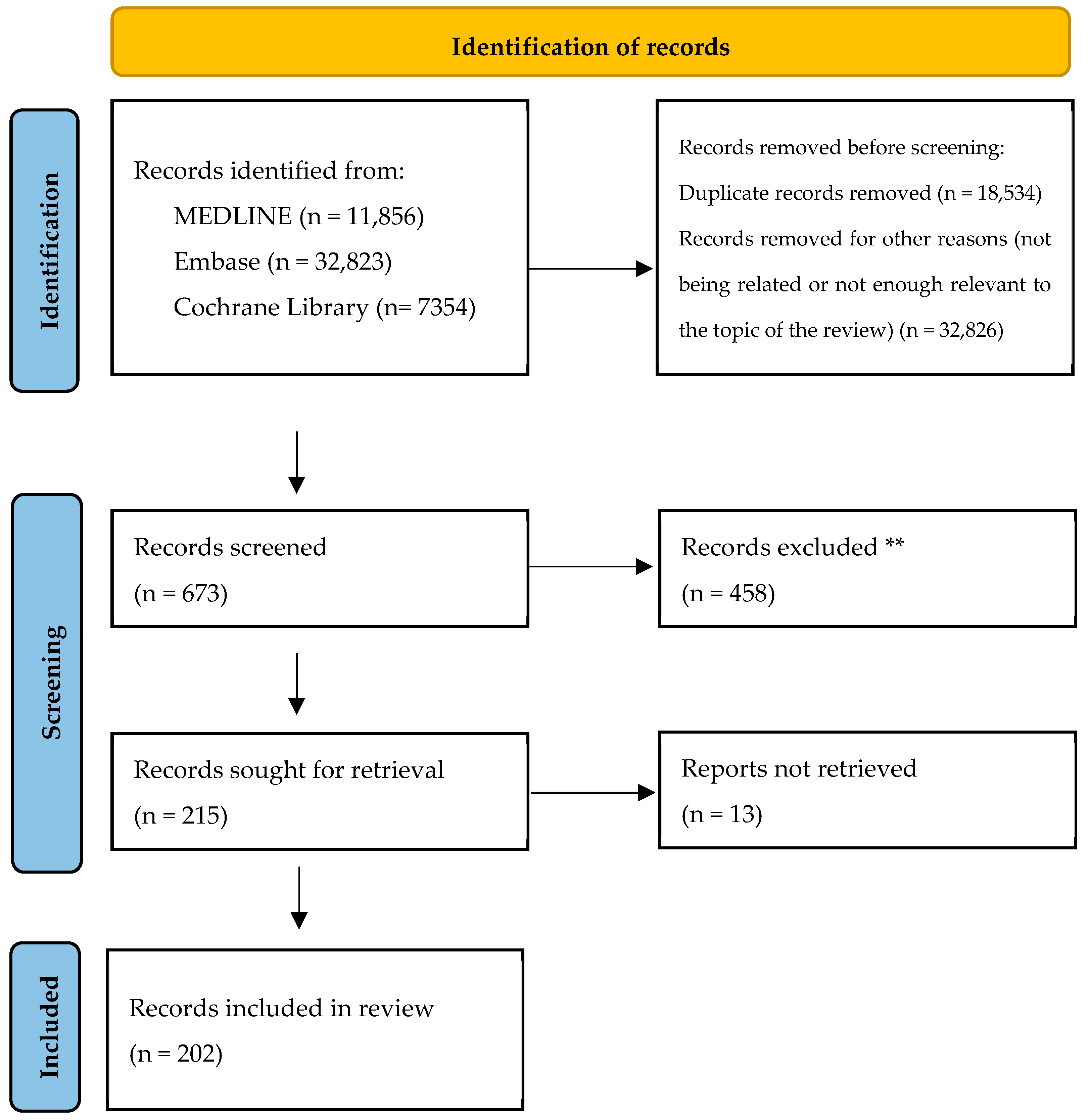
2. Materials and Methods
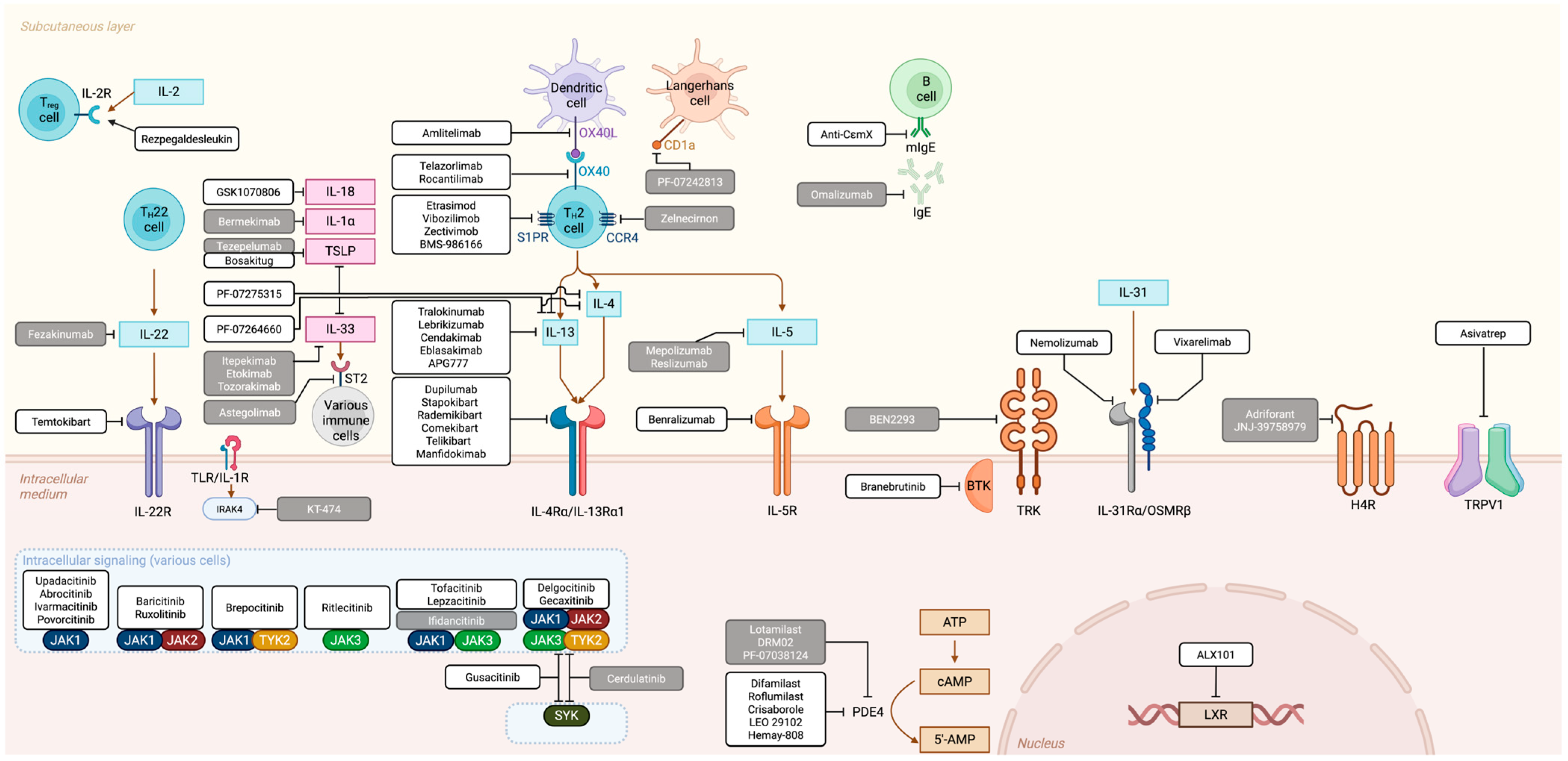
3. Therapeutic Landscape: Overview of Main Targets, Approved and Experimental Molecules
3.1. “T-Cell Inhibitor” Family
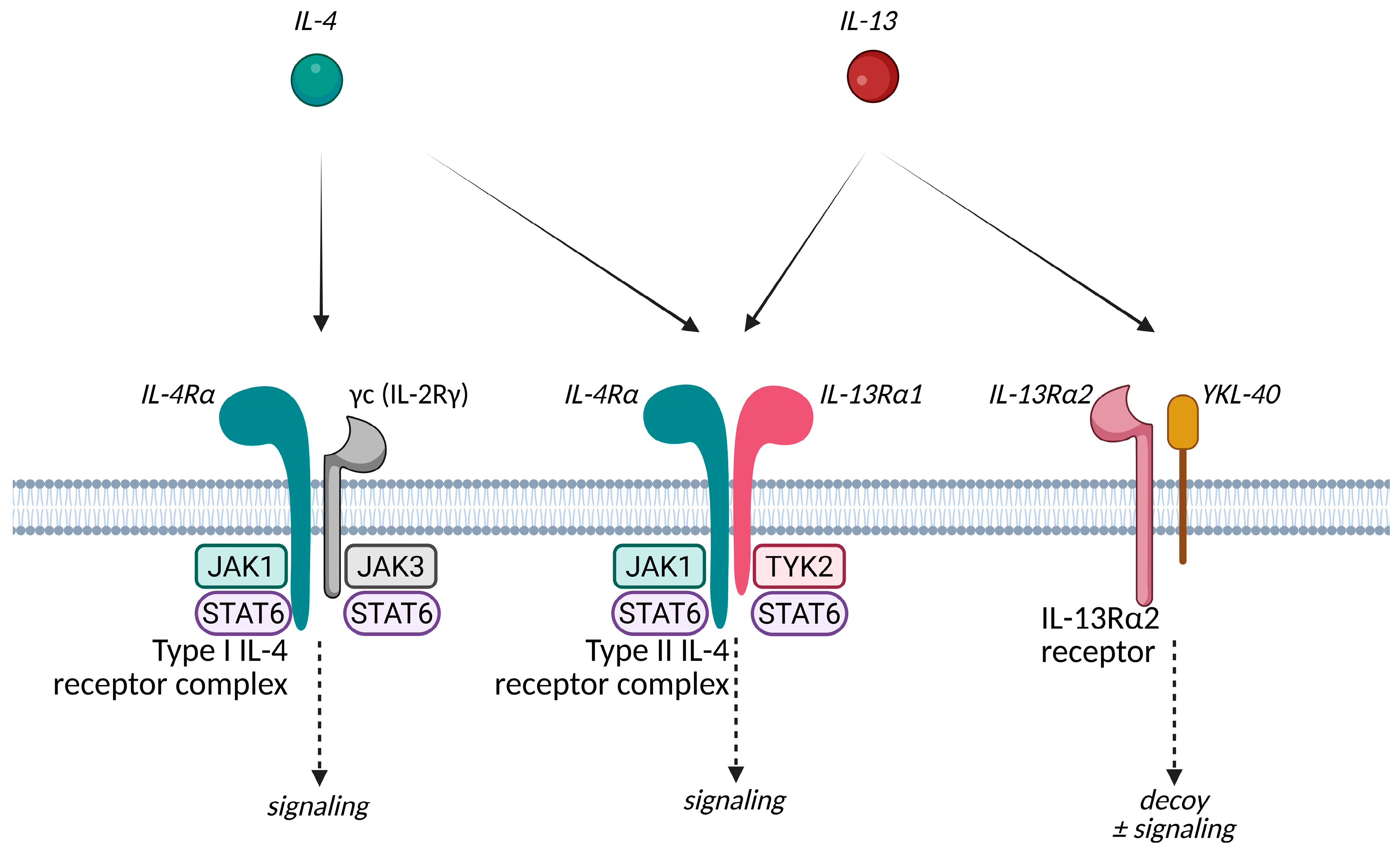
3.1.1. IL-4 and IL-13 Related Agents
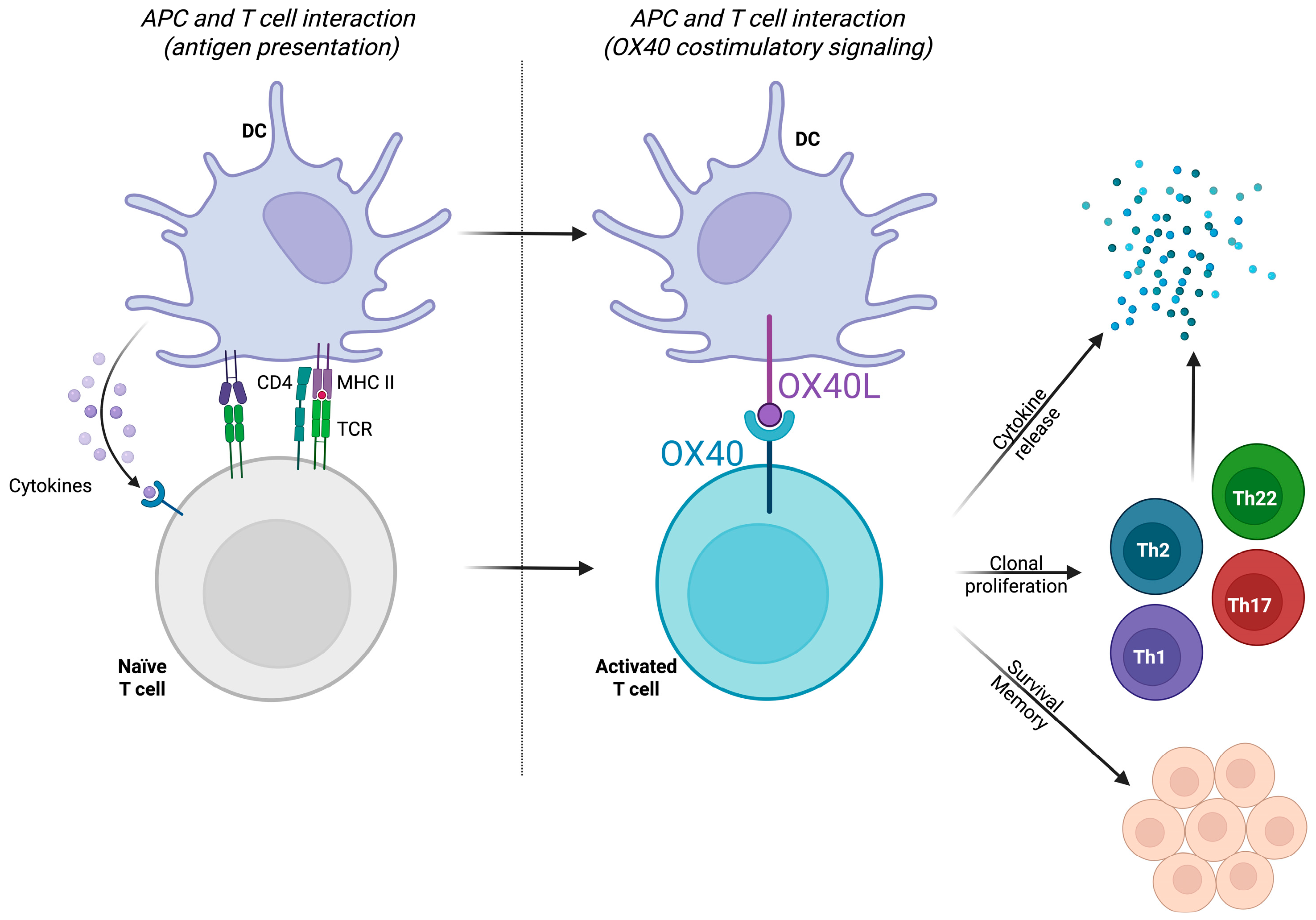
3.1.2. The OX40/OX40L Pathway
3.1.3. Other Extracellular Immune Mediators and Targets
3.2. “JAK Inhibitors” Family
3.3. Comparisons Between Families: What We Know So Far
3.4. Alternative Approaches
3.4.1. Other Interleukins
3.4.2. Additional Kinase Inhibitors
3.4.3. Eosinophils and IgE
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Facheris, P.; Jeffery, J.; Del Duca, E.; Guttman-Yassky, E. The Translational Revolution in Atopic Dermatitis: The Paradigm Shift from Pathogenesis to Treatment. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 448–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, S.M.; Tavecchio, S.; Marzano, A.V.; Buffon, S. Emerging Systemic Treatments for Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makowska, K.; Nowaczyk, J.; Blicharz, L.; Waśkiel-Burnat, A.; Czuwara, J.; Olszewska, M.; Rudnicka, L. Immunopathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis: Focus on Interleukins as Disease Drivers and Therapeutic Targets for Novel Treatments. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliva, M.; Renert-Yuval, Y.; Guttman-Yassky, E. The “omics” Revolution: Redefining the Understanding and Treatment of Allergic Skin Diseases. Curr. Opin. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2016, 16, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Renert-Yuval, Y.; Brunner, P.M. Atopic Dermatitis. Lancet 2025, 405, 583–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Villaverde, R.; Cebolla-Verdugo, M.; Prados-Carmona, A.; Pereyra Rodríguez, J.J.; Armario-Hita, J.C. Mechanism, Diagnostic and Therapeutic Novelties in Dermatology: Where Are We Going? Life 2024, 14, 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otsuka, A.; Wang, C.; Torisu-Itakura, H.; Matsuo, T.; Isaka, Y.; Anderson, P.; Piercy, J.; Austin, J.; Marwaha, S.; Tanaka, A. Patient and Family Burden in Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis and Its Treatment Pattern in Japan. Int. J. Dermatol. 2024, 63, e322–e334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buhl, T.; Werfel, T. Atopic Dermatitis—Perspectives and Unmet Medical Needs. JDDG—J. Ger. Soc. Dermatol. 2023, 21, 349–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados-Carmona, A.; Navarro-Triviño, F.J.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R.; Corell, A. Role of Interleukins in Dermatology: Exploring the Immune Mechanisms in Skin Diseases. JEADV Clin. Pract. 2024, 3, 1381–1398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, K.; Heitmiller, K.D.; Czarnowicki, T. An Update on the Pathophysiology of Atopic Dermatitis. Dermatol. Clin. 2017, 35, 317–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berna, R.; Mitra, N.; Lou, C.; Wan, J.; Hoffstad, O.; Wubbenhorst, B.; Nathanson, K.L.; Margolis, D.J. TSLP and IL-7R Variants Are Associated with Persistent Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 446–450.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y. ILC2s in Skin Disorders. Allergol. Int. 2023, 72, 201–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, L.; Fiocco, Z.; Satoh, T.K.; Peris, K.; French, L.E. Therapeutic Potential of Targeting Interleukin-1 Family Cytokines in Chronic Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Br. J. Dermatol. 2022, 186, 925–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.K.; Gupta, K.; Dwivedi, P.D. Pathophysiology of IL-33 and IL-17 in Allergic Disorders. Cytokine Growth Factor. Rev. 2017, 38, 22–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imai, Y.; Yasuda, K.; Sakaguchi, Y.; Haneda, T.; Mizutani, H.; Yoshimoto, T.; Nakanishi, K.; Yamanishi, K. Skin-Specific Expression of IL-33 Activates Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells and Elicits Atopic Dermatitis-like Inflammation in Mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 13921–13926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, Y.; Yasuda, K.; Nagai, M.; Kusakabe, M.; Kubo, M.; Nakanishi, K.; Yamanishi, K. IL-33–Induced Atopic Dermatitis–Like Inflammation in Mice Is Mediated by Group 2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Concert with Basophils. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 2185–2194.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryffel, B.; Alves-Filho, J.C. ILC2s and Basophils Team Up to Orchestrate IL-33–Induced Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 2077–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saluja, R.; Zoltowska, A.; Ketelaar, M.E.; Nilsson, G. IL-33 and Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin in Mast Cell Functions. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2016, 778, 68–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salimi, M.; Barlow, J.L.; Saunders, S.P.; Xue, L.; Gutowska-Owsiak, D.; Wang, X.; Huang, L.-C.; Johnson, D.; Scanlon, S.T.; McKenzie, A.N.J.; et al. A Role for IL-25 and IL-33–Driven Type-2 Innate Lymphoid Cells in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Exp. Med. 2013, 210, 2939–2950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegfried, E.C.; Hebert, A.A. Diagnosis of Atopic Dermatitis: Mimics, Overlaps, and Complications. J. Clin. Med. 2015, 4, 884–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herranz-Pinto, P.; Figueras Nart, I.; Monte-Boquet, E.; Tortajada Goitia, B. Improving the Management and Follow-up of Atopic Dermatitis: A Delphi Process Report of Consensus Between Hospital Dermatologists and Pharmacists. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2023, 114, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamilton, J.D.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Dhingra, N.; Cardinale, I.; Li, X.; Kostic, A.; Ming, J.E.; Radin, A.R.; Krueger, J.G.; Graham, N.; et al. Dupilumab Improves the Molecular Signature in Skin of Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 1293–1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jensen, J.M.; Scherer, A.; Wanke, C.; Bräutigam, M.; Bongiovanni, S.; Letzkus, M.; Staedtler, F.; Kehren, J.; Zuehlsdorf, M.; Schwarz, T.; et al. Gene Expression Is Differently Affected by Pimecrolimus and Betamethasone in Lesional Skin of Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy 2012, 67, 413–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tintle, S.; Shemer, A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Fujita, H.; Gilleaudeau, P.; Sullivan-Whalen, M.; Johnson-Huang, L.; Chiricozzi, A.; Cardinale, I.; Duan, S.; et al. Reversal of Atopic Dermatitis with Narrow-Band UVB Phototherapy and Biomarkers for Therapeutic Response. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 583–593.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.L.; Bieber, T.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Beck, L.A.; Blauvelt, A.; Cork, M.J.; Silverberg, J.I.; Deleuran, M.; Kataoka, Y.; Lacour, J.-P.; et al. Two Phase 3 Trials of Dupilumab versus Placebo in Atopic Dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2335–2348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunner, P.M.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Leung, D.Y.M. The Immunology of Atopic Dermatitis and Its Reversibility with Broad-Spectrum and Targeted Therapies. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, S65–S76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruiz-Villaverde, R.; Velasco-Amador, J.P.; Prados-Carmona, A.; Ruiz-Carrascosa, J.C. Switching from Reference Adalimumab to Biosimilar. Assessment of Clinical Outcomes in Psoriasis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2023, 62, e159–e161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados Carmona, A.; Husein-ElAhmed, H.; Navarro-Triviño, F.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R. Deciphering Atopic Dermatitis Heterogeneity: A Short-Review on the Translational Revolution from Endotypes to Immunotypes. J. Dtsch. Dermatol. Ges. 2025; pending publication. [Google Scholar]
- Furue, M.; Yamamura, K.; Kido-Nakahara, M.; Nakahara, T.; Fukui, Y. Emerging Role of Interleukin-31 and Interleukin-31 Receptor in Pruritus in Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 73, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabashima, K.; Irie, H. Interleukin-31 as a Clinical Target for Pruritus Treatment. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 638325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemmer, J.M.; Kuchner, M.; Datsi, A.; Oláh, P.; Julia, V.; Raap, U.; Homey, B. Interleukin-31 Signaling Bridges the Gap Between Immune Cells, the Nervous System and Epithelial Tissues. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 639097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakashima, C.; Otsuka, A.; Kabashima, K. Interleukin-31 and Interleukin-31 Receptor: New Therapeutic Targets for Atopic Dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Progneaux, A.; Evrard, C.; De Glas, V.; Fontaine, A.; Dotreppe, C.; De Vuyst, E.; Nikkels, A.F.; García-González, V.; Dumoutier, L.; Lambert de Rouvroit, C.; et al. Keratinocytes Activated by IL-4/IL-13 Express IL-2Rγ With Consequences on Epidermal Barrier Function. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 32, 660–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karo-Atar, D.; Bitton, A.; Benhar, I.; Munitz, A. Therapeutic Targeting of the Interleukin-4/Interleukin-13 Signaling Pathway: In Allergy and Beyond. BioDrugs 2018, 32, 201–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bitton, A.; Avlas, S.; Reichman, H.; Itan, M.; Karo-Atar, D.; Azouz, N.P.; Rozenberg, P.; Diesendruck, Y.; Nahary, L.; Rothenberg, M.E.; et al. A Key Role for IL-13 Signaling via the Type 2 IL-4 Receptor in Experimental Atopic Dermatitis. Sci. Immunol. 2020, 5, eaaw2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, L.; Shi, V.Y.; Chan, L.S. IL-4 up-Regulates Epidermal Chemotactic, Angiogenic, and pro-Inflammatory Genes and down-Regulates Antimicrobial Genes in Vivo and in Vitro: Relevant in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis. Cytokine 2013, 61, 419–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, B.; Yu, Z.; Liu, J.; Tian, Y.; Ruan, Y.; Kong, T.; Hou, M.; Yu, B.; Ling, S.; Wang, D.; et al. IL-4-Induced Decrease in Both the Number and CTLA-4 Expression of Treg Impairs Suppression of Th2 Type Inflammation in Severe Atopic Dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2024, 114, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, H.; Wan, H.; Zhang, D. Innate Lymphoid Cells: A New Key Player in Atopic Dermatitis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 1277120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leyva-Castillo, J.M.; Das, M.; Strakosha, M.; McGurk, A.; Artru, E.; Kam, C.; Alasharee, M.; Wesemann, D.R.; Tomura, M.; Karasuyama, H.; et al. IL-4 Acts on Skin-Derived Dendritic Cells to Promote the TH2 Response to Cutaneous Sensitization and the Development of Allergic Skin Inflammation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 154, 1462–1471.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T. Interleukin-13: Targeting an Underestimated Cytokine in Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy 2020, 75, 54–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Posadas, L.; Hodges, R.R.; Diebold, Y.; Dartt, D.A. Context-Dependent Regulation of Conjunctival Goblet Cell Function by Allergic Mediators. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 12162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ueta, M.; Mizushima, K.; Yokoi, N.; Naito, Y.; Kinoshita, S. Expression of the Interleukin-4 Receptor in Human Conjunctival Epithelial Cells. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2010, 94, 1239–1243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Junttila, I.S. Tuning the Cytokine Responses: An Update on Interleukin (IL)-4 and IL-13 Receptor Complexes. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Furue, M.; Ulzii, D.; Nakahara, T.; Tsuji, G.; Furue, K.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Kido-Nakahara, M. Implications of IL-13Rα2 in Atopic Skin Inflammation. Allergol. Int. 2020, 69, 412–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivaprasad, U.; Warrier, M.R.; Gibson, A.M.; Chen, W.; Tabata, Y.; Bass, S.A.; Rothenberg, M.E.; Khurana Hershey, G.K. IL-13Rα2 Has a Protective Role in a Mouse Model of Cutaneous Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2010, 185, 6802–6808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, T.; Zhu, Z.; Liu, W.; Lee, C.G.; Chen, Q.; Homer, R.J.; Elias, J.A. Cytokine Regulation of IL-13Rα2 and IL-13Rα1 in Vivo and in Vitro. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2003, 111, 720–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulzii, D.; Kido-Nakahara, M.; Nakahara, T.; Tsuji, G.; Furue, K.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Furue, M. Scratching Counteracts Il-13 Signaling by Upregulating the Decoy Receptor Il-13rα2 in Keratinocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Medina, S.F.; Gauldie, M.F.; Fabre, J.; Donnelly, A.C.; Kane, S.C.; Keane, R.P. Modulation of Pulmonary Fibrosis by IL-13R2. Am. J. Physiol. Lung Cell Mol. Physiol. 2015, 308, 710–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, E.J.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, M.N.; Kim, S.Y.; Kim, S.H.; Park, C.O.; Kim, K.W.; Lee, C.G.; Elias, J.A.; Jee, H.M.; et al. Chitinase 3-like 1 Drives Allergic Skin Inflammation via Th2 Immunity and M2 Macrophage Activation. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2019, 49, 1464–1474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fichtner-Feigl, S.; Strober, W.; Kawakami, K.; Puri, R.K.; Kitani, A. IL-13 Signaling through the IL-13α2 Receptor Is Involved in Induction of TGF-Β1 Production and Fibrosis. Nat. Med. 2006, 12, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Rodriguez, E.; Degenhardt, F.; Baurecht, H.; Wehkamp, U.; Volks, N.; Szymczak, S.; Swindell, W.R.; Sarkar, M.K.; Raja, K.; et al. Atopic Dermatitis Is an IL-13–Dominant Disease with Greater Molecular Heterogeneity Compared to Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leyva-Castillo, J.M.; Das, M.; Artru, E.; Yoon, J.; Galand, C.; Geha, R.S. Mast Cell–Derived IL-13 Downregulates IL-12 Production by Skin Dendritic Cells to Inhibit the TH1 Cell Response to Cutaneous Antigen Exposure. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 2305–2315.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, M. Regulation of Filaggrin, Loricrin, and Involucrin by IL-4, IL-13, IL-17A, IL-22, AHR, and NRF2: Pathogenic Implications in Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, K.; Ito, T.; Tsuji, G.; Ulzii, D.; Vu, Y.H.; Kido-Nakahara, M.; Nakahara, T.; Furue, M. The IL-13–OVOL1–FLG Axis in Atopic Dermatitis. Immunology 2019, 158, 281–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitamura, Y.; Nunomura, S.; Nanri, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Yoshihara, T.; Masuoka, M.; Tsuji, G.; Nakahara, T.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Conway, S.J.; et al. The IL-13/periostin/IL-24 Pathway Causes Epidermal Barrier Dysfunction in Allergic Skin Inflammation. Allergy 2018, 73, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.-P.; Nguyen, G.H.; Jin, H.-Z. MicroRNA-143 Inhibits IL-13-Induced Dysregulation of the Epidermal Barrier-Related Proteins in Skin Keratinocytes via Targeting to IL-13Rα1. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2016, 416, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitamura, Y.; Murai, M.; Mitoma, C.; Furue, M. NRF2 Activation Inhibits Both Tgf- β 1- and Il-13-Mediated Periostin Expression in Fibroblasts: Benefit of Cinnamaldehyde for Antifibrotic Treatment. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2018, 2018, 2475047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolodsick, J.E.; Toews, G.B.; Jakubzick, C.; Hogaboam, C.; Moore, T.A.; Mckenzie, A.; Wilke, C.A.; Chrisman, C.J.; Moore, B.B. Protection from Fluorescein Isothiocyanate-Induced Fibrosis in IL-13-Deficient, but Not IL-4-Deficient, Mice Results from Impaired Collagen Synthesis by Fibroblasts. J. Immunol. 2004, 172, 4068–4076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miake, S.; Tsuji, G.; Takemura, M.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Vu, Y.H.; Furue, M.; Nakahara, T. IL-4 Augments IL-31/IL-31 Receptor Alpha Interaction Leading to Enhanced Ccl 17 and Ccl 22 Production in Dendritic Cells: Implications for Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdis, C.A.; Arkwright, P.D.; Brüggen, M.-C.; Busse, W.; Gadina, M.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Kabashima, K.; Mitamura, Y.; Vian, L.; Wu, J.; et al. Type 2 Immunity in the Skin and Lungs. Allergy 2020, 75, 1582–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raap, U.; Weißmantel, S.; Gehring, M.; Eisenberg, A.M.; Kapp, A.; Fölster-Holst, R. IL-31 Significantly Correlates with Disease Activity and Th2 Cytokine Levels in Children with Atopic Dermatitis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2012, 23, 285–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, A.; Fujii, E.; Watanabe, T.; Takashima, Y.; Matsushita, H.; Furuhashi, T.; Morita, A. Distribution of IL-31 and Its Receptor Expressing Cells in Skin of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2014, 74, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabrese, L.; D’Onghia, M.; Lazzeri, L.; Rubegni, G.; Cinotti, E. Blocking the IL-4/IL-13 Axis versus the JAK/STAT Pathway in Atopic Dermatitis: How Can We Choose? J. Pers. Med. 2024, 14, 775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shirley, M. Dupilumab: First Global Approval. Drugs 2017, 77, 1115–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrucci, S.; Tavecchio, S.; Maronese, C.A.; Balato, A.; Di Brizzi, E.V.; Ortoncelli, M.; Ribero, S.; Girolomoni, G.; Maurelli, M.; Fortina, A.B.; et al. Short-, Mid- and Long-Term Efficacy of Dupilumab in Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Real-World Multicentre Italian Study of 2576 Patients. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 49, 1561–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Olesen, C.M.; Yüksel, Y.T.; Zachariae, C.; Lund, T.T.; Agner, T.; Petersen, T.S.; Thyssen, J.P. Treatment of Chronic Hand Eczema with Dupilumab—A Retrospective Follow-up Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, e557–e559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xará, J.; Farinha, P.; Lé, A.M.; Duarte, B.; Torres, T.; Gonçalo, M. Pregnancy and Breastfeeding Outcome in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Treated with Dupilumab: The Clinical Experience of Three Centers. Int. J. Dermatol. 2024, 63, e335–e337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendricks, A.J.; Yosipovitch, G.; Shi, V.Y. Dupilumab Use in Dermatologic Conditions beyond Atopic Dermatitis–a Systematic Review. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2021, 32, 19–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magdaleno-Tapial, J.; Torrijos Aguilar, A.; González-Delgado, V.; Hernández-Bel, P. Dupilumab to Treat Chronic Palmoplantar Eczema: A Retrospective Multicenter Cohort Study. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2024, 115, 628–631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, T.; Cruz, M.J.; Gonçalo, M.; Filipe, P.; Duarte, B.; Alves, J.; Alvarenga, J.M.; Rosa, G.; Flor, D.; Ramos, J.; et al. Dupilumab in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Multicentric, Long-Term, Real-World Portuguese Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2024, 14, 2209–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiricozzi, A.; Gori, N.; Ippoliti, E.; Maurelli, M.; Antonelli, F.; Coscarella, G.; Rizzo, E.; Di Nardo, L.; Girolomoni, G.; Peris, K. Long-Term Therapeutic Response to Dupilumab in Patients Affected by Prurigo Nodularis: A Real-World Retrospective Study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, e892–e895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T. In Search of the Holy Grail in Atopic Dermatitis: Will Dupilumab Become the First Disease-Modifying Atopic Dermatitis Drug? J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 694–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chiei-Gallo, A.; Barei, F.; Calzari, P.; Pisapia, A.; Marzano, A.V.; Ferrucci, S.M. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Dupilumab in Adolescents with Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A 3-Year Real-Life Study. Int. J. Dermatol. 2024, 64, 604–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, T.L.; Fan, Y.H.; Fan, K.S.; Juan, C.K.; Chen, Y.J.; Wu, C.Y. Reduced Atopic March Risk in Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis Patients Prescribed Dupilumab versus Conventional Immunomodulatory Therapy: A Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2024, 91, 466–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lauletta, G.; Martora, F.; di Vico, F.; Patruno, C.; Napolitano, M. Effectiveness, Safety, and Long-Term Continuation Rate Analysis of Dupilumab Treatment in Adolescents with Atopic Dermatitis: A Single-Center Real-Life Retrospective Study. Dermatitis 2025, 36, e401–e403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olbrich, H.; Sadik, C.D.; Ludwig, R.J.; Thaçi, D.; Boch, K. Dupilumab in Inflammatory Skin Diseases: A Systematic Review. Biomolecules 2023, 13, 634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Bissonnette, R.; Ungar, B.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Ardeleanu, M.; Esaki, H.; Suprun, M.; Estrada, Y.; Xu, H.; Peng, X.; et al. Dupilumab Progressively Improves Systemic and Cutaneous Abnormalities in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 155–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navarro-Triviño, F.J.; Prados-Carmona, A.; Aguilera, J.; de Gálvez, M.V.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R. Treatment of Refractory Solar Urticaria: Could Dupilumab Fill the Current Gap? JDDG—J. Ger. Soc. Dermatol. 2023, 21, 652–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le Floc’h, A.; Allinne, J.; Nagashima, K.; Scott, G.; Birchard, D.; Asrat, S.; Bai, Y.; Lim, W.K.; Martin, J.; Huang, T.; et al. Dual Blockade of IL-4 and IL-13 with Dupilumab, an IL-4Rα Antibody, Is Required to Broadly Inhibit Type 2 Inflammation. Allergy 2020, 75, 1188–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Zhang, L.; Wu, L.; Yang, B.; Wang, J.; Li, Y.; Li, J.; Diao, Q.; Sun, Q.; Zhu, X.; et al. Long-term Efficacy and Safety of Stapokibart for Moderate-to-severe Atopic Dermatitis: 52-week Results from a Phase 3 Trial. Allergy 2024, 80, 1348–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, J.-Y.; Yang, B.; Ding, Y.-F.; Wu, L.-M.; Zhang, L.-T.; Wang, J.-Y.; Lu, Q.-J.; Zhang, C.-L.; Zhang, F.-R.; et al. Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Stapokibart in Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: An Open-Label Extension, Nonrandomized Clinical Trial. BioDrugs 2024, 38, 681–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhang, W.; Xu, Y.; Dong, L.; Sun, Y.; Jia, Y.; Li, Z.; Chen, B.; Hou, J.; Zhang, J. Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, Safety, and Tolerability of Stapokibart in Healthy Volunteers and Adult Subjects with Atopic Dermatitis. Adv. Ther. 2024, 41, 2953–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Strober, B.; Feinstein, B.; Xu, J.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Simpson, E.L.; Li, P.; Longphre, M.; Song, J.; Guo, J.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Rademikibart (CBP-201), a next-Generation MAb Targeting IL-4Rα, in Adults with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Phase 2 Randomized Trial (CBP-201-WW001). J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 153, 1040–1049.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupardus, P.J.; Birnbaum, M.E.; Garcia, K.C. Molecular Basis for Shared Cytokine Recognition Revealed in the Structure of an Unusually High Affinity Complex between IL-13 and IL-13Rα2. Structure 2010, 18, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, B.; Breed, J.; Rees, D.G.; Gardener, M.J.; Vinall, L.M.K.; Kemp, B.; Spooner, J.; Keen, J.; Minter, R.; Uddin, F.; et al. Structural Characterisation Reveals Mechanism of IL-13-Neutralising Monoclonal Antibody Tralokinumab as Inhibition of Binding to IL-13Rα1 and IL-13Rα2. J. Mol. Biol. 2017, 429, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Blauvelt, A.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Paller, A.S.; Armstrong, A.W.; Drew, J.; Gopalan, R.; Simpson, E.L. Efficacy and Safety of Lebrikizumab, a High-Affinity Interleukin 13 Inhibitor, in Adults with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Phase 2b Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Dermatol. 2020, 156, 411–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Lynde, C.; Khattri, S.; Schlessinger, J.; Imafuku, S.; Tada, Y.; Morita, A.; Wiseman, M.; Kwiek, B.; et al. Cendakimab in Patients With Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2024, 160, 856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lytvyn, Y.; Gooderham, M. Targeting Interleukin 13 for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simpson, E.L.; Gooderham, M.; Wollenberg, A.; Weidinger, S.; Armstrong, A.; Soung, J.; Ferrucci, S.; Lima, R.G.; Witte, M.M.; Xu, W.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Lebrikizumab in Combination with Topical Corticosteroids in Adolescents and Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Randomized Clinical Trial (ADhere). JAMA Dermatol. 2023, 159, 182–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.L.; Merola, J.F.; Silverberg, J.I.; Reich, K.; Warren, R.B.; Staumont-Sallé, D.; Girolomoni, G.; Papp, K.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Thyssen, J.P.; et al. Safety of Tralokinumab in Adult Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: Pooled Analysis of Five Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase II and Phase III Trials. Br. J. Dermatol. 2022, 187, 888–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.A.; Thaçi, D.; Hamilton, J.D.; Graham, N.M.; Bieber, T.; Rocklin, R.; Ming, J.E.; Ren, H.; Kao, R.; Simpson, E.; et al. Dupilumab Treatment in Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 371, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.M.R.; Drucker, A.M.; Alikhan, A.; Bercovitch, L.; Cohen, D.E.; Darr, J.M.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Frazer-Green, L.; Paller, A.S.; Silverberg, J.I.; et al. American Academy of Dermatology Guidelines: Awareness of Comorbidities Associated with Atopic Dermatitis in Adults. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 86, 1335–1336.e18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beck, L.A.; Bissonnette, R.; Deleuran, M.; Nakahara, T.; Galus, R.; Coleman, A.; Gherardi, G.; Xiao, J.; Dingman, R.; Xu, C.; et al. Dupilumab in Adults With Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol. 2024, 160, 805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleming, P.; Drucker, A.M. Risk of Infection in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis Treated with Dupilumab: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2018, 78, 62–69.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eichenfield, L.F.; Bieber, T.; Beck, L.A.; Simpson, E.L.; Thaçi, D.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Deleuran, M.; Silverberg, J.I.; Ferrandiz, C.; Fölster-Holst, R.; et al. Infections in Dupilumab Clinical Trials in Atopic Dermatitis: A Comprehensive Pooled Analysis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2019, 20, 443–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wechsler, M.E.; Klion, A.D.; Paggiaro, P.; Nair, P.; Staumont-Salle, D.; Radwan, A.; Johnson, R.R.; Kapoor, U.; Khokhar, F.A.; Daizadeh, N.; et al. Effect of Dupilumab on Blood Eosinophil Counts in Patients With Asthma, Chronic Rhinosinusitis With Nasal Polyps, Atopic Dermatitis, or Eosinophilic Esophagitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2022, 10, 2695–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, L.A.; Thaçi, D.; Deleuran, M.; Blauvelt, A.; Bissonnette, R.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Hide, M.; Sher, L.; Hussain, I.; Chen, Z.; et al. Dupilumab Provides Favorable Safety and Sustained Efficacy for up to 3 Years in an Open-Label Study of Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2020, 21, 567–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stein Gold, L.; Thaçi, D.; Thyssen, J.P.; Gooderham, M.; Laquer, V.; Moore, A.; Natalie, C.R.; Zhao, F.; Meskimen, E.; Elmaraghy, H.; et al. Safety of Lebrikizumab in Adults and Adolescents with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: An Integrated Analysis of Eight Clinical Trials. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2023, 24, 595–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Sun, Y.; Liu, M.; Tang, J. Real-World Pharmacovigilance Analysis of Drug-Related Conjunctivitis Using the FDA Adverse Event Reporting System Database. Sci. Rep. 2025, 15, 13407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranez, V.; Ambrus, J. Immunologic Adverse Effects of Biologics for the Treatment of Atopy. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2020, 59, 220–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados-Carmona, A.; Navarro-Triviño, F.; Husein-ElAhmed, H.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R. Comparative Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Biologics and JAK Inhibitors in Atopic Dermatitis: Short- and Medium-to-Long-Term Analysis from a Regional Healthcare Network in Southern Spain. Front. Med. 2025, 12, 1658843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olaguibel, J.; Sastre, J.; Rodríguez, J.; del Pozo, V. Eosinophilia Induced by Blocking the IL-4/IL-13 Pathway: Potential Mechanisms and Clinical Outcomes. J. Investig. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 32, 165–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling, A.-S.; Loft, N.; Silverberg, J.I.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Thyssen, J.P. Real-World Evidence of Dupilumab Efficacy and Risk of Adverse Events: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeweiss, M.C.; Kim, S.C.; Wyss, R.; Schneeweiss, S.; Merola, J.F. Dupilumab and the Risk of Conjunctivitis and Serious Infection in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Propensity Score–Matched Cohort Study. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 300–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kychygina, A.; Cassagne, M.; Tauber, M.; Galiacy, S.; Paul, C.; Fournié, P.; Simon, M. Dupilumab-Associated Adverse Events During Treatment of Allergic Diseases. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 62, 519–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Jorizzo, J.L. Retrospective Analysis of Adverse Events with Dupilumab Reported to the United States Food and Drug Administration. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2021, 84, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traidl, S.; Harries, L.; Kienlin, P.; Begemann, G.; Roesner, L.M.; Werfel, T. Dupilumab Strengthens Herpes Simplex Virus Type 1–Specific Immune Responses in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 1460–1469.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geba, G.P.; Li, D.; Xu, M.; Mohammadi, K.; Attre, R.; Ardeleanu, M.; Musser, B. Attenuating the Atopic March: Meta-Analysis of the Dupilumab Atopic Dermatitis Database for Incident Allergic Events. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 756–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Armario-Hita, J.C.; Galán-Gutiérrez, M.; Dodero-Anillo, J.M.; Carrascosa, J.M.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R. Updated Review on Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 33, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furue, M.; Furue, M. Ox40l–Ox40 Signaling in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Croft, M.; Geng, B.; Rynkiewicz, N.; Lucchesi, D.; Peakman, M.; van Krinks, C.; Valdecantos, W.; Xing, H.; Weidinger, S. The Role of OX40 Ligand/OX40 Axis Signalling in Atopic Dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2024, 191, 488–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marfil-Cantón, M.; Prados-Carmona, A.; Cebolla-Verdugo, M.; Husein-ElAhmed, H.; Campos, F.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R. Anti-OX40 Biological Therapies in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Pavel, A.B.; Zhou, L.; Estrada, Y.D.; Zhang, N.; Xu, H.; Peng, X.; Wen, H.C.; Govas, P.; Gudi, G.; et al. GBR 830, an Anti-OX40, Improves Skin Gene Signatures and Clinical Scores in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 482–493.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rewerska, B.; Sher, L.D.; Alpizar, S.; Pauser, S.; Pulka, G.; Mozaffarian, N.; Salhi, Y.; Martinet, C.; Jabert, W.; Gudi, G.; et al. Phase 2b Randomized Trial of OX40 Inhibitor Telazorlimab for Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Glob. 2024, 3, 100195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lé, A.M.; Torres, T. OX40-OX40L Inhibition for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis—Focus on Rocatinlimab and Amlitelimab. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 2753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakagawa, H.; Iizuka, H.; Nemoto, O.; Shimabe, M.; Furukawa, Y.; Kikuta, N.; Ootaki, K. Safety, Tolerability and Efficacy of Repeated Intravenous Infusions of KHK4083, a Fully Human Anti-OX40 Monoclonal Antibody, in Japanese Patients with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2020, 99, 82–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyowa Kirin Announces Positive Phase 2 Results for KHK4083 in Patients with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis. Available online: https://www.kyowakirin.com/media_center/news_releases/2021/e20210218_01.html (accessed on 16 November 2025).
- Weidinger, S.; Bieber, T.; Cork, M. Treatment with Amlitelimab (KY1005, SAR445229): A Novel Nondepleting Anti-OX40Ligand (OX40L) MAb Reduces IL-13 Serum Levels in a Phase 2a Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial in Patients with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2022, 87, AB123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, S.; Bieber, T.; Cork, M.J.; Reich, A.; Wilson, R.; Quaratino, S.; Stebegg, M.; Brennan, N.; Gilbert, S.; O’Malley, J.T.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Amlitelimab, a Fully Human Nondepleting, Noncytotoxic Anti-OX40 Ligand Monoclonal Antibody, in Atopic Dermatitis: Results of a Phase IIa Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trial. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 189, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maurer, M.; Cheung, D.S.; Theess, W.; Yang, X.; Dolton, M.; Guttman, A.; Choy, D.F.; Dash, A.; Grimbaldeston, M.A.; Soong, W. Phase 2 Randomized Clinical Trial of Astegolimab in Patients with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 150, 1517–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, J.H.; Chen, Y.-L.; Ogg, G. CD1a and Skin T Cells: A Pathway for Therapeutic Intervention. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 49, 450–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.-J.; Im, D.-S. Blockage of Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Receptor 2 Attenuates 2,4-Dinitrochlorobenzene-Induced Atopic Dermatitis in Mice. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2020, 41, 1487–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Rosmarin, D.; Chovatiya, R.; Bieber, T.; Schleicher, S.; Beck, L.; Gooderham, M.; Chaudhry, S.; Fanton, C.; Yu, D.; et al. The Regulatory T Cell-Selective Interleukin-2 Receptor Agonist Rezpegaldesleukin in the Treatment of Inflammatory Skin Diseases: Two Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Phase 1b Trials. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 9230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prados-Carmona, A.; Navarro-Triviño, F.J.; Husein-ElAhmed, H.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R. Comparative Real-World Analysis of Baseline Demographic Characteristics and Comorbidities in Atopic Dermatitis Patients Initiating Biologics Versus JAK Inhibitors. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 1291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De la Torre-Gomar, F.J.; Velasco-Amador, J.P.; Prados-Carmona, Á.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R. Complete Response of Extensive Alopecia Areata Refractory to Baricitinib after Five Months of Treatment with Upadacitinib. J. Dermatol. Treat. 2024, 35, 2304630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados-Carmona, A.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R.; Navarro-Triviño, F.J. Could Baricitinib Be a Safe and Effective Therapeutic Alternative for Incoercible Pruritus in Patients with Dermatitis Herpetiformis? Int. J. Dermatol. 2024, 63, e24–e26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bizzarri, F.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R.; Morales-Garrido, P.; Ruiz-Carrascosa, J.C.; Cebolla-Verdugo, M.; Prados-Carmona, A.; Rodriguez-Troncoso, M.; Raya-Alvarez, E. JAKinhibs in Psoriatic Disease: Analysis of the Efficacy/Safety Profile in Daily Clinical Practice. Diagnostics 2024, 14, 988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavel, A.B.; Song, T.; Kim, H.J.; Del Duca, E.; Krueger, J.G.; Dubin, C.; Peng, X.; Xu, H.; Zhang, N.; Estrada, Y.D.; et al. Oral Janus Kinase/SYK Inhibition (ASN002) Suppresses Inflammation and Improves Epidermal Barrier Markers in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1011–1024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bissonnette, R.; Maari, C.; Forman, S.; Bhatia, N.; Lee, M.; Fowler, J.; Tyring, S.; Pariser, D.; Sofen, H.; Dhawan, S.; et al. The Oral Janus Kinase/Spleen Tyrosine Kinase Inhibitor ASN 002 Demonstrates Efficacy and Improves Associated Systemic Inflammation in Patients with Moderate-to-severe Atopic Dermatitis: Results from a Randomized Double-blind Placebo-controlled Study. Br. J. Dermatol. 2019, 181, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, D.M.R.; Drucker, A.M.; Alikhan, A.; Bercovitch, L.; Cohen, D.E.; Darr, J.M.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Frazer-Green, L.; Paller, A.S.; Schwarzenberger, K.; et al. Guidelines of Care for the Management of Atopic Dermatitis in Adults with Phototherapy and Systemic Therapies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2024, 90, e43–e56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Xie, X.; Chen, Q.; Li, W.; Song, Z.; Wang, X.; Ma, X.; Zeng, J.; Guo, J. Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Atopic Dermatitis: An Umbrella Review of Meta-Analyses. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1342810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chovatiya, R.; Paller, A.S. JAK Inhibitors in the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 927–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, X.; Zhao, K.; Meng, F.; Li, L.; Mu, Z.; Han, X. Efficacy and Safety of Janus Kinase Inhibitors for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Dermatology 2022, 238, 725–735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sedeh, F.B.; Henning, M.A.S.; Jemec, G.B.E.; Ibler, K.S. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Monoclonal Antibodies and Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2022, 102, adv00764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.; Kim, K.; Shin, K.; Kim, H.; Kim, B.; Kim, M.; Ko, H.; Kim, Y.H. The Safety of Systemic Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 52–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, C.; Penedones, A.; Mendes, D.; Batel Marques, F. The Safety of Systemic Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Eur. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2022, 78, 1923–1933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ireland, P.A.; Verheyden, M.; Jansson, N.; Sebaratnam, D.; Sullivan, J. Infection Risk with JAK Inhibitors in Dermatoses: A Meta-analysis. Int. J. Dermatol. 2024, 64, 24–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, S.Y.-C.; Phipatanakul, W.; Hawryluk, E.B.; Oyoshi, M.K.; Schneider, L.C.; Ma, K.S.-K. Comparative Safety of Oral Janus Kinase Inhibitors versus Dupilumab in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Population-Based Cohort Study. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2024, 154, 1195–1203.e3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Q.; Cui, L.; Hu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Gao, Y.; Shi, Y. Short-Term Efficacy and Safety of Biologics and Janus Kinase Inhibitors for Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Heliyon 2023, 9, e22014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leung, D.Y.M.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Deciphering the Complexities of Atopic Dermatitis: Shifting Paradigms in Treatment Approaches. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 769–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Dhingra, N.; Leung, D.Y.M. New Era of Biologic Therapeutics in Atopic Dermatitis. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2013, 13, 549–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renert-Yuval, Y.; Guttman-Yassky, E. Systemic Therapies in Atopic Dermatitis: The Pipeline. Clin. Dermatol. 2017, 35, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boguniewicz, M.; Fonacier, L.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Ong, P.Y.; Silverberg, J.; Farrar, J.R. Atopic Dermatitis Yardstick: Practical Recommendations for an Evolving Therapeutic Landscape. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2018, 120, 10–22.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T. Atopic Dermatitis: An Expanding Therapeutic Pipeline for a Complex Disease. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022, 21, 21–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.H.; Patel, K.R.; Rastogi, S.; Singam, V.; Vakharia, P.P.; Chopra, R.; Silverberg, J.I. Placebo Responses in Randomized Controlled Trials for Systemic Therapy in Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2020, 82, 62–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Thyssen, J.P.; Fahrbach, K.; Mickle, K.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Romero, W.; Cameron, M.C.; Myers, D.E.; Clibborn, C.; DiBonaventura, M. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Systemic Therapies Used in Moderate-to-severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Systematic Literature Review and Network Meta-analysis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1797–1810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chu, A.W.L.; Wong, M.M.; Rayner, D.G.; Guyatt, G.H.; Díaz Martinez, J.P.; Ceccacci, R.; Zhao, I.X.; McMullen, E.; Srivastava, A.; Wang, J.; et al. Systemic Treatments for Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema): Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 152, 1470–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Wijs, L.E.M.; Fujimoto, R.F.T.; Andrinopoulou, E.R.; Nijsten, T.; Hijnen, D.; Kataoka, Y. Dupilumab Treatment in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: A Comparative Cohort Study between the Netherlands and Japan Shows a Discrepancy in Patient-reported Outcome Measures. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 185, 555–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneeweiss, M.C.; Glynn, R.J.; Wyss, R.; Anand, P.; Jin, Y.; Landon, J.; Mostaghimi, A.; Merola, J.F.; Silverberg, J.I.; Rosmarin, D.M.; et al. A Scalable Approach to Assess the Safety of Recently Marketed Systemic Treatments for Atopic Dermatitis in Clinical Practice. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 145, 1070–1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, J.; Xiong, S.; Zhang, J.; Ye, Q.; Xue, R.; Tian, X.; Zhong, J.; Zhu, H.; Gao, A.; et al. Comparative Effectiveness of Upadacitinib versus Dupilumab for Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2024, 143, 113383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, R.W.; Lam, M.; Abuabara, K.; Simpson, E.L.; Drucker, A.M. Targeted Systemic Therapies for Adults with Atopic Dermatitis: Selecting from Biologics and JAK Inhibitors. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2024, 25, 179–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butala, S.; Castelo-Soccio, L.; Seshadri, R.; Simpson, E.L.; O’Shea, J.J.; Bieber, T.; Paller, A.S. Biologic Versus Small Molecule Therapy for Treating Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis: Clinical Considerations. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2023, 11, 1361–1373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Li, W.; Gong, M.; Gu, Y.; Zhang, H.; Dong, B.; Guo, Q.; Pang, X.; Xiang, Q.; He, X.; et al. Risk of Venous Thromboembolism with Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Inflammatory Immune Diseases: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Pharmacol. 2023, 14, 1189389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prados-Carmona, A.; Husein-ElAhmed, H.; Navarro-Triviño, F.J.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R. Atopic Dermatitis beyond Eczema: A Review on Its Systemic Impact through Pruritus and Associated Comorbidities. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2025, 68, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverberg, J.I.; Hong, H.C.-h.; Calimlim, B.M.; Lee, W.J.; Teixeira, H.D.; Collins, E.B.; Crowell, M.M.; Johnson, S.J.; Armstrong, A.W. Comparative Efficacy of Targeted Systemic Therapies for Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis without Topical Corticosteroids: An Updated Network Meta-Analysis. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 2247–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drucker, A.M.; Lam, M.; Elsawi, R.; Prieto-Merino, D.; Malek, R.; Ellis, A.G.; Yiu, Z.Z.N.; Rochwerg, B.; Di Giorgio, S.; Arents, B.W.M.; et al. Comparing Binary Efficacy Outcomes for Systemic Immunomodulatory Treatments for Atopic Dermatitis in a Living Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2024, 190, 184–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilla-Polo, M.; Morgado-Carrasco, D. Biologics Versus JAK Inhibitors. Part II: Risk of Infections. A Narrative Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2024, 14, 1983–2038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansilla-Polo, M.; Morgado-Carrasco, D. Biologics Versus JAK Inhibitors. Part I: Cancer Risk. A Narrative Review. Dermatol. Ther. 2024, 14, 1389–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yong, S.; Ting, B.; Malau, I.A.; Wu, S.; Huang, X.; Wang, J.; Jingling, L.; Wei, C. Comparative Efficacy of Biologics and Small Molecule Drugs in Treating Pediatric Atopic Dermatitis in Patients Aged 2–18 Years: A 12–16 Week Network Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2025, 36, e70045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T.; Thyssen, J.P.; Irvine, A.D.; Tsunemi, Y.; Chen, Y.-F.; Sun, L.; Schloebe, A.; Riedl, E.; Cork, M.J. Early Improvements in Signs and Symptoms Predict Clinical Response to Baricitinib in Patients with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2023, 48, 881–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibba, L.; Falcidia, C.; Di Giulio, S.; Bianco, M.; Valenti, M.; Facheris, P.; Narcisi, A.; Costanzo, A.; Gargiulo, L. Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Upadacitinib and Abrocitinib in Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A 52-Week Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2025, 14, 2953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Bruin-Weller, M.S.; Boesjes, C.M.; Achten, R.A.; Beck, L.A.; Irvine, A.D.; Vestergaard, C.; de Graaf, M.; van Wijk, F.; Bakker, D.S.; Weidinger, S. Biologics to Treat Atopic Dermatitis: Effectiveness, Safety, and Future Directions. Allergy, 2025; online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollenberg, A.; Simon, D.; Kulthanan, K.; Figueras-Nart, I.; Misery, L.; Tangsirisap, N.; Spina, L.; Lu, N.; Grond, S.; Eyerich, K. Baricitinib Treatment Rapidly Improves the Four Signs of Atopic Dermatitis Assessed by Eczema Area and Severity Index (EASI) Clinical Subscores. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2024, 38, 695–702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reich, K.; Teixeira, H.D.; de Bruin-Weller, M.; Bieber, T.; Soong, W.; Kabashima, K.; Werfel, T.; Zeng, J.; Huang, X.; Hu, X.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Upadacitinib in Combination with Topical Corticosteroids in Adolescents and Adults with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis (AD Up): Results from a Randomised, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled, Phase 3 Trial. Lancet 2021, 397, 2169–2181, Correction in Lancet 2021, 398, 746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bieber, T.; Simpson, E.L.; Silverberg, J.I.; Thaçi, D.; Paul, C.; Pink, A.E.; Kataoka, Y.; Chu, C.-Y.; DiBonaventura, M.; Rojo, R.; et al. Abrocitinib versus Placebo or Dupilumab for Atopic Dermatitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 1101–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, J.; Wu, H.; Ye, Y.; Xu, Q.; Shao, J.; Bai, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, J.; Li, Z. Efficacy, Safety, and Early Relapse After Cessation of Upadacitinib Versus Dupilumab in Adolescents with Moderate-to-Severe Atopic Dermatitis: A Real-World Study in China. Dermatitis 2024, 35, 636–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidbury, R.; Tom, W.L.; Bergman, J.N.; Cooper, K.D.; Silverman, R.A.; Berger, T.G.; Chamlin, S.L.; Cohen, D.E.; Cordoro, K.M.; Davis, D.M.; et al. Guidelines of Care for the Management of Atopic Dermatitis: Section 4. Prevention of Disease Flares and Use of Adjunctive Therapies and Approaches. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2014, 71, 1218–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.-C.; Wu, K.-H.; Chen, C.-Y.; Lin, W.-Y.; Chang, Y.-J.; Lin, M.-J.; Wu, H.-P. Advancements in Allergen Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 1316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, X.; Lin, L.; Zhu, C.; Yang, X.; Ni, Y.; Zhipeng, L.; Chong, J.; Han, Y. Efficacy and Safety of Nemolizumab for Treatment of Adult Atopic Dermatitis: A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Clinical Trials. J. Investig. Allergol. Clin. Immunol. 2021, 31, 190–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ständer, S.; Yosipovitch, G.; Legat, F.J.; Lacour, J.-P.; Paul, C.; Narbutt, J.; Bieber, T.; Misery, L.; Wollenberg, A.; Reich, A.; et al. Trial of Nemolizumab in Moderate-to-Severe Prurigo Nodularis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 706–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bağci, I.S.; Ruzicka, T. IL-31: A New Key Player in Dermatology and Beyond. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 858–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roh, Y.S.; Choi, J.; Sutaria, N.; Belzberg, M.; Kwatra, M.M.; Kwatra, S.G. IL-31 Inhibition as a Therapeutic Approach for the Management of Chronic Pruritic Dermatoses. Drugs 2021, 81, 895–905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orfali, R.L.; Aoki, V. Blockage of the IL-31 Pathway as a Potential Target Therapy for Atopic Dermatitis. Pharmaceutics 2023, 15, 577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bewley, A.; Homey, B.; Pink, A. Prurigo Nodularis: A Review of IL-31RA Blockade and Other Potential Treatments. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 12, 2039–2048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, S.; Bieber, T.; Ständer, S. Therapeutic Potential of Biologics in Prurigo Nodularis. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2022, 22, 47–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra-Baldrich, E.; Santamaría-Babí, L.F.; Francisco Silvestre, J. Nemolizumab: Un Innovador Tratamiento Biológico Para El Control de La Interleuquina 31 (IL-31) Clave En La Dermatitis Atópica y El Prurigo Nodular. Actas Dermosifiliogr. 2022, 113, 674–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, C.; Penedones, A.; Mendes, D.; Batel Marques, F. Topical Janus Kinase Inhibitors in Atopic Dermatitis: A Safety Network Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Clin. Pharm. 2023, 45, 830–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidbury, R.; Alikhan, A.; Bercovitch, L.; Cohen, D.E.; Darr, J.M.; Drucker, A.M.; Eichenfield, L.F.; Frazer-Green, L.; Paller, A.S.; Schwarzenberger, K.; et al. Guidelines of Care for the Management of Atopic Dermatitis in Adults with Topical Therapies. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023, 89, e1–e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyano, T.; Irvine, A.D.; Tanaka, R.J. A Mathematical Model to Identify Optimal Combinations of Drug Targets for Dupilumab Poor Responders in Atopic Dermatitis. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 77, 582–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, E.L.; Guttman-Yassky, E.; Pawlikowski, J.; Ghorayeb, E.G.; Ota, T.; Lebwohl, M.G. Interleukin-1α Inhibitor Bermekimab in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis: Randomized and Nonrandomized Studies. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2024, 316, 589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghafoori, P.; Fortunato, L.; Patel, D.S.; Ellis, J.; Wong, G.; Kelly, J.B.; Birch, H.; Chen, W.-H.; Uings, I. 678-Patient-Reported Outcomes for GSK1070806, an Anti-IL-18 Monoclonal Antibody: A Phase 1b, Randomised, Double-Blind, Parallel-Group Placebo-Controlled Study of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 2024, 191, ljae266.052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, E.V.; Suresh, R.V.; Dispenza, M.C. Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase Inhibition for the Treatment of Allergic Disorders. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2024, 133, 33–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roufosse, F. Targeting the Interleukin-5 Pathway for Treatment of Eosinophilic Conditions Other than Asthma. Front. Med. 2018, 5, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guttman-Yassky, E.; Bahadori, L.; Brooks, L.; Clark, K.L.; Grindebacke, H.; Ho, C.N.; Katial, R.; Pham, T.-H.; Walton, C.; Datto, C.J. Lack of Effect of Benralizumab on Signs and Symptoms of Moderate-to-severe Atopic Dermatitis: Results from the Phase 2 Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled HILLIER Trial. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2023, 37, e1211–e1214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holm, J.G.; Agner, T.; Sand, C.; Thomsen, S.F. Omalizumab for Atopic Dermatitis: Case Series and a Systematic Review of the Literature. Int. J. Dermatol. 2017, 56, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liour, S.S.; Tom, A.; Chan, Y.; Chang, T.W. Treating IgE-mediated Diseases via Targeting IgE-expressing B Cells Using an Anti-CεmX Antibody. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 27, 446–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| JAK1 | JAK2 | JAK3 | TYK2 | Administration Route in Dermatology | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Upadacitinib | ✓ | PO | |||
| Abrocitinib | ✓ | PO | |||
| Ivarmacitinib | ✓ | PO | |||
| Povorcitinib | ✓ | PO | |||
| Baricitinib | ✓ | ✓ | PO | ||
| Ruxolitinib | ✓ | ✓ | Topical | ||
| Tofacitinib | ✓ | ✓ | PO | ||
| Lepzacitinib | ✓ | ✓ | Topical | ||
| Ifidancitinib | ✓ | ✓ | Topical | ||
| Ritlecitinib | ✓ | PO | |||
| Deucravacitinib | ✓ | PO | |||
| Brepocitinib | ✓ | ✓ | PO/Topical | ||
| Zasocitinib | ✓ | PO | |||
| Delgocitinib | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Topical |
| Gecaxitinib | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | PO |
| Cerdulatinib | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | Topical |
| Gusacitinib | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | PO |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Prados-Carmona, A.; Husein-ElAhmed, H.; Navarro-Triviño, F.J.; Ruiz-Villaverde, R. From Pathways to Patients in Atopic Dermatitis: Advanced Systemic Therapies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 11487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311487
Prados-Carmona A, Husein-ElAhmed H, Navarro-Triviño FJ, Ruiz-Villaverde R. From Pathways to Patients in Atopic Dermatitis: Advanced Systemic Therapies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 2025; 26(23):11487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311487
Chicago/Turabian StylePrados-Carmona, Alvaro, Husein Husein-ElAhmed, Francisco José Navarro-Triviño, and Ricardo Ruiz-Villaverde. 2025. "From Pathways to Patients in Atopic Dermatitis: Advanced Systemic Therapies" International Journal of Molecular Sciences 26, no. 23: 11487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311487
APA StylePrados-Carmona, A., Husein-ElAhmed, H., Navarro-Triviño, F. J., & Ruiz-Villaverde, R. (2025). From Pathways to Patients in Atopic Dermatitis: Advanced Systemic Therapies. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 26(23), 11487. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms262311487








